

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2015, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 754-764.DOI: 10.11983/CBB14173 cstr: 32102.14.CBB14173
Previous Articles Next Articles
Qiong Jiang1,2, Youning Wang1, Lixiang Wang1,2, Zhengxi Sun1,2, Xia Li1*
Received:2014-09-22
Accepted:2015-01-14
Online:2015-11-01
Published:2015-09-06
Contact:
Li Xia
About author:? These authors contributed equally to this paper
Qiong Jiang, Youning Wang, Lixiang Wang, Zhengxi Sun, Xia Li. Validation of Reference Genes for Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis in Soybean Root Tissue under Salt Stress[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(6): 754-764.
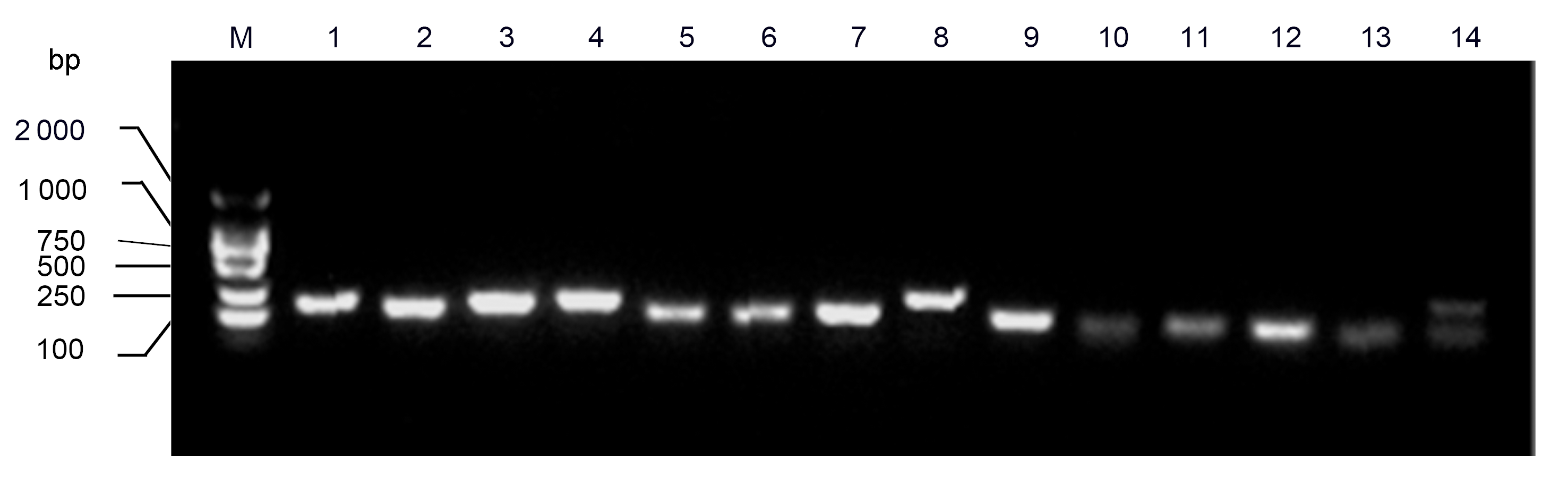
Figure 1 PCR products of fourteen reference genes. M: DNA marker; 1: ACT; 2: ACT2/7; 3: CYP2; 4: ELF1A; 5: ELF1B; 6: F-Box; 7: TUA; 8: UBC2; 9: U6; 10: miR1515a; 11: miR1520c; 12: miR1520d; 13: miR171a; 14: miR171b
| Method | Stability (high→low) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| Δ-CT methods | CYP2 | ACT | ELF1B | UBC2 | ACT2/7 | ELF1A | F-Box | TUA |
| Bestkeeper | ELF1B | TUA | UBC2 | CYP2 | ACT | ACT2/7 | ELF1A | F-Box |
| NormFinder | CYP2 | ACT | ELF1B | UBC2 | ELF1A | ACT2/7 | F-Box | TUA |
| Genorm | ELF1B /UBC2 | CYP2 | ACT | ACT2/7 | F-Box | ELF1A | TUA | |
| Recommended comprehensive ranking | ELF1B | CYP2 | UBC2 | ACT | ACT2/7 | TUA | ELF1A | F-Box |
Table 2 Stability ranking of candidate reference genes
| Method | Stability (high→low) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| Δ-CT methods | CYP2 | ACT | ELF1B | UBC2 | ACT2/7 | ELF1A | F-Box | TUA |
| Bestkeeper | ELF1B | TUA | UBC2 | CYP2 | ACT | ACT2/7 | ELF1A | F-Box |
| NormFinder | CYP2 | ACT | ELF1B | UBC2 | ELF1A | ACT2/7 | F-Box | TUA |
| Genorm | ELF1B /UBC2 | CYP2 | ACT | ACT2/7 | F-Box | ELF1A | TUA | |
| Recommended comprehensive ranking | ELF1B | CYP2 | UBC2 | ACT | ACT2/7 | TUA | ELF1A | F-Box |
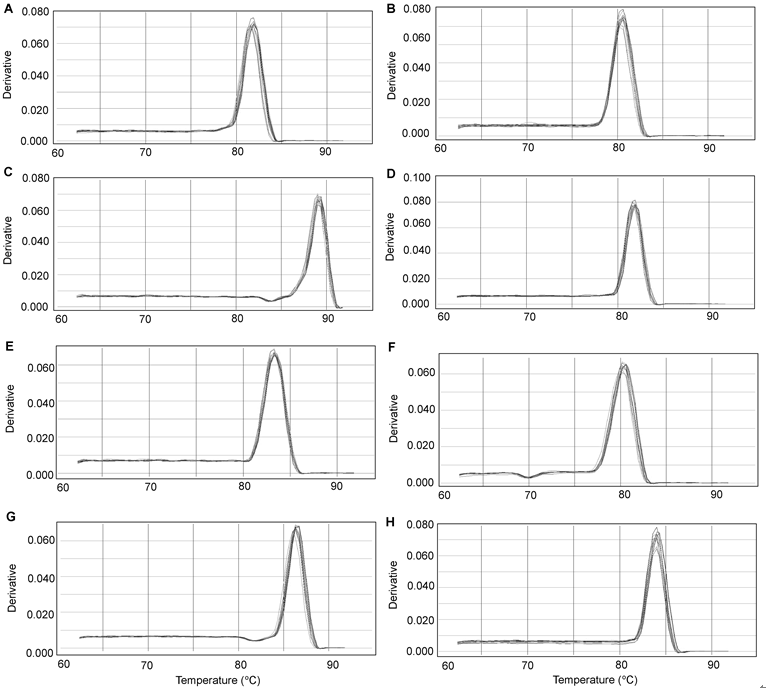
Figure 2 Real-time PCR melting curves of eight reference genes in soybean roots under salt stress(A) ACT; (B) ACT2/7; (C) CYP2; (D) ELF1A; (E) ELF1B; (F) F-Box; (G) TUA; (H) UBC2
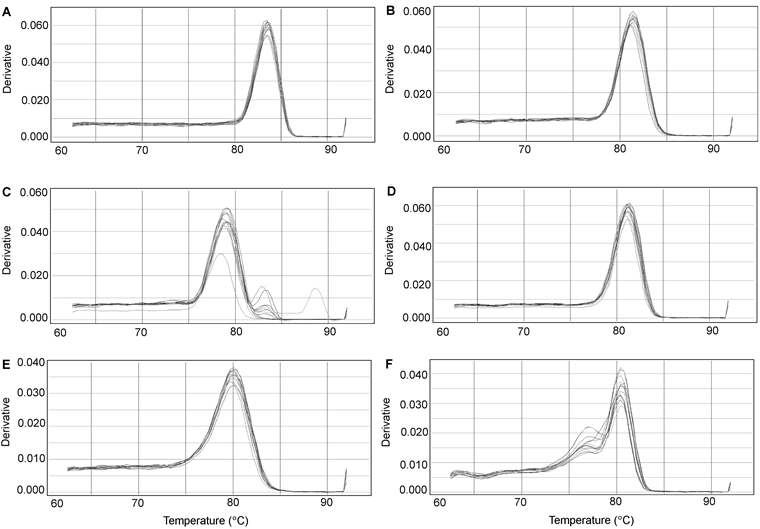
Figure 3 Real-time PCR melting curves of six miRNAs in soybean roots under salt stress(A) U6; (B) miR1515a; (C) miR1520c; (D) miR1520d; (E) miR171a; (F) miR171b
| Method | Stability (high→low) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Δ-CT methods | miR1520c | miR1515a | miR171a | U6 | miR1520d | miR171b |
| Bestkeeper | miR1515a | miR1520c | U6 | miR171a | miR1520d | miR171b |
| NormFinder | miR1520c | miR1515a | miR171a | U6 | miR1520d | miR171b |
| Genorm | U6/miR1520c | miR1515a | miR171a | miR1520d | miR171b | |
| Recommended comprehensive ranking | miR1520c | miR1515a | U6 | miR171a | miR1520d | miR171b |
Table 3 Stability ranking of candidate miRNA
| Method | Stability (high→low) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Δ-CT methods | miR1520c | miR1515a | miR171a | U6 | miR1520d | miR171b |
| Bestkeeper | miR1515a | miR1520c | U6 | miR171a | miR1520d | miR171b |
| NormFinder | miR1520c | miR1515a | miR171a | U6 | miR1520d | miR171b |
| Genorm | U6/miR1520c | miR1515a | miR171a | miR1520d | miR171b | |
| Recommended comprehensive ranking | miR1520c | miR1515a | U6 | miR171a | miR1520d | miR171b |
| [1] | 陈百明, 周小萍 (2004). 中国近期耕地资源与粮食综合生产能力的变化态势. 资源科学 26(5), 38-45. |
| [2] | 黄真池, 欧阳乐军, 张龙, 沙月娥, 曾富华 (2013). 桉属植物内参基因的筛选及评估. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版) 41, 67-72. |
| [3] | 李亮 (2010). 大豆根系盐胁迫基因表达谱的解析和耐盐基因的分离. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 20-54. |
| [4] | 李冉, 李建彩, 周国鑫, 娄永根 (2013). 水稻虫害诱导相关基因实时定量PCR中内参基因的选择. 植物学报 48, 184-191. |
| [5] | 刘金泊, 欧静, 姚富姣, 何磊, 奚耕思, 魏朝明 (2014). 磷化氢诱导下赤拟谷盗实时定量PCR内参基因的筛选. 农业生物技术学报 22, 257-264. |
| [6] | 苏晓娟, 樊保国, 袁丽钗, 崔秀娜, 卢善发 (2013). 实时荧光定量PCR分析中毛果杨内参基因的筛选和验证. 植物学报 48, 507-518. |
| [7] | 许硕 (2011). 野生大豆盐胁迫相关microRNA的功能分析. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 37-54. |
| [8] | 袁伟, 万红建, 杨悦俭 (2012). 植物实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的特点及选择. 植物学报 47, 427-436. |
| [9] | Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004). Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets.Cancer Res 64, 5245-5250. |
| [10] | Brunner AM, Yakovlev IA, Strauss SH (2004). Validating internal controls for quantitative plant gene expression studies.BMC Plant Biol 4, 14. |
| [11] | Bustin SA (2002). Quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR): trends and problems. J Mol Endocrinol 29, 23-39. |
| [12] | Chen CF, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou ZH, Lee DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, Lao KQ, Livak KJ, Guegler KJ (2005). Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT- PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 33, e179. |
| [13] | Czechowski T, Stitt M, Altmann T, Udvardi MK, Scheible WR (2005). Genome-wide identification and testing of superior reference genes for transcript normalization in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 139, 5-17. |
| [14] | Dheda K, Huggett JF, Bustin SA, Johnson MA, Rook G, Zumla A (2004). Validation of housekeeping genes for normalizing RNA expression in real-time PCR. Biotechniques 37, 112-114, 116, 118-119. |
| [15] | Doran JW (2002). Soil health and global sustainability: translating science into practice.Agr Ecosyst Environ 88, 119-127. |
| [16] | Doroudi R, Andersson M, Svensson PA, Ekman M, Jern S, Karlsson L (2005). Methodological studies of multi- ple reference genes as endogenous controls in vascular gene expression studies.Endothelium-J Endoth 12, 215-223. |
| [17] | Feng H, Huang XL, Zhang Q, Wei GR, Wang XJ, Kang ZS (2012). Selection of suitable inner reference genes for relative quantification expression of microRNA in wheat.Plant Physiol Bioch 51,116-122. |
| [18] | Galvan-Ampudia GS, Testerink C (2011). Salt stress signals shape the plant root.Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 296-302. |
| [19] | Guan RX, Qu Y, Guo Y, Yu LL, Liu Y, Jiang JH, Chen JG, Ren YL, Liu GY, Tian L, Jin LG, Liu ZX, Hong HL, Chang RZ, Gilliham M, Qiu LJ (2014). Salinity tolerance in soybean is modulated by natural variation in GmSALT3.Plant J 80, 937-950. |
| [20] | Jain M, Nijhawan A, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2006). Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345, 646-651. |
| [21] | Ji YX, Tu P, Wang K, Gao F, Yang WL, Zhu YG, Li SQ (2014). Defining reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis of anther development in rice. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 46, 305-312. |
| [22] | Jian B, Liu B, Bi YR, Hou WS, Wu CX, Han TF (2008). Validation of internal control for gene expression study in soybean by quantitative real-time PCR.BMC Mol Biol 9, 59. |
| [23] | Jiao YQ, Wang YH, Xue DW, Wang J, Yan MX, Liu GF, Dong GJ, Zeng DL, Lu ZF, Zhu XD, Qian Q, Li JY (2010). Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice.Nat Genet 42, 541-544. |
| [24] | Kim BR, Nam HY, Kim SU, Kim SI, Chang YJ (2003). Normalization of reverse transcription quantitative-PCR with housekeeping genes in rice.Biotechnol Lett 25, 1869-1872. |
| [25] | Kou SJ, Wu XM, Liu Z, Liu YL, Xu Q, Guo WW (2012). Selection and validation of suitable reference genes for miRNA expression normalization by quantitative RT-PCR in citrus somatic embryogenic and adult tissues.Plant Cell Rep 31, 2151-2163. |
| [26] | Kozera B, Rapacz M (2013). Reference genes in real-time PCR.J Appl Genet 54, 391-406. |
| [27] | Kulcheski FR, Marcelino-Guimaraes FC, Nepomuceno AL, Abdelnoor RV, Margis R (2010). The use of microRNAs as reference genes for quantitative polymerase chain reaction in soybean.Anal Biochem 406, 185-192. |
| [28] | Le DT, Aldrich DL, Valliyodan B, Watanabe Y, Van Ha C, Nishiyama R, Guttikonda SK, Quach TN, Gutierrez- Gonzalez JJ, Tran LSP, Nguyen HT (2012). Evaluation of candidate reference genes for normalization of quantitative RT-PCR in soybean tissues under various abiotic stress conditions.PLoS One 7, e46487. |
| [29] | Lee PD, Sladek R, Greenwood CMT, Hudson TJ (2002). Control genes and variability: absence of ubiquitous refe- rence transcripts in diverse mammalian expression studies.Genome Res 12, 292-297. |
| [30] | Li QF, Sun SSM, Yuan DY, Yu HX, Gu MH, Liu QQ (2010). Validation of candidate reference genes for the accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data in rice during seed development. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28, 49-57. |
| [31] | Libault M, Thibivilliers S, Bilgin DD, Radwan O, Benitez M, Clough SJ, Stacey G (2008). Identification of four soybean reference genes for gene expression normalization.Plant Genome 1, 44-54. |
| [32] | Lilly ST, Drummond RSM, Pearson MN, MacDiarmid RM (2011). Identification and validation of reference genes for normalization of transcripts from virus-infected Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24, 294-304. |
| [33] | Lin YL, Lai ZX (2010). Reference gene selection for qPCR analysis during somatic embryogenesis in longan tree.Plant Sci 178, 359-365. |
| [34] | Luo XY, Shi T, Sun HL, Song J, Ni ZJ, Gao ZH (2014). Selection of suitable inner reference genes for normalisation of microRNA expression response to abiotic stresses by RT-qPCR in leaves, flowers and young stems of pea- ch. Sci Hortic 165, 281-287. |
| [35] | Nakayama TJ, Rodrigues FA, Neumaier N, Marcelino- Guimarães FC, Farias JRB, De Oliveira MCN, Borém A, De Oliveira ACB, Emygdio BM, Nepomuceno AL (2014). Reference genes for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction studies in soybean plants under hypoxic conditions. Genet Mol Res 13, 860-871. |
| [36] | Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004). Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: Bestkeeper- excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26, 509-515. |
| [37] | Ramachandran V, Chen XM (2008). Degradation of micro- RNAs by a family of exoribonucleases in Arabidopsis.Science 321, 1490-1492. |
| [38] | Schmidt GW, Delaney SK (2010). Stable internal reference genes for normalization of real-time RT-PCR in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) during development and abiotic str- ess.Mol Genet Genomics 283, 233-241. |
| [39] | Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA (2000). Effect of experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: validation by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. J Biochem Biophys Methods 46, 69-81. |
| [40] | Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein SL (2006). Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR.BMC Mol Biol 7, 33. |
| [41] | Stolf-Moreira R, De Macedo Lemos EG, Abdelnoor RV, Beneventi MA, Rolla AAP, Pereira SDS, De Oliveira MCN, Nepomuceno AL, Marcelino-Guimarães FC (2011). Identification of reference genes for expression analysis by real-time quantitative PCR in drought-stres- sed soybean.Pesqui Agropecu Bras 46, 58-65. |
| [42] | Thellin O, Zorzi W, Lakaye B, De Borman B, Coumans B, Hennen G, Grisar T, Igout A, Heinen E (1999). Housekeeping genes as internal standards: use and limits. J Biotechnol 75, 291-295. |
| [43] | Turner M, Adhikari S, Subramanian S (2013). Optimizing stem-loop qPCR assays through multiplexed cDNA synthesis of U6 and miRNAs.Plant Signal Behav 8, e24918. |
| [44] | Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002). Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geo- metric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3, research 0034.1-0034.11. |
| [45] | Wang Y, Yu KF, Poysa V, Shi C, Zhou YH (2012). Selection of reference genes for normalization of qRT-PCR analysis of differentially expressed genes in soybean exposed to cadmium. Mol Biol Rep 39, 1585-1594. |
| [46] | Zhou L, Wang C, Liu RF, Han Q, Vandeleur RK, Du J, Tyerman S, Shou HX (2014). Constitutive overexpression of soybean plasma membrane intrinsic protein Gm- PIP1;6 confers salt tolerance.BMC Plant Biol 14, 181. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||