

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 840-847.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17208 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17208
张旭红1,2, 王頔2, 梁振旭1,2, 孙美玉2, 张金政2, 石雷1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2017-11-07
接受日期:2018-02-05
出版日期:2018-11-01
发布日期:2018-12-05
通讯作者:
石雷
作者简介:作者简介:白克智, 1959年开始在中国科学院植物研究所工作, 先后任助理研究员、研究员, 长期从事植物生长发育及其调控的研究。1986年,其主持的“满江红生物学特性研究”荣获中国科学院科技进步二等奖。曾任《植物生理学报》编委、《植物学报》常务编委、中国植物生长调节剂协会主任等职。
基金资助:
Zhang Xuhong1,2, Wang Di2, Liang Zhenxu1,2, Sun Meiyu2, Zhang Jinzheng2, Shi Lei1,2,*( )
)
Received:2017-11-07
Accepted:2018-02-05
Online:2018-11-01
Published:2018-12-05
Contact:
Shi Lei
摘要: 以欧洲百合(Lilium martagon)无菌苗鳞片为外植体, 探讨不同植物激素组合及光暗培养条件对愈伤组织诱导、增殖和再生不定芽的影响, 进而建立欧洲百合高效再生体系。结果显示, 诱导愈伤组织的最佳培养基为MS+0.2 mg?L-1 TDZ+0.5 mg?L-1 NAA, 诱导率为77.14%。在添加TDZ和NAA组合的培养基中进行继代培养, 愈伤组织极易褐化, 胚性活性下降; 采用添加6-BA和NAA组合的培养基可改善愈伤组织的褐化现象, MS+0.5 mg?L-1 6-BA+0.1 mg?L-1 NAA是愈伤组织增殖的最佳培养基, 增殖指数为2.93, 表明6-BA在愈伤组织状态维持中起关键作用。暗培养条件下愈伤组织的诱导率、增殖指数和芽再生系数最高, 分别可达77.14%、2.93和5.43, 且愈伤组织生长状态较好, 不定芽生根正常。研究建立的欧洲百合高效再生体系对于百合种质资源保存、基因工程育种及在国内的推广应用具有重要意义。
张旭红, 王頔, 梁振旭, 孙美玉, 张金政, 石雷. 欧洲百合愈伤组织诱导及植株再生体系的建立. 植物学报, 2018, 53(6): 840-847.
Zhang Xuhong, Wang Di, Liang Zhenxu, Sun Meiyu, Zhang Jinzheng, Shi Lei. Callus Induction and Establishment of a Plant Regeneration System with Lilium martagon. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(6): 840-847.
| No. | Concentrations of plant growth regulator (mg·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDZ | PIC | NAA | 6-BA | |
| CK | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 1 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 0.60 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.00 |
| 7 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 8 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.50 |
| 11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 1.00 |
表 1 欧洲百合愈伤组织诱导和增殖的培养基设计
Table 1 Media design for callus induction and proliferation of Lilium martagon
| No. | Concentrations of plant growth regulator (mg·L-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDZ | PIC | NAA | 6-BA | |
| CK | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 1 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 0.60 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.00 |
| 7 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 8 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| 10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.50 |
| 11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 1.00 |
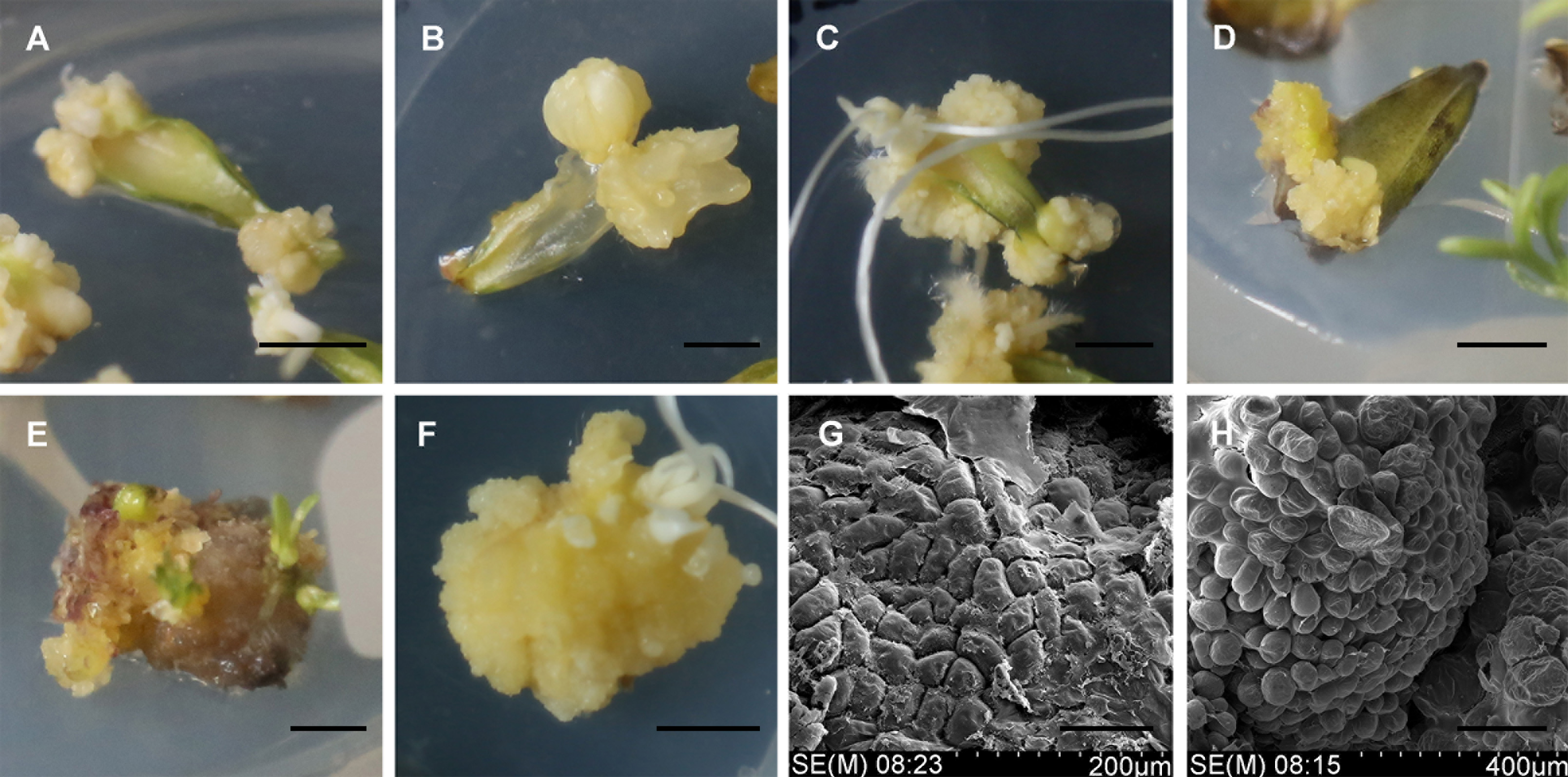
图 1 欧洲百合愈伤组织的诱导和增殖(A), (B) 在暗培养条件下, 添加TDZ和PIC的培养基中诱导的愈伤组织(Bar=5 mm); (C) 在暗培养条件下, 添加TDZ和NAA的培养基中诱导的愈伤组织(Bar=5 mm); (D) 在光培养条件(光周期为16小时光照/8小时黑暗)下, 添加TDZ和NAA的培养基中诱导的愈伤组织(Bar=5 mm); (E), (G) 在光培养条件(光周期为16小时光照/8小时黑暗)下增殖的愈伤组织((E) Bar=5 mm; (G) Bar=100 μm); (F), (H) 在暗培养条件下增殖的愈伤组织((F) Bar=5 mm; (H) Bar=200 μm)
Figure 1 The callus induction and proliferation of Lilium martagon(A), (B) Callus induction in MS medium containing TDZ and PIC in the dark (Bar=5 mm); (C) Callus induction in MS medium containing TDZ and NAA in the dark (Bar=5 mm); (D) Callus induction in MS medium containing TDZ and NAA under 16/8 h light/dark photoperiod (Bar=5 mm); (E), (G) Callus proliferation under 16/8 h light/dark photoperiod ((E) Bar=5 mm; (G) Bar=100 μm); (F), (H) Callus proliferation in the dark ((F) Bar=5 mm; (H) Bar=200 μm)
| No. | Rate of callus induced (%) | Number of buds/explant |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00 Dc | 1.09±0.25 Bc |
| 1 | 63.34±7.46 AB | 1.13±0.33 AB |
| 2 | 66.67±7.86 A | 0.69±0.24 C |
| 3 | 34.44±12.67 C | 1.49±0.29 A |
| 4 | 54.45±8.24 B | 1.16±0.23 AB |
| 5 | 77.14±7.82 a | 1.46±0.28 bc |
| 6 | 48.57±7.82 b | 1.57±0.29 b |
| 7 | 45.72±6.39 b | 1.74±0.26 ab |
| 8 | 68.57±15.65 a | 2.00±0.35 a |
表 2 不同激素组合对欧洲百合愈伤组织诱导的影响(暗培养)
Table 2 Effects of different plant growth regulators combi- nation on the callus induction of Lilium martagon (in the dark)
| No. | Rate of callus induced (%) | Number of buds/explant |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00 Dc | 1.09±0.25 Bc |
| 1 | 63.34±7.46 AB | 1.13±0.33 AB |
| 2 | 66.67±7.86 A | 0.69±0.24 C |
| 3 | 34.44±12.67 C | 1.49±0.29 A |
| 4 | 54.45±8.24 B | 1.16±0.23 AB |
| 5 | 77.14±7.82 a | 1.46±0.28 bc |
| 6 | 48.57±7.82 b | 1.57±0.29 b |
| 7 | 45.72±6.39 b | 1.74±0.26 ab |
| 8 | 68.57±15.65 a | 2.00±0.35 a |
| No. | Rate of callus induced (%) | Number of buds/explant |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00 c | 0.90±0.15 b |
| 5 | 32.86±12.64 a | 1.17±0.37 ab |
| 6 | 16.67±11.78 b | 1.37±0.48 a |
| 7 | 13.34±7.46 bc | 1.00±0.26 ab |
| 8 | 20.00±13.94 ab | 0.46±0.22 c |
表 3 不同浓度TDZ和NAA对欧洲百合愈伤组织诱导的影响(光周期为16小时光照/8小时黑暗)
Table 3 Effects of TDZ and NAA on the callus induction of Lilium martagon (under 16/8 h light/dark photoperiod)
| No. | Rate of callus induced (%) | Number of buds/explant |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00 c | 0.90±0.15 b |
| 5 | 32.86±12.64 a | 1.17±0.37 ab |
| 6 | 16.67±11.78 b | 1.37±0.48 a |
| 7 | 13.34±7.46 bc | 1.00±0.26 ab |
| 8 | 20.00±13.94 ab | 0.46±0.22 c |
| Light/dark condition | Proliferation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Photoperiod | 1.39±0.21 b |
| Dark condition | 1.86±0.30 a |
表 4 光暗培养条件对欧洲百合愈伤组织增殖的影响
Table 4 Effects of light/dark condition on callus proliferation of Lilium martagon
| Light/dark condition | Proliferation coefficient |
|---|---|
| Photoperiod | 1.39±0.21 b |
| Dark condition | 1.86±0.30 a |
| No. | Proliferation coefficient | Number of buds/callus |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | 2.24±0.17 b | 2.37±0.39 a |
| 10 | 2.93±0.51 a | 1.65±0.38 b |
| 11 | 1.86±0.30 b | 0.88±0.41 c |
表 5 不同浓度6-BA和NAA对欧洲百合愈伤组织增殖的影响(暗培养)
Table 5 Effects of 6-BA and NAA on callus proliferation of Lilium martagon (in the dark)
| No. | Proliferation coefficient | Number of buds/callus |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | 2.24±0.17 b | 2.37±0.39 a |
| 10 | 2.93±0.51 a | 1.65±0.38 b |
| 11 | 1.86±0.30 b | 0.88±0.41 c |
| Light/dark condition | Differentiation rate of callus (%) | Number of buds/callus |
|---|---|---|
| Photoperiod | 74.00±13.42 a | 2.86±0.88 b |
| Dark condition | 81.11±10.68 a | 5.43±1.60 a |
表 6 光暗培养条件对欧洲百合愈伤组织再生不定芽的影响
Table 6 Effects of light/dark condition on the callus differen- tiation of Lilium martagon
| Light/dark condition | Differentiation rate of callus (%) | Number of buds/callus |
|---|---|---|
| Photoperiod | 74.00±13.42 a | 2.86±0.88 b |
| Dark condition | 81.11±10.68 a | 5.43±1.60 a |
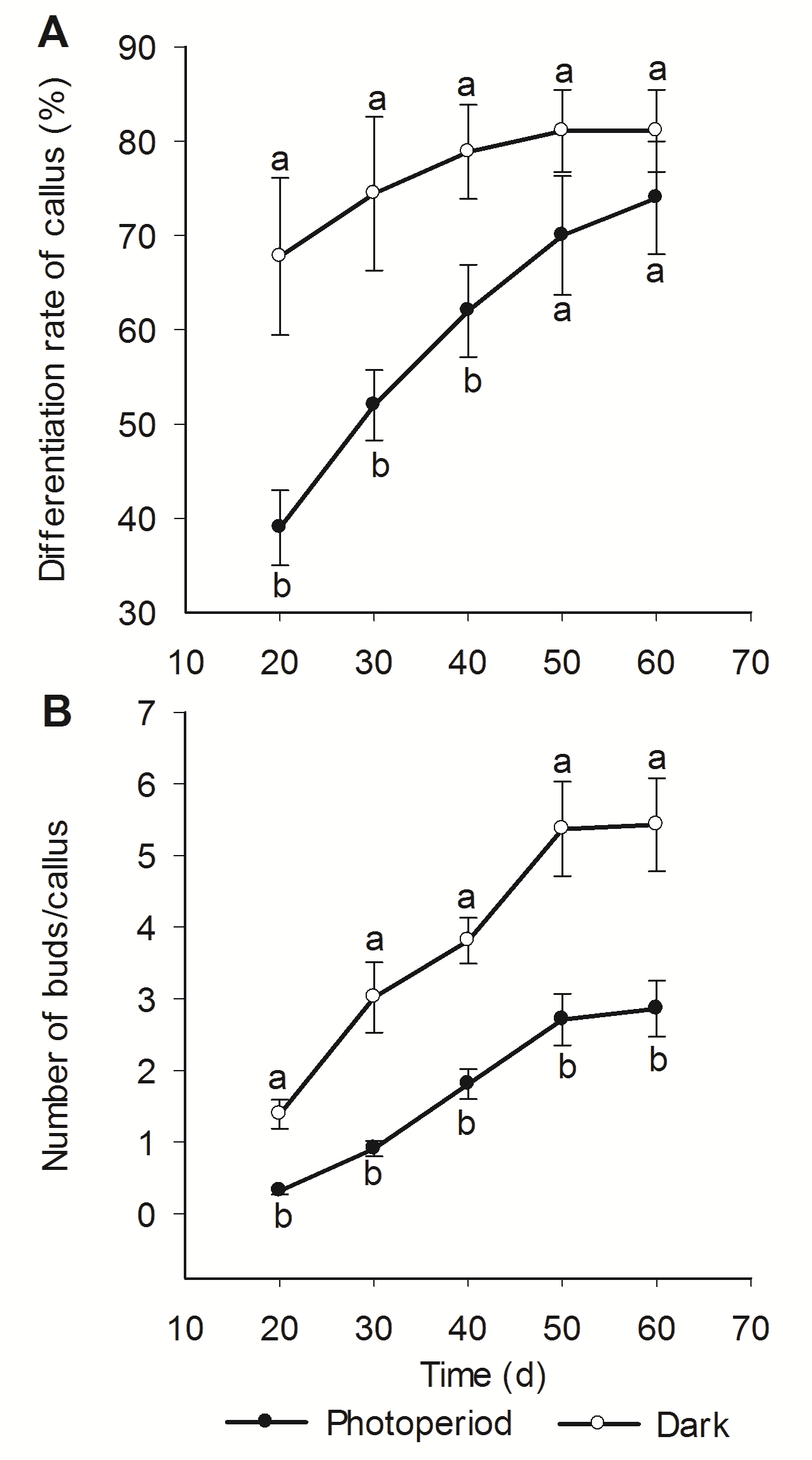
图 2 光暗培养条件下欧洲百合愈伤组织再生不定芽的动态变化(A) 再生率; (B) 不定芽再生系数
Figure 2 Dynamic change of callus differentiation of Lilium martagon cultured under different light/dark condition(A) Differentiation rate of callus; (B) Number of buds/callus

图 3 欧洲百合体胚发生和生根移栽(A)-(E) 暗培养条件下体胚的发育过程(Bar=0.5 mm); (F) 光培养条件下愈伤组织的再生(Bar=1 mm); (G)-(I) 光培养条件下分化的不定芽生根培养第1天、第5天和第15天(Bar=2 mm); (J)-(L) 暗培养条件下分化的不定芽生根培养第1天、第5天和第15天(Bar=2 mm); (M) 光培养条件下分化的不定芽生根(Bar=5 mm); (N) 暗培养条件下分化的不定芽生根(Bar=5 mm); (O) 完整植株(Bar=1 cm); (P) 移栽(Bar=2 cm)
Figure 3 Somatic embryogenesis and rooting of Lilium martagon(A)-(E) Developmental process of somatic embryos generated from callus cultured in the dark (Bar=0.5 mm); (F) Embryo-like structures obtained from callus under 16/8 h light/dark photoperiod (Bar=1 mm); (G)-(I) Day 1, 5 and 15 of rooting buds differentiated under 16/8 h light/dark photoperiod (Bar=2 mm); (J)-(L) Day 1, 5 and 15 of rooting buds differentiated in the dark (Bar=2 mm); (M) Rooting buds differentiated under 16/8 h light/dark photoperiod (Bar=5 mm); (N) Rooting buds differentiated in the dark (Bar=5 mm); (O) Plantlets (Bar=1 cm); (P) Transplantation (Bar=2 cm)
| [1] | 陈云凤, 张春荣, 黄霞, 黄学林 (2006). TDZ对植物体细胞胚胎发生的作用. 植物生理学通讯 42, 127-133. |
| [2] |
李晓艳, 陈莉, 辛海波, 义鸣放 (2009). 百合鳞片薄层细胞培养高效再生体系的建立. 华中农业大学学报 28, 351-355.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
李雪艳, 严瑞, 张静, 付麟岚, 段鑫, 王春夏, 孙红梅 (2016). 东方百合Tiger Woods离体快繁技术体系的建立. 沈阳农业大学学报 47, 654-660.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
李莺, 李星, 李生玲, 徐薇 (2013). ‘黄天霸’百合花器官愈伤组织诱导及植株再生. 热带作物学报 34, 1507-1512.
DOI URL |
| [5] | 马怡迪 (2015). 野生百合高效再生体系建立及愈伤组织增殖调控研究. 硕士论文. 杭州: 浙江大学. pp. 28-39. |
| [6] |
孙安妮, 张延龙, 牛立新, 王仙芝, 崔雅静, 王润丰 (2011). 宜昌百合体细胞胚诱导及植株再生. 西北农业学报 20, 142-146.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 孙红梅, 王锦霞, 段鑫, 张静, 李雪艳, 高鹤 (2015). 重瓣东方百合Double surprise离体快繁技术体系的建立. 沈阳农业大学学报 46, 391-397. |
| [8] | 王杰, 刘国锋, 包满珠, 黄莉 (2008). 麝香百合胚性愈伤组织状态的调整与植株再生. 园艺学报 35, 1795-1802. |
| [9] |
吴耿, 付春华, 黄永伟, 李为, 余龙江, 栗茂腾 (2011). 岩溶环境下华南忍冬气孔泌钙及其生物矿化. 植物学报 46, 658-664.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
徐晓峰, 黄学林 (2003). TDZ: 一种有效的植物生长调节剂. 植物学通报 20, 227-237.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 袁素霞, 李佳, 明军, 刘春, 徐雷锋, 袁迎迎 (2015). 百合未授粉子房离体培养胚胎形成及植株再生. 植物学报 50, 378-387. |
| [12] | 翟彦, 张宗勤, 贾敏, 王岩, 宋西德, 周雷 (2011). 百合体细胞胚胎发生和植株再生. 西北植物学报 31, 834-841. |
| [13] |
张翔宇, 陈杰, 吉云, 严显进, 王彩云, 阮培均, 王永 (2016). 淡黄花百合珠芽诱导脱分化的研究. 江苏农业科学 44, 58-61.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
张艺萍, 吴丽芳, 吴学尉, 崔光芬, 丁丁, 王继华 (2008). 东方百合胚性愈伤组织诱导和植株再生研究. 江西农业学报 20, 33-36, 39.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Bakhshaie M, Babalar M, Mirmasoumi M, Khalighi A (2010). Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration ofLilium ledebourii (Baker) Boiss, an endangered species. Plant Cell Tiss Org 102, 229-235.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Feldmaier C, McRae J (1982). Lilien. Stuttgart: Verlag Eugen Ulmer. |
| [17] | Kedra M, Bach A (2005). Morphogenesis of Lilium martagon L. explants in callus culture. Acta Biol Cracov Bot 47, 65-73. |
| [18] | Khosravi S, Azghandi AV, Mojtahedi N, Haddad R (2007). In vitro propagation of Lilium longiflorum var. Ceb-Dazzle through direct somatic embryogenesis. Pak J Biol Sci 10, 2517-2521. |
| [19] |
Mori S, Adachi Y, Horimoto S, Suzuki S, Nakano M (2005). Callus formation and plant regeneration in various Lilium species and cultivars. In Vitro Cell Dev-Pl 41, 783-788.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Qi YY, Du LJ, Quan YH, Tian FF, Liu YL, Wang YJ (2014). Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic cell suspension cultures and plant regeneration in Lilium tenuifolium Oriental × trumpet ‘Robina’. Acta Physiol Plant 36, 2047-2057. |
| [21] | Synge PM (1980). Lilies. London: B. T. Batsford. pp. 34-38. |
| [22] | Tang YP, Liu XQ, Gituru RW, Chen LQ (2010). Callus induction and plant regeneration from in vitro cultured lea- ves, petioles and scales of Lilium leucanthum(Baker) Bak- er. Biotechnol Biotec Eq 24, 2071-2076. |
| [1] | 李晶晶, 李艳飞, 王安琪, 王佳颖, 邓成燕, 卢敏, 马剑英, 戴思兰. 菊花品种‘万代风光’再生及遗传转化体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 刘玉泽, 王一菲, 任威蓁, 栗浩, 路斌, 路丙社, 于晓跃. 北美豆梨杂种幼胚挽救及再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 800-809. |
| [3] | 田旭平, 岳康杰, 王佳丽, 刘慧欣, 史子尹, 亢红伟. 毛建草愈伤组织诱导及植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 613-625. |
| [4] | 曾浩, 李佩芳, 郭至辉, 刘春林, 阮颖. 银扇草再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 433-440. |
| [5] | 武晓云, 廖敏凌, 李雪茹, 舒梓淳, 辛佳潼, 张伯晗, 戴思兰. 毛华菊3种瓣型株系再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 245-256. |
| [6] | 廖敏凌, 蒲娅, 武晓云, 马朝峰, 王文奎, 戴思兰. 平潭野菊混合瓣型株系再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 449-460. |
| [7] | 张冬瑞, 卜志刚, 陈玲玲, 常缨. 香鳞毛蕨的组织培养和快速繁殖体系构建[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 760-767. |
| [8] | 罗虹, 温小蕙, 周圆圆, 戴思兰. 芳香堆心菊离体再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 318-328. |
| [9] | 徐悦,曹英萍,王玉,付春祥,戴绍军. 发根农杆菌介导的菠菜毛状根遗传转化体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 515-521. |
| [10] | 赵喜亭, 蒋丽微, 王苗, 朱玉婷, 张文芳, 李明军. 怀黄菊间接体胚受体再生体系的建立及CmTGA1的遗传转化[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(4): 525-532. |
| [11] | 刘芳, 唐映红, 袁有美, 郭清泉, 沈帆, 陈建荣. 多肉植物劳尔的组织培养[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(2): 251-256. |
| [12] | 胡峰, 施琼, 黄烈健. 黑木相思愈伤组织诱导及植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(5): 603-610. |
| [13] | 陈雪, 张金柱, 潘兵兵, 桑成瑾, 马雪, 杨涛, 车代弟. 月季愈伤组织的诱导及植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 2011, 46(5): 569-574. |
| [14] | 范小峰;郭小强;肖朝霞;刘灵霞. 皱皮木瓜愈伤组织诱导与快速繁殖[J]. 植物学报, 2009, 44(06): 725-727. |
| [15] | 赵利铭;刘树君;宋松泉;. 甜高粱再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2008, 25(04): 465-468. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||