

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 245-261.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20209 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20209
Kai Fan, Fangting Ye, Zhijun Mao, Xinfeng Pan, Zhaowei Li, Wenxiong Lin*( )
)
Received:2020-12-25
Accepted:2021-03-25
Online:2021-05-01
Published:2021-04-30
Contact:
Wenxiong Lin
Kai Fan, Fangting Ye, Zhijun Mao, Xinfeng Pan, Zhaowei Li, Wenxiong Lin. Comparative Genomics of the Small Heat Shock Protein Family in Angiosperms[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 245-261.
| Protein name | Locus name | Subfamily | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NcsHSP01 | GWHPAAYW001658 | CI | 60 | 6.64 | 9.16 | 41.10 | 99.00 | -0.218 |
| NcsHSP02 | GWHPAAYW001878 | CII | 308 | 34.77 | 9.03 | 44.31 | 74.64 | -0.624 |
| NcsHSP03 | GWHPAAYW002745 | CV | 276 | 30.85 | 4.88 | 44.78 | 77.36 | -0.291 |
| NcsHSP04 | GWHPAAYW004666 | PX | 1189 | 132.46 | 5.86 | 44.51 | 85.53 | -0.300 |
| NcsHSP05 | GWHPAAYW006130 | ER | 218 | 24.32 | 5.46 | 64.70 | 95.14 | -0.411 |
| NcsHSP06 | GWHPAAYW006158 | CII | 378 | 43.02 | 8.36 | 50.40 | 74.76 | -0.780 |
| NcsHSP07 | GWHPAAYW006159 | CII | 662 | 75.02 | 9.13 | 55.90 | 79.64 | -0.665 |
| NcsHSP08 | GWHPAAYW006161 | CII | 314 | 35.79 | 8.86 | 47.40 | 79.39 | -0.709 |
| NcsHSP09 | GWHPAAYW006746 | CIII | 164 | 18.56 | 5.75 | 53.09 | 81.28 | -0.489 |
| NcsHSP10 | GWHPAAYW007213 | CIV | 132 | 14.36 | 6.83 | 58.83 | 82.80 | -0.117 |
| NcsHSP11 | GWHPAAYW009125 | CII | 165 | 19.09 | 5.48 | 54.83 | 69.03 | -0.921 |
| NcsHSP12 | GWHPAAYW010630 | MTII | 235 | 26.36 | 6.79 | 56.35 | 67.57 | -0.687 |
| NcsHSP13 | GWHPAAYW010715 | CI | 129 | 15.42 | 9.12 | 60.26 | 59.53 | -1.343 |
| NcsHSP14 | GWHPAAYW013759 | CVI | 154 | 17.47 | 5.57 | 46.32 | 73.96 | -0.573 |
| NcsHSP15 | GWHPAAYW014339 | CI | 156 | 17.60 | 5.24 | 55.71 | 73.72 | -0.552 |
| NcsHSP16 | GWHPAAYW014344 | CI | 158 | 18.29 | 8.92 | 54.19 | 74.05 | -0.682 |
| NcsHSP17 | GWHPAAYW015449 | MTI/CP | 208 | 23.47 | 6.01 | 36.92 | 78.75 | -0.667 |
| NcsHSP18 | GWHPAAYW018459 | CI | 833 | 94.56 | 6.14 | 53.05 | 69.45 | -0.668 |
| NcsHSP19 | GWHPAAYW019072 | CI | 163 | 18.55 | 6.19 | 62.44 | 71.04 | -0.601 |
| NcsHSP20 | GWHPAAYW019077 | CI | 337 | 37.62 | 7.83 | 57.71 | 78.66 | -0.457 |
Table 1 The identification and structural analysis of the sHSP members in waterlily, rice, Arabidopsis and grape
| Protein name | Locus name | Subfamily | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NcsHSP01 | GWHPAAYW001658 | CI | 60 | 6.64 | 9.16 | 41.10 | 99.00 | -0.218 |
| NcsHSP02 | GWHPAAYW001878 | CII | 308 | 34.77 | 9.03 | 44.31 | 74.64 | -0.624 |
| NcsHSP03 | GWHPAAYW002745 | CV | 276 | 30.85 | 4.88 | 44.78 | 77.36 | -0.291 |
| NcsHSP04 | GWHPAAYW004666 | PX | 1189 | 132.46 | 5.86 | 44.51 | 85.53 | -0.300 |
| NcsHSP05 | GWHPAAYW006130 | ER | 218 | 24.32 | 5.46 | 64.70 | 95.14 | -0.411 |
| NcsHSP06 | GWHPAAYW006158 | CII | 378 | 43.02 | 8.36 | 50.40 | 74.76 | -0.780 |
| NcsHSP07 | GWHPAAYW006159 | CII | 662 | 75.02 | 9.13 | 55.90 | 79.64 | -0.665 |
| NcsHSP08 | GWHPAAYW006161 | CII | 314 | 35.79 | 8.86 | 47.40 | 79.39 | -0.709 |
| NcsHSP09 | GWHPAAYW006746 | CIII | 164 | 18.56 | 5.75 | 53.09 | 81.28 | -0.489 |
| NcsHSP10 | GWHPAAYW007213 | CIV | 132 | 14.36 | 6.83 | 58.83 | 82.80 | -0.117 |
| NcsHSP11 | GWHPAAYW009125 | CII | 165 | 19.09 | 5.48 | 54.83 | 69.03 | -0.921 |
| NcsHSP12 | GWHPAAYW010630 | MTII | 235 | 26.36 | 6.79 | 56.35 | 67.57 | -0.687 |
| NcsHSP13 | GWHPAAYW010715 | CI | 129 | 15.42 | 9.12 | 60.26 | 59.53 | -1.343 |
| NcsHSP14 | GWHPAAYW013759 | CVI | 154 | 17.47 | 5.57 | 46.32 | 73.96 | -0.573 |
| NcsHSP15 | GWHPAAYW014339 | CI | 156 | 17.60 | 5.24 | 55.71 | 73.72 | -0.552 |
| NcsHSP16 | GWHPAAYW014344 | CI | 158 | 18.29 | 8.92 | 54.19 | 74.05 | -0.682 |
| NcsHSP17 | GWHPAAYW015449 | MTI/CP | 208 | 23.47 | 6.01 | 36.92 | 78.75 | -0.667 |
| NcsHSP18 | GWHPAAYW018459 | CI | 833 | 94.56 | 6.14 | 53.05 | 69.45 | -0.668 |
| NcsHSP19 | GWHPAAYW019072 | CI | 163 | 18.55 | 6.19 | 62.44 | 71.04 | -0.601 |
| NcsHSP20 | GWHPAAYW019077 | CI | 337 | 37.62 | 7.83 | 57.71 | 78.66 | -0.457 |
| Protein name | Locus name | Subfamily | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NcsHSP21 | GWHPAAYW019078 | CI | 156 | 17.38 | 5.69 | 54.61 | 75.00 | -0.449 |
| NcsHSP22 | GWHPAAYW019481 | CP | 222 | 25.65 | 9.17 | 54.03 | 60.63 | -0.880 |
| NcsHSP23 | GWHPAAYW022038 | CI | 159 | 18.24 | 5.60 | 65.94 | 69.18 | -0.648 |
| NcsHSP24 | GWHPAAYW025914 | CVI | 160 | 18.57 | 5.82 | 41.67 | 70.00 | -0.914 |
| NcsHSP25 | GWHPAAYW027820 | ER | 192 | 21.54 | 6.54 | 31.35 | 102.08 | -0.202 |
| NcsHSP26 | GWHPAAYW027821 | ER | 676 | 74.58 | 5.31 | 41.90 | 85.41 | -0.292 |
| NcsHSP27 | GWHPAAYW027823 | ER | 180 | 20.20 | 9.21 | 61.79 | 73.67 | -0.636 |
| NcsHSP28 | GWHPAAYW027825 | ER | 191 | 21.24 | 7.93 | 29.89 | 91.41 | -0.376 |
| NcsHSP29 | GWHPAAYW027826 | ER | 191 | 21.48 | 6.00 | 34.01 | 98.53 | -0.246 |
| NcsHSP30 | GWHPAAYW027987 | CP | 226 | 25.18 | 6.65 | 50.88 | 75.88 | -0.522 |
| NcsHSP31 | GWHPAAYW030961 | ER | 133 | 15.78 | 10.21 | 41.23 | 77.59 | -0.929 |
| NcsHSP32 | GWHPAAYW030963 | ER | 126 | 14.05 | 5.63 | 37.53 | 109.13 | -0.024 |
| NcsHSP33 | GWHPAAYW030964 | ER | 143 | 15.67 | 6.08 | 33.52 | 109.16 | 0.075 |
| OssHSP01 | LOC_Os01g04340.1 | CI | 150 | 16.65 | 6.31 | 34.230 | 77.200 | -0.536 |
| OssHSP02 | LOC_Os01g04350.1 | CI | 166 | 17.89 | 4.96 | 55.210 | 87.590 | 0.051 |
| OssHSP03 | LOC_Os01g04360.1 | CI | 149 | 16.90 | 6.76 | 47.050 | 69.870 | -0.648 |
| OssHSP04 | LOC_Os01g04370.1 | CI | 150 | 16.94 | 6.18 | 52.240 | 76.530 | -0.605 |
| OssHSP05 | LOC_Os01g04380.1 | CI | 150 | 16.96 | 6.18 | 52.240 | 73.930 | -0.617 |
| OssHSP06 | LOC_Os01g08860.1 | CII | 166 | 18.03 | 5.61 | 45.580 | 78.130 | -0.386 |
| OssHSP07 | LOC_Os02g03570.1 | CI | 177 | 18.87 | 6.93 | 52.450 | 71.750 | -0.406 |
| OssHSP08 | LOC_Os02g10710.1 | MTII | 219 | 23.59 | 7.74 | 47.270 | 86.030 | -0.320 |
| OssHSP09 | LOC_Os02g12610.1 | CII | 175 | 19.02 | 5.73 | 39.010 | 84.060 | -0.486 |
| OssHSP10 | LOC_Os02g48140.1 | CVII | 164 | 17.77 | 6.97 | 46.260 | 67.320 | -0.534 |
| OssHSP11 | LOC_Os02g52150.1 | MTI/CP | 221 | 24.15 | 7.96 | 48.750 | 77.330 | -0.519 |
| OssHSP12 | LOC_Os02g54140.1 | CIII | 172 | 18.60 | 7.85 | 40.550 | 77.150 | -0.538 |
| OssHSP13 | LOC_Os03g14180.1 | CP | 240 | 26.66 | 6.78 | 53.350 | 75.120 | -0.541 |
| OssHSP14 | LOC_Os03g15960.1 | CI | 161 | 17.91 | 5.79 | 57.860 | 64.780 | -0.680 |
| OssHSP15 | LOC_Os03g16020.1 | CI | 154 | 17.37 | 6.18 | 49.280 | 66.430 | -0.706 |
| OssHSP16 | LOC_Os03g16030.1 | CI | 161 | 18.08 | 6.77 | 58.690 | 61.680 | -0.746 |
| OssHSP17 | LOC_Os03g16040.1 | CI | 159 | 17.66 | 6.18 | 55.510 | 66.790 | -0.719 |
| OssHSP18 | LOC_Os04g36750.1 | ER | 215 | 23.23 | 5.34 | 35.060 | 82.650 | -0.365 |
| OssHSP19 | LOC_Os05g23140.1 | CP | 251 | 27.64 | 9.42 | 39.120 | 69.240 | -0.488 |
| OssHSP20 | LOC_Os05g42120.1 | CV | 203 | 22.28 | 4.82 | 54.030 | 69.800 | -0.330 |
| OssHSP21 | LOC_Os06g11610.1 | MTI/CP | 248 | 26.23 | 5.27 | 43.470 | 79.270 | -0.323 |
| OssHSP22 | LOC_Os06g14240.1 | PX | 146 | 16.02 | 8.13 | 36.730 | 84.790 | -0.292 |
| OssHSP23 | LOC_Os07g33350.1 | CIV | 219 | 23.76 | 11.74 | 93.800 | 71.320 | -0.642 |
| OssHSP24 | LOC_Os11g13980.1 | ER | 206 | 21.87 | 6.01 | 48.890 | 81.500 | -0.126 |
| AtsHSP01 | AT1G07400.1 | CI | 157 | 17.83 | 5.99 | 43.380 | 70.060 | -0.680 |
| AtsHSP02 | AT1G52560.1 | MTII | 232 | 26.54 | 6.86 | 45.660 | 68.880 | -0.869 |
| AtsHSP03 | AT1G53540.1 | CI | 157 | 17.60 | 5.36 | 53.800 | 71.970 | -0.578 |
| AtsHSP04 | AT1G54050.1 | CIII | 155 | 17.36 | 7.88 | 58.630 | 93.680 | -0.504 |
| AtsHSP05 | AT1G59860.1 | CI | 155 | 17.62 | 6.85 | 50.240 | 70.970 | -0.678 |
| AtsHSP06 | AT2G29500.1 | CI | 153 | 17.56 | 6.33 | 47.820 | 71.900 | -0.720 |
| AtsHSP07 | AT3G46230.1 | CI | 156 | 17.44 | 5.20 | 46.980 | 68.590 | -0.569 |
Table 1 (continued)
| Protein name | Locus name | Subfamily | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NcsHSP21 | GWHPAAYW019078 | CI | 156 | 17.38 | 5.69 | 54.61 | 75.00 | -0.449 |
| NcsHSP22 | GWHPAAYW019481 | CP | 222 | 25.65 | 9.17 | 54.03 | 60.63 | -0.880 |
| NcsHSP23 | GWHPAAYW022038 | CI | 159 | 18.24 | 5.60 | 65.94 | 69.18 | -0.648 |
| NcsHSP24 | GWHPAAYW025914 | CVI | 160 | 18.57 | 5.82 | 41.67 | 70.00 | -0.914 |
| NcsHSP25 | GWHPAAYW027820 | ER | 192 | 21.54 | 6.54 | 31.35 | 102.08 | -0.202 |
| NcsHSP26 | GWHPAAYW027821 | ER | 676 | 74.58 | 5.31 | 41.90 | 85.41 | -0.292 |
| NcsHSP27 | GWHPAAYW027823 | ER | 180 | 20.20 | 9.21 | 61.79 | 73.67 | -0.636 |
| NcsHSP28 | GWHPAAYW027825 | ER | 191 | 21.24 | 7.93 | 29.89 | 91.41 | -0.376 |
| NcsHSP29 | GWHPAAYW027826 | ER | 191 | 21.48 | 6.00 | 34.01 | 98.53 | -0.246 |
| NcsHSP30 | GWHPAAYW027987 | CP | 226 | 25.18 | 6.65 | 50.88 | 75.88 | -0.522 |
| NcsHSP31 | GWHPAAYW030961 | ER | 133 | 15.78 | 10.21 | 41.23 | 77.59 | -0.929 |
| NcsHSP32 | GWHPAAYW030963 | ER | 126 | 14.05 | 5.63 | 37.53 | 109.13 | -0.024 |
| NcsHSP33 | GWHPAAYW030964 | ER | 143 | 15.67 | 6.08 | 33.52 | 109.16 | 0.075 |
| OssHSP01 | LOC_Os01g04340.1 | CI | 150 | 16.65 | 6.31 | 34.230 | 77.200 | -0.536 |
| OssHSP02 | LOC_Os01g04350.1 | CI | 166 | 17.89 | 4.96 | 55.210 | 87.590 | 0.051 |
| OssHSP03 | LOC_Os01g04360.1 | CI | 149 | 16.90 | 6.76 | 47.050 | 69.870 | -0.648 |
| OssHSP04 | LOC_Os01g04370.1 | CI | 150 | 16.94 | 6.18 | 52.240 | 76.530 | -0.605 |
| OssHSP05 | LOC_Os01g04380.1 | CI | 150 | 16.96 | 6.18 | 52.240 | 73.930 | -0.617 |
| OssHSP06 | LOC_Os01g08860.1 | CII | 166 | 18.03 | 5.61 | 45.580 | 78.130 | -0.386 |
| OssHSP07 | LOC_Os02g03570.1 | CI | 177 | 18.87 | 6.93 | 52.450 | 71.750 | -0.406 |
| OssHSP08 | LOC_Os02g10710.1 | MTII | 219 | 23.59 | 7.74 | 47.270 | 86.030 | -0.320 |
| OssHSP09 | LOC_Os02g12610.1 | CII | 175 | 19.02 | 5.73 | 39.010 | 84.060 | -0.486 |
| OssHSP10 | LOC_Os02g48140.1 | CVII | 164 | 17.77 | 6.97 | 46.260 | 67.320 | -0.534 |
| OssHSP11 | LOC_Os02g52150.1 | MTI/CP | 221 | 24.15 | 7.96 | 48.750 | 77.330 | -0.519 |
| OssHSP12 | LOC_Os02g54140.1 | CIII | 172 | 18.60 | 7.85 | 40.550 | 77.150 | -0.538 |
| OssHSP13 | LOC_Os03g14180.1 | CP | 240 | 26.66 | 6.78 | 53.350 | 75.120 | -0.541 |
| OssHSP14 | LOC_Os03g15960.1 | CI | 161 | 17.91 | 5.79 | 57.860 | 64.780 | -0.680 |
| OssHSP15 | LOC_Os03g16020.1 | CI | 154 | 17.37 | 6.18 | 49.280 | 66.430 | -0.706 |
| OssHSP16 | LOC_Os03g16030.1 | CI | 161 | 18.08 | 6.77 | 58.690 | 61.680 | -0.746 |
| OssHSP17 | LOC_Os03g16040.1 | CI | 159 | 17.66 | 6.18 | 55.510 | 66.790 | -0.719 |
| OssHSP18 | LOC_Os04g36750.1 | ER | 215 | 23.23 | 5.34 | 35.060 | 82.650 | -0.365 |
| OssHSP19 | LOC_Os05g23140.1 | CP | 251 | 27.64 | 9.42 | 39.120 | 69.240 | -0.488 |
| OssHSP20 | LOC_Os05g42120.1 | CV | 203 | 22.28 | 4.82 | 54.030 | 69.800 | -0.330 |
| OssHSP21 | LOC_Os06g11610.1 | MTI/CP | 248 | 26.23 | 5.27 | 43.470 | 79.270 | -0.323 |
| OssHSP22 | LOC_Os06g14240.1 | PX | 146 | 16.02 | 8.13 | 36.730 | 84.790 | -0.292 |
| OssHSP23 | LOC_Os07g33350.1 | CIV | 219 | 23.76 | 11.74 | 93.800 | 71.320 | -0.642 |
| OssHSP24 | LOC_Os11g13980.1 | ER | 206 | 21.87 | 6.01 | 48.890 | 81.500 | -0.126 |
| AtsHSP01 | AT1G07400.1 | CI | 157 | 17.83 | 5.99 | 43.380 | 70.060 | -0.680 |
| AtsHSP02 | AT1G52560.1 | MTII | 232 | 26.54 | 6.86 | 45.660 | 68.880 | -0.869 |
| AtsHSP03 | AT1G53540.1 | CI | 157 | 17.60 | 5.36 | 53.800 | 71.970 | -0.578 |
| AtsHSP04 | AT1G54050.1 | CIII | 155 | 17.36 | 7.88 | 58.630 | 93.680 | -0.504 |
| AtsHSP05 | AT1G59860.1 | CI | 155 | 17.62 | 6.85 | 50.240 | 70.970 | -0.678 |
| AtsHSP06 | AT2G29500.1 | CI | 153 | 17.56 | 6.33 | 47.820 | 71.900 | -0.720 |
| AtsHSP07 | AT3G46230.1 | CI | 156 | 17.44 | 5.20 | 46.980 | 68.590 | -0.569 |
| Protein name | Locus name | Subfamily | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtsHSP08 | AT4G10250.1 | ER | 195 | 22.00 | 5.58 | 36.450 | 93.950 | -0.469 |
| AtsHSP09 | AT4G21870.1 | CIV | 134 | 15.39 | 5.17 | 73.930 | 93.810 | -0.325 |
| AtsHSP10 | AT4G25200.1 | MTI/CP | 210 | 23.61 | 6.46 | 58.790 | 80.760 | -0.649 |
| AtsHSP11 | AT4G27670.1 | CP | 227 | 25.34 | 8.49 | 46.860 | 72.070 | -0.641 |
| AtsHSP12 | AT5G12020.1 | CII | 155 | 17.62 | 6.32 | 38.840 | 80.390 | -0.617 |
| AtsHSP13 | AT5G12030.1 | CII | 156 | 17.69 | 5.59 | 44.370 | 75.000 | -0.596 |
| AtsHSP14 | AT5G37670.1 | PX | 137 | 15.70 | 7.94 | 50.680 | 86.640 | -0.512 |
| AtsHSP15 | AT5G51440.1 | MTI/CP | 210 | 23.47 | 8.96 | 52.510 | 84.000 | -0.558 |
| AtsHSP16 | AT5G54660.1 | CV | 192 | 21.66 | 5.47 | 38.030 | 71.560 | -0.500 |
| AtsHSP17 | AT5G59720.1 | CI | 161 | 18.13 | 6.77 | 48.090 | 67.200 | -0.657 |
| VvsHSP01 | VIT_200s0707g00010.1 | CIV | 136 | 15.69 | 4.89 | 53.490 | 82.430 | -0.315 |
| VvsHSP02 | VIT_200s0992g00020.1 | CIV | 136 | 15.70 | 5.01 | 54.190 | 82.430 | -0.312 |
| VvsHSP03 | VIT_201s0010g02290.1 | CP | 226 | 25.56 | 6.77 | 48.710 | 62.170 | -0.706 |
| VvsHSP04 | VIT_202s0154g00480.1 | MTI/CP | 201 | 22.45 | 9.24 | 45.150 | 77.060 | -0.531 |
| VvsHSP05 | VIT_202s0154g00490.1 | MTI/CP | 201 | 22.55 | 9.11 | 51.710 | 75.670 | -0.561 |
| VvsHSP06 | VIT_204s0008g01490.1 | CII | 156 | 17.34 | 5.94 | 41.520 | 82.500 | -0.444 |
| VvsHSP07 | VIT_204s0008g01500.1 | CII | 152 | 16.69 | 6.84 | 42.090 | 79.540 | -0.390 |
| VvsHSP08 | VIT_204s0008g01510.1 | CII | 156 | 17.40 | 5.77 | 44.190 | 76.220 | -0.462 |
| VvsHSP09 | VIT_204s0008g01520.1 | CII | 156 | 17.58 | 5.58 | 40.180 | 78.080 | -0.513 |
| VvsHSP10 | VIT_204s0008g01530.1 | CII | 480 | 53.16 | 8.89 | 39.780 | 68.600 | -0.713 |
| VvsHSP11 | VIT_204s0008g01550.1 | CII | 156 | 17.41 | 5.94 | 39.580 | 71.790 | -0.533 |
| VvsHSP12 | VIT_204s0008g01560.1 | CII | 113 | 12.66 | 8.66 | 38.840 | 83.540 | -0.473 |
| VvsHSP13 | VIT_204s0008g01570.1 | CII | 166 | 18.60 | 5.95 | 40.640 | 68.670 | -0.542 |
| VvsHSP14 | VIT_204s0008g01580.1 | CII | 156 | 17.42 | 6.62 | 42.220 | 76.790 | -0.510 |
| VvsHSP15 | VIT_204s0008g01590.1 | CII | 155 | 17.29 | 5.94 | 37.610 | 81.030 | -0.466 |
| VvsHSP16 | VIT_204s0008g01610.1 | CII | 158 | 18.14 | 6.33 | 40.180 | 75.820 | -0.617 |
| VvsHSP17 | VIT_204s0008g01620.1 | CII | 159 | 18.42 | 8.46 | 42.080 | 83.900 | -0.459 |
| VvsHSP18 | VIT_206s0004g05770.1 | CI | 144 | 16.31 | 6.93 | 33.000 | 75.070 | -0.642 |
| VvsHSP19 | VIT_208s0058g00210.1 | CI | 148 | 16.88 | 5.81 | 64.560 | 66.490 | -0.629 |
| VvsHSP20 | VIT_209s0002g00640.1 | CIII | 160 | 17.89 | 6.30 | 49.690 | 81.000 | -0.516 |
| VvsHSP21 | VIT_209s0002g06790.1 | MTII | 233 | 26.31 | 7.78 | 53.870 | 82.060 | -0.750 |
| VvsHSP22 | VIT_212s0035g01910.1 | ER | 250 | 28.39 | 7.94 | 49.940 | 89.400 | -0.388 |
| VvsHSP23 | VIT_213s0019g00860.1 | PX | 142 | 15.81 | 6.75 | 51.850 | 85.000 | -0.311 |
| VvsHSP24 | VIT_213s0019g02740.1 | CI | 151 | 17.17 | 5.81 | 46.350 | 74.110 | -0.553 |
| VvsHSP25 | VIT_213s0019g02760.1 | CI | 140 | 15.80 | 6.77 | 42.530 | 72.290 | -0.589 |
| VvsHSP26 | VIT_213s0019g02770.1 | CI | 151 | 17.10 | 5.81 | 48.460 | 72.850 | -0.554 |
| VvsHSP27 | VIT_213s0019g02780.1 | CI | 151 | 17.02 | 5.80 | 45.690 | 70.260 | -0.587 |
| VvsHSP28 | VIT_213s0019g02820.1 | CI | 151 | 17.12 | 5.81 | 47.080 | 70.260 | -0.591 |
| VvsHSP29 | VIT_213s0019g02840.1 | CI | 151 | 17.09 | 5.54 | 50.220 | 72.850 | -0.551 |
| VvsHSP30 | VIT_213s0019g02850.1 | CI | 151 | 17.05 | 5.80 | 45.440 | 70.260 | -0.590 |
| VvsHSP31 | VIT_213s0019g02900.1 | CI | 108 | 12.64 | 6.18 | 52.990 | 80.190 | -0.798 |
| VvsHSP32 | VIT_213s0019g02920.1 | CI | 136 | 15.27 | 5.70 | 46.020 | 79.490 | -0.552 |
| VvsHSP33 | VIT_213s0019g02930.1 | CI | 160 | 18.17 | 6.78 | 53.430 | 76.690 | -0.644 |
| VvsHSP34 | VIT_213s0019g03000.1 | CI | 160 | 18.15 | 7.93 | 55.700 | 76.690 | -0.644 |
Table 1 (continued)
| Protein name | Locus name | Subfamily | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtsHSP08 | AT4G10250.1 | ER | 195 | 22.00 | 5.58 | 36.450 | 93.950 | -0.469 |
| AtsHSP09 | AT4G21870.1 | CIV | 134 | 15.39 | 5.17 | 73.930 | 93.810 | -0.325 |
| AtsHSP10 | AT4G25200.1 | MTI/CP | 210 | 23.61 | 6.46 | 58.790 | 80.760 | -0.649 |
| AtsHSP11 | AT4G27670.1 | CP | 227 | 25.34 | 8.49 | 46.860 | 72.070 | -0.641 |
| AtsHSP12 | AT5G12020.1 | CII | 155 | 17.62 | 6.32 | 38.840 | 80.390 | -0.617 |
| AtsHSP13 | AT5G12030.1 | CII | 156 | 17.69 | 5.59 | 44.370 | 75.000 | -0.596 |
| AtsHSP14 | AT5G37670.1 | PX | 137 | 15.70 | 7.94 | 50.680 | 86.640 | -0.512 |
| AtsHSP15 | AT5G51440.1 | MTI/CP | 210 | 23.47 | 8.96 | 52.510 | 84.000 | -0.558 |
| AtsHSP16 | AT5G54660.1 | CV | 192 | 21.66 | 5.47 | 38.030 | 71.560 | -0.500 |
| AtsHSP17 | AT5G59720.1 | CI | 161 | 18.13 | 6.77 | 48.090 | 67.200 | -0.657 |
| VvsHSP01 | VIT_200s0707g00010.1 | CIV | 136 | 15.69 | 4.89 | 53.490 | 82.430 | -0.315 |
| VvsHSP02 | VIT_200s0992g00020.1 | CIV | 136 | 15.70 | 5.01 | 54.190 | 82.430 | -0.312 |
| VvsHSP03 | VIT_201s0010g02290.1 | CP | 226 | 25.56 | 6.77 | 48.710 | 62.170 | -0.706 |
| VvsHSP04 | VIT_202s0154g00480.1 | MTI/CP | 201 | 22.45 | 9.24 | 45.150 | 77.060 | -0.531 |
| VvsHSP05 | VIT_202s0154g00490.1 | MTI/CP | 201 | 22.55 | 9.11 | 51.710 | 75.670 | -0.561 |
| VvsHSP06 | VIT_204s0008g01490.1 | CII | 156 | 17.34 | 5.94 | 41.520 | 82.500 | -0.444 |
| VvsHSP07 | VIT_204s0008g01500.1 | CII | 152 | 16.69 | 6.84 | 42.090 | 79.540 | -0.390 |
| VvsHSP08 | VIT_204s0008g01510.1 | CII | 156 | 17.40 | 5.77 | 44.190 | 76.220 | -0.462 |
| VvsHSP09 | VIT_204s0008g01520.1 | CII | 156 | 17.58 | 5.58 | 40.180 | 78.080 | -0.513 |
| VvsHSP10 | VIT_204s0008g01530.1 | CII | 480 | 53.16 | 8.89 | 39.780 | 68.600 | -0.713 |
| VvsHSP11 | VIT_204s0008g01550.1 | CII | 156 | 17.41 | 5.94 | 39.580 | 71.790 | -0.533 |
| VvsHSP12 | VIT_204s0008g01560.1 | CII | 113 | 12.66 | 8.66 | 38.840 | 83.540 | -0.473 |
| VvsHSP13 | VIT_204s0008g01570.1 | CII | 166 | 18.60 | 5.95 | 40.640 | 68.670 | -0.542 |
| VvsHSP14 | VIT_204s0008g01580.1 | CII | 156 | 17.42 | 6.62 | 42.220 | 76.790 | -0.510 |
| VvsHSP15 | VIT_204s0008g01590.1 | CII | 155 | 17.29 | 5.94 | 37.610 | 81.030 | -0.466 |
| VvsHSP16 | VIT_204s0008g01610.1 | CII | 158 | 18.14 | 6.33 | 40.180 | 75.820 | -0.617 |
| VvsHSP17 | VIT_204s0008g01620.1 | CII | 159 | 18.42 | 8.46 | 42.080 | 83.900 | -0.459 |
| VvsHSP18 | VIT_206s0004g05770.1 | CI | 144 | 16.31 | 6.93 | 33.000 | 75.070 | -0.642 |
| VvsHSP19 | VIT_208s0058g00210.1 | CI | 148 | 16.88 | 5.81 | 64.560 | 66.490 | -0.629 |
| VvsHSP20 | VIT_209s0002g00640.1 | CIII | 160 | 17.89 | 6.30 | 49.690 | 81.000 | -0.516 |
| VvsHSP21 | VIT_209s0002g06790.1 | MTII | 233 | 26.31 | 7.78 | 53.870 | 82.060 | -0.750 |
| VvsHSP22 | VIT_212s0035g01910.1 | ER | 250 | 28.39 | 7.94 | 49.940 | 89.400 | -0.388 |
| VvsHSP23 | VIT_213s0019g00860.1 | PX | 142 | 15.81 | 6.75 | 51.850 | 85.000 | -0.311 |
| VvsHSP24 | VIT_213s0019g02740.1 | CI | 151 | 17.17 | 5.81 | 46.350 | 74.110 | -0.553 |
| VvsHSP25 | VIT_213s0019g02760.1 | CI | 140 | 15.80 | 6.77 | 42.530 | 72.290 | -0.589 |
| VvsHSP26 | VIT_213s0019g02770.1 | CI | 151 | 17.10 | 5.81 | 48.460 | 72.850 | -0.554 |
| VvsHSP27 | VIT_213s0019g02780.1 | CI | 151 | 17.02 | 5.80 | 45.690 | 70.260 | -0.587 |
| VvsHSP28 | VIT_213s0019g02820.1 | CI | 151 | 17.12 | 5.81 | 47.080 | 70.260 | -0.591 |
| VvsHSP29 | VIT_213s0019g02840.1 | CI | 151 | 17.09 | 5.54 | 50.220 | 72.850 | -0.551 |
| VvsHSP30 | VIT_213s0019g02850.1 | CI | 151 | 17.05 | 5.80 | 45.440 | 70.260 | -0.590 |
| VvsHSP31 | VIT_213s0019g02900.1 | CI | 108 | 12.64 | 6.18 | 52.990 | 80.190 | -0.798 |
| VvsHSP32 | VIT_213s0019g02920.1 | CI | 136 | 15.27 | 5.70 | 46.020 | 79.490 | -0.552 |
| VvsHSP33 | VIT_213s0019g02930.1 | CI | 160 | 18.17 | 6.78 | 53.430 | 76.690 | -0.644 |
| VvsHSP34 | VIT_213s0019g03000.1 | CI | 160 | 18.15 | 7.93 | 55.700 | 76.690 | -0.644 |
| Protein name | Locus name | Subfamily | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VvsHSP35 | VIT_213s0019g03010.1 | CI | 144 | 16.37 | 9.21 | 49.720 | 69.030 | -0.785 |
| VvsHSP36 | VIT_213s0019g03030.1 | CI | 108 | 12.67 | 6.76 | 37.260 | 77.500 | -0.817 |
| VvsHSP37 | VIT_213s0019g03050.1 | CI | 165 | 19.23 | 6.46 | 61.350 | 79.090 | -0.721 |
| VvsHSP38 | VIT_213s0019g03090.1 | CI | 160 | 18.17 | 5.43 | 62.670 | 73.690 | -0.673 |
| VvsHSP39 | VIT_213s0019g03160.1 | CI | 160 | 18.02 | 7.94 | 64.610 | 73.120 | -0.631 |
| VvsHSP40 | VIT_213s0019g03170.1 | CI | 159 | 18.19 | 6.17 | 51.140 | 71.010 | -0.655 |
| VvsHSP41 | VIT_216s0022g00510.1 | MTI/CP | 208 | 23.74 | 5.61 | 60.250 | 75.870 | -0.721 |
| VvsHSP42 | VIT_216s0098g01060.1 | CP | 227 | 25.03 | 6.35 | 44.280 | 72.600 | -0.505 |
| VvsHSP43 | VIT_218s0001g01570.1 | CVI | 163 | 18.28 | 6.33 | 48.000 | 71.720 | -0.790 |
| VvsHSP44 | VIT_218s0001g01610.1 | CVI | 159 | 18.00 | 5.74 | 44.410 | 72.890 | -0.731 |
| VvsHSP45 | VIT_218s0089g01270.1 | ER | 186 | 21.13 | 5.89 | 35.370 | 90.590 | -0.567 |
| VvsHSP46 | VIT_219s0014g05050.1 | CV | 192 | 22.39 | 5.35 | 48.680 | 70.470 | -0.754 |
| VvsHSP47 | VIT_219s0085g01050.1 | CVII | 146 | 16.45 | 5.90 | 50.360 | 72.740 | -0.530 |
Table 1 (continued)
| Protein name | Locus name | Subfamily | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VvsHSP35 | VIT_213s0019g03010.1 | CI | 144 | 16.37 | 9.21 | 49.720 | 69.030 | -0.785 |
| VvsHSP36 | VIT_213s0019g03030.1 | CI | 108 | 12.67 | 6.76 | 37.260 | 77.500 | -0.817 |
| VvsHSP37 | VIT_213s0019g03050.1 | CI | 165 | 19.23 | 6.46 | 61.350 | 79.090 | -0.721 |
| VvsHSP38 | VIT_213s0019g03090.1 | CI | 160 | 18.17 | 5.43 | 62.670 | 73.690 | -0.673 |
| VvsHSP39 | VIT_213s0019g03160.1 | CI | 160 | 18.02 | 7.94 | 64.610 | 73.120 | -0.631 |
| VvsHSP40 | VIT_213s0019g03170.1 | CI | 159 | 18.19 | 6.17 | 51.140 | 71.010 | -0.655 |
| VvsHSP41 | VIT_216s0022g00510.1 | MTI/CP | 208 | 23.74 | 5.61 | 60.250 | 75.870 | -0.721 |
| VvsHSP42 | VIT_216s0098g01060.1 | CP | 227 | 25.03 | 6.35 | 44.280 | 72.600 | -0.505 |
| VvsHSP43 | VIT_218s0001g01570.1 | CVI | 163 | 18.28 | 6.33 | 48.000 | 71.720 | -0.790 |
| VvsHSP44 | VIT_218s0001g01610.1 | CVI | 159 | 18.00 | 5.74 | 44.410 | 72.890 | -0.731 |
| VvsHSP45 | VIT_218s0089g01270.1 | ER | 186 | 21.13 | 5.89 | 35.370 | 90.590 | -0.567 |
| VvsHSP46 | VIT_219s0014g05050.1 | CV | 192 | 22.39 | 5.35 | 48.680 | 70.470 | -0.754 |
| VvsHSP47 | VIT_219s0085g01050.1 | CVII | 146 | 16.45 | 5.90 | 50.360 | 72.740 | -0.530 |
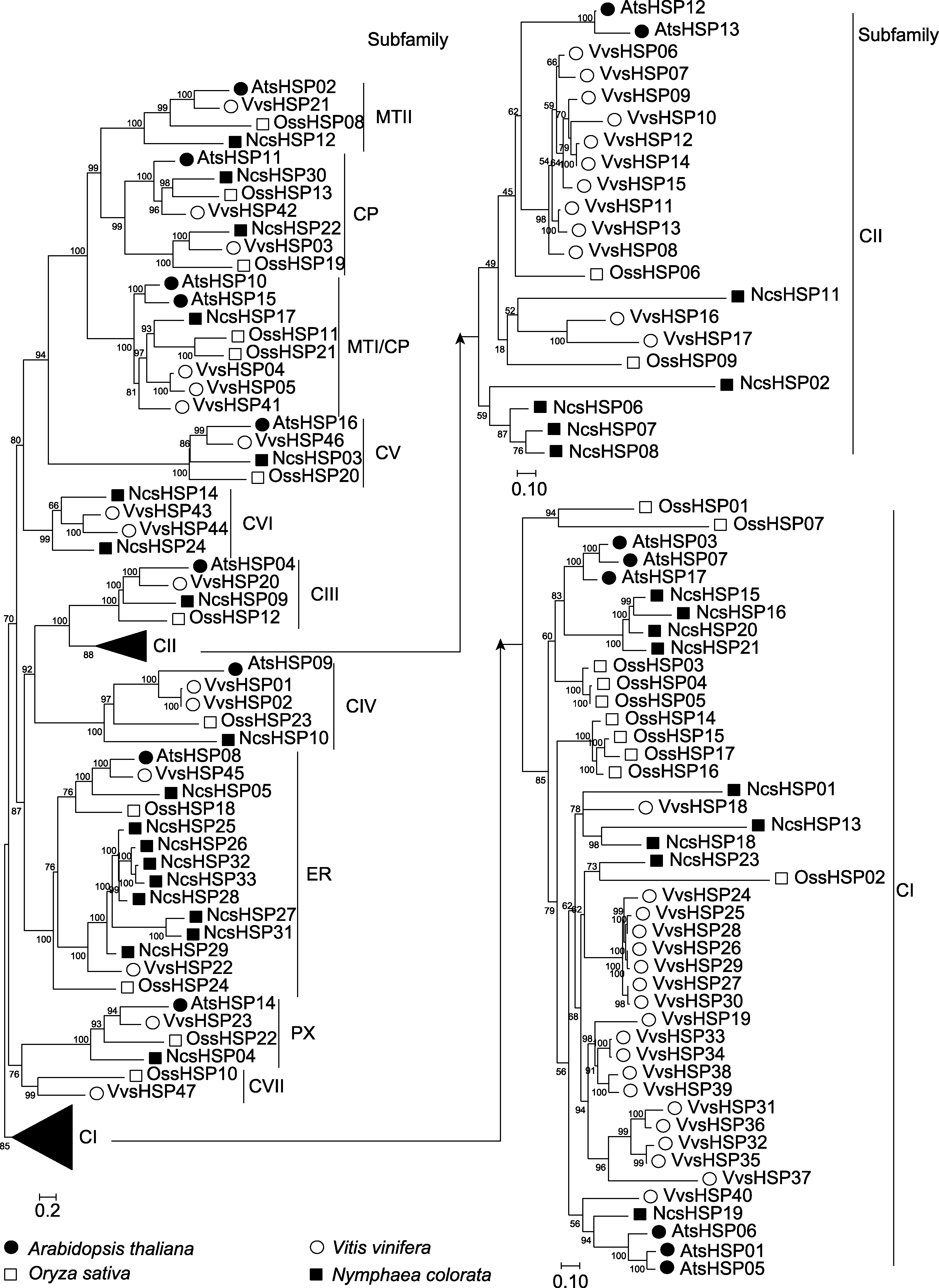
Figure 1 The phylogenetic analysis of sHSP members in waterlily, rice, Arabidopsis and grape The phylogenetic tree was constructed by IQ-tree software. The numbers in the clades stood for the bootstrap values.
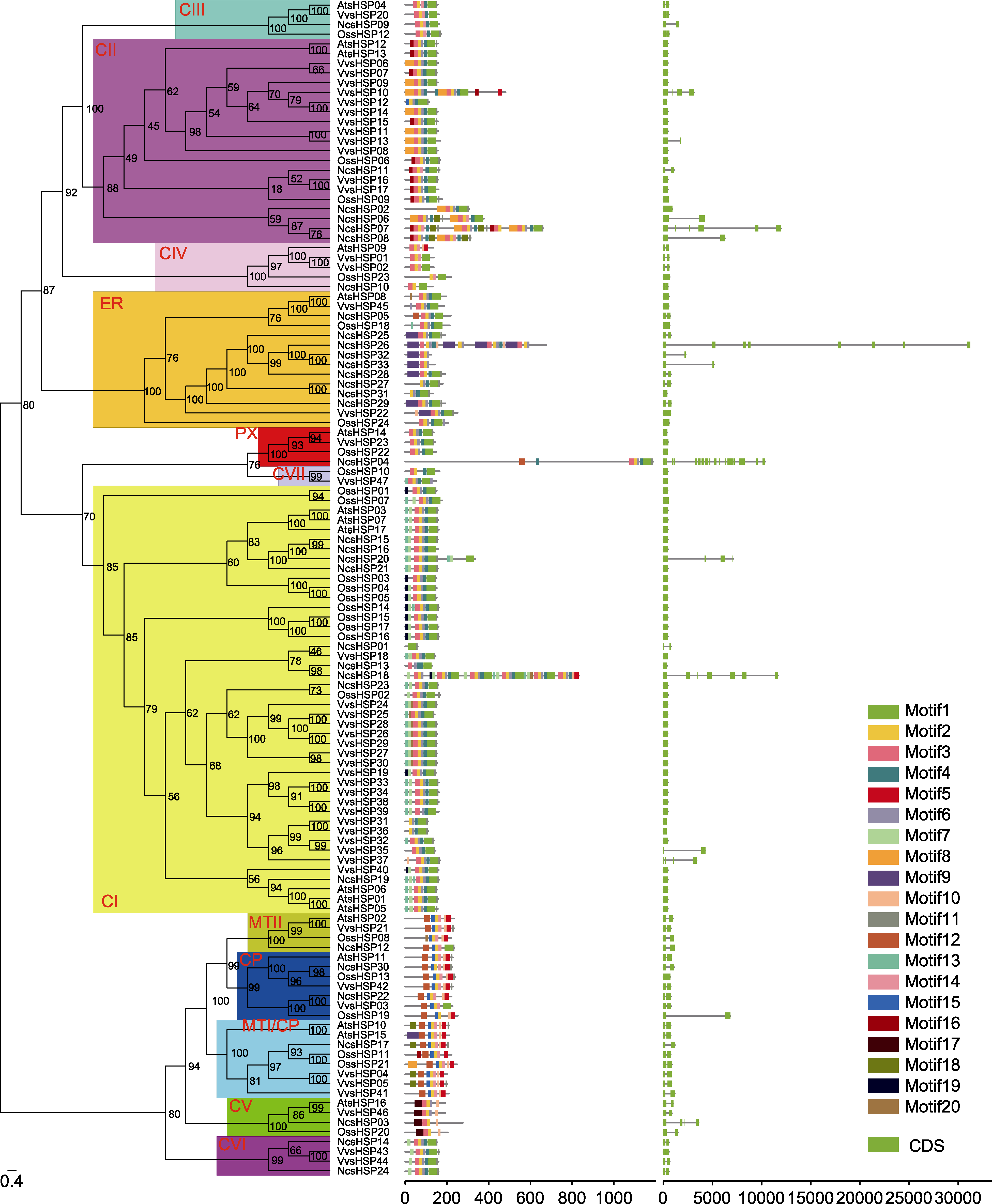
Figure 2 The phylogenetic analysis (left), conserved motif (middle), and gene structure (right) of the sHSF family in waterlily, rice, Arabidopsis and grape The phylogenetic tree (left) was constructed by IQ-tree software. The numbers in the clades stood for the bootstrap values, and sHSP subfamilies were indicated by red letters. The conserved motifs (middle) were identified by MEME software. Each conserved motif was marked by a specific color, and the location of motifs can be estimated using the scale at the bottom. The gene structures (right) were visualized according to the location of exons and introns. The exons and introns were represented by green box and black line, respectively. The location of exons and introns can be estimated using the scale at the bottom.
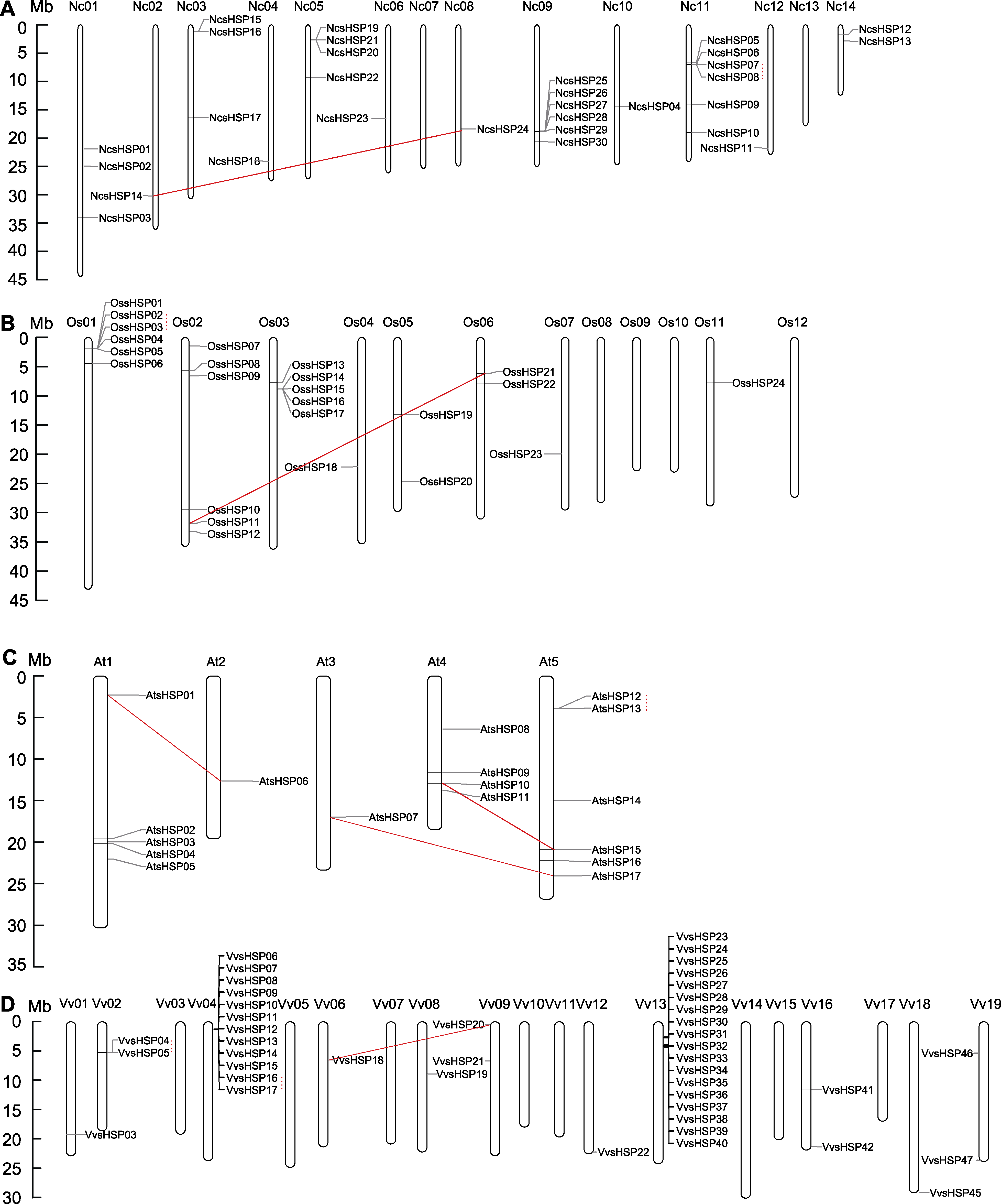
Figure 3 Chromosomal locations of NcsHSP (A), OssHSP (B), AtsHSP (C) and VvsHSP (D) on the waterlily, rice, Arabidopsis and grape chromosomes The solid lines and dot lines represented the segmental and tandem duplication events, respectively.
| Duplicated gene 1 | Duplicated gene 2 | Subfamily | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | Purifying selection | Duplicated type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NcsHSP07 | NcsHSP08 | CII | 0.067786 | 0.358961 | 0.188839 | Yes | Tandem |
| NcsHSP14 | NcsHSP24 | CVI | 0.346841 | 0.789231 | 0.439467 | Yes | Segmental |
| OssHSP03 | OssHSP04 | CI | 0.02811 | 0.129535 | 0.217006 | Yes | Tandem |
| OssHSP11 | OssHSP21 | MTI/CP | 0.303273 | 0.454245 | 0.66764 | Yes | Segmental |
| AtsHSP01 | AtsHSP06 | CI | 0.08714 | 1.101078 | 0.079141 | Yes | Segmental |
| AtsHSP07 | AtsHSP17 | CI | 0.110454 | 1.291145 | 0.085547 | Yes | Segmental |
| AtsHSP10 | AtsHSP15 | MTI/CP | 0.175047 | 1.17229 | 0.14932 | Yes | Segmental |
| AtsHSP12 | AtsHSP13 | CII | 0.060844 | 0.53554 | 0.113613 | Yes | Tandem |
| VvsHSP04 | VvsHSP05 | MTI/CP | 0.077421 | 0.10198 | 0.759181 | Yes | Tandem |
| VvsHSP16 | VvsHSP17 | CII | 0.212704 | 0.880614 | 0.241541 | Yes | Tandem |
| VvsHSP18 | VvsHSP40 | CI | 0.206071 | 1.642523 | 0.12546 | Yes | Segmental |
| VvsHSP43 | VvsHSP44 | CVI | 0.21995 | 0.81194 | 0.270894 | Yes | Tandem |
Table 2 Ka and Ks analysis for the duplicated sHSP members in waterlily, rice, Arabidopsis and grape
| Duplicated gene 1 | Duplicated gene 2 | Subfamily | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | Purifying selection | Duplicated type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NcsHSP07 | NcsHSP08 | CII | 0.067786 | 0.358961 | 0.188839 | Yes | Tandem |
| NcsHSP14 | NcsHSP24 | CVI | 0.346841 | 0.789231 | 0.439467 | Yes | Segmental |
| OssHSP03 | OssHSP04 | CI | 0.02811 | 0.129535 | 0.217006 | Yes | Tandem |
| OssHSP11 | OssHSP21 | MTI/CP | 0.303273 | 0.454245 | 0.66764 | Yes | Segmental |
| AtsHSP01 | AtsHSP06 | CI | 0.08714 | 1.101078 | 0.079141 | Yes | Segmental |
| AtsHSP07 | AtsHSP17 | CI | 0.110454 | 1.291145 | 0.085547 | Yes | Segmental |
| AtsHSP10 | AtsHSP15 | MTI/CP | 0.175047 | 1.17229 | 0.14932 | Yes | Segmental |
| AtsHSP12 | AtsHSP13 | CII | 0.060844 | 0.53554 | 0.113613 | Yes | Tandem |
| VvsHSP04 | VvsHSP05 | MTI/CP | 0.077421 | 0.10198 | 0.759181 | Yes | Tandem |
| VvsHSP16 | VvsHSP17 | CII | 0.212704 | 0.880614 | 0.241541 | Yes | Tandem |
| VvsHSP18 | VvsHSP40 | CI | 0.206071 | 1.642523 | 0.12546 | Yes | Segmental |
| VvsHSP43 | VvsHSP44 | CVI | 0.21995 | 0.81194 | 0.270894 | Yes | Tandem |
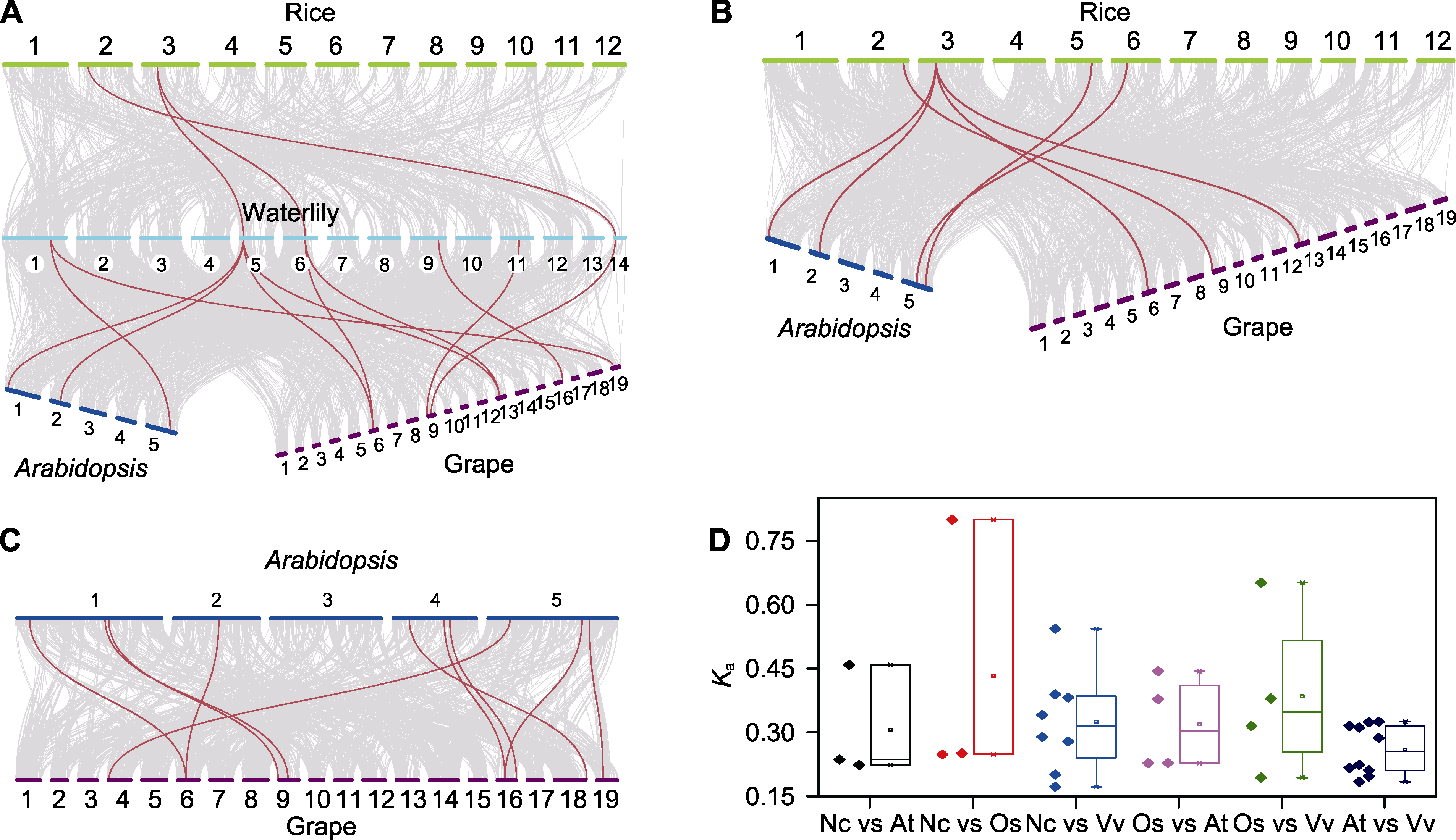
Figure 4 Synteny analysis of sHSP members in waterlily, rice, Arabidopsis and grape (A) Synteny analysis of sHSP members between waterlily and rice, Arabidopsis and grape; (B) Synteny analysis of sHSP members between rice and Arabidopsis and grape; (C) Synteny analysis of sHSP members between Arabidopsis and grape; (D) Comparison of Ka values of orthologous sHSPs between different species. (A)-(C) Gray lines connected orthologous genes, and orthologous sHSPs were marked with red lines.
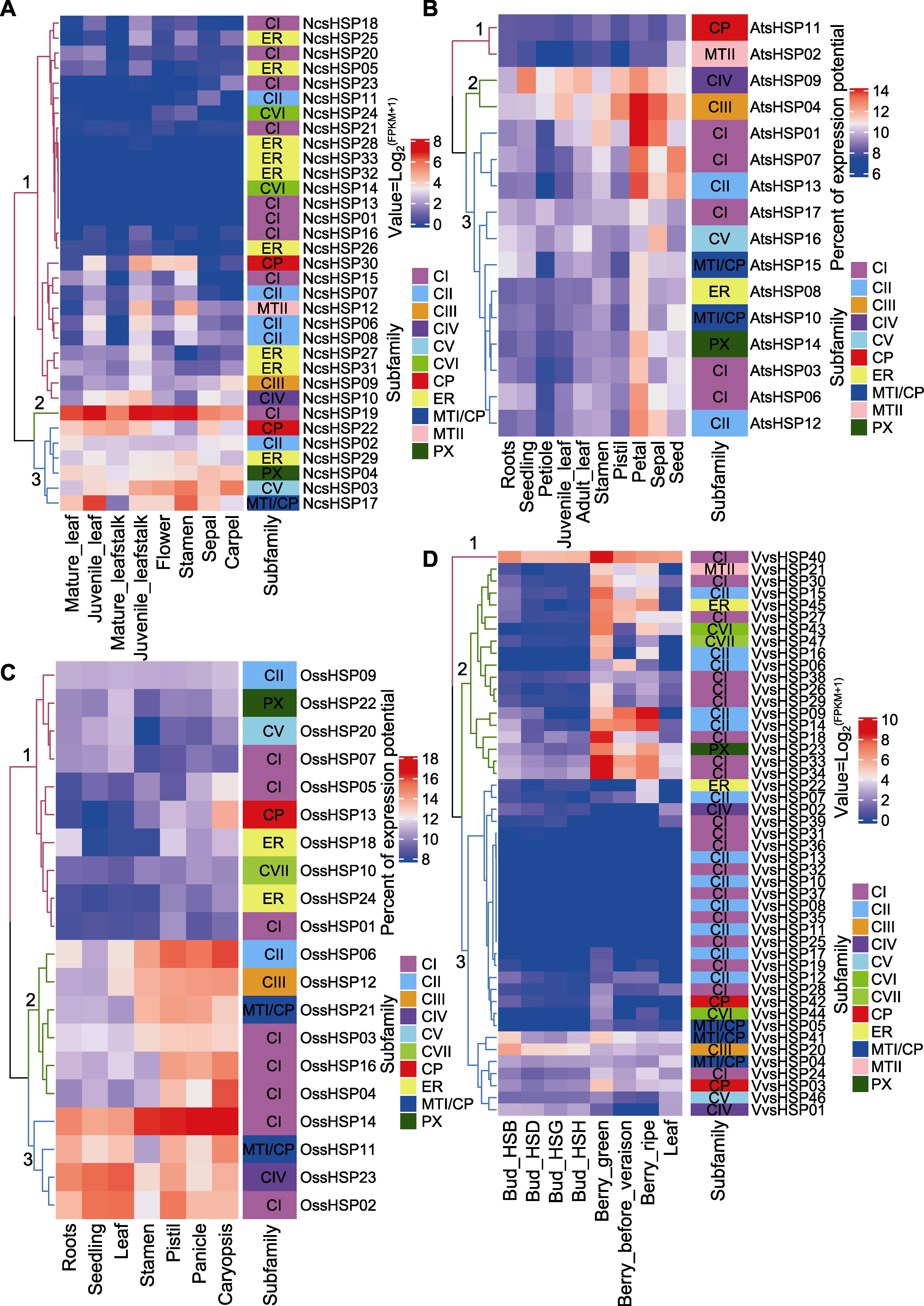
Figure 5 Expression profiles of NcsHSP (A), AtsHSP (B), OssHSP (C) and VvsHSP (D) in different tissues Two color bars represented expression level and sHSP subfamilies, respectively.
| 1 | 何福林, 张斌 (2019). 银杏(Ginkgo biloba) GbHsp20基因家族的鉴定及系统进化分析. 分子植物育种 17, 7368-7376. |
| 2 | 黄祥富, 黄上志, 傅家瑞 (1999). 植物热激蛋白的功能及其基因表达的调控. 植物学通报 16, 530-536. |
| 3 | 栗振义, 龙瑞才, 张铁军, 杨青川, 康俊梅 (2016). 植物热激蛋白研究进展. 生物技术通报 32(2), 7-13. |
| 4 | 刘德立 (1996). 植物热激蛋白及其功能. 植物学通报 13, 14-19. |
| 5 | 张宁, 姜晶, 史洁玮 (2017). 番茄HSP20基因家族的全基因组鉴定、系统进化及表达分析. 沈阳农业大学学报 48, 137-144. |
| 6 | 张奇艳, 雷忠萍, 宋银, 海江波, 贺道华 (2019). 陆地棉扩展蛋白基因的鉴定与特征分析. 中国农业科学 52, 3713-3732. |
| 7 |
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004). The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4, 10.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Chen CJ, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He YH, Xia R (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13, 1194-1202.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Dafny-Yelin M, Tzfira T, Vainstein A, Adam Z (2008). Non-redundant functions of sHSP-CIs in acquired thermotolerance and their role in early seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 67, 363-373.
DOI PMID |
| 10 |
Fan K, Chen YR, Mao ZJ, Fang Y, Li ZW, Lin WW, Zhang YQ, Liu JP, Huang JW, Lin WX (2020a). Pervasive duplication, biased molecular evolution and comprehensive functional analysis of the PP2C family in Glycine max. BMC Genomics 21, 465.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Fan K, Mao ZJ, Zheng JX, Chen YR, Li ZW, Lin WW, Zhang YQ, Huang JW, Lin WX (2020b). Molecular evolution and expansion of the KUP family in the allopolyploid cotton species Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense. Front Plant Sci 11, 545042.
DOI URL |
| 12 |
Fan K, Shen H, Bibi N, Li F, Yuan SN, Wang M, Wang XD (2015). Molecular evolution and species-specific expansion of the NAP members in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 57, 673-687.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Fan K, Wang M, Miao Y, Ni M, Bibi N, Yuan SN, Li F, Wang XD (2014). Molecular evolution and expansion analysis of the NAC transcription factor in Zea mays. PLoS One 9, e111837.
DOI URL |
| 14 | Guo CL, Guo RR, Xu XZ, Gao M, Li XQ, Song JY, Zheng Y, Wang XP (2014). Evolution and expression analysis of the grape (Vitis vinifera L.) WRKY gene family. J Exp Bot 6, 1513-1528. |
| 15 |
Guo LM, Li J, He J, Liu H, Zhang HM (2020). A class I cytosolic HSP20 of rice enhances heat and salt tolerance in different organisms. Sci Rep 10, 1383.
DOI URL |
| 16 | Guo M, Liu JH, Lu JP, Zhai YF, Wang H, Gong ZH, Wang SB, Lu MH (2015). Genome-wide analysis of the CaHsp20 gene family in pepper: comprehensive sequence and expression profile analysis under heat stress. Front Plant Sci 6, 806. |
| 17 |
Ji XR, Yu YH, Ni PY, Zhang GH, Guo DL (2019). Genome-wide identification of small heat-shock protein (HSP20) gene family in grape and expression profile during berry development. BMC Plant Biol 19, 433.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Jiao YN, Leebens-Mack J, Ayyampalayam S, Bowers JE, McKain M, McNeal J, Rolf M, Ruzicka DR, Wafula E, Wickett NJ, Wu XL, Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhang YT, Carpenter EJ, Deyholos MK, Kutchan TM, Chanderbali AS, Soltis PS, Stevenson DW, McCombie R, Pires JC, Wong GKS, Soltis DE, DePamphilis DW (2012). A genome triplication associated with early diversification of the core eudicots. Genome Biol 13, R3.
DOI URL |
| 19 |
Key JL, Lin CY, Chen YM (1981). Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78, 3526-3530.
DOI URL |
| 20 |
Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Li DH, Swarbreck D, Wilks C, Sasidharan R, Muller R, Dreher K, Alexander DL, Garcia-Hernandez M, Karthikeyan AS, Lee CH, Nelson WD, Ploetz L, Singh S, Wensel A, Huala E (2012). The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res 40, D1202-D1210.
DOI URL |
| 21 |
Li JB, Zhang J, Jia HX, Li Y, Xu XD, Wang LJ, Lu MZ (2016). The Populus trichocarpa PtHSP17.8 involved in heat and salt stress tolerances. Plant Cell Rep 35, 1587-1599.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Li JB, Zhang J, Jia HX, Yue ZQ, Lu MZ, Xin XB, Hu JJ (2018). Genome-wide characterization of the sHsp gene family in Salix suchowensis reveals its functions under different abiotic stresses. Int J Mol Sci 19, 3246.
DOI URL |
| 23 |
Li Q, Zhang N, Zhang LS, Ma H (2015). Differential evolution of members of the rhomboid gene family with conservative and divergent patterns. New Phytol 206, 368-380.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Ma W, Guan XY, Li J, Pan RH, Wang LY, Liu FJ, Ma HY, Zhu SJ, Hu J, Ruan YL, Chen XY, Zhang TZ (2019). Mitochondrial small heat shock protein mediates seed germination via thermal sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 4716-4721.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Ma W, Zhao T, Li J, Liu BL, Fang L, Hu Y, Zhang TZ (2016). Identification and characterization of the GhHsp20 gene family in Gossypium hirsutum. Sci Rep 6, 32517.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Maere S, de Bodt S, Raes J, Casneuf T, van Montagu M, Kuiper M, van de Peer Y (2005). Modeling gene and genome duplications in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 5454-5459.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Ouyang S, Zhu W, Hamilton J, Lin HN, Campbell M, Childs K, Thibaud-Nissen F, Malek RL, Lee Y, Zheng L, Orvis J, Haas B, Wortman J, Buell CR (2007). The TIGR Rice Genome Annotation Resource: improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res 35, D883-D887.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Park KC, Kim NS (2010). Intron loss mediated structural dynamics and functional differentiation of the polygalacturonase gene family in land plants. Genes Genom 32, 570-577.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL (2016). Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc 11, 1650-1667.
DOI URL |
| 30 |
Sarkar NK, Kim YK, Grover A (2009). Rice sHsp genes: genomic organization and expression profiling under stress and development. BMC Genomics 10, 393.
DOI URL |
| 31 |
Scharf KD, Siddique M, Vierling E (2001). The expanding family of Arabidopsis thaliana small heat stress proteins and a new family of proteins containing α-crystallin domains (Acd proteins). Cell Stress Chaperones 6, 225-237.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Shazadee H, Khan N, Wang JJ, Wang CC, Zeng JG, Huang ZY, Wang XY (2019). Identification and expression profiling of protein phosphatases (PP2C) gene family in Gossypium hirsutum L. Int J Mol Sci 20, 1395.
DOI URL |
| 33 |
Sun WN, Bernard C, Van De Cotte B, Van Montagu M, Verbruggen N (2010). At-HSP17.6A, encoding a small heat-shock protein in Arabidopsis, can enhance osmotolerance upon overexpression. Plant J 27, 407-415.
DOI URL |
| 34 |
The French-Italian Public Consortium for Grapevine Genome Characterization (2007). The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature 449, 463-467.
DOI URL |
| 35 |
van Montfort RLM, Basha E, Friedrich KL, Slingsby C, Vierling E (2001). Crystal structure and assembly of a eukaryotic small heat shock protein. Nat Struct Biol 8, 1025-1030.
PMID |
| 36 |
Wang L, Zhang SL, Zhang XM, Hu XY, Guo CL, Wang XP, Song JY (2018). Evolutionary and expression analysis of Vitis vinifera OFP gene family. Plant Syst Evol 304, 995-1008.
DOI URL |
| 37 |
Wang WX, Vinocur B, Shoseyov O, Altman A (2004). Role of plant heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones in the abiotic stress response. Trends Plant Sci 9, 244-252.
DOI URL |
| 38 |
Waters ER, Vierling E (2020). Plant small heat shock proteins—evolutionary and functional diversity. New Phytol 227, 24-37.
DOI URL |
| 39 |
Zhai MZ, Sun YD, Jia CX, Peng SB, Liu ZX, Yang GY (2016). Over-expression of JrsHSP17.3 gene from Juglans regia confer the tolerance to abnormal temperature and NaCl stresses. J Plant Biol 59, 549-558.
DOI URL |
| 40 |
Zhang K, Han YT, Zhao FL, Hu Y, Gao YR, Ma YF, Zheng Y, Wang YJ, Wen YQ (2015). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CDPK gene family in grape, Vitis spp. BMC Plant Biol 15, 164.
DOI PMID |
| 41 |
Zhang LS, Chen F, Zhang XT, Li Z, Zhao YY, Lohaus R, Chang XJ, Dong W, Ho SYW, Liu X, Song AX, Chen JH, Guo WL, Wang ZJ, Zhuang YY, Wang HF, Chen XQ, Hu J, Liu YH, Qin Y, Wang K, Dong SS, Liu Y, Zhang SZ, Yu XX, Wu Q, Wang LS, Yan XQ, Jiao YN, Kong HZ, Zhou XF, Yu CW, Chen YC, Li F, Wang JH, Chen W, Chen XL, Jia QD, Zhang C, Jiang YF, Zhang WB, Liu GH, Fu JY, Chen F, Ma H, van de Peer Y, Tang HB (2020a). The water lily genome and the early evolution of flowering plants. Nature 577, 79-84.
DOI URL |
| 42 |
Zhang LS, Wu SD, Chang XJ, Wang XJ, Zhao YP, Xia YP, Trigiano RN, Jiao YN, Chen F (2020b). The ancient wave of polyploidization events in flowering plants and their facilitated adaptation to environmental stress. Plant Cell Environ 43, 2847-2856.
DOI URL |
| 43 |
Zhang N, Shi JW, Zhao HY, Jiang J (2018). Activation of small heat shock protein (SlHSP17.7) gene by cell wall invertase inhibitor (SlCIF1) gene involved in sugar metabolism in tomato. Gene 679, 90-99.
DOI PMID |
| 44 |
Zhao P, Wang DD, Wang RQ, Kong NN, Zhang C, Yang CH, Wu WT, Ma HL, Chen Q (2018). Genome-wide analysis of the potato Hsp20 gene family: identification, genomic organization and expression profiles in response to heat stress. BMC Genomics 19, 61.
DOI URL |
| 45 | Zhu W, Lu MH, Gong ZH, Chen RG (2011). Cloning and expression of a small heat shock protein gene CaHSP24 from pepper under abiotic stress. Afr J Biotechnol 10, 4968-4975. |
| 46 |
Zhu YX, Yan HW, Wang YY, Feng L, Chen Z, Xiang Y (2016). Genome duplication and evolution of heat shock transcription factor (HSF) gene family in four model angiosperms. J Plant Growth Regul 35, 903-920.
DOI URL |
| 47 |
Zhuo XK, Zheng TX, Zhang ZY, Zhang YC, Jiang LB, Ahmad S, Sun LD, Wang J, Cheng TR, Zhang QX (2018). Genome-wide analysis of the NAC transcription factor gene family reveals differential expression patterns and cold-stress responses in the woody plant Prunus mume. Genes (Basel) 9, 494.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Ziyun Wang, Yanwen Lv, Yu Xiao, Chao Wu, Xinsheng Hu. Advances in Regulation and Evolutionary Mechanisms of Plant Gene Expression [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | Linfeng Xia, Rui Li, Haizheng Wang, Daling Feng, Chunyang Wang. Research Advances and Prospects in Charophytes Genomics [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 271-282. |
| [3] | Laipeng Zhao, Baike Wang, Tao Yang, Ning Li, Haitao Yang, Juan Wang, Huizhuan Yan. Investigation of the Regulation of Drought Tolerance by the SlHVA22l Gene in Tomato [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 558-573. |
| [4] | Zhengyong Duan, Min Ding, Yuzhuo Wang, Yibing Ding, Ling Chen, Ruiyun Wang, Zhijun Qiao. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of SBP Genes in Panicum miliaceum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [5] | Hanqian Zhao, Jiayi Song, Jie Yang, Yongjing Zhao, Wennian Xia, Weizhuo Gu, Zhongyi Wang, Nan Yang, Huizhen Hu. Identification of XTH Family Genes in Antirrhinum majus and Screening of Genes Involoved in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum Resistance and Stamen Petalization [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 188-203. |
| [6] | Lixia Han, Yongjian Wang, Xuan Liu. Comparisons between non-native species invasion and native species range expansion [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23396-. |
| [7] | Yinger Mao, Xiumei Zhou, Nan Wang, Xiuxiu Li, Yuke You, Shangbin Bai. Impact of Phyllostachys edulis expansion to Chinese fir forest on the soil bacterial community [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [8] | Zhenzhou Chu, Gulbar Yisilam, Zezhong Qu, Xinmin Tian. Comparative Analyses on the Chloroplast Genome of Three Sympatric Atraphaxis Species [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 417-432. |
| [9] | Nan Wu, Lei Qin, Kan Cui, Haiou Li, Zhongsong Liu, Shitou Xia. Cloning of Brassica napus EXA1 Gene and Its Regulation on Plant Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [10] | WANG Jing-Jing, WANG Jia-Hao, HUANG Zhi-Yun, Vanessa Chiamaka OKECHUKW, HU Die, QI Shan-Shan, DAI Zhi-Cong, DU Dao-Lin. Effects of endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria on the growth strategy of an invasive plant Sphagneticola trilobata under different nitrogen levels [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2023, 47(2): 195-205. |
| [11] | Feifei Wang, Zhenxiang Zhou, Yi Hong, Yangyang Gu, Chao Lü, Baojian Guo, Juan Zhu, Rugen Xu. Identification of the NF-YC Genes in Hordeum vulgare and Expression Analysis Under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 140-149. |
| [12] | Lulu Xie, Qingqing Cui, Chunjuan Dong, Qingmao Shang. Recent Advances in Molecular Mechanisms of Plant Graft Healing Process [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(5): 634-643. |
| [13] | Liurong Guan, Zupei Liu, Ran Xu, Penggen Duan, Guozheng Zhang, Haiyue Yu, Jing Li, Yuehua Luo, Yunhai Li. Identification of a New OsBRI1 Weak Allele and Analysis of its Function in Grain Size Control [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 279-286. |
| [14] | Biyue Yan, Fuchun Tong, Luhui Kuang, Zhijian Mou, Wenjia Wu, Hongyue Cai, Jun Wang, Shuguang Jian, Hai Ren, Zhanfeng Liu. The influence of harmful plant Wedelia biflora expansion on terrestrial mollusks in Xisha Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(10): 1182-1191. |
| [15] | Yegeng Fan,Lihang Qiu,Xing Huang,Huiwen Zhou,Chongkun Gan,Yangrui Li,Rongzhong Yang,Jianming Wu,Rongfa Chen. Expression Analysis of Key Genes in Gibberellin Biosynthesis and Related Phytohormonal Dynamics During Sugarcane Internode Elongation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(4): 486-496. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||