

植物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 171-181.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21191 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21191
艾金祥1, 宋嘉怡1, 严浙楠1, 王志超1, 陈文倩1, 吴玉环2,3, 王燕燕1, 潘蕾蕾1, 许俞韬1, 刘鹏1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-10
接受日期:2022-02-07
出版日期:2022-03-01
发布日期:2022-03-24
通讯作者:
刘鹏
作者简介:*E-mail: sky79@zjnu.cn基金资助:
Jinxiang Ai1, Jiayi Song1, Zhenan Yan1, Zhichao Wang1, Wenqian Chen1, Yuhuan Wu2,3, Yanyan Wang1, Leilei Pan1, Yutao Xu1, Peng Liu1,*( )
)
Received:2021-11-10
Accepted:2022-02-07
Online:2022-03-01
Published:2022-03-24
Contact:
Peng Liu
摘要: 铅胁迫是影响植物生长的主要非生物因素之一。以二年生虎舌红(Ardisia mamillata)和朱砂根(A. crenata)为实验材料, 探究外源褪黑素(MT)处理对不同浓度铅胁迫下2种植物生理响应及DNA损伤的调控效应。结果表明, 相同处理时间内, 随着铅胁迫浓度的升高, 虎舌红与朱砂根的3种抗氧化酶活性、脯氨酸(Pro)及可溶性蛋白(SP)含量均先升高后降低, 而丙二醛(MDA)含量先降低后升高, 根尖胼胝质含量持续升高, 根系DNA损伤加剧。施加适宜浓度的外源褪黑素(MT)后, 不同浓度铅胁迫下2种植物的抗氧化酶活性得到有效增强, 且均在100 µmol∙L-1 MT处理时达到最大值, Pro和SP含量均显著升高, MDA含量则先显著降低而后缓慢升高, 根尖胼胝质含量持续增加, 根系DNA损伤得到改善; 随着MT浓度的持续升高, 其缓解作用逐渐减弱。相较于虎舌红, 朱砂根对铅胁迫的抗性更强, 生理响应更稳定。施加外源MT可有效缓解铅胁迫对虎舌红和朱砂根的毒害作用(缓解效果朱砂根>虎舌红), 增强二者对铅毒的耐受性, 其中100 µmol∙L-1 MT处理下缓解效果最佳。研究揭示了虎舌红和朱砂根抗铅性的优劣及外源MT对铅毒的缓解效应, 为紫金牛属植物抗铅性研究提供理论参考。
艾金祥, 宋嘉怡, 严浙楠, 王志超, 陈文倩, 吴玉环, 王燕燕, 潘蕾蕾, 许俞韬, 刘鹏. 褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红和朱砂根生理响应及DNA损伤的调控效应. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 171-181.
Jinxiang Ai, Jiayi Song, Zhenan Yan, Zhichao Wang, Wenqian Chen, Yuhuan Wu, Yanyan Wang, Leilei Pan, Yutao Xu, Peng Liu. Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Physiological Response and DNA Damage of Ardisia mamillata and A. crenata Under Lead Stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 171-181.
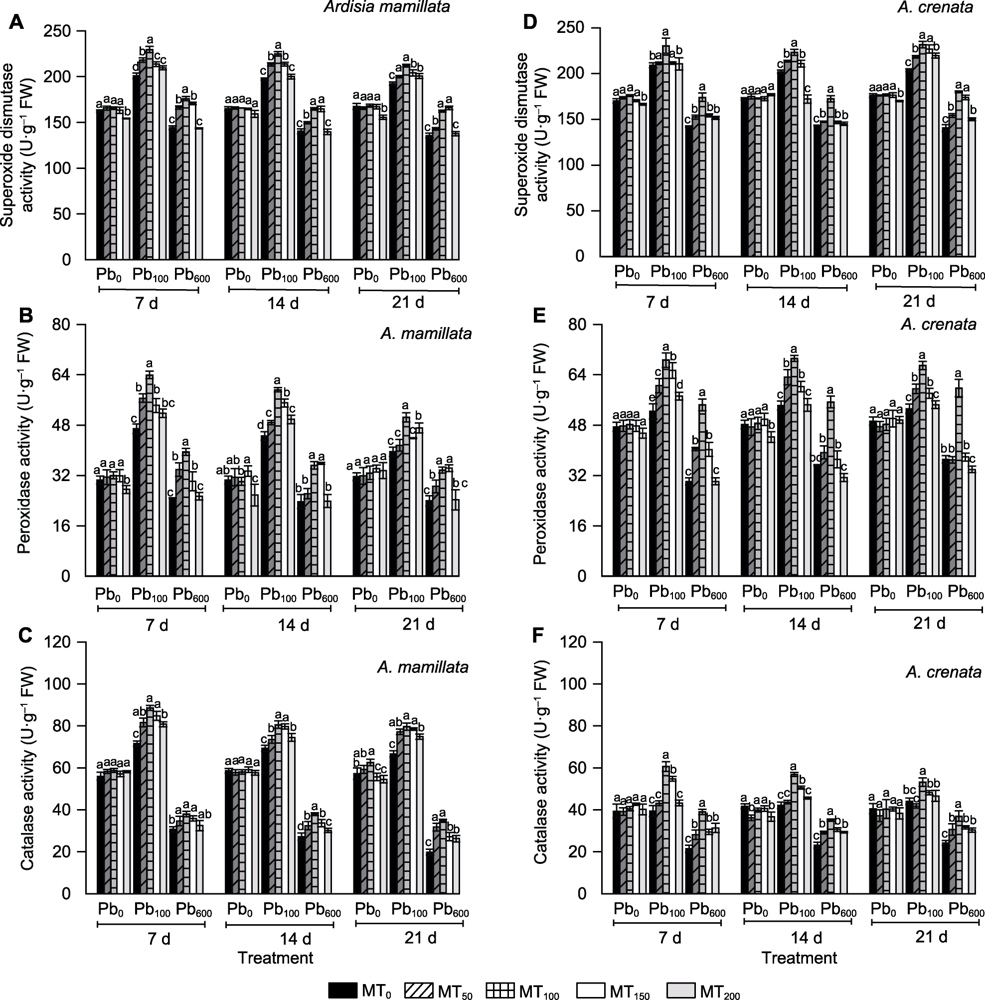
图1 不同浓度褪黑素处理对铅胁迫下虎舌红(A-C)和朱砂根(D-F)抗氧化酶系统的影响 Pb0、Pb100和Pb600表示铅浓度分别为0、100和600 µmol∙L-1; MT0、MT50、MT100、MT150和MT200表示褪黑素处理浓度分别为0、50、100、150和200 µmol∙L-1。不同小写字母表示相同时期不同处理组间在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 1 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on antioxidant enzyme system of Ardisia mamillata (A-C) and A. crenata (D-F) under lead stress Pb0, Pb100, and Pb600 represent 0, 100, and 600 µmol∙L-1 of Pb, respectively; MT0, MT50, MT100, MT150, and MT200 represent 0, 50, 100, 150, and 200 µmol∙L-1 of melatonin, respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments during the same stage at 0.05 level.
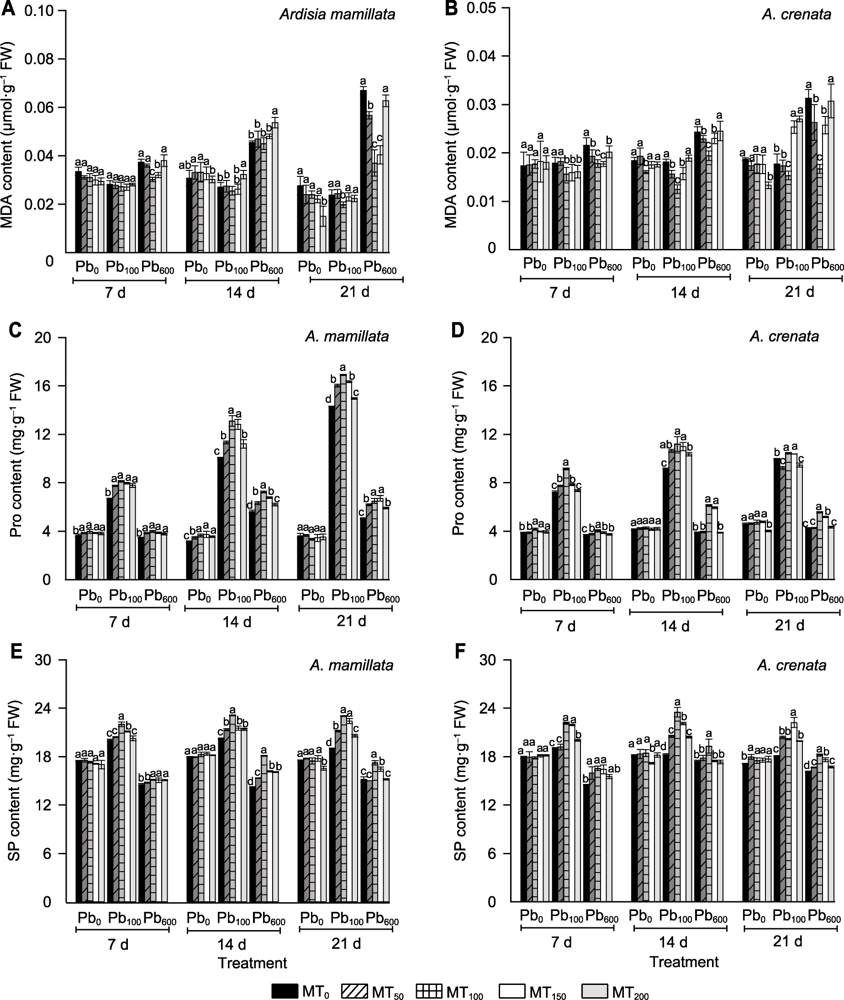
图2 不同浓度褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红与朱砂根叶片丙二醛(MDA) (A, B)、脯氨酸(Pro) (C, D)和可溶性蛋白(SP) (E, F)含量的影响 (A), (C), (E) 虎舌红; (B), (D), (F) 朱砂根。Pb0、Pb100、Pb600、MT0、MT50、MT100、MT150和MT200同图1。不同小写字母表示相同时期不同处理组间在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 2 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on the contents of malondialdehyde (MDA) (A, B), proline (Pro) (C, D) and soluble protein (SP) (E, F) in leaves of Ardisia mamillata and A. crenata under lead stress (A), (C), (E) Ardisia mamillata; (B), (D), (F) A. crenata. Pb0, Pb100, Pb600, MT0, MT50, MT100, MT150, and MT200 are the same as shown in Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments during the same stage at 0.05 level.
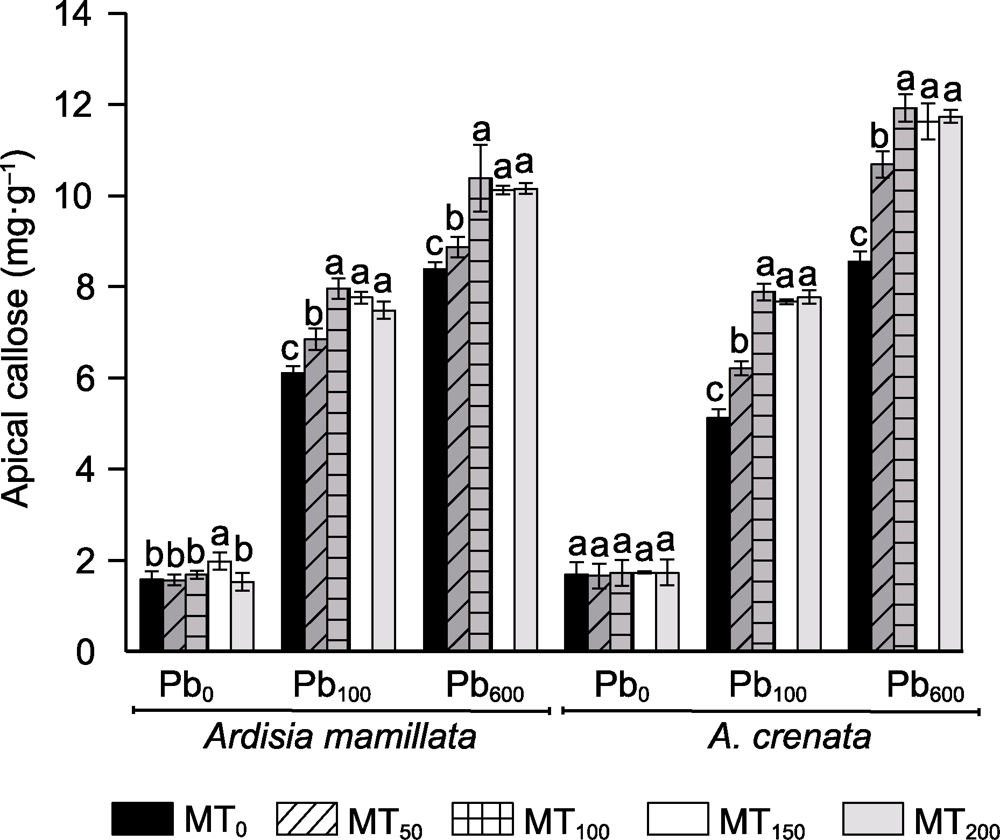
图3 不同浓度褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红与朱砂根根尖胼胝质含量的影响 Pb0、Pb100、Pb600、MT0、MT50、MT100、MT150和MT200同图1。不同小写字母表示相同时期不同处理组间在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 3 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on callose content in root tips of Ardisia mamillata and A. crenata under lead stress Pb0, Pb100, Pb600, MT0, MT50, MT100, MT150, and MT200 are the same as shown in Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments during the same stage at 0.05 level.
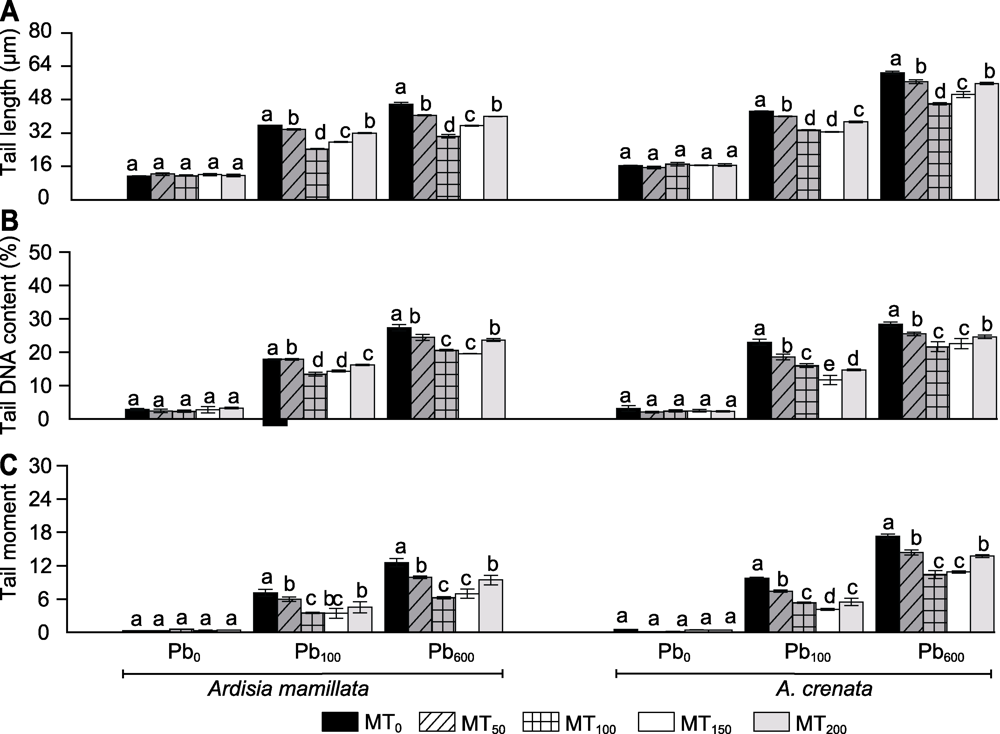
图4 不同浓度褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红和朱砂根彗星尾长(A)、尾部DNA含量(B)及尾距(C)的影响 Pb0、Pb100、Pb600、MT0、MT50、MT100、MT150和MT200同图1。不同小写字母表示相同时期不同处理组间在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 4 Effect of different concentrations of melatonin on tail length (A), tail DNA content (B), and tail moment (C) of Ardisia mamillata and A. crenata under lead stress Pb0, Pb100, Pb600, MT0, MT50, MT100, MT150, and MT200 are the same as shown in Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments during the same stage at 0.05 level.
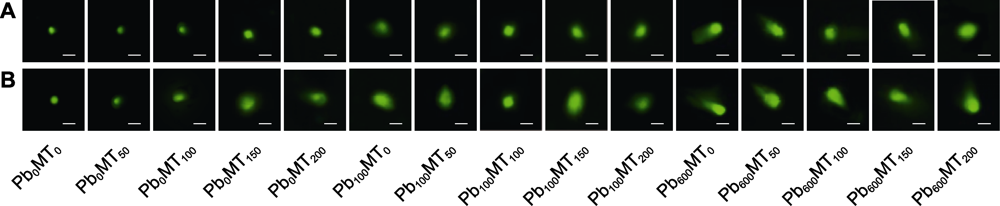
图5 不同浓度褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红(A)和朱砂根(B)根系DNA损伤的影响 Bars=20 μm
Figure 5 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on DNA damage in roots of Ardisia mamillata (A) and A. crenata (B) under lead stress Bars=20 μm
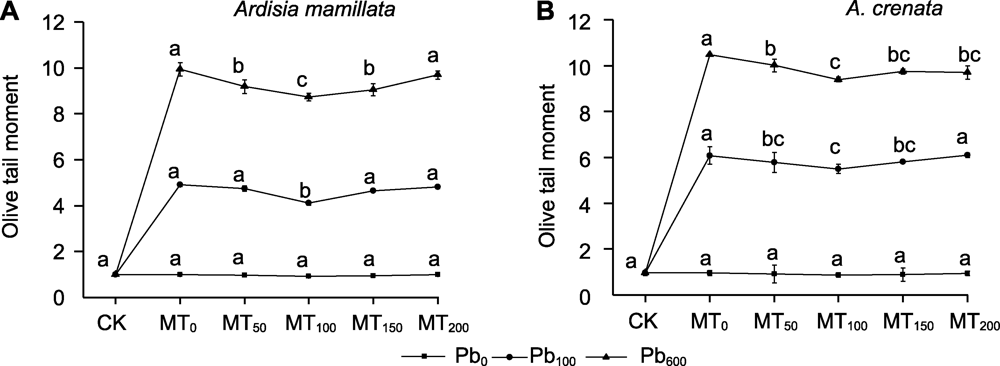
图6 不同浓度褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红(A)和朱砂根(B)根系Olive尾距(OTM)值的影响 Pb0、Pb100、Pb600、MT0、MT50、MT100、MT150和MT200同图1。不同小写字母表示相同时期不同处理组间在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 6 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on Olive tail moment (OTM) value in roots of Ardisia mamillata (A) and A. crenata (B) under lead stress Pb0, Pb100, Pb600, MT0, MT50, MT100, MT150, and MT200 are the same as in Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among the treatments during the same stage at 0.05 level.
| [1] | 安婷婷, 黄帝, 王浩, 张一, 陈应龙 (2021). 植物响应镉胁迫的生理生化机制研究进展. 植物学报 56, 347-362. |
| [2] | 陈旋, 胡颖, 孙明升, 贾婕, 杨章旗 (2021). 外源调节物质对铅胁迫下格木幼苗生理特性的影响. 林业科学 57(2), 39- 48. |
| [3] |
顾红雅, 左建儒, 漆小泉, 杨淑华, 陈之端, 钱前, 林荣呈, 王雷, 萧浪涛, 王小菁, 陈凡, 姜里文, 白永飞, 种康, 王台 (2021). 2020年中国植物科学若干领域重要研究进展. 植物学报 56, 119-133.
DOI |
| [4] | 郭炜 (2008). 紫外辐照导致植物细胞DNA损伤的彗星电泳检测及生理指标的测定. 硕士论文. 济南: 山东大学. pp. 18-20. |
| [5] | 韩航, 陈顺钰, 薛凌云, 侯晓龙, 蔡丽平, 刘爱琴, 周垂帆 (2018). 铅胁迫对金丝草生长及生理生化的影响. 草业学报 27(4), 131-138. |
| [6] | 何玲莉, 沈虹, 王燕, 王娟娟, 龚义勤, 徐良, 柳李旺 (2015). 铅胁迫下萝卜基因组DNA甲基化分析. 核农学报 29, 1278- 1284. |
| [7] | 李春燕, 王进鑫, 王敏, 陈科皓, 王榆鑫, 宋清玉 (2016). 铅胁迫下干旱对国槐和紫穗槐幼苗抗氧化酶活性的影响. 干旱地区农业研究 34(3), 174-178. |
| [8] | 李冬, 王艳芳, 王悦华, 温烜琳, 蔡慧英, 郑晓蕾, 陈彤彤, 刘领 (2019). 外源褪黑素对镉胁迫下豌豆种子萌发、幼苗抗性生理及镉含量的影响. 核农学报 33, 2271-2279. |
| [9] | 李合生 (2000). 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 164-169. |
| [10] | 凌育赵, 刘经亮, 吴晓天, 刘佩珊 (2019). 虎舌红根茎三萜皂苷类成分的研究. 中成药 41, 2139-2144. |
| [11] | 刘灿玉, 王允, 张逸, 曹逼力, 徐坤 (2015). 铅胁迫对姜叶片活性氧代谢的影响. 园艺学报 42, 2215-2222. |
| [12] | 刘仕翔, 黄益宗, 罗泽娇, 黄永春, 杨秀文 (2017). 褪黑素对水稻镉积累及其化学结合形态的影响. 应用生态学报 28, 1588-1594. |
| [13] | 骆永明, 滕应 (2018). 我国土壤污染的区域差异与分区治理修复策略. 中国科学院院刊 33, 145-152. |
| [14] | 吕潇, 王聿双, 张晓倩, 刘海学 (2016). 不同浓度铅胁迫对向日葵幼苗蛋白质结构和表达的影响. 华北农学报 31(2), 60-64. |
| [15] | 齐晓媛, 王文莉, 胡少卿, 刘梦雨, 郑成淑, 孙宪芝 (2021). 外源褪黑素对高温胁迫下菊花光合和生理特性的影响. 应用生态学报 32, 2496-2504. |
| [16] |
邱丽丽, 赵琪, 张玉红, 戴绍军 (2017). 植物质膜蛋白质组的逆境应答研究进展. 植物学报 52, 128-147.
DOI |
| [17] | 孙清斌, 沈仁芳, 尹春芹, 赵学强 (2016). 铝胁迫下胡枝子根尖胼胝质形成规律及影响因素. 生态学报 36, 1073-1082. |
| [18] | 王芳, 李永生, 王汉宁, 彭云玲, 方永丰, 王威, 马原忠 (2016). 钙对铅胁迫下玉米幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 水土保持学报 30(3), 202-207. |
| [19] |
武亮, 戚益军 (2020). 小RNA, 大本领: 22 nt siRNAs在植物适应逆境中的重要作用. 植物学报 55, 270-273.
DOI |
| [20] | 徐向东, 孙艳, 郭晓芹, 孙波, 张坚 (2011). 高温胁迫下外源褪黑素对黄瓜幼苗光合作用及叶绿素荧光的影响. 核农学报 25, 179-184. |
| [21] | 叶江华, 贾小丽, 陈晓婷, 林舜贤, 李远华, 王飞权, 胡永乐, 王海斌 (2017). 铅胁迫下不同茶树的生理响应及其亚细胞水平铅分布特性分析. 中国农业科技导报 19(11), 92-99. |
| [22] | 张建新, 郦枫, 马丽, 张晓晓, 吴玉环, 杨云峰, 徐根娣, 刘鹏 (2017). 镉胁迫下朱砂根和虎舌红生理响应及其镉抗性. 水土保持学报 31(5), 321-327. |
| [23] | 张庆雯, 王兆昊, 祁静静, 谢宇, 雷天刚, 何永睿, 陈善春, 姚利晓 (2021). 植物胼胝质合成酶研究进展. 园艺学报 48, 661-675. |
| [24] | 张伟, 李锟, 李东, 祁献芳, 康文艺 (2011). 朱砂根化学成分和药理作用研究进展. 中国实验方剂学杂志 17(11), 279- 282. |
| [25] | 张镇川, 何冰, 李甜, 靳亚忠, 耿雪青 (2021). 冠菌素对番茄防御基因表达、胼胝质沉积及细菌生长的影响. 四川农业大学学报 39, 27-34. |
| [26] | 赵成凤, 王晨光, 李红杰, 郑学慧, 杨梅, 张仁和 (2021). 干旱及复水条件下外源褪黑素对玉米叶片光合作用的影响. 生态学报 41, 1431-1439. |
| [27] | 赵丽娟, 麻冬梅, 王文静, 马巧利, 李嘉文, 苏立娜 (2021). 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下紫花苜蓿幼苗抗氧化能力以及光合作用效率的影响. 西北植物学报 41, 1355-1363. |
| [28] | 钟鸣, 陈琢, 刘宛, 李培军, 台培东 (2012). 逆境胁迫下植物DNA损伤和DNA错配修复研究进展. 生态学杂志 31, 2404- 2411. |
| [29] |
Debnath B, Hussain M, Irshad M, Mitra S, Li M, Liu S, Qiu DL (2018). Exogenous melatonin mitigates acid rain stress to tomato plants through modulation of leaf ultrastructure, photosynthesis and antioxidant potential. Molecules 23, 388.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Ellinger D, Naumann M, Falter C, Zwikowics C, Jamrow T, Manisseri C, Somerville SC, Voigt CA (2013). Elevated early callose deposition results in complete penetration resistance to powdery mildew in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 161, 1433-1444.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Ellinger D, Voigt CA (2014). Callose biosynthesis in Arabidopsis with a focus on pathogen response: what we have learned within the last decade. Ann Bot 114, 1349- 1358.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Etesami H, Jeong BR (2018). Silicon (Si): review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Ecotox Environ Safe 147, 881-896.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Izbiańska K, Arasimowicz-Jelonek M, Deckert J (2014). Phenylpropanoid pathway metabolites promote tolerance response of lupine roots to lead stress. Ecotox Environ Safe 110, 61-67.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Köhle H, Jeblick W, Poten F, Blaschek W, Kauss H (1985). Chitosan-elicited callose synthesis in soybean cells as a Ca2+-dependent process. Plant Physiol 77, 544-551.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Li JH, Arkorful E, Cheng SY, Zhou QQ, Li H, Chen X, Sun K, Li XH (2018). Alleviation of cold damage by exogenous application of melatonin in vegetatively propagated tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Sci Hortic 238, 356-362.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Nedukha OM (2015). Callose: localization, functions, and synthesis in plant cells. Cytol Genet 49, 49-57.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Samardakiewicz S, Krzesłowska M, Bilski H, Bartosiewicz R, Woźny A (2012). Is callose a barrier for lead ions entering Lemna minor L. root cells? Protoplasma 249, 347-351.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Shahid M, Arshad M, Kaemmerer M, Pinelli E, Probst A, Baque D, Pradere P, Dumat C (2012). Long-term field metal extraction by Pelargonium: phytoextraction efficiency in relation to plant maturity. Int J Phytoremediat 14, 493- 505.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Teh CY, Shaharuddin NA, Ho CL, Mahmood M (2016). Exogenous proline significantly affects the plant growth and nitrogen assimilation enzymes activities in rice (Oryza sativa) under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 38, 151.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Tiryaki I, Keles H (2012). Reversal of the inhibitory effect of light and high temperature on germination of Phacelia tanacetifolia seeds by melatonin. J Pineal Res 52, 332- 339.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Wu HH, Li BS, Iwakawa HO, Pan YJ, Tang XL, Linghu QY, Liu YL, Sheng SX, Feng L, Zhang H, Zhang XY, Tang ZH, Xia XL, Zhai JX, Guo HW (2020). Plant 22-nt siRNAs mediate translational repression and stress adaptation. Nature 581, 89-93.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Zhao DK, Wang HP, Chen SY, Yu DQ, Reiter RJ (2021). Phytomelatonin: an emerging regulator of plant biotic stress resistance. Trends Plant Sci 26, 70-82.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杜锦瑜, 孙震, 苏彦龙, 王贺萍, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 赵彦, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草咖啡酸氧甲基转移酶基因AmCOMT1的鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 383-396. |
| [2] | 蔡淑钰, 刘建新, 王国夫, 吴丽元, 宋江平. 褪黑素促进镉胁迫下番茄种子萌发的调控机理[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 720-732. |
| [3] | 毛轩雯, 王志超, 阮心依, 孙靖菲, 张雅婷, 陆锦灏, 邵甜甜, 王娴, 肖佳敏, 肖莉, 叶梦瑶, 吴玉环, 刘鹏. 外源有机酸对铝胁迫下菊芋生理响应系统的调控效应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 573-589. |
| [4] | 张琦, 张文静, 袁宪凯, 李明, 赵强, 杜艳丽, 杜吉到. 褪黑素对盐胁迫下普通菜豆芽期核酸修复的调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 108-121. |
| [5] | 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| [6] | 曾引伟, 曹玉曼, 沙煦旸, 李淑霞, 杨培志, 呼天明, 刘金隆. 一种简单有效的非损伤观测根瘤和根系形态的方法[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(5): 661-670. |
| [7] | 陈成, 董爱武, 苏伟. 拟南芥组蛋白分子伴侣AtHIRA参与体细胞同源重组及盐胁迫响应[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 42-50. |
| [8] | 康丽娜, 吴福忠, 杨万勤, 谭波, 夏磊. 铅胁迫对欧美杂交杨幼苗碳、氮和磷积累与分配的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(6): 578-586. |
| [9] | 聂志刚;王艳;李韶山. 重金属诱导拟南芥原生质体DNA 损伤的单细胞凝胶电泳检测[J]. 植物学报, 2009, 44(01): 117-123. |
| [10] | 王静 蒋磊 王艳 李韶山. 紫外辐射诱导植物叶片DNA损伤敏感性差异[J]. 植物学报, 2007, 24(02): 189-193. |
| [11] | 徐楠, 施国新, 曾晓敏, 丁小余, 徐勤松, 陈源. Hg2+胁迫对浮萍体细胞DNA一级结构和抗氧化酶系的损伤(英文)[J]. 植物生态学报, 2003, 27(3): 299-303. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||