

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 126-138.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17130 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17130
收稿日期:2017-07-12
接受日期:2017-10-31
出版日期:2018-01-01
发布日期:2018-08-10
通讯作者:
葛磊
基金资助:
Qianqian Zhang1,2, Tong Zheng1, Qian Yu1, Lei Ge1,*( )
)
Received:2017-07-12
Accepted:2017-10-31
Online:2018-01-01
Published:2018-08-10
Contact:
Lei Ge
摘要: 干细胞巢的维持与后代细胞的分化是多细胞高等生物个体发育的基础。生长素对植物茎尖和根尖分生组织的形态建成, 尤其是对位于植物这2个末端的分生组织中心的干细胞巢的活性维持起着至关重要的作用。该文综述了近几年在植物根尖干细胞发育领域的研究进展, 主要阐释了PLT蛋白途径、SCR-SHR蛋白途径以及环境因子多信号调控模块维持植物根尖分生组织中干细胞巢稳定的机制, 揭示了生长素可以通过就近合成、极性运输以及信号转导3种方式参与这些信号模块的调控, 从而维持生长素在根尖静止中心细胞附近干细胞巢的浓度梯度, 精确地平衡植物干细胞巢中细胞的增殖与分化。
张倩倩, 郑童, 予茜, 葛磊. 生长素与植物根尖干细胞巢的维持. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 126-138.
Qianqian Zhang, Tong Zheng, Qian Yu, Lei Ge. Auxin and the Maintenance of Root Stem Cell Niches in Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(1): 126-138.
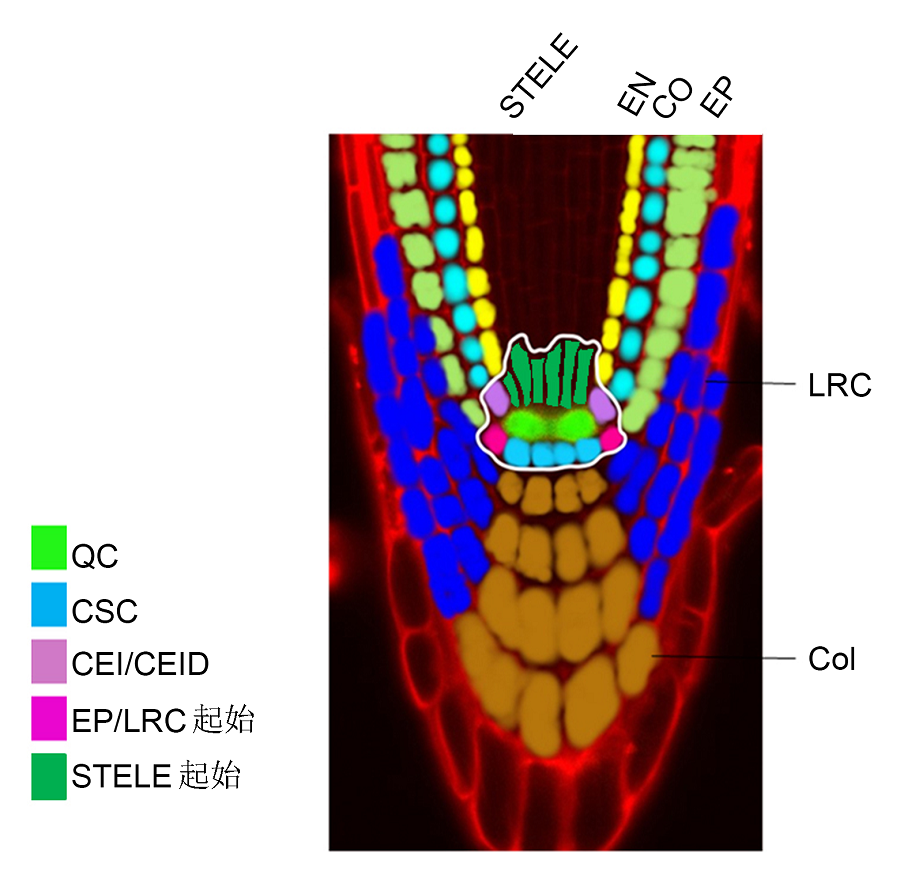
图1 拟南芥根尖及干细胞巢结构组成根尖分生组织(RAM)放射状细胞层排列方式, 从内到外分别是中柱(STELE)、内皮层(EN)、皮层(CO)、表皮(EP)、侧根冠(LRC)、静止中心(QC)、小柱细胞(Col)、小柱干细胞(CSC)、皮层/内皮层起始子细胞(CEI/CEID)、表皮/侧根冠(EP/LRC)、表皮/侧根冠起始细胞和中柱起始细胞。白色加粗轮廓为干细胞巢区, 分别为静止中心细胞(绿色)、小柱起始细胞(淡蓝色)、皮层/内皮层起始细胞(淡紫色)、表皮和侧根冠起始细胞(玫红色)以及中柱起始细胞(暗绿色)。
Figure 1 The root apical and the stem cell niche structure of Arabidopsis thalianaRadial pattern of cell layers in root apical meristem (RAM) from central to outsides: stele (STELE), endodermis (EN), cortex (CO), epidermis (EP), lateral root cap (LRC), quiescent center (QC), columella (Col), columella stem cell (CSC), cortex/endodermal initial/daughter cell (CEI/CEID), epidermis/later root cap (EP/LRC), EP/LRC initiation cell and stele initiation cells. Thick white line surrounds root stem cells, QC (green), CSC (light blue), CEI/CEID (light purple), EP/LRC initiation cell (rose red) and stele initiation cell (dark green).
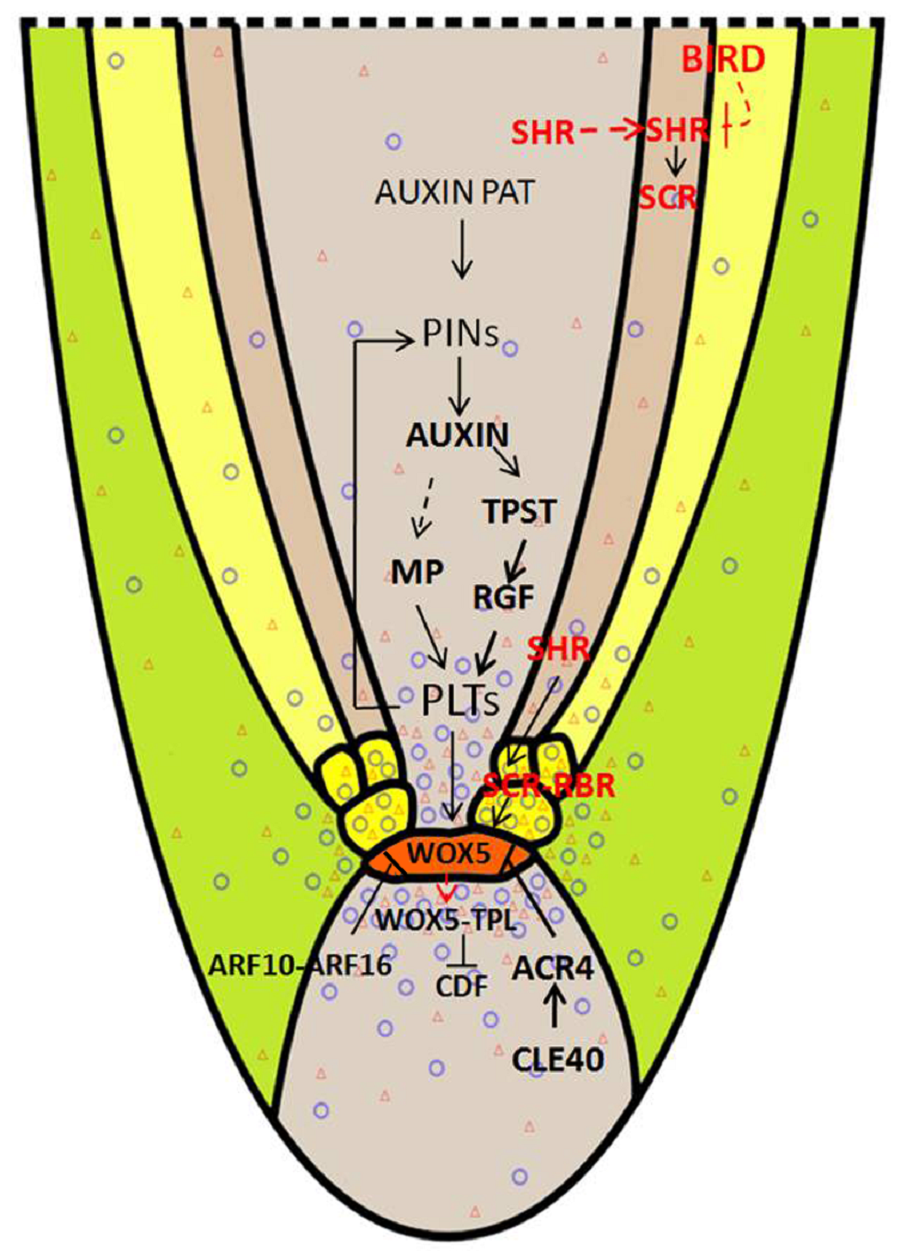
图2 根尖干细胞巢维持的调控网络模式图根尖干细胞巢维持途径主要有2条: PLT途径和SHR-SCR途径。PLTs (红色三角的密度)蛋白梯度和生长素的浓度梯度(紫色圆圈的密度)维持干细胞巢区的活性; BIRDs蛋白参与限制SHR转移到皮层, 从而与SCR蛋白一起作用界定内皮层与皮层细胞的界限。WOX5既可以维持QC的稳定性, 也可在CSC细胞抑制CDF4活性, 进而维持干细胞活性。CLE40通过与ACR4结合, 以及ARF10和ARF16的表达, 也可将WOX5的表达限制在QC内。橘黄色代表静止中心细胞, 浅黄色代表皮层细胞, 淡红色代表内皮层细胞; 黑色箭头表示促进作用; ⊥表示抑制作用;红色虚线箭头表示蛋白在细胞间移动。
Figure 2 The regulation network for maintenance of the root stem cell nicheThe two major pathways for root stem cell niche maintenance: PLT pathway and SHR-SCR pathway. PLTs protein gradient (density of red triangles) and auxin concentration gradient (density of purple circles) maintain the activity of stem cell niche; BIRDs proteins are involved in repressing the transfer of SHR from endodermis to cortex cells, and work with SCR protein to define the boundary between endodermis and cortex. WOX5 not only maintains the stability of QC, but also repress the activity of CDF4 in CSC cells to maintain the acti- vity of stem cells. CLE40 restricts the expression of WOX5 in QC through binding to ACR4.And the expression of ARF10 and ARF16 has the same effect on WOX5. QC cells are co- lored in orange, cortex cells are colored in light yellow, and endodermis cells are colored in light red; black arrow represents promoted function; ⊥ represents inhibited function; red dotted arrow represents protein movement between cells.
| [1] | 于倩倩, 孔祥培, 丁兆军 (2015). 中国科学家在生长素信号转导领域取得突破性研究进展. 植物学报 50, 535-537. |
| [2] | 于燕杰, 张大兵, 袁政 (2016). WOX蛋白家族调控干细胞发育分子机制的研究进展. 植物学报 51, 565-574. |
| [3] | Adamowski M, Friml J (2015). PIN-dependent auxin trans- port: action, regulation, and evolution.Plant Cell 27, 20-32. |
| [4] | Aida M, Beis D, Heidstra R, Willemsen V, Blilou I, Galinha C, Nussaume L, Noh YS, Amasino R, Scheres B (2004). ThePLETHORA genes mediate patterning of the Arabi- dopsis root stem cell niche. Cell 119, 109-120. |
| [5] | Blilou I, Xu J, Wildwater M, Willemsen V, Paponov I, Friml J, Heidstra R, Aida M, Palme K, Scheres B (2005). The PIN auxin efflux facilitator network controls growth and patterning in Arabidopsis roots.Nature 433, 39-44. |
| [6] | Boutilier K, Offringa R, Sharma VK, Kieft H, Ouellet T, Zhang LM, Hattori J, Liu CM, van Lammeren AAM, Miki BLA, Custers JBM, van Lookeren Campagne MM (2002). Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a con- version from vegetative to embryonic growth.Plant Cell 14, 1737-1749. |
| [7] | Brand U, Fletcher JC, Hobe M, Meyerowitz EM, Simon R (2000). Dependence of stem cell fate in Arabidopsis on a feedback loop regulated by CLV3 activity.Science 289, 617-619. |
| [8] | Chen QG, Dai XH, De-Paoli H, Cheng YF, Takebayashi Y, Kasahara H, Kamiya Y, Zhao YD (2014a). Auxin over- production in shoots cannot rescue auxin deficiencies in Arabidopsis roots.Plant Cell Physiol 55, 1072-1079. |
| [9] | Chen X, Grandont L, Li HJ, Hauschild R, Paque S, Abuzeineh A, Rakusová H, Benkova E, Perrot-Rech- enmann C, Friml J (2014b). Inhibition of cell expansion by rapid ABP1-mediated auxin effect on microtubules.Nature 516, 90-93. |
| [10] | Cruz-Ramírez A, Díaz-Triviño S, Blilou I, Grieneisen VA, Sozzani R, Zamioudis C, Miskolczi P, Nieuwland J, Benjamins R, Dhonukshe P, Caballero-Pérez J, Horv- ath B, Long YC, Mähönen AP, Zhang HT, Xu J, Murray JAH, Benfey PN, Bako L, Marée AFM, Scheres B (2012). A bistable circuit involving SCARECROW-RET- INOBLASTOMA integrates cues to inform asymmetric stem cell division.Cell 150, 1002-1015. |
| [11] | Cruz-Ramírez A, Díaz-Triviño S, Wachsman G, Du Y, Arteága-Vázquez M, Zhang H, Benjamins R, Blilou I, Neef AB, Chandler V, Scheres B (2013). A SCARE- CROW-RETINOBLASTOMA protein network controls pro- tective quiescence in the Arabidopsis root stem cell organizer.PLoS Biol 11, e1001724. |
| [12] | Cui HC, Levesque MP, Vernoux T, Jung JW, Paquette AJ, Gallagher KL, Wang JY, Blilou I, Scheres B, Benfey PN (2007). An evolutionarily conserved mechanism delimiting SHR movement defines a single layer of endodermis in plants. Science 316, 421-425. |
| [13] | De Smet I, Vassileva V, De Rybel B, Levesque MP, Grunewald W, Van Damme D, Van Noorden G, Naudts M, Van Isterdael G, De Clercq R, Wang JY, Meuli N, Vanneste S, Friml J, Hilson P, Jürgens G, Ingram GC, Inzé D, Benfey PN, Beeckman T (2008). Receptor-like kinase ACR4 restricts formative cell divisions in the Ara- bidopsis root.Science 322, 594-597. |
| [14] | Dello Ioio R, Linhares FS, Scacchi E, Casamitjana- Martinez E, Heidstra R, Costantino P, Sabatini S (2007). Cytokinins determine Arabidopsis root-meristem size by controlling cell differentiation.Curr Biol 17, 678-682. |
| [15] | Dello Ioio R, Nakamura K, Moubayidin L, Perilli S, Tani- guchi M, Morita MT, Aoyama T, Costantino P, Sabatini S (2008). A genetic framework for the control of cell division and differentiation in the root meristem.Science 322, 1380-1384. |
| [16] | Dharmasiri N, Dharmasiri S, Estelle M (2005a). The F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor.Nature 435, 441-445. |
| [17] | Dharmasiri N, Dharmasiri S, Weijers D, Lechner E, Yamada M, Hobbie L, Ehrismann JS, Jurgens G, Estelle M (2005b). Plant development is regulated by a family of auxin receptor F box proteins.Dev Cell 9, 109-119. |
| [18] | Di Laurenzio L, Wysocka-Diller J, Malamy JE, Pysh L, Helariutta Y, Freshour G, Hahn MG, Feldmann KA, Benfey PN (1996). TheSCARECROW gene regulates an asymmetric cell division that is essential for generating the radial organization of the Arabidopsis root. Cell 86, 423-433. |
| [19] | Ding ZJ, Friml J (2010). Auxin regulates distal stem cell differentiation in Arabidopsis roots.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 12046-12051. |
| [20] | Dolan L, Janmaat K, Willemsen V, Linstead P, Poethig S, Roberts K, Scheres B (1993). Cellular organisation of theArabidopsis thaliana root. Development 119, 71-84. |
| [21] | Forzani C, Aichinger E, Sornay E, Willemsen V, Laux T, Dewitte W, Murray JAH (2014). WOX5 suppressesCYC- LIN D activity to establish quiescence at the center of the root stem cell niche. Curr Biol 24, 1939-1944. |
| [22] | Galinha C, Hofhuis H, Luijten M, Willemsen V, Blilou I, Heidstra R, Scheres B (2007). PLETHORA proteins as dose-dependent master regulators of Arabidopsis root de- velopment.Nature 449, 1053-1057. |
| [23] | Gao YB, Zhang Y, Zhang D, Dai XH, Estelle M, Zhao YD (2015). Auxin binding protein 1 (ABP1) is not required for either auxin signaling or Arabidopsis development.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 2275-2280. |
| [24] | Gutierrez C (2005). Coupling cell proliferation and develop- ment in plants.Nat Cell Biol 7, 535-541. |
| [25] | Helariutta Y, Fukaki H, Wysocka-Diller J, Nakajima K, Jung J, Sena G, Hauser MT, Benfey PN (2000). TheSHORT-ROOT gene controls radial patterning of the Arabidopsis root through radial signaling. Cell 101, 555-567. |
| [26] | Heyman J, Cools T, Vandenbussche F, Heyndrickx KS, Van Leene J, Vercauteren I, Vanderauwera S, Van- depoele K, De Jaeger G, Van Der Straeten D, De Veylder L (2013). ERF115 controls root quiescent center cell division and stem cell replenishment.Science 342, 860-863. |
| [27] | Hong JH, Savina M, Du J, Devendran A, Ramakanth KK, Tian X, Sim WS, Mironova VV, Xu J (2017). A sacrifice- for-survival mechanism protects root stem cell niche from chilling stress.Cell 170, 102-113. |
| [28] | Hwang I, Sheen J, Müller B (2012). Cytokinin signaling networks.Annu Rev Plant Biol 63, 353-380. |
| [29] | Korasick DA, Westfall CS, Lee SG, Nanao MH, Dumas R, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ, Jez JM, Strader LC (2014). Molecular basis for AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR protein interaction and the control of auxin response repression.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 5427-5432. |
| [30] | Laux T, Würschum T, Breuninger H (2004). Genetic regula- tion of embryonic pattern formation.Plant Cell 16(Suppl), S190-S202. |
| [31] | Long YC, Smet W, Cruz-Ramírez A, Castelijns B, de Jonge W, Mähönen AP, Bouchet BP, Perez GS, Akh- manova A, Scheres B, Blilou I (2015). Arabidopsis BIRD zinc finger proteins jointly stabilize tissue boundaries by confining the cell fate regulator SHORT-ROOT and con- tributing to fate specification.Plant Cell 27, 1185-1199. |
| [32] | Mähönen AP, Tusscher KT, Siligato R, Smetana O, Díaz-Triviño S, Salojärvi J, Wachsman G, Prasad K, Heidstra R, Scheres B (2014). PLETHORA gradient formation mechanism separates auxin responses.Nature 515, 125-129. |
| [33] | Matsuzaki Y, Ogawa-Ohnishi M, Mori A, Matsubayashi Y (2010). Secreted peptide signals required for maintenance of root stem cell niche in Arabidopsis.Science 329, 1065-1067. |
| [34] | Mayer KFX, Schoof H, Haecker A, Lenhard M, Jürgens G, Laux T (1998). Role ofWUSCHEL in regulating stem cell fate in the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Cell 95, 805-815. |
| [35] | Mockaitis K, Estelle M (2008). Auxin receptors and plant development: a new signaling paradigm.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 24, 55-80. |
| [36] | Moreno-Risueno MA, Sozzani R, Yardımcı GG, Petricka JJ, Vernoux T, Blilou I, Alonso J, Winter CM, Ohler U, Scheres B, Benfey PN (2015). Transcriptional control of tissue formation throughout root development.Science 350, 426-430. |
| [37] | Moubayidin L, Di Mambro R, Sozzani R, Pacifici E, Salvi E, Terpstra I, Bao DP, van Dijken A, Dello Ioio R, Perilli S, Ljung K, Benfey PN, Heidstra R, Costantino P, Sabatini S (2013). Spatial coordination between stem cell activity and cell differentiation in the root meristem.Dev Cell 26, 405-415. |
| [38] | Moubayidin L, Perilli S, Dello Ioio R, Di Mambro R, Costantino P, Sabatini S (2010). The rate of cell diffe- rentiation controls the Arabidopsis root meristem growth phase.Curr Biol 20, 1138-1143. |
| [39] | Nanao MH, Vinos-Poyo T, Brunoud G, Thévenon E, Mazzoleni M, Mast D, Lainé S, Wang SC, Hagen G, Li HB, Guilfoyle TJ, Parcy F, Vernoux T, Dumas R (2014). Structural basis for oligomerization of auxin transcriptional regulators.Nat Commun 5, 3617. |
| [40] | Ortega-Martínez O, Pernas M, Carol RJ, Dolan L (2007). Ethylene modulates stem cell division in theArabidopsis thaliana root. Science 317, 507-510. |
| [41] | Paque S, Mouille G, Grandont L, Alabadí D, Gaertner C, Goyallon A, Muller P, Primard-Brisset C, Sormani R, Blázquez MA, Perrot-Rechenmann C (2014). AUXIN BINDING PROTEIN1 links cell wall remodeling, auxin signaling, and cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 280-295. |
| [42] | Parry G, Calderon-Villalobos LI, Prigge M, Peret B, Dharmasiri S, Itoh H, Lechner E, Gray WM, Bennett M, Estelle M (2009). Complex regulation of the TIR1/AFB family of auxin receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 22540-22545. |
| [43] | Pi LM, Aichinger E, van der Graaff E, Llavata-Peris CI, Weijers D, Hennig L, Groot E, Laux T (2015). Organizer- derived WOX5 signal maintains root columella stem cells through chromatin-mediated repression ofCDF4 expres- sion. Dev Cell 33, 576-588. |
| [44] | Rademacher EH, Lokerse AS, Schlereth A, Llavata-Peris CI, Bayer M, Kientz M, Freire Rios A, Borst JW, Lukowitz W, Jürgens G, Weijers D (2012). Different auxin response machineries control distinct cell fates in the early plant embryo.Dev Cell 22, 211-222. |
| [45] | Santuari L, Sanchez-Perez GF, Luijten M, Rutjens B, Terpstra I, Berke L, Gorte M, Prasad K, Bao DP, Timmermans-Hereijgers JLPM, Maeo K, Nakamura K, Shimotohno A, Pencik A, Novak O, Ljung K, van Heesch S, de Bruijn E, Cuppen E, Willemsen V, Mähönen AP, Lukowitz W, Snel B, de Ridder D, Scheres B, Heidstra R (2016). ThePLETHORA gene regulatory network guides growth and cell differentiation in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 28, 2937-2951. |
| [46] | Sarkar AK, Luijten M, Miyashima S, Lenhard M, Hashi- moto T, Nakajima K, Scheres B, Heidstra R, Laux T (2007). Conserved factors regulate signaling inArabi- dopsis thaliana shoot and root stem cell organizers. Nature 446, 811-814. |
| [47] | Schlereth A, Moller B, Liu WL, Kientz M, Flipse J, Rade- macher EH, Schmid M, Jürgens G, Weijers D (2010). MONOPTEROS controls embryonic root initiation by regulating a mobile transcription factor.Nature 464, 913-916. |
| [48] | Schnittger A, Schöbinger U, Stierhof YD, Hülskamp M (2002). Ectopic B-type cyclin expression induces mitotic cycles in endoreduplicating Arabidopsis trichomes.Curr Biol 12, 415-420. |
| [49] | Sena G, Wang XN, Liu HY, Hofhuis H, Birnbaum KD (2009). Organ regeneration does not require a functional stem cell niche in plants.Nature 457, 1150-1153. |
| [50] | Sozzani R, Cui H, Moreno-Risueno MA, Busch W, Van Norman JM, Vernoux T, Brady SM, Dewitte W, Murray JAH, Benfey PN (2010). Spatiotemporal regulation of cell-cycle genes by SHORTROOT links patterning and growth.Nature 466, 128-132. |
| [51] | Stahl Y, Wink RH, Ingram GC, Simon R (2009). A signaling module controlling the stem cell niche in Arabidopsis root meristems.Curr Biol 19, 909-914. |
| [52] | Steinmann T, Geldner N, Grebe M, Mangold S, Jackson CL, Paris S, Gälweiler L, Palme K, Jürgens G (1999). Coordinated polar localization of auxin efflux carrier PIN1 by GNOM ARF GEF.Science 286, 316-318. |
| [53] | Tian HY, Wabnik K, Niu TT, Li HB, Yu QQ, Pollmann S, Vanneste S, Govaerts W, Rolčík J, Geisler M, Friml J, Ding ZJ (2014). WOX5-IAA17 feedback circuit-mediated cellular auxin response is crucial for the patterning of root stem cell niches in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant 7, 277-289. |
| [54] | Tromas A, Paque S, Stierlé V, Quettier AL, Muller P, Lechner E, Genschik P, Perrot-Rechenmann C (2013). Auxin-binding protein 1 is a negative regulator of the SCF (TIR1/AFB) pathway.Nat Commun 4, 2496. |
| [55] | Vilarrasa-Blasi J, González-García MP, Frigola D, Fàbre- gas N, Alexiou KG, López-Bigas N, Rivas S, Jauneau A, Lohmann JU, Benfey PN, Ibañes, Caño-Delgado AI (2014). Regulation of plant stem cell quiescence by a brassinosteroid signaling module.Dev Cell 30, 36-47. |
| [56] | Wang RH, Estelle M (2014). Diversity and specificity: auxin perception and signaling through the TIR1/AFB pathway.Curr Opin Plant Biol 21, 51-58. |
| [57] | Welch D, Hassan H, Blilou I, Immink R, Heidstra R, Scheres B (2007). Arabidopsis JACKDAW and MAGPIE zinc finger proteins delimit asymmetric cell division and stabilize tissue boundaries by restricting SHORT-ROOT action.Genes Dev 21, 2196-2204. |
| [58] | Wildwater M, Campilho A, Perez-Perez JM, Heidstra R, Blilou I, Korthout H, Chatterjee J, Mariconti L, Gruissem W, Scheres B (2005). TheRETINOBLA- STOMA-RELATED gene regulates stem cell maintenance in Arabidopsis roots. Cell 123, 1337-1349. |
| [59] | Xu J, Hofhuis H, Heidstra R, Sauer M, Friml J, Scheres B (2006). A molecular framework for plant regeneration.Science 311, 385-388. |
| [60] | Xu TD, Dai N, Chen JS, Nagawa S, Cao M, Li HJ, Zhou ZM, Chen X, De Rycke R, Rakusova H, Wang WY, Jones AM, Friml J, Patterson SE, Bleecker AB, Yang Z (2014). Cell surface ABP1-TMK auxin-sensing complex activates ROP GTPase signaling.Science 343, 1025-1028. |
| [61] | Yamada M, Greenham K, Prigge MJ, Jensen PJ, Estelle M (2009). TheTRANSPORT INHIBITOR RESPONSE2 gene is required for auxin synthesis and diverse aspects of plant development. Plant Physiol 151, 168-179. |
| [62] | Zhang HM, Han W, De Smet I, Talboys P, Loya R, Hassan A, Rong HL, Jurgens G, Paul Knox J, Wang MH (2010). ABA promotes quiescence of the quiescent centre and suppresses stem cell differentiation in the Arabidopsis pri- mary root meristem.Plant J 64, 764-774. |
| [63] | Zhou WK, Wei LR, Xu J, Zhai QZ, Jiang HL, Chen R, Chen Q, Sun JQ, Chu JF, Zhu LH, Liu CM, Li CY (2010). Arabidopsis tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase acts in the au- xin/PLETHORA pathway in regulating postembryonic main- tenance of the root stem cell niche.Plant Cell 22, 3692-3709. |
| [1] | 周玉滢, 陈辉, 刘斯穆. 植物非典型Aux/IAA蛋白应答生长素研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [2] | 孔祥培, 张蒙悦, 丁兆军. 柳暗花明:胞外生长素信号感受的新突破[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 861-865. |
| [3] | 园园, 恩和巴雅尔, 齐艳华. 植物GH3基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 770-782. |
| [4] | 周淑瑶, 李建明, 毛娟. AtGH3.17调控拟南芥生长素和油菜素甾醇的响应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 373-384. |
| [5] | 叶青, 闫晓燕, 陈慧泽, 冯金林, 韩榕. 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点对拟南芥主根生长方向的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 623-634. |
| [6] | 李彬琪, 闫佳慧, 李豪, 辛伟, 田云鹤, 杨贞标, 唐文鑫. 黄瓜卷须缠绕过程中小G蛋白活性变化[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 299-307. |
| [7] | 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [8] | 王静文, 王兴军, 马长乐, 李膨呈. 植物核糖体应激响应机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 80-89. |
| [9] | 李艳艳, 齐艳华. 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [10] | 林雨晴, 齐艳华. 生长素输出载体PIN家族研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 151-165. |
| [11] | 黄荣峰, 徐通达. 生长素通过MAPK介导的超长链脂肪酸合成调控侧根发育[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 6-9. |
| [12] | 姚玉婷,马家琦,冯晓莉,潘建伟,王超. 磷酸肌醇激酶FAB1调控拟南芥根毛伸长[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 126-136. |
| [13] | 张淑辉,王红,王文茹,吴雪莲,肖元松,彭福田. 蔗糖对桃幼苗生长发育及其SnRK1酶活性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 744-752. |
| [14] | 贺祯媚,李东明,齐艳华. 植物ABCB亚家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 688-698. |
| [15] | 胡孔琴, 丁兆军. 非TIR1受体依赖型激活生长素信号的新机制[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 293-295. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||