

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (5): 783-798.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22134 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22134
黄慧梅1, 高永康1, 台玉莹1, 刘超1, 曲德杰1, 汤锐恒1, 王幼宁2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-28
接受日期:2022-10-24
出版日期:2023-09-01
发布日期:2023-09-21
通讯作者:
*E-mail: youningwang@nwafu.edu.cn
作者简介:第一联系人:† 共同第一作者。
基金资助:
Huang Huimei1, Gao Yongkang1, Tai Yuying1, Liu Chao1, Qu Dejie1, Tang Ruiheng1, Wang Youning2( )
)
Received:2022-06-28
Accepted:2022-10-24
Online:2023-09-01
Published:2023-09-21
Contact:
*E-mail: youningwang@nwafu.edu.cn
About author:First author contact:† These authors contributed equally to this paper.
摘要: 氮素作为植物生长发育所需的大量元素, 对植物生长发育及作物产量具有重要作用。施入氮肥是植物及作物的主要氮素来源。面对当下过度施肥造成面源污染加剧的现状, 提高作物氮素利用效率, 实现“减肥增产”的绿色增产增效模式, 是促进我国农业可持续发展及保障国家粮食安全的重要措施。当土壤氮匮缺时, 硝酸盐转运蛋白NRT2家族成员对根系吸收及转运硝酸盐至关重要, 其中NRT2.1在植物缺氮时主要负责根部的硝酸根吸收。该文重点总结了模式植物拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)及重要粮油作物中NRT2家族蛋白特别是NRT2.1的功能及调控机理研究进展, 旨在为后续挖掘NRT2在提高作物产量方面的潜力及分子调控机制研究提供重要依据。
黄慧梅, 高永康, 台玉莹, 刘超, 曲德杰, 汤锐恒, 王幼宁. 硝酸盐转运蛋白NRT2在植物中的功能及分子机制研究进展. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 783-798.
Huang Huimei, Gao Yongkang, Tai Yuying, Liu Chao, Qu Dejie, Tang Ruiheng, Wang Youning. Research Advances in Elucidating the Function and Molecular Mechanism of the Nitrate Transporter 2 (NRT2) Proteins in Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 783-798.
| 基因名 | 位点 | 基因空间表达 | 低氮响应 | 功能 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组织定位 | 亚细胞定位 | |||||
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | ||||||
| AtNRT2.1 | AT1G08090 | 主根 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 介导高亲和硝酸盐吸收 | Orsel et al., |
| AtNRT2.2 | AT1G08100 | 根 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 介导高亲和硝酸盐吸收 | Orsel et al., et al., 2007 |
| AtNRT2.3 | AT5G60780 | 根 | - | 无 | - | Okamoto et al., |
| AtNRT2.4 | AT5G60770 | 主根、侧根及茎的韧皮部 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 在极低浓度硝酸盐下介导NO3-吸收及转运 | Kiba et al., |
| AtNRT2.5 | AT1G12940 | 主根和侧根的根毛区及韧皮部 | 细胞膜 | 抑制 | 氮饥饿下介导NO3-吸收及转运 | Okamoto et al., |
| AtNRT2.6 | AT3G45060 | 在所有组织中均表达, 在根和叶中高表达 | 细胞膜 | 无 | 响应病原菌侵染 | Dechorgnat et al., |
| AtNRT2.7 | AT5G14570 | 种子 | 液泡膜 | 无 | 种子胚中的NO3-积累 | Chopin et al., |
| 水稻(Oryza sativa) | ||||||
| OsNRT2.1 | LOC_Os02g02190 | 主根和侧根 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 介导高亲和硝酸盐吸收 | Feng et al., |
| OsNRT2.2 | LOC_Os02g02170 | 主根和侧根 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 介导高亲和硝酸盐吸收 | Feng et al., |
| OsNRT2.4 | LOC_Os01g36720 | 侧根原基基 部和茎 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 双亲和硝酸盐转运, 介导硝酸盐从源到库的再分配 | Feng et al., |
| OsNRT2.5/O-sNRT2.3a | LOC_Os01g50820 | 根部中柱木质部薄壁细胞 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 在极低浓度硝酸盐下介导NO3-从根部向地上部的长距离运输 | Tang et al., |
| OsNRT2.3b | LOC_Os01g50820 | 茎和叶的韧皮部, 在根中有微弱表达 | 细胞膜 | 无 | 介导NO3-转运, 感知韧皮部细胞的胞质pH值以平衡NO3?和NH4+吸收 | Feng et al., |
| 玉米(Zea mays) | ||||||
| ZmNRT2.1 | GRMZM2G010280_P01 | 根部皮层细胞 | - | 诱导 | - | Trevisan et al., |
| ZmNRT2.2 | GRMZM2G010251_P01 | 皮层、中柱及侧根原基 | - | 诱导 | - | Trevisan et al., |
| ZmNRT2.3 | GRMZM2G163866_P01 | - | - | - | - | Plett et al., |
| ZmNRT2.5 | GRMZM2G455124_P01 | 在根、叶、穗轴、雄穗和苞叶中高表达 | - | 诱导 | - | Fujita et al., Sabermanesh et al., |
表1 拟南芥、水稻和玉米中NRT2成员的研究汇总
Table 1 Summary of identified NRT2 transporters in Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa and Zea mays
| 基因名 | 位点 | 基因空间表达 | 低氮响应 | 功能 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组织定位 | 亚细胞定位 | |||||
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | ||||||
| AtNRT2.1 | AT1G08090 | 主根 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 介导高亲和硝酸盐吸收 | Orsel et al., |
| AtNRT2.2 | AT1G08100 | 根 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 介导高亲和硝酸盐吸收 | Orsel et al., et al., 2007 |
| AtNRT2.3 | AT5G60780 | 根 | - | 无 | - | Okamoto et al., |
| AtNRT2.4 | AT5G60770 | 主根、侧根及茎的韧皮部 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 在极低浓度硝酸盐下介导NO3-吸收及转运 | Kiba et al., |
| AtNRT2.5 | AT1G12940 | 主根和侧根的根毛区及韧皮部 | 细胞膜 | 抑制 | 氮饥饿下介导NO3-吸收及转运 | Okamoto et al., |
| AtNRT2.6 | AT3G45060 | 在所有组织中均表达, 在根和叶中高表达 | 细胞膜 | 无 | 响应病原菌侵染 | Dechorgnat et al., |
| AtNRT2.7 | AT5G14570 | 种子 | 液泡膜 | 无 | 种子胚中的NO3-积累 | Chopin et al., |
| 水稻(Oryza sativa) | ||||||
| OsNRT2.1 | LOC_Os02g02190 | 主根和侧根 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 介导高亲和硝酸盐吸收 | Feng et al., |
| OsNRT2.2 | LOC_Os02g02170 | 主根和侧根 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 介导高亲和硝酸盐吸收 | Feng et al., |
| OsNRT2.4 | LOC_Os01g36720 | 侧根原基基 部和茎 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 双亲和硝酸盐转运, 介导硝酸盐从源到库的再分配 | Feng et al., |
| OsNRT2.5/O-sNRT2.3a | LOC_Os01g50820 | 根部中柱木质部薄壁细胞 | 细胞膜 | 诱导 | 在极低浓度硝酸盐下介导NO3-从根部向地上部的长距离运输 | Tang et al., |
| OsNRT2.3b | LOC_Os01g50820 | 茎和叶的韧皮部, 在根中有微弱表达 | 细胞膜 | 无 | 介导NO3-转运, 感知韧皮部细胞的胞质pH值以平衡NO3?和NH4+吸收 | Feng et al., |
| 玉米(Zea mays) | ||||||
| ZmNRT2.1 | GRMZM2G010280_P01 | 根部皮层细胞 | - | 诱导 | - | Trevisan et al., |
| ZmNRT2.2 | GRMZM2G010251_P01 | 皮层、中柱及侧根原基 | - | 诱导 | - | Trevisan et al., |
| ZmNRT2.3 | GRMZM2G163866_P01 | - | - | - | - | Plett et al., |
| ZmNRT2.5 | GRMZM2G455124_P01 | 在根、叶、穗轴、雄穗和苞叶中高表达 | - | 诱导 | - | Fujita et al., Sabermanesh et al., |
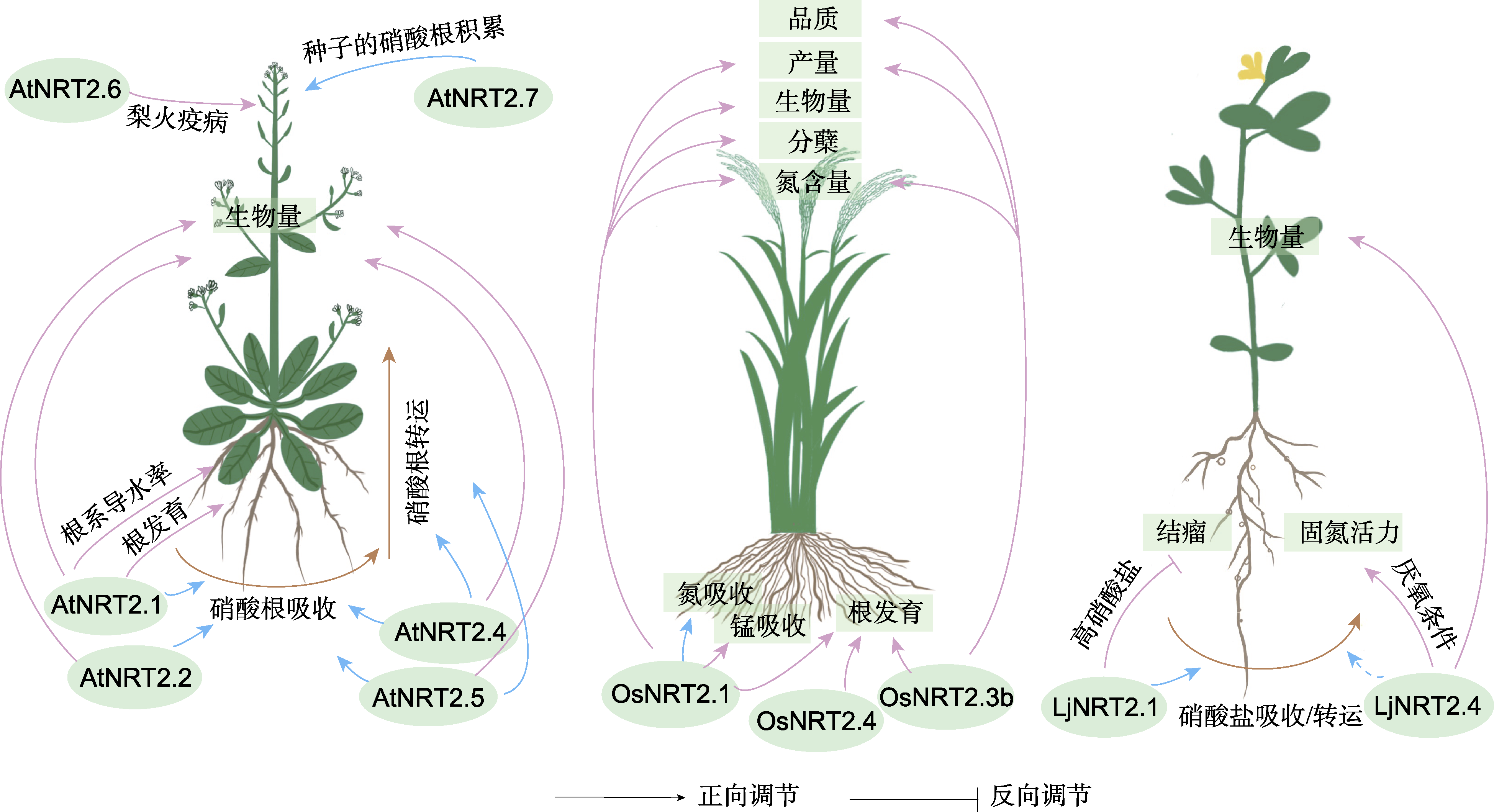
图1 NRT2家族蛋白对拟南芥、水稻和百脉根氮吸收与转运及其它生物学过程的调控作用 蓝色线条表示已经明确具有氮吸收及转运功能的NRT2家族成员; 棕色线条表示硝酸根吸收及转运; 蓝色虚线代表功能尚不明确; 紫色线条指示目前在拟南芥、水稻及百脉根中NRT2蛋白参与调控的其它生物学过程。
Figure 1 The functions of NRT2 family proteins in nitrate uptake and allocation and their roles in other biological processes in Arabidopsis, rice, and lotus Blue lines represent NRT2 family members identified as involved in nitrate uptake and allocation; brown lines indicate the uptake and allocation of NO3-; the blue dotted line indicates the function is unknown; purple lines indicate the other biological functions of NRT2 proteins in Arabidopsis, rice, and lotus.
| 转录因子 | 转录因子蛋白家族 | 靶基因(NRT) | 结合元件/位点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 初级硝酸盐信号途径 | ||||
| NLP6 | RWP-RK | NRT1.1/NPF6.3和NRT2.1 | NRE | Konishi and Yanagisawa, |
| NLP7 | RWP-RK | NRT1.1/NPF6.3、NRT2.1和NRT2.2 | NRE | Yu et al., |
| LjNLP1 | RWP-RK | LjNRT2.1 | NRE | Marchive et al., |
| NIGT1 | NIGT | NRT2.1 | GAATC | Maeda et al., |
| TGA1/TGA4 | bZIP | NRT2.1和NRT2.2 | TGACG | Alvarez et al., |
| LBD37/38/39 | ASL/LBD | NRT2.1和NRT2.2 | GCGGCG | Rubin et al., |
| 系统性硝酸盐信号通路 | ||||
| TCP20 | TCP | NRT1.1/NPF6.3和NRT2.1 | GCCCR | Guan et al., |
| HY5 | bZIP | NRT2.1 | C/G box | Chen et al., |
表2 参与调控NRT2的转录因子
Table 2 Transcription factors involved in regulating NRT2
| 转录因子 | 转录因子蛋白家族 | 靶基因(NRT) | 结合元件/位点 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 初级硝酸盐信号途径 | ||||
| NLP6 | RWP-RK | NRT1.1/NPF6.3和NRT2.1 | NRE | Konishi and Yanagisawa, |
| NLP7 | RWP-RK | NRT1.1/NPF6.3、NRT2.1和NRT2.2 | NRE | Yu et al., |
| LjNLP1 | RWP-RK | LjNRT2.1 | NRE | Marchive et al., |
| NIGT1 | NIGT | NRT2.1 | GAATC | Maeda et al., |
| TGA1/TGA4 | bZIP | NRT2.1和NRT2.2 | TGACG | Alvarez et al., |
| LBD37/38/39 | ASL/LBD | NRT2.1和NRT2.2 | GCGGCG | Rubin et al., |
| 系统性硝酸盐信号通路 | ||||
| TCP20 | TCP | NRT1.1/NPF6.3和NRT2.1 | GCCCR | Guan et al., |
| HY5 | bZIP | NRT2.1 | C/G box | Chen et al., |
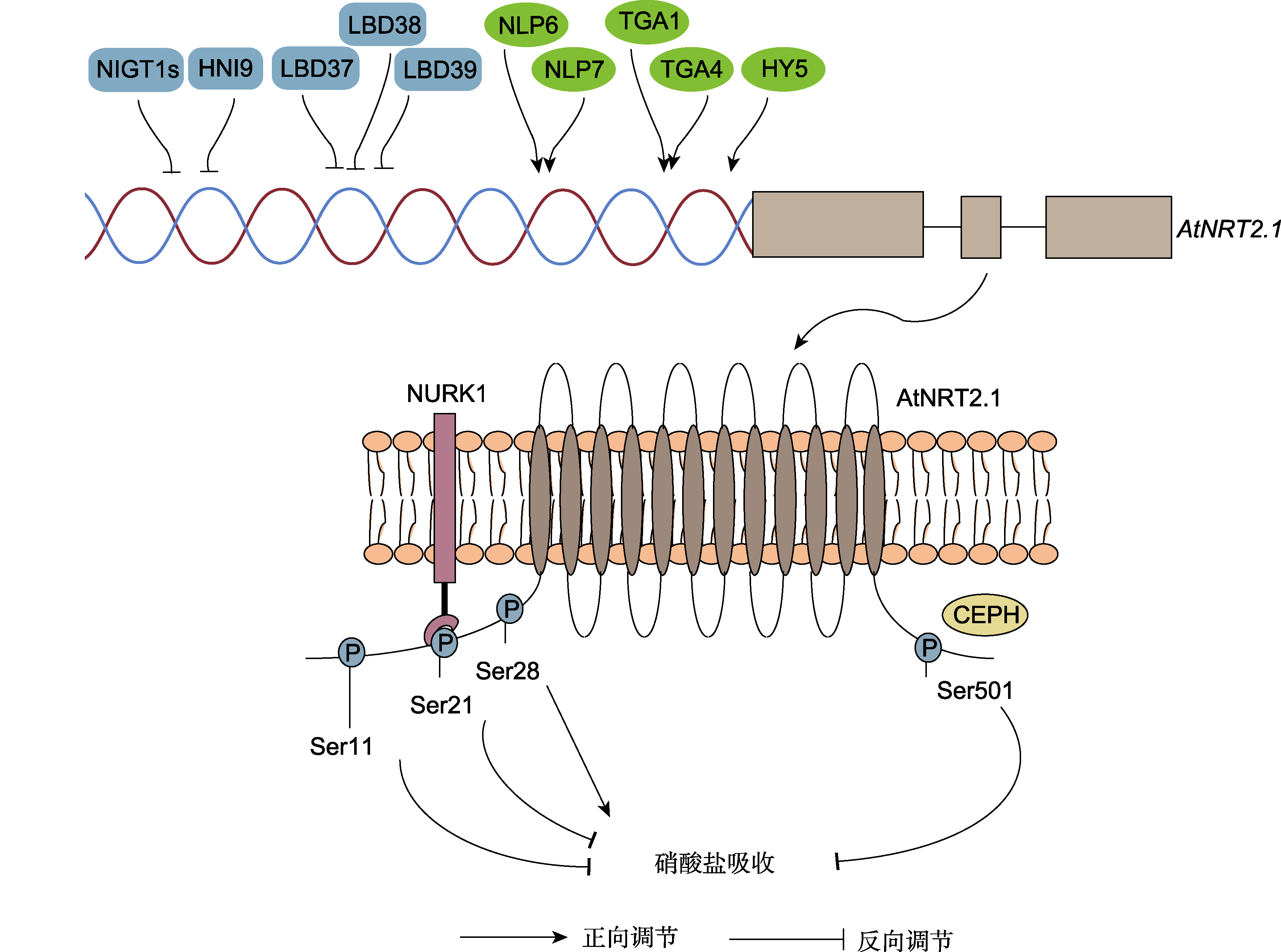
图2 拟南芥硝酸盐转运蛋白AtNRT2.1的分子调控机制总结 双螺旋表示AtNRT2.1的启动子区域, 受到多个转录因子的直接调控。其中蓝色矩形代表转录抑制子, 绿色椭圆形代表转录激活子。定位在质膜上的AtNRT2.1蛋白通过与NURK1激酶或CEPH磷酸酶的互作发生磷酸化或去磷酸化修饰。目前明确调控硝酸根吸收活性的磷酸化位点包括N端Ser11、Ser21、Ser28及C端Ser501。
Figure 2 A summary of the molecular regulatory mechanism of nitrate transporter AtNRT2.1 in Arabidopsis The double stand represents the promoter region of AtNRT2.1. Several transcription factors are involved in repressing or activating the expression of AtNRT2.1. The blue rectangle and green ellipse indicate transcriptional repressor and activator, respectively. AtNRT2.1 is located in the plasma membrane and could interact with NURK1 kinase or CEPH phosphatase. Phosphorylation at N-terminal Ser11, Ser21, Ser28, and C-terminal Ser501 are critical for nitrate uptake activity of AtNRT2.1.
| [1] | 陈景光 (2017). OsNAR2.1参与水稻氮素利用的生物学功能及其机制研究. 博士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 1-213. |
| [2] | 陈景光, 张勇, 谭雅文, 徐国华, 范晓荣 (2016). 过量表达OsNRT2.1对水稻日本晴生长和氮素利用效率的影响. 分子植物育种 14, 1-9. |
| [3] | 李宝珍, 范晓荣, 徐国华 (2009). 植物吸收利用铵态氮和硝态氮的分子调控. 植物生理学通讯 45, 80-88. |
| [4] |
李纯, 孙春玉, 陈静, 林彦萍, 王义, 张美萍 (2018). 主要协同转运蛋白超家族的研究进展. 生物技术通报 34(8), 43-49.
DOI |
| [5] | 陆海燕, 李胜元, 唐仲, 徐国华, 范晓荣 (2015). 超表达OsNRT2.3b促进水稻武育粳7号生长和提高籽粒产量. 分子植物育种 13, 497-504. |
| [6] |
王孝林, 王二涛 (2019). 根际微生物促进水稻氮利用的机制. 植物学报 54, 285-287.
DOI |
| [7] |
Alvarez JM, Riveras E, Vidal EA, Gras DE, Contreras- López O, Tamayo KP, Aceituno F, Gómez I, Ruffel S, Lejay L, Jordana X, Gutiérrez RA (2014). Systems approach identifies TGA1 and TGA4 transcription factors as important regulatory components of the nitrate response of Arabidopsis thaliana roots. Plant J 80, 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Cerezo M, Tillard P, Filleur S, Muños S, Daniel-Vedele F, Gojon A (2001). Major alterations of the regulation of root NO3- uptake are associated with the mutation of Nrt2.1 and Nrt2.2 genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 127, 262-271.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Chen JG, Liu XQ, Liu SH, Fan XR, Zhao LM, Song MQ, Fan XR, Xu GH (2020). Co-overexpression of OsNAR2.1 and OsNRT2.3a increased agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in transgenic rice plants. Front Plant Sci 11, 1245.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Chen JG, Zhang Y, Tan YW, Zhang M, Zhu LL, Xu GH, Fan XR (2016a). Agronomic nitrogen-use efficiency of rice can be increased by driving OsNRT2.1 expression with the OsNAR2.1 promoter. Plant Biotech J 14, 1705-1715.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Chen XB, Yao QF, Gao XH, Jiang CF, Harberd NP, Fu XD (2016b). Shoot-to-root mobile transcription factor HY5 coordinates plant carbon and nitrogen acquisition. Curr Biol 26, 640-646.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Chopin F, Orsel M, Dorbe MF, Chardon F, Truong HN, Miller AJ, Krapp A, Daniel-Vedele F (2007). The Arabidopsis ATNRT2.7 nitrate transporter controls nitrate content in seeds. Plant Cell 19, 1590-1602.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Cooper HD, Clarkson DT (1989). Cycling of amino-nitrogen and other nutrients between shoots and roots in cereals—a possible mechanism integrating shoot and root in the regulation of nutrient uptake. J Exp Bot 40, 753-762.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Dechorgnat J, Francis KL, Dhugga KS, Rafalski JA, Tyerman SD, Kaiser BN (2019). Tissue and nitrogen- linked expression profiles of ammonium and nitrate transporters in maize. BMC Plant Biol 19, 206.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Dechorgnat J, Patrit O, Krapp A, Fagard M, Daniel-Vedele F (2012). Characterization of the Nrt2.6 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana: a link with plant response to biotic and abiotic stress. PLoS One 7, e42491. |
| [16] |
Fan XR, Naz M, Fan XR, Xuan W, Miller AJ, Xu GH (2017). Plant nitrate transporters: from gene function to application. J Exp Bot 68, 2463-2475.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Fan XR, Tang Z, Tan YW, Zhang Y, Luo BB, Yang M, Lian XM, Shen QR, Miller AJ, Xu GH (2016). Overexpression of a pH-sensitive nitrate transporter in rice increases crop yields. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 7118-7123.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Feng HM, Li B, Zhi Y, Chen JG, Li R, Xia XD, Xu GH, Fan XR (2017). Overexpression of the nitrate transporter, OsNRT2.3b, improves rice phosphorus uptake and tran- slocation. Plant Cell Rep 36, 1287-1296.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Feng HM, Yan M, Fan XR, Li BZ, Shen QR, Miller AJ, Xu GH (2011). Spatial expression and regulation of rice high-affinity nitrate transporters by nitrogen and carbon status. J Exp Bot 62, 2319-2332.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Filleur S, Daniel-Vedele F (1999). Expression analysis of a high-affinity nitrate transporter isolated from Arabidopsis thaliana by differential display. Planta 207, 461-469.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Forde BG (2000). Nitrate transporters in plants: structure, function and regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465, 219-235.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Fowler D, Coyle M, Skiba U, Sutton MA, Cape JN, Reis S, Sheppard LJ, Jenkins A, Grizzetti B, Galloway JN, Vitousek P, Leach A, Bouwman AF, Butterbach-Bahl K, Dentener F, Stevenson D, Amann M, Voss M (2013). The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Phil Trans R Soc B 368, 20130164.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Fujita K, Sato H, Sawada O, Sendo S (1995). Husk leaves contribution to dry matter and grain production as well as N distribution in flint corn (Zea mays L.) genotypes differing in husk leaf area. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 41, 587-596.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Galván A, Quesada A, Fernández E (1996). Nitrate and nitrite are transported by different specific transport systems and by a bispecific transporter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biol Chem 271, 2088-2092.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Guan PZ, Wang RC, Nacry P, Breton G, Kay SA, Pruneda-Paz JL, Davani A, Crawford NM (2014). Nitrate foraging by Arabidopsis roots is mediated by the transcription factor TCP20 through the systemic signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 15267-15272.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Hachiya T, Sakakibara H (2017). Interactions between nitrate and ammonium in their uptake, allocation, assimilation, and signaling in plants. J Exp Bot 68, 2501-2512.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Ho CH, Lin SH, Hu HC, Tsay YF (2009). CHL1 functions as a nitrate sensor in plants. Cell 138, 1184-1194.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Hu B, Wang W, Ou SJ, Tang JY, Li H, Che RH, Zhang ZH, Chai XY, Wang HR, Wang YQ, Liang CZ, Liu LC, Piao ZZ, Deng QY, Deng K, Xu C, Liang Y, Zhang LH, Li LG, Chu CC (2015). Variation in NRT1.1B contributes to nitrate-use divergence between rice subspecies. Nat Genet 47, 834-838.
DOI |
| [29] |
Ishikawa S, Ito Y, Sato Y, Fukaya Y, Takahashi M, Morikawa H, Ohtake N, Ohyama T, Sueyoshi K (2009). Two- component high-affinity nitrate transport system in barley: membrane localization, protein expression in roots and a direct protein-protein interaction. Plant Biotechnol 26, 197-205.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Jacquot A, Chaput V, Mauries A, Li Z, Tillard P, Fizames C, Bonillo P, Bellegarde F, Laugier E, Santoni V, Hem S, Martin A, Gojon A, Schulze W, Lejay L (2020). NRT2.1 C-terminus phosphorylation prevents root high affinity nitrate uptake activity in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 228, 1038-1054.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Katayama H, Mori M, Kawamura Y, Tanaka T, Mori M, Hasegawa H (2009). Production and characterization of transgenic rice plants carrying a high-affinity nitrate transporter gene (OsNRT2.1). Breed Sci 59, 237-243.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Kiba T, Feria-Bourrellier AB, Lafouge F, Lezhneva L, Boutet-Mercey S, Orsel M, Bréhaut V, Miller A, Daniel-Vedele F, Sakakibara H, Krapp A (2012). The Arabidopsis nitrate transporter NRT2.4 plays a double role in roots and shoots of nitrogen-starved plants. Plant Cell 24, 245-258.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Konishi M, Yanagisawa S (2013). Arabidopsis NIN-like transcription factors have a central role in nitrate signaling. Nat Commun 4, 1617.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Kotur Z, Mackenzie N, Ramesh S, Tyerman SD, Kaiser BN, Glass ADM (2012). Nitrate transport capacity of the Arabidopsis thaliana NRT2 family members and their interactions with AtNAR2.1. New Phytol 194, 724-731.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Laugier E, Bouguyon E, Mauriès A, Tillard P, Gojon A, Lejay L (2012). Regulation of high-affinity nitrate uptake in roots of Arabidopsis depends predominantly on posttranscriptional control of the NRT2.1/NAR2.1 tran-sport system. Plant Physiol 158, 1067-1078.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Leghari SJ, Wahocho NA, Laghari GM, Laghari AH, Bhabhan GM, Talpur KH, Bhutto TA, Wahocho SA, Lashari AA (2016). Role of nitrogen for plant growth and development: a review. Adv Environ Biol 10, 209-218. |
| [37] |
Lejay L, Tillard P, Lepetit M, Olive FD, Filleur S, Daniel- Vedele F, Gojon A (1999). Molecular and functional regulation of two NO3- uptake systems by N- and C-status of Arabidopsis plants. Plant J 18, 509-519.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Lezhneva L, Kiba T, Feria-Bourrellier AB, Lafouge F, Boutet-Mercey S, Zoufan P, Sakakibara H, Daniel- Vedele F, Krapp A (2014). The Arabidopsis nitrate transporter NRT2.5 plays a role in nitrate acquisition and remobilization in nitrogen-starved plants. Plant J 80, 230-241.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Li GW, Tillard P, Gojon A, Maurel C (2016). Dual regulation of root hydraulic conductivity and plasma membrane aquaporins by plant nitrate accumulation and high-affinity nitrate transporter NRT2.1. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 733-742.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Li WB, Wang Y, Okamoto M, Crawford NM, Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM (2007). Dissection of the AtNRT2.1:AtNRT2.2 inducible high-affinity nitrate transporter gene cluster. Plant Physiol 143, 425-433.
DOI URL |
| [41] | Li Z, Wu XN, Jaquot A, Lejay L, Schulze WX (2020). A phospho-switch in the N-terminus of NRT2.1 affects nitrate uptake by controlling the interaction of NRT2.1 with NAR2.1.bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.01.08.898254 |
| [42] |
Little DY, Rao HY, Oliva S, Daniel-Vedele F, Krapp A, Malamy JE (2005). The putative high-affinity nitrate transporter NRT2.1 represses lateral root initiation in response to nutritional cues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 13693-13698.
PMID |
| [43] |
Liu XQ, Huang DM, Tao JY, Miller AJ, Fan XR, Xu GH (2014). Identification and functional assay of the interaction motifs in the partner protein OsNAR2.1 of the two- component system for high-affinity nitrate transport. New Phytol 204, 74-80.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Luo BB, Chen JG, Zhu LL, Liu SH, Li B, Lu H, Ye GY, Xu GH, Fan XR (2018). Overexpression of a high-affinity nitrate transporter OsNRT2.1 increases yield and manganese accumulation in rice under alternating wet and dry condition. Front Plant Sci 9, 1192.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Luo L, Zhang YL, Xu GH (2020). How does nitrogen shape plant architecture? J Exp Bot 71, 4415-4427.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Maeda Y, Konishi M, Kiba T, Sakuraba Y, Sawaki N, Kurai T, Ueda Y, Sakakibara H, Yanagisawa S (2018). A NIGT1-centred transcriptional cascade regulates nitrate signaling and incorporates phosphorus starvation signals in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 9, 1376.
DOI |
| [47] |
Marchive C, Roudier F, Castaings L, Bréhaut V, Blondet E, Colot V, Meyer C, Krapp A (2013). Nuclear retention of the transcription factor NLP7 orchestrates the early response to nitrate in plants. Nat Commun 4, 1713.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Medici A, Krouk G (2014). The primary nitrate response: a multifaceted signaling pathway. J Exp Bot 65, 5567-5576.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Menz J, Li Z, Schulze WX, Ludewig U (2016). Early nitrogen-deprivation responses in Arabidopsis roots reveal distinct differences on transcriptome and (phospho-) proteome levels between nitrate and ammonium nutrition. Plant J 88, 717-734.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Misawa F, Ito M, Nosaki S, Nishida H, Watanabe M, Suzuki T, Miura K, Kawaguchi M, Suzaki T (2022). Nitrate transport via NRT2.1 mediates NIN-LIKE PROTEIN-de- pendent suppression of root nodulation in Lotus japonicus. Plant Cell 34, 1844-1862.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Näsholm T, Kielland K, Ganeteg U (2009). Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol 182, 31-48.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
Naz M, Luo BB, Guo XY, Li B, Chen JG, Fan XR (2019). Overexpression of nitrate transporter OsNRT2.1 enhances nitrate-dependent root elongation. Genes 10, 290.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Ohkubo Y, Kuwata K, Matsubayashi Y (2021). A type 2C protein phosphatase activates high-affinity nitrate uptake by dephosphorylating NRT2.1. Nat Plants 7, 310-316.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Okamoto M, Kumar A, Li WB, Wang Y, Siddiqi MY, Crawford NM, Glass ADM (2006). High-affinity nitrate transport in roots of Arabidopsis depends on expression of the NAR2-like gene AtNRT3.1. Plant Physiol 140, 1036-1046.
PMID |
| [55] |
Okamoto M, Vidmar JJ, Glass ADM (2003). Regulation of NRT1 and NRT2 gene families of Arabidopsis thaliana: responses to nitrate provision. Plant Cell Physiol 44, 304-317.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Orsel M, Chopin F, Leleu O, Smith SJ, Krapp A, Daniel- Vedele F, Miller AJ (2006). Characterization of a two- component high-affinity nitrate uptake system in Arabidopsis. Physiology and protein-protein interaction. Plant Physiol 142, 1304-1317.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Orsel M, Eulenburg K, Krapp A, Daniel-Vedele F (2004). Disruption of the nitrate transporter genes AtNRT2.1 and AtNRT2.2 restricts growth at low external nitrate concentration. Planta 219, 714-721. |
| [58] |
Orsel M, Krapp A, Daniel-Vedele F (2002). Analysis of the NRT2 nitrate transporter family in Arabidopsis. Structure and gene expression. Plant Physiol 129, 886-896.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Pao SS, Paulsen IT, Saier MH Jr (1998). Major facilitator superfamily. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62, 1-34.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Plett D, Toubia J, Garnett T, Tester M, Kaiser BN, Baumann U (2010). Dichotomy in the NRT gene families of dicots and grass species. PLoS One 5, e15289. |
| [61] |
Quesada A, Galvan A, Fernandez E (1994). Identification of nitrate transporter genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 5, 407-419.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Remans T, Nacry P, Pervent M, Girin T, Tillard P, Lepetit M, Gojon A (2006). A central role for the nitrate transporter NRT2.1 in the integrated morphological and physiological responses of the root system to nitrogen limitation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 140, 909-921.
PMID |
| [63] |
Rubin G, Tohge T, Matsuda F, Saito K, Scheible WR (2009). Members of the LBD family of transcription factors repress anthocyanin synthesis and affect additional nitrogen responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 3567-3584.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Sabermanesh K, Holtham LR, George J, Roessner U, Boughton BA, Heuer S, Tester M, Plett DC, Garnett TP (2017). Transition from a maternal to external nitrogen source in maize seedlings. J Integr Plant Biol 59, 261-274.
DOI |
| [65] |
Scheible WR, Gonzalez-Fontes A, Lauerer M, Muller-Rober B, Caboche M, Stitt M (1997). Nitrate acts as a signal to induce organic acid metabolism and repress starch metabolism in tobacco. Plant Cell 9, 783-798.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Tang Z, Fan XR, Li Q, Feng HM, Miller AJ, Shen QR, Xu GH (2012). Knockdown of a rice stelar nitrate transporter alters long-distance translocation but not root influx. Plant Physiol 160, 2052-2063.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Tong YP, Zhou JJ, Li ZS, Miller AJ (2005). A two-component high-affinity nitrate uptake system in barley. Plant J 41, 442-450.
DOI PMID |
| [68] | Trevisan S, Borsa P, Botton A, Varotto S, Malagoli M, Ruperti B, Quaggiotti S (2008). Expression of two maize putative nitrate transporters in response to nitrate and sugar availability. Plant Biol 10, 462-475. |
| [69] |
Tsay YF, Chiu CC, Tsai CB, Ho CH, Hsu PK (2007). Nitrate transporters and peptide transporters. FEBS Lett 581, 2290-2300.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Unkles SE, Hawker KL, Grieve C, Campbell EI, Montague P, Kinghorn JR (1991). crnA encodes a nitrate transporter in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88, 204-208.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Valkov VT, Sol S, Rogato A, Chiurazzi M (2020). The functional characterization of LjNRT2.4 indicates a novel, positive role of nitrate for an efficient nodule N2-fixation activity. New Phytol 228, 682-696.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Vidmar JJ, Zhuo DG, Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM (2000). Isolation and characterization of HvNRT2.3 and HvNRT2.4, cDNAs encoding high-affinity nitrate transporters from roots of barley. Plant Physiol 122, 783-792.
DOI PMID |
| [73] |
Wang YY, Cheng YH, Chen KE, Tsay YF (2018). Nitrate transport, signaling, and use efficiency. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69, 85-122.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Wang YY, Hsu PK, Tsay YF (2012). Uptake, allocation and signaling of nitrate. Trends Plant Sci 17, 458-467.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Wei J, Zheng Y, Feng HM, Qu HY, Fan XR, Yamaji N, Ma JF, Xu GH (2018). OsNRT2.4 encodes a dual-affinity nitrate transporter and functions in nitrate-regulated root growth and nitrate distribution in rice. J Exp Bot 69, 1095-1107.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Widiez T, El Kafafi ES, Girin T, Berr A, Ruffel S, Krouk G, Vayssières A, Shen WH, Coruzzi GM, Gojon A, Lepetit M (2011). High nitrogen insensitive 9 (HNI9)-mediated systemic repression of root NO3- uptake is associated with changes in histone methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 13329-13334.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Wirth J, Chopin F, Santoni V, Viennois G, Tillard P, Krapp A, Lejay L, Daniel-Vedele F, Gojon A (2007). Regulation of root nitrate uptake at the NRT2.1 protein level in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 282, 23541-23552.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Yan M, Fan XR, Feng HM, Miller AJ, Shen QR, Xu GH (2011). Rice OsNAR2.1 interacts with OsNRT2.1, OsNRT- 2.2 and OsNRT2.3a nitrate transporters to provide uptake over high and low concentration ranges. Plant Cell Environ 34, 1360-1372.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Yong ZH, Kotur Z, Glass ADM (2010). Characterization of an intact two-component high-affinity nitrate transporter from Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 63, 739-748.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
Yu LH, Wu J, Tang H, Yuan Y, Wang SM, Wang YP, Zhu QS, Li SG, Xiang CB (2016). Overexpression of Arabidopsis NLP7 improves plant growth under both nitrogen-limiting and -sufficient conditions by enhancing nitrogen and carbon assimilation. Sci Rep 6, 27795.
DOI |
| [81] |
Zhang HM, Forde BG (2000). Regulation of Arabidopsis root development by nitrate availability. J Exp Bot 51, 51-59.
PMID |
| [82] |
Zhang JY, Liu YX, Zhang N, Hu B, Jin T, Xu HR, Qin Y, Yan PX, Zhang XN, Guo XX, Hui J, Cao SY, Wang X, Wang C, Wang H, Qu BY, Fan GY, Yuan LX, Garrido-Oter R, Chu CC, Bai Y (2019). NRT1.1B is associated with root microbiota composition and nitrogen use in field-grown rice. Nat Biotechnol 37, 676-684.
DOI |
| [83] |
Zhang SN, Zhang YY, Li KN, Yan M, Zhang JF, Yu M, Tang S, Wang LY, Qu HY, Luo L, Xuan W, Xu GH (2021). Nitrogen mediates flowering time and nitrogen use efficiency via floral regulators in rice. Curr Biol 31, 671-683.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
Zhou JJ, Fernández E, Galván A, Miller AJ (2000). A high affinity nitrate transport system from Chlamydomonas requires two gene products. FEBS Lett 466, 225-227.
DOI PMID |
| [85] |
Zhuo DG, Okamoto M, Vidmar JJ, Glass ADM (1999). Regulation of a putative high-affinity nitrate transporter (Nrt2;1At) in roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 17, 563-568.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Zou X, Liu MY, Wu WH, Wang Y (2020). Phosphorylation at Ser28 stabilizes the Arabidopsis nitrate transporter NRT2.1 in response to nitrate limitation. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 865-876.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [2] | 何璐梅, 马伯军, 陈析丰. 植物执行者抗病基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 671-680. |
| [3] | 车佳航, 李纬楠, 秦英之, 陈金焕. 木本植物叶色变异机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 319-328. |
| [4] | 朱晓华, 高程, 王聪, 赵鹏. 尿素对土壤细菌与真菌多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22636-. |
| [5] | 罗韶凡, 蒋凯, 黄卫昌. 植物花距表型趋同进化和发育机制多样化的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23249-. |
| [6] | 冯晓敏, 高翔, 臧华栋, 胡跃高, 任长忠, 郝志萍, 吕慧卿, 曾昭海. 燕麦-绿豆间作效应及氮素转移特性[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 122-131. |
| [7] | 王琦, 许艳丽, 闫鹏, 董好胜, 张薇, 卢霖, 董志强. PAC对谷子花后土壤氮素供应和叶片抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 90-107. |
| [8] | 孔照胜, 杨文强, 王柏臣, 林荣呈. 豆科饲草碳氮高效固定、转运和同化利用研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 764-773. |
| [9] | 王璐瑶, 陈謇, 赵守清, 闫慧莉, 许文秀, 刘若溪, 麻密, 虞轶俊, 何振艳. 水稻镉积累特性的生理和分子机制研究概述[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 236-249. |
| [10] | 张慧, 刘倩, 黄晓磊. 社会性昆虫级型和行为分化机制研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 507-516. |
| [11] | 宋松泉, 刘军, 杨华, 张文虎, 张琪, 高家东. 细胞分裂素调控种子发育、休眠与萌发的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 218-231. |
| [12] | 刘鑫, 荣晓莹, 张元明. 古尔班通古特沙漠生物土壤结皮对氨氧化微生物生态位的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 43-52. |
| [13] | 陈孙禄, 詹成芳, 蒋红, 李琳涵, 张红生. 水稻籽粒灌浆速率的分子机制与遗传调控研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 80-89. |
| [14] | 宣伟, 徐国华. 植物适应土壤氮素环境的基因选择: 以水稻为例[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 1-5. |
| [15] | 张璐,何新华. C3和C4植物的氮素利用机制[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 228-239. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||