

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 804-815.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25014 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25014
贾盖亚1,2, 张娜3, 李宏伟2, 李滨2, 李振声2, 孔照胜1, 郑琪2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-24
接受日期:2025-07-08
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-07-08
通讯作者:
*郑琪, 中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所研究员, 硕士生导师。2011年入选中国科学院青年创新促进会。2022年获中国科学院“特聘骨干”岗位。主要从事小麦-偃麦草远缘杂交后代的分子遗传学研究及小麦耐盐育种工作。主持国家自然科学基金、中国科学院STS、中国科学院战略性先导科技专项子课题和国家农业科技重大项目子课题等科研项目。在国际主流刊物上累计发表论文30余篇。获国家授权发明专利12项、植物新品种权7项, 审定小麦新品种3个。E-mail: qzheng@genetics.ac.cn
基金资助:
Jia Gaiya1,2, Zhang Na3, Li Hongwei2, Li Bin2, Li Zhensheng2, Kong Zhaosheng1, Zheng Qi2,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-24
Accepted:2025-07-08
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-07-08
Contact:
*E-mail: qzheng@genetics.ac.cn
摘要: 由于人工驯化与现代育种操作, 普通小麦(Triticum aestivum)的遗传多样性日渐狭窄, 更容易受到病虫害威胁。通过远缘杂交将野生近缘种的抗病基因导入小麦, 有助于拓宽小麦的遗传基础, 为培育抗病品种提供新抗原。十倍体长穗偃麦草(Thinopyrum ponticum)是小麦遗传改良中应用最广泛的近缘物种之一, 对小麦锈病等多种病害表现出良好的抗性。利用远缘杂交和染色体工程, 创制了1份小麦-长穗偃麦草种质材料WTS135, 对叶锈菌(Puccinia triticina)生理小种THTT表现出免疫。系谱分析表明, 其叶锈病抗性来源于长穗偃麦草外源染色体。基因组原位杂交(GISH)-荧光原位杂交分析显示, 1对十倍体长穗偃麦草染色体替换了小麦7D染色体。液相芯片分析表明, 外源染色体属于第7部分同源群, 其近着丝粒区的信号密度及丰度明显较低, 与GISH分析结果互相佐证, 因此推测WTS135是1个7St (7D)的二体异代换系。分子标记检测显示, WTS135携带的抗病基因与已知的长穗偃麦草第7部分同源群抗叶锈病基因Lr19和Lr29不同, 推测有可能为1个抗叶锈病新基因。借助Specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing技术, 开发了10个长穗偃麦草特异引物, 用于快速追踪WTS135中的外源染色质。表型调查显示, WTS135的产量与轮回亲本济麦22无显著差异, 可直接用于小麦的抗病育种。
贾盖亚, 张娜, 李宏伟, 李滨, 李振声, 孔照胜, 郑琪. 抗叶锈病小偃麦代换系WTS135的遗传学分析与分子标记开发. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 804-815.
Jia Gaiya, Zhang Na, Li Hongwei, Li Bin, Li Zhensheng, Kong Zhaosheng, Zheng Qi. Genetic Analysis and Molecular Marker Development for the WTS135‒a Common Wheat-Thinopyrum ponticum Substitution Line with Leaf Rust Resistance. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 804-815.
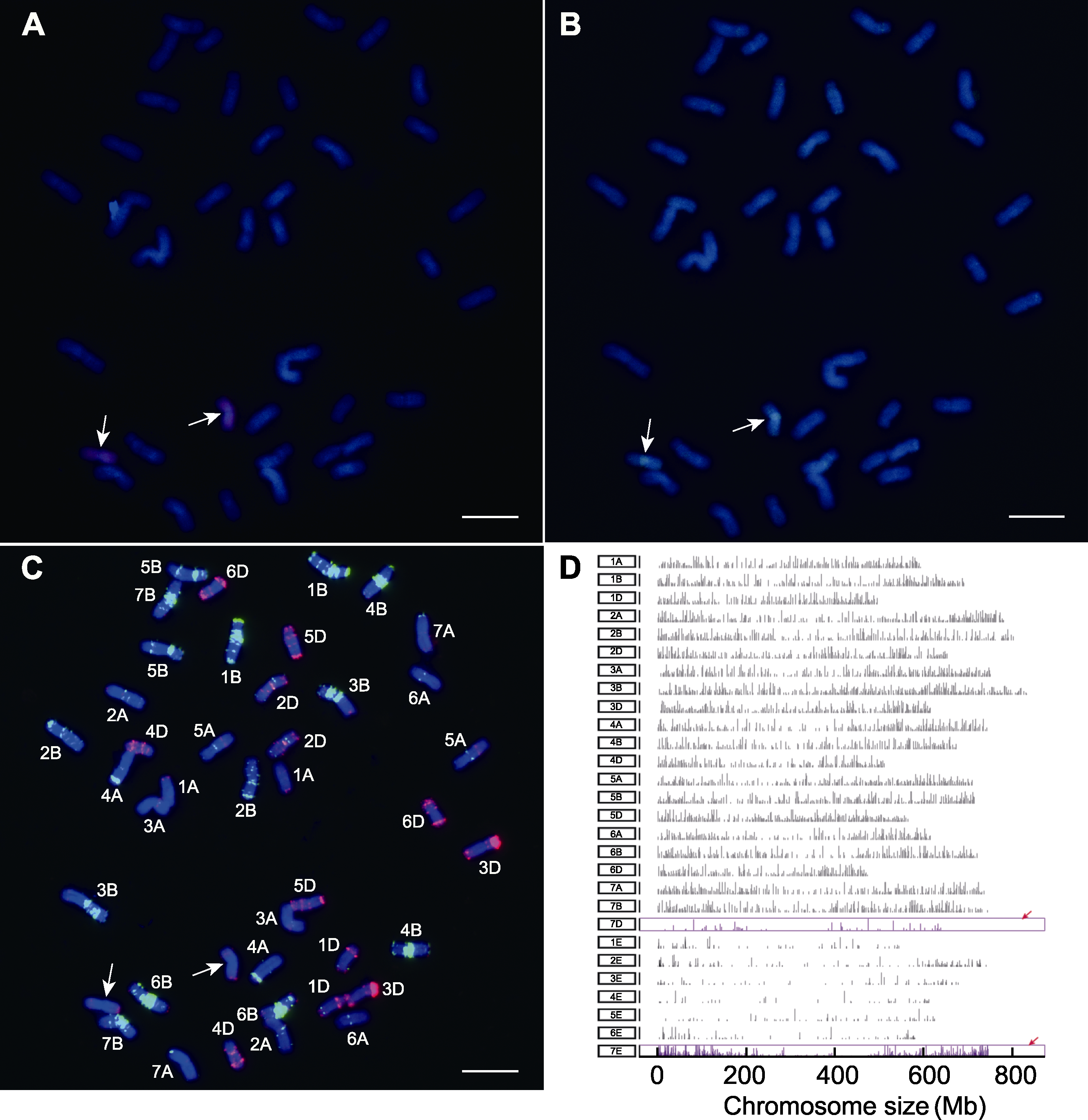
图1 WTS135的GISH、mc-FISH及液相芯片分析 (A) 以十倍体长穗偃麦草基因组DNA为探针, 中国春基因组DNA作封阻的GISH结果; (B) 以拟鹅观草基因组DNA为探针, 二倍体长穗偃麦草基因组作封阻的GISH结果; (C) 使用寡核苷酸探针套作探针的mc-FISH结果; (D) WTS135液相芯片结果。白色箭头表示外源染色体, 紫色框代表染色体的增加或缺失。Bars=20 μm。
Figure 1 GISH, mc-FISH, and liquid chip analysis of WTS135 (A) GISH analysis using Thinopyrum ponticum gDNA as a probe and Chinese Spring gDNA as a block; (B) GISH analysis using Pseudoroegneria stipifolia gDNA as a probe and Th. elongatum gDNA as a block; (C) Mc-FISH analysis using combined oligo probes; (D) The liquid chip analysis of WTS135. The white arrows indicate exogenous chromosomes, purple frames indicate chromosome additions or deletions. Bars=20 μm.
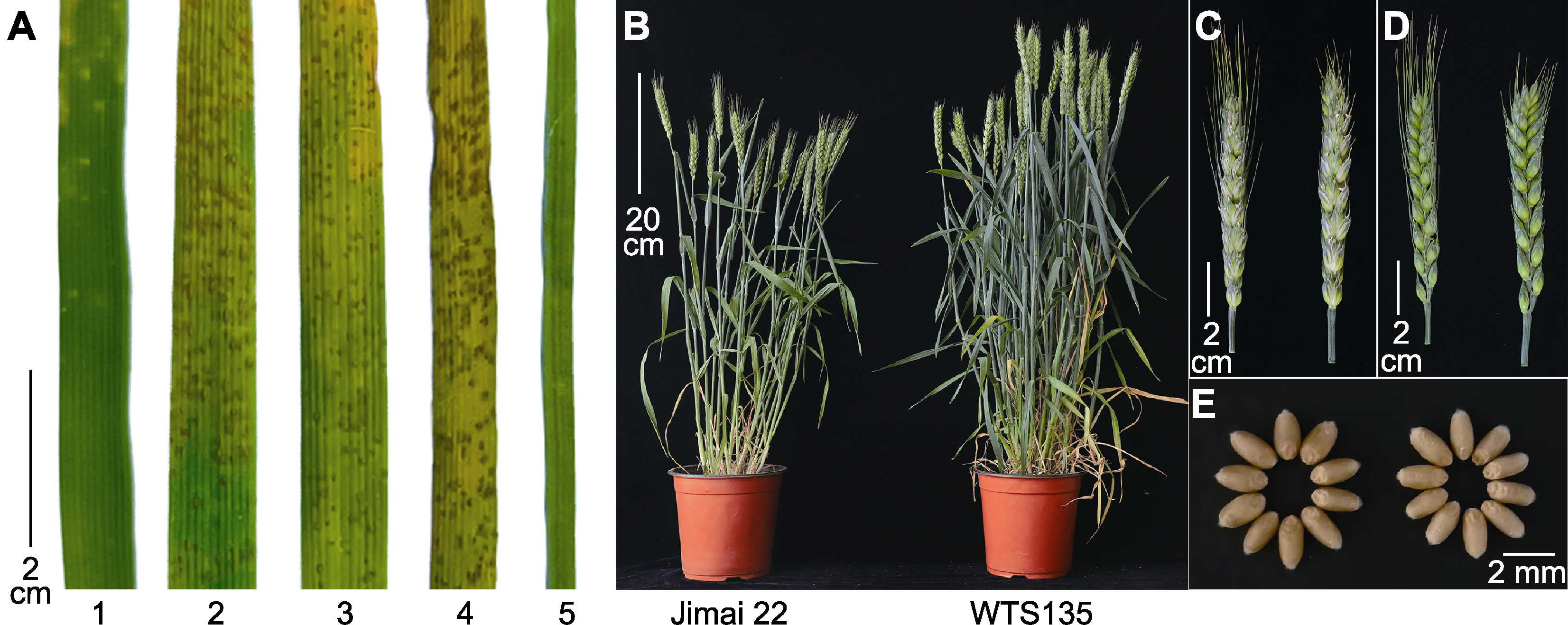

图2 WTS135及其亲本的叶锈病抗性评价及WTS135和济麦22的农艺性状 (A) WTS135及其亲本的叶锈病抗性评价(1: WTS135; 2: 小偃81; 3: 济麦22; 4: 中农28; 5: 十倍体长穗偃麦草); (B) 成株; (C) 主穗正面观(WTS135 (右), 济麦22 (左)); (D) 主穗侧面观(WTS135 (右), 济麦22 (左)); (E) 成熟籽粒(WTS135 (右), 济麦22 (左))。
Figure 2 Evaluation for leaf rust resistance in WTS135 and its parents, and agronomic traits of WTS135 and Jimai 22 (A) Evaluation for leaf rust resistance in WTS135 and its parents (1: WTS135; 2: Xiaoyan 81; 3: Jimai 22, 4: Zhongnong 28, 5: Thinopyrum ponticum); (B) Adult plants; (C) Front view of the main spike (WTS135 (right), Jimai 22 (left)); (D) Lateral view of the main spike (WTS135 (right), Jimai 22 (left)); (E) Matured seeds (WTS135 (right), Jimai 22 (left)).
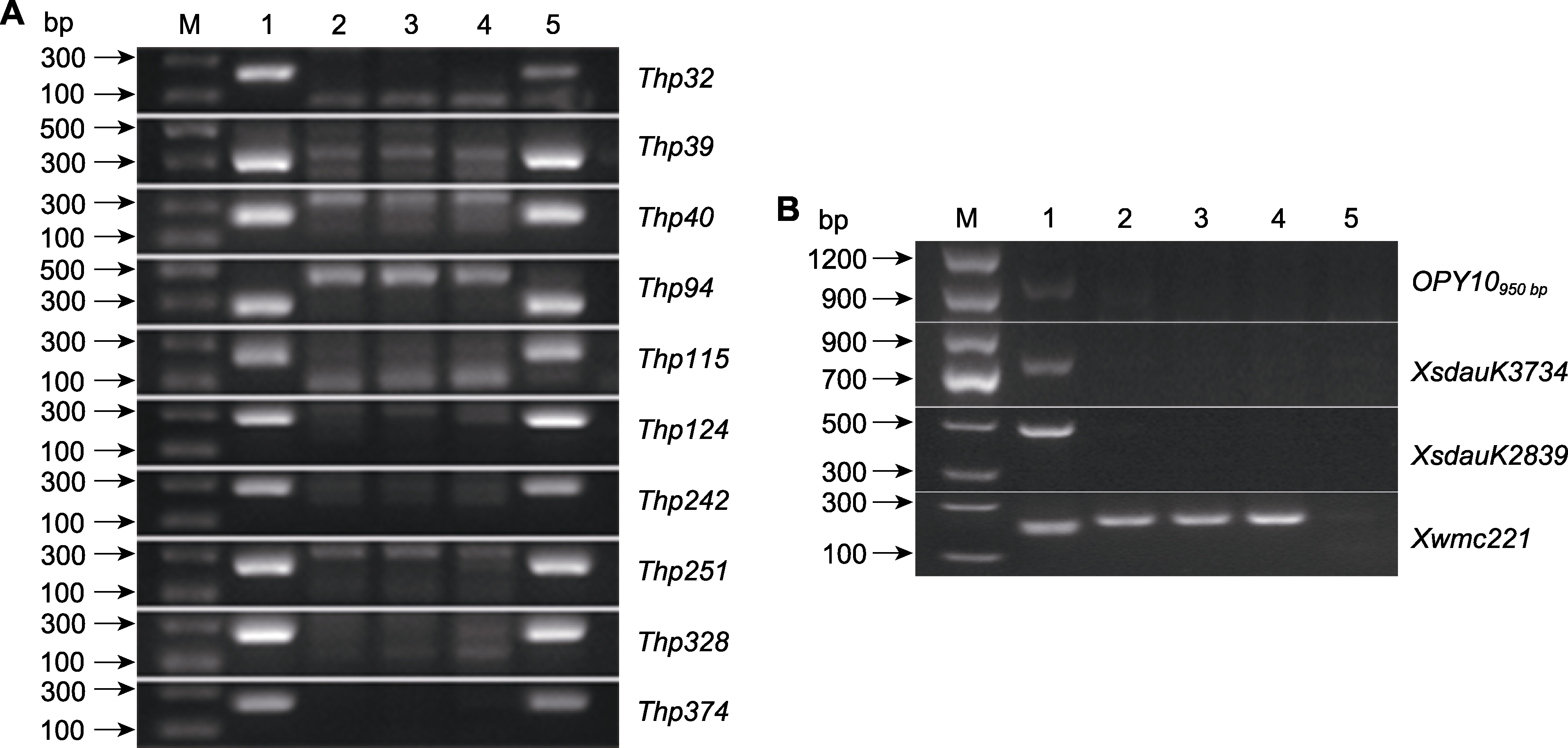
图3 10对长穂偃麦草特异引物的扩增结果(A)及Lr19和Lr29基因分子标记检测结果(B) M: Marker; 1: 长穗偃麦草; 2: 小偃81; 3: 济麦22; 4: 中农28; 5: WTS135
Figure 3 Amplification results of 10 pairs of Thinopyrum ponticum-specific primers (A) and the results of molecular marker detection of Lr19 and Lr29 (B) M: Marker; 1: Thinopyrum ponticum; 2: Xiaoyan 81; 3: Jimai 22; 4: Zhongnong 28; 5: WTS135
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5ʹ→3ʹ) | Fragment size (bp) | Annealing temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thp32 | F: TTGCAGCAGATCGAATCAAG R: CCTTCTTTCCCCGTTACTGTT | 237 | 51 |
| Thp39 | F: GCATCATCTGCATTGTCGTC R: TCTGCACATGATACCCCAGA | 290 | 52 |
| Thp40 | F: GACCATGTAGGTGCAACGTG R: AATCACAAAGCCCCTCCTTT | 270 | 52 |
| Thp94 | F: CCAAACCAACAAGCACATTG R: AGCACCTTTTGGATGACTGC | 285 | 51 |
| Thp115 | F: ACAAGCAGACGACAATGCAA R: TGAGTATTTCGAGGGTTGTGG | 220 | 52 |
| Thp124 | F: AGGCTGGATGACCGAGTATG R: GATCCAGTCGTGGAAGGTGT | 295 | 55 |
| Thp242 | F: CTGCATGAGCAGAGTCTGGA R: GAACTCCATTCACAGCAGCA | 290 | 54 |
| Thp251 | F: TTTTCTTTGCTGCCTTCGTT R: GCTTGTGGTGAAGCAAATCA | 260 | 51 |
| Thp328 | F: ATTTTCGCCACTCGTCATTC R: CTCTTGAAGGGGTCCAGACA | 270 | 51 |
| Thp374 | F: GCCCAGCAGACAGGTAAGTT R: CAGTGACGAACATCCCCTTT | 255 | 53 |
表1 WTS135中长穗偃麦草特异引物
Table 1 Thinopyrum ponticum-specific primers in WTS135
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5ʹ→3ʹ) | Fragment size (bp) | Annealing temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thp32 | F: TTGCAGCAGATCGAATCAAG R: CCTTCTTTCCCCGTTACTGTT | 237 | 51 |
| Thp39 | F: GCATCATCTGCATTGTCGTC R: TCTGCACATGATACCCCAGA | 290 | 52 |
| Thp40 | F: GACCATGTAGGTGCAACGTG R: AATCACAAAGCCCCTCCTTT | 270 | 52 |
| Thp94 | F: CCAAACCAACAAGCACATTG R: AGCACCTTTTGGATGACTGC | 285 | 51 |
| Thp115 | F: ACAAGCAGACGACAATGCAA R: TGAGTATTTCGAGGGTTGTGG | 220 | 52 |
| Thp124 | F: AGGCTGGATGACCGAGTATG R: GATCCAGTCGTGGAAGGTGT | 295 | 55 |
| Thp242 | F: CTGCATGAGCAGAGTCTGGA R: GAACTCCATTCACAGCAGCA | 290 | 54 |
| Thp251 | F: TTTTCTTTGCTGCCTTCGTT R: GCTTGTGGTGAAGCAAATCA | 260 | 51 |
| Thp328 | F: ATTTTCGCCACTCGTCATTC R: CTCTTGAAGGGGTCCAGACA | 270 | 51 |
| Thp374 | F: GCCCAGCAGACAGGTAAGTT R: CAGTGACGAACATCCCCTTT | 255 | 53 |
| Traits | Jimai 22 | WTS135 |
|---|---|---|
| Plant height (cm) | 69.00±3.00 | 82.25±1.26** |
| Effective tiller number | 13.33±1.53 | 23.75±1.71** |
| Spike length (cm) | 8.80±0.56 | 8.83±0.57 |
| Spikelet number per spike | 20.67±0.58 | 19.50±1.00 |
| Kernel number per spikelet | 43.67±2.89 | 47.50±3.87 |
| Total kernel number | 517.33±62.05 | 755.75±15.17** |
| Yield per plant (g) | 21.56±2.66 | 22.73±0.50 |
| Thousand-kernel weight (g) | 41.67±1.12** | 30.07±0.11 |
表2 WTS135与济麦22的农艺性状对比
Table 2 Comparison of agronomic traits between WTS135 and Jimai 22
| Traits | Jimai 22 | WTS135 |
|---|---|---|
| Plant height (cm) | 69.00±3.00 | 82.25±1.26** |
| Effective tiller number | 13.33±1.53 | 23.75±1.71** |
| Spike length (cm) | 8.80±0.56 | 8.83±0.57 |
| Spikelet number per spike | 20.67±0.58 | 19.50±1.00 |
| Kernel number per spikelet | 43.67±2.89 | 47.50±3.87 |
| Total kernel number | 517.33±62.05 | 755.75±15.17** |
| Yield per plant (g) | 21.56±2.66 | 22.73±0.50 |
| Thousand-kernel weight (g) | 41.67±1.12** | 30.07±0.11 |
| [1] | Deng PC, Du X, Wang YZ, Yang XY, Cheng XF, Huang CX, Li TT, Li TD, Chen CH, Zhao JX, Wang CY, Liu XL, Tian ZR, Ji WQ (2024). GenoBaits®WheatplusEE: a targeted capture sequencing panel for quick and accurate identification of wheat-Thinopyrum derivatives. Theor Appl Genet 137, 36. |
| [2] | Duan ZY, Xu XY, Li X, Li ZF, Ma J, Yao ZJ (2021). Leaf rust resistance gene analysis of 12 wheat cultivars in main producing areas. Crops 37(5), 20-27. (in Chinese) |
| 段振盈, 徐新玉, 李星, 李在峰, 马骏, 姚占军 (2021). 12个主产区历史小麦品种抗叶锈病基因分析. 作物杂志 37(5), 20-27. | |
| [3] |
Friebe B, Jiang J, Gill BS, Dyck PL (1993). Radiation- induced nonhomoeologous wheat-Agropyron intermedium chromosomal translocations conferring resistance to leaf rust. Theor Appl Genet 86, 141-149.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Friebe B, Jiang J, Raupp WJ, McIntosh RA, Gill BS (1996). Characterization of wheat-alien translocations conferring resistance to diseases and pests: current status. Euphytica 91, 59-87. |
| [5] | Fu SL, Lv ZL, Qi B, Guo X, Li J, Liu B, Han FP (2012). Molecular cytogenetic characterization of wheat-Thinopyrum elongatum addition, substitution and translocation lines with a novel source of resistance to wheat Fusarium Head Blight. J Genet Genomics 39, 103-110. |
| [6] | Gupta SK, Charpe A, Prabhu KV, Haque QMR (2006). Identification and validation of molecular markers linked to the leaf rust resistance gene Lr19 in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 113, 1027-1036. |
| [7] |
Han FP, Lamb JC, Birchler JA (2006). High frequency of centromere inactivation resulting in stable dicentric chromosomes of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 3238-3243.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | He ZL, Zhang HK, Gao SH, Lercher MJ, Chen WH, Hu SN (2016). Evolview v2: an online visualization and management tool for customized and annotated phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res 44, W236-W241. |
| [9] | Huang XY, Zhu MQ, Zhuang LF, Zhang SY, Wang JJ, Chen XJ, Wang DR, Chen JY, Bao YG, Guo J, Zhang JL, Feng YG, Chu CG, Du P, Qi ZJ, Wang HG, Chen PD (2018). Structural chromosome rearrangements and polymorphisms identified in Chinese wheat cultivars by high- resolution multiplex oligonucleotide FISH. Theor Appl Genet 131, 1967-1986. |
| [10] | Ibba MI, Gupta OP, Govindan V, Johnson AAT, Brinch- Pedersen H, Nikolic M, Taleon V (2022). Editorial: wheat biofortification to alleviate global malnutrition. Front Nutr 9, 1001443. |
| [11] |
Jiang J, Friebe B, Gill BS (1994). Chromosome painting of Amigo wheat. Theor Appl Genet 89, 811-813.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Knott DR (1968). Translocations involving Triticum chromosomes and Agropyron chromosomes carrying rust resistance. Can J Genet Cytol 10, 695-696. |
| [13] |
Leng YK, Sun K, Chen XY, Li WW (2015). Suspension arrays based on nanoparticle-encoded microspheres for high-throughput multiplexed detection. Chem Soc Rev 44, 5552-5595.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Li JB, Guan HX, Wang YQ, Dong CM, Trethowan R, McIntosh RA, Zhang P (2024). Cytological and molecular characterization of wheat lines carrying leaf rust and stem rust resistance genes Lr24 and Sr24. Sci Rep 14, 12816. |
| [15] | Li MZ, Wang YZ, Liu XJ, Li XF, Wang HG, Bao YG (2021). Molecular cytogenetic identification of a novel wheat- Thinopyrum ponticum 1JS (1B) substitution line resistant to powdery mildew and leaf rust. Front Plant Sci 12, 727734. |
| [16] | Li ZS, Li B, Tong YP (2008). The contribution of distant hybridization with decaploid Agropyron elongatum to wheat improvement in China. J Genet Genomics 35, 451-456. |
| [17] | Lin GF, Chen H, Tian B, Sehgal SK, Singh L, Xie JZ, Rawat N, Juliana P, Singh N, Shrestha S, Wilson DL, Shult H, Lee H, Schoen AW, Tiwari VK, Singh RP, Guttieri MJ, Trick HN, Poland J, Bowden RL, Bai GH, Gill B, Liu SZ (2022). Cloning of the broadly effective wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr42 transferred from Aegilops tauschii. Nat Commun 13, 3044. |
| [18] | Ling HQ, Ma B, Shi XL, Liu H, Dong LL, Sun H, Cao YH, Gao Q, Zheng SS, Li Y, Yu Y, Du HL, Qi M, Li Y, Lu H, Yu HW, Cui Y, Wang N, Chen CL, Wu HL, Zhao Y, Zhang JC, Li YW, Zhou WJ, Zhang BR, Hu WJ, van Eijk MJT, Tang JF, Witsenboer HMA, Zhao SC, Li ZS, Zhang AM, Wang DW, Liang CZ (2018). Genome sequence of the progenitor of wheat A subgenome Triticum urartu. Nature 557, 424-428. |
| [19] | Mago R, Zhang P, Xia XD, Zhang JP, Hoxha S, Lagudah E, Graner A, Dundas I (2019). Transfer of stem rust resistance gene SrB from Thinopyrum ponticum into wheat and development of a closely linked PCR-based marker. Theor Appl Genet 132, 371-382. |
| [20] | Mapuranga J, Chang JY, Zhao JJ, Liang ML, Li RL, Wu YH, Zhang N, Zhang LR, Yang WX (2023). The underexplored mechanisms of wheat resistance to leaf rust. Plants (Basel) 12, 3996. |
| [21] |
Niu Z, Klindworth DL, Yu G, Friesen TL, Chao S, Jin Y, Cai X, Ohm JB, Rasmussen JB, Xu SS (2014). Development and characterization of wheat lines carrying stem rust resistance gene Sr43 derived from Thinopyrum ponticum. Theor Appl Genet 127, 969-980.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Peto FH (1936). Hybridization of Triticum and Agropyron. II. Cytology of the male parents and F1 generation. Can J Res 14c, 203-214. |
| [23] | Pirseyedi SM, Somo M, Poudel RS, Cai XW, McCallum B, Saville B, Fetch T, Chao SAM, Marais F (2015). Characterization of recombinants of the Aegilops peregrina-derived Lr59 translocation of common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 128, 2403-2414. |
| [24] | Prasad P, Savadi S, Bhardwaj SC, Gupta PK (2020). The progress of leaf rust research in wheat. Fungal Biol 124, 537-550. |
| [25] | Reynolds M, Foulkes J, Furbank R, Griffiths S, King J, Murchie E, Parry M, Slafer G (2012). Achieving yield gains in wheat. Plant Cell Environ 35, 1799-1823. |
| [26] | Roelfs AP, Singh RP, Saari EE (1992). Rust Diseases of Wheat: Concepts and Methods of Disease Management. Mexico: CIMMYT. pp. 7-14. |
| [27] |
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984). Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81, 8014-8018.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Sears ER (1973). Agropyron -wheat transfers induced by homoeologous pairing. In:Proceedings of the Fourth International Wheat Genetics Symposium Alien Genetic Material. pp.191-199. |
| [29] | Sears ER (1977). Analysis of wheat-Agropyron recombinant chromosomes. In:Proceedings of the 8th Eucarpia Congress. pp. 63-72. |
| [30] | Sharma D, Knott DR (1966). The transfer of leaf-rust resistance from Agropyron to Triticum by irradiation. Can J Genet Cytol 8, 137-143. |
| [31] | Singh A, Pallavi JK, Gupta P, Prabhu KV (2012). Identification of microsatellite markers linked to leaf rust resistance gene Lr25 in wheat. J Appl Genet 53, 19-25. |
| [32] |
Singh RP, Singh PK, Rutkoski J, Hodson DP, He XY, Jørgensen LN, Hovmøller MS, Huerta-Espino J (2016). Disease impact on wheat yield potential and prospects of genetic control. Annu Rev Phytopathol 54, 303-322.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Smith EL, Schlehuber AM, Young HC Jr, Edwards LH (1968). Registration of agent wheat (reg. no. 471). Crop Sci 8, 511-512. |
| [34] | Tar M, Purnhauser L, Csősz L, Mesterházy Á, Gyulai G (2002). Identification of molecular markers for an efficient leaf rust resistance gene (Lr29) in wheat. Acta Biol Szeged 46, 133-134. |
| [35] | Tripathi AD, Mishra R, Maurya KK, Singh RB, Wilson DW (2019). Estimates for world population and global food availability for global health. In: Singh RB, Watson RR, Takahashi T, eds. The Role of Functional Food Security in Global Health. London: Academic Press. pp. 3-24. |
| [36] | Tsitsin NV (1965). Remote hybridisation as a method of creating new species and varieties of plants. Euphytica 14, 326-330. |
| [37] |
Wang K, Li MY, Hakonarson H (2010). ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38, 164.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | Wang SW, Wang CY, Feng XB, Zhao JX, Deng PC, Wang YJ, Zhang H, Liu XL, Li TD, Chen CH, Wang BT, Ji WQ (2022). Molecular cytogenetics and development of St-chromosome-specific molecular markers of novel stripe rust resistant wheat-Thinopyrum intermedium and wheat- Thinopyrum ponticum substitution lines. BMC Plant Biol 22, 111. |
| [39] | Wang YZ, Cao Q, Zhang JJ, Wang SW, Chen CH, Wang CY, Zhang H, Wang YJ, Ji WQ (2020). Cytogenetic analysis and molecular marker development for a new wheat-Thinopyrum ponticum 1JS (1D) disomic substitution line with resistance to stripe rust and powdery mildew. Front Plant Sci 11, 1282. |
| [40] | Xu SS, Lyu ZF, Zhang N, Li MZ, Wei XY, Gao YH, Cheng XX, Ge WY, Li XF, Bao YG, Yang ZJ, Ma X, Wang HW, Kong LR (2023). Genetic mapping of the wheat leaf rust resistance gene Lr19 and development of translocation lines to break its linkage with yellow pigment. Theor Appl Genet 136, 200. |
| [41] | Yang GT, Deng PC, Ji WQ, Fu SL, Li HW, Li B, Li ZS, Zheng Q (2023a). Physical mapping of a new powdery mildew resistance locus from Thinopyrum ponticum chromosome 4AgS. Front Plant Sci 14, 1131205. |
| [42] | Yang GT, Zhang N, Boshoff WHP, Li HW, Li B, Li ZS, Zheng Q (2023b). Identification and introgression of a novel leaf rust resistance gene from Thinopyrum intermedium chromosome 7JS into wheat. Theor Appl Genet 136, 231. |
| [43] | Zhang JL, Jie YZ, Yan LJ, Wang MM, Dong YL, Pang YF, Ren CC, Song J, Chen XD, Li XJ, Zhang PP, Yang DY, Zhang Y, Qi ZJ, Ru ZG (2024). Development and identification of a novel wheat-Thinopyrum ponticum disomic substitution line DS5Ag(5D) with new genes conferring resistance to powdery mildew and leaf rust. BMC Plant Biol 24, 718. |
| [44] |
Zhang L, Shi CC, Li LR, Li M, Meng QF, Yan HF, Liu DQ (2020). Race and virulence analysis of Puccinia triticina in China in 2014 and 2015. Plant Dis 104, 455-464.
DOI PMID |
| [45] | Zhang WJ, Lukaszewski AJ, Kolmer J, Soria MA, Goyal S, Dubcovsky J (2005). Molecular characterization of durum and common wheat recombinant lines carrying leaf rust resistance (Lr19 (Lr19) and yellow pigment (Y) genes from Lophopyrum ponticum. Theor Appl Genet 111, 573-582. |
| [46] |
Zhang XY, Dong YS, Wang RRC (1996). Characterization of genomes and chromosomes in partial amphiploids of the hybrid Triticum aestivum × Thinopyrum ponticum by in situ hybridization, isozyme analysis, and RAPD. Genome 39, 1062-1071.
DOI PMID |
| [47] | Zhao GY, Zou C, Li K, Wang K, Li TB, Gao LF, Zhang XX, Wang HJ, Yang ZJ, Liu X, Jiang WK, Mao L, Kong XY, Jiao YN, Jia JZ (2017). The Aegilops tauschii genome reveals multiple impacts of transposons. Nat Plants 3, 946-955. |
| [48] | Zhou JM (2020). Fighting Fusarium head blight in wheat—a remedy from afar. Chin Bull Bot 55, 123-125. (in Chinese) |
|
周俭民 (2020). 小麦抗赤霉病利器——他山之石. 植物学报 55, 123-125.
DOI |
|
| [49] |
Zhu C, Wang YZ, Chen CH, Wang CY, Zhang AC, Peng NN, Wang YJ, Zhang H, Liu XL, Ji WQ (2017). Molecular cytogenetic identification of a wheat-Thinopyrum ponticum substitution line with stripe rust resistance. Genome 60, 860-867.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 许庭旸, 刘雨辰, 王万鹏, 苏航, 苏昆龙, 吴振映, 吕明, 李福利, 王小山, 付春祥. 喷施不同植物生长调节剂对盐碱地小麦生长发育的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 354-362. |
| [2] | 杨志刚, 张鹏程, 常海文, 康立茹, 左毅, 向浩鑫, 韩凤英. 基于形态学性状和SSR标记的辣椒种质资源遗传多样性分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 218-234. |
| [3] | 左毅, 刘红兵, 杨志刚, 李彬, 向浩鑫, 朱纯真, 王雷. 基于全基因组关联分析筛选山桐子性别分子标记(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 414-421. |
| [4] | 刘笑, 杜琬莹, 张云秀, 唐成名, 李华伟, 夏海勇, 樊守金, 孔令安. NO3-缓解小麦根部NH4+毒性机理(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 397-413. |
| [5] | 王文静, 朱钰, 张洪铭, 韦陆丹, 易庆平, 余晓敏, 刘雨菡, 张莉雪, 程文翰, 何燕红. 万寿菊舌状花花冠裂片突变体的形态鉴定及连锁标记开发[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 893-904. |
| [6] | 武棒棒, 郝宇琼, 杨淑斌, 黄雨茜, 关攀锋, 郑兴卫, 赵佳佳, 乔玲, 李晓华, 刘维仲, 郑军. 山西小麦籽粒叶黄素含量变异及遗传特性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 535-547. |
| [7] | 孙尚, 胡颖颖, 韩阳朔, 薛超, 龚志云. 水稻染色体双链寡核苷酸荧光原位杂交技术[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 433-439. |
| [8] | 白明义, 彭金荣, 傅向东. 赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号通路双重调控助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 194-198. |
| [9] | 张凡凡, 邢新滢, 石文清, 沈懿, 程祝宽. 植物寡核苷酸荧光原位杂交技术方法[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 274-284. |
| [10] | 李宏伟, 郑琪, 李滨, 李振声. 长穗偃麦草分子育种基础研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 792-801. |
| [11] | 谭文清, 陈军, 才宏伟. 黑麦草生物学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 802-813. |
| [12] | 孔令让. 另辟蹊径破解小麦条锈病的基因密码[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 405-408. |
| [13] | 胡滨滨, 薛治慧, 张翠. 植物小RNA荧光原位杂交实验方法[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 330-338. |
| [14] | 车明哲, 王亚军, 马创新, 漆小泉. 大麦抗叶锈病慢锈性鉴定技术及抗性评价方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 573-576. |
| [15] | 周俭民. 小麦抗赤霉病利器——他山之石[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 123-125. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||