

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 185-193.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19013 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19013
Special Issue: 逆境生物学专辑 (2019年54卷2期)
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lulu Li,Wenchao Yin,Mei Niu,Wenjing Meng,Xiaoxing Zhang,Hongning Tong( )
)
Received:2019-01-18
Accepted:2019-03-19
Online:2019-03-01
Published:2019-09-01
Contact:
Hongning Tong
Lulu Li,Wenchao Yin,Mei Niu,Wenjing Meng,Xiaoxing Zhang,Hongning Tong. Functional Analysis of Brassinosteroids in Salt Stress Responses in Rice[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 185-193.
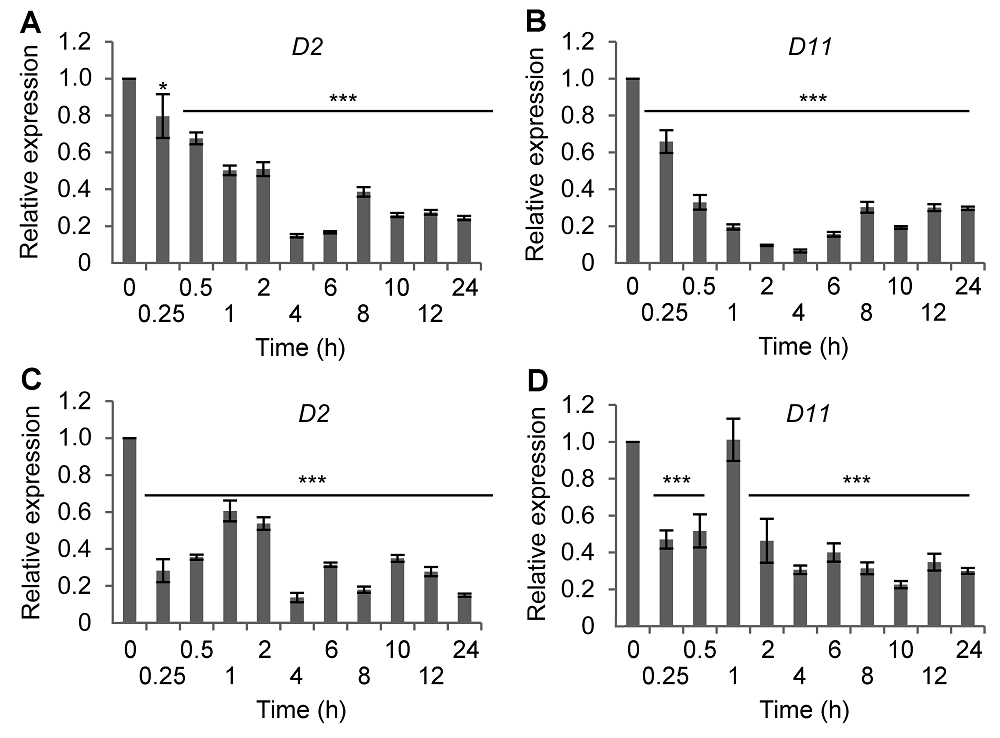
Figure 1 Time-course expression of BR synthetic genes in rice following salt or ABA treatment(A) D2 expression after NaCl treatment; (B) D11 expression after NaCl treatment; (C) D2 expression after ABA treatment; (D) D11 expression after ABA treatment. * P<0.05; *** P<0.001
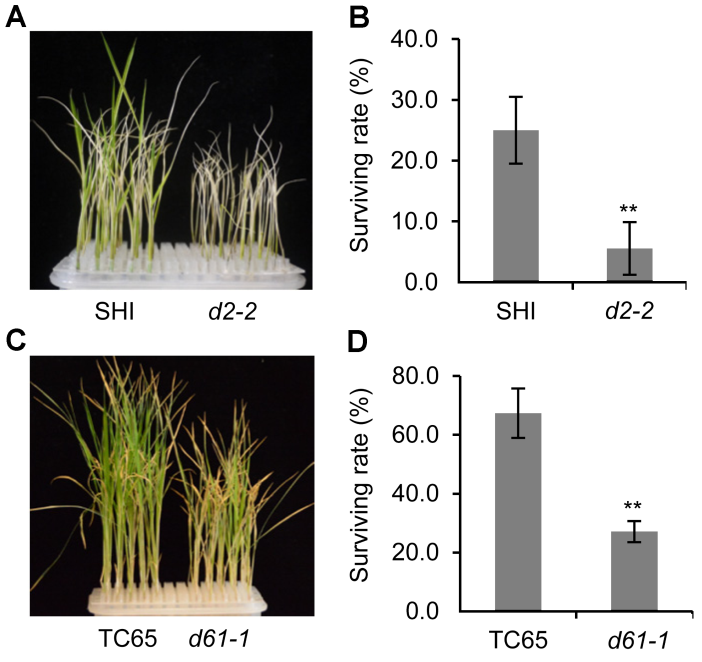
Figure 2 Survival rate of rice BR defective mutants and the wild type under salt stress(A) Growth status of d2-2 mutant and the wild type after salt treatment; (B) Statistic data of the survival rate of d2-2 and the wild type after salt treatment; (C) Growth status of d61-1 mutant and the wild type after salt treatment; (D) Statistic data of the survival rate of d61-1 and the wild type after salt treatment. ** P<0.01
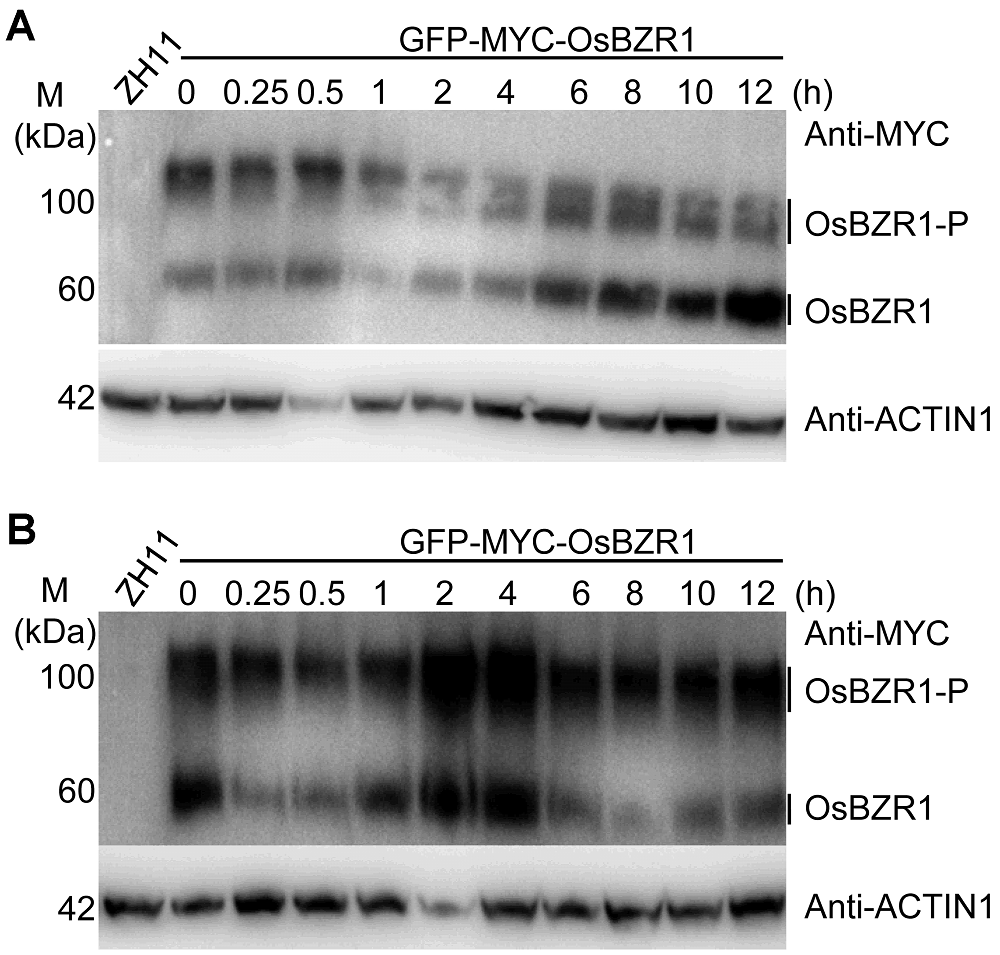
Figure 3 Effects of BR and salt stress on OsBZR1 proteins in rice(A) Effect of BR treatment on OsBZR1 proteins; (B) Effect of salt treatment on OsBZR1 proteins
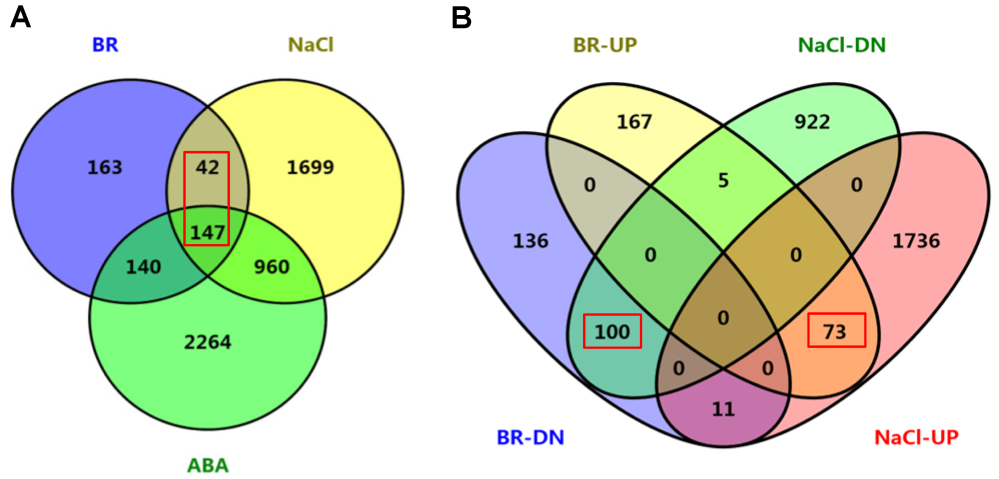
Figure 4 Co-regulation analyses of BR-, ABA- and NaCl-regulated genes of rice(A) Co-regulated gene numbers between BR-, ABA- and NaCl-regulated different expression genes (DEGs); (B) Co-regulation analyses among BR-upregulated (BR-UP), BR-downregulated (BR-DN), NaCl-upregulated (NaCl-UP) and NaCl-downregulated (NaCl-DN) genes. Distribution of the gene numbers was indicated.
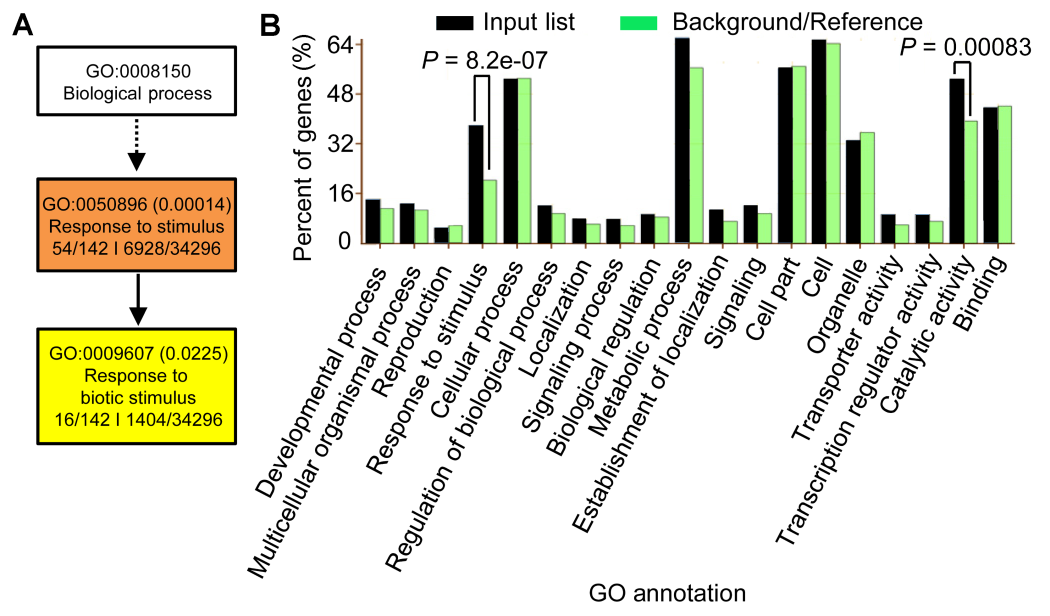
Figure 5 Gene Ontology analyses of the 189 BR-NaCl co-regulated genes of rice(A) GO analyses in term of the biological process; (B) GO analyses in terms of biological process, cellular component, and molecular function
| [1] | 李钱峰, 鲁军, 余佳雯, 张昌泉, 刘巧泉 ( 2018). 油菜素内酯与脱落酸互作调控植物生长与抗逆的分子机制研究进展. 植物生理学报 54, 370-378. |
| [2] | 王沛雅, 周剑平, 王治业, 张军, 强维亚, 杨涛, 郭琪, 杨晖 ( 2014). 油菜素内酯合成酶基因DAS5促进杨树生长及提高抗旱性的作用. 植物学报 49, 407-416. |
| [3] | 吴家富, 杨博文, 向珣朝, 许亮, 颜李梅 ( 2017). 不同水稻种质在不同生育期耐盐鉴定的差异. 植物学报 52, 77-88. |
| [4] | 俞仁培, 陈德明 ( 1999). 我国盐渍土资源及其开发利用. 土壤通报 30, 158-159. |
| [5] |
Choe S ( 2006). Brassinosteroid biosynthesis and inactiva- tion. Physiol Plant 126, 539-548.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Divi UK, Krishna P ( 2009). Brassinosteroid: a biotechno- logical target for enhancing crop yield and stress tole- rance. N Biotechnol 26, 131-136.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Feng Y, Yin YH, Fei SZ ( 2015). Down-regulation of BdBRI1, a putative brassinosteroid receptor gene produces a dwarf phenotype with enhanced drought tolerance in Brachy- podium distachyon. Plant Sci 234, 163-173. |
| [8] | Grove MD, Spencer GF, Rohwedder WK, Mandava N, Worley JF, Warthen JD Jr, Steffens GL, Flippen- Anderson JL, Cook JC Jr ( 1979). Brassinolide, a plant growth-promoting steroid isolated from Brassica napus pollen. Nature 281, 216-217. |
| [9] |
Ha YM, Shang Y, Nam KH ( 2016). Brassinosteroids modu- late ABA-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 67, 6297-6308.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
He JX, Gendron JM, Sun Y, Gampala SSL, Gendron N, Sun CQ, Wang ZY ( 2005). BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 307, 1634-1638.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
He JX, Gendron JM, Yang YL, Li JM, Wang ZY ( 2002). The GSK3-like kinase BIN2 phosphorylates and destabilizes BZR1, a positive regulator of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 10185-10190.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M ( 2004). Bras- sinosteroids and rice architecture. J Pestic Sci 29, 184-188.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Hong Z, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Umemura K, Uozu S, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M ( 2003). A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450. Plant Cell 15, 2900-2910. |
| [14] |
Khripach V, Zhabinskii V, De Groot A ( 2000). Twenty years of brassinosteroids: steroidal plant hormones warrant better crops for the XXI century. Ann Bot 86, 441-447.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kim TW, Wang ZY ( 2010). Brassinosteroid signal transduc- tion from receptor kinases to transcription factors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61, 681-704.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Krishna P, Prasad BD, Rahman T ( 2017). Brassinosteroid action in plant abiotic stress tolerance. In: Russinova E, Caño-Delgado AI, eds. Brassinosteroids. New York: Hum- ana Press. pp. 193-202. |
| [17] |
Morinaka Y, Sakamoto T, Inukai Y, Agetsuma M, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M ( 2006). Morphological alteration caused by brassinosteroid insensitivity increases the biomass and grain production of rice. Plant Physiol 141, 924-931.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Nakashima K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K ( 2013). ABA signaling in stress-response and seed development. Plant Cell Rep 32, 959-970.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Nolan TM, Brennan B, Yang MR, Chen JN, Zhang MC, Li ZH, Wang XL, Bassham DC, Walley J, Yin YH ( 2017). Selective autophagy of BES1 mediated by DSK2 balances plant growth and survival. Dev Cell 41, 33-46.e7. |
| [20] |
Peleg Z, Blumwald E ( 2011). Hormone balance and abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 290-295.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Ryu H, Kim K, Cho H, Park J, Choe S, Hwang I ( 2007). Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of BZR1 mediated by phos- phorylation is essential in Arabidopsis brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell 19, 2749-2762.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, Sunohara H, Fujioka S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Mizutani M, Sakata K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Tanaka H, Kitano H, Matsuoka M ( 2006). Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency inc- rease biomass production and grain yield in rice. Nat Bio- technol 24, 105-109.
DOI |
| [23] |
Singh AP, Savaldi-Goldstein S ( 2015). Growth control: brassinosteroid activity gets context. J Exp Bot 66, 1123-1132.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Sun Y, Fan XY, Cao DM, Tang WQ, He K, Zhu JY, He JX, Bai MY, Zhu SW, Oh E, Patil S, Kim TW, Ji HK, Wong WH, Rhee SY, Wang ZY ( 2010). Integration of bras- sinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 19, 765-777.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Tong HN, Chu CC ( 2016). Reply: brassinosteroid regulates gibberellin synthesis to promote cell elongation in rice: critical comments on ross and quittenden's letter. Plant Cell 28, 833-835. |
| [26] | Tong HN, Chu CC ( 2018). Functional specificities of bras- sinosteroid and potential utilization for crop improvement. Trends Plant Sci 23, 1016-1028. |
| [27] |
Tong HN, Liu LC, Jin Y, Du L, Yin YH, Qian Q, Zhu LH, Chu CC ( 2012). DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 24, 2562-2577.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Tong HN, Xiao YH, Liu DP, Gao SP, Liu LC, Yin YH, Jin Y, Qian Q, Chu CC ( 2014). Brassinosteroid regulates cell elongation by modulating gibberellin metabolism in rice. Plant Cell 26, 4376-4393.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Wang ZY, Nakano T, Gendron J, He JX, Chen M, Vafeados D, Yang YL, Fujioka S, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J ( 2002). Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates bras- sinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Dev Cell 2, 505-513.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Wu CY, Trieu A, Radhakrishnan P, Kwok SF, Harris S, Zhang K, Wang JL, Wan JM, Zhai HQ, Takatsuto S, Matsumoto S, Fujioka S, Feldmann KA, Pennell RI ( 2008). Brassinosteroids regulate grain filling in rice. Plant Cell 20, 2130-2145.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M ( 2000). Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive 1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 12, 1591-1606. |
| [32] | Yang MR, Li CX, Cai ZY, Hu YM, Nolan T, Yu FF, Yin YH, Xie Q, Tang GL, Wang XL ( 2017). SINAT E3 ligases control the light-mediated stability of the brassinosteroid- activated transcription factor BES1 in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 41, 47-58.e4. |
| [33] | Yin WC, Dong NN, Niu M, Zhang XX, Li LL, Liu J, Liu B, Tong HN ( 2018). Brassinosteroid-regulated plant growth and development and gene expression in soybean. Crop J. DOI: 10.1016/j.cj.2018.10.003. |
| [34] |
Yin YH, Wang ZY, Mora-Garcia S, Li JM, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J ( 2002). BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell 109, 181-191.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Yu XF, Li L, Zola J, Aluru M, Ye HX, Foudree A, Guo HQ, Anderson S, Aluru S, Liu P, Rodermel S, Yin YH ( 2011). A brassinosteroid transcriptional network revealed by genome-wide identification of BESI target genes in Ara- bidopsis thaliana . Plant J 65, 634-646. |
| [36] |
Zhao X, Dou LR, Gong ZZ, Wang XF, Mao TL ( 2019). BES1 hinders ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE5 and promotes seed germination in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 221, 908-918.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Zhu JK ( 2001). Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6, 66-71. |
| [1] |
Juan Cui, Xiaoyu Yu, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun, Wenfu Chen.
Analysis of Texture Factors and Genetic Basis Influencing the Differences in Eating Quality between Northeast China and Japanese Japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | Zhao Ling, Guan Ju, Liang Wenhua, Zhang Yong, Lu Kai, Zhao Chunfang, Li Yusheng, Zhang Yadong. Mapping of QTLs for Heat Tolerance at the Seedling Stage in Rice Based on a High-density Bin Map [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | Xu Tiantian, Yang Peijian, Zhou Xiaoxi, Cao Yi, Chen Yanhong, Liu Guoyuan, Zhang Jian, Wei Hui. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics and Expression Characteristics of Lagerstroemia indica GolS Family Genes [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 393-406. |
| [4] | Xinyu Li, Yue Gu, Feifei Xu, Jinsong Bao. Research Progress on Post-translational Modifications of Starch Biosynthesis-related Proteins in Rice Endosperm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [5] | Jianguo Li, Yi Zhang, Wenjun Zhang. Iron Plaque Formation and Its Effects on Phosphorus Absorption in Rice Roots [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [6] | Ruifeng Yao, Daoxin Xie. Activation and Termination of Strigolactone Signal Perception in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [7] | Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Yinuo Zhang, Jiaxing Zheng, Chaoyu Zhu, Yuhan Ye, Yuexing Wang, Wennan Shang, Zhenghao Fu, Xinxuan Xu, Richeng Wu, Mei Lu, Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao. Genetic Locus Mining and Candidate Gene Analysis of Antioxidant Traits in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [8] | Jiahui Huang, Huimin Yang, Xinyu Chen, Chaoyu Zhu, Yanan Jiang, Chengxiang Hu, Jinjin Lian, Tao Lu, Mei Lu, Weilin Zhang, Yuchun Rao. Response Mechanism of Rice Mutant pe-1 to Low Light Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [9] | Jinyu Du, Zhen Sun, Yanlong Su, Heping Wang, Yaling Liu, Zhenying Wu, Feng He, Yan Zhao, Chunxiang Fu. Identification and Functional Analysis of an Agropyron mongolicum Caffeic Acid 3-O-methyltransferase Gene AmCOMT1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 383-396. |
| [10] | Jianmin Zhou. A Combat Vehicle with a Smart Brake [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [11] | Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Zhenan Zhu, Zhining Zhang, Lihai Wang, Jun Chen, Sanfeng Li, Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Qianqian Zhong, Wenjing Yin, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTLs Associated with Rice Panicle Traits and Candidate Gene Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [12] | Yanli Fang, Chuanyu Tian, Ruyi Su, Yapei Liu, Chunlian Wang, Xifeng Chen, Wei Guo, Zhiyuan Ji. Mining and Preliminary Mapping of Rice Resistance Genes Against Bacterial Leaf Streak [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [13] | Bao Zhu, Jiangzhe Zhao, Kewei Zhang, Peng Huang. OsCKX9 is Involved in Regulating the Rice Lamina Joint Development and Leaf Angle [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [14] | Dai Ruohui, Qian Xinyu, Sun Jinglei, Lu Tao, Jia Qiwei, Lu Tianqi, Lu Mei, Rao Yuchun. Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Leaf Color Regulation and Related Genes in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [15] | Tian Chuanyu, Fang Yanli, Shen Qing, Wang Hongjie, Chen Xifeng, Guo Wei, Zhao Kaijun, Wang Chunlian, Ji Zhiyuan. Genotypic Diversity and Pathogenisity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Isolated from Southern China in 2019-2021 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||