

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (2): 246-255.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24143 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24143
郭政1, 邵香君2, 鲁海雯1, 侯丹1, 孔思梦1, 李翔宇1, 刘华倩1, 林新春1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-18
接受日期:2024-11-15
出版日期:2025-03-10
发布日期:2024-11-26
通讯作者:
林新春
基金资助:
Zheng Guo1, Xiangjun Shao2, Haiwen Lu1, Dan Hou1, Simeng Kong1, Xiangyu Li1, Huaqian Liu1, Xinchun Lin1,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-18
Accepted:2024-11-15
Online:2025-03-10
Published:2024-11-26
Contact:
Xinchun Lin
摘要: 由于大部分竹类植物开花周期长、花期难以预测且结实率低, 导致竹子育种一直是竹类植物研究的难题。多倍体育种作为植物育种的一种常用手段, 能够通过人工诱导获得具有优良性状的后代。在竹子育种中, 有关多倍体育种的研究较少。在已有马来甜龙竹(Dendrocalamus asper)再生体系的基础上, 分别使用液体悬浮法和固体培养基混培法对马来甜龙竹胚性愈伤组织进行秋水仙素处理。结果表明, 对于愈伤组织分化率和褐化率, 基于液体悬浮法用50 mg∙L-1秋水仙素处理愈伤组织48-72小时效果最佳。实验共得到再生植株54株, 其中对照组7株。利用流式细胞仪检测所有再生植株, 成功得到染色体加倍植株16株。在染色体加倍率方面, 采用100 mg∙L-1秋水仙素处理48小时产生的染色体加倍植株数量最多, 染色体加倍率达54.54%。与六倍体相比, 十二倍体植株的叶片更大、更厚, 下表皮气孔更大, 暗示其在抗逆生理方面具有一定的优越性。研究提出的基于竹子离体再生体系的高效率多倍体育种技术, 为培育竹类多倍体新种质提供了新方法。
郭政, 邵香君, 鲁海雯, 侯丹, 孔思梦, 李翔宇, 刘华倩, 林新春. 马来甜龙竹多倍体高效诱导及鉴定. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 246-255.
Zheng Guo, Xiangjun Shao, Haiwen Lu, Dan Hou, Simeng Kong, Xiangyu Li, Huaqian Liu, Xinchun Lin. Efficient Induction and Identification of Polyploids in Dendrocalamus asper. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 246-255.
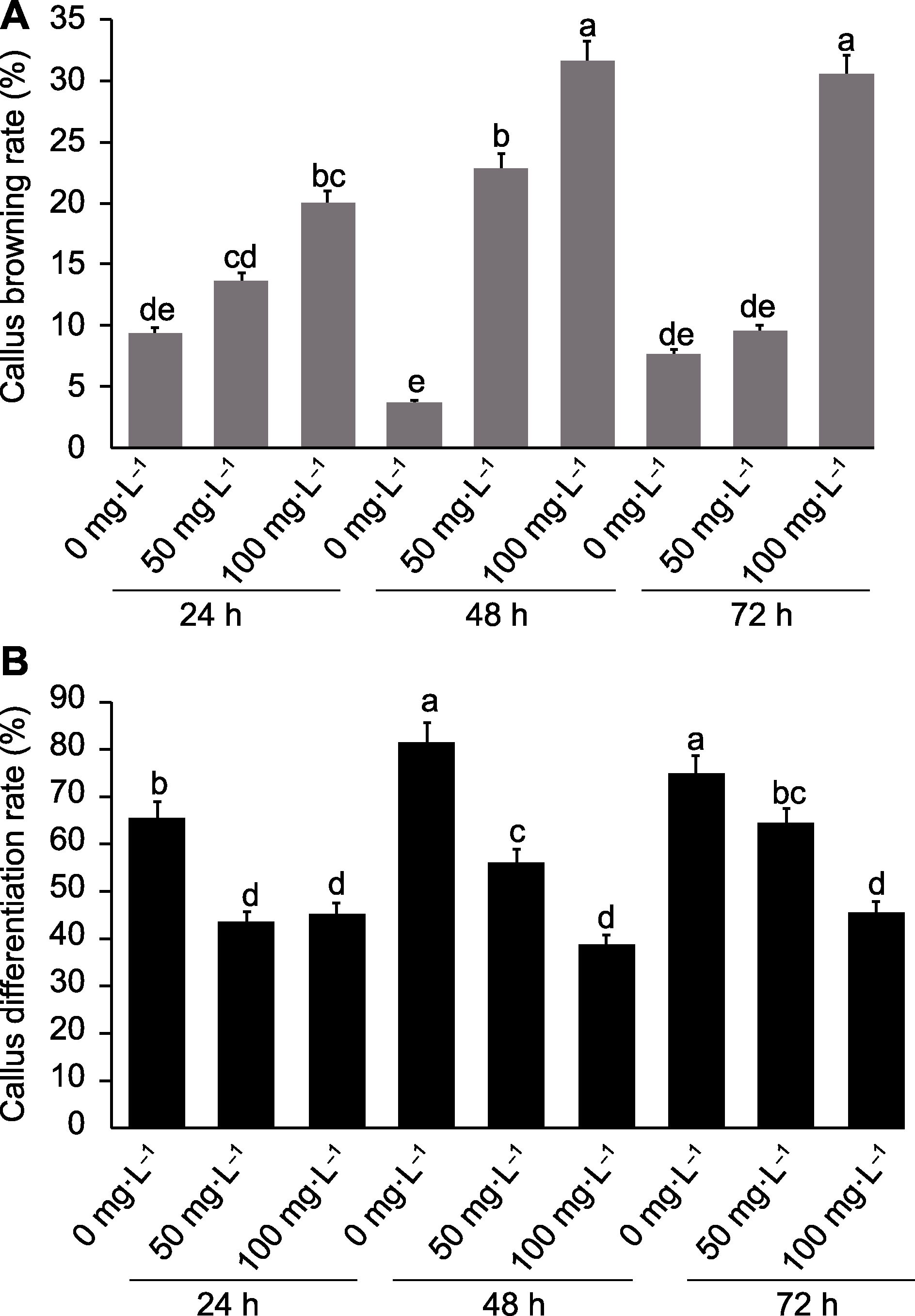
图1 基于液体悬浮法用秋水仙素处理马来甜龙竹愈伤组织的结果 (A) 不同秋水仙素浓度和不同处理时间愈伤组织褐化率; (B) 不同秋水仙素浓度和不同处理时间愈伤组织分化率。数据为平均值±标准差(n=10), 不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著。
Figure 1 Results of colchicine treatment of Dendrocalamus asper calluses based on liquid suspension method (A) Callus browning rate at different colchicine concentrations and treatment times; (B) Callus differentiation rate at different colchicine concentrations and treatment times. Data are means ± SD (n=10), and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments.
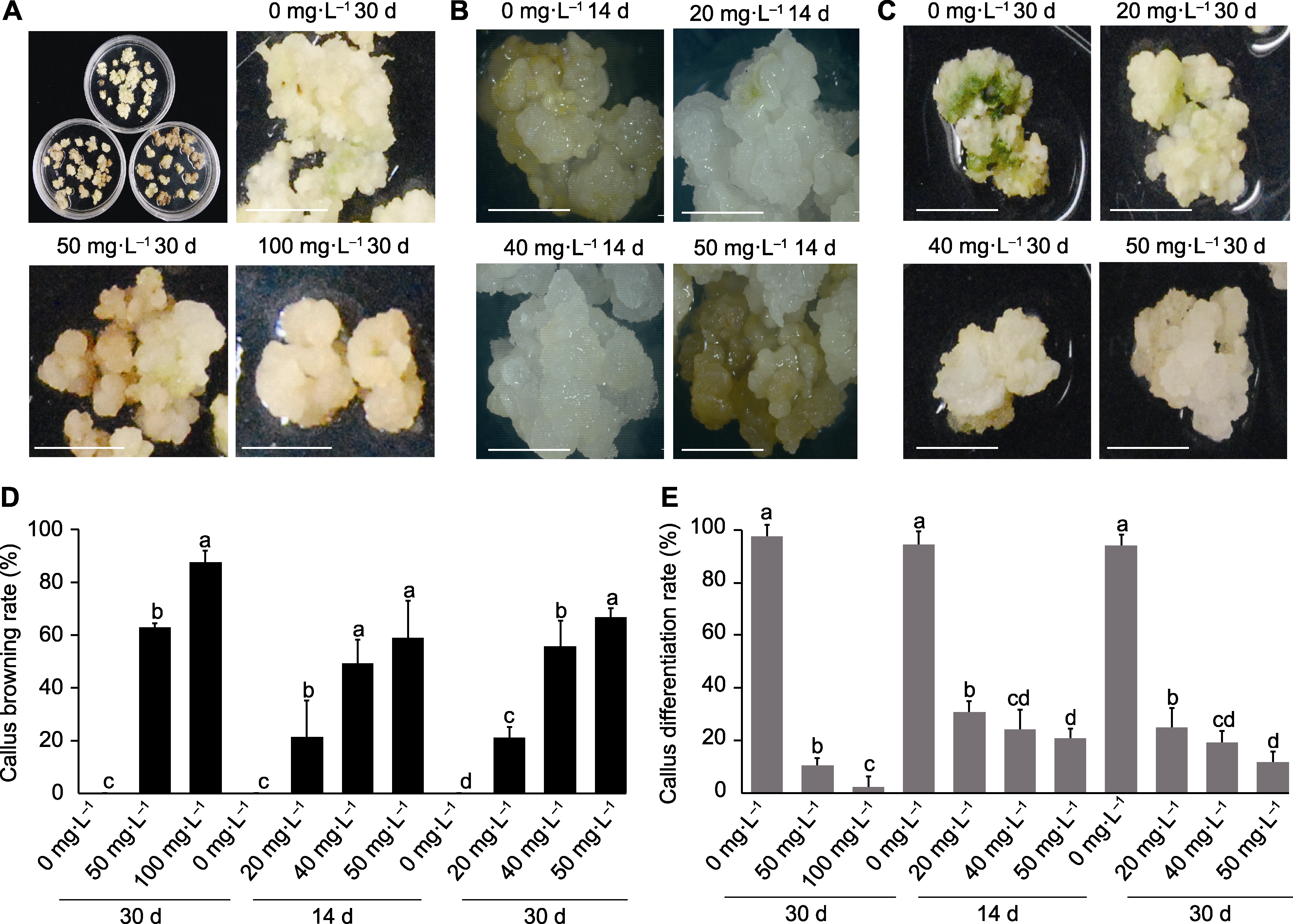
图2 基于固体培养基混培法用秋水仙素处理马来甜龙竹愈伤组织的结果 (A) 0、50和100 mg∙L-1秋水仙素处理30天; (B) 0、20、40和50 mg∙L-1秋水仙素处理14天; (C) 0、20、40和50 mg∙L-1秋水仙素处理30天; (D) 愈伤组织褐化率; (E) 愈伤组织分化率。数据为平均值±标准差(n=10), 不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著。Bars= 5 mm
Figure 2 Results of colchicine treatment of Dendrocalamus asper calluses based on solid medium mixed culture method (A) Treat with 0, 50, and 100 mg∙L-1 colchicine for 30 days; (B) Treat with 0, 20, 40, and 50 mg∙L-1 colchicine for 14 days; (C) Treat with 0, 20, 40, and 50 mg∙L-1 colchicine for 30 days; (D) Callus browning rate; (E) Callus differentiation rate. Data are means ± SD (n=10), and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments. Bars=5 mm
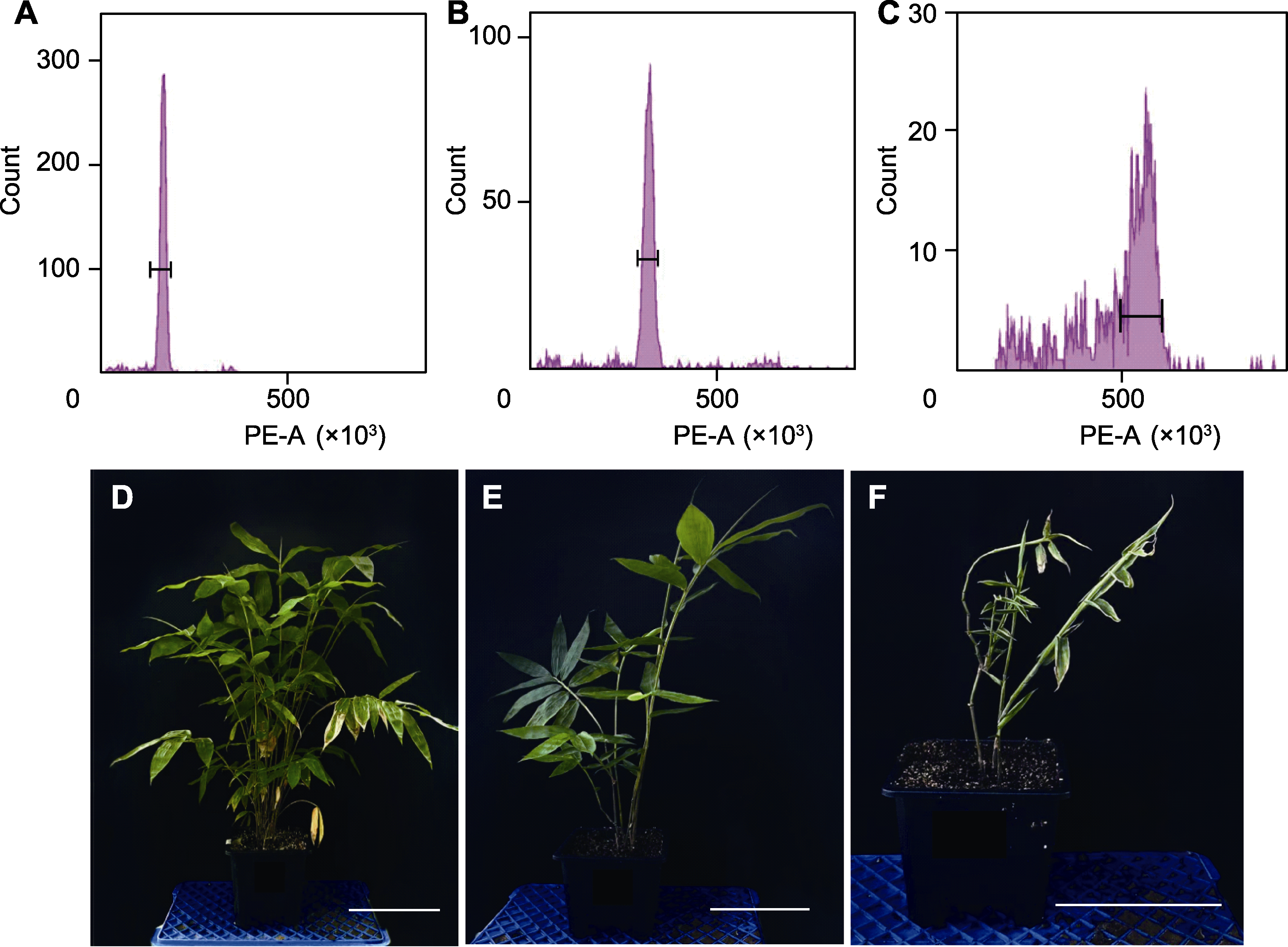
图3 马来甜龙竹不同多倍体流式细胞仪分析和形态学观察结果 (A), (D) 对照组六倍体(6×); (B), (E) 实验组十二倍体(12×); (C), (F) 实验组十八倍体(18×)。Bars=20 cm
Figure 3 Results of flow cytometry analysis and morphological observation of different polyploids in Dendrocalamus asper (A), (D) Control group of hexaploid (6×); (B), (E) Experimental group of dodecaploid (12×); (C), (F) Experimental group of octaploid (18×). Bars=20 cm
| Colchicine concentration and treatment time | Number of chromosome doubling | Number of regenerated plantlets obtained | Doubling rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid suspension method | 50 mg∙L-1, 24 h | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| 50 mg∙L-1, 48 h | 2 | 7 | 28.57 | |
| 50 mg∙L-1, 72 h | 3 | 8 | 37.50 | |
| 100 mg∙L-1, 24 h | 0 | 5 | 0 | |
| 100 mg∙L-1, 48 h | 6 | 11 | 54.54 | |
| 100 mg∙L-1, 72 h | 2 | 6 | 33.33 | |
| Solid medium mixed culture method | 40 mg∙L-1, 14 d | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 40 mg∙L-1, 30 d | 1 | 1 | 100 | |
| 50 mg∙L-1, 14 d | 1 | 1 | 100 |
表1 马来甜龙竹再生苗染色体加倍率
Table 1 Chromosome doubling rate of regenerated plantlets of Dendrocalamus asper
| Colchicine concentration and treatment time | Number of chromosome doubling | Number of regenerated plantlets obtained | Doubling rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid suspension method | 50 mg∙L-1, 24 h | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| 50 mg∙L-1, 48 h | 2 | 7 | 28.57 | |
| 50 mg∙L-1, 72 h | 3 | 8 | 37.50 | |
| 100 mg∙L-1, 24 h | 0 | 5 | 0 | |
| 100 mg∙L-1, 48 h | 6 | 11 | 54.54 | |
| 100 mg∙L-1, 72 h | 2 | 6 | 33.33 | |
| Solid medium mixed culture method | 40 mg∙L-1, 14 d | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 40 mg∙L-1, 30 d | 1 | 1 | 100 | |
| 50 mg∙L-1, 14 d | 1 | 1 | 100 |
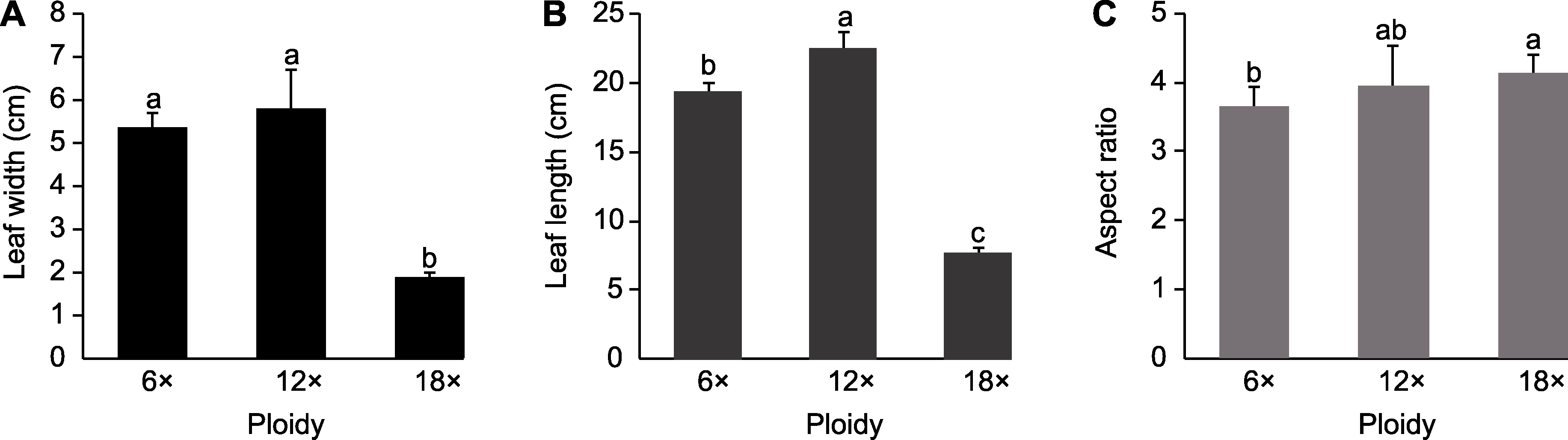
图4 不同倍性马来甜龙竹叶片形态学特征 (A) 叶宽比较; (B) 叶长比较; (C) 长宽比比较。数据为平均值±标准差(n=10), 不同小写字母表示3种倍性之间差异显著。
Figure 4 Morphological characteristics of Dendrocalamus asper leaves with different ploidy (A) Comparison of leaf width; (B) Comparison of leaf length; (C) Comparison of aspect ratio. Data are means ± SD (n=10), and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the three ploidies.
| Ploidy | Blade thickness (μm) | Upper skin thickness (μm) | Lower skin thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6× | 82.83±7.19 c | 9.47±0.56 c | 7.19±0.30 b |
| 12× | 121.86±5.30 b | 15.19±0.86 b | 8.02±1.58 b |
| 18× | 168.74±11.47 a | 23.12±0.53 a | 15.06±0.50 a |
表2 不同倍性马来甜龙竹叶片组织参数分析
Table 2 Analysis of leaf tissue parameters of Dendrocalamus asper with different ploidy
| Ploidy | Blade thickness (μm) | Upper skin thickness (μm) | Lower skin thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6× | 82.83±7.19 c | 9.47±0.56 c | 7.19±0.30 b |
| 12× | 121.86±5.30 b | 15.19±0.86 b | 8.02±1.58 b |
| 18× | 168.74±11.47 a | 23.12±0.53 a | 15.06±0.50 a |
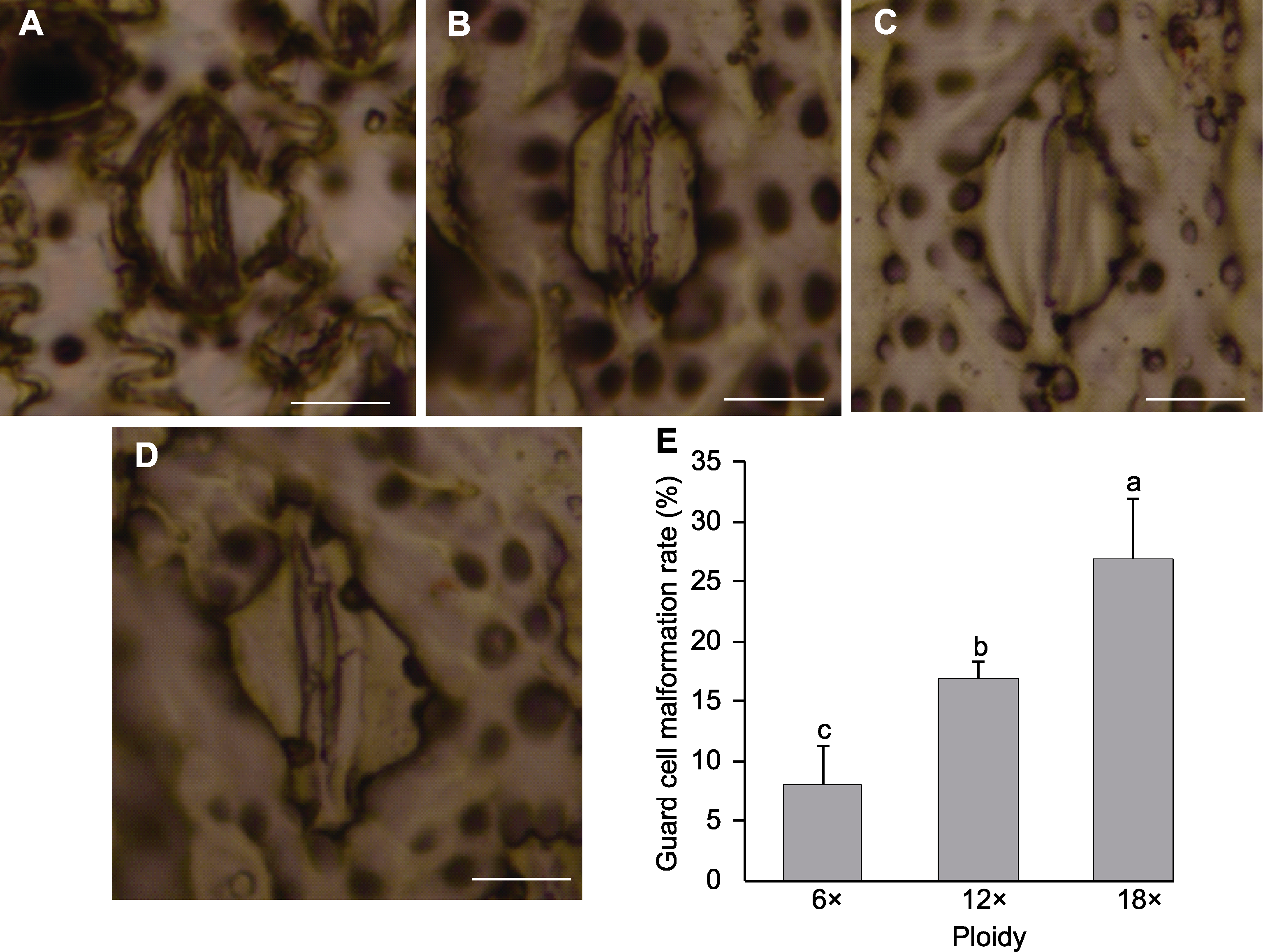
图5 不同倍性马来甜龙竹保卫细胞观察 (A) 对照组六倍体(6×); (B) 实验组十二倍体(12×); (C) 实验组十八倍体(18×); (D) 畸形保卫细胞; (E) 保卫细胞畸形率(不同小写字母表示3种倍性之间差异显著)。Bars=10 μm
Figure 5 Observation of guard cells of different ploidy of Dendrocalamus asper (A) Control group of hexaploid (6×); (B) Experimental group of dodecaploid (12×); (C) Experimental group of octaploid (18×); (D) Malformed guard cells; (E) Guard cell malformation rate (different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the three ploidies.). Bars=10 μm
| Ploidy | Guard cells | |
|---|---|---|
| Length (μm) | Width (μm) | |
| 6× | 20.25±1.30 c | 7.04±1.02 b |
| 12× | 28.37±2.20 b | 8.40±0.81 a |
| 18× | 36.54±5.58 a | 8.96±1.32 a |
表3 不同倍性马来甜龙竹气孔参数
Table 3 Stomatal parameters of Dendrocalamus asper with different ploidy
| Ploidy | Guard cells | |
|---|---|---|
| Length (μm) | Width (μm) | |
| 6× | 20.25±1.30 c | 7.04±1.02 b |
| 12× | 28.37±2.20 b | 8.40±0.81 a |
| 18× | 36.54±5.58 a | 8.96±1.32 a |
| [1] | 曹嘉雯 (2022). 软枣猕猴桃多倍体诱导及倍性鉴定. 硕士论文. 长春: 吉林农业大学. pp. 42-44. |
| [2] | 陈松河, 马丽娟, 丁振华, 罗祺, 刘婧 (2018). 5种牡竹属笋用竹竹笋营养成分之比较. 竹子学报 37(4), 4-8, 19. |
| [3] |
符勇耀, 蔡莉, 李丰耀, 杨文俊, 徐文姬, 姜思佳, 杨利平 (2024). 兰州百合多倍体离体诱导及其分子细胞鉴定. 草业学报 33(7), 172-181.
DOI |
| [4] | 高志民 (2023). 竹类植物遗传育种研究进展. 世界竹藤通讯 21, 1-9. |
| [5] | 郭恒琳, 勾晓婉 (2024). 作物倍性育种研究进展. 现代农业科技 (2), 20-26. |
| [6] | 国家林业和草原局 (2021). 林业和草原统计年鉴2021. 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 10-11. |
| [7] |
李高科, 陈琦, 孟鑫, 林海建 (2021). 秋水仙素加倍玉米单倍体胚性愈伤组织的初步研究. 植物遗传资源学报 22, 1606-1614.
DOI |
| [8] | 李霖锋, 刘宝 (2019). 植物多倍化与多倍体基因组进化研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学 49, 327-337. |
| [9] | 李淑洁, 裴怀弟, 刘新星, 陈军, 江晶, 张朝巍 (2023). 植物染色体加倍的表型和遗传学效应研究进展. 寒旱农业科学 2, 1079-1084. |
| [10] | 罗静, 周厚成, 王永清 (2005). 园艺植物化学诱变与抗性突变体筛选研究进展. 中国农学通报 21(8), 302-305. |
| [11] | 石庆华, 刘平, 刘孟军 (2012). 果树倍性育种研究进展. 园艺学报 39, 1639-1654. |
| [12] | 唐军荣, 李斌, 朱丽娜, 张俊, 何承忠, 李贤忠, 辛培尧 (2016). 滇杨多倍体苗期叶片形态及光合生理比较分析. 林业科学研究 29, 103-109. |
| [13] | 陶抵辉, 刘明月, 肖君泽, 邓建平 (2007). 生物多倍体诱导方法研究进展. 生命科学研究 (S1), 6-13. |
| [14] |
王江银, 徐婉宁, 苏洋, 张博 (2023). 干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿和黄花苜蓿实生苗叶片形态及解剖结构变化. 华北农学报 38(S1), 228-236.
DOI |
| [15] | 徐克凡, 彭忠明, 皮培尧, 周明兵, 汤定钦 (2024). 开花雷竹埋鞭繁育竹种间杂交育种的开花小苗. 分子植物育种 1-11. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.s.20240131.1413.004.html. |
| [16] | 徐鹏飞, 杨艳红, 张毓婷, 陈云, 汤定钦 (2020). 毛竹四倍体诱导及初步鉴定. 林业科学 56(8), 55-62. |
| [17] |
张俊芳, 刘庆华, 王奎玲, 刘庆超, 孙阳 (2009). 秋水仙素诱导青岛百合四倍体研究. 核农学报 23, 454-457.
DOI |
| [18] | 张立荣, 陈南 (2009). 分离植物叶片上、下表皮新方法. 生物学通报 44(12), 49-50, 63. |
| [19] | 张云洁, 蔡昌杨, 冉取丙, 高鸿烨, 朱强 (2021). 竹子遗传改良技术研究进展. 世界林业研究 34(5), 26-31. |
| [20] |
周慧文, 冯斗, 严华兵 (2015). 秋水仙素离体诱导多倍体研究进展. 核农学报 29, 1307-1315.
DOI |
| [21] | Charoenphun N, Pakeechai K (2023). Effect of thickness on qualities of dried sweet bamboo shoots (Dendrocalamus asper Backer) products. J Food Health Bioenviron Sci 14, 1-8. |
| [22] | Correia S, Braga A, Martins J, Correia B, Pinto G, Canhoto J (2023). Effects of polyploidy on physiological performance of acclimatized Solanum betaceum Cav. plants under water deficit. Forests 14, 208. |
| [23] | Jin Y, Zhao Y, Ai S, Chen X, Liu X, Wang H, Han Y, Ma F, Li C (2022). Induction of polyploid Malus prunifolia and analysis of its salt tolerance. Tree Physiol 42, 2100-2115. |
| [24] | Kong CK, Tan YN, Chye FY, Sit NW (2020). Nutritional compositions, biological activities, and phytochemical contents of the edible bamboo shoot, Dendrocalamus asper, from Malaysia. Int Food Res J 27, 546-556. |
| [25] | Li XY, Zhang LY, Wei XC, Datta T, Wei F, Xie ZQ (2024). Polyploidization: a biological force that enhances stress resistance. Int J Mol Sci 25, 1957. |
| [26] | Mangena P (2023). Impact of polyploidy induction for salinity stress mitigation in soybean (Glycine max L. Merrill). Plants 12, 1356. |
| [27] | Mustafa AA, Derise MR, Yong WTL, Rodrigues KF (2021). A concise review of Dendrocalamus asper and related bamboos: germplasm conservation, propagation and molecular biology. Plants 10, 1897. |
| [28] | Qiao GR, Liu MY, Song KL, Li HY, Yang HQ, Yin YF, Zhuo RY (2017). Phenotypic and comparative transcriptome analysis of different ploidy plants in Dendrocalamus latiflorus Munro. Front Plant Sci 8, 1371. |
| [29] | Sun HY, Wang JF, Li H, Li TK, Gao ZM (2023). Advancements and challenges in bamboo breeding for sustainable development. Tree Physiol 43, 1705-1717. |
| [30] | Wang P, Mu X, Gao YG, Zhang J, Du J (2020). Successful induction and the systematic characterization of tetraploids in Cerasus humilis for subsequent breeding. Sci Hortic 265, 109-216. |
| [31] | Zang QL, Liu QQ, Zhuge F, Wang XQ, Lin XC (2019). In vitro regeneration via callus induction in Dendrocalamus asper (Schult.) Backer. Propag Ornamental Plants 19, 66-71. |
| [32] |
Zhao HS, Sun S, Ding YL, Wang Y, Yue XH, Du X, Wei Q, Fan GY, Sun HY, Lou YF, Yang HM, Wang J, Xu X, Li LC, Yang KB, Xu H, Wang JL, Zhu CL, Wang SN, Shan XM, Hou YG, Wang Y, Fei BH, Liu X, Jiang ZH, Gao ZM (2021). Analysis of 427 genomes reveals moso bamboo population structure and genetic basis of property traits. Nat Commun 12, 5466.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Zhou J, Guo F, Fu J, Xiao Y, Wu J (2020). In vitro polyploid induction using colchicine for Zingiber officinale Roscoe cv. ‘Fengtou’ ginger. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 142, 87-94. |
| [1] | 李宇琛, 赵海霞, 姜希萍, 黄馨田, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 赵彦, 付春祥. 根癌农杆菌介导的蒙古冰草稳定遗传转化体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 600-612. |
| [2] | 田旭平, 岳康杰, 王佳丽, 刘慧欣, 史子尹, 亢红伟. 毛建草愈伤组织诱导及植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 613-625. |
| [3] | 曾浩, 李佩芳, 郭至辉, 刘春林, 阮颖. 银扇草再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 433-440. |
| [4] | 张尚文, 黄诗宇, 杨天为, 李婷, 张向军, 高曼熔. 基于正交实验的赤苍藤组培快繁体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 99-109. |
| [5] | 刘小飞, 孙映波, 黄丽丽, 杨钰钗, 朱根发, 于波. 黑鹅绒海芋体细胞胚发生和植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 750-759. |
| [6] | 刘叶飞, 赵海霞, 姜希萍, 邱锐, 周昕越, 赵彦, 付春祥. 野大麦高效组培快繁及农杆菌介导的愈伤侵染体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 440-448. |
| [7] | 逯锦春, 曹丽娜, 佟冠杰, 王鑫颖, 张利英, 喻锌, 李荟芳, 李彦慧. 大花银莲花愈伤组织诱导及再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 217-226. |
| [8] | 李楚然, 付羚, 刘云, 杨晓琴, 朱国磊, 解思达, 马焕成, 赵平. 樟叶越桔细胞悬浮培养条件的优化[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 227-235. |
| [9] | 李艳敏, 蒋卉, 符真珠, 张晶, 袁欣, 王慧娟, 高杰, 董晓宇, 王利民, 张和臣. 芍药花药愈伤组织诱导及体细胞胚发生[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 443-450. |
| [10] | 罗钱, 张燕莎, 欧静. 郁金樱愈伤组织诱导及植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 451-461. |
| [11] | 杜鹏飞, 王玉, 曹英萍, 杨松, 孙志超, 毛德才, 鄢家俊, 李达旭, 孙美贞, 付春祥, 白史且. 基因枪介导的老芒麦遗传转化体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 62-70. |
| [12] | 张冬瑞, 卜志刚, 陈玲玲, 常缨. 香鳞毛蕨的组织培养和快速繁殖体系构建[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 760-767. |
| [13] | 刘建飞, 刘炎, 刘克俭, 池阳, 霍志发, 霍永洪, 由香玲. 长白落叶松体胚发生再生体系优化[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 605-612. |
| [14] | 肖燕,王振兴,李东明,齐艳华,恩和巴雅尔. 羊草成熟胚诱导愈伤组织及植株再生系统的优化[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 192-198. |
| [15] | 张文婷,何燕红,舒宁,邢景景,刘宝骏,包满珠,刘国锋. 金黄花滇百合植株再生与离体快繁技术体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 773-778. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||