

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 554-557.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19119 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19119
收稿日期:2019-07-08
接受日期:2019-07-16
出版日期:2019-09-01
发布日期:2019-03-01
通讯作者:
严建兵
Received:2019-07-08
Accepted:2019-07-16
Online:2019-09-01
Published:2019-03-01
Contact:
Jianbing Yan
摘要: 密植是提高作物单位面积产量、促进粮食增产的重要途径之一。叶夹角是影响玉米(Zea mays)密植的关键因子。中国农业大学田丰课题组最近克隆了2个调控玉米叶夹角的数量性状位点(QTL)——UPA1和UPA2, 揭示了这2个位点的功能基因(brd1和ZmRAVL1)通过油菜素内酯(BR)信号通路调控叶夹角。UPA2位于ZmRAVL1上游9.5 kb, 可与DRL1蛋白结合。另一个影响玉米叶夹角的蛋白LG1可以激活ZmRAVL1的表达; DRL1蛋白与LG1蛋白直接互作抑制LG1对ZmRAVL1的激活表达。玉米祖先种大刍草(teosinte)的UPA2位点序列与DRL1蛋白结合能力更强, 导致大刍草ZmRAVL1的表达受到更强的抑制, 下调表达的ZmRAVL1进一步使下游基因brd1的表达下调, 进而降低叶环区的内源BR水平, 导致叶夹角变小。将大刍草的UPA2等位基因导入到玉米中或对玉米中ZmRAVL1进行基因编辑, 在密植条件下均可显著提高玉米产量。上述发现为高产玉米品种的分子育种改良提供了重要理论基础和基因资源。
刘杰, 严建兵. 大刍草稀有等位基因促进玉米密植高产. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 554-557.
Jie Liu, Jianbing Yan. A Teosinte Rare Allele Increases Maize Plant Density and Yield. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(5): 554-557.
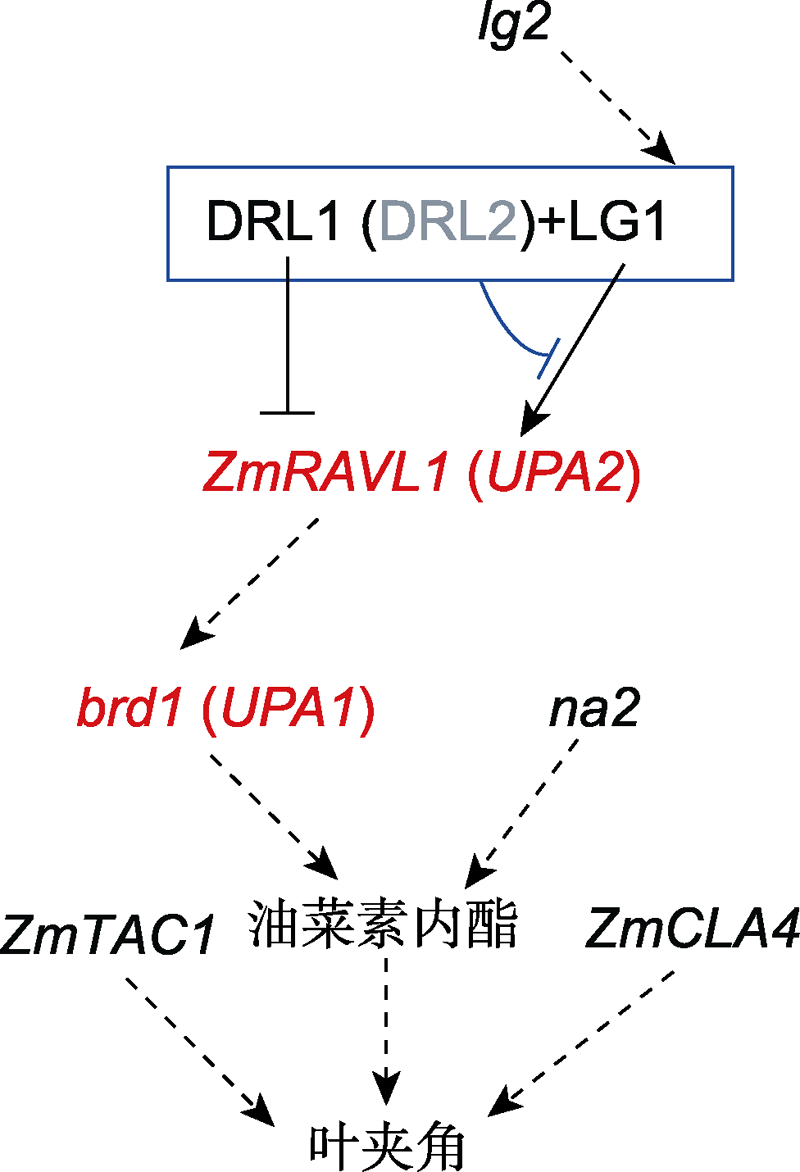
图1 玉米叶夹角的调控途径 lg2调控lg1, 但具体机制未知。LG1激活ZmRAVL1的表达, DRL1抑制ZmRAVL1的表达, DRL1与LG1蛋白互作抑制LG1对ZmRAVL1的激活作用(DRL2可能具有与DRL1类似的功能)。ZmRAVL1调控下游brd1的表达, brd1和nana plant2 (na2)都参与油菜素内酯(brassinosteroid, BR)的生物合成。这些基因均通过BR途径调控玉米叶夹角形成。实线表示机制已被阐明, 虚线表示机制未知。
Figure 1 A proposed pathway regulating the leaf angle in maize lg2 regulates lg1 with an unknown mechanism. LG1 and DRL1 activates and represses the expression of ZmRAVL1, respectively. The DRL1-LG1 complex represses the LG1- activated ZmRAVL1 expression (DRL2 may have a similar function as DRL1). ZmRAVL1 regulates the expression of brd1, which, together with nana plant2 (na2), are involved in the biosynthesis of brassinosteroid (BR) and eventually regulate leaf angle. Solid and dash lines indicate the clear and unclear regulatory mechanism, respectively.
| 1 | 明博, 谢瑞芝, 侯鹏, 李璐璐, 王克如, 李少昆 (2017). 2005-2016年中国玉米种植密度变化分析. 中国农业科学 50, 1960-1972. |
| 2 | Best NB, Hartwig T, Budka J, Fujioka S, Johal G, Schulz B, Dilkes BP (2016). nana plant2 encodes a maize ortholog of the Arabidopsis brassinosteroid biosynthesis gene DWARF1, identifying developmental interactions between brassinosteroids and gibberellins. Plant Physiol 171, 2633-2647. |
| 3 | Choe S, Dilkes BP, Gregory BD, Ross AS, Yuan H, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Tanaka A, Yoshida S, Tax FE, Feldmann KA (1999). The Arabidopsis dwarf1 mutant is defective in the conversion of 24-methylenecholesterol to campesterol in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 119, 897-907. |
| 4 | Harper L, Freeling M (1996). Interactions of liguleless1 and liguleless2 function during ligule induction in maize. Genetics 144, 1871-1882. |
| 5 | Je BI, Piao HL, Park SJ, Park SH, Kim CM, Xuan YH, Park SH, Huang J, Do Choi Y, An G, Wong HL, Fujioka S, Kim MC, Shimamoto K, Han CD (2010). RAV-Like1 maintains brassinosteroid homeostasis via the coordinated activation of BRI1 and biosynthetic genes in rice. Plant Cell 22, 1777-1791. |
| 6 | Ku L, Wei X, Zhang S, Zhang J, Guo S, Chen Y (2011). Cloning and characterization of a putative TAC1 ortholog associated with leaf angle in maize(Zea mays L.). PLoS One 6, e20621. |
| 7 | Lee EA, Tollenaar M (2007). Physiological basis of successful breeding strategies for maize grain yield. Crop Sci 47, S202-S215. |
| 8 | Li P, Wang Y, Qian Q, Fu Z, Wang M, Zeng D, Li B, Wang X, Li J (2007). LAZY1 controls rice shoot gravitropism through regulating polar auxin transport. Cell Res 17, 402-410. |
| 9 | Moreno MA, Harper LC, Krueger RW, Dellaporta SL, Freeling M (1997). liguleless1 encodes a nuclear-localized protein required for induction of ligules and auricles during maize leaf organogenesis. Genes Dev 11, 616-628. |
| 10 | Strable J, Wallace JG, Unger-Wallace E, Briggs S, Bradbury PJ, Buckler ES, Vollbrecht E (2017). Maize YABBY genes drooping leaf1 and drooping leaf2 regulate plant architecture. Plant Cell 29, 1622-1641. |
| 11 | Tian J, Wang C, Xia J, Wu L, Xu G, Wu W, Li D, Qin W, Han X, Chen Q, Jin W, Tian F (2019). Teosinte ligule allele narrows plant architecture and enhances high- density maize yields. Science 365, 658-664. |
| 12 | Walsh J, Waters CA, Freeling M (1998). The maize gene liguleless2 encodes a basic leucine zipper protein involved in the establishment of the leaf blade-sheath boundary. Genes Dev 12, 208-218. |
| 13 | Yu B, Lin Z, Li H, Li X, Li J, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhu Z, Zhai W, Wang X, Xie D, Sun C (2007). TAC1, a major quantitative trait locus controlling tiller angle in rice. Plant J 52, 891-898. |
| 14 | Zhang J, Ku LX, Han ZP, Guo SL, Liu HJ, Zhang ZZ, Cao LR, Cui XJ, Chen YH (2014). The ZmCLA4 gene in the qLA4-1 QTL controls leaf angle in maize( Zea mays L.). J Exp Bot 65, 5063-5076. |
| [1] | 唐远翔, 熊仕臣, 朱洪锋, 张新生, 游成铭, 刘思凝, 谭波, 徐振锋. 长期氮添加对四川盆地西缘常绿阔叶林优势树种凋落叶产量及碳氮磷归还的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 720-731. |
| [2] | 许庭旸, 刘雨辰, 王万鹏, 苏航, 苏昆龙, 吴振映, 吕明, 李福利, 王小山, 付春祥. 喷施不同植物生长调节剂对盐碱地小麦生长发育的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 354-362. |
| [3] | 李园, 范开建, 安泰, 李聪, 蒋俊霞, 牛皓, 曾伟伟, 衡燕芳, 李虎, 付俊杰, 李慧慧, 黎亮. 玉米自然群体自交系农艺性状的多环境全基因组预测初探[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1041-1053. |
| [4] | 杨娟, 赵月磊, 陈晓远, 王宝宝, 王海洋. 玉米开花期调控机理及育种应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 912-931. |
| [5] | 闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| [6] | 张强, 赵振宇, 李平华. 基因编辑技术在玉米中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 978-998. |
| [7] | 杨文丽, 李钊, 刘志铭, 张志华, 杨今胜, 吕艳杰, 王永军. 不同熟期玉米叶片衰老特性及其对叶际细菌的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1024-1040. |
| [8] | 吴锁伟, 安学丽, 万向元. 玉米雄性不育机理及其在工程核不育制种中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [9] | 郑名敏, 黄强, 张鹏, 刘孝伟, 赵卓凡, 易洪杨, 荣廷昭, 曹墨菊. 玉米细胞质雄性不育及育性恢复研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 999-1006. |
| [10] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [11] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [12] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [13] | 程可心, 杜尧, 李凯航, 王浩臣, 杨艳, 金一, 何晓青. 玉米与叶际微生物组的互作遗传机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(2): 215-228. |
| [14] | 周文期, 周玉乾, 李永生, 何海军, 杨彦忠, 王晓娟, 连晓荣, 刘忠祥, 胡筑兵. 玉米ZmICE2基因调控气孔发育[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 866-881. |
| [15] | 于熙婷, 黄学辉. 现代玉米起源新见解——两类大刍草的混血[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 857-860. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
