

植物学报 ›› 2016, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 235-250.DOI: 10.11983/CBB15022 cstr: 32102.14.CBB15022
收稿日期:2015-02-12
接受日期:2015-06-23
出版日期:2016-03-01
发布日期:2016-03-31
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Tian Cheng, Qiang Wei, Guanglin Li*( )
)
Received:2015-02-12
Accepted:2015-06-23
Online:2016-03-01
Published:2016-03-31
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要: 萜类化合物具有重要的生理、生态作用和药用价值, 萜类合成酶(TPS)是合成萜类化合物的关键酶。通过整合中粒咖啡(Coffee canephora)的基因组和转录组数据, 利用生物信息学方法, 鉴定出43个萜类合成酶全长基因, 并对这些基因的分子进化、结构、复制、表达及功能分化的机理进行了探究。 结果表明, 中粒咖啡萜类合成酶基因可以分为5个亚家族(a、b、c、e/f、g), 不同亚家族的基因结构差异很大; 串联复制是基因家族扩增的主要原因; 表达分析结果表明, 萜类合成酶基因在不同组织中的表达差异明显; 中粒咖啡萜类合成酶基因启动子区的顺式调控元件可能与基因的功能分化相关; 不同亚家族之间的功能差异主要由亚家族特异的氨基酸决定。
程甜, 魏强, 李广林. 中粒咖啡萜类合成酶基因家族的生物信息学分析. 植物学报, 2016, 51(2): 235-250.
Tian Cheng, Qiang Wei, Guanglin Li. Bioinformatics Analysis of the TPS Gene Family in Coffee canephora. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(2): 235-250.
| ID | Aa | PI | Conserved motifs | Locb | Tplenc | Chr. | Strand | Begin | End | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NSE/DTE | |||||||||
| Cc01_g19400 | 822 | 5.69 | Na | Na | Na | Na | C | 54 | 1 | - | 36232113 | 36239469 |
| Cc02_g11820 | 589 | 5.63 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | C | 36 | 2 | + | 9762146 | 9765886 |
| Cc02_g11830 | 587 | 5.63 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | C | 34 | 2 | + | 9775928 | 9779555 |
| Cc02_g11870 | 605 | 6.24 | Na | RXQ | DDXXD | DDXXSXXXE | C | 32 | 2 | + | 9817486 | 9821171 |
| Cc02_g12790 | 843 | 5.71 | Na | RXK | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | S | 143 | 2 | - | 10962357 | 10968950 |
| Cc02_g12800 | 721 | 5.93 | Na | RXK | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 2 | - | 10974562 | 10979896 |
| Cc02_g20930 | 510 | 5 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXTXXXE | C | 41 | 2 | - | 18646492 | 18649797 |
| Cc02_g29500 | 487 | 5.83 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | Na | C | - | 2 | + | 30876701 | 30879109 |
| Cc02_g29590 | 553 | 5.1 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 2 | + | 31081548 | 31090061 |
| Cc02_g35640 | 599 | 5.32 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXTXXXE | C | 48 | 2 | + | 49559875 | 49563902 |
| Cc03_g14100 | 569 | 5.51 | RL(x)8W | RXR | DGXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 3 | + | 27992091 | 28002647 |
| Cc04_g16380 | 567 | 5.66 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 4 | + | 26533839 | 26536938 |
| Cc04_g16390 | 470 | 5.68 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 4 | + | 26575942 | 26580763 |
| Cc04_g16400 | 568 | 5.62 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 4 | + | 26628007 | 26631524 |
| Cc04_g16520 | 545 | 5.71 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXG | _ | - | 4 | + | 26837450 | 26841294 |
| Cc04_g16530 | 571 | 5.07 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | Na | _ | - | 4 | + | 26861073 | 26866930 |
| Cc05_g05380 | 612 | 5.99 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 5 | + | 19945840 | 19951165 |
| Cc05_g05400 | 614 | 5.49 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | C | 42 | 5 | + | 19959720 | 19964609 |
| Cc05_g05410 | 603 | 5.27 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | C | 42 | 5 | + | 19970432 | 19976641 |
| Cc05_g05490 | 624 | 6.27 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NEXXTXXXE | M | 35 | 5 | + | 20061653 | 20068755 |
| Cc05_g05500 | 739 | 6.3 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | NEXXTXXXE | _ | - | 5 | + | 20064933 | 20069377 |
| Cc05_g13060 | 551 | 5.44 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 5 | - | 26746571 | 26750238 |
| Cc05_g13070 | 550 | 5.76 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 5 | - | 26767977 | 26770620 |
| Cc08_g06940 | 553 | 5.33 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXGXXXD | _ | - | 8 | - | 18458061 | 18462018 |
| Cc08_g06960 | 553 | 5.37 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXGXXXD | _ | - | 8 | - | 18474336 | 18480348 |
| Cc08_g07420 | 714 | 5.35 | Na | RXV | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | _ | - | 8 | - | 19681648 | 19689451 |
| Cc08_g07480 | 597 | 6.64 | Na | Na | Na | Na | _ | - | 8 | + | 19801873 | 19809275 |
| Cc08_g07530 | 735 | 6.47 | Na | Na | Na | Na | S | 22 | 8 | + | 20232648 | 20240540 |
| Cc08_g07540 | 536 | 5.52 | Na | Na | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | S | 29 | 8 | + | 20247389 | 20255575 |
| Cc10_g12310 | 565 | 5.3 | RQ(x)8S | RXM | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | C | 40 | 10 | + | 21701855 | 21705459 |
| Cc10_g12320 | 598 | 5.35 | RQ(x)8S | RXM | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | C | 39 | 10 | - | 21708529 | 21712087 |
| Cc10_g12360 | 544 | 5.25 | KQ(x)8W | RXI | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | _ | - | 10 | + | 21847515 | 21853384 |
| Cc00_g06380 | 552 | 5.2 | RQ(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 0 | + | 50283228 | 50288386 |
| Cc00_g06390 | 581 | 5.57 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | M | 83 | 0 | - | 50369458 | 50372316 |
| Cc00_g06420 | 580 | 4.92 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | M | 83 | 0 | + | 50428795 | 50431627 |
| Cc00_g09030 | 553 | 5.18 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXGXXXD | _ | - | 0 | + | 78120342 | 78123629 |
| Cc00_g13600 | 426 | 5.11 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | S | 23 | 0 | - | 101152670 | 101155134 |
| Cc00_g16490 | 584 | 5.63 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXTXXXE | C | 44 | 0 | + | 112444838 | 112448504 |
| Cc00_g16500 | 480 | 5.17 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 0 | + | 112472815 | 112475864 |
| Cc00_g17280 | 693 | 5.37 | Na | Na | Na | Na | _ | - | 0 | + | 115693382 | 115700157 |
| Cc00_g20580 | 555 | 5.02 | RQ(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 0 | - | 131112913 | 131117645 |
| Cc00_g27830 | 609 | 5.25 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXTXXXE | C | 40 | 0 | - | 174429457 | 174432386 |
| Cc00_g31970 | 459 | 9.03 | Na | Na | Na | Na | _ | - | 0 | - | 189453118 | 189455434 |
表1 中粒咖啡TPS基因及其编码蛋白的特征
Table 1 The feature of TPS genes and their encoded proteins in Coffee canephora
| ID | Aa | PI | Conserved motifs | Locb | Tplenc | Chr. | Strand | Begin | End | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NSE/DTE | |||||||||
| Cc01_g19400 | 822 | 5.69 | Na | Na | Na | Na | C | 54 | 1 | - | 36232113 | 36239469 |
| Cc02_g11820 | 589 | 5.63 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | C | 36 | 2 | + | 9762146 | 9765886 |
| Cc02_g11830 | 587 | 5.63 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | C | 34 | 2 | + | 9775928 | 9779555 |
| Cc02_g11870 | 605 | 6.24 | Na | RXQ | DDXXD | DDXXSXXXE | C | 32 | 2 | + | 9817486 | 9821171 |
| Cc02_g12790 | 843 | 5.71 | Na | RXK | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | S | 143 | 2 | - | 10962357 | 10968950 |
| Cc02_g12800 | 721 | 5.93 | Na | RXK | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 2 | - | 10974562 | 10979896 |
| Cc02_g20930 | 510 | 5 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXTXXXE | C | 41 | 2 | - | 18646492 | 18649797 |
| Cc02_g29500 | 487 | 5.83 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | Na | C | - | 2 | + | 30876701 | 30879109 |
| Cc02_g29590 | 553 | 5.1 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 2 | + | 31081548 | 31090061 |
| Cc02_g35640 | 599 | 5.32 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXTXXXE | C | 48 | 2 | + | 49559875 | 49563902 |
| Cc03_g14100 | 569 | 5.51 | RL(x)8W | RXR | DGXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 3 | + | 27992091 | 28002647 |
| Cc04_g16380 | 567 | 5.66 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 4 | + | 26533839 | 26536938 |
| Cc04_g16390 | 470 | 5.68 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 4 | + | 26575942 | 26580763 |
| Cc04_g16400 | 568 | 5.62 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 4 | + | 26628007 | 26631524 |
| Cc04_g16520 | 545 | 5.71 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXG | _ | - | 4 | + | 26837450 | 26841294 |
| Cc04_g16530 | 571 | 5.07 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | Na | _ | - | 4 | + | 26861073 | 26866930 |
| Cc05_g05380 | 612 | 5.99 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 5 | + | 19945840 | 19951165 |
| Cc05_g05400 | 614 | 5.49 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | C | 42 | 5 | + | 19959720 | 19964609 |
| Cc05_g05410 | 603 | 5.27 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | C | 42 | 5 | + | 19970432 | 19976641 |
| Cc05_g05490 | 624 | 6.27 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NEXXTXXXE | M | 35 | 5 | + | 20061653 | 20068755 |
| Cc05_g05500 | 739 | 6.3 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | NEXXTXXXE | _ | - | 5 | + | 20064933 | 20069377 |
| Cc05_g13060 | 551 | 5.44 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 5 | - | 26746571 | 26750238 |
| Cc05_g13070 | 550 | 5.76 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 5 | - | 26767977 | 26770620 |
| Cc08_g06940 | 553 | 5.33 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXGXXXD | _ | - | 8 | - | 18458061 | 18462018 |
| Cc08_g06960 | 553 | 5.37 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXGXXXD | _ | - | 8 | - | 18474336 | 18480348 |
| Cc08_g07420 | 714 | 5.35 | Na | RXV | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | _ | - | 8 | - | 19681648 | 19689451 |
| Cc08_g07480 | 597 | 6.64 | Na | Na | Na | Na | _ | - | 8 | + | 19801873 | 19809275 |
| Cc08_g07530 | 735 | 6.47 | Na | Na | Na | Na | S | 22 | 8 | + | 20232648 | 20240540 |
| Cc08_g07540 | 536 | 5.52 | Na | Na | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | S | 29 | 8 | + | 20247389 | 20255575 |
| Cc10_g12310 | 565 | 5.3 | RQ(x)8S | RXM | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | C | 40 | 10 | + | 21701855 | 21705459 |
| Cc10_g12320 | 598 | 5.35 | RQ(x)8S | RXM | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | C | 39 | 10 | - | 21708529 | 21712087 |
| Cc10_g12360 | 544 | 5.25 | KQ(x)8W | RXI | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | _ | - | 10 | + | 21847515 | 21853384 |
| Cc00_g06380 | 552 | 5.2 | RQ(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 0 | + | 50283228 | 50288386 |
| Cc00_g06390 | 581 | 5.57 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | M | 83 | 0 | - | 50369458 | 50372316 |
| Cc00_g06420 | 580 | 4.92 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | M | 83 | 0 | + | 50428795 | 50431627 |
| Cc00_g09030 | 553 | 5.18 | RP(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXGXXXD | _ | - | 0 | + | 78120342 | 78123629 |
| Cc00_g13600 | 426 | 5.11 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXTXXXE | S | 23 | 0 | - | 101152670 | 101155134 |
| Cc00_g16490 | 584 | 5.63 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXTXXXE | C | 44 | 0 | + | 112444838 | 112448504 |
| Cc00_g16500 | 480 | 5.17 | Na | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXGXXXE | _ | - | 0 | + | 112472815 | 112475864 |
| Cc00_g17280 | 693 | 5.37 | Na | Na | Na | Na | _ | - | 0 | + | 115693382 | 115700157 |
| Cc00_g20580 | 555 | 5.02 | RQ(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | NDXXSXXXE | _ | - | 0 | - | 131112913 | 131117645 |
| Cc00_g27830 | 609 | 5.25 | RR(x)8W | RXR | DDXXD | DDXXTXXXE | C | 40 | 0 | - | 174429457 | 174432386 |
| Cc00_g31970 | 459 | 9.03 | Na | Na | Na | Na | _ | - | 0 | - | 189453118 | 189455434 |
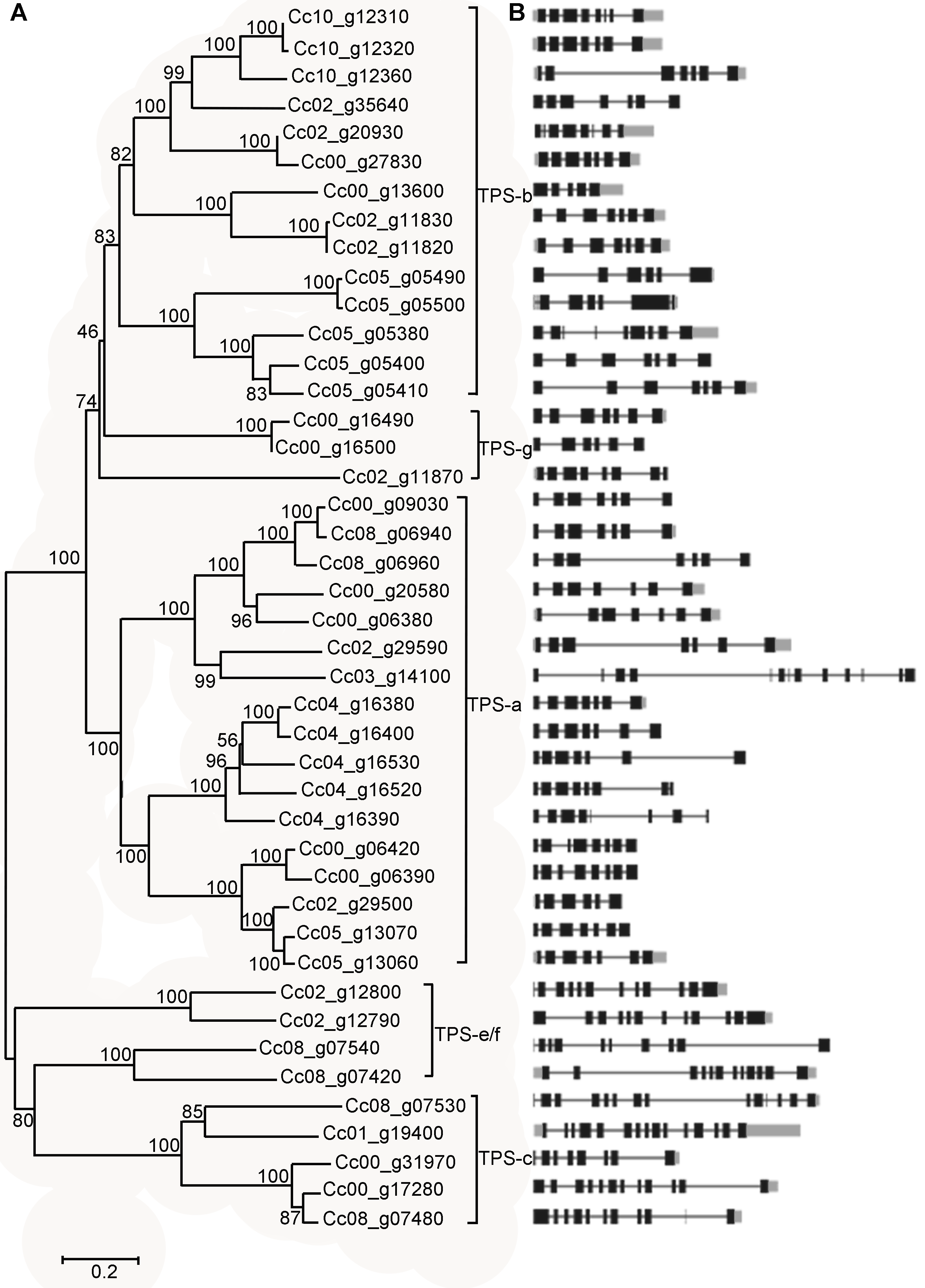
图1 中粒咖啡TPS家族的系统进化树(A)以及基因结构(B) 分支上的数字表示Bootstrap值。左下角是数值为0.2的比例尺, 代表氨基酸替换率。黑色部分代表外显子, 黑色线代表内含子, 灰色部分代表非编码区(UTR)。
Figure 1 Phylogenetic analysis (A) and schematic diagram (B) of gene structure in Coffee canephora TPS gene family Bootstrapping values are indicated along the branches. The scale bar corresponds to 0.2 estimated amino acid substitutions. Black boxes represent the exons, black lines represent the introns, and grey boxes represent the UTR regions.
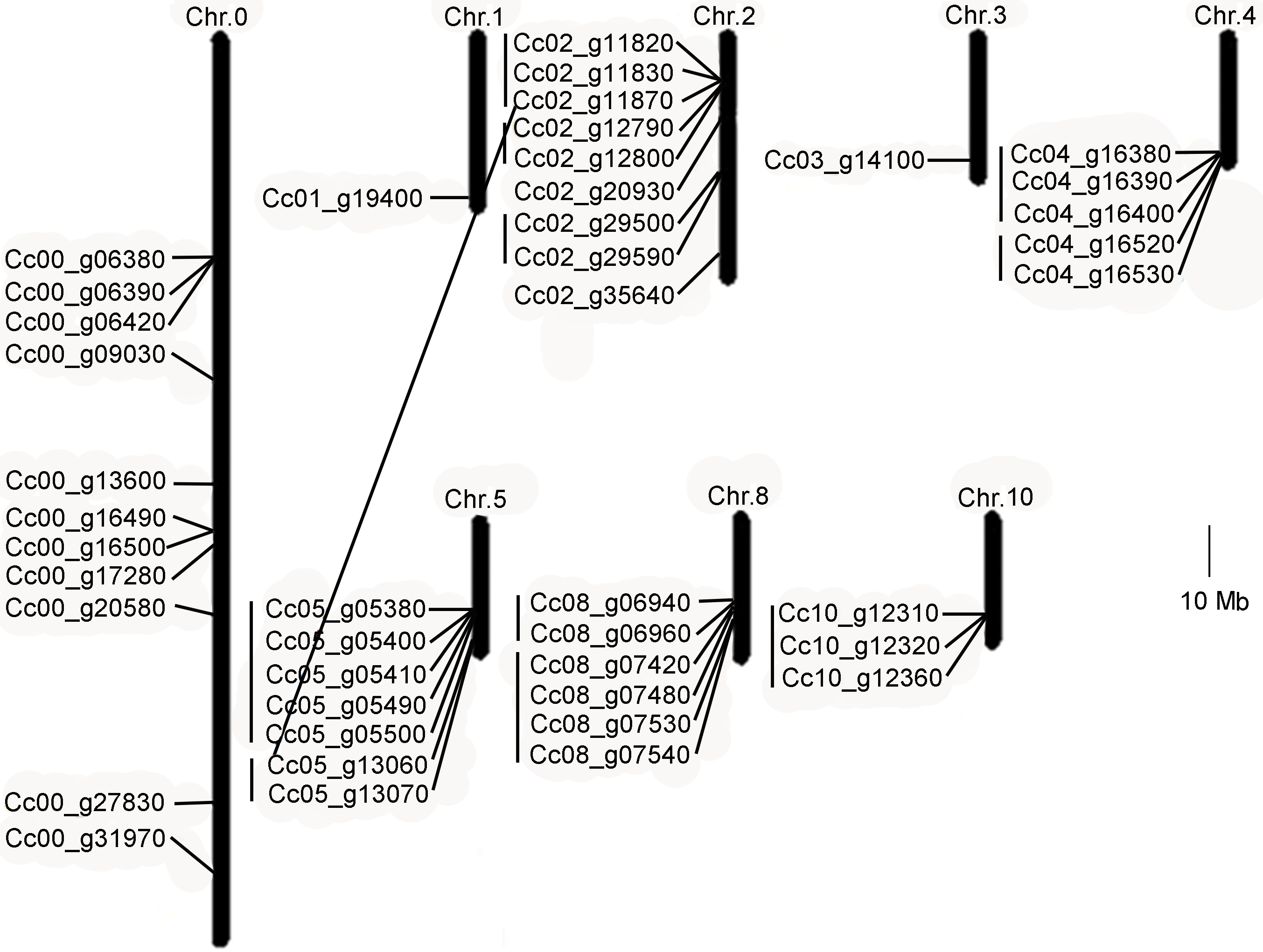
图3 中粒咖啡TPS基因在染色体上的分布及基因复制情况 连接线表示TPS基因在染色体上的复制。
Figure 3 Chromosomal distribution and duplication events of Coffee canephora TPS genes The TPS genes duplicated on chromosomal are connected by lines.
| Gene duplication | Chromosome | Total pairs | Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segmental duplication | 2/5 | 1 | Cc02_g11870/Cc05_g13060 |
| Tandem duplication | 2 | 3 | Cc02_g11820/Cc02_g11830/Cc02_g11870 Cc02_g12790/Cc02_g12800 Cc02_g29500/Cc02_g29590 |
| 4 | 2 | Cc04_g16380/Cc04_g16390/Cc04_g16400 Cc04_g16520/Cc04_g16530 | |
| 5 | 2 | Cc05_g05380/Cc05_g05400/Cc05_g05410/Cc05_g05490/Cc05_g05500 Cc05_g13060/Cc05_g13070 | |
| 8 | 2 | Cc08_g06940/Cc08_g06960 Cc08_g07420/Cc08_g07480/Cc08_g07530/Cc08_g07540 | |
| 10 | 1 | Cc10_g12310 /Cc10_g12320/Cc10_g12360 | |
| 0 | 2 | Cc00_g06380/Cc00_g06390/Cc00_g06420 Cc00_g16490/Cc00_g16500 |
表2 中粒咖啡TPS基因在各染色体上的基因复制事件
Table 2 The gene duplication of TPS genes in each chromosome of Coffee canephora
| Gene duplication | Chromosome | Total pairs | Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segmental duplication | 2/5 | 1 | Cc02_g11870/Cc05_g13060 |
| Tandem duplication | 2 | 3 | Cc02_g11820/Cc02_g11830/Cc02_g11870 Cc02_g12790/Cc02_g12800 Cc02_g29500/Cc02_g29590 |
| 4 | 2 | Cc04_g16380/Cc04_g16390/Cc04_g16400 Cc04_g16520/Cc04_g16530 | |
| 5 | 2 | Cc05_g05380/Cc05_g05400/Cc05_g05410/Cc05_g05490/Cc05_g05500 Cc05_g13060/Cc05_g13070 | |
| 8 | 2 | Cc08_g06940/Cc08_g06960 Cc08_g07420/Cc08_g07480/Cc08_g07530/Cc08_g07540 | |
| 10 | 1 | Cc10_g12310 /Cc10_g12320/Cc10_g12360 | |
| 0 | 2 | Cc00_g06380/Cc00_g06390/Cc00_g06420 Cc00_g16490/Cc00_g16500 |
| Tissue | Total number | Gene ID |
|---|---|---|
| Root | 10 | Cc02_g35640/Cc05_g05400/Cc04_g16520/Cc04_g16530/Cc00_g06420/ Cc00_g06390/Cc08_g07420/Cc08_g07530/Cc00_g31790/Cc00_g17280 |
| Stamen | 1 | Cc05_g05410 |
| Pistil | 2 | Cc05_g05490/Cc05_g05500 |
| Leaf | 5 | Cc08_g06960/Cc00_g20580/Cc00_g06380/Cc05_g13070/Cc02_g12800 |
| Perisperm | 2 | Cc02_g29500/Cc05_g13060 |
| Endosperm | 0 | - |
表3 中粒咖啡TPS基因在各组织中特异表达
Table 3 The specific expression of TPS genes in different tissues of Coffee canephora
| Tissue | Total number | Gene ID |
|---|---|---|
| Root | 10 | Cc02_g35640/Cc05_g05400/Cc04_g16520/Cc04_g16530/Cc00_g06420/ Cc00_g06390/Cc08_g07420/Cc08_g07530/Cc00_g31790/Cc00_g17280 |
| Stamen | 1 | Cc05_g05410 |
| Pistil | 2 | Cc05_g05490/Cc05_g05500 |
| Leaf | 5 | Cc08_g06960/Cc00_g20580/Cc00_g06380/Cc05_g13070/Cc02_g12800 |
| Perisperm | 2 | Cc02_g29500/Cc05_g13060 |
| Endosperm | 0 | - |
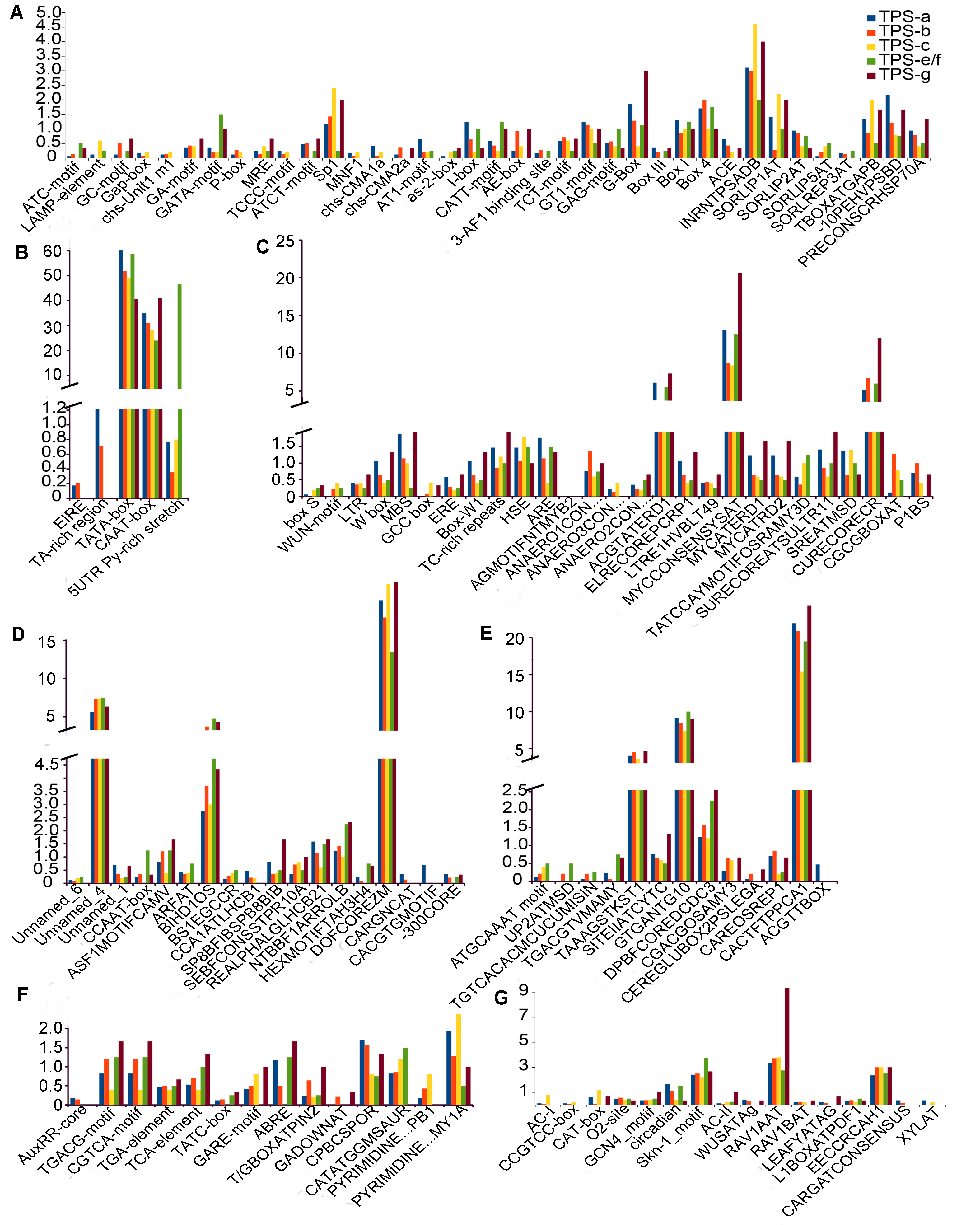
图5 TPS基因启动子区顺式调控元件 (A) 光调节相关元件; (B) 启动子相关元件; (C) 环境胁迫相关元件; (D) 位点结合相关元件; (E) 其它顺式调控元件; (F) 激素应答相关元件; (G) 生长发育相关元件。横坐标代表顺式调控元件; 纵坐标代表TPS各亚家族顺式调控元件数目的平均值; 不同颜色代表不同的亚家族。
Figure 5 Cis-acting regulatory elements identified in the promoter region of TPS genes (A) Light cycle-related elements; (B) Promoter related elements; (C) Environmental stress-related elements; (D) Sites binding-related elements; (E) Other elements; (F) Hormonal responses-related elements; (G) Development related elements. Abscissa represents the cis-acting regulatory elements; Ordinate represents the average values of cis-acting regulatory elements in each TPS subfamilies; Different colors represent different subfamilies.
| TPS subfamilies | θI | θSEa | θLRTb | Qk>0.9 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPS-a vs TPS-b | 0.2336 | 0.0718 | 10.5762 | 495 | P<0.05 |
| TPS-a vs TPS-c | 0.5456 | 0.1277 | 18.2501 | 490, 495, 581, 744, 748, 749, 780, 786, 789, 795, 798, 799, 823 | P<0.05 |
| TPS-a vs TPS-e/f | - | - | - | - | - |
| TPS-b vs TPS-c | 0.7888 | 0.1487 | 28.1539 | 712 | P<0.05 |
| TPS-b vs TPS-e/f | - | - | - | - | - |
| TPS-c vs TPS-e/f | - | - | - | - | - |
表4 I型功能分歧分析结果
Table 4 Analysis of type I function divergence
| TPS subfamilies | θI | θSEa | θLRTb | Qk>0.9 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPS-a vs TPS-b | 0.2336 | 0.0718 | 10.5762 | 495 | P<0.05 |
| TPS-a vs TPS-c | 0.5456 | 0.1277 | 18.2501 | 490, 495, 581, 744, 748, 749, 780, 786, 789, 795, 798, 799, 823 | P<0.05 |
| TPS-a vs TPS-e/f | - | - | - | - | - |
| TPS-b vs TPS-c | 0.7888 | 0.1487 | 28.1539 | 712 | P<0.05 |
| TPS-b vs TPS-e/f | - | - | - | - | - |
| TPS-c vs TPS-e/f | - | - | - | - | - |
| TPS subfamilies | θII | θSE | Qk>0.9 | No. of sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPS-a vs TPS-b | -0.2809 | 0.3299 | - | - |
| TPS-a vs TPS-c | 0.1136 | 0.2283 | 481, 485, 487, 488, 489, 490*, 494, 495*, 501, 503, 511, 514, 517, 518, 522, 523, 525, 531, 532, 533, 534, 536, 556, 557, 558, 560, 563, 570, 572, 578, 581*, 584, 626, 716, 717, 721, 723, 725, 744*, 747, 748*, 749*, 750, 752, 753, 754, 758, 760, 761, 766, 769, 770, 772, 777, 781, 782, 785, 786*, 789*, 797, 798*, 799*, 826, 827, 881, 882, 883, 935, 938, 970, 971, 972, 974, 977, 979, 981, 983, 985, 987, 990, 991 | 81 |
| TPS-a vs TPS-e/f | -50.0228 | 12.2240 | - | - |
| TPS-b vs TPS-c | 0.1510 | 0.2615 | 481, 482, 484, 485, 486, 488, 489, 490, 494, 495, 500, 501, 503, 511, 513, 514, 516, 518, 522, 528, 529, 531, 532, 534, 556, 557, 558, 560, 563, 566, 570, 571, 578, 580, 583, 584, 708, 716, 717, 720, 721, 723, 724, 725, 742, 744, 747, 748, 749, 750, 752, 753, 754, 760, 761, 766, 767, 769, 770, 772, 777, 782, 785, 786, 789, 797, 798, 826, 827, 881, 882, 883, 935, 938, 939, 969, 970, 971, 974, 979, 983, 985, 987 | 83 |
| TPS-b vs TPS-e/f | -43.8071 | 13.1252 | - | - |
| TPS-c vs TPS-e/f | -5.2707 | 1.8369 | - | - |
表5 II型功能分歧分析结果
Table 5 Analysis of type II function divergence
| TPS subfamilies | θII | θSE | Qk>0.9 | No. of sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPS-a vs TPS-b | -0.2809 | 0.3299 | - | - |
| TPS-a vs TPS-c | 0.1136 | 0.2283 | 481, 485, 487, 488, 489, 490*, 494, 495*, 501, 503, 511, 514, 517, 518, 522, 523, 525, 531, 532, 533, 534, 536, 556, 557, 558, 560, 563, 570, 572, 578, 581*, 584, 626, 716, 717, 721, 723, 725, 744*, 747, 748*, 749*, 750, 752, 753, 754, 758, 760, 761, 766, 769, 770, 772, 777, 781, 782, 785, 786*, 789*, 797, 798*, 799*, 826, 827, 881, 882, 883, 935, 938, 970, 971, 972, 974, 977, 979, 981, 983, 985, 987, 990, 991 | 81 |
| TPS-a vs TPS-e/f | -50.0228 | 12.2240 | - | - |
| TPS-b vs TPS-c | 0.1510 | 0.2615 | 481, 482, 484, 485, 486, 488, 489, 490, 494, 495, 500, 501, 503, 511, 513, 514, 516, 518, 522, 528, 529, 531, 532, 534, 556, 557, 558, 560, 563, 566, 570, 571, 578, 580, 583, 584, 708, 716, 717, 720, 721, 723, 724, 725, 742, 744, 747, 748, 749, 750, 752, 753, 754, 760, 761, 766, 767, 769, 770, 772, 777, 782, 785, 786, 789, 797, 798, 826, 827, 881, 882, 883, 935, 938, 939, 969, 970, 971, 974, 979, 983, 985, 987 | 83 |
| TPS-b vs TPS-e/f | -43.8071 | 13.1252 | - | - |
| TPS-c vs TPS-e/f | -5.2707 | 1.8369 | - | - |
| [1] | 郭安源, 朱其慧, 陈新, 罗静初 (2007). GSDS: 基因结构显示系统. 遗传 29, 1023-1026. |
| [2] |
Argüello-Astorga GR, Herrera-Estrella LR (1996). Ancestral multipartite units in light-responsive plant promoters have structural features correlating with specific phototransduction pathways. Plant Physiol 112, 1151-1166.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Aubourg S, Lecharny A, Bohlmann J (2002). Genomic analysis of the terpenoid synthase (AtTPS) gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Genet Genomics 267, 730-745.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Bohlmann J, Meyer-Gauen G, Croteau R (1998). Plant terpenoid synthases: molecular biology and phylogenetic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 4126-4133.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Cardenas C, Quesada AR, Medina MA (2011). Antiangio- genic and anti-inflammatory properties of kahweol, a coffee diterpene. PLoS One 6, e23407. |
| [6] |
Chartier A, Beaumesnil M, de Oliveira AL, Elfakir C, Bostyn S (2013). Optimization of the isolation and quantitation of kahweol and cafestol in green coffee oil. Talanta 117, 102-111.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Chen F, Tholl D, Bohlmann J, Pichersky E (2011). The family of terpene synthases in plants: a mid-size family of genes for specialized metabolism that is highly diversified through out the kingdom. Plant J 66, 212-229. |
| [8] |
Chen H, Li G, Köllner TG, Jia Q, Gershenzon J, Chen F (2014). Positive Darwinian selection is a driving force for the diversification of terpenoid biosynthesis in the genus Oryza. BMC Plant Biol 14, 239.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Denoeud F, Carretero-Paulet L, Dereeper A, Droc G, Guyot R, Pietrella M, Zheng C, Alberti A, Anthony F, Aprea G, Aury JM, Bento P, Bernard M, Bocs S, Campa C, Cenci A, Combes MC, Crouzillat D, Da Silva C, Daddiego L, De Bellis F, Dussert S, Garsmeur O, Gayraud T, Guignon V, Jahn K, Jamilloux V, Joët T, Labadie K, Lan T, Leclercq J, Lepelley M, Leroy T, Li LT, Librado P, Lopez L, Muñoz A, Noel B, Pallavicini A, Perrotta G, Poncet V, Pot D, Priyono RM, Rouard M, Rozas J, Tranchant-Dubreuil C, VanBuren R, Zhang Q, Andrade AC, Argout X, Bertrand B, de Kochko A, Graziosi G, Henry RJ, Jayarama MR, Nagai C, Rounsley S, Sankoff D, Giuliano G, Albert VA, Wincker P, Lashermes P (2014). The coffee genome provides insight into the convergent evolution of caffeine biosynthesis. Science 345, 1181-1184.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Dereeper A, Bocs S, Rouard M, Guignon V, Ravel S, Tranchant-Dubreuil C, Poncet V, Garsmeur O, Lashermes P, Droc G (2015). The coffee genome hub: a resource for coffee genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 43, D1028-D1035. |
| [11] |
Eddy SR (1998). Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 14, 755-763.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Falara V, Akhtar T, Nguyen TT, Spyropoulou EA, Bleeker PM, Schauvinhold I, Matsuba Y, Bonini ME, Schilmiller AL, Last RL, Schuurink RC, Pichersky E (2011). The tomato terpene synthase gene family. Plant Physiol 157, 770-789.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Finn RD, Mistry J, Schuster-Bockler B, Griffiths-Jones S, Hollich V, Lassmann T, Moxon S, Marshall M, Khanna A, Durbin R, Eddy SR, Sonnhammer EL, Bateman A (2006). Pfam: clans, web tools and services. Nucleic Acids Res 34, D247-D251. |
| [14] |
Gu X (1999). Statistical methods for testing functional divergence after gene duplication. Mol Biol Evol 16, 1664-1674.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Gu X (2006). A simple statistical method for estimating type-II (cluster-specific) functional divergence of protein sequences. Mol Biol Evol 23, 1937-1945.
PMID |
| [16] |
Gu X, Zou Y, Su Z, Huang W, Zhou Z, Arendsee Z, Zeng Y (2013). An update of DIVERGE software for functional divergence analysis of protein family. Mol Biol Evol 30, 1713-1719.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Gubler F, Jacobsen JV (1992). Gibberellin-responsive ele- ments in the promoter of a barley high-pI alphaamylase gene. Plant Cell 4, 1435-1441.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999). Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27, 297-300. |
| [19] |
Irmisch S, Jiang Y, Chen F, Gershenzon J, Kollner TG (2014). Terpene synthases and their contribution to herbivore-induced volatile emission in western balsam poplar (Populus trichocarpa). BMC Plant Biol 14, 270.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY, Fraser M, Li W, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G, Pesseat S, Quinn AF, Sangrador-Vegas A, Scheremetjew M, Yong SY, Lopez R, Hunter S (2014). InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinforma- tics 30, 1236-1240. |
| [21] |
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T (2002). MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 3059-3066.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Kessler A, Baldwin IT (2001). Defensive function of herbivore-induced plant volatile emissions in nature. Science 291, 2141-2144.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Lam LK, Sparnins VL, Wattenberg LW (1982). Isolation and identification of kahweol palmitate and cafestol pa- lmitate as active constituents of green coffee beans that enhance glutathione S-transferase activity in the mouse. Cancer Res 42, 1193-1198.
PMID |
| [24] |
Lee KJ, Choi JH, Jeong HG (2007). Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of the coffee diterpenes kahweol and cafestol on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 45, 2118-2125.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 325-327. |
| [26] |
Liu J, Huang F, Wang X, Zhang M, Zheng R, Wang J, Yu D (2014). Genome-wide analysis of terpene synthases in soybean: functional characterization of GmTPS3. Gene 544, 83-92.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Liu Y, Jiang HY, Chen WJ, Qian YX, Ma Q, Cheng BJ, Zhu SW (2011). Genome-wide analysis of the auxin response factor (ARF) gene family in maize (Zea mays). Plant Gro- wth Regul 63, 225-234. |
| [28] |
Lois R, Dietrich A, Hahlbrock K, Schulz W (1989). A phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from parsley: structure, regulation and identification of elicitor and light responsive cis-acting elements. EMBO J 8, 1641-1648.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Martin DM, Aubourg S, Schouwey MB, Daviet L, Schalk M, Toub O, Lund ST, Bohlmann J (2010). Functional annotation, genome organization and phylogeny of the grapevine (Vitis vinifera) terpene synthase gene family based on genome assembly, FLcDNA cloning, and enzyme assays. BMC Plant Biol 10, 226.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Menkens AE, Schindler U, Cashmore AR (1995). The G-box: a ubiquitous regulatory DNA element in plants bound by the GBF family of bZIP proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 20, 506-510.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Parker MT, Zhong Y, Dai X, Wang S, Zhao P (2014). Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analysis of terpene synthases in Arabidopsis and Medicago. IET Syst Biol 8, 146-153. |
| [32] |
Pastuglia M, Roby D, Dumas C, Cock JM (1997). Rapid induction by wounding and bacterial infection of an S gene family receptor-like kinase gene in Brassica oleracea. Plant Cell 9, 49-60.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Pichersky E, Bernatzky R, Tanksley SD, Breidenbach RB, Kausch AP, Cashmore AR (1985). Molecular characterization and genetic mapping of two clusters of genes encoding chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins in Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Gene 40, 247-258.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Pichersky E, Gershenzon J (2002). The formation and function of plant volatiles: perfumes for pollinator attraction and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5, 237-243.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Pichersky E, Noel JP, Dudareva N (2006). Biosynthesis of plant volatiles: nature’s diversity and ingenuity. Science 311, 808-811.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Rebers M, Kaneta T, Kawaide H, Yamaguchi S, Yang YY, Imai R, Sekimoto H, Kamiya Y (1999). Regulation of gibberellin biosynthesis genes during flower and early fruit development of tomato. Plant J 17, 241-250.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Rouster J, Leah R, Mundy J, Cameron-Mills V (1997). Identification of a methyl jasmonate-responsive region in the promoter of a lipoxygenase 1 gene expressed in barley grain. Plant J 11, 513-523.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | Shu Y, Liu JQ, Peng XR, Wan LS, Zhou L, Zhang T, Qiu MH (2014). Characterization of diterpenoid glucosides in roasted puer coffee beans. J Agric Food Chem 62, 2631-2637. |
| [39] |
Simpson SD, Nakashima K, Narusaka Y, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003). Two different novel cis-acting elements of erd1, a clpA homologous Arabidopsis gene function in induction by dehydration stress and dark-induced senescence. Plant J 33, 259-270.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Solovyev V, Kosarev P, Seledsov I, Vorobyev D (2006). Automatic annotation of eukaryotic genes, pseudogenes and promoters. Genome Biol 7, 1-12. |
| [41] |
Takaiwa F, Oono K, Wing D, Kato A (1991). Sequence of three members and expression of a new major subfamily of glutelin genes from rice. Plant Mol Biol 17, 875-885.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Wu C, Washida H, Onodera Y, Harada K, Takaiwa F (2000). Quantitative nature of the Prolamin-box, ACGT and AACA motifs in a rice glutelin gene promoter: minimal cis-element requirements for endosperm-specific gene ex- pression. Plant J 23, 415-421.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Yang CQ, Wu XM, Ruan JX, Hu WL, Mao YB, Chen XY, Wang LJ (2013). Isolation and characterization of terpene synthases in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Phytochemistry 96, 46-56. |
| [44] |
Yang J, Yan R, Roy A, Xu D, Poisson J, Zhang Y (2015). The I-TASSER Suite: protein structure and function prediction. Nat Methods 12, 7-8.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Yin G, Xu H, Xiao S, Qin Y, Li Y, Yan Y, Hu Y (2013). The large soybean (Glycine max) WRKY TF family expanded by segmental duplication events and subsequent divergent selection among subgroups. BMC Plant Biol 13, 148.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 杨莉, 曲茜彤, 陈子航, 邹婷婷, 王全华, 王小丽. 菠菜AT-hook基因家族鉴定与表达谱分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 377-392. |
| [2] | 徐聪, 张飞宇, 俞道远, 孙新, 张峰. 土壤动物的分子分类预测策略评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22252-. |
| [3] | 赵宇慧, 李秀秀, 陈倬, 鲁宏伟, 刘羽诚, 张志方, 梁承志. 生物信息学分析方法I: 全基因组关联分析概述[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 715-732. |
| [4] | 李格,孟小庆,李宗芸,朱明库. 甘薯盐胁迫响应基因IbMYB3的表达特征及生物信息学分析[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 38-48. |
| [5] | 程广前,贾克利,李娜,邓传良,李书粉,高武军. 石刁柏核质体DNA的生物信息学分析及染色体定位[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 328-334. |
| [6] | 刘魏, 童永鳌, 白洁. 水稻雄配子体发育过程中tRNA片段的生物信息学分析[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(5): 625-633. |
| [7] | 王倩, 孙文静, 包颖. 植物颗粒结合淀粉合酶GBSS基因家族的进化[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(2): 179-187. |
| [8] | 王玲, 郭长奎, 任丁, 马红. 水稻非生物胁迫响应基因OsMIP1的表达与进化分析[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(1): 43-53. |
| [9] | 贾乐东, 李施蒙, 许代香, 曲存民, 李加纳, 王瑞. 甘蓝型油菜BnMYB80基因的生物信息学分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(5): 620-630. |
| [10] | 徐晓婷, 王志恒, DimitarDimitrov. 批量下载GenBank基因序列数据的新工具——NCBIminer[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(4): 550-555. |
| [11] | 包颖, 郭昌锋, 陈少华, 刘梅. 植物查尔酮合成酶超基因家族的分子进化[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(1): 55-71. |
| [12] | 张贵慰, 曾珏, 郭维, 罗琼. 水稻AT-hook基因家族生物信息学分析[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(1): 49-62. |
| [13] | 黄儒, 苍晶, 于晶, 卢宝伟, 刘丽杰, 王健飞, 郭人铭, 徐琛. 冬小麦小RNA高通量测序及生物信息学分析[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(1): 8-18. |
| [14] | 朱新宇, 吕万胜, 余春梅, 汪保华. 根瘤感受样基因的进化: 结构歧异与功能分化[J]. 植物学报, 2013, 48(5): 519-530. |
| [15] | 孙欣, 高莹, 杨云锋. 环境微生物的宏基因组学研究新进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(4): 393-400. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||