

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 62-73.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24068 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24068
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Qingyang Li, Cui Liu, Li He, Shan Peng, Jiayin Ma, Ziyi Hu, Hongbo Liu*( )
)
Received:2024-05-05
Accepted:2024-07-23
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-07-29
Contact:
* E-mail: hbliu@zafu.edu.cnQingyang Li, Cui Liu, Li He, Shan Peng, Jiayin Ma, Ziyi Hu, Hongbo Liu. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the BnaA02.CPSF6 Gene from Brassica napus[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 62-73.
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| BnaA02.CPSF6-FP | GGAGCTTTAAGATGGATGAAGGAG | Gene cloning |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-RP | CCTAGTCATTATTCAGTTGTAAGCCG | |
| 35S-GFP-BnaA02.CPSF6-FP | GACAGCCCAGATCAACTAGTATGGATGAAGGAGATGGGAGAGATG | Subcellular localization |
| 35S-GFP-BnaA02.CPSF6-RP | CTTGCTCACCATGGATCCTTCAGTTGTAAGCCGCCTTCGTTTC | |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-qRT-FP | GGAACAGAAGTCGATCGTCCAGAG | qRT-PCR |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-qRT-RP | GAGAGCCTTCTTTCTGTTACAAGGC | |
| BnaUBC9-FP | GCATCTGCCTCGACATCTTGA | Reference gene |
| BnaUBC9-RP | CGATAGCAGCACCTTGGAGATA | |
| 35S-BnaA02.CPSF6-NOS-FP | GGGACTCTTGACCATGGATGGATGAAGGAGATGGGAGAGATG | Vector construction |
| 35S-BnaA02.CPSF6-NOS-RP | CAATTCACACGTGACGCGTTTATTCAGTTGTAAGCCGCCTTCG |
Table 1 Primer information
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| BnaA02.CPSF6-FP | GGAGCTTTAAGATGGATGAAGGAG | Gene cloning |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-RP | CCTAGTCATTATTCAGTTGTAAGCCG | |
| 35S-GFP-BnaA02.CPSF6-FP | GACAGCCCAGATCAACTAGTATGGATGAAGGAGATGGGAGAGATG | Subcellular localization |
| 35S-GFP-BnaA02.CPSF6-RP | CTTGCTCACCATGGATCCTTCAGTTGTAAGCCGCCTTCGTTTC | |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-qRT-FP | GGAACAGAAGTCGATCGTCCAGAG | qRT-PCR |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-qRT-RP | GAGAGCCTTCTTTCTGTTACAAGGC | |
| BnaUBC9-FP | GCATCTGCCTCGACATCTTGA | Reference gene |
| BnaUBC9-RP | CGATAGCAGCACCTTGGAGATA | |
| 35S-BnaA02.CPSF6-NOS-FP | GGGACTCTTGACCATGGATGGATGAAGGAGATGGGAGAGATG | Vector construction |
| 35S-BnaA02.CPSF6-NOS-RP | CAATTCACACGTGACGCGTTTATTCAGTTGTAAGCCGCCTTCG |
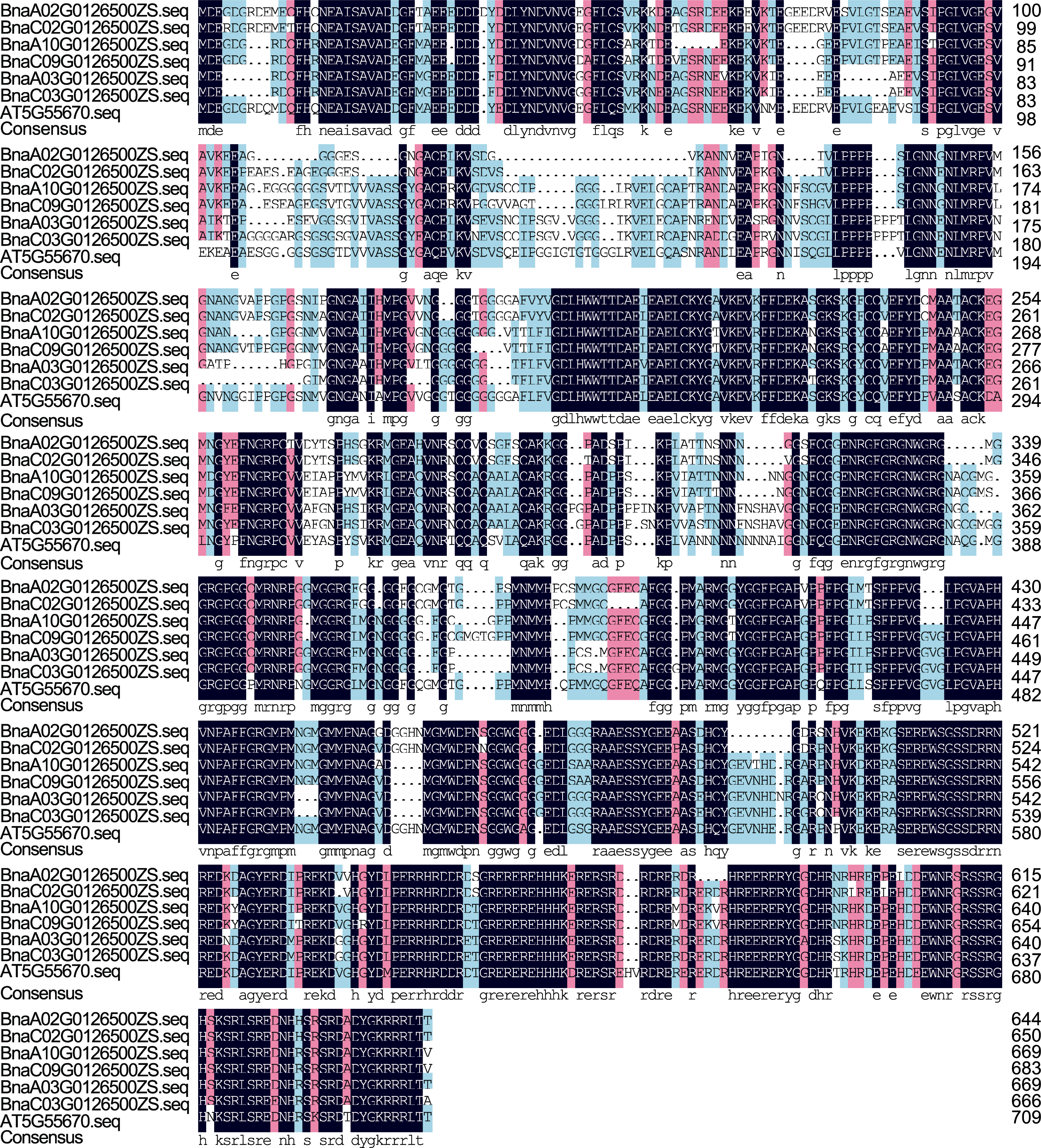
Figure 1 Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the BnaCPSF6s protein The black-purple background in the figure indicates that all sequences at the locus are aligned; the cyan-blue and pink backgrounds indicate partial alignment; and the white color indicates that the sequence does not match other sample sequences.
| Element name | Sequence | Quantity | Function | Position (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATC-motif | AGTAATCT | 1 | Light responsive element | -160 (-) |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 6 | Light responsive element | -368 (-); -705 (-); -889 (-); -1225 (-); -1803 (-) |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 9 | Light responsive element | -407 (+/-); -566 (+/-); -928 (+/-); -1087 (+/-); -1292 (+/-); -1443 (+/-); -1689 (+/-); -1842 (+/-); -1992 (+/-) |
| I-box | AAGATAAGGCT | 1 | Light responsive element | -473 (-) |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 3 | Light responsive element | -1274 (+); -1372 (+); -1770 (+) |
| G-box | CACGTT | 3 | Light responsive element | -687 (-); -1207 (-); -1603 (-) |
| MYB-like sequence | TAACCA | 4 | MYB-like binding site | -367 (+); -888 (+); -1404 (+); -1802 (+) |
| CCAAT-box | CAACGG | 1 | MYBHv1 binding site | -1591 (-) |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 3 | Abscisic acid responsiveness | -687 (+) |
Table 2 Analysis of cis-regulatory elements in the promoter region of BnaA02.CPSF6
| Element name | Sequence | Quantity | Function | Position (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATC-motif | AGTAATCT | 1 | Light responsive element | -160 (-) |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 6 | Light responsive element | -368 (-); -705 (-); -889 (-); -1225 (-); -1803 (-) |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 9 | Light responsive element | -407 (+/-); -566 (+/-); -928 (+/-); -1087 (+/-); -1292 (+/-); -1443 (+/-); -1689 (+/-); -1842 (+/-); -1992 (+/-) |
| I-box | AAGATAAGGCT | 1 | Light responsive element | -473 (-) |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 3 | Light responsive element | -1274 (+); -1372 (+); -1770 (+) |
| G-box | CACGTT | 3 | Light responsive element | -687 (-); -1207 (-); -1603 (-) |
| MYB-like sequence | TAACCA | 4 | MYB-like binding site | -367 (+); -888 (+); -1404 (+); -1802 (+) |
| CCAAT-box | CAACGG | 1 | MYBHv1 binding site | -1591 (-) |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 3 | Abscisic acid responsiveness | -687 (+) |
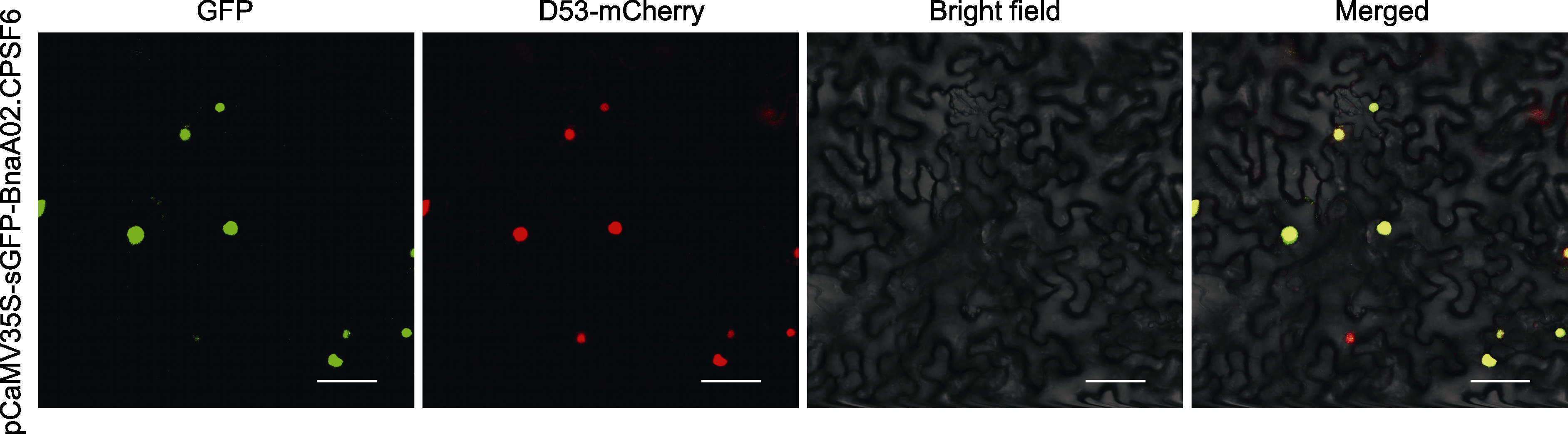
Figure 3 Subcellular localization of BnaA02.CPSF6 GFP is BnaA02.CPSF6 fusion green fluorescence protein; D53-mCherry is a nuclear marker protein; Bright field is brightfield microscope; Merged is fusion field. Bars=50 μm
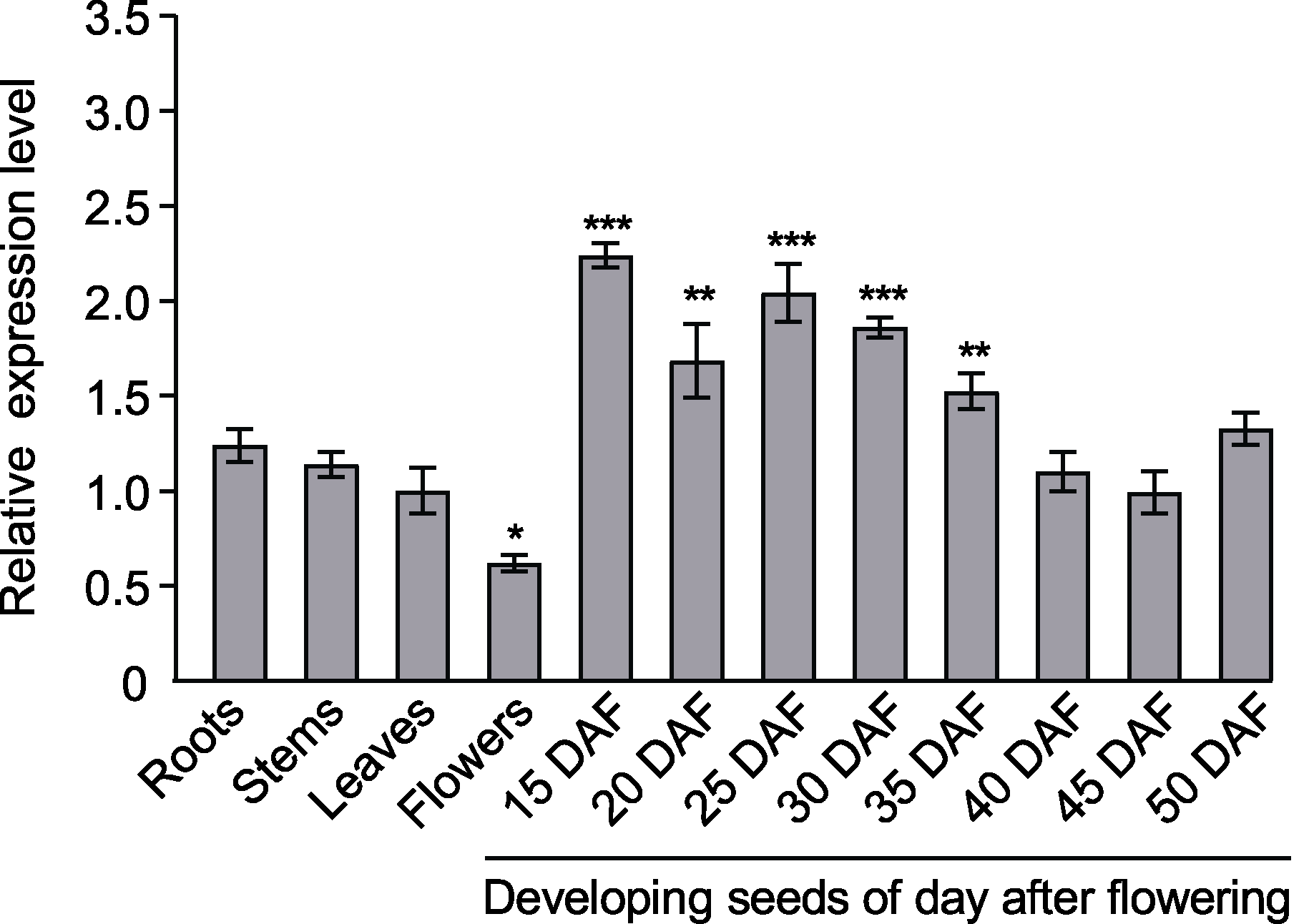
Figure 4 Analysis of the expression pattern of BnaA02. CPSF6 in different tissues of Brassica napus DAF: Days after flowering; Reference gene: B. napus SUMO- conjugating enzyme gene (BnaUBC9). Three biological replicates were used (n=3). * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001
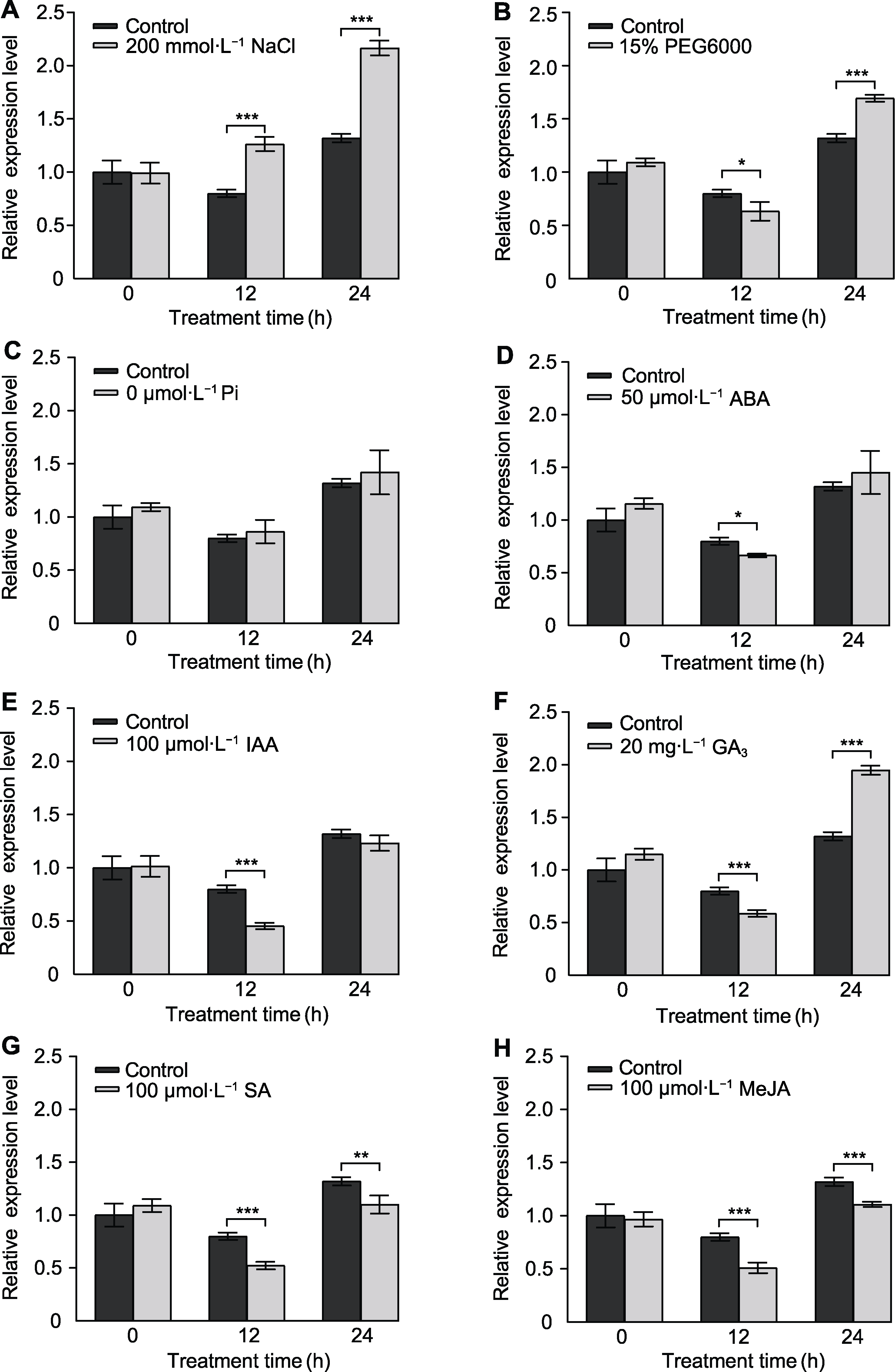
Figure 5 Expression pattern analysis of BnaA02.CPSF6 under abiotic stress and exogenous hormone treatments (A) Salt treatment; (B) Drought treatment; (C) Low phosphorus treatment; (D) Abscisic acid (ABA) treatment; (E) Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) treatment; (F) Gibberellic acid (GA3) treatment; (G) Salicylic acid (SA) treatment; (H) Methyl jasmonate (MeJA) treatment. Three biological replicates were used (n=3). * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001
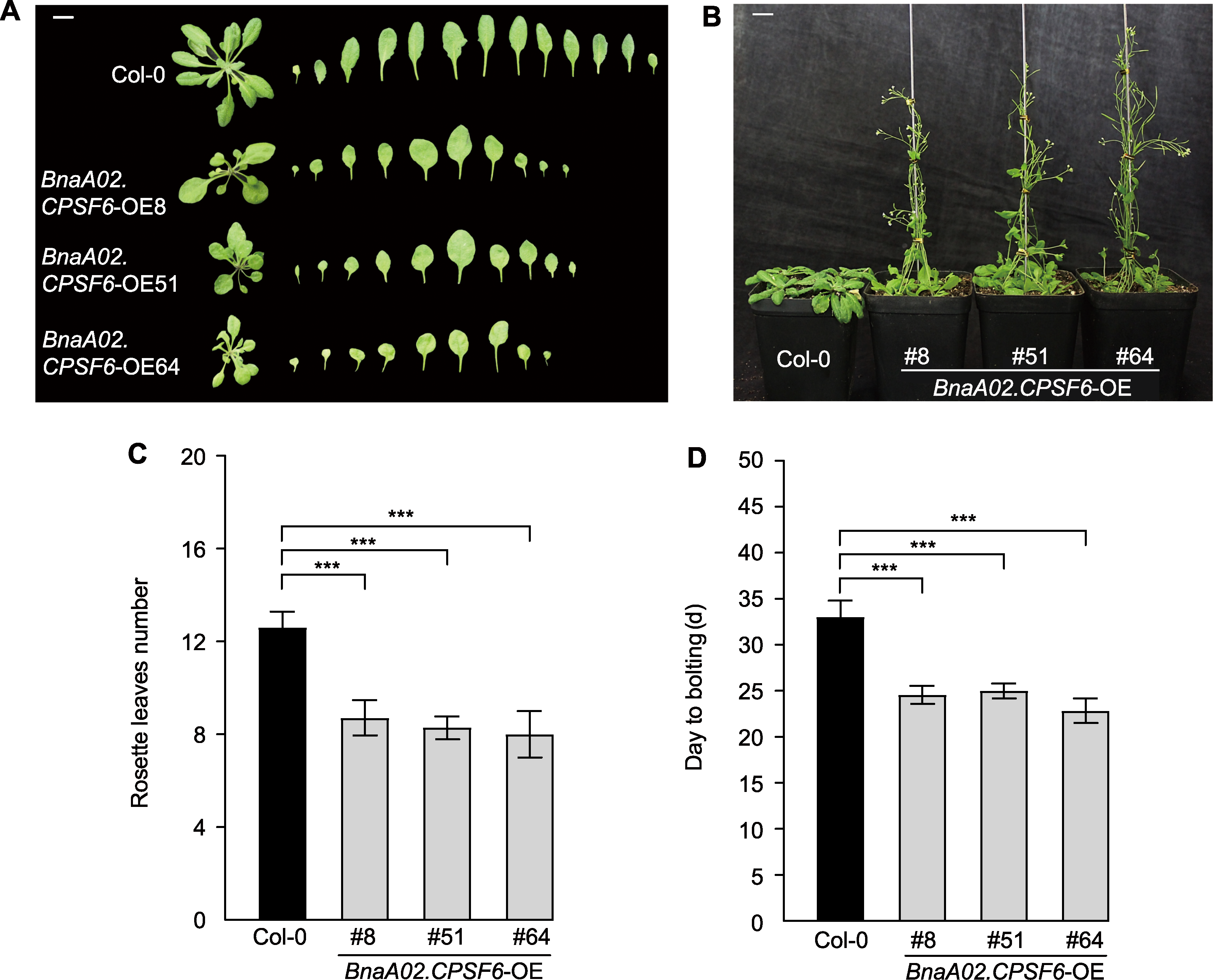
Figure 6 Overexpression of BnaA02.CPSF6 leads to the early-flowering of Arabidopsis thaliana (A) Rosette leaf phenotype at flowering (bar=1 cm); (B) Phenotype at 30 days under normal conditions (bar=1 cm); (C) Number of rosette leaves at flowering; (D) Bolting time (time from sowing to the appearance of the flower stalk). Three biological replicates were used (n=3). The number of rosette leaves from each genotype were counted with five replicate samples. *** P<0.001
| [1] | Bao SJ, Hua CM, Shen LS, Yu H (2020). New insights into gibberellin signaling in regulating flowering in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 62,118-131. |
| [2] |
Boreikaitė V, Passmore LA (2023). 3′-end processing of eukaryotic mRNA: machinery, regulation, and impact on gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem 92, 199-225.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Brown KM, Gilmartin GM (2003). A mechanism for the regulation of pre-mRNA 3′ processing by human cleavage factor Im. Mol Cell 12, 1467-1476.
PMID |
| [4] | Cai FF, Shao CS, Sun YQ (2022). The role of alternative splicing in floral transition. Chin Bull Bot 57, 69-79. (in Chinese) |
|
蔡芳芳, 邵长生, 孙玉强 (2022). 可变剪切在植物成花转换中的作用. 植物学报 57, 69-79.
DOI |
|
| [5] | Cui GX, Hou J, Tong L, Xu ZR (2010). Light responsive elements and binding proteins of plant genes. Plant Physiol Commun 46, 991-1000. (in Chinese) |
| 崔国新, 侯杰, 佟玲, 许志茹 (2010). 植物基因光反应元件及其结合蛋白. 植物生理学通讯 46, 991-1000. | |
| [6] | Dai YQ, Luo LJ, Zhao Z (2023). Genetic robustness control of auxin output in priming organ initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120, e2221606120. |
| [7] |
Eckardt NA (2002). Alternative splicing and the control of flowering time. Plant Cell 14, 743-747.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Edwalds-Gilbert G, Milcarek C (1995). The binding of a subunit of the general polyadenylation factor cleavage- polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) to polyadenylation sites changes during B cell development. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (33), 229-233. |
| [9] |
Feng W, Jacob Y, Veley KM, Ding L, Yu XH, Choe G, Michaels SD (2011). Hypomorphic alleles reveal FCA- independent roles for FY in the regulation of FLOWERING LOCUS C. Plant Physiol 155, 1425-1434.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Hao SQ, Zhang LD, Zhao DH, Zhou JW, Ye CT, Qu HD, Li QQ (2023). Inhibitor AN3661 reveals biological functions of Arabidopsis CLEAVAGE and POLYADENYLATION SPECIFICITY FACTOR 73. Plant Physiol 193, 537-554. |
| [11] | Hardy JG, Norbury CJ (2016). Cleavage factor Im (CFIm) as a regulator of alternative polyadenylation. Biochem Soc Trans 44, 1051-1057. |
| [12] |
Henderson IR, Liu FQ, Drea S, Simpson GG, Dean C (2005). An allelic series reveals essential roles for FY in plant development in addition to flowering-time control. Development 132, 3597-3607.
PMID |
| [13] | Herr AJ, Molnàr A, Jones A, Baulcombe DC (2006). Defective RNA processing enhances RNA silencing and influences flowering of Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 14994-15001. |
| [14] |
Hornyik C, Terzi LC, Simpson GG (2010). The spen family protein FPA controls alternative cleavage and polyadenylation of RNA. Dev Cell 18(2), 203-213.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Hou YF, Sun J, Wu BX, Gao YY, Nie HB, Nie ZT, Quan SX, Wang Y, Cao XF, Li SS (2021). CPSF30-L-mediated recognition of mRNA m6A modification controls alternative polyadenylation of nitrate signaling-related gene transcripts in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 14, 688-699. |
| [16] |
Huang Y, Zhao PS, Xie LL, Xu JS, Cheng Y, Zhang XK, Xu BB (2024). Analysis on yield composition and breeding strategy of winter rape varieties in the Yangtze River Basin. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 46, 13-18. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
黄郢, 赵培森, 谢伶俐, 徐劲松, 程勇, 张学昆, 许本波 (2024). 长江流域冬油菜品种产量构成及育种策略分析. 中国油料作物学报 46, 13-18.
DOI |
|
| [17] | Kumar A, Clerici M, Muckenfuss LM, Passmore LA, Jinek M (2019). Mechanistic insights into mRNA 3′-end processing. Curr Opin Struct Biol 59, 143-150. |
| [18] | Li GC, Niu QC, Leng BF, Ding YF, Tong T, Fan LX (2024). The decade of rapeseed industry in the new era: development and its path choice. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 46, 228-235. (in Chinese) |
|
李谷成, 牛秋纯, 冷博峰, 丁逸飞, 童婷, 范丽霞 (2024). 新时代十年: 我国油菜产业发展与路径选择. 中国油料作物学报 46, 228-235.
DOI |
|
| [19] | Li QX, Zhang L, Wang Y, Huang XX (2019). The research progress of gibberellin on the regulation of flowering and floral organ development in plant. Chin J Cell Biol 41, 746-758. (in Chinese) |
| 李巧峡, 张丽, 王玉, 黄小霞 (2019). 赤霉素调控植物开花及花器官发育的研究进展. 中国细胞生物学学报 41, 746-758. | |
| [20] | Lin JC, Xu RQ, Wu XH, Shen YJ, Li QQ (2017). Role of cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 100: anchoring poly (A) sites and modulating transcription termination. Plant J 91, 829-839. |
| [21] |
Liu YT, Wu GX, Zhao YP, Wang HHL, Dai ZY, Xue WC, Yang J, Wei HB, Shen RX, Wang HY (2021). DWARF53 interacts with transcription factors UB2/UB3/TSH4 to regulate maize tillering and tassel branching. Plant Physiol 187, 947-962.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Ma LY, Guo C, Li QQ (2014). Role of alternative polyadenylation in epigenetic silencing and antisilencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 9-10.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Macknight R, Duroux M, Laurie R, Dijkwel P, Simpson G, Dean C (2002). Functional significance of the alternative transcript processing of the Arabidopsis floral promoter FCA. Plant Cell 14, 877-888.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Mandel CR, Bai Y, Tong L (2008). Protein factors in pre- mRNA 3′-end processing. Cell Mol Life Sci 65, 1099-1122.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Mouradov A, Cremer F, Coupland G (2002). Control of flowering time: interacting pathways as a basis for diversity. Plant Cell 14, S111-S130. |
| [26] |
Proudfoot N (2004). New perspectives on connecting messenger RNA 3′ end formation to transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16, 272-278.
PMID |
| [27] |
Quesada V, Macknight R, Dean C, Simpson GG (2003). Autoregulation of FCA pre-mRNA processing controls Arabidopsis flowering time. EMBO J 22, 3142-3152.
PMID |
| [28] |
Schul W, Groenhout B, Koberna K, Takagaki Y, Jenny A, Manders EM, Raska I, van Driel R, de Jong L (1996). The RNA 3′ cleavage factors CstF 64 kDa and CPSF 100 kDa are concentrated in nuclear domains closely associated with coiled bodies and newly synthesized RNA. EMBO J 15, 2883-2892.
PMID |
| [29] | Song PZ, Yang JB, Wang CL, Lu Q, Shi LQ, Tayier S, Jia GF (2021). Arabidopsis N6-methyladenosine reader CPSF30-L recognizes FUE signals to control polyadenylation site choice in liquid-like nuclear bodies. Mol Plant 14, 571-587. |
| [30] | Thomas PE, Wu XH, Liu M, Gaffney B, Ji GL, Li QQ, Hunt AG (2012). Genome-wide control of polyadenylation site choice by CPSF30 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 4376-4388. |
| [31] | Tzafrir I, Pena-Muralla R, Dickerman A, Berg M, Rogers R, Hutchens S, Sweeney TC, McElver J, Aux G, Patton D, Meinke D (2004). Identification of genes required for embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 135, 1206-1220. |
| [32] | Venkataraman K, Brown KM, Gilmartin GM (2005). Analysis of a noncanonical poly (A) site reveals a tripartite mechanism for vertebrate poly (A) site recognition. Genes Dev 19, 1315-1327. |
| [33] | Wang XP, Niu YL, Zheng Y (2021). Multiple functions of MYB transcription factors in abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 22, 6125. |
| [34] |
Yang Q, Coseno M, Gilmartin GM, Doublié S (2011). Crystal structure of a human cleavage factor CFIm25/CFIm68/RNA complex provides an insight into poly(A) site recognition and RNA looping. Structure 19, 368-377.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Yu ZB, Lin JC, Li QQ (2019). Transcriptome analyses of FY mutants reveal its role in mRNA alternative polyadenylation. Plant Cell 31, 2332-2352. |
| [36] | Zhang CS, Wei T, Zhou YP, Fan T, Lü TX, Tian CE (2021). Progress in flowering regulation mechanisms of FLC. Chin Bull Bot 56,651-663. (in Chinese) |
|
张长生, 魏滔, 周玉萍, 范甜, 吕天晓, 田长恩 (2021). FLC调控植物成花的分子机制研究新进展. 植物学报 56, 651-663.
DOI |
|
| [37] | Zhang XJ, Nomoto M, Garcia-León M, Takahashi N, Kato M, Yura K, Umeda M, Rubio V, Tada Y, Furumoto T, Aoyama T, Tsuge T (2022). CFI 25 subunit of cleavage factor I is important for maintaining the diversity of 3′ UTR lengths in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) heynh. Plant Cell Physiol 63, 369-383. |
| [1] | Liuqing Yang, Jin Wang, Jingli Yan, Qinqin Chen, Haokun Cheng, Chun Li, Peiyu Zhao, Bo Yang, Yuanqing Jiang. Analysis of Expression Characteristics and Identification of Interaction Proteins of BnaABF2 Transcription Factor in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 49-61. |
| [2] | Yaping Wang, Wenquan Bao, Yu’e Bai. Advances in the Application of Single-cell Transcriptomics in Plant Growth, Development and Stress Response [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [3] | Tao Wang, Jinglei Feng, Cui Zhang. Research Progress on Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Stress Affecting the Growth and Development of Maize [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [4] | Hengyu Yan, Zhaoxia Li, Yubin Li. Research Progress on Heat Stress Impact on Maize Growth and Heat-Tolerant Maize Screening in China [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| [5] | Duxian Lu, Yanyan Zhang, Yan Liu, Yanjun Li, Xinxiu Zuo, Jinxing Lin, Yaning Cui. Recent Advances of Non-coding RNA in Plant Growth, Development and Stress Response [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 709-725. |
| [6] | Yi Song, Hanghang Chen, Xin Cui, Zhifeng Lu, Shipeng Liao, Yangyang Zhang, Xiaokun Li, Rihuan Cong, Tao Ren, Jianwei Lu. Potassium Nutrient Status-mediated Leaf Growth of Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus) and Its Effect on Phyllosphere Microorganism [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 54-65. |
| [7] | Xinhai Zeng, Rui Chen, Yu Shi, Chaoyue Gai, Kai Fan, Zhaowei Li. Research Advances in Biological Functions of Plant SPL Transcription Factors [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 982-997. |
| [8] | Zhang Yingchuan, Wu Xiaomingyu, Tao Baolong, Chen Li, Lu Haiqin, Zhao Lun, Wen Jing, Yi Bin, Tu Jinxing, Fu Tingdong, Shen Jinxiong. Bna-miR43 Mediates the Response of Drought Tolerance in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 701-711. |
| [9] | Huang Huimei, Gao Yongkang, Tai Yuying, Liu Chao, Qu Dejie, Tang Ruiheng, Wang Youning. Research Advances in Elucidating the Function and Molecular Mechanism of the Nitrate Transporter 2 (NRT2) Proteins in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 783-798. |
| [10] | Yanan Xu, Jiarong Yan, Xin Sun, Xiaomei Wang, Yufeng Liu, Zhouping Sun, Mingfang Qi, Tianlai Li, Feng Wang. Red and Far-red Light Regulation of Plant Growth, Development, and Abiotic Stress Responses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 622-637. |
| [11] | Jia Zhang, Qidong Li, Cui Li, Qinghai Wang, Xincun Hou, Chunqiao Zhao, Shuhe Li, Qiang Guo. Research Progress on MATE Transporters in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 461-474. |
| [12] | Nan Wu, Lei Qin, Kan Cui, Haiou Li, Zhongsong Liu, Shitou Xia. Cloning of Brassica napus EXA1 Gene and Its Regulation on Plant Disease Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [13] | Qi Wang, Yunzhe Wu, Xueying Liu, Lili Sun, Hong Liao, Xiangdong Fu. The Rice Receptor-like Kinases Function as Key Regulators of Plant Development and Adaptation to the Environment [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(2): 199-213. |
| [14] | Deshuai Liu, Lei Yao, Weirong Xu, Mei Feng, Wenkong Yao. Research Progress of Melatonin in Plant Stress Resistance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| [15] | Jianru Yue, Yunjian He, Tianqi Qiu, Nannan Guo, Xueping Han, Xianling Wang. Research Advances in the Molecular Mechanisms of Plant Microtubules in Regulating Hypocotyl Elongation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 363-371. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||