

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 597-610.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24151 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24151
李晶晶†, 李艳飞†, 王安琪, 王佳颖, 邓成燕, 卢敏, 马剑英, 戴思兰*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-10
接受日期:2025-01-20
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-01-21
通讯作者:
*戴思兰, 北京林业大学园林学院教授, 博士生导师, 享受国务院政府特殊津贴。现任国家林业和草原局菊花产业国家创新联盟理事长, 中国风景园林学会菊花分会副理事长, 《植物学报》资深编委。曾获首届全国林业教学名师、宝钢优秀教师奖、中国观赏园艺特别荣誉奖、教育部自然科学二等奖等荣誉奖励。先后主持30余项国家和省部级科研项目。发表学术论文400余篇, 出版著作2部。其研究团队以菊花为主要材料, 从菊花的历史文化、品种资源收集、整理和评价到花色、花型、开花期和抗逆性等观赏品质形成的遗传调控机理, 以及菊花优异新种质创制、产业化栽培技术等进行全面研究, 取得了一系列重要突破性进展和研究成果。E-mail: silandai@sina.com
作者简介:†共同第一作者
基金资助:
Jingjing Li†, Yanfei Li†, Anqi Wang, Jiaying Wang, Chengyan Deng, Min Lu, Jianying Ma, Silan Dai*( )
)
Received:2024-10-10
Accepted:2025-01-20
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-01-21
Contact:
E-mail: silandai@sina.com
About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 菊花品种万代风光(Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’)的色素背景适宜利用分子育种技术调控花瓣铁离子浓度进而培育蓝色花, 且其在夏秋两季均可开花, 是研究菊花开花期分子调控机理的重要材料, 但缺少高效的再生体系和遗传转化体系。以该品种为实验材料, 研究不同外植体类型和植物生长调节剂组合对其再生的影响, 并探讨农杆菌介导的遗传转化方法中相关因素对遗传转化效率的影响。结果表明, 适宜菊花万代风光再生的最适外植体为茎间薄层, 最适培养基为MS+1.5 mg∙L-1 6-BA+0.6 mg∙L-1 NAA, 分化率为70.06%, 不定芽生成系数为3.37; 实验确定茎间薄层分化和不定芽生根的卡那霉素选择压分别为7.5 mg∙L-1和5.0 mg∙L-1。预培养1天、OD600=0.8、处理5分钟及黑暗条件下共培养3天为最佳遗传转化体系。经过卡那霉素筛选共获得抗性苗15株, PCR鉴定发现2株阳性苗, 转化效率为13.33%。研究结果为利用这一独特品种资源解析菊花基因功能和进行定向改良的分子育种奠定了基础, 也为其它菊花品种的再生和转化体系建立提供参考。
李晶晶, 李艳飞, 王安琪, 王佳颖, 邓成燕, 卢敏, 马剑英, 戴思兰. 菊花品种万代风光再生及遗传转化体系的建立. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 597-610.
Jingjing Li, Yanfei Li, Anqi Wang, Jiaying Wang, Chengyan Deng, Min Lu, Jianying Ma, Silan Dai. Establishment of Regeneration and Genetic Transformation System for Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 597-610.
| No. | 6-BA (mg∙L-1) | KT (mg∙L-1) | NAA (mg∙L-1) | 2,4-D (mg∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| A2 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| A3 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| A4 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| A5 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 |
| A6 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 |
| A7 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| A8 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| A9 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| A10 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| A11 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.4 |
| A12 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.6 |
表1 愈伤组织诱导及不定芽分化培养基配方
Table 1 Culture media for callus induction and adventitious bud differentiation
| No. | 6-BA (mg∙L-1) | KT (mg∙L-1) | NAA (mg∙L-1) | 2,4-D (mg∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| A2 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| A3 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| A4 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| A5 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 |
| A6 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 |
| A7 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| A8 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| A9 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| A10 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| A11 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.4 |
| A12 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.6 |

图1 植物表达载体pBI121的结构 RB: T-DNA区段右边界; NOS-pro: 农杆菌胭脂碱合成酶基因启动子; KanR: 卡那霉素抗性筛选标记基因; NOS-ter: 农杆菌胭脂碱合成酶基因终止子; CaMV35S-pro: 花椰菜花叶病毒35S启动子; CcVIT: 矢车菊液泡铁离子转运蛋白基因; LB: T-DNA区段左边界
Figure 1 The structure of plant expression vector pBI121 RB: Right border of T-DNA region; NOS-pro: Agrobacterium tumefaciens nopaline synthase gene promoter; KanR: Kanamycin resistance screening marker gene; NOS-ter: A. tumefaciens nopaline synthase gene terminator; CaMV35S-pro: Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; CcVIT: Centaurea cyanus vacuolar iron transport protein gene; LB: Left border of T-DNA region
| Treatments | Pre-cul- ture time (d) | Concentration of Agrobacterium tumefaciens (OD600) | Infection time (min) | Co-culture time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0.6 | 5 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.8 | 10 | 2 |
| 3 | 0 | 1.0 | 15 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.6 | 10 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.8 | 15 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 1.0 | 5 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 | 0.6 | 15 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 | 0.8 | 5 | 3 |
| 9 | 2 | 1.0 | 10 | 1 |
表2 菊花万代风光遗传转化体系筛选正交试验表
Table 2 Orthogonal experimental table for genetic transformation screening of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| Treatments | Pre-cul- ture time (d) | Concentration of Agrobacterium tumefaciens (OD600) | Infection time (min) | Co-culture time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0.6 | 5 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.8 | 10 | 2 |
| 3 | 0 | 1.0 | 15 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 | 0.6 | 10 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 0.8 | 15 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 1.0 | 5 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 | 0.6 | 15 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 | 0.8 | 5 | 3 |
| 9 | 2 | 1.0 | 10 | 1 |
| No. | Leaf | Petioles | Transverse thin cell layers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | |
| A1 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 57.32±6.87 a | 1.85±0.29 a | 36.51±5.50 c | 3.37±0.28 a |
| A2 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 42.79±4.28 b | 2.53±0.32 b |
| A3 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 70.06±2.84 a | 3.37±0.22 a |
| A4 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 f | 0.00±0.00 g |
| A5 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 9.79±2.29 e | 1.11±0.19 ef |
| A6 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 f | 0.00±0.00 g |
| A7 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 36.35±3.38 b | 1.62±0.60 a | 45.93±1.28 b | 1.51±0.31 d |
| A8 | 8.59±0.44 b | 1.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 41.95±1.88 b | 1.62±0.21 d |
| A9 | 19.44±4.81 a | 1.28±0.25 a | 22.56±4.55 c | 1.11±0.19 b | 46.30±3.21 b | 2.73±0.22 b |
| A10 | 8.33±0.00 b | 1.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 31.31±3.50 c | 1.44±0.27 de |
| A11 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 16.67±0.00 d | 1.00±0.00 f |
| A12 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 8.33±0.00 d | 1.00±0.00 b | 34.98±3.90 c | 2.07±0.12 c |
表3 不同植物生长调节剂组合对菊花万代风光不同外植体再生的影响
Table 3 Effects of different plant growth regulators combinations on the regeneration of different explants of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| No. | Leaf | Petioles | Transverse thin cell layers | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | |
| A1 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 57.32±6.87 a | 1.85±0.29 a | 36.51±5.50 c | 3.37±0.28 a |
| A2 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 42.79±4.28 b | 2.53±0.32 b |
| A3 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 70.06±2.84 a | 3.37±0.22 a |
| A4 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 f | 0.00±0.00 g |
| A5 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 9.79±2.29 e | 1.11±0.19 ef |
| A6 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 f | 0.00±0.00 g |
| A7 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 36.35±3.38 b | 1.62±0.60 a | 45.93±1.28 b | 1.51±0.31 d |
| A8 | 8.59±0.44 b | 1.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 41.95±1.88 b | 1.62±0.21 d |
| A9 | 19.44±4.81 a | 1.28±0.25 a | 22.56±4.55 c | 1.11±0.19 b | 46.30±3.21 b | 2.73±0.22 b |
| A10 | 8.33±0.00 b | 1.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 31.31±3.50 c | 1.44±0.27 de |
| A11 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 e | 0.00±0.00 c | 16.67±0.00 d | 1.00±0.00 f |
| A12 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 c | 8.33±0.00 d | 1.00±0.00 b | 34.98±3.90 c | 2.07±0.12 c |
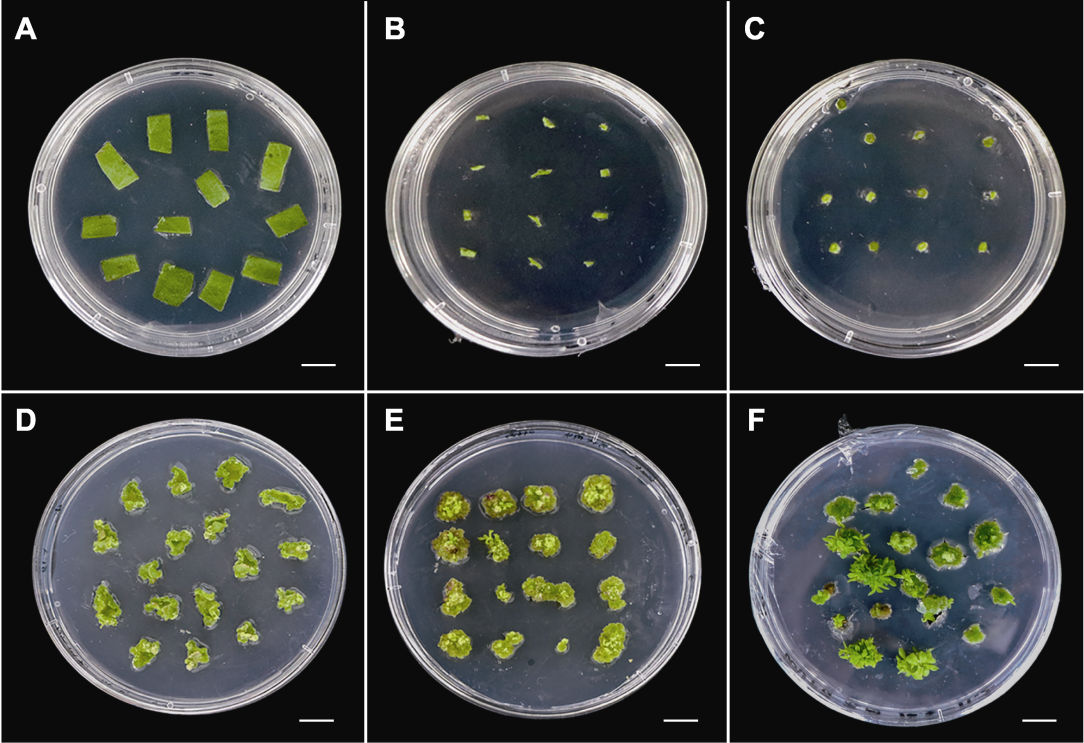
图2 菊花万代风光不同外植体的再生状况 (A)-(C) 叶片、叶柄和茎间薄层在A7培养基(表1)中培养0天的状态; (D)-(F) 叶片、叶柄和茎间薄层在A7培养基中培养35天的再生状况。Bars=1 cm
Figure 2 Regeneration of different explants of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’ (A)-(C) State of leaf, petioles, and transverse thin cell layers cultured in A7 medium (Table 1) for 0 day; (D)-(F) Regeneration of leaf, petioles, and transverse thin cell layers cultured in A7 medium for 35 days. Bars=1 cm
| Concentration of kanamycin (mg∙L-1) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 97.22±4.81 ab | 69.44±12.73 a |
| 2.5 | 100.00±0.00 a | 16.67±8.34 b |
| 5 | 80.44±4.72 bc | 5.56±4.81 bc |
| 7.5 | 63.89±12.73 cd | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 10 | 50.00±8.33 de | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 15 | 33.33±16.67 e | 0.00±0.00 c |
表4 卡那霉素对菊花万代风光茎间薄层分化的影响
Table 4 Effect of kanamycin on transverse thin cell layers of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| Concentration of kanamycin (mg∙L-1) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 97.22±4.81 ab | 69.44±12.73 a |
| 2.5 | 100.00±0.00 a | 16.67±8.34 b |
| 5 | 80.44±4.72 bc | 5.56±4.81 bc |
| 7.5 | 63.89±12.73 cd | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 10 | 50.00±8.33 de | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 15 | 33.33±16.67 e | 0.00±0.00 c |
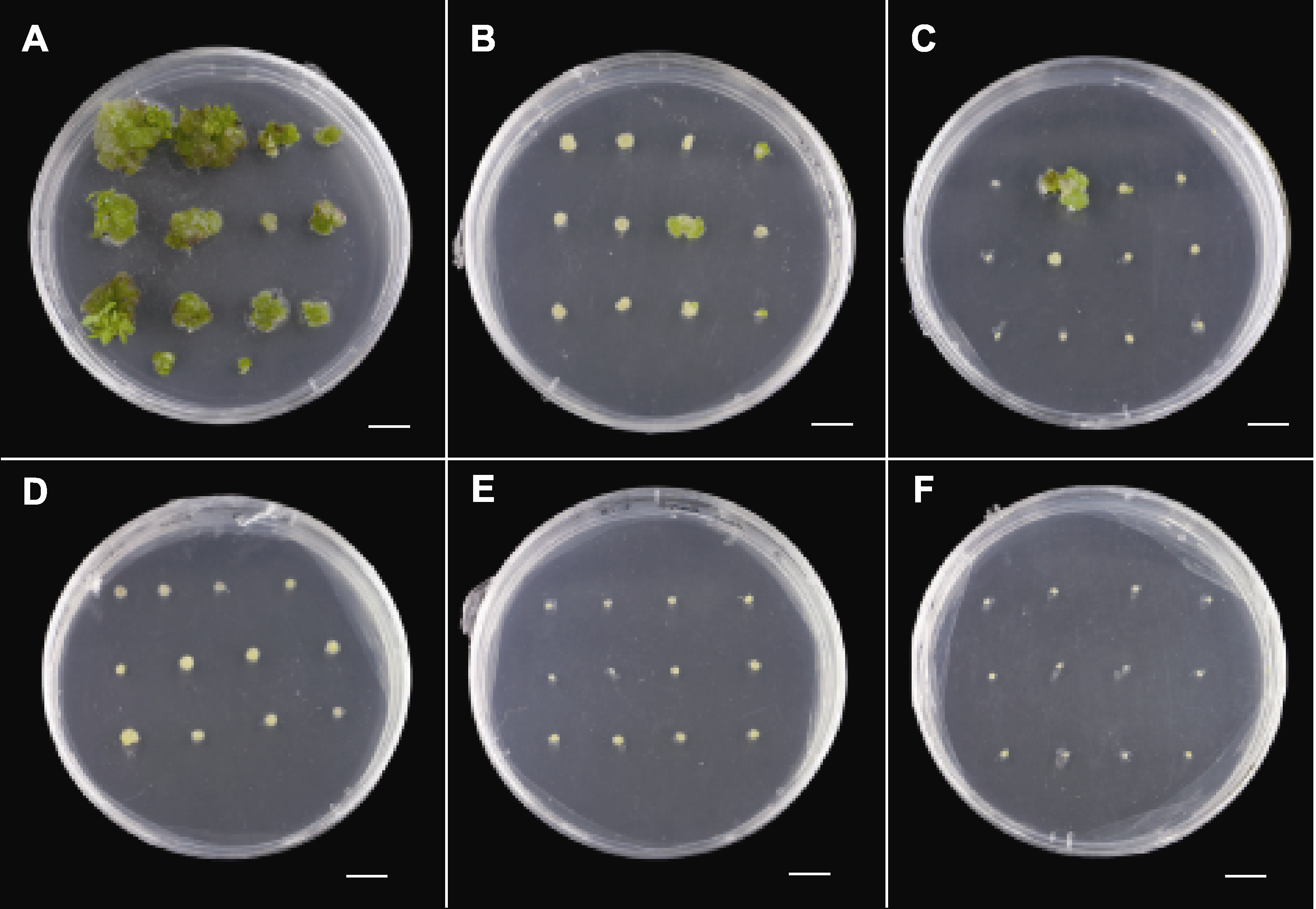
图3 卡那霉素对菊花万代风光茎间薄层分化的影响 (A)-(F) 茎间薄层在含0、2.5、5、7.5、10和15 mg∙L-1卡那霉素的A3培养基(表1)中的生长状况。Bars=1 cm
Figure 3 Effect of kanamycin on transverse thin cell layers of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’ (A)-(F) Growth of transverse thin cell layers in A3 culture medium (Table 1) containing 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, and 15 mg∙L-1 kanamycin. Bars=1 cm
| Concentration of kanamycin (mg∙L-1) | Rooting rate (%) | Average number of roots |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 88.89±19.25 a | 3.56±1.02 a |
| 3 | 30.44±4.72 b | 0.50±0.17 b |
| 5 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b |
| 7.5 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b |
| 10 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b |
| 12 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b |
表5 卡那霉素对菊花万代风光不定芽生根的影响
Table 5 Effect of kanamycin on rooting of adventitious bud of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| Concentration of kanamycin (mg∙L-1) | Rooting rate (%) | Average number of roots |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 88.89±19.25 a | 3.56±1.02 a |
| 3 | 30.44±4.72 b | 0.50±0.17 b |
| 5 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b |
| 7.5 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b |
| 10 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b |
| 12 | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b |

图4 卡那霉素对菊花万代风光不定芽生根的影响 (A)-(F) 不定芽在含0、3、5、7.5、10和12 mg∙L-1卡那霉素的MS培养基中的生根状况。Bars=1 cm
Figure 4 Effect of kanamycin on rooting of adventitious bud of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’ (A)-(F) Rooting of adventitious buds in MS culture media containing 0, 3, 5, 7.5, 10, and 12 mg∙L-1 kanamycin. Bars=1 cm
| Treatments | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Browning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80.91±10.48 bc | 3.33±5.77 c | 0.33±0.58 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 2 | 94.84±4.51 a | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 3 | 86.96±5.54 b | 1.85±3.21 c | 0.33±0.58 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 4 | 71.11±7.70 cd | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 5 | 79.55±9.91 bc | 8.84±0.44 bc | 1.33±0.58 a | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 6 | 64.07±7.56 d | 14.44±6.76 ab | 1.83±1.04 a | 28.52±5.70 a |
| 7 | 81.85±3.61 bc | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 18.15±3.61 b |
| 8 | 95.96±3.51 a | 21.00±9.78 a | 1.38±0.40 a | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 9 | 96.08±6.79 a | 1.96±3.40 c | 0.33±0.58 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
表6 不同转化条件对菊花万代风光抗性芽生长的影响
Table 6 Effect of different transformation conditions on the growth of resistant buds of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| Treatments | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Browning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80.91±10.48 bc | 3.33±5.77 c | 0.33±0.58 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 2 | 94.84±4.51 a | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 3 | 86.96±5.54 b | 1.85±3.21 c | 0.33±0.58 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 4 | 71.11±7.70 cd | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 5 | 79.55±9.91 bc | 8.84±0.44 bc | 1.33±0.58 a | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 6 | 64.07±7.56 d | 14.44±6.76 ab | 1.83±1.04 a | 28.52±5.70 a |
| 7 | 81.85±3.61 bc | 0.00±0.00 c | 0.00±0.00 b | 18.15±3.61 b |
| 8 | 95.96±3.51 a | 21.00±9.78 a | 1.38±0.40 a | 0.00±0.00 c |
| 9 | 96.08±6.79 a | 1.96±3.40 c | 0.33±0.58 b | 0.00±0.00 c |

图5 菊花万代风光遗传转化体系筛选 (A)-(I) 茎间薄层在处理1-9 (同表2)中的生长状况。Bars=1 cm
Figure 5 Genetic transformation screening of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’ (A)-(I) Growth of transverse thin cell layers in treatments 1-9 (see Table 2). Bars=1 cm
| Pre-cultivation time (d) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Brow- ning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 87.57 a | 1.73 a | 0.22 b | 0.00 a |
| 1 | 71.58 b | 7.76 a | 1.06 a | 9.51 a |
| 2 | 91.29 a | 7.66 a | 0.57 ab | 6.05 a |
表7 预培养时间对菊花万代风光抗性芽生长的影响
Table 7 Effect of pre-culture time on the growth of resistant buds in Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| Pre-cultivation time (d) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Brow- ning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 87.57 a | 1.73 a | 0.22 b | 0.00 a |
| 1 | 71.58 b | 7.76 a | 1.06 a | 9.51 a |
| 2 | 91.29 a | 7.66 a | 0.57 ab | 6.05 a |
| Concentration of Agrobacterium (OD600) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Browning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 77.96 b | 1.11 b | 0.11 b | 6.05 a |
| 0.8 | 90.11 a | 9.95 a | 0.90 a | 0.00 a |
| 1.0 | 82.37 ab | 6.09 ab | 0.83 ab | 9.51 a |
表8 农杆菌菌液浓度对菊花万代风光抗性芽生长的影响
Table 8 Effect of Agrobacterium concentration on the growth of resistant buds in Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| Concentration of Agrobacterium (OD600) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Browning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 77.96 b | 1.11 b | 0.11 b | 6.05 a |
| 0.8 | 90.11 a | 9.95 a | 0.90 a | 0.00 a |
| 1.0 | 82.37 ab | 6.09 ab | 0.83 ab | 9.51 a |
| Infection time (min) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Browning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 80.31 a | 12.93 a | 1.18 a | 9.51 a |
| 10 | 87.34 a | 0.65 b | 0.11 b | 0.00 a |
| 15 | 82.78 a | 3.56 b | 0.56 ab | 6.05 a |
表9 侵染时间对菊花万代风光抗性芽生长的影响
Table 9 Effect of infection time on the growth of resistant buds in Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| Infection time (min) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Browning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 80.31 a | 12.93 a | 1.18 a | 9.51 a |
| 10 | 87.34 a | 0.65 b | 0.11 b | 0.00 a |
| 15 | 82.78 a | 3.56 b | 0.56 ab | 6.05 a |
| Co-culture time (d) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Browning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85.51 a | 4.71 a | 0.67 a | 0.00 b |
| 2 | 80.25 a | 4.81 a | 0.61 a | 15.56 a |
| 3 | 84.68 a | 7.62 a | 0.57 a | 0.00 b |
表10 共培养时间对菊花万代风光抗性芽生长的影响
Table 10 Effect of co-culture time on the growth of resistant buds in Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’
| Co-culture time (d) | Callus formation rate (%) | Differentiation rate (%) | Coefficient of adventitious bud production | Browning rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85.51 a | 4.71 a | 0.67 a | 0.00 b |
| 2 | 80.25 a | 4.81 a | 0.61 a | 15.56 a |
| 3 | 84.68 a | 7.62 a | 0.57 a | 0.00 b |
| Factors | Pre-cultivation time (d) | Concentration of Agrobacterium tumefaciens (OD600) | Infectation time (min) | Co-culture time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 5.18 | 3.33 | 38.77 | 14.13 |
| K2 | 23.28 | 29.84 | 1.96 | 14.44 |
| K3 | 22.96 | 18.25 | 10.69 | 22.85 |
| k1 | 1.73 | 1.11 | 12.92 | 4.71 |
| k2 | 7.76 | 9.95 | 0.65 | 4.81 |
| k3 | 7.65 | 6.08 | 3.56 | 7.62 |
| R | 5.93 | 8.84 | 12.27 | 2.80 |
表11 不同转化条件下菊花万代风光抗性芽分化率的极差分析
Table 11 Range analysis of resistance bud differentiation rate of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’ under different transformation conditions
| Factors | Pre-cultivation time (d) | Concentration of Agrobacterium tumefaciens (OD600) | Infectation time (min) | Co-culture time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 5.18 | 3.33 | 38.77 | 14.13 |
| K2 | 23.28 | 29.84 | 1.96 | 14.44 |
| K3 | 22.96 | 18.25 | 10.69 | 22.85 |
| k1 | 1.73 | 1.11 | 12.92 | 4.71 |
| k2 | 7.76 | 9.95 | 0.65 | 4.81 |
| k3 | 7.65 | 6.08 | 3.56 | 7.62 |
| R | 5.93 | 8.84 | 12.27 | 2.80 |
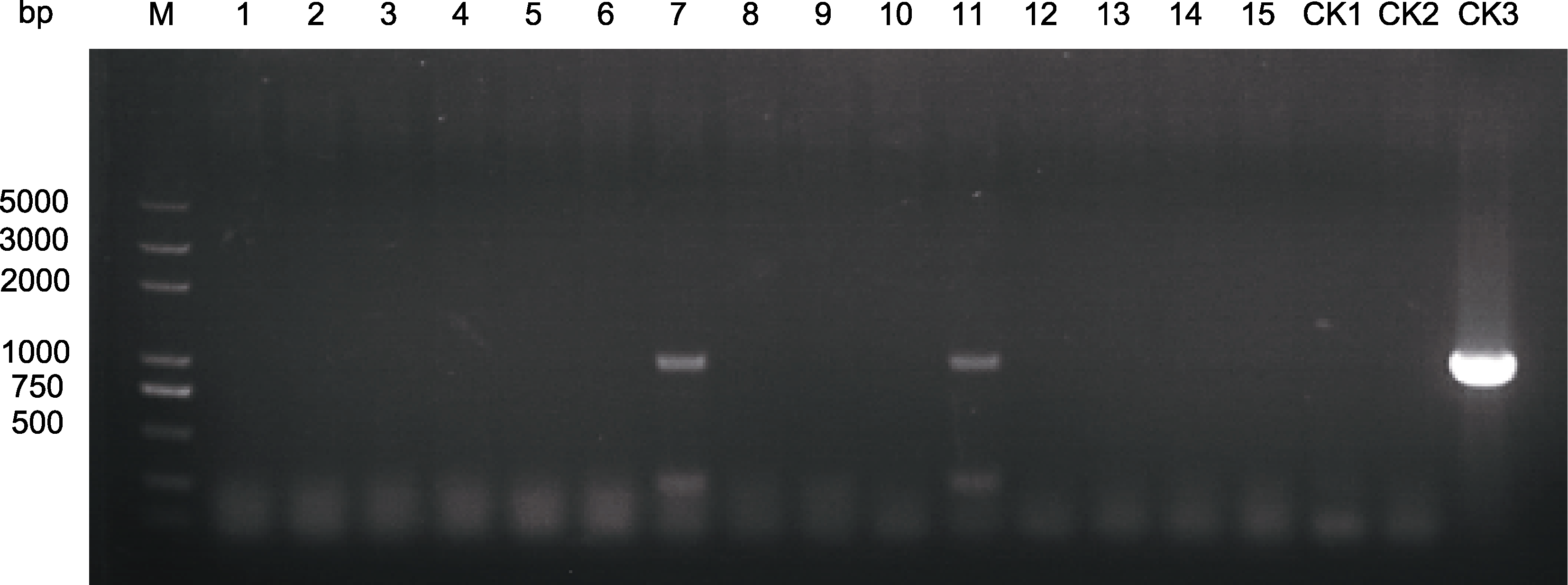
图6 菊花万代风光抗性苗PCR检测
Figure 6 PCR amplification on the resistant plantlets of Chrysanthemum × morifolium ‘Wandai Fengguang’ M: DL2000 plus DNA marker; 1-15: 抗性苗; CK1: ddH2O; CK2: 野生型; CK3: 质粒 M: DL2000 plus DNA marker; 1-15: Resistant plantlets; CK1: ddH2O; CK2: Wild type; CK3: Plasmid
| [1] |
戴思兰, 洪艳 (2016). 基于花青素苷合成和呈色机理的观赏植物花色改良分子育种. 中国农业科学 49, 529-542.
DOI |
| [2] | 郭兆奎, 万秀清, 魏继承, 于艳华, 于金涛 (1999). 适于PCR分析的烤后烟叶DNA提取方法的研究. 中国烟草科学 20 (4), 5-8. |
| [3] | 韩科厅 (2010). 花青素苷合成关键结构基因导入对菊花花色的影响. 博士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 41-47. |
| [4] | 何姗 (2020). 农杆菌介导CmWRKY15-1基因对菊花的遗传转化. 硕士论文. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学. pp. 12-14. |
| [5] | 洪艳, 白新祥, 孙卫, 贾锋炜, 戴思兰 (2012). 菊花品种花色表型数量分类研究. 园艺学报 39, 1330-1340. |
| [6] | 贾红梅, 王碧玉, 刘迪, 毛洪玉 (2017). 农杆菌介导CBL基因对菊花品种‘C008’的转化. 西北林学院学报 32, 184-189. |
| [7] | 姜宁宁, 付建新, 戴思兰 (2012). 中国传统菊花品种‘小林静’再生及转化体系的建立. 生物技术通报 28(4), 87-92. |
| [8] | 李辛雷, 陈发棣, 王红, 房伟民, 管志勇 (2004). 菊花外植体再生体系的研究. 上海农业学报 20(2), 13-16. |
| [9] | 李亚军, 李悦, 黄河, 戴思兰 (2018). 切花菊‘粉贵人’高效再生体系的建立. 见: 中国观赏园艺研究进展2018. 哈尔滨: 中国园艺学会观赏园艺专业委员会. pp. 427-434. |
| [10] |
廖敏凌, 蒲娅, 武晓云, 马朝峰, 王文奎, 戴思兰 (2023). 平潭野菊混合瓣型株系再生体系的建立. 植物学报 58, 449-460.
DOI |
| [11] | 刘明星 (2020). 盆栽小菊‘Branfountain Pink’遗传转化体系的建立. 硕士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 14-30. |
| [12] |
逯锦春, 曹丽娜, 佟冠杰, 王鑫颖, 张利英, 喻锌, 李荟芳, 李彦慧 (2022). 大花银莲花愈伤组织诱导及再生体系的建立. 植物学报 57, 217-226.
DOI |
| [13] |
罗虹, 温小蕙, 周圆圆, 戴思兰 (2020). 芳香堆心菊离体再生体系的建立. 植物学报 55, 318-328.
DOI |
| [14] | 马琦 (2020). 少芽切花菊分枝性及其遗传转化体系的研究. 硕士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 23-30. |
| [15] | 亓帅, 付建新, 王翊, 杨立文, 戴思兰 (2014). 甘菊下胚轴遗传转化体系的建立. 分子植物育种 12, 356-362. |
| [16] | 曲爱爱 (2016). 菊花遗传转化体系建立及VtF3'5'H基因转化‘南农粉翠’的研究. 硕士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 23-30. |
| [17] | 时颂, 李青, 赵霜, 戴思兰, 李娜娜 (2013). 不同切花菊品种及处理对愈伤组织诱导和分化的影响. 东北林业大学学报 41, 77-81. |
| [18] | 滕如萍, 张佳祺, 刘晓芬, 余璐, 张潮, 李方 (2025). 菊花‘神马’组培再生体系的优化. 分子植物育种 23, 1550-1557. |
| [19] | 王碧玉 (2017). 菊花再生及遗传转化体系的研究. 硕士论文. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学. pp. 8-15. |
| [20] | 王想 (2018). 神农香菊单萜合酶基因的克隆及对野菊的遗传转化. 硕士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学. pp. 36-38. |
| [21] | 王亚琴 (2020). 万寿菊再生和遗传转化体系的建立及重要性状的遗传分析. 硕士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 4-7. |
| [22] | 王亚琴, 韦陆丹, 王文静, 刘宝骏, 张春玲, 张俊卫, 何燕红 (2020). 万寿菊再生体系的建立及优化. 植物学报 55, 749-759. |
| [23] | 王自布, 莫国秀, 罗会兰, 张德英 (2015). 菊花不同外植体组培快繁及其再生体系的研究. 北方园艺 (18), 106-109. |
| [24] | 魏曼曼, 王江民, Imtiaz M, 洪波 (2014). 菊花花色嵌合花瓣的离体培养及植株再生. 北京林业大学学报 36(4), 107-112. |
| [25] |
武晓云, 廖敏凌, 李雪茹, 舒梓淳, 辛佳潼, 张伯晗, 戴思兰 (2024). 毛华菊3种瓣型株系再生体系的建立. 植物学报 59, 245-256.
DOI |
| [26] | 吴志苹, 高亦珂, 范敏, 高耀辉 (2020). 菊花‘金不凋’再生及遗传转化体系的构建. 分子植物育种 18, 150-158. |
| [27] | 徐式近, 徐忠传 (2013). 不同菊花品种高效直接再生体系的构建. 江苏农业科学 41(11), 52-54, 100. |
| [28] | 许志茹, 陈智华, 姜艳东, 侯杰, 佟玲, 李玉花 (2013). 露地菊离体再生体系建立及BrDFR基因遗传转化. 园艺学报 40, 1517-1526. |
| [29] | 阳淑金, 宋爱萍, 何深颖, 朱晓晨, 孙静, 高姣姣, 王银杰, 陈发棣, 蒋甲福 (2015). CaMV 35S启动子在菊花中驱动GUS外源基因的表达分析. 南京农业大学学报 38, 554-559. |
| [30] |
余晓敏, 王亚琴, 刘雨菡, 易庆平, 程文翰, 朱钰, 段枫, 张莉雪, 何燕红 (2023). 根癌农杆菌介导万寿菊遗传转化体系的建立. 植物学报 58, 760-769.
DOI |
| [31] |
赵静雅, 徐素娟, 陈发棣, 滕年军 (2019). 匍匐型地被菊再生及遗传转化体系的建立. 核农学报 33, 1686-1697.
DOI |
| [32] | 赵伶俐, 石少川, 张启翔, 高亦珂 (2011). 农杆菌介导的地被菊遗传转化体系的优化. 分子植物育种 9, 74-80. |
| [33] | Adedeji OS, Naing AH, Kim CK (2020). Protoplast isolation and shoot regeneration from protoplast-derived calli of Chrysanthemum cv. White ND. Plant Cell Tissue organ Cult 141, 571-581. |
| [34] | Bernula D, Benkő P, Kaszler N, Domonkos I, Valkai I, Szőllősi R, Ferenc G, Ayaydin F, Fehér A, Gémes K (2020). Timely removal of exogenous cytokinin and the prevention of auxin transport from the shoot to the root affect the regeneration potential of Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 140, 327-339. |
| [35] |
Brugliera F, Tao GQ, Tems U, Kalc G, Mouradova E, Price K, Stevenson K, Nakamura N, Stacey I, Katsumoto Y, Tanaka Y, Mason JG (2013). Violet/blue chrysanthemums—metabolic engineering of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway results in novel petal colors. Plant Cell Physiol 54, 1696-1710.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Han XY, Luo YT, Lin JY, Wu HY, Sun H, Zhou LJ, Chen SM, Guan ZY, Fang WM, Zhang F, Chen FD, Jiang JF (2021). Generation of purple-violet chrysanthemums via anthocyanin B-ring hydroxylation and glucosylation introduced from Osteospermum hybrid F3'5'H and Clitoria ternatea A3'5'GT. Ornamental Plant Res 1, 4. |
| [37] | Huang H, Hu K, Han KT, Xiang QY, Dai SL (2013). Flower colour modification of chrysanthemum by suppression of F3'H and overexpression of the exogenous Senecio cruentus F3'5'H gene. PLoS One 8, e74395. |
| [38] | Li YF, Wang JY, Lu CF, Wang ZM, Deng CY, Gao K, Li JJ, Fang ZJ, Liu H, Hong Y, Dai SL (2024). Flavonoid extracts from chrysanthemum with appropriate anthocyanins turn blue when exposed to iron ions. Hortic Plant J 10, 837-852. |
| [39] | Lim KB, Kwon SJ, Lee SI, Hwang YJ, Naing AH (2012). Influence of genotype, explant source, and gelling agent on in vitro shoot regeneration of chrysanthemum. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 53, 329-335. |
| [40] | Long Y, Yang Y, Pan GT, Shen YO (2022). New insights into tissue culture plant-regeneration mechanisms. Front Plant Sci 13, 926752. |
| [41] | Momonoi K, Yoshida K, Mano S, Takahashi H, Nakamori C, Shoji K, Nitta A, Nishimura M (2009). A vacuolar iron transporter in tulip, TgVit1, is responsible for blue coloration in petal cells through iron accumulation. Plant J 59, 437-447. |
| [42] | Naing AH, Park KI, Chung MY, Lim KB, Kim CK (2016). Optimization of factors affecting efficient shoot regeneration in chrysanthemum cv. Shinma. Braz J Bot 39, 975-984. |
| [43] |
Noda N, Aida R, Kishimoto S, Ishiguro K, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Tanaka Y, Ohmiya A (2013). Genetic engineering of novel bluer-colored chrysanthemums produced by accumulation of delphinidin-based anthocyanins. Plant Cell Physiol 54, 1684-1695.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Noda N, Yoshioka S, Kishimoto S, Nakayama M, Douzono M, Tanaka Y, Aida R (2017). Generation of blue chrysanthemums by anthocyanin B-ring hydroxylation and glucosylation and its coloration mechanism. Sci Adv 3, e1602785. |
| [45] | Renou JP, Brochard P, Jalouzot R (1993). Recovery of transgenic chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflora Tzvelev) after hygromycin resistance selection. Plant Sci 89, 185-197. |
| [46] | Shiono M, Matsugaki N, Takeda K (2005). Structure of the blue cornflower pigment. Nature 436, 791. |
| [47] |
Shoji K, Miki N, Nakajima N, Momonoi K, Kato C, Yoshida K (2007). Perianth bottom-specific blue color development in tulip cv. Murasakizuisho requires ferric ions. Plant Cell Physiol 48, 243-251.
PMID |
| [48] | Shoji K, Momonoi K, Tsuji T (2010). Alternative expression of vacuolar iron transporter and ferritin genes leads to blue/purple coloration of flowers in tulip cv. ‘Murasakizuisho’. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 215-224. |
| [49] | Song JY, Mattson NS, Jeong BR (2011). Efficiency of shoot regeneration from leaf, stem, petiole and petal explants of six cultivars of Chrysanthemum morifolium. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 107, 295-304. |
| [50] | Takeda K, Osakabe A, Saito S, Furuyama D, Tomita A, Kojima Y, Yamadera M, Sakuta M (2005). Components of protocyanin, a blue pigment from the blue flowers of Centaurea cyanus. Phytochemistry 66, 1607-1613. |
| [51] | Takeda K, Yamaguchi S, Iwata K, Tsujino Y, Fujimori T, Husain SZ (1996). A malonylated anthocyanin and flavonols in the blue flowers of Meconopsis. Phytochemistry 42, 863-865. |
| [52] |
Tanaka M, Fujimori T, Uchida I, Yamaguchi S, Takeda K (2001). A malonylated anthocyanin and flavonols in blue Meconopsis flowers. Phytochemistry 56, 373-376.
PMID |
| [53] |
Yoshida K, Negishi T (2013). The identification of a vacuolar iron transporter involved in the blue coloration of cornflower petals. Phytochemistry 94, 60-67.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 张汝鑫, 李晨荣, 王童欣, 黎洁, 李霆格, 许慧娴, 李梅儿, 赵莹1, 彭婷, 王健. 大花三色堇再生体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(6): 1-0. |
| [2] | 刘玉泽, 王一菲, 任威蓁, 栗浩, 路斌, 路丙社, 于晓跃. 北美豆梨杂种幼胚挽救及再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 800-809. |
| [3] | 曾浩, 李佩芳, 郭至辉, 刘春林, 阮颖. 银扇草再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 433-440. |
| [4] | 武晓云, 廖敏凌, 李雪茹, 舒梓淳, 辛佳潼, 张伯晗, 戴思兰. 毛华菊3种瓣型株系再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 245-256. |
| [5] | 廖敏凌, 蒲娅, 武晓云, 马朝峰, 王文奎, 戴思兰. 平潭野菊混合瓣型株系再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 449-460. |
| [6] | 罗钱, 张燕莎, 欧静. 郁金樱愈伤组织诱导及植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 451-461. |
| [7] | 张冬瑞, 卜志刚, 陈玲玲, 常缨. 香鳞毛蕨的组织培养和快速繁殖体系构建[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 760-767. |
| [8] | 罗虹, 温小蕙, 周圆圆, 戴思兰. 芳香堆心菊离体再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 318-328. |
| [9] | 徐悦,曹英萍,王玉,付春祥,戴绍军. 发根农杆菌介导的菠菜毛状根遗传转化体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 515-521. |
| [10] | 张旭红, 王頔, 梁振旭, 孙美玉, 张金政, 石雷. 欧洲百合愈伤组织诱导及植株再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(6): 840-847. |
| [11] | 安佰义, 郭才南, 包文慧, 李凤飞, 赵赫, 陈丽, 安丰云. 白檀离体快繁技术[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(5): 693-699. |
| [12] | 吴国栋, 修宇, 王华芳. 优化子叶节转化法培育大豆MtDREB2A转基因植株[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 59-71. |
| [13] | 赵喜亭, 蒋丽微, 王苗, 朱玉婷, 张文芳, 李明军. 怀黄菊间接体胚受体再生体系的建立及CmTGA1的遗传转化[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(4): 525-532. |
| [14] | 孙卫;李崇晖;王亮生;戴思兰*. 菊花不同花色品种中花青素苷代谢分析[J]. 植物学报, 2010, 45(03): 327-336. |
| [15] | 张莉俊, 戴思兰, . 菊花种质资源研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2009, 44(05): 526-535. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||