

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 393-406.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24118 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24118
• RESEARCH ARTICLES • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu Tiantian1,2, Yang Peijian1,2, Zhou Xiaoxi1,2, Cao Yi1,2, Chen Yanhong1,2, Liu Guoyuan1,2, Zhang Jian1,2, Wei Hui1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-04
Accepted:2024-11-12
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2024-11-26
Contact:
*E-mail: 15850682752@163.com
Xu Tiantian, Yang Peijian, Zhou Xiaoxi, Cao Yi, Chen Yanhong, Liu Guoyuan, Zhang Jian, Wei Hui. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics and Expression Characteristics of Lagerstroemia indica GolS Family Genes[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 393-406.
| Gene name | Gene ID | Length (bp) | Number of amino acids (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Aliphatic index | Instability index | GRAVY | Subcelluar location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiGolS1 | evm.model.Chr1.208 | 1215 | 404 | 46.00 | 9.45 | 92.20 | 57.70 | -0.086 | C |
| LiGolS2 | evm.model.Chr3.1524 | 1146 | 381 | 42.91 | 8.71 | 82.10 | 49.57 | -0.263 | CP |
| LiGolS3 | evm.model.Chr4.803 | 990 | 329 | 37.72 | 4.75 | 78.81 | 50.39 | -0.329 | C |
| LiGolS4 | evm.model.Chr4.806 | 990 | 329 | 37.85 | 4.78 | 78.51 | 48.28 | -0.338 | C |
| LiGolS5 | evm.model.Chr5.968 | 984 | 327 | 37.69 | 4.76 | 80.76 | 53.39 | -0.318 | C |
| LiGolS6 | evm.model.Chr8.101 | 1050 | 349 | 39.71 | 8.16 | 90.32 | 47.76 | -0.148 | CP |
| LiGolS7 | evm.model.Chr8.200 | 1164 | 387 | 43.06 | 7.63 | 87.93 | 44.71 | -0.095 | CP |
| LiGolS8 | evm.model.Chr10.348 | 1125 | 374 | 42.24 | 9.11 | 93.56 | 49.52 | -0.062 | M |
| LiGolS9 | evm.model.Chr18.633 | 1215 | 404 | 46.12 | 9.22 | 94.36 | 51.32 | -0.071 | CP |
| LiGolS10 | evm.model.Chr22.379 | 1143 | 380 | 42.83 | 8.32 | 90.79 | 49.38 | -0.138 | V |
| LiGolS11 | evm.model.Chr23.402 | 1167 | 388 | 43.97 | 9.36 | 88.97 | 57.29 | -0.151 | C |
| LiGolS12 | evm.model.Chr23.618 | 1149 | 382 | 43.30 | 8.85 | 94.40 | 48.35 | -0.109 | CP |
| LiGolS13 | evm.model.Chr24.816 | 1038 | 345 | 38.60 | 7.69 | 92.75 | 43.61 | -0.027 | CP |
Table 1 Molecular characterization of the LiGolS genes
| Gene name | Gene ID | Length (bp) | Number of amino acids (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Aliphatic index | Instability index | GRAVY | Subcelluar location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiGolS1 | evm.model.Chr1.208 | 1215 | 404 | 46.00 | 9.45 | 92.20 | 57.70 | -0.086 | C |
| LiGolS2 | evm.model.Chr3.1524 | 1146 | 381 | 42.91 | 8.71 | 82.10 | 49.57 | -0.263 | CP |
| LiGolS3 | evm.model.Chr4.803 | 990 | 329 | 37.72 | 4.75 | 78.81 | 50.39 | -0.329 | C |
| LiGolS4 | evm.model.Chr4.806 | 990 | 329 | 37.85 | 4.78 | 78.51 | 48.28 | -0.338 | C |
| LiGolS5 | evm.model.Chr5.968 | 984 | 327 | 37.69 | 4.76 | 80.76 | 53.39 | -0.318 | C |
| LiGolS6 | evm.model.Chr8.101 | 1050 | 349 | 39.71 | 8.16 | 90.32 | 47.76 | -0.148 | CP |
| LiGolS7 | evm.model.Chr8.200 | 1164 | 387 | 43.06 | 7.63 | 87.93 | 44.71 | -0.095 | CP |
| LiGolS8 | evm.model.Chr10.348 | 1125 | 374 | 42.24 | 9.11 | 93.56 | 49.52 | -0.062 | M |
| LiGolS9 | evm.model.Chr18.633 | 1215 | 404 | 46.12 | 9.22 | 94.36 | 51.32 | -0.071 | CP |
| LiGolS10 | evm.model.Chr22.379 | 1143 | 380 | 42.83 | 8.32 | 90.79 | 49.38 | -0.138 | V |
| LiGolS11 | evm.model.Chr23.402 | 1167 | 388 | 43.97 | 9.36 | 88.97 | 57.29 | -0.151 | C |
| LiGolS12 | evm.model.Chr23.618 | 1149 | 382 | 43.30 | 8.85 | 94.40 | 48.35 | -0.109 | CP |
| LiGolS13 | evm.model.Chr24.816 | 1038 | 345 | 38.60 | 7.69 | 92.75 | 43.61 | -0.027 | CP |
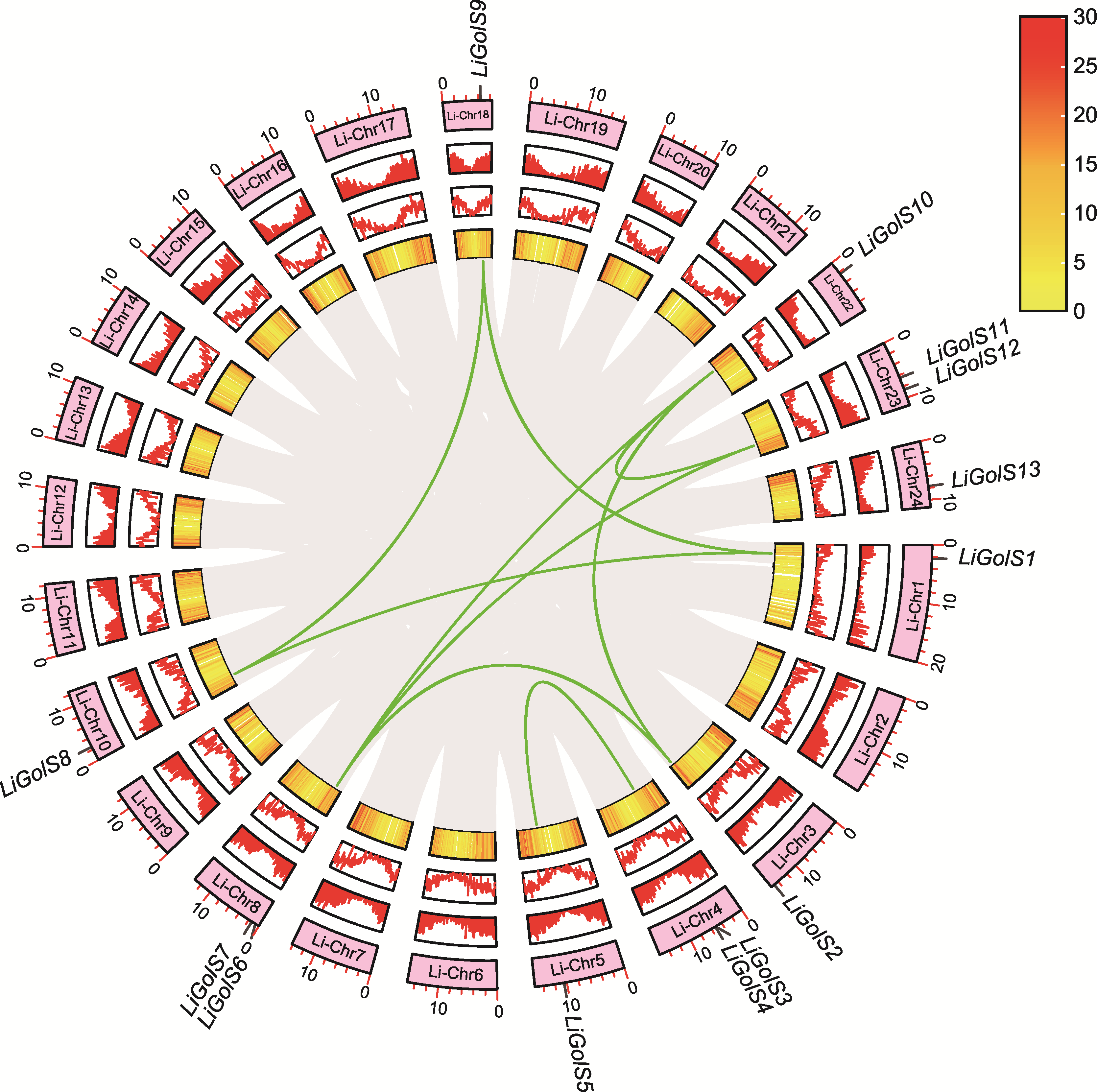
Figure 2 Collinearity analysis of LiGolS genes The ring, from the outside to the inside, represents the location of genes on chromosomes, gene density and collinear regions (the green lines represent LiGolS genes).
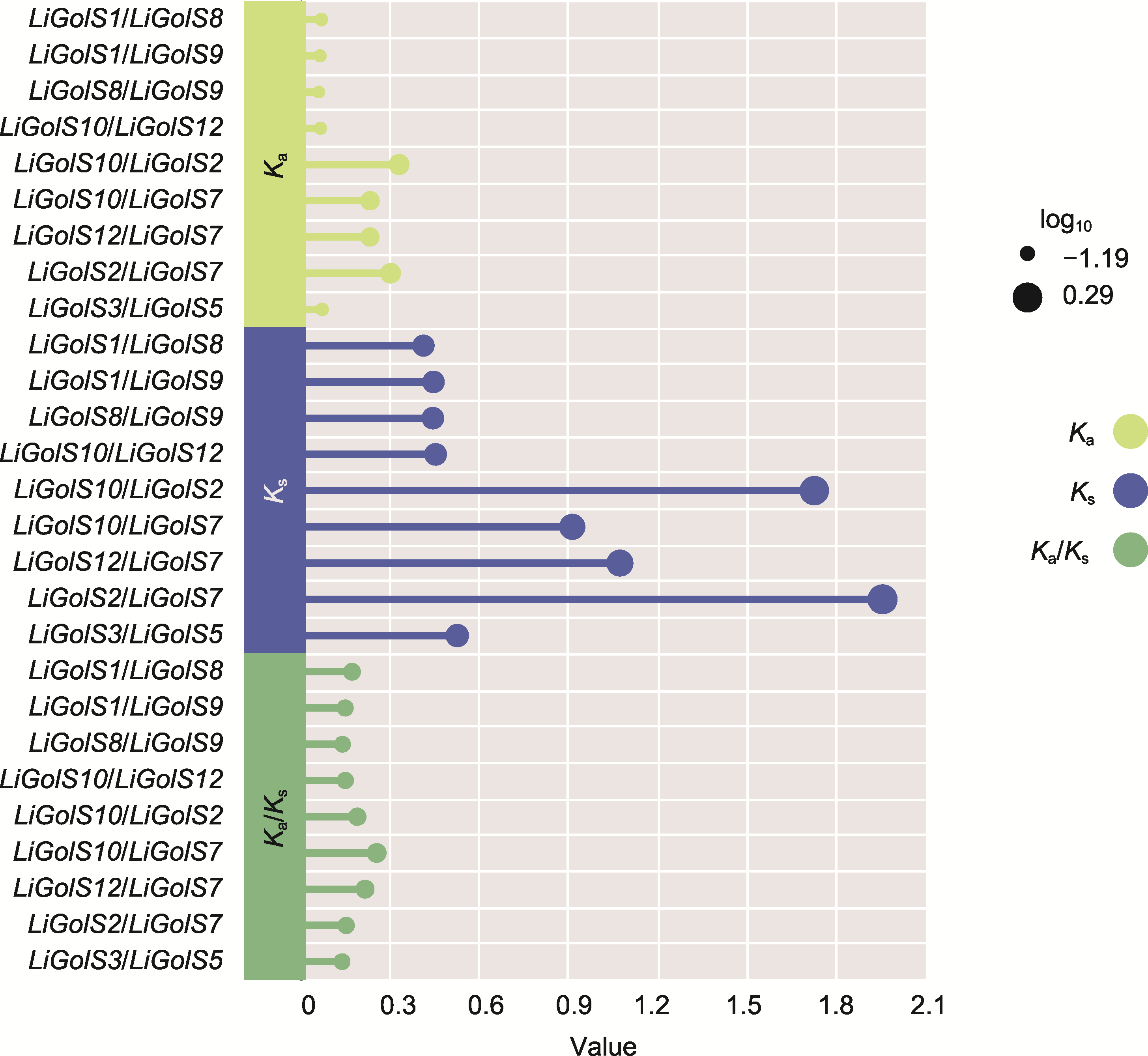
Figure 3 The ratio of non-synonymous (Ka), synonymous (Ks) and Ka/Ks of LiGolS genes The evolutionary pressure of genes can be inferred by calculating the Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks. The Ka and Ks values of LiGolS genes were calculated using the Simple Ka/Ks_Calculator program of TBtools v2.119. Each circle on the chart represents a collinearity gene pair, and the length of the rod corresponds to the Ka, Ks, and Ka/Ks values at a specific site.
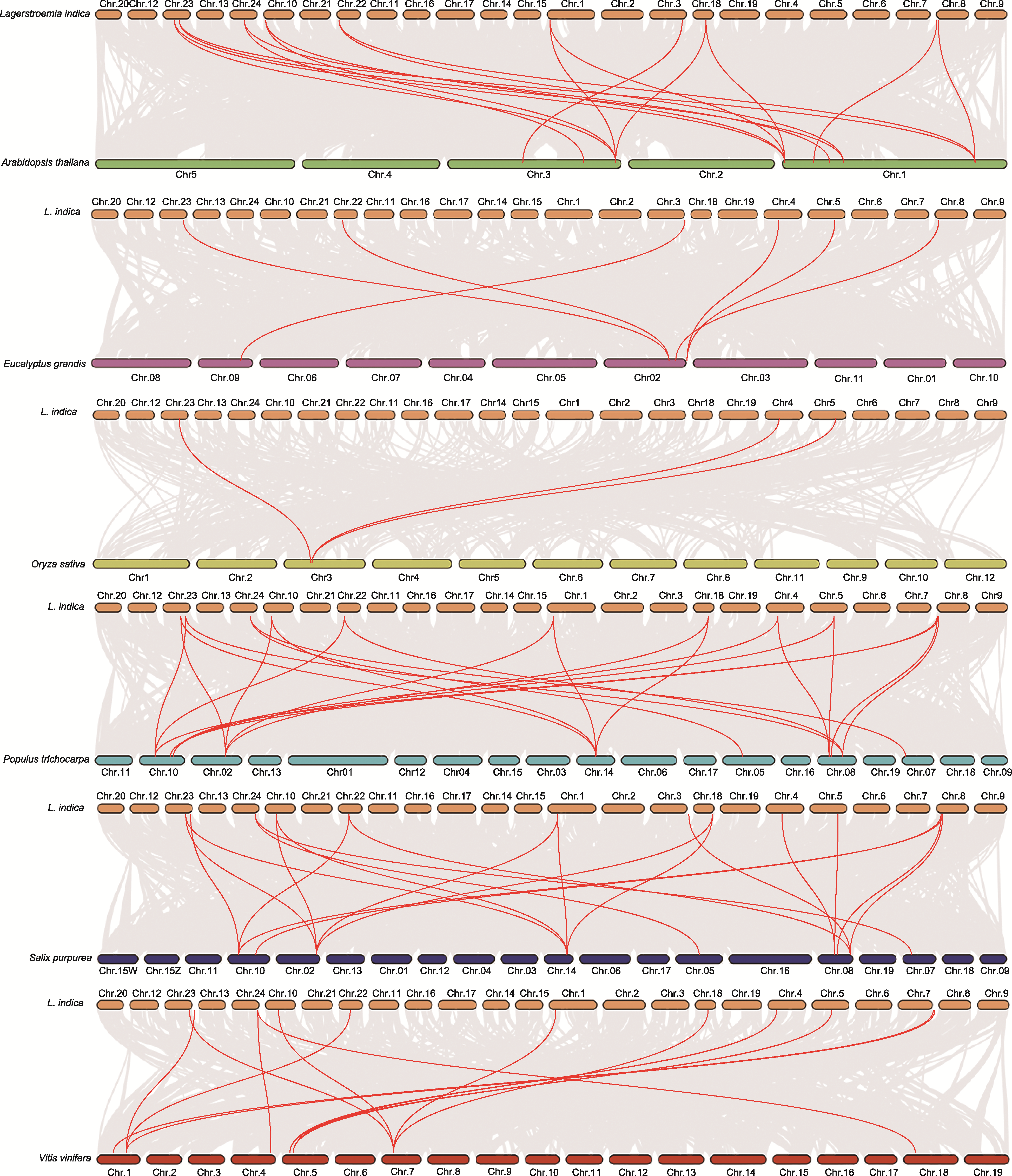
Figure 4 Collinearity analysis of GolS genes among different species The gray lines represent collinear gene pairs, the red lines represent collinear GolS gene pairs. The chromosomes are represented by rectangles of different colors. Orange: Lagerstroemia indica; Green: Arabidopsis thaliana; Purple: Eucalyptus grandis; Yellow: Oryza sativa; Sky blue: Populus trichocarpa; Blue: Salix purpurea; Red: Vitis vinifera
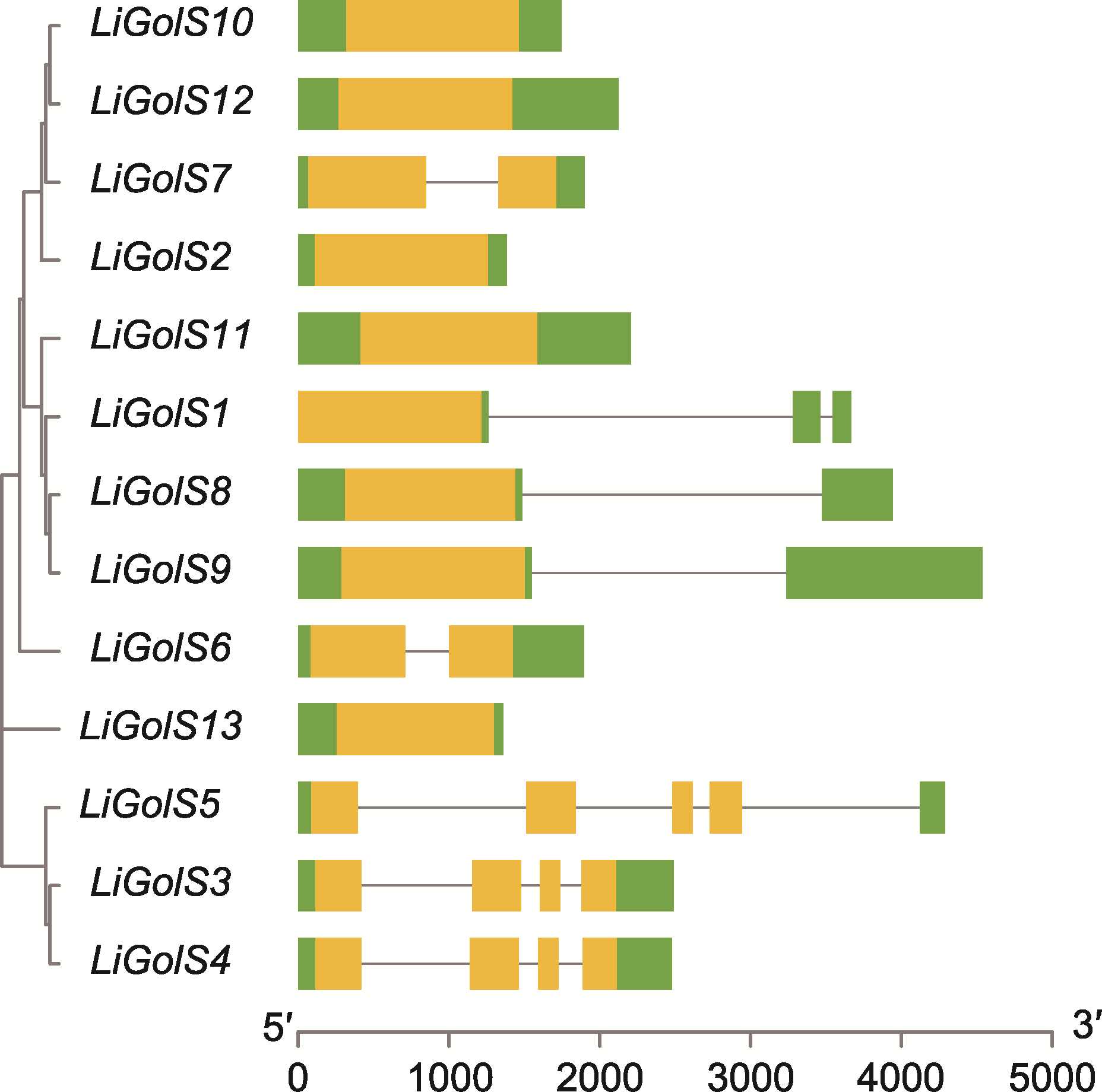
Figure 5 Gene structure of 13 LiGolS genes Untranslated regions (UTRs) are represented by green rectangles, exons are represented by yellow rectangles, and introns are represented by black lines.
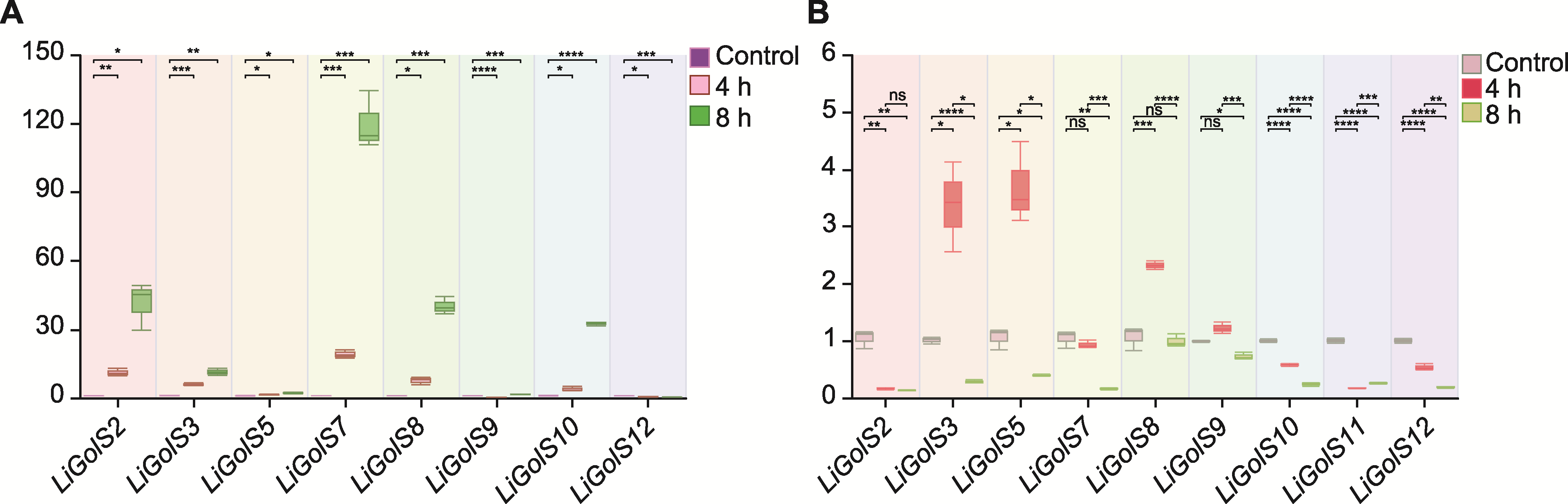
Figure 9 Analysis of LiGolS gene expression patterns under salt stress (A) Expression levels of LiGolS genes in the leaves; (B) Expression levels of LiGolS genes in the roots. ns means no statistical significance. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001; **** P<0.0001
| [1] | Artimo P, Jonnalagedda M, Arnold K, Baratin D, Csardi G, de Castro E, Duvaud S, Flegel V, Fortier A, Gasteiger E, Grosdidier A, Hernandez C, Ioannidis V, Kuznetsov D, Liechti R, Moretti S, Mostaguir K, Redaschi N, Rossier G, Xenarios I, Stockinger H (2012). ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res 40, W597-W603. |
| [2] | Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW (2006). MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 34, W369-W373. |
| [3] | Bateman A, Coin L, Durbin R, Finn RD, Hollich V, Griffiths-Jones S, Khanna A, Marshall M, Moxon S, Sonnhammer ELL, Studholme DJ, Yeats C, Eddy SR (2004). The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 32, D138-D141. |
| [4] | Chen CJ, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He YH, Xia R (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit develo- a)ped for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13, 1194-1202. |
| [5] | Chou KC, Shen HB (2010). Plant-mPLoc: a top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS One 5, e11335. |
| [6] |
da Silveira Falavigna V, Porto DD, Miotto YE, dos Santos HP, de Oliveira PR, Margis-Pinheiro M, Pasquali G, Revers LF (2018). Evolutionary diversification of galactinol synthases in Rosaceae: adaptive roles of galactinol and raffinose during apple bud dormancy. J Exp Bot 69, 1247-1259.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | ElSayed AI, Rafudeen MS, Golldack D (2014). Physiological aspects of raffinose family oligosaccharides in plants: protection against abiotic stress. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 16, 1-8. |
| [8] | Fan YH, Yu MN, Liu M, Zhang R, Sun W, Qian MC, Duan HC, Chang W, Ma JQ, Qu CM, Zhang K, Lei B, Lu K (2017). Genome-wide identification, evolutionary and expression analyses of the GALACTINOL SYNTHASE gene family in rapeseed and tobacco. Int J Mol Sci 18, 2768. |
| [9] | Filiz E, Ozyigit II, Vatansever R (2015). Genome-wide identification of galactinol synthase (GolS) genes in Solanum lycopersicum and Brachypodium distachyon. Comput Biol Chem 58, 149-157. |
| [10] | Gawłowska M, Święcicki W, Lahuta L, Kaczmarek Z (2017). Raffinose family oligosaccharides in seeds of Pisum wild taxa, type lines for seed genes, domesticated and advanced breeding materials. Genet Resour Crop Evol 64, 569-578. |
| [11] | Gu L, Zhang YM, Zhang MS, Li T, Dirk LMA, Downie B, Zhao TY (2016). ZmGOLS2, a target of transcription factor ZmDREB2A, offers similar protection against abiotic stress as ZmDREB2A. Plant Mol Biol 90, 157-170. |
| [12] |
Guerra D, Crosatti C, Khoshro HH, Mastrangelo AM, Mica E, Mazzucotelli E (2015). Post-transcriptional and post-translational regulations of drought and heat response in plants: a spider's web of mechanisms. Front Plant Sci 6, 57.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Guo ZJ, Ma DN, Li J, Wei MY, Zhang LD, Zhou LC, Zhou XX, He SS, Wang L, Shen YJ, Li QQ, Zheng HL (2022). Genome-wide identification and characterization of aquaporins in mangrove plant Kandelia obovata and its role in response to the intertidal environment. Plant Cell Environ 45, 1698-1718. |
| [14] | Huang TW, Luo XL, Fan ZP, Yang YN, Wan W (2021). Genome-wide identification and analysis of the sucrose synthase gene family in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Gene 769, 145191. |
| [15] |
Kollist H, Zandalinas SI, Sengupta S, Nuhkat M, Kangasjärvi J, Mittler R (2019). Rapid responses to abiotic stress: priming the landscape for the signal transduction network. Trends Plant Sci 24, 25-37.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 325-327. |
| [17] | Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2012). SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 40, D302-D305. |
| [18] | Liu D, Wang KA, Ni P, Wang QY, Zhu K, Wei WL (2022). Identification of soybean GolS gene family and analysis of expression patterns under salt and drought stresses. Chin J Biotechnol 38, 3757-3772. (in Chinese) |
| 刘丹, 王柯蔼, 倪蓬, 王秋艳, 朱康, 危文亮 (2022). 大豆GolS基因家族鉴定及盐旱胁迫下的表达分析. 生物工程学报 38, 3757-3772. | |
| [19] | Liu YD, Zhang L, Chen LJ, Ma H, Ruan YY, Xu T, Xu CQ, He Y, Qi MF (2016). Molecular cloning and expression of an encoding galactinol synthase gene (AnGolS1) in seedling of Ammopiptanthus nanus. Sci Rep 6, 36113. |
| [20] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCTmethod. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Montillet JL, Chamnongpol S, Rustérucci C, Dat J, van de Cotte B, Agnel JP, Battesti C, Inzé D, Van Breusegem F, Triantaphylidès C (2005). Fatty acid hydroperoxides and H2O2 in the execution of hypersensitive cell death in tobacco leaves. Plant Physiol 138, 1516-1526.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Obata T, Fernie AR (2012). The use of metabolomics to dissect plant responses to abiotic stresses. Cell Mol Life Sci 69, 3225-3243.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Panikulangara TJ, Eggers-Schumacher G, Wunderlich M, Stransky H, Schöffl F (2004). Galactinol synthase1. A novel heat shock factor target gene responsible for heat- induced synthesis of raffinose family oligosaccharides in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136, 3148-3158. |
| [24] | Sami F, Yusuf M, Faizan M, Faraz A, Hayat S (2016). Role of sugars under abiotic stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 109, 54-61. |
| [25] |
Saravitz DM, Pharr DM, Carter TE (1987). Galactinol synthase activity and soluble sugars in developing seeds of four soybean genotypes. Plant Physiol 83, 185-189.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Selvaraj MG, Ishizaki T, Valencia M, Ogawa S, Dedicova B, Ogata T, Yoshiwara K, Maruyama K, Kusano M, Saito K, Takahashi F, Shinozaki K, Nakashima K, Ishitani M (2017). Overexpression of an Arabidopsis thaliana galactinol synthase gene improves drought tolerance in transgenic rice and increased grain yield in the field. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 1465-1477.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Sengupta S, Mukherjee S, Parween S, Majumder AL (2012). Galactinol synthase across evolutionary diverse taxa: functional preference for higher plants? FEBS Lett 586, 1488-1496.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Sprenger N, Keller F (2000). Allocation of raffinose family oligosaccharides to transport and storage pools in Ajuga reptans: the roles of two distinct galactinol synthases. Plant J 21, 249-258.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Taji T, Ohsumi C, Iuchi S, Seki M, Kasuga M, Kobayashi M, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2002). Important roles of drought- and cold-inducible genes for galactinol synthase in stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 29, 417-426. |
| [30] | Verma SS, Chinnusamy V, Bansa KC (2008). A simplified floral dip method for transformation of Brassica napus and B. carinata. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 17, 197-200. |
| [31] | Vinson CC, Mota APZ, Porto BN, Oliveira TN, Sampaio I, Lacerda AL, Danchin EGJ, Guimaraes PM, Williams TCR, Brasileiro ACM (2020). Characterization of raffinose metabolism genes uncovers a wild Arachis galactinol synthase conferring tolerance to abiotic stresses. Sci Rep 10, 15258. |
| [32] | Wang LX, Lin YX, Hou GY, Yang M, Peng YT, Jiang YY, He CX, She MS, Chen Q, Li MY, Zhang Y, Zhang YT, Wang Y, He W, Wang XR, Tang HR, Luo Y (2024). A histone deacetylase, FaSRT1-2, plays multiple roles in regulating fruit ripening, plant growth and stresses resistance of cultivated strawberry. Plant Cell Environ 47, 2258-2273. |
| [33] |
You J, Wang YY, Zhang YJ, Dossa K, Li DH, Zhou R, Wang LH, Zhang XR (2018). Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of genes involved in raffinose accumulation in sesame. Sci Rep 8, 4331.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Yu CM, Liu GY, Qin J, Wan X, Guo AF, Wei H, Chen YH, Lian BL, Zhong F, Zhang J (2024). Genomic and transcriptomic studies on flavonoid biosynthesis in Lagerstroemia indica. BMC Plant Biol 24, 171. |
| [35] | Zhang Z, Li J, Zhao XQ, Wang J, Wong GKS, Yu J (2006). KaKs_calculator: calculating Ka and Ks through model selection and model averaging. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 4, 259-263. |
| [36] | Zhou Y, Liu Y, Wang SS, Shi C, Zhang R, Rao J, Wang X, Gu XG, Wang YS, Li DX, Wei CL (2017). Molecular cloning and characterization of galactinol synthases in Camellia sinensis with different responses to biotic and abiotic stressors. J Agric Food Chem 65, 2751-2759. |
| [37] | Zhuo CL, Wang T, Lu SY, Zhao YQ, Li XG, Guo ZF (2013). A cold responsive galactinol synthase gene from Medicago falcata (MfGolS1) is induced by myo-inositol and confers multiple tolerances to abiotic stresses. Physiol Plant 149, 67-78. |
| [38] | Zuther E, Büchel K, Hundertmark M, Stitt M, Hincha DK, Heyer AG (2004). The role of raffinose in the cold acclimation response of Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 576, 169-173. |
| [1] | Jinyu Du, Zhen Sun, Yanlong Su, Heping Wang, Yaling Liu, Zhenying Wu, Feng He, Yan Zhao, Chunxiang Fu. Identification and Functional Analysis of an Agropyron mongolicum Caffeic Acid 3-O-methyltransferase Gene AmCOMT1 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 383-396. |
| [2] | Feifei Wang, Zhenxiang Zhou, Yi Hong, Yangyang Gu, Chao Lü, Baojian Guo, Juan Zhu, Rugen Xu. Identification of the NF-YC Genes in Hordeum vulgare and Expression Analysis Under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 140-149. |
| [3] | Qi Zhang, Wenjing Zhang, Xiankai Yuan, Ming Li, Qiang Zhao, Yanli Du, Jidao Du. The Regulatory Mechanism of Melatonin on Nucleic Acid Repairing of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) at the Sprout Stage Under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 108-121. |
| [4] | Nan Zhang,Ziguang Liu,Shichen Sun,Shengyi Liu,Jianhui Lin,Yifang Peng,Xiaoxu Zhang,He Yang,Xi Cen,Juan Wu. Response of AtR8 lncRNA to Salt Stress and Its Regulation on Seed Germination in Arabidopsis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 421-429. |
| [5] | Dongdong Cao,Shanyu Chen,Yebo Qin,Huaping Wu,Guanhai Ruan,Yutao Huang. Regulatory Mechanism of Salicylic Acid on Seed Germination Under Salt Stress in Kale [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(1): 49-61. |
| [6] | Lulu Li,Wenchao Yin,Mei Niu,Wenjing Meng,Xiaoxing Zhang,Hongning Tong. Functional Analysis of Brassinosteroids in Salt Stress Responses in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 185-193. |
| [7] | Shuhua Guo, Yongjiang Sun, Yanjie Niu, Ning Han, Heng Zhai, Yuanpeng Du. Effect of Alkaline Salt Stress on Photosystem Activity of Grape F1 Generation Hybrids [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(2): 196-202. |
| [8] | Chen Xu, Xiaolong Liu, Qian Li, Fenglou Ling, Zhihai Wu, Zhian Zhang. Effect of Salt Stress on Photosynthesis and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics of Rice Leaf for Nitrogen Levels [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(2): 185-195. |
| [9] | Cheng Chen, Aiwu Dong, Wei Su. Histone Chaperone AtHIRA is Involved in Somatic Homologous Recombination and Salinity Response in Arabidopsis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(1): 42-50. |
| [10] | Baoling Liu, Li Zhang, Yan Sun,Jinai Xue, Changyong Gao, Lixia Yuan, Jiping Wang, Xiaoyun Jia, Runzhi Li. Genome-wide Characterization of bZIP Transcription Factors in Foxtail Millet and Their Expression Profiles in Response to Drought and Salt Stresses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(4): 473-487. |
| [11] | Lin Qi, Xinfu Bai, Weihao Niu, Zhenhua Zhang. Effect of Rhizosphere Ventilation on Growth of Cotton Seedlings Under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(1): 16-23. |
| [12] | Qiong Jiang, Youning Wang, Lixiang Wang, Zhengxi Sun, Xia Li. Validation of Reference Genes for Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis in Soybean Root Tissue under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(6): 754-764. |
| [13] | Shasha Chen, Zhuanzhuan He, Shengxiu Jiang, Jiajia Xing, Xiuyun Lü, Haiyan Lan. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Calcium-dependent Phosphokinase Genes in Chenopodium album Under Stresses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2014, 49(2): 139-149. |
| [14] | Zhangxiong Han, Li Li, Xinwen Xu, Xiangfang Lü, Hongxia Yue, Zhen Bian, Lizheng Li. Effect of NaCl on Physiological Features of 4 Legume Seedlings in Desert Areas of Xinjiang, China [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(5): 491-499. |
| [15] | Yan Liu, Lijing Xing, Junhua Li, Shaojun Dai. Rice B-box Zinc Finger Protein OsBBX25 is Involved in the Abiotic Response [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(4): 366-378. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||