

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 414-421.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24029 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24029
左毅1,5, 刘红兵2, 杨志刚1,6, 李彬1,5, 向浩鑫1,4, 朱纯真1,4, 王雷1,3,4,5,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-28
接受日期:2024-05-06
出版日期:2024-05-10
发布日期:2024-05-10
通讯作者:
王雷
基金资助:
Yi Zuo1,5, Hongbing Liu2, Zhigang Yang1,6, Bin Li1,5, Haoxin Xiang1,4, Chunzhen Zhu1,4, Lei Wang1,3,4,5,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-28
Accepted:2024-05-06
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-10
Contact:
Lei Wang
摘要: 山桐子(Idesia polycarpa)是我国特有且极具开发潜力的油料树种, 果实含油率高且油品好。在苗期通过分子生物学手段对山桐子进行性别鉴定, 可有效降低种苗培养成本。在前期组装的染色体级别高质量山桐子基因组基础上, 进一步对山桐子雌雄群体进行全基因组重测序, 根据雌雄株系的特异性片段, 确定山桐子属于ZW/ZZ性别决定类型; 并根据3.365×107个SNPs, 结合性别表型进行全基因组关联分析, 找到控制性别的19号染色体, 并将性别决定区段定位到35 Mb附近; 针对显著性位点, 开发了性别共显性CAPS分子标记。该方法可在幼苗期快速、高效鉴定山桐子的性别, 极大地降低了山桐子育苗环节的生产成本, 也可在山桐子种质鉴定及分子标记辅助育种等方面为产业提供技术支撑。
左毅, 刘红兵, 杨志刚, 李彬, 向浩鑫, 朱纯真, 王雷. 基于全基因组关联分析筛选山桐子性别分子标记(长英文摘要). 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 414-421.
Yi Zuo, Hongbing Liu, Zhigang Yang, Bin Li, Haoxin Xiang, Chunzhen Zhu, Lei Wang. Identification of Sex Determination Molecular Marker Based on Genome-wide Association Study of Idesia polycarpa. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 414-421.
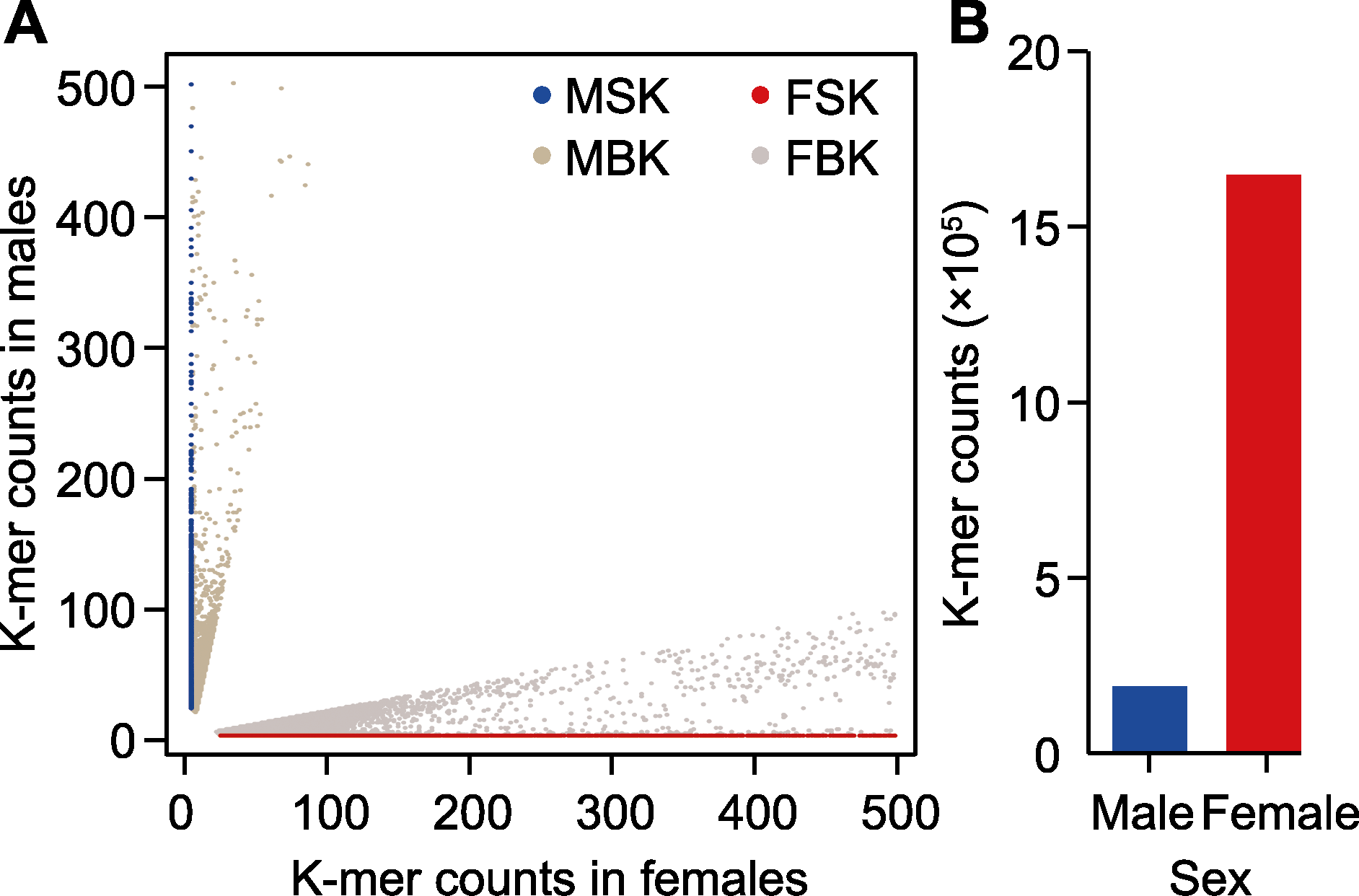
图1 山桐子性别决定类型 (A) 性别特异35 bp K-mers的分布图(MSK: 雄株特异K-mers; MBK: 雄株偏好性K-mers; FSK: 雌株特异K-mers; FBK: 雌株偏好性K-mers)。(B) 雌株与雄株之间特异性K-mers数量差异统计图。
Figure 1 The sex-determination system in Idesia polycarpa (A) Distribution of sex-specific K-mers (MSK: Male-specific K-mers; MBK: Male-biased K-mers; FSK: Female-specific K-mers; FBK: Female-biased K-mers.). (B) The histogram shows the quantitative differences between MSK and FSK.
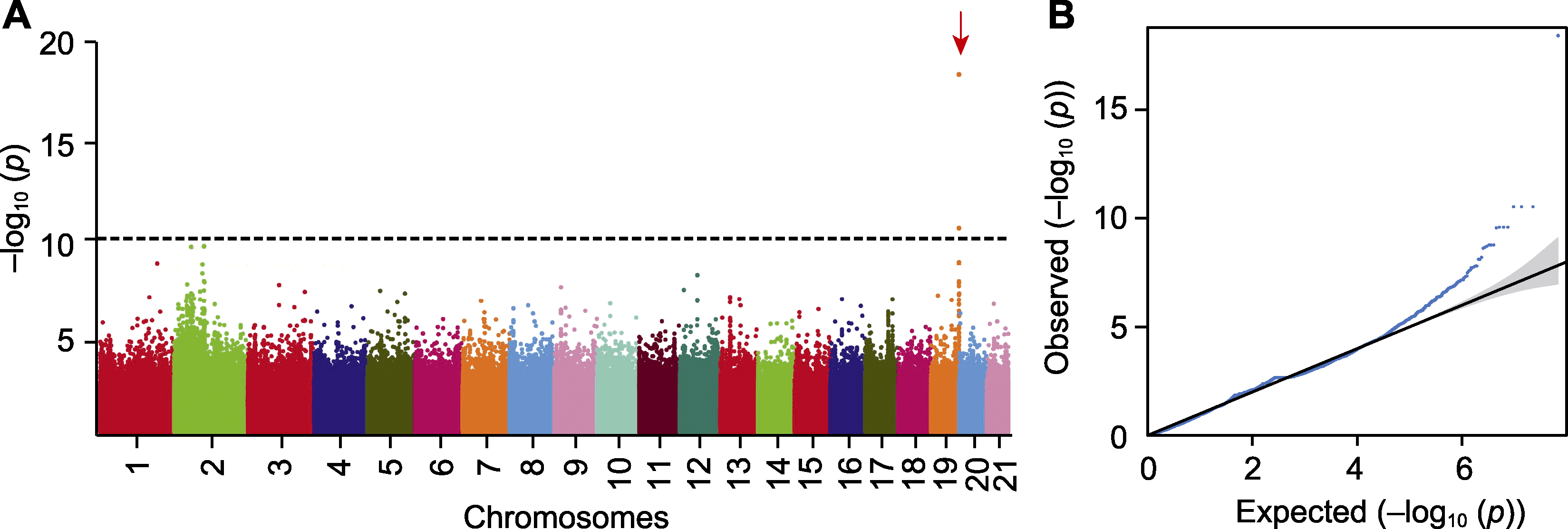
图3 山桐子性别全基因组关联分析(GWAS)的曼哈顿图(A)和QQ图(B)Figure 3 Manhattan plot (A) and QQ plot (B) of sex phenotype in genome-wide association study (GWAS) 红色箭头指示显著的峰值。
The red arrow indicates the significant peak.
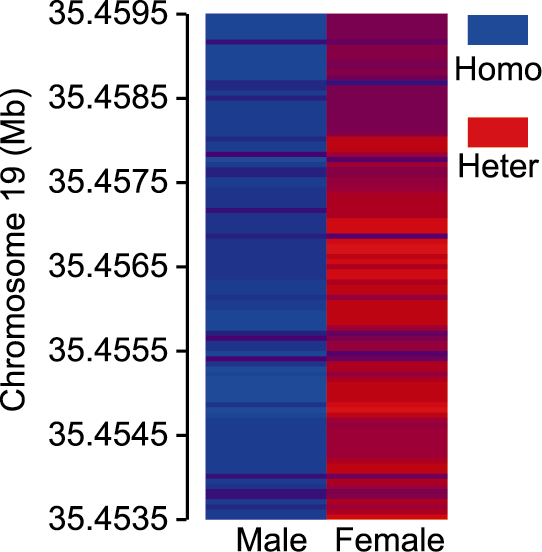
图4 雌雄群体在性别决定区间单核䒤酸多态性(SNPs)的杂合度统计分析Figure 4 Heterozygosity statistics of single nucleotide poly- morphisms (SNPs) in sex determination region between ma- le and female groups Homo: 纯合子; Heter: 杂合子
Homo: Homozygous; Heter: Heterozygous
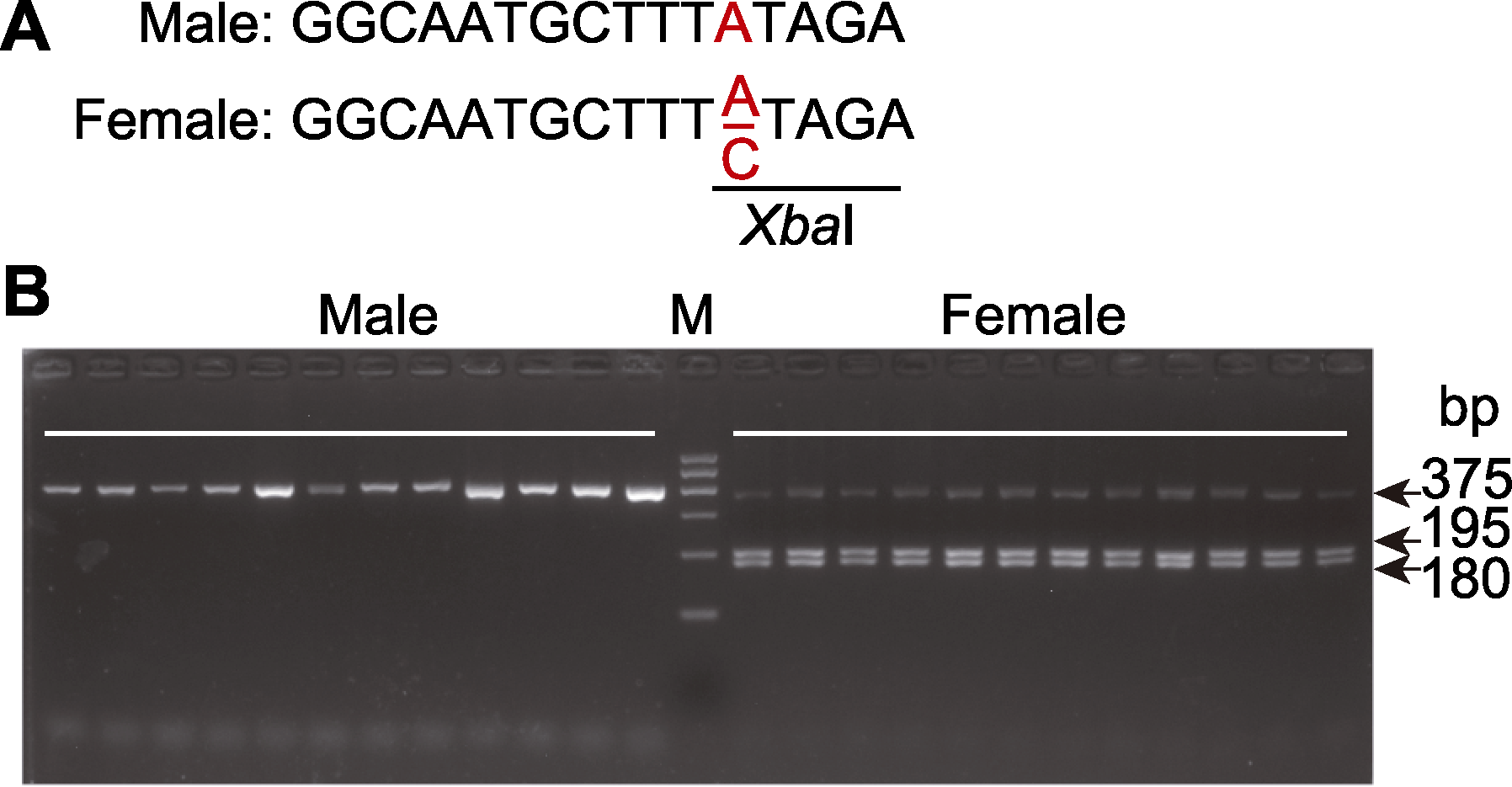
图5 酶切扩增多态性序列(CAPS)分子标记和琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定山桐子性别 (A) 雄株与雌株之间的序列差异可被特定的限制性内切酶识别; (B) CAPS分子标记可通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳获得的带型区分雌雄株, 只有1条带型(375 bp)的是雄株, 有3条带型(375、195和180 bp)的是雌株。M: DNA分子标记。从上到下读600 bp到100 bp按梯度递减。
Figure 5 The cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS) marker and agarose gel electrophoresis were applied for sex determination (A) The sequence difference can be recognized by specific restriction enzyme between male and female; (B) The fragment difference was determined by agarose gel electrophoresis. The unique band of 375 bp was associated with male, while the three bands (375 bp, 195 bp and 180 bp) were associated with female. M: DNA marker. The DNA ladder measures from 600 bp to 100 bp.
| [1] | 卢翔, 李效文, 郑坚, 王金旺, 夏海涛, 陈秋夏 (2010). 木本油料树种山桐子研究进展. 农业科技通讯 (5), 123-127. |
| [2] | 四川森迪科技发展股份有限公司 (2017). 一种毛叶山桐子幼苗雌雄株的鉴别方法. 中国专利, CN201710128456.X.2017-03-06. |
| [3] | 张志成, 王国礼 (1981). 一种优良的木本油料树——水冬瓜. 陕西林业科技 (5), 54-55. |
| [4] | Akagi T, Henry IM, Ohtani H, Morimoto T, Beppu K, Kataoka I, Tao R (2018). A Y-encoded suppressor of feminization arose via lineage-specific duplication of a cytokinin response regulator in kiwifruit. Plant Cell 30, 780-795. |
| [5] | Akagi T, Henry IM, Tao R, Comai L (2014). A Y-chromosome- encoded small RNA acts as a sex determinant in persimmons. Science 346, 646-650. |
| [6] | Coelho SM, Mignerot L, Cock JM (2019). Origin and evo- lution of sex-determination systems in the brown algae. New Phytol 222, 1751-1756. |
| [7] | Dong N, Tang XS, Tang L (2016). Screening and analysis of sex-related ISSR molecular marker in Idesia polycarpa Maxim. var. vestita Diels. J Sichuan Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 53, 465-470. (in Chinese) |
| 董娜, 唐晓姗, 唐琳 (2016). 毛叶山桐子性别相关ISSR分子标记的筛选与分析. 四川大学学报(自然科学版) 53, 465-470 | |
| [8] | Feng C, Wang XW, Wu SS, Ning WD, Song B, Yan JB, Cheng SF (2022). HAPPE: a tool for population haplotype analysis and visualization in editable excel tables. Front Plant Sci 13, 927407. |
| [9] |
Geraldes A, Hefer CA, Capron A, Kolosova N, Martinez-Nuñez F, Soolanayakanahally RY, Stanton B, Guy RD, Mansfield SD, Douglas CJ, Cronk QCB (2015). Recent Y chromosome divergence despite ancient origin of dioecy in poplars (Populus). Mol Ecol 24, 3243-3256.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Jeon SA, Park JL, Park SJ, Kim JH, Goh SH, Han JY, Kim SY (2021). Comparison between MGI and Illumina se- quencing platforms for whole genome sequencing. Genes Genomics 43, 713-724. |
| [11] | Lee GA, Koh HJ, Chung HK, Dixit A, Chung JW, Ma KH, Lee SY, Lee JR, Lee GS, Gwag JG, Kim TS, Park YJ (2009). Development of SNP-based CAPS and dCAPS markers in eight different genes involved in starch biosynthesis in rice. Mol Breeding 24, 93-101. |
| [12] | Li TT, Li FS, Mei LJ, Li N, Yao M, Tang L (2020). Tran- scriptome analysis of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. var vestita Diels flowers during sex differentiation. J For Res 31, 2463-2478. |
| [13] | Lu J, Chen YN, Yin TM (2021). Research progress on sex determination genes of woody plants. Chin Bull Bot 56, 90-103. (in Chinese) |
| 陆静, 陈赢男, 尹佟明 (2021). 木本植物性别决定基因研究进展. 植物学报 56, 90-103. | |
| [14] | Mei LJ, Dong N, Li FS, Li N, Yao M, Chen F, Tang L (2017). Transcriptome analysis of female and male flower buds of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. var. vestita Diels. Elect-ron J Biotechn 29, 39-46. |
| [15] | Pakull B, Groppe K, Mecucci F, Gaudet M, Sabatti M, Fladung M (2011). Genetic mapping of linkage group XIX and identification of sex-linked SSR markers in a Populus tremula × Populus tremuloides cross. Can J For Res 41, 245-253. |
| [16] | Pakull B, Groppe K, Meyer M, Markussen T, Fladung M (2009). Genetic linkage mapping in aspen (Populus tremula L. and Populus tremuloides Michx). Tree Genet Genomes 5, 505-515. |
| [17] | Paolucci I, Gaudet M, Jorge V, Beritognolo I, Terzoli S, Kuzminsky E, Muleo R, Mugnozza GS, Sabatti M (2010). Genetic linkage maps of Populus alba L. and comparative mapping analysis of sex determination across Populus species. Tree Genet Genomes 6, 863-875. |
| [18] | Peto FH (1938). Cytology of poplar species and natural hybrids. Can J Res 16c, 445-455. |
| [19] |
Renner SS, Müller NA (2021). Plant sex chromosomes defy evolutionary models of expanding recombination suppression and genetic degeneration. Nat Plants 7, 392-402.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Renner SS, Ricklefs RE (1995). Dioecy and its correlates in the flowering plants. Am J Bot 82, 596-606. |
| [21] | Sabatti M, Gaudet M, Müller NA, Kersten B, Gaudiano C, Mugnozza GS, Fladung M, Beritognolo I (2020). Long- term study of a subdioecious Populus × canescens family reveals sex lability of females and reproduction behaviour of cosexual plants. Plant Rep 33, 1-17. |
| [22] |
Sanderson BJ, Feng GQ, Hu N, Carlson CH, Smart LB, Keefover-Ring K, Yin TM, Ma T, Liu JQ, DiFazio SP, Olson MS (2021). Sex determination through X-Y heterogamety in Salix nigra. Heredity 126, 630-639.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Shu YJ, Li Y, Zhu ZL, Bai X, Cai H, Ji W, Guo DJ, Zhu YM (2011). SNPs discovery and CAPS marker conversion in soybean. Mol Biol Rep 38, 1841-1846.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Stratton M (2008). Genome resequencing and genetic variation. Nat Biotechnol 26, 65-66.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Walas Ł, Mandryk W, Thomas PA, Tyrała-Wierucka Ż, Iszkulo G (2018) Sexual systems in gymnosperms: a re- view. Basic Appl Ecol 31, 1-9. |
| [26] |
Wang SH, Li Y, Li ZQ, Chang L, Li L (2015). Identification of an SCAR marker related to female phenotype in Idesia polycarpa Maxim. Genet Mol Res 14, 2015-2022.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Wu ZW, Xie SX, Liu Q, Du WJ (2010). Research progress and application prospect of Idesia polycarpa. Guizhou Ag- ric Sci 38, 161-164. (in Chinese) |
| 吴志文, 谢双喜, 刘青, 杜文军 (2010). 山桐子的研究进展及应用前景. 贵州农业科学 38, 161-164. | |
| [28] | Xue LJ, Wu HT, Chen YN, Li XP, Hou J, Lu J, Wei SY, Dai XG, Olson MS, Liu JQ, Wang MX, Charlesworth D, Yin TM (2020). Two antagonistic effect genes mediate sepa- ration of sexes in a fully dioecious plant. bioRxiv. [2020- 03-15]. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.15.993022 |
| [29] | Yan L (2018). Research and Development of Sex-related Molecular Markers in Idesia polycarpa. Master’s thesis. Wuhan: Yangtze University. pp. 17-19. (in Chinese) |
| 严莉 (2018). 山桐子性别相关分子标记的研究与开发. 硕士论文. 武汉: 长江大学. pp. 17-19. | |
| [30] | Yin TM, DiFazio SP, Gunter LE, Zhang XY, Sewell MM, Woolbright SA, Allan GJ, Kelleher CT, Douglas CJ, Wang MX, Tuskan GA (2008). Genome structure and emerging evidence of an incipient sex chromosome in Populus. Genome Res 18, 422-430. |
| [31] | Zhang X, Lü MR (2021). Component analysis, development and utilization of Idesia polycarpa. Cereal Food Ind 28(2), 53-57, 60. (in Chinese) |
| 张旋, 吕名蕊 (2021). 毛叶山桐子成分分析及开发利用. 粮食与食品工业 28(2), 53-57, 60. | |
| [32] | Zhao YH, Li XX, Chen Z, Lu HW, Liu YC, Zhang ZF, Liang CZ (2020). An overview of genome-wide association studies in plants. Chin Bull Bot 55, 715-732. (in Chinese) |
| 赵宇慧, 李秀秀, 陈倬, 鲁宏伟, 刘羽诚, 张志方, 梁承志 (2020). 生物信息学分析方法I: 全基因组关联分析概述. 植物学报 55, 715-732. | |
| [33] | Zuo Y, Liu HB, Li B, Zhao H, Li XL, Chen JT, Wang L, Zheng QB, He YQ, Zhang JS, Wang MX, Liang CZ, Wang L (2024). The Idesia polycarpa genome provides insights into its evolution and oil biosynthesis. Cell Rep 43, 113909. |
| [1] | 杨志刚, 张鹏程, 常海文, 康立茹, 左毅, 向浩鑫, 韩凤英. 基于形态学性状和SSR标记的辣椒种质资源遗传多样性分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 218-234. |
| [2] | 罗兰莎, 宋雯佩, 化青珠, 李大卫, 梁红, 张宪智. 植物性别决定基因及其表观遗传调控研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 278-290. |
| [3] | 王文静, 朱钰, 张洪铭, 韦陆丹, 易庆平, 余晓敏, 刘雨菡, 张莉雪, 程文翰, 何燕红. 万寿菊舌状花花冠裂片突变体的形态鉴定及连锁标记开发[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 893-904. |
| [4] | 李宏伟, 郑琪, 李滨, 李振声. 长穗偃麦草分子育种基础研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 792-801. |
| [5] | 谭文清, 陈军, 才宏伟. 黑麦草生物学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 802-813. |
| [6] | 彭丹, 武志强. 植物雌雄异株性别决定研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21416-. |
| [7] | 陈向向, 盖中帅, 翟军团, 徐劲东, 焦培培, 吴智华, 李志军. 中国西北地区天然胡杨群体遗传多样性及核心保护单元的构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1638-1649. |
| [8] | 张梦华, 张宪春. 中国薄叶卷柏复合群的物种划分[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1607-1619. |
| [9] | 陆静, 陈赢男, 尹佟明. 木本植物性别决定基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 90-103. |
| [10] | 李媛媛, 刘超男, 王嵘, 罗水兴, 农寿千, 王静雯, 陈小勇. 分子标记在濒危物种保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 367-375. |
| [11] | 张亚红, 贾会霞, 王志彬, 孙佩, 曹德美, 胡建军. 滇杨种群遗传多样性与遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 355-365. |
| [12] | 赵颖, 马荣, 尹永香, 张志东, 田呈明. 新疆不同来源金黄壳囊孢的多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1122-1131. |
| [13] | 朱宇佳, 焦凯丽, 罗秀俊, 冯尚国, 王慧中. 基于SSR分子标记的酸浆属植物亲缘关系研究[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(3): 305-312. |
| [14] | 秦力, 陈景丽, 潘长田, 叶蕾, 卢钢. 植物性染色体进化及性别决定基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(6): 841-848. |
| [15] | 杨洁, 赫佳, 王丹碧, 施恩, 杨文宇, 耿其芳, 王中生. InDel标记的研究和应用进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(2): 237-243. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||