

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (3): 394-403.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22259 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22259
所属专题: 大食物观
金佳怡1, 罗怿婷1, 杨惠敏1, 芦涛1, 叶涵斐1, 谢继毅1, 王珂欣1, 陈芊羽1, 方媛1, 王跃星2( ), 饶玉春1(
), 饶玉春1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-08
接受日期:2023-02-09
出版日期:2023-05-01
发布日期:2023-05-17
通讯作者:
*E-mail: wangyuexing@caas.cn; ryc@zjnu.cn
基金资助:
Jiayi Jin1, Yiting Luo1, Huimin Yang1, Tao Lu1, Hanfei Ye1, Jiyi Xie1, Kexin Wang1, Qianyu Chen1, Yuan Fang1, Yuexing Wang2( ), Yuchun Rao1(
), Yuchun Rao1( )
)
Received:2022-11-08
Accepted:2023-02-09
Online:2023-05-01
Published:2023-05-17
Contact:
*E-mail: wangyuexing@caas.cn; ryc@zjnu.cn
摘要: 水稻(Oryza sativa)是我国主要粮食作物之一。提高水稻叶片叶绿素含量, 进而提高其光合作用效率是实现高产稳产的重要途径之一。该研究以父系籼稻品种华占(HZ)、母系粳稻品种热研2号(Nekken2)及其构建的120个重组自交系(RILs)为实验材料, 在分蘖期和成熟期分别对亲本及其后代剑叶的叶绿素含量(SPAD值)进行测定, 同时基于已构建的高密度遗传连锁图谱进行QTL定位。结果共挖掘到20个与叶绿素含量相关的QTLs (分蘖期7个, 成熟期13个), LOD值最高达4.77。利用qRT-PCR方法检测QTL区间内与叶绿素含量相关的候选基因的表达, 发现LOC_Os06g11780、LOC_Os06g12360、LOC_Os06g39716、LOC_Os08g42610、LOC_Os02g18500、LOC_Os03g21240、LOC_Os03g21400、LOC_Os03g21780、LOC_Os03g30950及LOC_Os03g40550基因的表达量在双亲间差异显著。结合基因表达量及亲本叶绿素表型数据, 推测LOC_Os06g11780、LOC_Os06g12360和LOC_Os08g42610的高表达极大地提高了水稻叶绿素含量, 进而有效提高植物光合产能。研究结果为筛选和培育高光能利用效率的水稻新品种提供了有利的遗传资源, 并为揭示水稻叶绿素含量的动态变化规律及分子调控机制奠定了重要基础。
金佳怡, 罗怿婷, 杨惠敏, 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 谢继毅, 王珂欣, 陈芊羽, 方媛, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻叶绿素含量QTL定位与候选基因表达分析. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 394-403.
Jiayi Jin, Yiting Luo, Huimin Yang, Tao Lu, Hanfei Ye, Jiyi Xie, Kexin Wang, Qianyu Chen, Yuan Fang, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. QTL Mapping and Expression Analysis on Candidate Genes Related to Chlorophyll Content in Rice. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 394-403.
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| LOC_Os06g11780-F-qrt | TGTTGGTCCCTGAAAACTCC |
| LOC_Os06g11780-R-qrt | TCAAGCAAATTCACCCATGA |
| LOC_Os06g12360-F-qrt | ATGCAAAAAGGAGAGGCTGA |
| LOC_Os06g12360-R-qrt | ATGCCGATCAGGAATCTCAC |
| LOC_Os06g39650-F-qrt | GTGCTCTTCAACCAGTGCAA |
| LOC_Os06g39650-R-qrt | AGATTGGCACAGCATGTCAG |
| LOC_Os06g39716-F-qrt | CAACCTTTTCGTAGGCATCC |
| LOC_Os06g39716-R-qrt | TTGAAATTGACTGGGCTTGA |
| LOC_Os08g42610-F-qrt | GCTCGCACACTGAAAACAAA |
| LOC_Os08g42610-R-qrt | ATGGGATAGGCCCCAAATAG |
| LOC_Os02g18500-F-qrt | AGGAGGAGGTGTTGGGAACT |
| LOC_Os02g18500-R-qrt | ATGCAGTTGTTGATGGCGTA |
| LOC_Os03g21240-F-qrt | TATGCCTTTGCACCAGAGTG |
| LOC_Os03g21240-R-qrt | CAGCATTCGACGACTGAGAA |
| LOC_Os03g21400-F-qrt | AGGAAAGCGGAGAAGAAAGG |
| LOC_Os03g21400-R-qrt | TTAGACACCAGGCAGCTGTG |
| LOC_Os03g21780-F-qrt | CTCCCTTCCACTCCTCCTTC |
| LOC_Os03g21780-R-qrt | CTTCTCCTCCTCGACACCAG |
| LOC_Os03g30950-F-qrt | TCTTCTTCTCCATGGCCTGT |
| LOC_Os03g30950-R-qrt | AGCAGGGAAGGAAGTCGTG |
| LOC_Os03g40550-F-qrt | CTTTGCTCCCTGCCTTGTAG |
| LOC_Os03g40550-R-qrt | CACGTCTCGGAGCTCTTTTC |
表1 qRT-PCR所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| LOC_Os06g11780-F-qrt | TGTTGGTCCCTGAAAACTCC |
| LOC_Os06g11780-R-qrt | TCAAGCAAATTCACCCATGA |
| LOC_Os06g12360-F-qrt | ATGCAAAAAGGAGAGGCTGA |
| LOC_Os06g12360-R-qrt | ATGCCGATCAGGAATCTCAC |
| LOC_Os06g39650-F-qrt | GTGCTCTTCAACCAGTGCAA |
| LOC_Os06g39650-R-qrt | AGATTGGCACAGCATGTCAG |
| LOC_Os06g39716-F-qrt | CAACCTTTTCGTAGGCATCC |
| LOC_Os06g39716-R-qrt | TTGAAATTGACTGGGCTTGA |
| LOC_Os08g42610-F-qrt | GCTCGCACACTGAAAACAAA |
| LOC_Os08g42610-R-qrt | ATGGGATAGGCCCCAAATAG |
| LOC_Os02g18500-F-qrt | AGGAGGAGGTGTTGGGAACT |
| LOC_Os02g18500-R-qrt | ATGCAGTTGTTGATGGCGTA |
| LOC_Os03g21240-F-qrt | TATGCCTTTGCACCAGAGTG |
| LOC_Os03g21240-R-qrt | CAGCATTCGACGACTGAGAA |
| LOC_Os03g21400-F-qrt | AGGAAAGCGGAGAAGAAAGG |
| LOC_Os03g21400-R-qrt | TTAGACACCAGGCAGCTGTG |
| LOC_Os03g21780-F-qrt | CTCCCTTCCACTCCTCCTTC |
| LOC_Os03g21780-R-qrt | CTTCTCCTCCTCGACACCAG |
| LOC_Os03g30950-F-qrt | TCTTCTTCTCCATGGCCTGT |
| LOC_Os03g30950-R-qrt | AGCAGGGAAGGAAGTCGTG |
| LOC_Os03g40550-F-qrt | CTTTGCTCCCTGCCTTGTAG |
| LOC_Os03g40550-R-qrt | CACGTCTCGGAGCTCTTTTC |
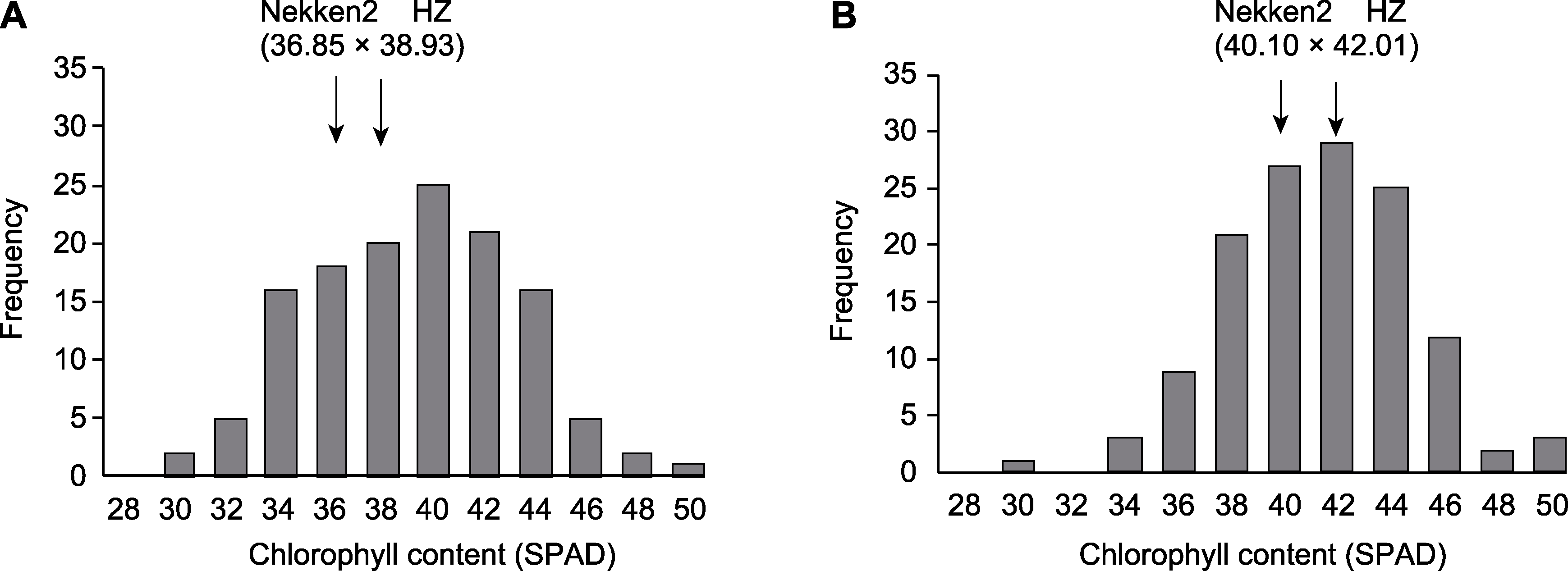
图1 水稻重组自交系中叶绿素含量分布 (A) 分蘖期; (B) 成熟期
Figure 1 Distribution of chlorophyll content in recombinant inbred lines of rice (A) Tillering stage; (B) Maturing stage
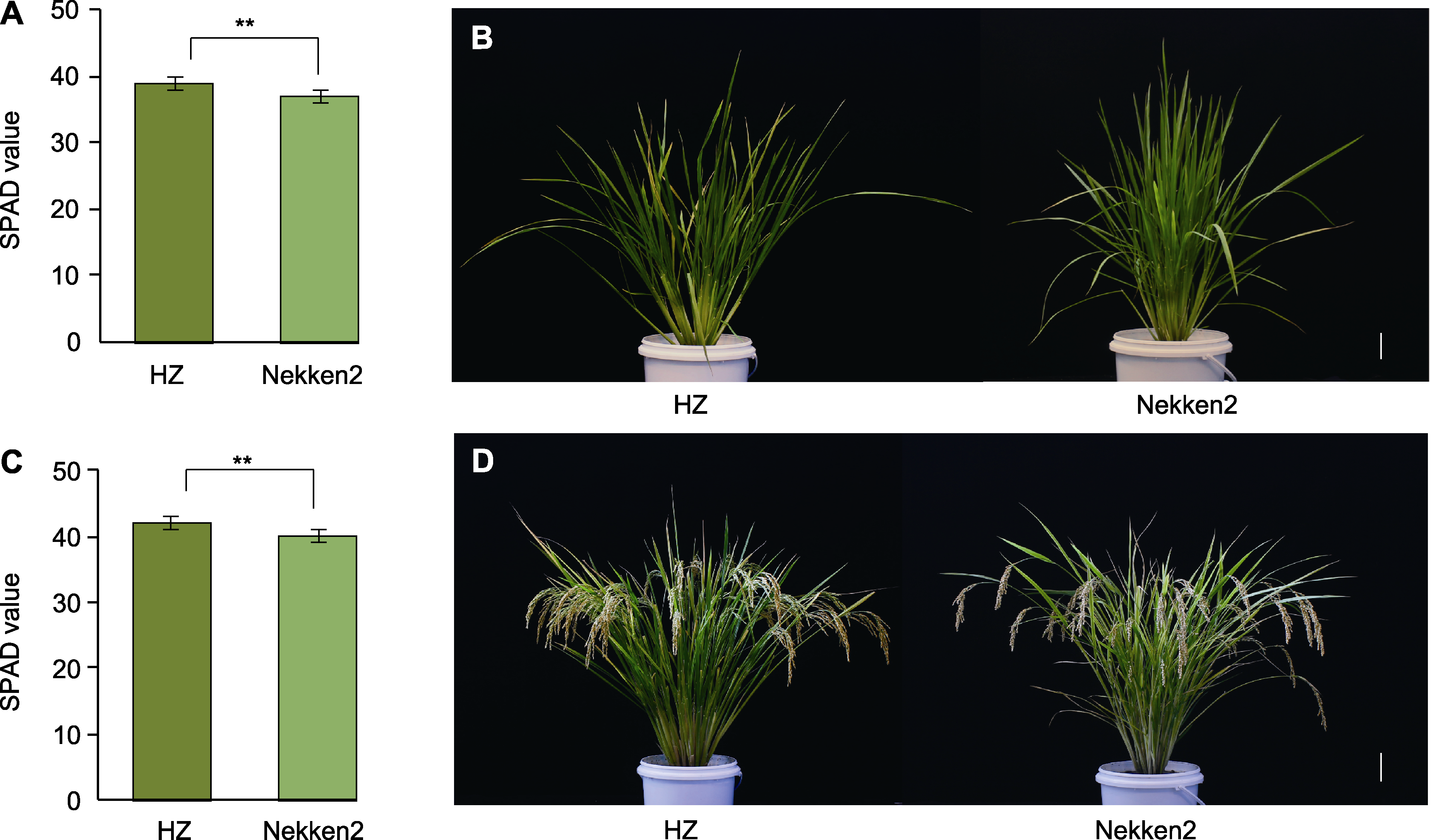

图2 父本华占与母本热研2号的SPAD值及表型 (A) 分蘖期水稻植株的SPAD值; (B) 分蘖期水稻植株的表型(bar=10 cm); (C) 成熟期水稻植株的SPAD值; (D) 成熟期水稻植株的表型(bar=10 cm)
Figure 2 SPAD value and phenotype of the male parent HZ and the female parent Nekken2 (A) SPAD value of rice plant at tillering stage; (B) Phenotype of rice plant at tillering stage (bar=10 cm); (C) SPAD value of rice plant at maturing stage; (D) Phenotype of rice plant at maturing stage (bar=10 cm)
| Trait | QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Likelihood of odd (LOD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll content at tillering stage | qFLCC6.1 | 6 | 6015262-6720585 | 25.79-28.81 | 3.13 |
| qFLCC6.2 | 6 | 22337450-23745958 | 95.75-101.79 | 2.92 | |
| qFLCC6.3 | 6 | 24051716-24198880 | 103.10-103.73 | 2.13 | |
| qFLCC6.4 | 6 | 25991018-26126806 | 111.42-111.99 | 2.12 | |
| qFLCC8.1 | 8 | 26687999-27132649 | 114.40-116.31 | 2.50 | |
| qFLCC8.2 | 8 | 27513012-27730624 | 117.94-118.87 | 2.28 | |
| qFLCC9.1 | 9 | 20982305-21030827 | 89.95-90.15 | 2.09 | |
| Chlorophyll content at maturing stage | qFLCC1.1 | 1 | 2407127-2649258 | 10.32-11.36 | 2.63 |
| qFLCC2.1 | 2 | 10729809-10871055 | 45.99-46.60 | 2.01 | |
| qFLCC3.1 | 3 | 8989609-9140871 | 38.54-39.18 | 2.00 | |
| qFLCC3.2 | 3 | 11602077-12505077 | 49.73-53.61 | 4.77 | |
| qFLCC3.3 | 3 | 17425033-18170152 | 74.70-77.90 | 2.38 | |
| qFLCC3.4 | 3 | 19142858-20859360 | 82.06-89.42 | 2.29 | |
| qFLCC3.5 | 3 | 22349012-22880743 | 95.80-98.08 | 2.59 | |
| qFLCC3.6 | 3 | 23094070-24507431 | 98.99-105.06 | 3.25 | |
| qFLCC4.1 | 4 | 867957-1087636 | 3.72-4.66 | 2.40 | |
| qFLCC4.2 | 4 | 2647701-3012559 | 11.35-12.91 | 2.30 | |
| qFLCC4.3 | 4 | 6230638-6599549 | 26.71-28.29 | 2.46 | |
| qFLCC7.1 | 7 | 9758981-9899583 | 41.83-42.68 | 2.45 | |
| qFLCC11.1 | 11 | 3100542-3229790 | 13.29-13.85 | 2.27 |
表2 水稻重组自交系群体叶绿素含量的QTL分析
Table 2 QTL analysis of chlorophyll content of rice recombinant inbred lines
| Trait | QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Likelihood of odd (LOD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll content at tillering stage | qFLCC6.1 | 6 | 6015262-6720585 | 25.79-28.81 | 3.13 |
| qFLCC6.2 | 6 | 22337450-23745958 | 95.75-101.79 | 2.92 | |
| qFLCC6.3 | 6 | 24051716-24198880 | 103.10-103.73 | 2.13 | |
| qFLCC6.4 | 6 | 25991018-26126806 | 111.42-111.99 | 2.12 | |
| qFLCC8.1 | 8 | 26687999-27132649 | 114.40-116.31 | 2.50 | |
| qFLCC8.2 | 8 | 27513012-27730624 | 117.94-118.87 | 2.28 | |
| qFLCC9.1 | 9 | 20982305-21030827 | 89.95-90.15 | 2.09 | |
| Chlorophyll content at maturing stage | qFLCC1.1 | 1 | 2407127-2649258 | 10.32-11.36 | 2.63 |
| qFLCC2.1 | 2 | 10729809-10871055 | 45.99-46.60 | 2.01 | |
| qFLCC3.1 | 3 | 8989609-9140871 | 38.54-39.18 | 2.00 | |
| qFLCC3.2 | 3 | 11602077-12505077 | 49.73-53.61 | 4.77 | |
| qFLCC3.3 | 3 | 17425033-18170152 | 74.70-77.90 | 2.38 | |
| qFLCC3.4 | 3 | 19142858-20859360 | 82.06-89.42 | 2.29 | |
| qFLCC3.5 | 3 | 22349012-22880743 | 95.80-98.08 | 2.59 | |
| qFLCC3.6 | 3 | 23094070-24507431 | 98.99-105.06 | 3.25 | |
| qFLCC4.1 | 4 | 867957-1087636 | 3.72-4.66 | 2.40 | |
| qFLCC4.2 | 4 | 2647701-3012559 | 11.35-12.91 | 2.30 | |
| qFLCC4.3 | 4 | 6230638-6599549 | 26.71-28.29 | 2.46 | |
| qFLCC7.1 | 7 | 9758981-9899583 | 41.83-42.68 | 2.45 | |
| qFLCC11.1 | 11 | 3100542-3229790 | 13.29-13.85 | 2.27 |
| Chromosome | QTL locus | Gene ID | Functional annotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | qFLCC6.1 | LOC_Os06g11780 | MYB family transcription factor, putative, expressed | |
| 6 | qFLCC6.1 | LOC_Os06g12360 | Pentatricopeptide, putative, expressed | |
| 6 | qFLCC6.2 | LOC_Os06g39650 | Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | Jiang et al., |
| 6 | qFLCC6.2 | LOC_Os06g39716 | Chloroplast 30S ribosomal protein S18, putative, expressed | |
| 8 | qFLCC8.1 | LOC_Os08g42610 | Pentatricopeptide, putative, expressed |
表3 水稻分蘖期叶绿素含量相关候选基因的功能
Table 3 The function of candidate genes related to chlorophyll content of rice at tillering stage
| Chromosome | QTL locus | Gene ID | Functional annotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | qFLCC6.1 | LOC_Os06g11780 | MYB family transcription factor, putative, expressed | |
| 6 | qFLCC6.1 | LOC_Os06g12360 | Pentatricopeptide, putative, expressed | |
| 6 | qFLCC6.2 | LOC_Os06g39650 | Pentatricopeptide repeat protein | Jiang et al., |
| 6 | qFLCC6.2 | LOC_Os06g39716 | Chloroplast 30S ribosomal protein S18, putative, expressed | |
| 8 | qFLCC8.1 | LOC_Os08g42610 | Pentatricopeptide, putative, expressed |
| Chromosome | QTL locus | Gene ID | Functional annotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | qFLCC2.1 | LOC_Os02g18500 | Chlorophyllase-2, chloroplast precursor, putative | |
| 3 | qFLCC3.2 | LOC_Os03g21240 | Transcription factor with a MYB domain; PHOSPHATE RESPONSE 1 | Guo et al., |
| 3 | qFLCC3.2 | LOC_Os03g21400 | Cytochrome P450 gene; gibberellin 13-oxidase | |
| 3 | qFLCC3.2 | LOC_Os03g21780 | Pentatricopeptide repeat domain containing protein, putative, expressed | |
| 3 | qFLCC3.3 | LOC_Os03g30950 | Acyl-desaturase, chloroplast precursor, putative, expressed | |
| 3 | qFLCC3.5 | LOC_Os03g40550 | pfkB-type carbohydrate kinase family protein |
表4 水稻成熟期叶绿素含量相关候选基因的功能
Table 4 The function of candidate genes related to chlorophyll content of rice at maturing stage
| Chromosome | QTL locus | Gene ID | Functional annotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | qFLCC2.1 | LOC_Os02g18500 | Chlorophyllase-2, chloroplast precursor, putative | |
| 3 | qFLCC3.2 | LOC_Os03g21240 | Transcription factor with a MYB domain; PHOSPHATE RESPONSE 1 | Guo et al., |
| 3 | qFLCC3.2 | LOC_Os03g21400 | Cytochrome P450 gene; gibberellin 13-oxidase | |
| 3 | qFLCC3.2 | LOC_Os03g21780 | Pentatricopeptide repeat domain containing protein, putative, expressed | |
| 3 | qFLCC3.3 | LOC_Os03g30950 | Acyl-desaturase, chloroplast precursor, putative, expressed | |
| 3 | qFLCC3.5 | LOC_Os03g40550 | pfkB-type carbohydrate kinase family protein |
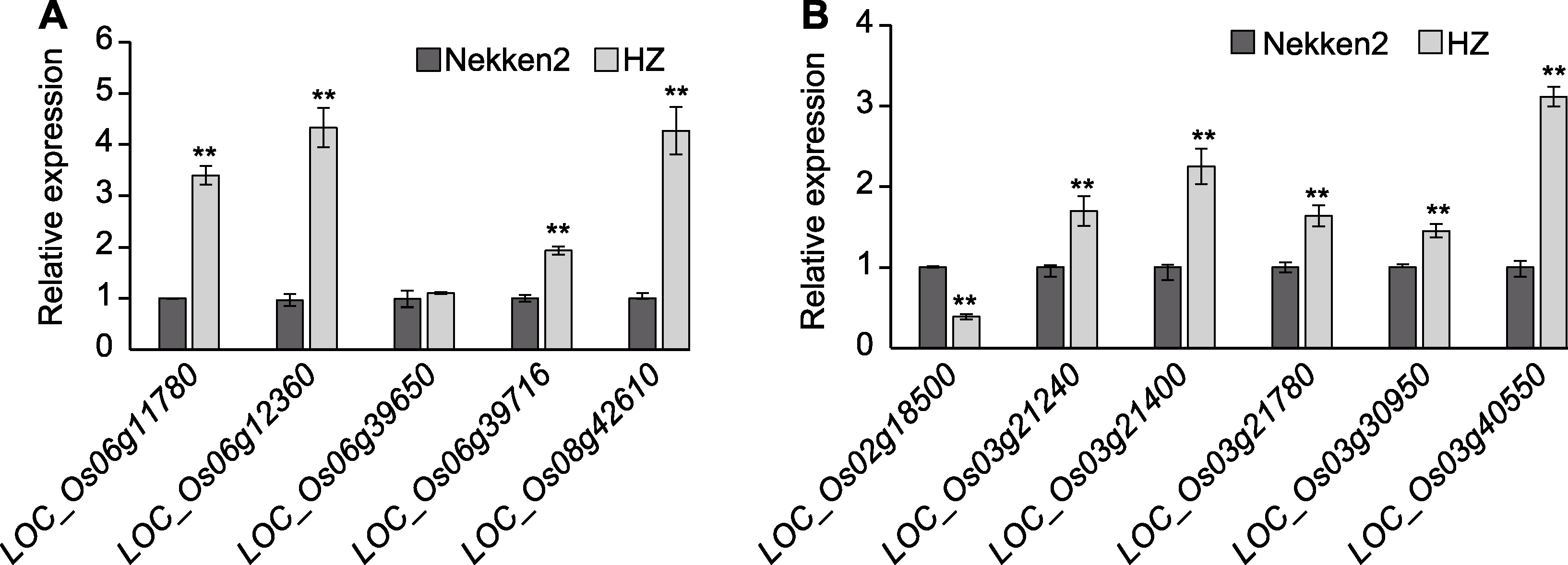
图4 水稻叶绿素含量相关基因表达量差异 (A) 分蘖期叶绿素含量相关基因表达量; (B) 成熟期叶绿素含量相关基因表达量。**表示在0.01水平差异显著。
Figure 4 Differences in the expression level of the genes related to chlorophyll content in rice (A) Expression of genes related to chlorophyll content at tillering stage; (B) Expression of genes related to chlorophyll content at maturing stage. ** indicate significant differences at 0.01 level.
| [1] |
范淑秀, 王嘉宇, 毛艇, 徐正进 (2010). 水稻孕穗期叶绿素含量的QTL定位. 华北农学报 25(4), 69-72.
DOI |
| [2] | 姜树坤, 张喜娟, 王嘉宇, 徐正进, 陈温福, 张凤鸣 (2012). 水稻叶绿素含量的动态QTL剖析. 东北农业大学学报 43 (7), 47-52. |
| [3] | 李景芳, 王宝祥, 刘艳, 刘金波, 陈庭木, 孙志广, 杨波, 邢运高, 迟铭, 徐波, 徐大勇 (2022). PPR蛋白在水稻生长发育中的功能研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报 23, 358-367. |
| [4] | 李永洪, 李传旭, 刘成元, 何珊, 向箭宇, 谢戎 (2018). 利用岗46B/A232重组自交系群体分析叶绿素含量相关QTL. 西南农业学报 31, 2223-2228. |
| [5] | 刘进 (2013). 水稻重要农艺性状QTL分析及叶绿素含量相关基因分子定位. 硕士论文. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学. pp. 40-54. |
| [6] | 刘进, 王嘉宇, 姜树坤, 徐正进 (2012). 水稻叶绿素含量动态QTL分析. 植物生理学报 48, 577-583. |
| [7] | 刘进, 姚晓云, 范淑秀, 黎毛毛, 郭乃辉, 王鑫瑞, 王嘉宇, 陈温福 (2018). 水稻叶绿素含量和穗部性状的QTL及其相互关系分析. 沈阳农业大学学报 49, 641-648. |
| [8] | 梅银国, 唐志明, 李华军, 李信年, 华国来, 李晓方 (2012). 水稻叶片叶绿素含量与衰老的关系. 湖北农业科学 51, 2177-2179. |
| [9] | 王春华 (2018). 中国粮食安全现状与应对策略分析. 粮食问题研究 (5), 40-42. |
| [10] | 王红梅, 张敏, 陶诗顺 (2008). 水稻叶绿素含量与发根率的关系研究. 安徽农业科学 36, 3265-3269. |
| [11] | 王兰, 黄李超, 代丽萍, 杨窑龙, 徐杰, 冷语佳, 张光恒, 胡江, 朱丽, 高振宇, 董国军, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 曾大力 (2014). 利用日本晴/9311重组自交系群体定位水稻成熟期叶形相关性状QTL. 中国水稻科学 28, 589-597. |
| [12] |
杨凯如, 贾绮玮, 金佳怡, 叶涵斐, 王盛, 陈芊羽, 管易安, 潘晨阳, 辛德东, 方媛, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2022). 水稻黄绿叶调控基因YGL18的克隆与功能解析. 植物学报 57, 276-287.
DOI |
| [13] | 杨树明, 刘关所, 张素华 (2017). 不同生长环境下水稻孕穗期叶绿素QTL定位. 云南大学学报(自然科学版) 39, 684-690. |
| [14] | 姚晓云, 杨平, 黄永萍, 彭志勤, 刘进, 吴延寿, 邹国兴, 尹建华 (2022). 水稻叶绿素含量主效QTL定位. 江西农业学报 34(2), 8-14. |
| [15] |
叶涵斐, 殷文晶, 管易安, 杨凯如, 陈芊羽, 俞淑颖, 朱旭东, 辛德东, 章薇, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2022). 水稻籽粒维生素E QTL挖掘及候选基因分析. 植物学报 57, 157-170.
DOI |
| [16] |
赵凌, 张勇, 魏晓东, 梁文化, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 姚姝, 王才林, 张亚东 (2022). 利用高密度Bin图谱定位水稻抽穗期剑叶叶绿素含量QTL. 中国农业科学 55, 825-836.
DOI |
| [17] |
甄晓宇, 杨坚群, 栗鑫鑫, 刘兆新, 高芳, 赵继浩, 李颖, 钱必长, 李金融, 杨东清, 李向东 (2019). 播种深度对花生生育进程和叶片衰老的影响及其生理机制. 作物学报 45, 1386-1397.
DOI |
| [18] |
周纯, 焦然, 胡萍, 林晗, 胡娟, 徐娜, 吴先美, 饶玉春, 王跃星 (2019). 水稻早衰突变体LS-es1的基因定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报 54, 606-619.
DOI |
| [19] | 周振翔 (2016). 水稻叶片叶绿素含量对光合生理及产量的影响. 硕士论文. 扬州: 扬州大学. pp. 1-10. |
| [20] | 邹阳 (2020). 水稻MYB转录因子家族成员的鉴定及其抗逆调控机制研究. 硕士论文. 福州: 福建农林大学. pp. 1-7. |
| [21] | 左海龙 (2008). 控制水稻叶片叶绿素含量及其降解相关基因的遗传定位. 博士论文. 上海: 上海师范大学. pp. 28-32. |
| [22] | Dong YJ, Yang ZN, Xu JL, Lin DZ, Sugimoto Y, Luo LJ, Mei HW (2007). Quantitative trait loci for leaf chlorophyll content at two developmental stages of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Commun Biometry Crop Sci 2, 1-7. |
| [23] |
Guo MN, Ruan WY, Li CY, Huang FL, Zeng M, Liu YY, Yu YN, Ding XM, Wu YR, Wu ZC, Mao CZ, Yi KK, Wu P, Mo XR (2015). Integrative comparison of the role of the PHOSPHATE RESPONSE 1 subfamily in phosphate signaling and homeostasis in rice. Plant Physiol 168, 1762-1776.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
He L, Zhang S, Qiu ZN, Zhao J, Nie WD, Lin HY, Zhu ZG, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Zhu L (2018). FRUCTOKINASE-LIKE PROTEIN 1 interacts with TRXz to regulate chloroplast development in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 94-111.
DOI |
| [25] |
Huang LC, Dai LP, Wang L, Leng YJ, Yang YL, Xu J, Hu J, Rao YC, Zhang GH, Zhu L, Dong GJ, Guo LB, Qian Q, Zeng DL (2015). Genetic dissection for chlorophyll content of the top three leaves during grain filling in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Growth Regul 34, 381-391.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Huang YJ, Zhao HX, Gao F, Yao PF, Deng RY, Li CL, Chen H, Wu Q (2018). A R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene, FtMYB13, from Tartary buckwheat improves salt/ drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 132, 238-248.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Jiang GH, Xiang YH, Zhao JY, Yin DD, Zhao XF, Zhu LH, Zhai WX (2014). Regulation of inflorescence branch development in rice through a novel pathway involving the pentatricopeptide repeat protein sped1-D. Genetics 197, 1395-1407.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Jiang SK, Zhang XJ, Xu ZJ, Chen WF (2010). Comparison between QTLs for chlorophyll content and genes controlling chlorophyll biosynthesis and degradation in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agronom Sin 36, 376-384.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Mae T (1997). Physiological nitrogen efficiency in rice: nitrogen utilization, photosynthesis, and yield potential. Plant Soil 196, 201-210.
DOI URL |
| [31] | McCouch SR, Cho YC, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M (1997). Report on QTL no-menclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14, 11-13. |
| [32] |
Xie WB, Feng Q, Yu HH, Huang XH, Zhao Q, Xing YZ, Yu SB, Han B, Zhang QF (2010). Parent-independent genotyping for constructing an ultrahigh-density linkage map based on population sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 10578-10583.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Zhang GH, Li SY, Wang L, Ye WJ, Zeng DL, Rao YC, Peng YL, Hu J, Yang YL, Xu J, Ren DY, Gao ZY, Zhu L, Dong GJ, Hu XM, Yan MX, Guo LB, Li CY, Qian Q (2014). LSCHL4 from japonica cultivar, which is allelic to NAL1, increases yield of indica super rice 93-11. Mol Plant 7, 1350-1364.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Zuo HL, Xiao K, Dong YJ, Xu JL, Li ZK, Luo LJ, Mei HW (2007). Molecular detection of quantitative trait loci for leaf chlorophyll content at different growth-stages of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Asian J Plant Sci 6, 518-522.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [7] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [8] | 廖星鑫, 牛祎, 多兴武, 阿克也得力·居玛哈孜, 买热哈巴·阿不都克尤木, 热孜瓦尼姑丽·胡甫尔, 兰海燕, 曹婧. 异源表达异子蓬SaPEPC2基因提高烟草抗旱性和光合特性(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 585-599. |
| [9] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [10] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [11] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [12] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [13] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [14] | 李伟斌, 张红霞, 张玉书, 陈妮娜. 昼夜不对称增温对长白山阔叶红松林碳汇能力的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(9): 1225-1233. |
| [15] | 蒋海港, 曾云鸿, 唐华欣, 刘伟, 李杰林, 何国华, 秦海燕, 王丽超, 姚银安. 三种藓类植物固碳耗水节律调节作用[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(7): 988-997. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||