

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 38-48.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19094 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19094
收稿日期:2019-05-22
接受日期:2019-11-27
出版日期:2020-01-01
发布日期:2019-12-20
通讯作者:
朱明库
基金资助:
Ge Li,Xiaoqing Meng,Zongyun Li,Mingku Zhu( )
)
Received:2019-05-22
Accepted:2019-11-27
Online:2020-01-01
Published:2019-12-20
Contact:
Mingku Zhu
摘要: MYB转录因子具有多种生物学功能, 在植物响应生物和非生物胁迫中发挥重要作用。该文从盐胁迫后的甘薯(Ipomoea batatas)水培苗转录组数据(RNA-seq)中筛选出2个受盐胁迫显著上调表达的MYB基因, 分别命名为IbMYB3和IbMYB4。多种非生物胁迫和植物生长物质处理下的基因表达分析显示, IbMYB3受逆境诱导显著上调表达, 暗示其可能参与甘薯非生物胁迫响应。生物信息学分析表明, IbMYB3开放阅读框长度为1 059 bp, 编码353个氨基酸残基, 蛋白分子量为39.41 kDa, 理论等电点(PI)为5.26, 为酸性带负电的亲水性蛋白。亚细胞定位结果表明, IbMYB3蛋白定位于细胞核, 具有较强的转录激活活性。上述结果表明, IbMYB3转录因子可能在甘薯非生物胁迫响应过程中发挥重要调控作用, 研究结果为进一步探明IbMYB3基因的功能奠定了基础。
李格,孟小庆,李宗芸,朱明库. 甘薯盐胁迫响应基因IbMYB3的表达特征及生物信息学分析. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 38-48.
Ge Li,Xiaoqing Meng,Zongyun Li,Mingku Zhu. Expression Patterns and Bioinformatic Analyses of Salt Stress Responsive Gene IbMYB3 in Ipomoea batatas. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(1): 38-48.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| FIbMYB3-F | ATGGGAAGATCTCCATGCTG |
| FIbMYB3-R | TTTACAGCAAATCTTCGAAATCTA |
| FIbMYB4-F | ATGGGGAGATCACCATGCT |
| FIbMYB4-R | TTGTTCTGGACAAATATCTACAGAA |
| QIbMYB3-F | GCCAGCCAACTTGAGTACCG |
| QIbMYB3-R | AAGAACCGAGTCCAACCCG |
| QIbMYB4-F | ATCCACTCCCACCTTGTACGAC |
| QIbMYB4-R | TCCAAAACAGCCGCCATAGT |
| QIbARF-F | CTTTGCCAAGAAGGAGATGC |
| QIbARF-R | TCTTGTCCTGACCACCAACA |
| IbMYB3-EGFP- XbaI-F | CCGTCTAGAATGGGAAGATCTCCATGCTGT |
| IbMYB3-EGFP- BamHI-R | CGCGGATCCCAGCAAATCTTCGAAATCTAAG |
| IbMYB3-BD-F | CCGGAATTCATGGGAAGATCTCCATGCTGT |
| IbMYB3-BD-R | CGCGGATCCTTACAGCAAATCTTCGAAATCTAAG |
表1 实验所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in the experiment
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| FIbMYB3-F | ATGGGAAGATCTCCATGCTG |
| FIbMYB3-R | TTTACAGCAAATCTTCGAAATCTA |
| FIbMYB4-F | ATGGGGAGATCACCATGCT |
| FIbMYB4-R | TTGTTCTGGACAAATATCTACAGAA |
| QIbMYB3-F | GCCAGCCAACTTGAGTACCG |
| QIbMYB3-R | AAGAACCGAGTCCAACCCG |
| QIbMYB4-F | ATCCACTCCCACCTTGTACGAC |
| QIbMYB4-R | TCCAAAACAGCCGCCATAGT |
| QIbARF-F | CTTTGCCAAGAAGGAGATGC |
| QIbARF-R | TCTTGTCCTGACCACCAACA |
| IbMYB3-EGFP- XbaI-F | CCGTCTAGAATGGGAAGATCTCCATGCTGT |
| IbMYB3-EGFP- BamHI-R | CGCGGATCCCAGCAAATCTTCGAAATCTAAG |
| IbMYB3-BD-F | CCGGAATTCATGGGAAGATCTCCATGCTGT |
| IbMYB3-BD-R | CGCGGATCCTTACAGCAAATCTTCGAAATCTAAG |
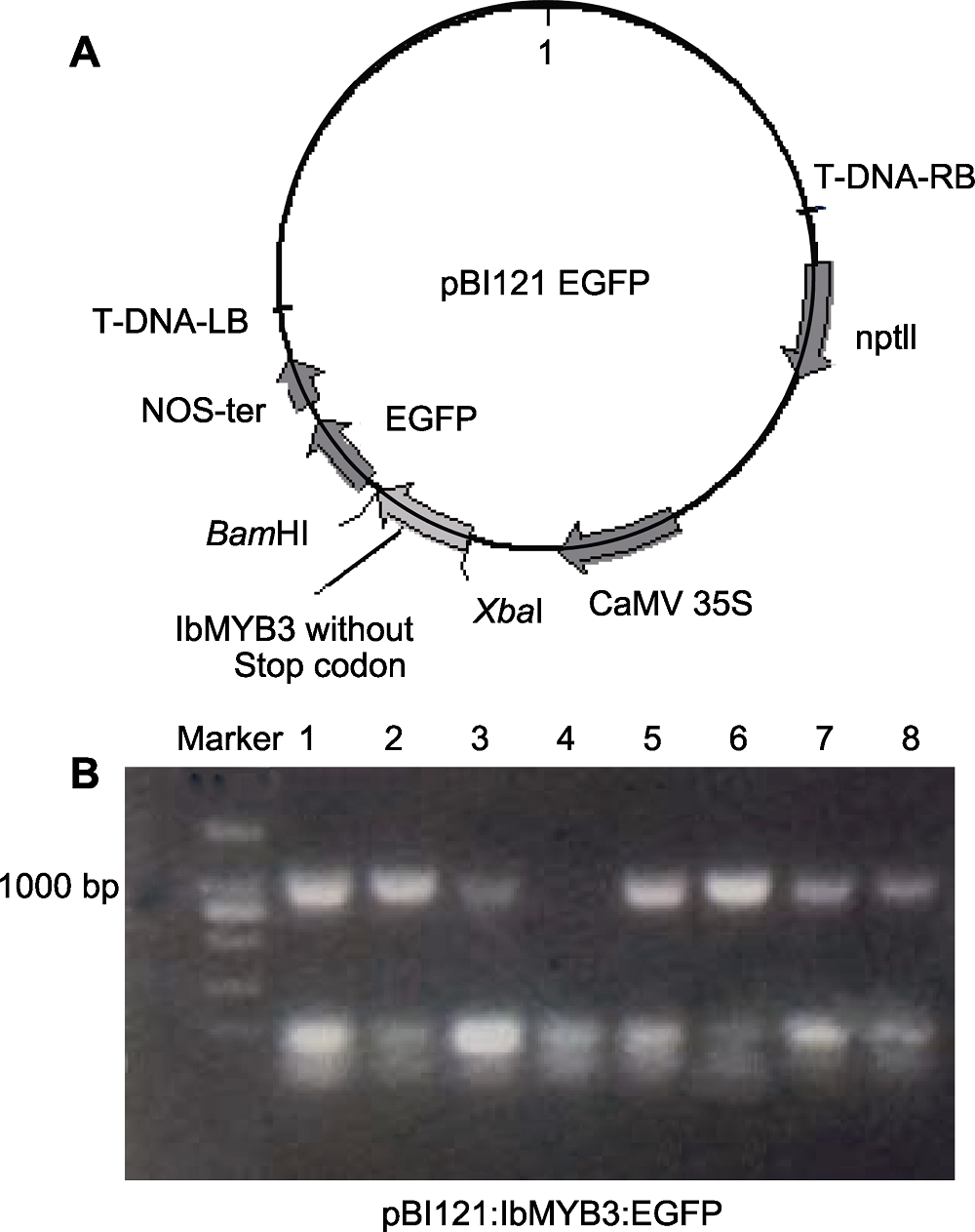
图1 亚细胞定位载体pBI121:IbMYB3:EGFP的构建 (A) pBI121:IbMYB3:EGFP融合蛋白载体图谱; (B) 转化的农杆菌检测(1-8泳道分别代表载体转入农杆菌后的菌落PCR鉴定结果)。
Figure 1 Construction of pBI121:IbMYB3:EGFP subcellular localization vector (A) Vector map of pBI121:IbMYB3:EGFP fusion protein construction; (B) Detection in Agrobacterium (Lanes 1-8 represent the PCR identification results after the vector was transferred into Agrobacterium, respectively).
| Gene name | Gene ID | RNA-seq of Xu22 root control (FPKM) | RNA-seq of Xu22 root after salt-treatment (FPKM) | Log2 FC (Fold change) | Swiss protein annotation (OS=Arabidopsis thaliana) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IbMYB3 | c57279.graph_c0 | 0.07874256 | 44.64485107 | 7.975299063 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| IbMYB4 | c53945.graph_c0 | 1.095722132 | 20.97216423 | 4.085231265 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
表2 IbMYB3和IbMYB4基因的RNA-seq数据信息
Table 2 The RNA-seq data information of IbMYB3 and IbMYB4 genes
| Gene name | Gene ID | RNA-seq of Xu22 root control (FPKM) | RNA-seq of Xu22 root after salt-treatment (FPKM) | Log2 FC (Fold change) | Swiss protein annotation (OS=Arabidopsis thaliana) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IbMYB3 | c57279.graph_c0 | 0.07874256 | 44.64485107 | 7.975299063 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
| IbMYB4 | c53945.graph_c0 | 1.095722132 | 20.97216423 | 4.085231265 | Myb-like DNA-binding domain |
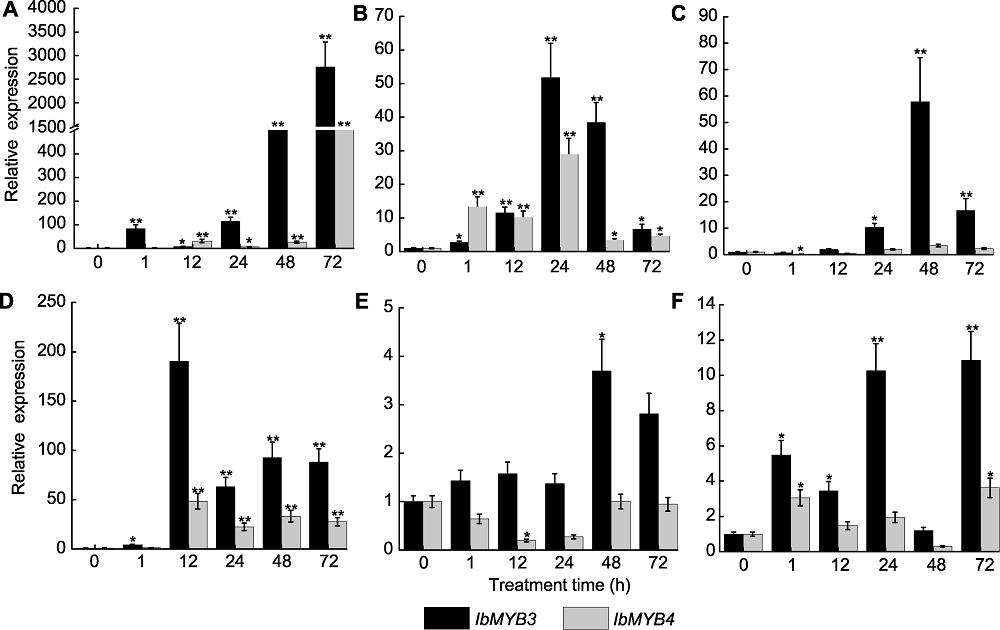
图3 不同处理下水培甘薯苗根中IbMYB3和IbMYB4基因的相对表达 (A) 100 mmol∙L-1 NaCl; (B) 20% PEG6000; (C) 100 μmol∙L-1乙烯合成前体氨基环丙烷羧酸(ACC); (D) 100 μmol∙L-1脱落酸(ABA); (E) 100 μmol∙L-1赤霉素(GA); (F) 100 μmol∙L-1茉莉酸(JA)。*和**分别表示在P<0.05和P<0.01水平差异显著。
Figure 3 Relative expression analysis of IbMYB3 and IbMYB4 in roots of hydroponic sweetpotato plantlets under different treatments (A) 100 mmol∙L-1 NaCl; (B) 20% PEG6000; (C) 100 μmol∙L-1 ethylene precursor 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC); (D) 100 μmol∙L-1 abscisic acid (ABA); (E) 100 μmol∙L-1 gibberellic acid (GA); (F) 100 μmol∙L-1 jasmonate acid (JA). * and ** indicate significant differences at P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively.
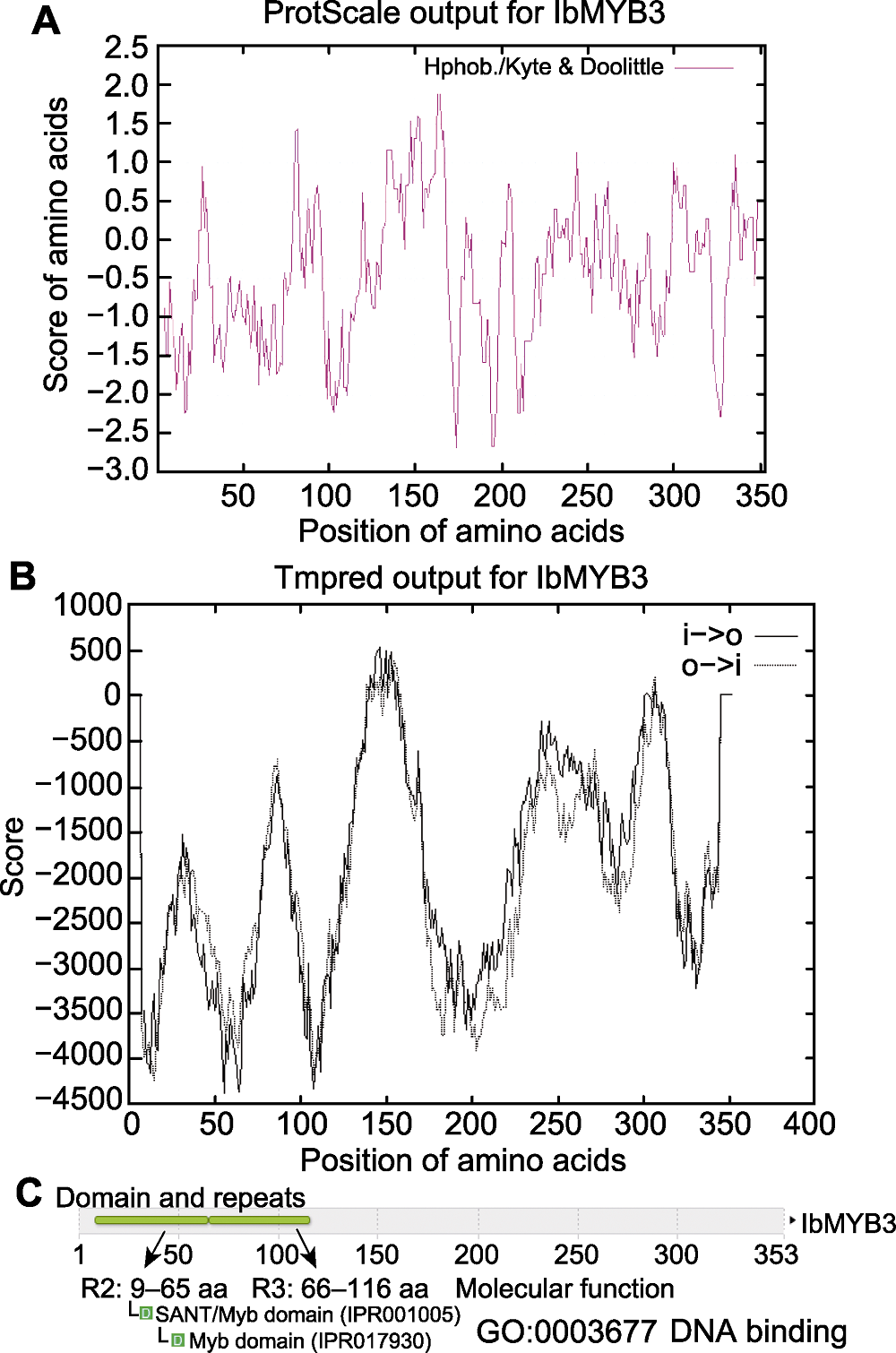
图4 IbMYB3蛋白氨基酸序列分析 (A) 疏水性分析; (B) 跨膜区(TM)预测; (C) 功能域预测
Figure 4 Amino acid sequence analysis of IbMYB3 protein (A) Hydrophobic analysis; (B) Prediction of transmembrane (TM) region; (C) Domain prediction
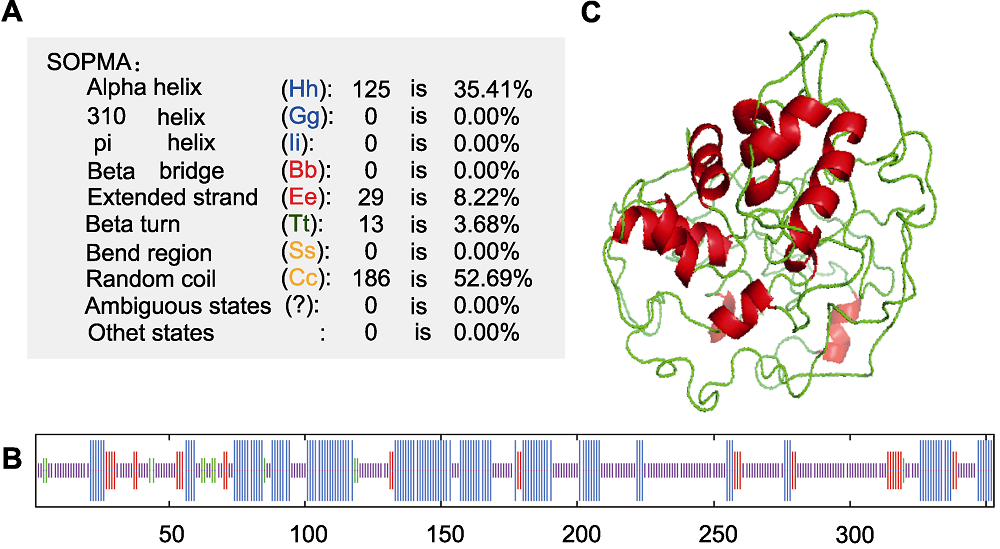
图5 IbMYB3蛋白结构预测 (A), (B) SOPMA预测的二级结构; (C) 预测的四级结构
Figure 5 Structural prediction of IbMYB3 protein (A), (B) Secondary structure predicted by SOPMA; (C) Predicted tertiary structure
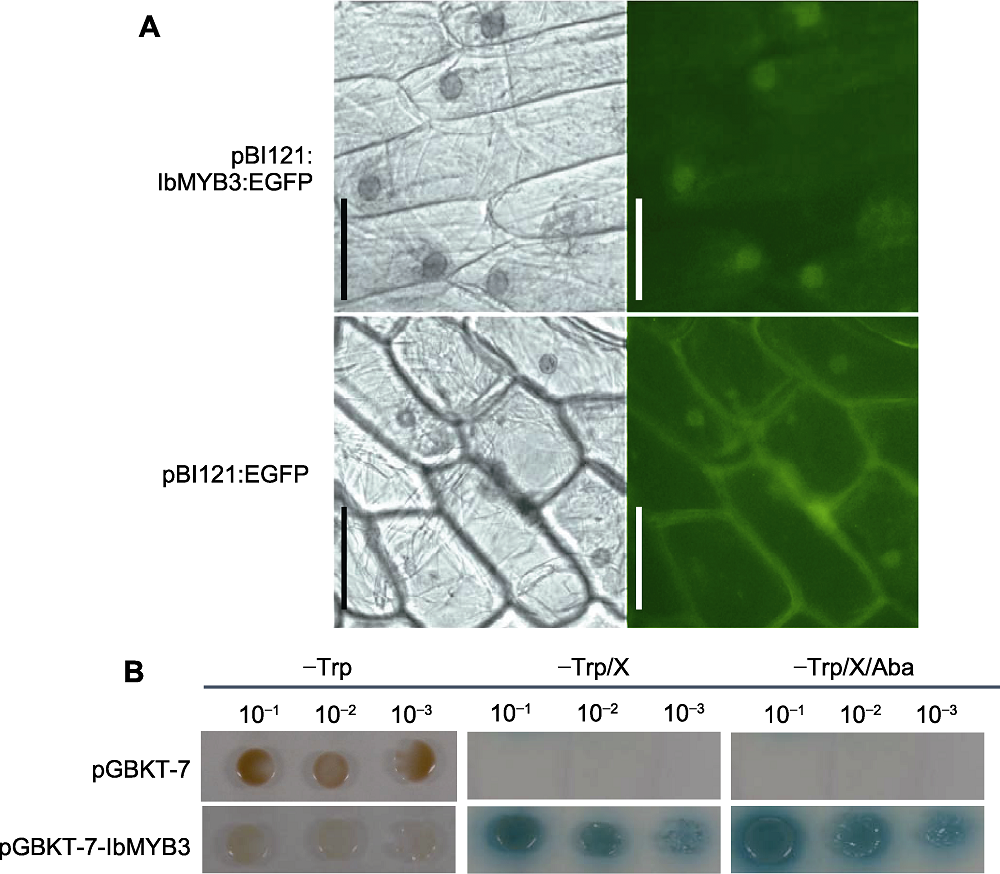
图6 IbMYB3蛋白在洋葱表皮细胞中的亚细胞定位与转录激活活性分析 (A) IbMYB3与EGFP融合蛋白在洋葱下表皮细胞中的亚细胞定位; (B) IbMYB3的转录激活活性分析。Bars=4 μm
Figure 6 Subcellular localization in onion epidermal cells and transcriptional activation activity analysis of IbMYB3 protein (A) Subcellular localization of IbMYB3 and EGFP fusion protein in the onion lower epidermis cells; (B) Transcriptional activation activity analysis of IbMYB3 protein. Bars=4 μm
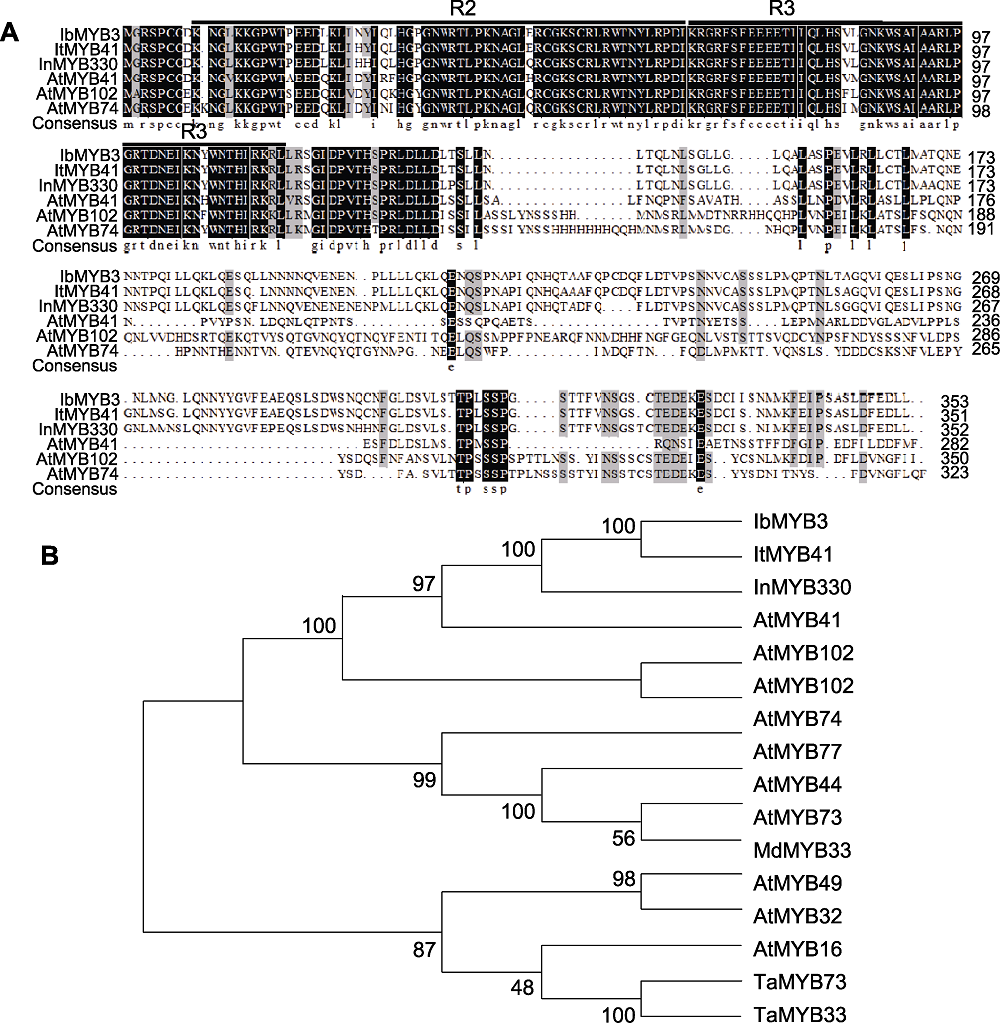
图7 MYB蛋白序列比对及系统发生树 (A) IbMYB3与其它非甘薯物种中盐胁迫耐受相关MYB蛋白序列比对; (B) IbMYB3与其它物种中盐胁迫耐受相关MYB蛋白的系统发生树
Figure 7 MYB proteins sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree (A) Proteins sequence alignment between IbMYB3 and the MYB proteins associated with salt stress tolerance in species other than sweetpotato; (B) Phylogenetic tree of IbMYB3 and the MYB proteins associated with salt stress tolerance in other species
| [1] | 柏洁 (2014). 甘薯抗病相关基因SGT1的克隆与表达研究. 硕士论文. 福州: 福建农林大学. pp. 10-51. |
| [2] | 代红军, 柯玉琴, 潘廷国 (2001). NACl胁迫下甘薯苗期叶片活性氧代谢与甘薯耐盐性的关系. 宁夏农学院学报 22, 15-18. |
| [3] | 贾乐东, 李施蒙, 许代香, 曲存民, 李加纳, 王瑞 (2016). 甘蓝型油菜BnMYB80基因的生物信息学分析. 植物学报 51, 620-630. |
| [4] | 李丰 (2017). 甘薯淀粉合成相关基因的克隆与分子标记开发. 硕士论文. 济南: 山东大学. pp. 5-22. |
| [5] | 李志亮, 吴忠义, 王玉文, 邢浩春, 叶嘉, 张秀海, 黄丛林 (2013). 甘薯转基因研究进展. 生物技术通报 ( 9), 1-6. |
| [6] | 杨俊, 张敏, 张鹏 (2011). 甘薯遗传转化及其在分子育种中的应用. 植物生理学报 47, 427-436. |
| [7] | 张祎曼 (2018). 浅析中国西北地区土壤盐碱化现状及修复对策. 当代化工研究 ( 1), 26-27. |
| [8] | 朱明库, 孟小庆, 蔡敬, 李格, 李宗芸 (2017). 甘薯盐胁迫诱导IbDEAD1基因的克隆、生物信息学及表达分析. 江苏师范大学学报(自然科学版) 35(3), 23-29. |
| [9] | 祝志欣, 鲁迎青 (2016). 花青素代谢途径与植物颜色变异. 植物学报 51, 107-119. |
| [10] | Ambawat S, Sharma P, Yadav NR, Yadav RC (2013). MYB transcription factor genes as regulators for plant responses: an overview. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19, 307-321. |
| [11] | An CH, Lee KW, Lee SH, Jeong YJ, Woo SG, Chun H, Park YI, Kwak SS, Kim CY (2015). Heterologous expression of IbMYB1a by different promoters exhibits different patterns of anthocyanin accumulation in tobacco. Plant Physiol Biochem 89, 1-10. |
| [12] | Baumann K, Perez-Rodriguez M, Bradley D, Venail J, Bailey P, Jin HL, Koes R, Roberts K, Martin C (2007). Control of cell and petal morphogenesis by R2R3 MYB transcription factors. Development 134, 1691-1701. |
| [13] | Bian XF, Xie YZ, Guo XD, Jia ZD, Ma PY (2014). Research advance on molecular mechanism of abiotic and biotic stress resistance in sweet potato. Agric Sci Technol 15, 901-906, 941. |
| [14] | Cheng YJ, Kim MD, Deng XP, Kwak SS, Chen W (2013). Enhanced salt stress tolerance in transgenic potato plants expressing IbMYB1, a sweet potato transcription factor. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 1737-1746. |
| [15] | Chu H, Jeong JC, Kim WJ, Chung DM, Jeon HK, Ahn YO, Kim SH, Lee HS, Kwak SS, Kim CY (2013). Expression of the sweetpotato R2R3-type IbMYB1a gene induces anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plant 148, 189-199. |
| [16] | Cominelli E, Sala T, Calvi D, Gusmaroli G, Tonelli C (2008). Over-expression of the Arabidopsis AtMYB41 gene alters cell expansion and leaf surface permeability. Plant J 53, 53-64. |
| [17] | Denekamp M, Smeekens SC (2003). Integration of wounding and osmotic stress signals determines the expression of the AtMYB102 transcription factor gene. Plant Physiol 132, 1415-1423. |
| [18] | Du H, Yang SS, Liang Z, Feng BR, Liu L, Huang YB, Tang YX (2012). Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 12, 106. |
| [19] | Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010). MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15, 573-581. |
| [20] | Gates DJ, Strickler SR, Mueller LA, Olson BJSC, Smith SD (2016). Diversification of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in the tomato family Solanaceae. J Mol Evol 83, 26-37. |
| [21] | Jia N, Liu JQ, Sun YF, Tan PH, Cao H, Xie YY, Wen BT, Gu TY, Liu JM, Li MM, Huang YT, Lu J, Jin N, Sun LC, Xin FJ, Fan B (2018). Citrus sinensis MYB transcription factors CsMYB330 and CsMYB308 regulate fruit juice sac lignification through fine-tuning expression of the Cs4CL1 gene. Plant Sci 277, 334-343. |
| [22] | Jung C, Seo JS, Han SW, Koo YJ, Kim CH, Song SI, Nahm BH, Choi YD, Cheong JJ (2008). Overexpression of AtMYB44 enhances stomatal closure to confer abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 146, 623-635. |
| [23] | Kang C, He SZ, Zhai H, Li RJ, Zhao N, Liu QC (2018). A sweetpotato auxin response factor gene (IbARF5) is involved in carotenoid biosynthesis and salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 9, 1307. |
| [24] | Kelley LA, Mezulis S, Yates CM, Wass MN, Sternberg MJE (2015). The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat Protoc 10, 845-858. |
| [25] | Khan K, Kumar V, Niranjan A, Shanware A, Sane VA (2019). JcMYB1, a Jatropha R2R3MYB transcription factor gene, modulates lipid biosynthesis in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Physiol 60, 462-475. |
| [26] | Kosma DK, Murmu J, Razeq FM, Santos P, Bourgault R, Molina I, Rowland O (2014). AtMYB41 activates ectopic suberin synthesis and assembly in multiple plant species and cell types. Plant J 80, 216-229. |
| [27] | Lippold F, Sanchez DH, Musialak M, Schlereth A, Scheible WR, Hincha DK, Udvardi MK (2009). AtMyb41 regulates transcriptional and metabolic responses to osmotic stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 149, 1761-1772. |
| [28] | Liu CG, Jun JH, Dixon RA (2014). MYB5 and MYB14 play pivotal roles in seed coat polymer biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 165, 1424-1439. |
| [29] | Liu DG, He SZ, Song XJ, Zhai H, Liu N, Zhang DD, Ren ZT, Liu QC (2015). IbSIMT1, a novel salt-induced methyltransferase gene from Ipomoea batatas, is involved in salt tolerance. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120, 701-715. |
| [30] | Liu QC (2017). Improvement for agronomically important traits by gene engineering in sweetpotato. Breed Sci 67, 15-26. |
| [31] | Lotkowska ME, Tohge T, Fernie AR, Xue GP, Balazadeh S, Mueller-Roeber B (2015). The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB112 promotes anthocyanin formation during salinity and under high light stress. Plant Physiol 169, 1862-1880. |
| [32] | Mu RL, Cao YR, Liu YF, Lei G, Zou HF, Liao Y, Wang HW, Zhang WK, Ma B, Du JZ, Yuan M, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2009). An R2R3-type transcription factor gene AtMYB59 regulates root growth and cell cycle progression in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 19, 1291-1304. |
| [33] | Nair R, Rost B (2003). Better prediction of sub-cellular localization by combining evolutionary and structural information. Proteins 53, 917-930. |
| [34] | Park SC, Kim YH, Ji CY, Park S, Jeong JC, Lee HS, Kwak SS (2012). Stable internal reference genes for the normalization of Real-Time PCR in different sweetpotato cultivars subjected to abiotic stress conditions. PLoS One 7, e51502. |
| [35] | Park SC, Kim YH, Kim SH, Jeong YJ, Kim CY, Lee JS, Bae JY, Ahn MJ, Jeong JC, Lee HS, Kwak SS (2015). Overexpression of the IbMYB1 gene in an orange-fleshed sweet potato cultivar produces a dual-pigmented transgenic sweet potato with improved antioxidant activity. Physiol Plant 153, 525-537. |
| [36] | Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001). The R2R3- MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4, 447-456. |
| [37] | Sun W, Cao ZY, Li Y, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2007). A simple and effective method for protein subcellular localization using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of onion epidermal cells. Biologia 62, 529-532. |
| [38] | Wang B, Zhai H, He SZ, Zhang H, Ren ZT, Zhang DD, Liu QC (2016). A vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene, IbNHX2, enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic sweetpotato. Sci Hortic 201, 153-166. |
| [39] | Wu PP, Peng MS, Li ZG, Yuan N, Hu Q, Foster CE, Saski C, Wu GH, Sun DF, Luo H (2019). DRMY1, a Myb-like protein, regulates cell expansion and seed production in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 60, 285-302. |
| [40] | Xu R, Wang YH, Zheng H, Lu W, Wu CG, Huang JG, Yan K, Yang GD, Zheng CC (2015). Salt-induced transcription factor MYB74 is regulated by the RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 66, 5997-6008. |
| [41] | Yang J, Moeinzadeh MH, Kuhl H, Helmuth J, Xiao P, Haas S, Liu GL, Zheng JL, Sun Z, Fan WJ, Deng GF, Wang HX, Hu FH, Zhao SS, Fernie AR, Boerno S, Timmermann B, Zhang P, Vingron M (2017). Haplotype-resolved sweet potato genome traces back its hexaploidization history. Nat Plants 3, 696-703. |
| [42] | Zhai H, Wang FB, Si ZZ, Huo JX, Xing L, An YY, He SZ, Liu QC (2016). A myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase gene, IbMIPS1, enhances salt and drought tolerance and stem nematode resistance in transgenic sweet potato. Plant Biotechnol J 14, 592-602. |
| [43] | Zhang TQ, Zhao YL, Wang YC, Liu ZY, Gao CQ (2018). Comprehensive analysis of MYB gene family and their expressions under abiotic stresses and hormone treatments in Tamarix hispida. Front Plant Sci 9, 1303. |
| [44] | Zhao Y, Cheng XY, Liu XD, Wu HF, Bi HH, Xu HX (2018). The wheat MYB transcription factor TaMYB 31 is involved in drought stress responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 9, 1426. |
| [45] | Zhu ZG, Li GR, Liu L, Zhang QT, Han Z, Chen XS, Li B (2019). A R2R3-MYB transcription factor, VvMYBC2L2, functions as a transcriptional repressor of anthocyanin biosynthesis in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Molecules 24, 92. |
| [1] | 张文晶, 杨晓萌, 高侃, 魏欣仪, 石雪彤, 王瑞瑄, 武凤霞, 康菊清. 十字花科植物ABI4序列演化与转录激活活性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(6): 676-686. |
| [2] | 赖先军,张义正,古英洪,颜朗. 转昆虫抗冻蛋白基因增强甘薯抗冻能力[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 9-20. |
| [3] | 程广前,贾克利,李娜,邓传良,李书粉,高武军. 石刁柏核质体DNA的生物信息学分析及染色体定位[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 328-334. |
| [4] | 王晶珊 孙世孟 王维华 毕英娜 徐丽娟 孟祥霞. 甘薯同一不亲和群内品种间体细胞杂种[J]. 植物学报, 2004, 21(03): 306-311. |
| [5] | 程龙军 郭得平 葛红娟. 甘薯块根特异蛋白——Sporamin的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2001, 18(06): 672-677. |
| [6] | 兰平 李文凤 朱水芳 王振镒. 甘薯丛枝病植原体的PCR检测[J]. 植物学报, 2001, 18(02): 210-215. |
| [7] | 崔红 陈睦传. 甘薯生物技术研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 1999, 16(06): 653-657. |
| [8] | 崔红 丁群星 桂耀林 郭仲琛. 2,4 -D对甘薯体细胞胚胎发生的调控[J]. 植物学报, 1999, 16(04): 411-415. |
| [9] | 刘聪莉 张志芬 徐丽娟 孟祥霞 王晶珊. 甘薯叶柄原生质体有效植株再生[J]. 植物学报, 1999, 16(04): 420-424. |
| [10] | 卢从明 张其德 匡廷云. 水分胁迫对甘薯叶肉细胞光合电子传递的影响[J]. 植物学报, 1994, 11(01): 43-47. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||