

植物学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 733-742.DOI: 10.11983/CBB16218 cstr: 32102.14.CBB16218
收稿日期:2016-11-14
接受日期:2016-12-11
出版日期:2017-11-01
发布日期:2018-02-22
通讯作者:
杜远鹏
基金资助:
Fu Qingqing, Sun Lulong, Zhai Heng, Du Yuanpeng*( )
)
Received:2016-11-14
Accepted:2016-12-11
Online:2017-11-01
Published:2018-02-22
Contact:
Du Yuanpeng
摘要: 以耐盐性较强的砧木1103P为对照品种, 对左山一×SO4杂种砧木F1代的6个株系(A15、A17、A34、A35、A38和A48)及左山一×101-1杂种F1代2个株系(B24和B26)的一年生盆栽扦插苗进行100 mmol·L-1 NaCl胁迫处理, 以各自无盐胁迫为对照处理。20天后, 根据表型计算盐害指数, 测定叶绿素含量、光合气体交换参数、叶绿素荧光参数以及生长量指标; 以各项生长指标的耐盐系数为耐盐指标, 通过主成分分析、相关性分析、隶属函数分析和聚类分析等方法对葡萄株系进行综合评价。结果表明, A34和A35植株无盐害症状, 盐害级数为0; A15和A17植株有少部分叶片边缘焦枯, 盐害级数为1。盐胁迫大幅度降低了1103P和B26等株系的叶绿素含量、光合速率、新梢生长量和生物量; 而A15、A17、A34和A35植株的各项指标降低幅度较小。将生物量等12个单项指标转换成3个相互独立的综合指标, 通过聚类分析, 发现A34、A35、A15和A17植株的耐盐性较强, A38、A48和B24植株的耐盐性中等, 1103P和B26植株的耐盐性较弱, 与盐害分级结果一致。
付晴晴, 孙鲁龙, 翟衡, 杜远鹏. 葡萄种间杂交砧木育种F1代植株耐盐性分析. 植物学报, 2017, 52(6): 733-742.
Fu Qingqing, Sun Lulong, Zhai Heng, Du Yuanpeng. Salt Tolerant Evaluation of F1-generation Hybrids in Grape. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(6): 733-742.
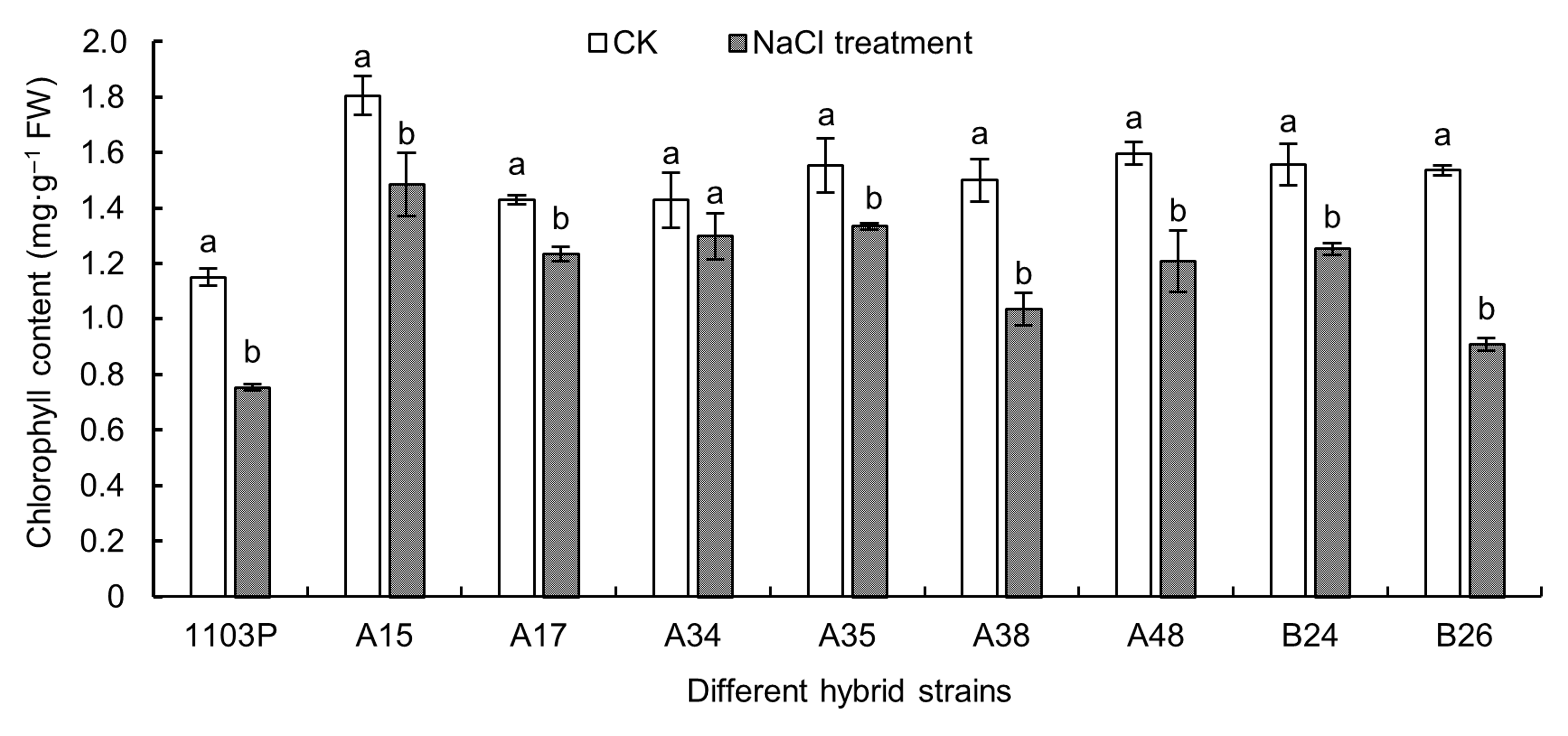
图2 NaCl胁迫对各葡萄株系叶片叶绿素含量的影响不同小写字母表示同一株系不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 2 Effects of NaCl stress on chlorophyll content in different grape hybrid strainsDifferent lowercase letters indicate significant differences under different treatments of the same strain (P<0.05).
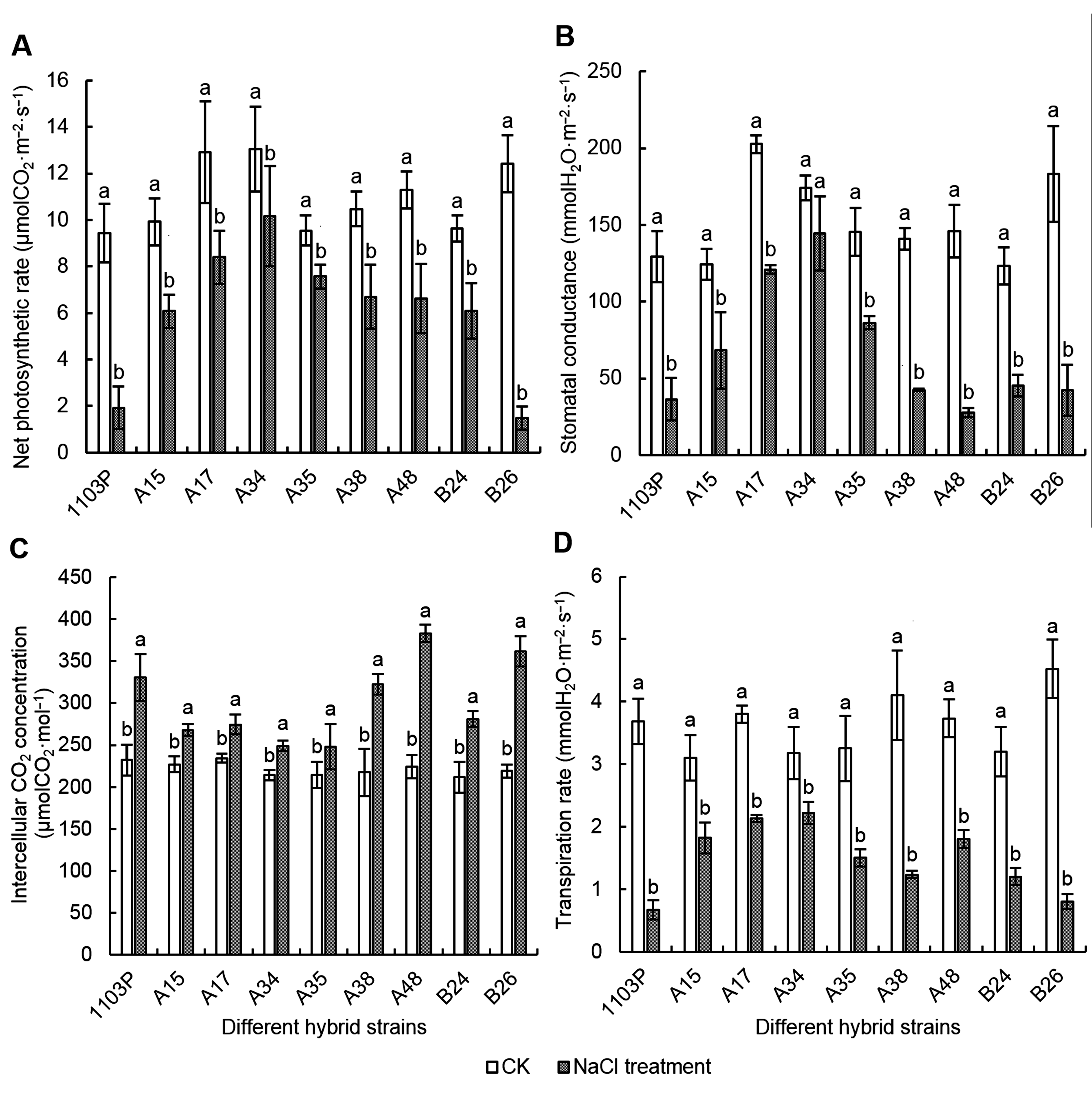
图3 NaCl胁迫对各葡萄株系叶片Pn、Gs、Ci和Tr的影响Pn: 净光合速率; Gs: 气孔导度; Ci: 胞间CO2浓度; Tr: 蒸腾速率。不同小写字母表示同一株系不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 3 Effects of NaCl stress on Pn, Gs, Ci and Tr of different grape hybrid strainsPn: Net photosynthetic rate; Gs: Stomatal conductance; Ci: Intercellular CO2 concentration; Tr: Transpiration rate. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences under different treatments of the same strain (P<0.05).
| Strains | NaCl concentration (mmol·L-1) | Fv/Fm | ΦPSII | Wk | RC/CSm | Ψ0 | qP | NPQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103p | 0 | 0.811±0.007 a | 0.612±0.053 a | 0.387±0.009 ef | 776.5±34.8 abc | 0.545±0.065 a | 0.856±0.026 ab | 0.703±0.139 g |
| 100 | 0.285±0.150 f | 0.153±0.062 e | 0.536±0.072 b | 111.7±94.21 h | 0.21±0.079 e | 0.322±0.131 f | 4.608±0.81 bc | |
| A15 | 0 | 0.827±0.018 a | 0.61±0.027 a | 0.385±0.025 ef | 793±51.51 ab | 0.539±0.040 a | 0.857±0.012 ab | 1.256±0.04 fg |
| 100 | 0.68±0.024 cde | 0.35±0.071 cd | 0.515±0.045 bc | 621.1±73.95 cd | 0.383±0.062 cd | 0.662±0.051 e | 3.017±0.46 de | |
| A17 | 0 | 0.818±0.023 a | 0.601±0.057 a | 0.402±0.016 ef | 643.2±55.1 bcd | 0.507±0.08 abc | 0.863±0.028 a | 0.908±0.049 g |
| 100 | 0.70±0.016 bcde | 0.425±0.01 cd | 0.475±0.037 cd | 514.9±76.19 de | 0.347±0.059 d | 0.76±0.020 bcd | 1.62±0.146 fg | |
| A34 | 0 | 0.818±0.009 a | 0.609±0.033 a | 0.401±0.016 ef | 668.1±33.3 bcd | 0.52±0.044 ab | 0.875±0.009 a | 1.137±0.07 fg |
| 100 | 0.768±0.023 abc | 0.463±0.03 bc | 0.436±0.014 de | 568.7±19.40 de | 0.491±0.02 abc | 0.712±0.019 de | 2.057±0.403 ef | |
| A35 | 0 | 0.824±0.008 a | 0.543±0.04 ab | 0.397±0.022 ef | 631.3±74.80 cd | 0.517±0.018 ab | 0.82±0.014 abc | 2.235±0.251 ef |
| 100 | 0.75±0.006 abcd | 0.39±0.035 cd | 0.415±0.03 def | 528±25.68 de | 0.395±0.07 bcd | 0.76±0.027 bcd | 2.982±1.11 de | |
| A38 | 0 | 0.813±0.007 a | 0.607±0.023 a | 0.352±0.014 f | 773.3±37.2 abc | 0.563±0.078 a | 0.887±0.018 a | 0.856±0.103 g |
| 100 | 0.629±0.059 e | 0.324±0.065 d | 0.528±0.035 bc | 280.7±130.3 fg | 0.302±0.042 de | 0.682±0.048 de | 5.53±0.287 ab | |
| A48 | 0 | 0.816±0.012 a | 0.607±0.079 a | 0.39±0.022 ef | 748.5±49.6 abc | 0.53±0.042 a | 0.873±0.011 a | 1.076±0.085 g |
| 100 | 0.633±0.077 de | 0.368±0.03 cd | 0.58±0.051 ab | 418.6±51.03 ef | 0.275±0.054 de | 0.675±0.076 de | 3.396±0.391 d | |
| B24 | 0 | 0.806±0.003 ab | 0.576±0.098 a | 0.388±0.011 ef | 901.3±65.99 a | 0.534±0.034 a | 0.861±0.015 a | 1.335±0.26 fg |
| 100 | 0.646±0.030 de | 0.344±0.036 d | 0.548±0.028 ab | 653.5±44.5 bcd | 0.35±0.048 d | 0.715±0.051 de | 3.614±0.07 cd | |
| B26 | 0 | 0.818±0.012 a | 0.57±0.039 ab | 0.369±0.004 f | 875.6±38.21 a | 0.55±0.038 a | 0.851±0.018 ab | 1.27±0.114 fg |
| 100 | 0.256±0.108 f | 0.093±0.079 e | 0.616±0.062 a | 151.3±128.4 gh | 0.188±0.047 e | 0.307±0.307 f | 6.42±1.076 a |
表1 盐胁迫对葡萄叶片叶绿素荧光参数的影响
Table 1 Effects of NaCl stress on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in leaves of grape
| Strains | NaCl concentration (mmol·L-1) | Fv/Fm | ΦPSII | Wk | RC/CSm | Ψ0 | qP | NPQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103p | 0 | 0.811±0.007 a | 0.612±0.053 a | 0.387±0.009 ef | 776.5±34.8 abc | 0.545±0.065 a | 0.856±0.026 ab | 0.703±0.139 g |
| 100 | 0.285±0.150 f | 0.153±0.062 e | 0.536±0.072 b | 111.7±94.21 h | 0.21±0.079 e | 0.322±0.131 f | 4.608±0.81 bc | |
| A15 | 0 | 0.827±0.018 a | 0.61±0.027 a | 0.385±0.025 ef | 793±51.51 ab | 0.539±0.040 a | 0.857±0.012 ab | 1.256±0.04 fg |
| 100 | 0.68±0.024 cde | 0.35±0.071 cd | 0.515±0.045 bc | 621.1±73.95 cd | 0.383±0.062 cd | 0.662±0.051 e | 3.017±0.46 de | |
| A17 | 0 | 0.818±0.023 a | 0.601±0.057 a | 0.402±0.016 ef | 643.2±55.1 bcd | 0.507±0.08 abc | 0.863±0.028 a | 0.908±0.049 g |
| 100 | 0.70±0.016 bcde | 0.425±0.01 cd | 0.475±0.037 cd | 514.9±76.19 de | 0.347±0.059 d | 0.76±0.020 bcd | 1.62±0.146 fg | |
| A34 | 0 | 0.818±0.009 a | 0.609±0.033 a | 0.401±0.016 ef | 668.1±33.3 bcd | 0.52±0.044 ab | 0.875±0.009 a | 1.137±0.07 fg |
| 100 | 0.768±0.023 abc | 0.463±0.03 bc | 0.436±0.014 de | 568.7±19.40 de | 0.491±0.02 abc | 0.712±0.019 de | 2.057±0.403 ef | |
| A35 | 0 | 0.824±0.008 a | 0.543±0.04 ab | 0.397±0.022 ef | 631.3±74.80 cd | 0.517±0.018 ab | 0.82±0.014 abc | 2.235±0.251 ef |
| 100 | 0.75±0.006 abcd | 0.39±0.035 cd | 0.415±0.03 def | 528±25.68 de | 0.395±0.07 bcd | 0.76±0.027 bcd | 2.982±1.11 de | |
| A38 | 0 | 0.813±0.007 a | 0.607±0.023 a | 0.352±0.014 f | 773.3±37.2 abc | 0.563±0.078 a | 0.887±0.018 a | 0.856±0.103 g |
| 100 | 0.629±0.059 e | 0.324±0.065 d | 0.528±0.035 bc | 280.7±130.3 fg | 0.302±0.042 de | 0.682±0.048 de | 5.53±0.287 ab | |
| A48 | 0 | 0.816±0.012 a | 0.607±0.079 a | 0.39±0.022 ef | 748.5±49.6 abc | 0.53±0.042 a | 0.873±0.011 a | 1.076±0.085 g |
| 100 | 0.633±0.077 de | 0.368±0.03 cd | 0.58±0.051 ab | 418.6±51.03 ef | 0.275±0.054 de | 0.675±0.076 de | 3.396±0.391 d | |
| B24 | 0 | 0.806±0.003 ab | 0.576±0.098 a | 0.388±0.011 ef | 901.3±65.99 a | 0.534±0.034 a | 0.861±0.015 a | 1.335±0.26 fg |
| 100 | 0.646±0.030 de | 0.344±0.036 d | 0.548±0.028 ab | 653.5±44.5 bcd | 0.35±0.048 d | 0.715±0.051 de | 3.614±0.07 cd | |
| B26 | 0 | 0.818±0.012 a | 0.57±0.039 ab | 0.369±0.004 f | 875.6±38.21 a | 0.55±0.038 a | 0.851±0.018 ab | 1.27±0.114 fg |
| 100 | 0.256±0.108 f | 0.093±0.079 e | 0.616±0.062 a | 151.3±128.4 gh | 0.188±0.047 e | 0.307±0.307 f | 6.42±1.076 a |
| Strains | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103P | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.56 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 0.87 |
| A15 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.71 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| A17 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.97 |
| A34 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.98 |
| A35 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 0.60 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.99 |
| A38 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.92 |
| A48 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.96 | 1.03 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.88 | 0.98 |
| B24 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.49 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.91 |
| B26 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.96 | 0.51 | 0.68 | 1.29 | 0.85 |
表2 NaCl胁迫下各葡萄株系各单项指标的耐盐系数
Table 2 Salt tolerant coefficient of every single index of each grape strains under NaCl stress
| Strains | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103P | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.56 | 0.67 | 0.92 | 0.87 |
| A15 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.71 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| A17 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.97 |
| A34 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.98 |
| A35 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.89 | 0.61 | 0.88 | 0.60 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.99 |
| A38 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.92 |
| A48 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.96 | 1.03 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.88 | 0.98 |
| B24 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.49 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.91 |
| B26 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.96 | 0.51 | 0.68 | 1.29 | 0.85 |
| Growth parameters | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| X2 | 0.881** | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| X3 | 0.437 | 0.523 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| X4 | 0.111 | 0.278 | 0.592 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X5 | 0.266 | 0.431 | 0.893** | 0.711* | 1.000 | |||||||
| X6 | 0.516 | 0.678* | 0.271 | 0.522 | 0.284 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X7 | 0.458 | 0.525 | 0.852** | 0.309 | 0.576 | 0.275 | 1.000 | |||||
| X8 | -0.358 | -0.321 | 0.378 | 0.628 | 0.495 | -0.317 | 0.116 | 1.000 | ||||
| X9 | 0.373 | 0.473 | 0.984** | 0.702* | 0.898** | 0.347 | 0.821** | 0.436 | 1.000 | |||
| X10 | 0.376 | 0.588 | 0.833** | 0.770* | 0.909** | 0.644 | 0.605 | 0.245 | 0.874** | 1.000 | ||
| X11 | 0.301 | 0.297 | -0.501 | -0.137 | -0.564 | 0.615 | -0.273 | 0.678* | -0.456 | -0.203 | 1.000 | |
| X12 | 0.324 | 0.363 | 0.926** | 0.608 | 0.763* | 0.196 | 0.890** | 0.519 | 0.935** | 0.720* | -0.483 | 1.000 |
表3 NaCl胁迫下各单项指标的相关系数矩阵
Table 3 Correlation matrix of every single index under NaCl stress
| Growth parameters | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | |||||||||||
| X2 | 0.881** | 1.000 | ||||||||||
| X3 | 0.437 | 0.523 | 1.000 | |||||||||
| X4 | 0.111 | 0.278 | 0.592 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X5 | 0.266 | 0.431 | 0.893** | 0.711* | 1.000 | |||||||
| X6 | 0.516 | 0.678* | 0.271 | 0.522 | 0.284 | 1.000 | ||||||
| X7 | 0.458 | 0.525 | 0.852** | 0.309 | 0.576 | 0.275 | 1.000 | |||||
| X8 | -0.358 | -0.321 | 0.378 | 0.628 | 0.495 | -0.317 | 0.116 | 1.000 | ||||
| X9 | 0.373 | 0.473 | 0.984** | 0.702* | 0.898** | 0.347 | 0.821** | 0.436 | 1.000 | |||
| X10 | 0.376 | 0.588 | 0.833** | 0.770* | 0.909** | 0.644 | 0.605 | 0.245 | 0.874** | 1.000 | ||
| X11 | 0.301 | 0.297 | -0.501 | -0.137 | -0.564 | 0.615 | -0.273 | 0.678* | -0.456 | -0.203 | 1.000 | |
| X12 | 0.324 | 0.363 | 0.926** | 0.608 | 0.763* | 0.196 | 0.890** | 0.519 | 0.935** | 0.720* | -0.483 | 1.000 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.24 | -0.24 | 0.35 | 0.554 |
| CI2 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.04 | -0.02 | -0.03 | 0.44 | 0.14 | -0.42 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.42 | -0.03 | 0.252 |
| CI3 | -0.04 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.105 |
表4 NaCl胁迫下各综合指标的相关系数及贡献率
Table 4 Correlation of comprehensive indexes and their contribution rates under NaCl stress
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CI1 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.24 | -0.24 | 0.35 | 0.554 |
| CI2 | 0.46 | 0.47 | 0.04 | -0.02 | -0.03 | 0.44 | 0.14 | -0.42 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.42 | -0.03 | 0.252 |
| CI3 | -0.04 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.83 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.105 |
| Strains | CI1 | CI2 | CI3 | U(X1) | U(X2) | U(X3) | Value D | Salt tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103P | 1.39 | 0.67 | 2.63 | 0.20 | 0.46 | 0.00 | 0.252 | Weaker |
| A15 | 1.68 | 0.82 | 3.19 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0.761 | Strong |
| A17 | 1.76 | 0.69 | 3.15 | 0.85 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 0.758 | Strong |
| A34 | 1.76 | 0.92 | 3.21 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.907 | Strong |
| A35 | 1.85 | 0.67 | 3.12 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 0.826 | Strong |
| A38 | 1.48 | 0.88 | 2.76 | 0.36 | 0.92 | 0.23 | 0.499 | Medium |
| A48 | 1.61 | 0.46 | 2.94 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.418 | Medium |
| B24 | 1.49 | 0.64 | 2.70 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.353 | Medium |
| B26 | 1.27 | 0.56 | 2.67 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.066 | Weaker |
| Index weight | 0.608 | 0.277 | 0.115 |
表5 NaCl胁迫下各株系的综合指标值、权重、隶属函数值、D值及综合评价
Table 5 Each strain’s comprehensive index, index weight, membership function value, value D and comprehensive evaluation under NaCl stress
| Strains | CI1 | CI2 | CI3 | U(X1) | U(X2) | U(X3) | Value D | Salt tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1103P | 1.39 | 0.67 | 2.63 | 0.20 | 0.46 | 0.00 | 0.252 | Weaker |
| A15 | 1.68 | 0.82 | 3.19 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.97 | 0.761 | Strong |
| A17 | 1.76 | 0.69 | 3.15 | 0.85 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 0.758 | Strong |
| A34 | 1.76 | 0.92 | 3.21 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.907 | Strong |
| A35 | 1.85 | 0.67 | 3.12 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.84 | 0.826 | Strong |
| A38 | 1.48 | 0.88 | 2.76 | 0.36 | 0.92 | 0.23 | 0.499 | Medium |
| A48 | 1.61 | 0.46 | 2.94 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.418 | Medium |
| B24 | 1.49 | 0.64 | 2.70 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.353 | Medium |
| B26 | 1.27 | 0.56 | 2.67 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.066 | Weaker |
| Index weight | 0.608 | 0.277 | 0.115 |
| [1] | 高建明, 夏卜贤, 袁庆华, 罗峰, 韩芸, 桂枝, 裴忠有, 孙守钧 (2012). 高粱种质材料幼苗期耐盐碱性评价. 应用生态学报 23,1303-1310. |
| [2] | 贺普超 (1999). 葡萄学(第1版). 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 23. |
| [3] | 何伟, 艾军, 范书田, 杨义明, 王振兴, 赵滢, 乔永在, 张亚凤, 李晓燕 (2015). 葡萄品种及砧木抗寒性评价方法研究. 果树学报 32, 1135-1142. |
| [4] | 黄毅, 张玉龙 (2004). 保护地生产条件下的土壤退化问题及其防治对策. 土壤通报 35, 212-216. |
| [5] | 金立桥, 车兴凯, 张子山, 高辉远 (2015). 高温、强光下黄瓜叶片PSII供体侧和受体侧的伤害程度与快速荧光参数Wk变化的关系. 植物生理学报 51, 969-976. |
| [6] | 李丰先, 周宇飞, 王艺陶, 孙璐, 白薇, 闫彤, 许文娟, 黄瑞冬 (2013). 高粱品种萌发期耐碱性筛选与综合鉴定. 中国农业科学 46, 1762-1771. |
| [7] |
李鹏民, 高辉远, Strasser RJ (2005). 快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学分析在光合作用研究中的应用. 植物生理与分子生物学学报 31, 559-566.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
李晓芬, 尚庆茂, 张志刚, 王立浩, 张宝玺 (2008). 多元统计分析方法在辣椒品种耐盐性评价中的应用. 园艺学报 35, 351-356.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 廖祥儒, 贺普超, 万怡震, 朱新产 (1996). 盐胁迫对葡萄离体新梢叶片的伤害作用. 果树科学 13(4), 211-214. |
| [10] |
刘家尧, 衣艳君, 张其德 (1998). 盐胁迫对不同抗盐性小麦叶片荧光诱导动力学的影响. 植物学通报 15(2), 47-50.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 罗海波, 马苓, 段伟, 李绍华, 王利军 (2010). 高温胁迫对‘赤霞珠’葡萄光合作用的影响. 中国农业科学 43, 2744-2750. |
| [12] | 莫伟平, 周琳耀, 张静逸, 黄俊波, 贝学文, 付欣雨, 王惠聪, 黄旭明 (2013). 遮阴和环剥对荔枝枝梢生长和光合生理的影响. 园艺学报 40, 117-124. |
| [13] | 钮福祥, 华希新, 郭小丁, 邬景禹, 李洪民, 丁成伟 (1996). 甘薯品种抗旱性生理指标及其综合评价初探. 作物学报 22, 392-398. |
| [14] | 秦红艳 (2010). 山葡萄种质资源耐盐性评价研究. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 33-40. |
| [15] |
孙璐, 周宇飞, 李丰先, 肖木辑, 陶冶, 许文娟, 黄瑞冬 (2012). 盐胁迫对高粱幼苗光合作用和荧光特性的影响. 中国农业科学 45, 3265-3272.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 王邦锡, 何军贤, 黄久常 (1992). 水分胁迫导致小麦叶片光合作用下降的非气孔因素. 植物生理学报 18, 77-84. |
| [17] |
王军, 周美学, 许如根, 吕超, 黄祖六 (2007). 大麦耐湿性鉴定指标和评价方法研究. 中国农业科学 40, 2145-2152.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 王业遴, 马凯, 姜卫兵, 凌志奋, 顾平, 吴兵, 陈炳泉, 应宝清 (1990). 五种果树耐盐力试验初报. 中国果树 (3), 8-12. |
| [19] | 薛忠财, 高辉远, 柳洁 (2011). 野生大豆和栽培大豆光合机构对NaCl胁迫的不同响应. 生态学报 31, 3101-3109. |
| [20] |
杨升, 张华新, 杨秀艳, 陈秋夏, 武海雯 (2015). NaCl胁迫下不同种源沙枣的生长表现差异. 林业科学 51(9), 51-58.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 杨淑萍, 危常州, 梁永超 (2013). 新疆主要棉花品种耐盐性筛选与鉴定. 干旱区研究 30, 1129-1135. |
| [22] | 张菂, 陈昌盛, 李鹏民, 马锋旺 (2013). 利用快速荧光、延迟荧光和820 nm光反射同步测量技术探讨干旱对平邑甜茶叶片光合机构的伤害机制. 植物生理学报 49, 551-560. |
| [23] |
赵俊香, 任翠梅, 吴凤芝, 刘守伟, 王殿奎 (2015). 16份菊芋种质苗期耐盐碱性筛选与综合鉴定. 中国生态农业学报 23, 620-627.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 赵世杰, 史国安, 董新纯 (2002). 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社. pp. 55-57. |
| [25] | 赵昕, 吴雨霞, 赵敏桂, 何建新 (2007). NaCl胁迫对盐芥和拟南芥光合作用的影响. 植物学通报 24, 154-160. |
| [26] |
Appenroth KJ, St?ckel J, Srivastava A, Strasser RJ (2001). Multiple effects of chromate on the photosynthetic apparatus of Spirodela polyrhiza as probed by OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements. Environ Pollut 115, 49-64.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] |
Chartzoulakis K, Klapaki G (2000). Response of two greenhouse pepper hybrids to NaCl salinity during different growth stages.Sci Hortic 86, 247-260.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2000). Oxygen processing in photosynthesis: a molecular approach.New Phytol 146, 359-388.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Galet P (1991). Precis de Pathologie Viticole (6th Edn). pp. 285. |
| [30] |
Gilmore AM (1997). Mechanistic aspects of xanthophyll cycle-dependent photoprotection in higher plant chloroplasts and leaves.Physiol Plant 99, 197-209.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Grotkopp E, Rejmánek M, Rost TL (2002). Toward a causal explanation of plant invasiveness: seedling growth and life-history strategies of 29 pine ( Pinus) species. Am Nat 159, 396-419.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
Hernández JA, Olmos E, Corpas FJ, Sevilla F, Del Río LA (1995). Salt-induced oxidative stress in chloroplasts of pea plants.Plant Sci 105, 151-167.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Hoshida H, Tanaka Y, Hibino T, Hayashi Y, Tanaka A, Takabe T, Takabe T (2000). Enhanced tolerance to salt stress in transgenic rice that over expresses chloroplast glutamine synthetase.Plant Mol Biol 43, 103-111.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Lu CM, Zhang JH (1999). Effects of water stress on photosystem II photochemistry and its thermo stability in wheat plants.J Exp Bot 50, 1199-1206.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Munns R, Tester M (2008). Mechanisms of salinity tolerance.Annu Rev Plant Biol 59, 651-681.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Samra JS (1985). Sodicity tolerance of grapes with reference to the uptake of nutrients.Indian J Hortic 42, 12-17. |
| [37] |
Strasser BJ (1997). Donor side capacity of photosystem II probed by chlorophyll a fluorescence transients.Photosynth Res 52, 147-155.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Troncoso A, Matte C, Cantos M, Lavee S (1999). Evaluation of salt tolerance of in vitro-grown grapevine rootstock varieties. Vitis 38, 55-60. |
| [39] |
Walker RR, T?r?kfalvy E, Scott NS, Kriedemann PE (1981). An analysis of photosynthetic response to salt treatment in Vitis vinifera. Aust J Plant Physiol 8, 359-374.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Xu CC, Li DQ, Zou Q, Zhang JH (1999). Effect of drought on chlorophyll fluorescence and xanthophyll cycle components in winter wheat leaves with different ages.Acta Phytophys Sin 25, 29-37. |
| [43] |
Zhu JK (2002). Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol 53, 247-273.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Yamasaki T, Yamakawa T, Yamane Y, Koike H, Satoh K, Katoh S (2002). Temperature acclimation of photosynthesis and related changes in photosystem II electron tran- sport in winter wheat.Plant Physiol 128, 1087-1097.
DOI URL PMID |
| [42] |
Yang XH, Chen XY, Ge QY, Li B, Tong YP, Zhang AM, Li ZS, Kuang TY, Lu CM (2006). Tolerance of photosynthesis to photoinhibition, high temperature and drought stress in flag leaves of wheat: a comparison between a hybridization line and its parents grown under field conditions.Plant Sci 171, 389-397.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 张琨, 钱敏, 汪阳, 李志华, 孔令娜, 李明洋, 马瑾煜, 努尔艾合麦提•玉苏普, 陈乙一, 成沂芮, 张焕仕, 覃凤飞, 渠晖. 紫花苜蓿耐阴性综合评价及其鉴定指标的筛选[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 773-787. |
| [2] | 范惠玲, 路妍, 金文海, 王慧, 彭小星, 武学霞, 刘玉皎. 基于根系表型性状的蚕豆耐盐碱性鉴定与综合评价(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 204-217. |
| [3] | 郭政, 邵香君, 鲁海雯, 侯丹, 孔思梦, 李翔宇, 刘华倩, 林新春. 马来甜龙竹多倍体高效诱导及鉴定[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 246-255. |
| [4] | 巴苏艳, 赵春艳, 刘媛, 方强. 通过虫体花粉识别构建植物‒传粉者网络: 人工模型与AI模型高度一致[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24088-. |
| [5] | 段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [6] | 王露露, 杨智, 杨永. 利用标本组学推进植物超级DNA条形码研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 831-842. |
| [7] | 孙蓉, 杨宇琭, 李亚军, 张会, 李旭凯. 谷子PLATZ转录因子基因家族的鉴定和分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 548-559. |
| [8] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [9] | 宋雅静, 欧晋稳, 张古文, 冯志娟, 卜远鹏, 王斌, 龚亚明, 徐建强, 刘娜. 豌豆茎基腐病病原菌分离鉴定及其对杀菌剂的敏感性测定[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 132-139. |
| [10] | 牛晓锋, 王晓梅, 张研, 赵志鹏, 樊恩源. 鲟鱼分子鉴定方法的整合应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 22034-. |
| [11] | 徐聪, 张飞宇, 俞道远, 孙新, 张峰. 土壤动物的分子分类预测策略评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22252-. |
| [12] | 孙翌昕, 李英滨, 李玉辉, 李冰, 杜晓芳, 李琪. 高通量测序技术在线虫多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22266-. |
| [13] | 王楠, 黄菁华, 霍娜, 杨盼盼, 张欣玥, 赵世伟. 宁南山区不同植被恢复方式下土壤线虫群落特征:形态学鉴定与高通量测序法比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1513-1529. |
| [14] | 夏正俊, 李玉卓, 朱金龙, 吴红艳, 徐坤, 翟红. 快速、无损大豆种子连续取样技术及其DNA制备[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 56-61. |
| [15] | 贺闽, 尹俊杰, 冯志明, 朱孝波, 赵剑华, 左示敏, 陈学伟. 水稻稻瘟病和纹枯病抗性鉴定方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 577-587. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||