

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (2): 188-203.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23107 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23107
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hanqian Zhao, Jiayi Song, Jie Yang, Yongjing Zhao, Wennian Xia, Weizhuo Gu, Zhongyi Wang, Nan Yang, Huizhen Hu*( )
)
Received:2023-08-07
Accepted:2024-01-30
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-10
Contact:
* E-mail: Hanqian Zhao, Jiayi Song, Jie Yang, Yongjing Zhao, Wennian Xia, Weizhuo Gu, Zhongyi Wang, Nan Yang, Huizhen Hu. Identification of XTH Family Genes in Antirrhinum majus and Screening of Genes Involoved in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum Resistance and Stamen Petalization[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 188-203.
| Gene name | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| AmUBI | ATCCACCCTTCACCTTGTG | TTGTCAATGGTATCCGAGC |
| AmXTH1 | AAGGACAGAGGCAATGGGTG | AACCTGAGAACTCGGCAGTG |
| AmXTH2 | TATGGAACGGAACGGGTTGG | TGCCAATTGTTTGGTGCGTT |
| AmXTH3 | CGCCAAGATCTTCCGAGGAG | CAGCGACGAGTTTGAGTTGC |
| AmXTH4 | AAAAGACCAAGCAATGGGCG | CTGCATCGTCGCATGTTGTC |
| AmXTH5 | TATGGTTCGATCCCACTGCG | CGAACGGTGCCTTTTTCCAG |
| AmXTH6 | GTGTTTGTGAACGGGCAAGG | TGCCCAACCATCTCCATTCC |
| AmXTH7 | TGGTTTGATCCAACGGCTGA | TCCGTTGCCCAACTACTTCC |
| AmXTH8 | TGCAGCTCTCAATCTGCCAA | GTAAAACGCGACGACGATGC |
| AmXTH9 | GGCCGAATGCTTTCGCTATC | AGTTCCGGCTGAGTTTCCTG |
| AmXTH10 | TCGCATTCCCGACTAACCAG | TACACGAATTCGAGAGCCCG |
| AmXTH11 | ACGAAAGCTCCGTTTGTTGC | TCTCCCATTGGCGTGAAGTC |
| AmXTH12 | GGCCAAATGCTGTCGCTATC | CAGTTCCGGCTGAGTTTCCT |
| AmXTH13 | TACATCGGGCTCTGGTTTCG | ATCGTGTGCGTCTCCTTGAG |
| AmXTH14 | CCCAAAAGCCAGCCAATGAG | GGCTTCGCAAAAGTGCAAGT |
| AmXTH15 | CCACCGAGGAATCACTCCAG | TCTAGATTACGTCGTGCCGC |
| AmXTH16 | TGCCGATGATTGGGCTACAC | TCAGGGGAAAGTTCACAGGC |
| AmXTH17 | CAGGCTCCCTTTACCGCTTA | CGGGGGTGAGATCCCAATAC |
| AmXTH18 | AGAACCACGACGAACTGGAC | AGGATGCTGTAACGATGCGA |
| AmXTH19 | ACCTTCCCCTGGCTACTACC | TTCCTGAGGTTCTGTCGAGC |
| AmXTH20 | TTCCTTGGCAATGTACCGGC | GCTGATCTGCAAGCTCATGG |
| AmXTH21 | CCTCTGGAATCCTCAACGCA | CACTAGTCCGCCTCTTGTCG |
| AmXTH22 | CGCTGAGTCAGTAGGTGTGG | TTTTCACTAGCCCGCCTCTC |
| AmXTH23 | AAGTTCTGCGACACTCAGGG | TAGTGTAGCTGCTGCGAACC |
| AmXTH24 | GTGGTTCGACCCGTCTAAGG | CTCCCCATTGCATCAACCCT |
| AmXTH25 | GATGGATCAGAGTGGGCGAC | CCCACTGCAACCCAGTAGTC |
| AmXTH26 | TGGGGCTATTTGAGCACTCG | GCCGAATGTGATTGTCAGCC |
| AmXTH27 | TGGAACCCAATGGCTTGGAC | GGGTTGAGTTGCAAACTGGG |
| AmXTH28 | CGACCCCTCCGAAGATTTCC | GCTATCCGCGTTCCAAATGC |
| AmXTH29 | CGATTCTCACATTCGGCAGC | AGCTCGTCGCGTACTGTATC |
| AmXTH30 | GAGCGGTTGTTCCGCATTTG | GCGTGAGAGCATGGTTCCTT |
| AmXTH31 | TTTCGACATCACGTGGGGAG | TCCCAGGGACAAGCTTCAAC |
| AmXTH32 | TCTACCGAGACAAATGGCCG | CAAGCGCATCTGGAAACGAG |
| AmXTH33 | ATGAAGATATTTATTGTGCA | AGATACCAATGGGAATCTTC |
Table 1 The sequences of qRT-PCR primers
| Gene name | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| AmUBI | ATCCACCCTTCACCTTGTG | TTGTCAATGGTATCCGAGC |
| AmXTH1 | AAGGACAGAGGCAATGGGTG | AACCTGAGAACTCGGCAGTG |
| AmXTH2 | TATGGAACGGAACGGGTTGG | TGCCAATTGTTTGGTGCGTT |
| AmXTH3 | CGCCAAGATCTTCCGAGGAG | CAGCGACGAGTTTGAGTTGC |
| AmXTH4 | AAAAGACCAAGCAATGGGCG | CTGCATCGTCGCATGTTGTC |
| AmXTH5 | TATGGTTCGATCCCACTGCG | CGAACGGTGCCTTTTTCCAG |
| AmXTH6 | GTGTTTGTGAACGGGCAAGG | TGCCCAACCATCTCCATTCC |
| AmXTH7 | TGGTTTGATCCAACGGCTGA | TCCGTTGCCCAACTACTTCC |
| AmXTH8 | TGCAGCTCTCAATCTGCCAA | GTAAAACGCGACGACGATGC |
| AmXTH9 | GGCCGAATGCTTTCGCTATC | AGTTCCGGCTGAGTTTCCTG |
| AmXTH10 | TCGCATTCCCGACTAACCAG | TACACGAATTCGAGAGCCCG |
| AmXTH11 | ACGAAAGCTCCGTTTGTTGC | TCTCCCATTGGCGTGAAGTC |
| AmXTH12 | GGCCAAATGCTGTCGCTATC | CAGTTCCGGCTGAGTTTCCT |
| AmXTH13 | TACATCGGGCTCTGGTTTCG | ATCGTGTGCGTCTCCTTGAG |
| AmXTH14 | CCCAAAAGCCAGCCAATGAG | GGCTTCGCAAAAGTGCAAGT |
| AmXTH15 | CCACCGAGGAATCACTCCAG | TCTAGATTACGTCGTGCCGC |
| AmXTH16 | TGCCGATGATTGGGCTACAC | TCAGGGGAAAGTTCACAGGC |
| AmXTH17 | CAGGCTCCCTTTACCGCTTA | CGGGGGTGAGATCCCAATAC |
| AmXTH18 | AGAACCACGACGAACTGGAC | AGGATGCTGTAACGATGCGA |
| AmXTH19 | ACCTTCCCCTGGCTACTACC | TTCCTGAGGTTCTGTCGAGC |
| AmXTH20 | TTCCTTGGCAATGTACCGGC | GCTGATCTGCAAGCTCATGG |
| AmXTH21 | CCTCTGGAATCCTCAACGCA | CACTAGTCCGCCTCTTGTCG |
| AmXTH22 | CGCTGAGTCAGTAGGTGTGG | TTTTCACTAGCCCGCCTCTC |
| AmXTH23 | AAGTTCTGCGACACTCAGGG | TAGTGTAGCTGCTGCGAACC |
| AmXTH24 | GTGGTTCGACCCGTCTAAGG | CTCCCCATTGCATCAACCCT |
| AmXTH25 | GATGGATCAGAGTGGGCGAC | CCCACTGCAACCCAGTAGTC |
| AmXTH26 | TGGGGCTATTTGAGCACTCG | GCCGAATGTGATTGTCAGCC |
| AmXTH27 | TGGAACCCAATGGCTTGGAC | GGGTTGAGTTGCAAACTGGG |
| AmXTH28 | CGACCCCTCCGAAGATTTCC | GCTATCCGCGTTCCAAATGC |
| AmXTH29 | CGATTCTCACATTCGGCAGC | AGCTCGTCGCGTACTGTATC |
| AmXTH30 | GAGCGGTTGTTCCGCATTTG | GCGTGAGAGCATGGTTCCTT |
| AmXTH31 | TTTCGACATCACGTGGGGAG | TCCCAGGGACAAGCTTCAAC |
| AmXTH32 | TCTACCGAGACAAATGGCCG | CAAGCGCATCTGGAAACGAG |
| AmXTH33 | ATGAAGATATTTATTGTGCA | AGATACCAATGGGAATCTTC |
| Gene name | Gene ID | aa | Mw (Da) | PI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY | TMHs | SP | Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AmXTH1 | Am01g06240.T01 | 332 | 38077.94 | 6.37 | 43.80 | 71.30 | -0.386 | 1 | 0 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH2 | Am01g11700.T01 | 260 | 29353.74 | 4.69 | 35.11 | 69.35 | -0.338 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH3 | Am01g14580.T01 | 285 | 32755.11 | 9.27 | 38.06 | 72.53 | -0.351 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH4 | Am01g53840.T01 | 290 | 33175.18 | 5.71 | 37.36 | 64.83 | -0.420 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH5 | Am02g07210.T01 | 299 | 34771.82 | 5.28 | 34.83 | 58.70 | -0.548 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH6 | Am02g15330.T01 | 221 | 25980.24 | 8.95 | 43.60 | 61.76 | -0.759 | 0 | 0 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH7 | Am02g15340.T01 | 292 | 33675.55 | 6.13 | 24.95 | 64.38 | -0.576 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH8 | Am02g39070.T01 | 340 | 39403.82 | 8.40 | 34.62 | 74.56 | -0.463 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH9 | Am03g04070.T01 | 287 | 32230.44 | 8.56 | 34.96 | 74.46 | -0.207 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH10 | Am03g04080.T01 | 287 | 32205.26 | 9.17 | 33.76 | 68.71 | -0.290 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH11 | Am03g04460.T01 | 285 | 32026.84 | 8.21 | 31.88 | 64.04 | -0.437 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH12 | Am03g04470.T01 | 278 | 31310.26 | 8.31 | 36.83 | 71.98 | -0.216 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH13 | Am03g04480.T01 | 284 | 32223.01 | 4.82 | 36.01 | 69.75 | -0.270 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH14 | Am03g08020.T01 | 288 | 32721.81 | 6.52 | 27.02 | 65.31 | -0.416 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH15 | Am03g08030.T01 | 320 | 36873.73 | 8.63 | 30.08 | 70.41 | -0.503 | 1 | 0 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH16 | Am04g01960.T01 | 303 | 35029.58 | 6.18 | 32.05 | 63.99 | -0.456 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH17 | Am04g29790.T01 | 276 | 32119.17 | 5.00 | 47.65 | 66.81 | -0.341 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH18 | Am05g24170.T01 | 350 | 40742.43 | 9.15 | 47.11 | 73.17 | -0.491 | 0 | 0 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH19 | Am05g28140.T01 | 293 | 32825.66 | 7.08 | 40.82 | 65.60 | -0.503 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH20 | Am05g34130.T01 | 294 | 34194.77 | 8.56 | 37.68 | 72.96 | -0.397 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH21 | Am06g03100.T02 | 293 | 32816.60 | 5.12 | 40.48 | 65.97 | -0.393 | 0 | 0 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH22 | Am06g03110.T02 | 294 | 32795.53 | 5.12 | 36.12 | 67.41 | -0.404 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH23 | Am06g09100.T01 | 296 | 34193.50 | 8.22 | 48.24 | 68.21 | -0.451 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH24 | Am06g11340.T01 | 304 | 35193.12 | 5.93 | 38.12 | 55.43 | -0.663 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH25 | Am06g16890.T01 | 315 | 35592.11 | 7.14 | 51.07 | 73.59 | -0.295 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH26 | Am06g38850.T01 | 288 | 32908.11 | 5.84 | 43.84 | 71.46 | -0.362 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH27 | Am07g22440.T01 | 282 | 32198.49 | 8.70 | 39.91 | 74.65 | -0.420 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH28 | Am07g32570.T01 | 290 | 33298.41 | 8.13 | 54.79 | 62.90 | -0.449 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH29 | Am08g01110.T01 | 285 | 32630.86 | 6.38 | 35.18 | 69.12 | -0.371 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH30 | Am08g26720.T01 | 298 | 34067.63 | 9.48 | 56.25 | 66.48 | -0.351 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH31 | Am08g29760.T01 | 280 | 31431.47 | 5.93 | 39.93 | 68.64 | -0.286 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH32 | Am08g29770.T01 | 647 | 73526.80 | 6.98 | 38.61 | 88.42 | -0.058 | 1 | 0 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH33 | Am08g29790.T02 | 271 | 30595.34 | 6.41 | 31.72 | 63.32 | -0.379 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
Table 2 Physical and chemical characteristics, and subcellular localization of XTH gene family in Antirrhinum majus
| Gene name | Gene ID | aa | Mw (Da) | PI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | GRAVY | TMHs | SP | Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AmXTH1 | Am01g06240.T01 | 332 | 38077.94 | 6.37 | 43.80 | 71.30 | -0.386 | 1 | 0 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH2 | Am01g11700.T01 | 260 | 29353.74 | 4.69 | 35.11 | 69.35 | -0.338 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH3 | Am01g14580.T01 | 285 | 32755.11 | 9.27 | 38.06 | 72.53 | -0.351 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH4 | Am01g53840.T01 | 290 | 33175.18 | 5.71 | 37.36 | 64.83 | -0.420 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH5 | Am02g07210.T01 | 299 | 34771.82 | 5.28 | 34.83 | 58.70 | -0.548 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH6 | Am02g15330.T01 | 221 | 25980.24 | 8.95 | 43.60 | 61.76 | -0.759 | 0 | 0 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH7 | Am02g15340.T01 | 292 | 33675.55 | 6.13 | 24.95 | 64.38 | -0.576 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH8 | Am02g39070.T01 | 340 | 39403.82 | 8.40 | 34.62 | 74.56 | -0.463 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH9 | Am03g04070.T01 | 287 | 32230.44 | 8.56 | 34.96 | 74.46 | -0.207 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH10 | Am03g04080.T01 | 287 | 32205.26 | 9.17 | 33.76 | 68.71 | -0.290 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH11 | Am03g04460.T01 | 285 | 32026.84 | 8.21 | 31.88 | 64.04 | -0.437 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH12 | Am03g04470.T01 | 278 | 31310.26 | 8.31 | 36.83 | 71.98 | -0.216 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH13 | Am03g04480.T01 | 284 | 32223.01 | 4.82 | 36.01 | 69.75 | -0.270 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH14 | Am03g08020.T01 | 288 | 32721.81 | 6.52 | 27.02 | 65.31 | -0.416 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH15 | Am03g08030.T01 | 320 | 36873.73 | 8.63 | 30.08 | 70.41 | -0.503 | 1 | 0 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH16 | Am04g01960.T01 | 303 | 35029.58 | 6.18 | 32.05 | 63.99 | -0.456 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH17 | Am04g29790.T01 | 276 | 32119.17 | 5.00 | 47.65 | 66.81 | -0.341 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH18 | Am05g24170.T01 | 350 | 40742.43 | 9.15 | 47.11 | 73.17 | -0.491 | 0 | 0 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH19 | Am05g28140.T01 | 293 | 32825.66 | 7.08 | 40.82 | 65.60 | -0.503 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH20 | Am05g34130.T01 | 294 | 34194.77 | 8.56 | 37.68 | 72.96 | -0.397 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH21 | Am06g03100.T02 | 293 | 32816.60 | 5.12 | 40.48 | 65.97 | -0.393 | 0 | 0 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH22 | Am06g03110.T02 | 294 | 32795.53 | 5.12 | 36.12 | 67.41 | -0.404 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH23 | Am06g09100.T01 | 296 | 34193.50 | 8.22 | 48.24 | 68.21 | -0.451 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH24 | Am06g11340.T01 | 304 | 35193.12 | 5.93 | 38.12 | 55.43 | -0.663 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH25 | Am06g16890.T01 | 315 | 35592.11 | 7.14 | 51.07 | 73.59 | -0.295 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH26 | Am06g38850.T01 | 288 | 32908.11 | 5.84 | 43.84 | 71.46 | -0.362 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH27 | Am07g22440.T01 | 282 | 32198.49 | 8.70 | 39.91 | 74.65 | -0.420 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH28 | Am07g32570.T01 | 290 | 33298.41 | 8.13 | 54.79 | 62.90 | -0.449 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH29 | Am08g01110.T01 | 285 | 32630.86 | 6.38 | 35.18 | 69.12 | -0.371 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH30 | Am08g26720.T01 | 298 | 34067.63 | 9.48 | 56.25 | 66.48 | -0.351 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall |
| AmXTH31 | Am08g29760.T01 | 280 | 31431.47 | 5.93 | 39.93 | 68.64 | -0.286 | 1 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH32 | Am08g29770.T01 | 647 | 73526.80 | 6.98 | 38.61 | 88.42 | -0.058 | 1 | 0 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
| AmXTH33 | Am08g29790.T02 | 271 | 30595.34 | 6.41 | 31.72 | 63.32 | -0.379 | 0 | 1 | Cell wall, cytoplasmic |
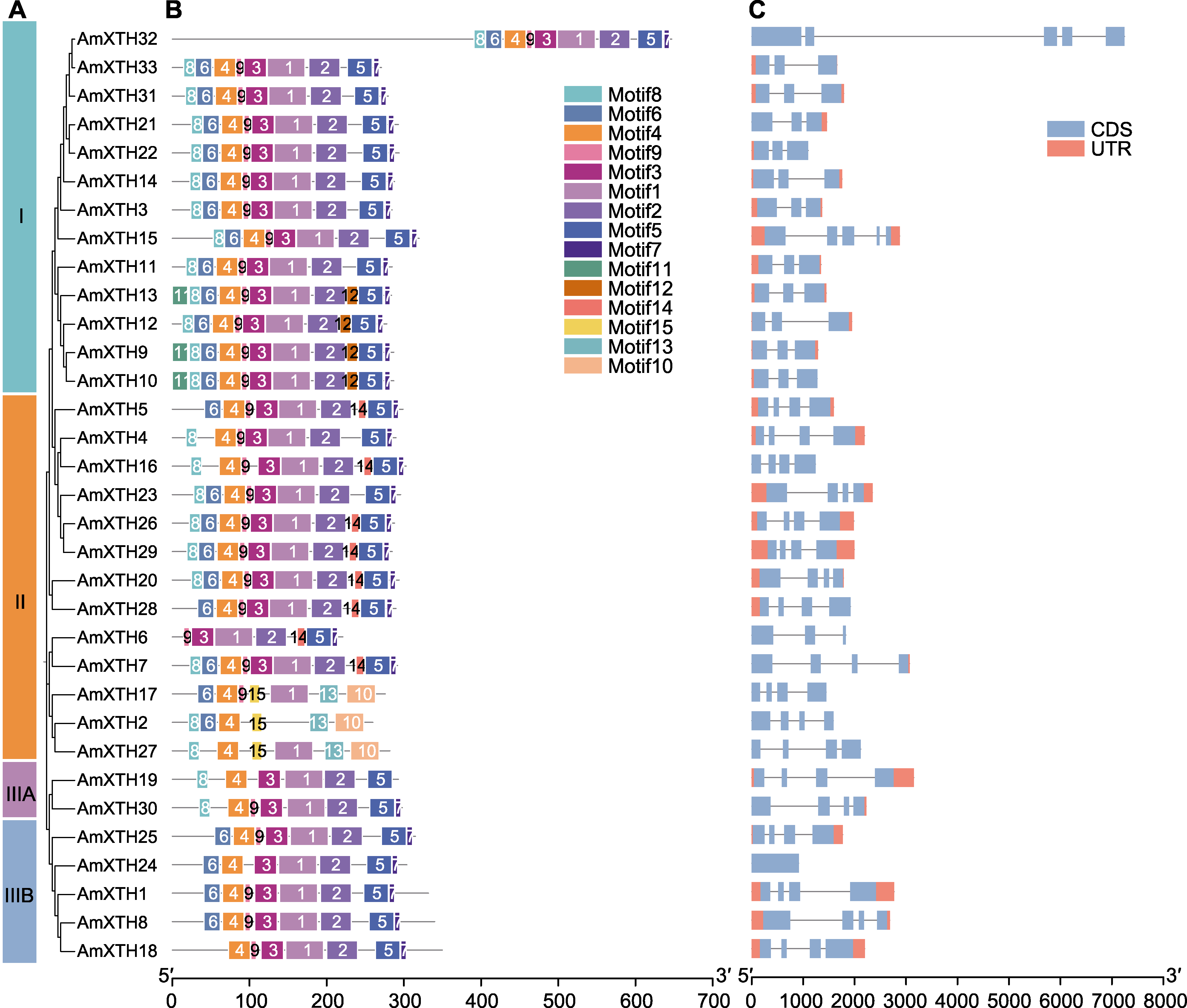
Figure 2 Phylogenetic relationship (A), conserved motif (B) and gene structures (C) of XTH family in Antirrhinum majus CDS: Coding sequence; UTR: Untranslated region
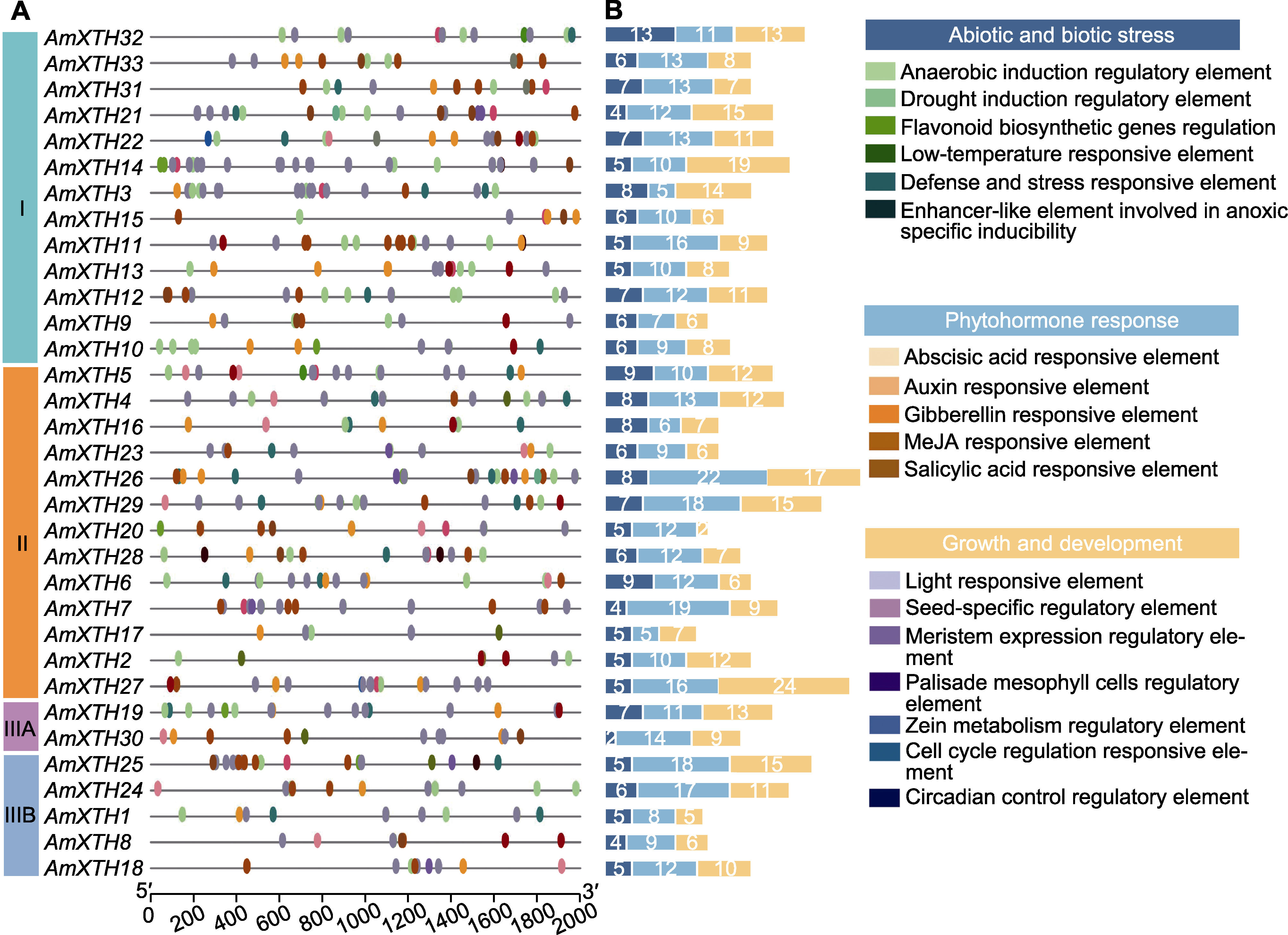
Figure 4 Analysis of cis-acting elements of the XTH family gene in Antirrhinum majus (A) Response elements; (B) Response type and number of response elements
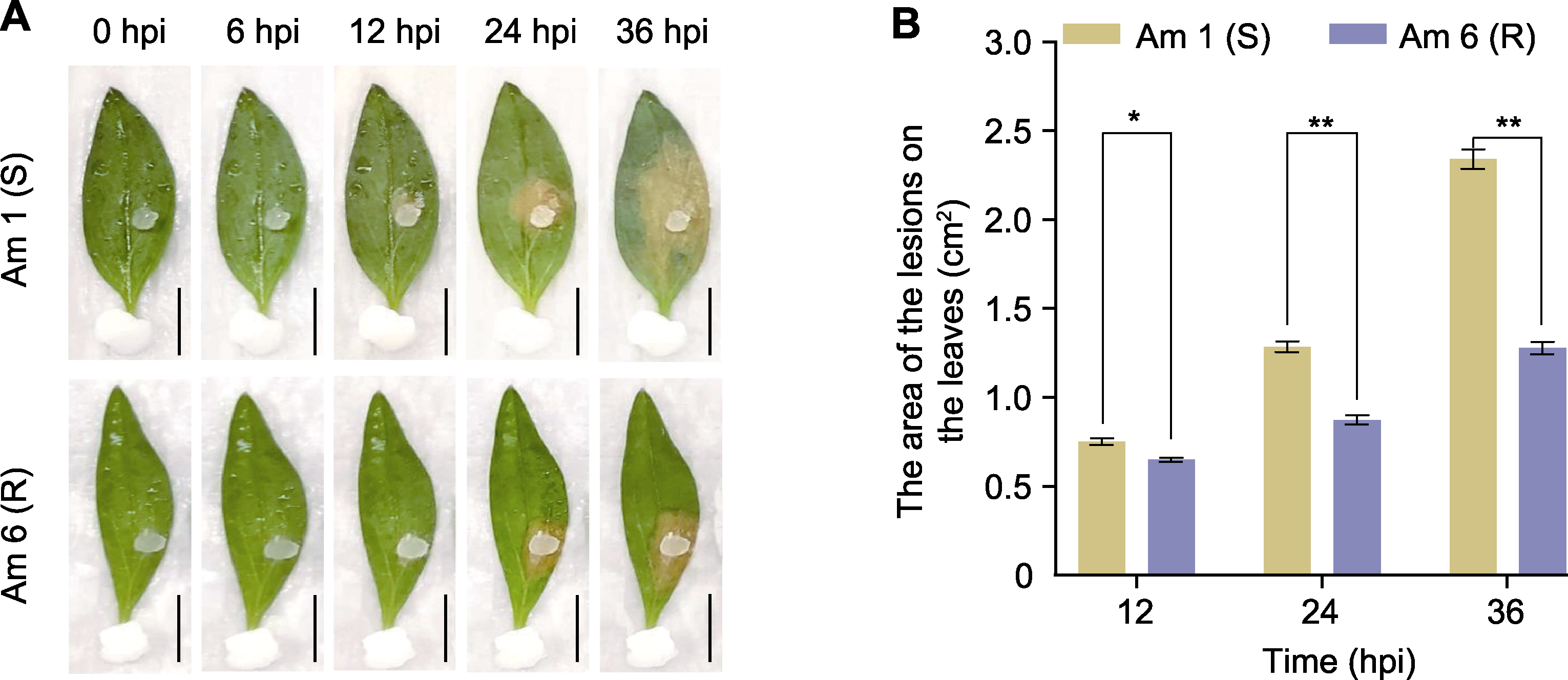
Figure 5 Phenotype (A) and the area of the lesions on Antirrhinum majus leaves (B) in vitro inoculation of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; hpi: Hours post-inoculation. Bars=1 cm
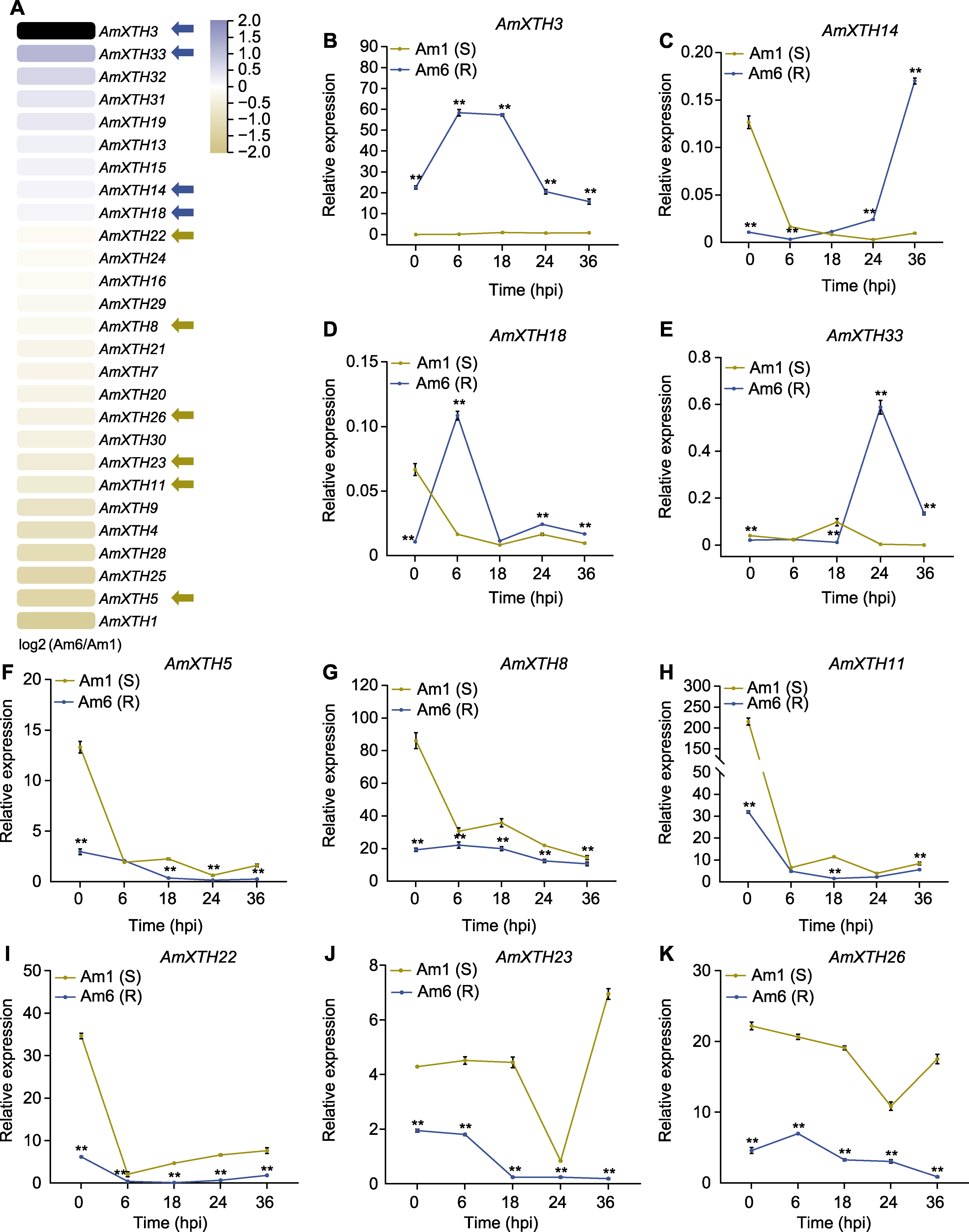
Figure 6 Differentially expressed AmXTH genes in RNA-seq analysis (A) and qRT-PCR verification (B)-(K) Blue arrows indicate genes expression significant higher in resistant material than in susceptible material, and yellow arrows indicate genes expression significant lower in resistant material than in susceptible material. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; hpi: Hours post-inoculation
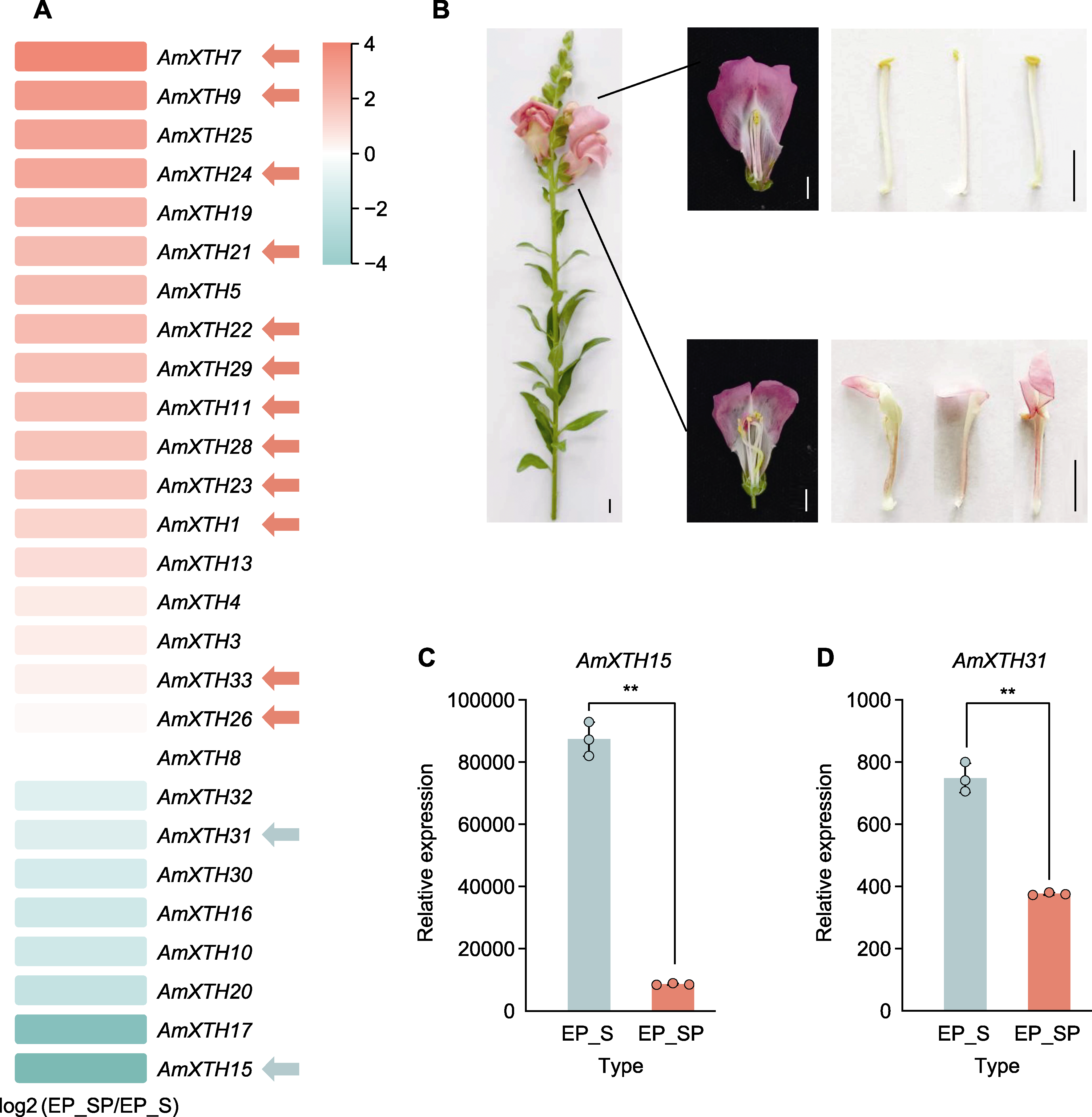
Figure 7 Differentially expressed AmXTH genes in RNA-seq analysis (A), phenotype observation of stamen petalization (B) and qRT-PCR verification of AmXTH genes involved in stamen petalization (C), (D) Red arrows indicate genes expression significant higher in petalized stamen than in normal stamen, and green arrows indicate genes expression significant lower in petalized stamen than in normal stamen. ** P<0.01。Bars=1 cm
| [1] | Cardarelli M, Cecchetti V (2014). Auxin polar transport in stamen formation and development: how many actors? Front Plant Sci 5, 333. |
| [2] |
Claverie J, Balacey S, Lemaître-Guillier C, Brulé D, Chiltz A, Granet L, Noirot E, Daire X, Darblade B, Héloir MC, Poinssot B (2018). The cell wall-derived xyloglucan is a new DAMP triggering plant immunity in Vitis vinifera and Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 9, 1725.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | de Azevedo Souza C, Li SD, Lin AZ, Boutrot F, Grossmann G, Zipfel C, Somerville SC (2017). Cellulose-derived oligomers act as damage-associated molecular patterns and trigger defense-like responses. Plant Physiol 173, 2383-2398. |
| [4] |
Divol F, Vilaine F, Thibivilliers S, Kusiak C, Sauge MH, Dinant S (2007). Involvement of the xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolases encoded by celery XTH1 and Arabidopsis XTH33 in the phloem response to aphids. Plant Cell Environ 30, 187-201.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Fan TG (2014). Action of Excessive Petal Formation Caused by Rose AGAMOUS Gene Related to Floral Organ Development Under Low Temperature. Master’s thesis. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University. pp. 9-48. (in Chinese) |
| 范天刚 (2014). 月季花器官发育基因AGAMOUS对低温导致花朵过度重瓣化的作用研究. 硕士论文. 保定: 河北农业大学. pp. 9-48. | |
| [6] | Guo XM, Stotz HU (2007). Defense against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Arabidopsis is dependent on jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, and ethylene signaling. Mol Plant Mirobe Interact 20, 1384-1395. |
| [7] |
Han Y, Ban QY, Hou YL, Meng K, Suo JT, Rao JP (2016). Isolation and characterization of two persimmon xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolase (XTH) genes that have divergent functions in cell wall modification and fruit postharvest softening. Front Plant Sci 7, 624.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Harada T, Torii Y, Morita S, Onodera R, Hara Y, Yokoyama R, Nishitani K, Satoh S (2011). Cloning, characterization, and expression of xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase and expansion genes associated with petal growth and development during carnation flower opening. J Exp Bot 62, 815-823.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Hu HZ, Tang YW, Wu J, Chen FZ, Yang YD, Pan XC, Dong X, Jin XD, Liu S, Du XZ (2021). Brassica napus mediator subunit16 induces BnMED25- and BnWRKY33-activated defense signaling to confer Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance. Front Plant Sci 12, 663536.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Hu HZ, Zhang R, Feng SQ, Wang YM, Wang YT, Fan CF, Li Y, Liu ZY, Schneider R, Xia T, Ding SY, Persson S, Peng LC (2018). Three AtCesA6-like members enhance biomass production by distinctively promoting cell growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 976-988.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Huang X, Tian DK, Zhang WW, Zeng SJ, Mo HB (2014). Comparison of floral organ morphological development between single and double flowers in Nelumbo nucifera. Plant Diver Resour 36, 303-309. (in Chinese) |
| 黄秀, 田代科, 张微微, 曾宋君, 莫海波 (2014). 荷花“重瓣化”的花器官形态发育比较观察. 植物分类与资源学报 36, 303-309. | |
| [12] |
Hyodo H, Yamakawa S, Takeda Y, Tsuduki M, Yokota A, Nishitani K, Kohchi T (2003). Active gene expression of a xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase gene, XTH9, in inflorescence apices is related to cell elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 52, 473-482.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Jia XL, He BX, Guo DD, Guo ML (2018). Research progress in the function of expansins and xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase. Plant Physiol J 54, 1659-1668. (in Chinese) |
| 贾鑫磊, 何贝轩, 郭丹丹, 郭美丽 (2018). 膨胀素和木葡聚糖内转葡糖基酶/水解酶基因的功能研究进展. 植物生理学报 54, 1659-1668. | |
| [14] | Jiang JF (2022). Bioinformatics Analysis of Ginseng XTH Family Genes and Function Analysis of Two PgXTH Genes. Master’s thesis. Changchun: Jilin University. pp. 1-69. (in Chinese) |
| 江俊峰 (2022). 人参XTH家族基因生物信息学分析及两个PgXTH基因的功能分析. 硕士论文. 长春: 吉林大学. pp. 1-69. | |
| [15] |
Li MM, Zhang DF, Gao Q, Luo YF, Zhang H, Ma B, Chen CH, Whibley A, Zhang Y, Cao YH, Li Q, Guo H, Li JH, Song YZ, Zhang Y, Copsey L, Li Y, Li XX, Qi M, Wang JW, Chen Y, Wang D, Zhao JY, Liu GC, Wu B, Yu LL, Xu CY, Li J, Zhao SC, Zhang YJ, Hu SN, Liang CZ, Yin Y, Coen E, Xue YB (2019a). Genome structure and evolution of Antirrhinum majus L. Nat Plants 5, 174-183.
DOI |
| [16] |
Li Q, Hu AH, Dou WF, Qi JJ, Long Q, Zou XP, Lei TG, Yao LX, He YR, Chen SC (2019b). Systematic analysis and functional validation of citrus XTH genes reveal the role of Csxth04 in citrus bacterial canker resistance and tolerance. Front Plant Sci 10, 1109.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Luo WP, Chen SP, Gong YX (2008). Breeding and pest control of Antirrhinum majus. Chin Flower Horticul (8), 23-25. (in Chinese) |
| 罗维平, 陈少萍, 龚衍熙 (2008). 金鱼草的繁殖与病虫害防治. 中国花卉园艺 (8), 23-25. | |
| [19] |
Malinowski R, Fry SC, Zuzga S, Wiśniewska A, Godlewski M, Noyszewski A, Barczak-Brzyżek A, Malepszy S, Filipecki M (2018). Developmental expression of the cucumber Cs-XTH1 and Cs-XTH3 genes, encoding xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolases, can be influenced by mechanical stimuli. Acta Physiol Plant 40, 130.
DOI |
| [20] |
Marciniak K, Przedniczek K (2019). Comprehensive insight into gibberellin- and jasmonate-mediated stamen development. Genes 10, 811.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Miedes E, Suslov D, Vandenbussche F, Kenobi K, Ivakov A, Van Der straeten D, Lorences EP, Mellerowicz EJ, Verbelen JP, Vissenberg K (2013). Xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (XTH) overexpression affects growth and cell wall mechanics in etiolated Arabidopsis hypocotyls. J Exp Bot 64, 2481-2497. |
| [22] |
Pitaksaringkarn W, Matsuoka K, Asahina M, Miura K, Sage-Ono K, Ono M, Yokoyama R, Nishitani K, Ishii T, Iwai H, Satoh S (2014). XTH20 and XTH19 regulated by ANAC071 under auxin flow are involved in cell proliferation in incised Arabidopsis inflorescence stems. Plant J 80, 604-614.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Sasidharan R, Pierik R (2010). Cell wall modification involving XTHs controls phytochrome-mediated petiole elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav 5, 1491-1492. |
| [24] | Shi YY, Li DY, Zhang HJ, Song FM (2011). Cell wall-mediated disease resistance and its molecular mechanism in plants. Plant Physiol J 47, 661-668. (in Chinese) |
| 师莹莹, 李大勇, 张慧娟, 宋凤鸣 (2011). 植物细胞壁介导的抗病性及其分子机制. 植物生理学报 47, 661-668. | |
| [25] | Sun R, Yang YL, Li YJ, Zhang H, Li XK (2023). Genome- wide identification and analysis of PLATZ transcription factor gene family in foxtail millet. Chin Bull Bot 58, 548-559. (in Chinese) |
| 孙蓉, 杨宇琭, 李亚军, 张会, 李旭凯 (2023). 谷子PLATZ转录因子基因家族的鉴定和分析. 植物学报 58, 548-559. | |
| [26] |
Takahashi D, Johnson KL, Hao PF, Tuong T, Erban A, Sampathkumar A, Bacic A, Livingston DP, Kopka J, Kuroha T, Yokoyama R, Nishitani K, Zuther E, Hincha DK (2021). Cell wall modification by the xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase XTH19 influences freezing tolerance after cold and sub-zero acclimation. Plant Cell Environ 44, 915-930.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Tian YR, Fan TG, Zhang G, Li YH (2016). Expression and analysis of key genes of excessive double flowers in rose caused by low temperature. Chin J Tropical Crops 37, 1147-1154. (in Chinese) |
| 田亚然, 范天刚, 张钢, 李永红 (2016). 低温引起月季花朵过度重瓣化关键基因的表达及分析. 热带作物学报 37, 1147-1154. | |
| [28] | Wang RS (2019). Cloning and Functional Analysis of the AmDEFH28 Gene of Antirrhinum majus. Master’s thesis. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University.pp:1-67. (in Chinese) |
| 王瑞生 (2019). 金鱼草AmDEFH28基因克隆和功能分析. 硕士论文. 合肥: 安徽农业大学. pp. 1-67. | |
| [29] |
Watanabe Y, Niki T, Norikoshi R, Nakano M, Ichimura K (2022). Soluble carbohydrate concentration and expression of expansin and xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/ hydrolase genes in epidermal and parenchyma cells during lily flower opening. J Plant Physiol 270, 153615.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Witasari LD, Huang FC, Hoffmann T, Rozhon W, Fry SC, Schwab W (2019). Higher expression of the strawberry xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase genes FvXTH9 and FvXTH6 accelerates fruit ripening. Plant J 100, 1237-1253.
DOI |
| [31] | Wu D, Liu AQ, Qu XY, Liang JY, Song M (2020). Genome- wide identification, and phylogenetic and expression profiling analyses of XTH gene families in Brassica rapa L. and Brassica oleracea L. BMC Genomics 21, 782. |
| [32] |
Wu J, Zhou YM, Wang YP (2018). Research progress on molecular mechanisms of Brassica napus-Sclerotinia sclerotiorum interaction. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 40, 721-729. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
吴健, 周永明, 王幼平 (2018). 油菜与核盘菌互作分子机理研究进展. 中国油料作物学报 40, 721-729.
DOI |
|
| [33] | Wu N, Qin L, Cui K, Li HO, Liu ZS, Xia ST (2023). Cloning of Brassica napus EXA1 gene and its regulation on plant disease resistance. Chin Bull Bot 58, 385-393. (in Chinese) |
| 吴楠, 覃磊, 崔看, 李海鸥, 刘忠松, 夏石头 (2023). 甘蓝型油菜EXA1的克隆及其对植物抗病的调控作用. 植物学报 58, 385-393. | |
| [34] |
Xu PP, Fang S, Chen HY, Cai WM (2020). The brassinosteroid-responsive xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase 19 (XTH19) and XTH23 genes are involved in lateral root development under salt stress in Arabidopsis. Plant J 104, 59-75.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Xu TS (2021). Cell Wall Components Changes in Red Skin Ginseng and Function Analysis of Two Non-typical XTH Family Genes. Master’s thesis. Changchun: Jilin University. pp. 1-59. (in Chinese) |
| 徐天舒 (2021). 红皮病人参细胞壁组分变化及两个非典型XTH家族基因的功能探究. 硕士论文. 长春: 吉林大学. pp. 1-59. | |
| [36] | Xu XW (2023). Identification and Functional Analysis of Broad-spectrum Resistance Protein Induced by P1 Protein of Sugarcane Streak Mosaic Virus. Master’s thesis. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University. pp. 6-79. (in Chinese) |
| 徐小伟 (2023). 甘蔗线条花叶病毒P1蛋白诱导的广谱抗病蛋白的鉴定及功能研究. 硕士论文. 扬州: 扬州大学. pp. 6-79. | |
| [37] | Xuan Y (2020). Excavation of the Key Genes of Xyloglucan Metabolic Pathway and Primary Funcational Analysis of MtXTH 3 in Medicago truncatula Under Environmental Stresses. Doctoral dissertation. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. pp. 1-151. (in Chinese) |
| 宣云 (2020). 响应环境胁迫的蒺藜苜蓿XG代谢途径关键基因的挖掘及MtXTH3功能初步研究. 博士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 1-151. | |
| [38] | Yan J, Liu YQ, Hou SW (2018). Recent advances in disease resistance proteins in plant immunity. Chin Bull Bot 53, 250-263. (in Chinese) |
|
闫佳, 刘雅琼, 侯岁稳 (2018). 植物抗病蛋白研究进展. 植物学报 53, 250-263.
DOI |
|
| [39] |
Yang Y, Miao YF, Zhong SW, Fang Q, Wang YG, Dong B, Zhao HB (2022). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of XTH gene family during floweropening stages in Osmanthus fragrans. Plants 11, 1015.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Zhang R, Hu Z, Wang YT, Hu HZ, Li FC, Li M, Ragauskas A, Xia T, Han HY, Tang JF, Yu HZ, Xu BQ, Peng LC (2023). Single-molecular insights into the breakpoint of cellulose nanofibers assembly during saccharification. Nat Commun 14, 1100.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | Zhao XH, Wang QJ, Li C, Chen XD, Xiao W, Gao DS, Fu XL (2018). Genome-wide identification of ethylene responsive factor (ERF) family genes in peach and screening of genes related to germination. Chin Bull Bot 53, 612-624. (in Chinese) |
|
赵雪惠, 王庆杰, 李晨, 陈修德, 肖伟, 高东升, 付喜玲 (2018). 桃ERF转录因子家族生物信息学分析及芽萌发相关基因筛选. 植物学报 53, 612-624.
DOI |
| [1] | Jin Wang, Li Qi, Zhengzhu Zhang. Differential Gene Expression of Endogenous Glycosidases Induced by Pathogenic Fungi Infection in Leaves of Camellia sinensis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(5): 552-559. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||