

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 210-217.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15053 cstr: 32102.14.CBB15053
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Danlong Jing, Yan Xia, Shougong Zhang, Junhui Wang*( )
)
Received:2015-03-12
Accepted:2015-07-14
Online:2016-03-01
Published:2016-03-31
Contact:
E-mail: Danlong Jing, Yan Xia, Shougong Zhang, Junhui Wang. Expression Analysis of B-class MADS-box Genes from Catalpa speciosa[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(2): 210-217.
| Primer name | Primer sequences (5′→ 3′) |
|---|---|
| FLAP3F | GCAAACTCAAATCTTGAAAATC |
| FLAP3R | CACATTATGCGACAGAATTCAT |
| FLPIF | GAGAACCAAATTAAGAGAAAGACCA |
| FLPIR | GCACCAAGACAACCACATACGTA |
| RTactinF | ATGATGCTCCAAGAGCTGTG |
| RTactinR | AGCAAGATCGAGACGTAGGA |
| RTAP3F | TACATCAGCCCCATTATAACGA |
| RTAP3R | TTATTCAAGCAAGGCAAACGTG |
| RTPIF | ACCACAAGTTGTCTGGGAAGAG |
| RTPIR | AATCTGCAACTCCCTGATGATC |
| qRTactinF | GATGATGCTCCAAGAGCTGT |
| qRTactinR | TCCATATCATCCCAGTTGCT |
| qRTAP3F | CTTGAAGAAGCTGAAGGAGGTT |
| qRTAP3R | CTTGCTGGTATCAATCTGGTTG |
| qRTPIF | GAGAATGACAGCATGCAGATTG |
| qRTPIR | ATTATCGTCCATTGGATCCAGA |
Table 1 The sequences of primers
| Primer name | Primer sequences (5′→ 3′) |
|---|---|
| FLAP3F | GCAAACTCAAATCTTGAAAATC |
| FLAP3R | CACATTATGCGACAGAATTCAT |
| FLPIF | GAGAACCAAATTAAGAGAAAGACCA |
| FLPIR | GCACCAAGACAACCACATACGTA |
| RTactinF | ATGATGCTCCAAGAGCTGTG |
| RTactinR | AGCAAGATCGAGACGTAGGA |
| RTAP3F | TACATCAGCCCCATTATAACGA |
| RTAP3R | TTATTCAAGCAAGGCAAACGTG |
| RTPIF | ACCACAAGTTGTCTGGGAAGAG |
| RTPIR | AATCTGCAACTCCCTGATGATC |
| qRTactinF | GATGATGCTCCAAGAGCTGT |
| qRTactinR | TCCATATCATCCCAGTTGCT |
| qRTAP3F | CTTGAAGAAGCTGAAGGAGGTT |
| qRTAP3R | CTTGCTGGTATCAATCTGGTTG |
| qRTPIF | GAGAATGACAGCATGCAGATTG |
| qRTPIR | ATTATCGTCCATTGGATCCAGA |
| Length of flower buds (mm) | The stages and morphology of C. speciosa |
|---|---|
| 1−3 | In early stage of floral buds formation, the petals and stamens differentiated and elongated rapidly |
| 4−13 | At flower buds elongation stage, the size of petals and stamens increased rapidly |
| 30−55 | At flowering phase, the stamens reached mature stage, and the petals completely opened |
Table 2 The size of the flower buds of Catalpa speciosa
| Length of flower buds (mm) | The stages and morphology of C. speciosa |
|---|---|
| 1−3 | In early stage of floral buds formation, the petals and stamens differentiated and elongated rapidly |
| 4−13 | At flower buds elongation stage, the size of petals and stamens increased rapidly |
| 30−55 | At flowering phase, the stamens reached mature stage, and the petals completely opened |

Figure 2 Comparison of deduced amino acid sequences encoded by CaspAP3 and CaspPI, and related members of AP3 and PI subfamily The first underlined regions represent the MADS domain and the second K domain, the region between the MADS- and K-domain is I domain. The PI-derived motif, euAP3 motif and PI motif are boxed.
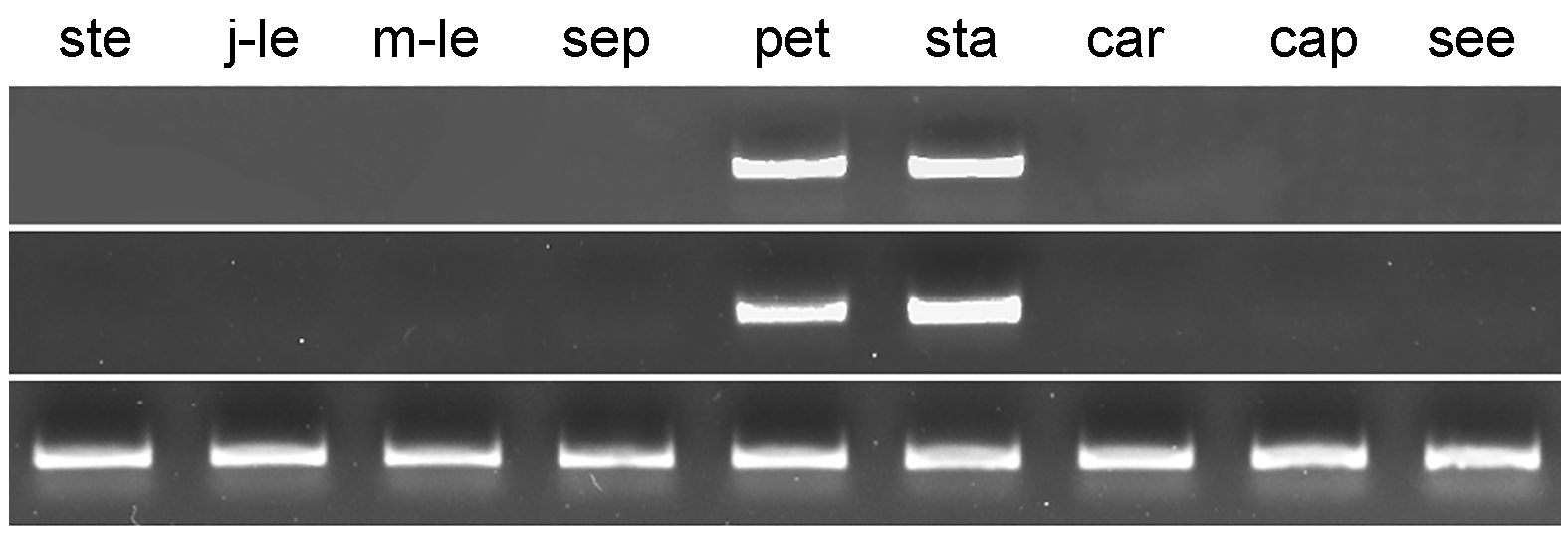
Figure 3 Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of CaspAP3 and CaspPI gene in different tissues of Catalpa speciosa ste: Stem; j-le: Juvenile-leaf; m-le: Mature leaves; sep: Sepal; pet: Petal; sta: Stamen; car: Carpel; cap: Capsule; see: Seed
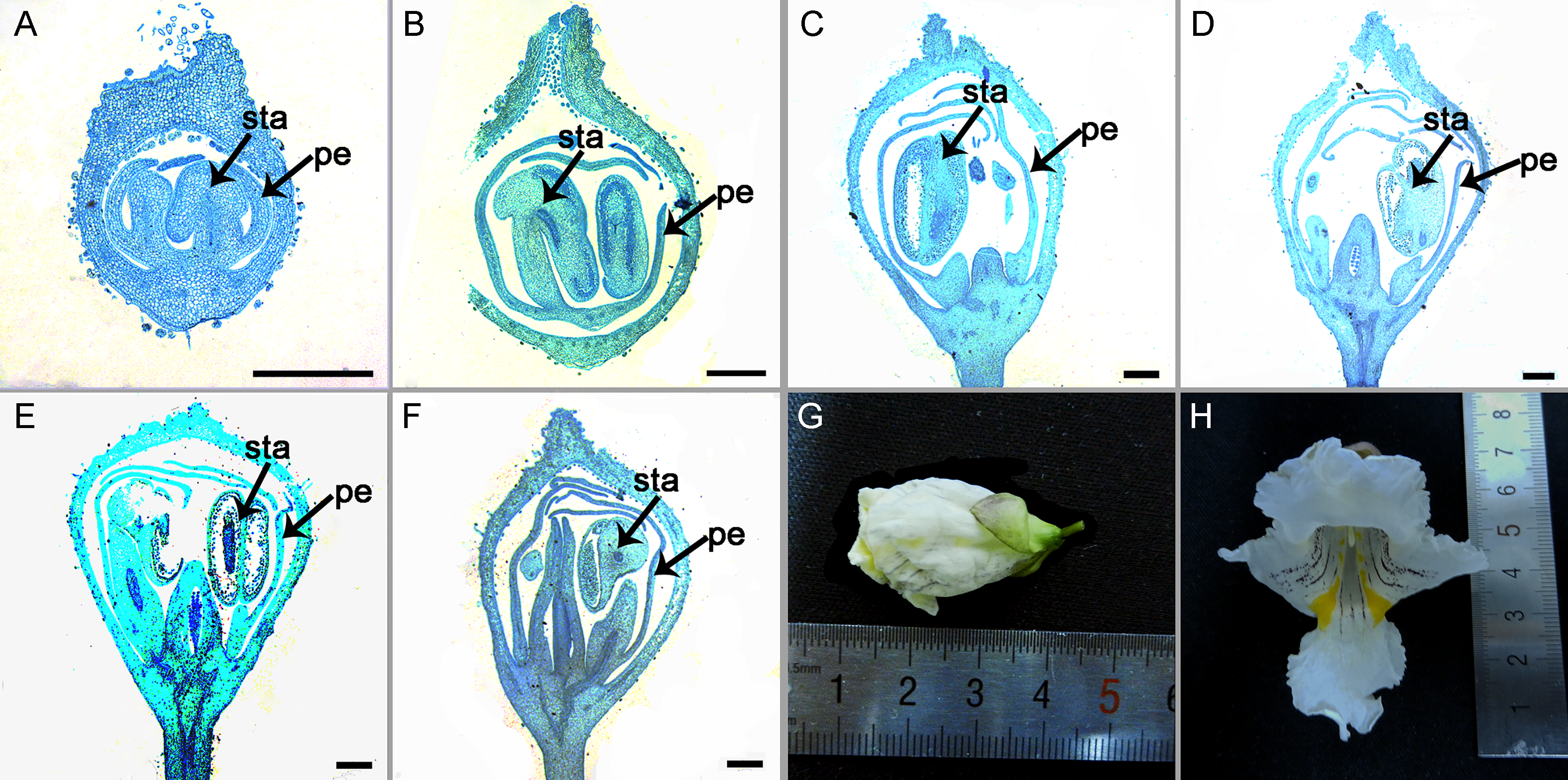
Figure 4 The characterization of the floral organ in Catalpa speciosa (A)−(C) The flower buds of 1−3 mm, the newly differentiated petal and stamen; (D)−(F) The flower buds of 4−13 mm, the sizes of petal and stamen increased rapidly; (G), (H) The flower buds of 30−55 mm, the petal and stamen reached mature stage, and the flowers reached anthesis. pe: Petal; sta: Stamen. Bar=500 μm
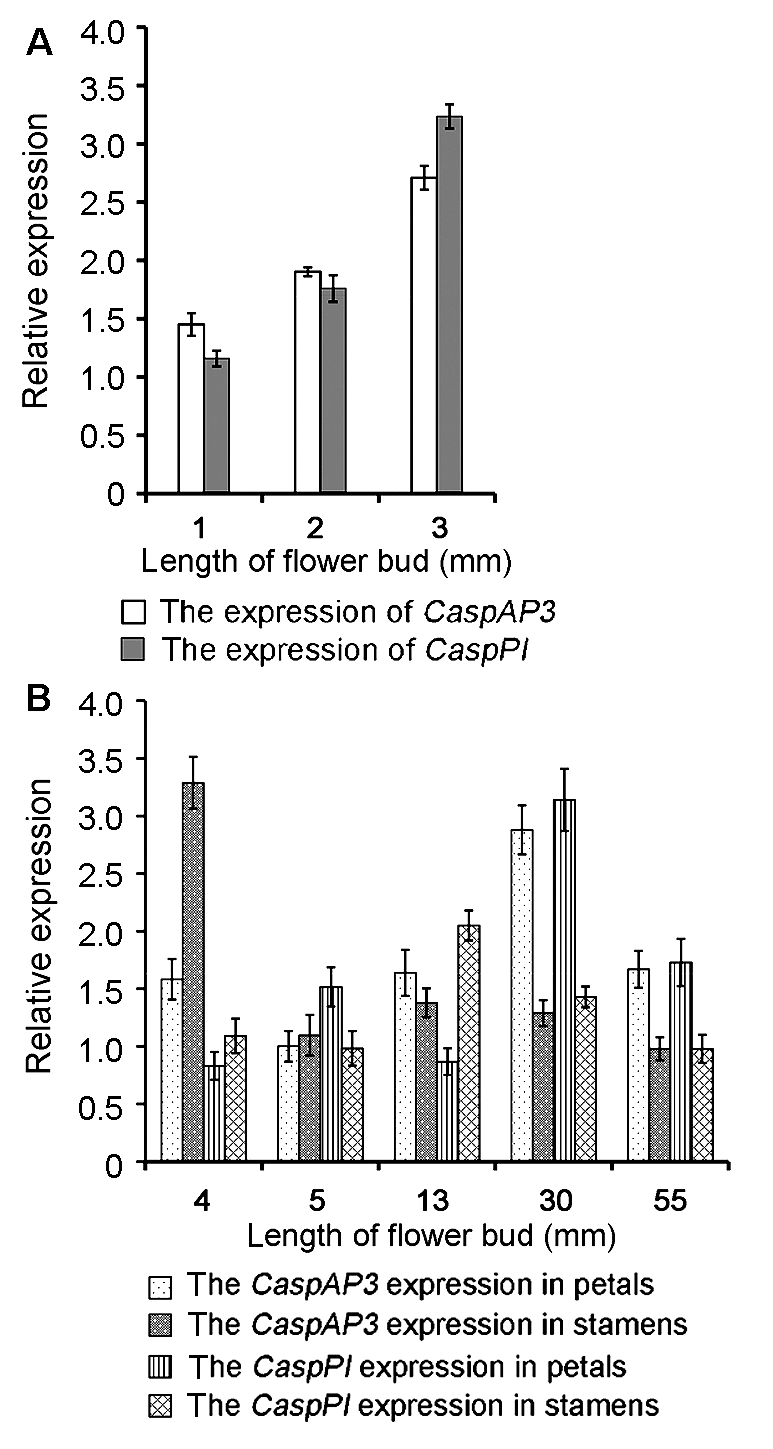
Figure 5 Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of CaspAP3 and CaspPI expressed in floral buds of Catalpa speciosa at different developmental stages (A) Relative expression patterns of CaspAP3 and CaspPI at differentiation stage of flowers; (B) Relative expression patterns of CaspAP3 and CaspPI at elongation and flowering stages of flowers
| [1] | 陈晓 (2002). 黄金树及其在北京的园林应用价值. 北京园林 18, 24-25. |
| [2] | 陈旭辉, 江莎, 古松, 许珂, 王永周, 丁锐, 黄俊哲 (2009). 黄金树花器官发生及发育的形态观察. 园艺学报 36, 285-290. |
| [3] |
李利平, 刘海燕, 陈发菊 (2013). 黄金树大、小孢子发生及雌、雄配子体发育的细胞学观察. 植物研究 33, 145-148.
DOI |
| [4] | 张冰玉, 苏晓华, 周祥明 (2008). 林木花发育的基因调控. 植物学通报 25, 476-482. |
| [5] | Bowman JL (1997). Evolutionary conservation of angiosperm flower development at the molecular and genetic levels. J Biosci 22, 515-527. |
| [6] | Chen MK, Hsieh WP, Yang CH (2012). Functional analysis reveals the possible role of the C-terminal sequences and PI motif in the function of lily (Lilium longiflorum) PISTILLATA (PI) orthologues. J Exp Bot 63, 941-961. |
| [7] |
Endress PK (2011). Evolutionary diversification of the flowers in angiosperms. Am J Bot 98, 370-396.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Goto K, Meyerowitz EM (1994). Function and regulation of the Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene PISTILLATA. Genes Dev 8, 1548-1560. |
| [9] |
Hernández-Hernández T, Martínez-Castilla LP, Alvarez- Buylla ER (2007). Functional diversification of B MADS- box homeotic regulators of flower development: adaptive evolution in protein-protein interaction domains after major gene duplication events. Mol Biol Evol 24, 465-481.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Jack T, Brockman LL, Meyerowitz EM (1992). The homeotic gene APETALA3 of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a MADS box and is expressed in petals and stamens. Cell 68, 683-697.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Jing D, Liu Z, Zhang B, Ma J, Han Y, Chen F (2014). Two ancestral APETALA3homologs from the basal angiosperm Magnolia wufengensis (Magnoliaceae) can affect flower development of Arabidopsis. Gene 537, 100-107. |
| [12] | Jing D, Xia Y, Chen F, Wang Z, Zhang S, Wang J (2015). Ectopic expression of a Catalpa bungei (Bignoniaceae) PISTILLATA homologue rescues the petal and stamen identities in Arabidopsis pi-1 mutant. Plant Sci 231, 40-51. |
| [13] | Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992). The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8, 275-282. |
| [14] | Kim S, Koh J, Yoo MJ, Kong H, Hu Y, Ma H, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2005). Expression of floral MADS-box genes in basal angiosperms: implications on evolution of floral regulators and the perianth. Plant J 43, 724-744. |
| [15] | Kim S, Yoo MJ, Albert VA, Farris JS, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2004). Phylogeny and diversification of B-function MADS- box genes in angiosperms: evolutionary and functional implications of a 260-million-year-old duplication. Am J Bot 91, 2102-2118. |
| [16] | Kramer EM, Di Stilio VS, Schluter PM (2003). Complex patterns of gene duplication in the APETALA3 and PISTILLATA lineages of the Ranunculaceae. Int J Plant Sci 164, 1-11. |
| [17] |
Kramer EM, Dorit RL, Irish VF (1998). Molecular evolution of genes controlling petal and stamen development: duplication and divergence within the APETALA3 and PISTILLATA MADS-box gene lineages. Genetics 149, 765-783.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Krizek BA, Meyerowitz EM (1996). Mapping the protein regions responsible for the functional specificities of the Arabidopsis MADS domain organ-identity proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 4063-4070.
PMID |
| [19] |
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008). MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9, 299-306.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Riechmann JL, Krizek BA, Meyerowitz EM (1996). Dimeri- zation specificity of Arabidopsis MADS domain homeotic proteins APETALA1, APETALA3, PISTILLATA, and AG- AMOUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 4793-4798.
PMID |
| [22] | Soltis DE, Chanderbali AS, Kim S, Buzgo M, Soltis PS (2007). The ABC model and its applicability to basal angiosperms. Ann Bot 100, 155-163. |
| [23] |
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011). MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28, 2731-2739.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Theissen G, Becker A, Di Rosa A, Kanno A, Kim JT, Münster T, Winter KU, Saedler H (2000). A short history of MADS-box genes in plants. Plant Mol Biol 42, 115-149.
PMID |
| [25] | Theissen G, Saedler H (2001). Plant biology—Floral quartets. Nature 409, 469-471. |
| [26] |
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994). CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22, 4673-4680.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Viaene T, Vekemans D, Irish VF, Geeraerts A, Huysmans S, Janssens S, Smets E, Geuten K (2009). Pistillata- duplications as a mode for floral diversification in (Basal) asterids. Mol Biol Evol 26, 2627-2645.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Ziyang Wang, Shengxue Liu, Zhirui Yang, Feng Qin. Genetic Dissection of Drought Resistance in Maize [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [2] | Suowei Wu, Xueli An, Xiangyuan Wan. Molecular Mechanisms of Male Sterility and their Applications in Biotechnology-based Male-sterility Hybrid Seed Production in Maize [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [3] | Qiaoxia Li, Youlong Li, Jigang Li, Chenlong Chen, Kun Sun. Effects of photoperiods on the development of chasmogamous and cleistogamous flowers in Viola monbeigii and V. dissecta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 23484-. |
| [4] | Lumei He, Bojun Ma, Xifeng Chen. Advances on the Executor Resistance Genes in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 671-680. |
| [5] | Fuhui Sun, Huiyi Fang, Xiaohui Wen, Liangsheng Zhang. Phylogenetic and Expression Analysis of MADS-box Gene Family in Rhododendron ovatum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 404-416. |
| [6] | Xia Wang, Wei Yan, Zhiqin Zhou, Zhenyi Chang, Minting Zheng, Xiaoyan Tang, Jianxin Wu. Identification and Mapping of a Rice Male Sterility Mutant ms102 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 42-55. |
| [7] | Jing Lu, Yingnan Chen, Tongming Yin. Research Progress on Sex Determination Genes of Woody Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 90-103. |
| [8] | Wang Yunqian, Su Yanhong, Yang Rui, Li Xin, Li Jing, Zeng Qianchun, Luo Qiong. Rice Blast Resistance of Wild Rice in Yunnan [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(4): 477-486. |
| [9] | Yuanbao Cai, Xiangyan Yang, Guangming Sun, Qiang Huang, Yeqiang Liu, Shaopeng Li, Zhili Zhang. Cloning of Flowering-related Gene AcMADS1 and Characterization of Expression in Tissues of Pineapple (Ananas comosus) [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2014, 49(6): 692-703. |
| [10] | Danlong Jing, Jiang Ma, Bo Zhang, Yiyang Han, Zhixiong Liu, Faju Chen. Expression Analysis of MwAG in Different Organs and Developmental Stages of Magnolia wufengensis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(2): 145-150. |
| [11] | Yujing Wang, Minchun Li, Wang Wu, Hanying Wu, Yinong Xu. Cloning and Characterization of an AP2/EREBP Gene TmAP2-1 from Tetraena mongolica [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(1): 23-33. |
| [12] | Shaofeng Li, Xiaohua Su, Bingyu Zhang. Research Progress in Gene Cloning in Forest Trees [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(1): 79-107. |
| [13] | Zhonghua Wang;*;Tingjie Yu. Research Advances in the Key Enzymes Involved in Rice Starch Quality Regulation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(06): 741-752. |
| [14] | Qijiang Xu;Lufei Guan;Xiaonü Wu;Li Sun;Wenbo Tan;Yuzhe Nie;Yuhua Li. Cloning and Expression Analysis of MADS-box Genes from Lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum) [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(04): 415-429. |
| [15] | Bei Guo;Lei Hu;Xin He;Xuemei Chen*;Xiangning Jiang . Trehalose-6-phosphate Synthase Transgenic Tobacco Enhanced Tolerance to Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(01): 41-49. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||