

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 435-448.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24189 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24189
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiong Lianglin1,2, Liang Guolu1,2, Guo Qigao1,2, Jing Danlong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-05
Accepted:2025-02-22
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2025-02-26
Contact:
*E-mail: jingdanlong@swu.edu.cn
Xiong Lianglin, Liang Guolu, Guo Qigao, Jing Danlong. Advances in the Regulation of Alternative Splicing of Genes in Plants in Response to Abiotic Stress[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 435-448.
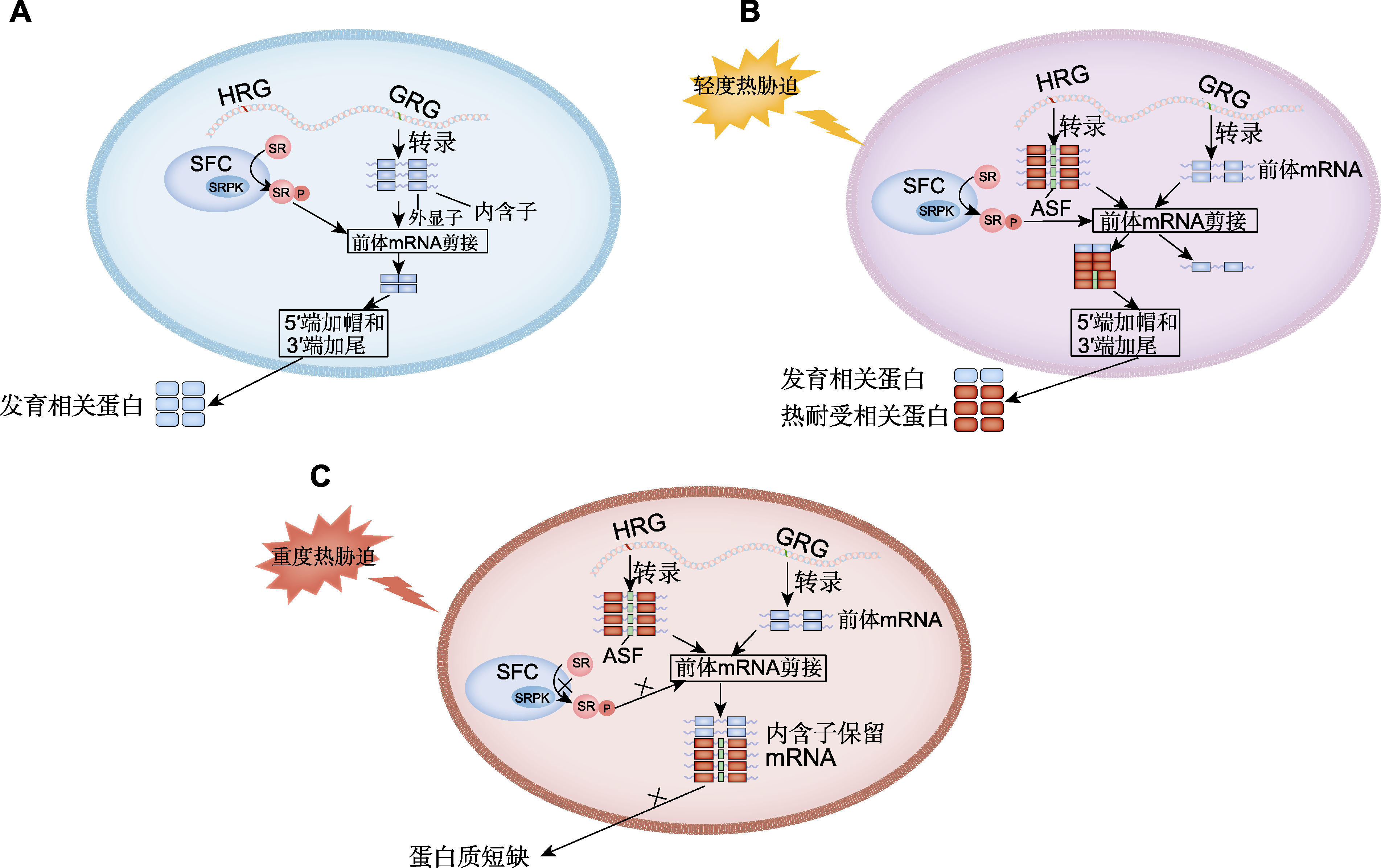
Figure 2 The mechanism of precursor mRNA regulation mediated by serine/arginine-rich (SR) proteins under normal conditions and different degrees of heat stress (refer to Ling et al., 2021) (A) Schematic diagram of constitutive splicing in plants under normal development (under normal conditions, heat-responsive genes (HRG) are not activated or are barely expressed, while growth-related genes (GRGs) are actively transcribed. SR proteins are efficiently phosphorylated (e.g., phosphorylated by SR protein kinase (SRPK) in the splicing factor complex (SFC)), thus participating in constitutive splicing and generating many development-related proteins); (B) Schematic diagram of alternative splicing in plants under mild heat stress (under mild heat stress (e.g., 32°C for 6 hours), HRGs including heat-inducible SR genes are transcriptionally activated. Phosphorylated SR proteins participate in constitutive or alternative splicing of HRGs. GRGs are suppressed at the transcriptional level, but their pre-mRNAs may still be alternative spliced by phosphorylated SR proteins to produce functionally distinct isoforms. Through this mechanism, plant cells produce a large number of heat-tolerant proteins to cope with heat stress); (C) Schematic diagram of alternative splicing in plants under severe heat stress (under severe heat stress (e.g., 45°C for 90 minutes), HRGs including heat-inducible SR genes are activated at the transcriptional level. However, under severe heat stress, the dephosphorylation of SR proteins (e.g., caused by the deficiency of SRPK) leads to a deficiency of active splicing factors, resulting in the accumulation of intron-retained transcripts of HRGs and GRGs in the nucleus, and leads to an extremely low number of functional transcripts. Therefore, there is a shortage of heat-tolerant proteins and development-related proteins in plant cells). ASF: Alternative spliced fragment; ×: The process is inhibited.
| 物种 | 基因 | 功能 | 胁迫类型 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtHsfA2 | 维持热休克蛋白相关基因的表达水平 | 热胁迫 | Charng et al., |
| AtSIZ1 | 促进热休克蛋白相关基因表达 | 热胁迫 | Ishida et al., | |
| AtIRE1 | 通过调节转录因子bZIP60前体mRNA剪接上调BIP3蛋白的表达 | 热胁迫 | Ling et al., | |
| AtZIFL1 | 产生剪接变体, 靶向叶片气孔保卫细胞的质膜并介导耐旱性 | 干旱胁迫 | Remy et al., | |
| AtSPCH | 降低气孔密度, 减少水分蒸发 | 干旱胁迫 | Wang et al., | |
| AtSR | 使剪接因子丰度和活性发生动态变化, 影响靶基因表达 | 冷胁迫 | Syed et al., | |
| AtLUC7 | 参与冷胁迫条件下内含子的剪接调节 | 冷胁迫 | de Francisco Amorim et al., | |
| AtSR45 | SR45.1亚型通过调节SOS基因表达以控制离子稳态和赋予耐盐性 | 盐胁迫 | Albaqami et al., | |
| AtSR34b | 通过IRT1的剪接和稳定性促进IRT1蛋白积累 | 盐胁迫 | Zhang et al., | |
| AtSAD1 | 提高盐胁迫响应基因的剪接效率 | 盐胁迫 | Cui et al., | |
| AtSKIP | 参与剪接位点的识别或切割 | 盐胁迫 | Feng et al., | |
| AtRCD1 | RCD1的剪接变体可减少盐诱导的细胞死亡 | 盐胁迫 | Hong et al., | |
| 水稻(Oryza sativa) | OsIRE1 | 调节热胁迫响应基因OsbZIP74的前体mRNA剪接 | 热胁迫 | Ling et al., |
| 小麦(Triticum aestivum) | TaHSFA6e | TaHSFA6e的剪接变体可增强下游热休克蛋白基因的转录活性 | 热胁迫 | Wen et al., |
| 毛白杨(Populus tomentosa) | PtoRSZ21 | 通过调节PtoATG2b的剪接影响植物的水分利用效率和抗逆能力 | 干旱胁迫 | Huang et al., |
| 玉米(Zea mays) | ZmPP2C26 | ZmPP2C26的2个剪接变体负向调节干旱耐受性 | 干旱胁迫 | Lu et al., |
| 茶树(Camellia sinensis) | CsWRKY21 | CsWRKY21的剪接变体抑制ABA分解相关基因的表达 | 冷胁迫 | Mi et al., |
| 谷子(Setaria italica) | SiCYP19 | 剪接变体可以提高脯氨酸含量和促进活性氧清除 | 盐胁迫 | Zhang et al., |
| 胡杨(Populus euphratica) | PeuHKT1;3 | 产生PeuHKT1;3a变体, 改变离子选择性 | 盐胁迫 | Lv et al., |
| 大豆(Glycine max) | GmPeNTL9 | 剪接变体激活抗氧化清除系统 | 盐胁迫 | Liu et al., |
| GmSnRK1.1 | 调节转录因子的活性和稳定性 | 盐胁迫 | Liu et al., |
Table 1 Alternative splicing-related genes involved in regulating plant responses to abiotic stress in different species
| 物种 | 基因 | 功能 | 胁迫类型 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) | AtHsfA2 | 维持热休克蛋白相关基因的表达水平 | 热胁迫 | Charng et al., |
| AtSIZ1 | 促进热休克蛋白相关基因表达 | 热胁迫 | Ishida et al., | |
| AtIRE1 | 通过调节转录因子bZIP60前体mRNA剪接上调BIP3蛋白的表达 | 热胁迫 | Ling et al., | |
| AtZIFL1 | 产生剪接变体, 靶向叶片气孔保卫细胞的质膜并介导耐旱性 | 干旱胁迫 | Remy et al., | |
| AtSPCH | 降低气孔密度, 减少水分蒸发 | 干旱胁迫 | Wang et al., | |
| AtSR | 使剪接因子丰度和活性发生动态变化, 影响靶基因表达 | 冷胁迫 | Syed et al., | |
| AtLUC7 | 参与冷胁迫条件下内含子的剪接调节 | 冷胁迫 | de Francisco Amorim et al., | |
| AtSR45 | SR45.1亚型通过调节SOS基因表达以控制离子稳态和赋予耐盐性 | 盐胁迫 | Albaqami et al., | |
| AtSR34b | 通过IRT1的剪接和稳定性促进IRT1蛋白积累 | 盐胁迫 | Zhang et al., | |
| AtSAD1 | 提高盐胁迫响应基因的剪接效率 | 盐胁迫 | Cui et al., | |
| AtSKIP | 参与剪接位点的识别或切割 | 盐胁迫 | Feng et al., | |
| AtRCD1 | RCD1的剪接变体可减少盐诱导的细胞死亡 | 盐胁迫 | Hong et al., | |
| 水稻(Oryza sativa) | OsIRE1 | 调节热胁迫响应基因OsbZIP74的前体mRNA剪接 | 热胁迫 | Ling et al., |
| 小麦(Triticum aestivum) | TaHSFA6e | TaHSFA6e的剪接变体可增强下游热休克蛋白基因的转录活性 | 热胁迫 | Wen et al., |
| 毛白杨(Populus tomentosa) | PtoRSZ21 | 通过调节PtoATG2b的剪接影响植物的水分利用效率和抗逆能力 | 干旱胁迫 | Huang et al., |
| 玉米(Zea mays) | ZmPP2C26 | ZmPP2C26的2个剪接变体负向调节干旱耐受性 | 干旱胁迫 | Lu et al., |
| 茶树(Camellia sinensis) | CsWRKY21 | CsWRKY21的剪接变体抑制ABA分解相关基因的表达 | 冷胁迫 | Mi et al., |
| 谷子(Setaria italica) | SiCYP19 | 剪接变体可以提高脯氨酸含量和促进活性氧清除 | 盐胁迫 | Zhang et al., |
| 胡杨(Populus euphratica) | PeuHKT1;3 | 产生PeuHKT1;3a变体, 改变离子选择性 | 盐胁迫 | Lv et al., |
| 大豆(Glycine max) | GmPeNTL9 | 剪接变体激活抗氧化清除系统 | 盐胁迫 | Liu et al., |
| GmSnRK1.1 | 调节转录因子的活性和稳定性 | 盐胁迫 | Liu et al., |
| [1] | Albaqami M, Laluk K, Reddy ASN (2019). The Arabidopsis splicing regulator SR45 confers salt tolerance in a splice isoform-dependent manner. Plant Mol Biol 100, 379-390. |
| [2] | Alhabsi A, Butt H, Kirschner GK, Blilou I, Mahfouz MM (2024). SCR106 splicing factor modulates abiotic stress responses by maintaining RNA splicing in rice. J Exp Bot 75, 802-818. |
| [3] |
Barnabás B, Jäger K, Fehér A (2008). The effect of drought and heat stress on reproductive processes in cereals. Plant Cell Environ 31, 11-38.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Blencowe BJ (2006). Alternative splicing: new insights from global analyses. Cell 126, 37-47. |
| [5] | Butt H, Bazin J, Prasad KVSK, Awad N, Crespi M, Reddy ASN, Mahfouz MM (2022). The rice serine/arginine splicing factor RS33 regulates pre-mRNA splicing during abiotic stress responses. Cells 11, 1796. |
| [6] | Calixto CPG, Guo WB, James AB, Tzioutziou NA, Entizne JC, Panter PE, Knight H, Nimmo HG, Zhang RX, Brown JWS (2018). Rapid and dynamic alternative splicing impacts the Arabidopsis cold response transcriptome. Plant Cell 30, 1424-1444. |
| [7] | Calixto CPG, Tzioutziou NA, James AB, Hornyik C, Guo WB, Zhang RX, Nimmo HG, Brown JWS (2019). Cold- dependent expression and alternative splicing of Arabidopsis long non-coding RNAs. Front Plant Sci 10, 235. |
| [8] |
Calvo SE, Pagliarini DJ, Mootha VK (2009). Upstream open reading frames cause widespread reduction of protein expression and are polymorphic among humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 7507-7512.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Charng YY, Liu HC, Liu NY, Chi WT, Wang CN, Chang SH, Wang TT (2007). A heat-inducible transcription factor, HsfA2, is required for extension of acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143, 251-262. |
| [10] | Chen YH, Weng X, Zhou XX, Gu JB, Hu Q, Luo QW, Wen MF, Li C, Wang ZY (2022). Overexpression of cassava RSZ21b enhances drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 268, 153574. |
| [11] |
Cho S, Hoang A, Sinha R, Zhong XY, Fu XD, Krainer AR, Ghosh G (2011). Interaction between the RNA binding domains of Ser-Arg splicing factor 1 and U1-70K snRNP protein determines early spliceosome assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 8233-8238.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Cui P, Zhang SD, Ding F, Ali S, Xiong LM (2014). Dynamic regulation of genome-wide pre-mRNA splicing and stress tolerance by the Sm-like protein LSm5 in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 15, R1. |
| [13] | de Francisco Amorim M, Willing EM, Szabo EX, Francisco-Mangilet AG, Droste-Borel I, Maček B, Schneeberger K, Laubinger S (2018). The U1 snRNP subunit LUC7 modulates plant development and stress responses via regulation of alternative splicing. Plant Cell 30, 2838-2854. |
| [14] | Ding F, Cui P, Wang ZY, Zhang SD, Ali S, Xiong LM (2014). Genome-wide analysis of alternative splicing of pre-mRNA under salt stress in Arabidopsis. BMC Genomics 15, 431. |
| [15] | Egawa C, Kobayashi F, Ishibashi M, Nakamura T, Nakamura C, Takumi S (2006). Differential regulation of transcript accumulation and alternative splicing of a DREB2 homolog under abiotic stress conditions in common wheat. Genes Genet Syst 81, 77-91. |
| [16] |
Erkelenz S, Mueller WF, Evans MS, Busch A, Scöneweis K, Hertel KJ, Schaal H (2013). Position-dependent splicing activation and repression by SR and hnRNP proteins rely on common mechanisms. RNA 19, 96-102.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Fedoroff NV, Battisti DS, Beachy RN, Cooper PJM, Fischhoff DA, Hodges CN, Knauf VC, Lobell D, Mazur BJ, Molden D, Reynolds MP, Ronald PC, Rosegrant MW, Sanchez PA, Vonshak A, Zhu JK (2010). Radically rethinking agriculture for the 21st century. Science 327, 833-834. |
| [18] | Feng JL, Li JJ, Gao ZX, Lu YR, Yu JY, Zheng Q, Yan SN, Zhang WJ, He H, Ma LG, Zhu ZG (2015). SKIP confers osmotic tolerance during salt stress by controlling alternative gene splicing in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 8, 1038-1052. |
| [19] | Gallegos J (2018). Alternative splicing plays a major role in plant response to cold temperatures. Plant Cell 30, 1378-1379. |
| [20] | Gan JH, Qiu YQ, Tao YL, Zhang LN, Okita TW, Yan YY, Tian L (2024). RNA-seq analysis reveals transcriptome reprogramming and alternative splicing during early response to salt stress in tomato root. Front Plant Sci 15, 1394223. |
| [21] |
Graveley BR (2001). Alternative splicing: increasing diversity in the proteomic world. Trends Genet 17, 100-107.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Gu JB, Ma SY, Zhang YN, Wang D, Cao SQ, Wang ZY (2020). Genome-wide identification of cassava serine/arginine-rich proteins: insights into alternative splicing of pre- mRNAs and response to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Physiol 61, 178-191. |
| [23] | Gu JB, Xia ZQ, Luo YH, Jiang XY, Qian BL, Xie H, Zhu JK, Xiong LM, Zhu JH, Wang ZY (2018). Spliceosomal protein U1A is involved in alternative splicing and salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 46, 1777-1792. |
| [24] | Guan QM, Wu JM, Zhang YY, Jiang CH, Liu RY, Chai CL, Zhu JH (2013). A DEAD Box RNA helicase is critical for pre-mRNA splicing, cold-responsive gene regulation, and cold tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 342-356. |
| [25] | Hong YC, Gao Y, Pang J, Shi HZ, Li TT, Meng HY, Kong DL, Chen YJ, Zhu JK, Wang Z (2023). The Sm core protein SmEb regulates salt stress responses through maintaining proper splicing of RCD1 pre-mRNA in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 65, 1383-1393. |
| [26] | Huang R, Jin ZY, Zhang DH, Li LZ, Zhou JX, Xiao L, Li P, Zhang MJ, Tian CD, Zhang WK, Zhong LS, Quan MY, Zhao R, Du L, Liu LJ, Li ZH, Zhang DQ, Du QZ (2024). Rare variations within the serine/arginine-rich splicing factor PtoRSZ21 modulate stomatal size to determine drought tolerance in Populus. New Phytol 243, 1776-1794. |
| [27] |
Huertas R, Catalá R, Jiménez-Gómez JM, Castellano MM, Crevillén P, Piñeiro M, Jarillo JA, Salinas J (2019). Arabidopsis SME1 regulates plant development and response to abiotic stress by determining spliceosome activity specificity. Plant Cell 31, 537-554.
DOI |
| [28] |
Ikeda M, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M (2011). Arabidopsis HsfB1 and HsfB2b act as repressors of the expression of heat-inducible Hsfs but positively regulate the acquired thermotolerance. Plant Physiol 157, 1243-1254.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Ings J, Mur LAJ, Robson PRH, Bosch M (2013). Physiological and growth responses to water deficit in the bioenergy crop Miscanthus × giganteus. Front Plant Sci 4, 468. |
| [30] | Ishida T, Yoshimura M, Miura K, Sugimoto K (2012). MMS21/HPY2 and SIZ1, two Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligases, have distinct functions in development. PLoS One 7, e46897. |
| [31] | Jian YQ, Chen X, Sun KW, Liu ZY, Cheng DN, Cao J, Liu JZ, Cheng XF, Wu L, Zhang F, Luo YM, Hahn M, Ma ZH, Yin YN (2023). SUMOylation regulates pre-mRNA splicing to overcome DNA damage in fungi. New Phytol 237, 2298-2315. |
| [32] |
Jiang JF, Liu XN, Liu CH, Liu GT, Li SH, Wang LJ (2017). Integrating omics and alternative splicing reveals insights into grape response to high temperature. Plant Physiol 173, 1502-1518.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Kim T, Hwang H, Bang G, Ha J, Park YJ, Kim JY (2024). Understanding the molecular mechanisms of drought tolerance in wild soybean (Glycine soja) through multi-omics-based alternative splicing predictions. Environ Exp Bot 225, 105872. |
| [34] |
Kwak JS, Song JT, Seo HS (2024). E3 SUMO ligase SIZ1 splicing variants localize and function according to external conditions. Plant Physiol 195, 1601-1623.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Laloum T, Martín G, Duque P (2018). Alternative splicing control of abiotic stress responses. Trend Plant Sci 23, 140-150. |
| [36] | Lee BH, Kapoor A, Zhu JH, Zhu JK (2006). STABILIZED1, a stress-upregulated nuclear protein, is required for pre- mRNA splicing, mRNA turnover, and stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18, 1736-1749. |
| [37] |
Li SX, Yu X, Cheng ZH, Zeng CY, Li WB, Zhang LS, Peng M (2020). Large-scale analysis of the cassava transcriptome reveals the impact of cold stress on alternative splicing. J Exp Bot 71, 422-434.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Lim KH, Han Z, Jeon HY, Kach J, Jing EX, Weyn-Vanhentenryck S, Downs M, Corrionero A, Oh R, Scharner J, Venkatesh A, Ji S, Liau G, Ticho B, Nash H, Aznarez I (2020). Antisense oligonucleotide modulation of non-productive alternative splicing upregulates gene expression. Nat Commun 11, 3501.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Ling Y, Alshareef S, Butt H, Lozano-Juste J, Li LX, Galal AA, Moustafa A, Momin AA, Tashkandi M, Richardson DN, Fujii H, Arold S, Rodriguez PL, Duque P, Mahfouz MM (2017). Pre-mRNA splicing repression triggers abiotic stress signaling in plants. Plant J 89, 291-309. |
| [40] |
Ling Y, Mahfouz MM, Zhou SX (2021). Pre-mRNA alternative splicing as a modulator for heat stress response in plants. Trends Plant Sci 26, 1153-1170.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | Liu JJ, Sun N, Liu M, Liu JC, Du BJ, Wang XJ, Qi XT (2013). An autoregulatory loop controlling Arabidopsis HsfA2 expression: role of heat shock-induced alternative splicing. Plant Physiol 162, 512-521. |
| [42] | Liu SR, Li B, Liang QX, Liu AR, Qu LH, Yang JH (2020). Classification and function of RNA-protein interactions. WIREs RNA 11, e1601. |
| [43] | Liu X, Li ML, Chen T, Zhang R, Wang YY, Xiao JL, Ding XD, Zhang SZ, Li Q (2024). A global survey of bicarbonate stress-induced pre-mRNA alternative splicing in soybean via integrative analysis of Iso-seq and RNA-seq. Int J Biol Macromol 278, 135067. |
| [44] | Liu YM, Cao L, Wu X, Wang S, Zhang PM, Li ML, Jiang JH, Ding XD, Cao XY (2023). Functional characterization of wild soybean (Glycine soja) GsSnRK1.1 protein kinase in plant resistance to abiotic stresses. J Plant Physiol 280, 153881. |
| [45] | Liu ZS, Qin JX, Tian XJ, Xu SB, Wang Y, Li HX, Wang XM, Peng HR, Yao YY, Hu ZR, Ni ZF, Xin MM, Sun QX (2018). Global profiling of alternative splicing landscape responsive to drought, heat and their combination in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Biotechnol J 16, 714-726. |
| [46] |
Lopato S, Mayeda A, Krainer AR, Barta A (1996). Pre- mRNA splicing in plants: characterization of Ser/Arg splicing factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 3074-3079.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Lorković ZJ, Kirk DAW, Lambermon MHL, Filipowicz W (2000). Pre-mRNA splicing in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci 5, 160-167.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Lu CA, Huang CK, Huang WS, Huang TS, Liu HY, Chen YF (2020). DEAD-Box RNA helicase 42 plays a critical role in pre-mRNA splicing under cold stress. Plant Physiol 182, 255-271. |
| [49] | Lu FZ, Li WC, Peng YL, Cao Y, Qu JT, Sun FA, Yang QQ, Lu YL, Zhang XH, Zheng LJ, Fu FL, Yu HQ (2022). ZmPP2C26 alternative splicing variants negatively regulate drought tolerance in maize. Front Plant Sci 13, 851531. |
| [50] | Lv JJ, Zhou FF, Wei QQ, Long XQ, Tian WJ, Zhai JJ, Wang JJ, Zhang Q, Wan DS (2024). An alternative 3′ splice site of PeuHKT1; 3 improves the response to salt stress through enhancing affinity to K+ in Populus. Plant Physiol Biochem, 212, 108776. |
| [51] | Manley JL, Tacke R (1996). SR proteins and splicing control. Genes Dev 10, 1569-1579. |
| [52] | Martín G, Márquez Y, Mantica F, Duque P, Irimia M (2021). Alternative splicing landscapes in Arabidopsis thaliana across tissues and stress conditions highlight major functional differences with animals. Genome Biol 22, 35. |
| [53] | Matera AG, Wang ZF (2014). A day in the life of the spliceosome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15, 108-121. |
| [54] |
Matsukura S, Mizoi J, Yoshida T, Todaka D, Ito Y, Maruyama K, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010). Comprehensive analysis of rice DREB2-type genes that encode transcription factors involved in the expression of abiotic stress-responsive genes. Mol Genet Genomics 283, 185-196.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | Mi XZ, Tang MS, Zhu JX, Shu MT, Wen HL, Zhu JY, Wei CL (2024). Alternative splicing of CsWRKY21positively regulates cold response in tea plant. Plant Physiol Biochem 208, 108473. |
| [56] |
Miura K, Furumoto T (2013). Cold signaling and cold response in plants. Int J Mol Sci 14, 5312-5337.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Miura K, Rus A, Sharkhuu A, Yokoi S, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG, Baek D, Koo YD, Jin JB, Bressan RA, Yun DJ, Hasegawa PM (2005). The Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 controls phosphate deficiency responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 7760-7765. |
| [58] | Muthusamy M, Yoon EK, Kim JA, Jeong MJ, Lee SI (2020). Brassica rapa SR45a regulates drought tolerance via the alternative splicing of target genes. Genes 11, 182. |
| [59] | Ner-Gaon H, Halachmi R, Savaldi-Goldstein S, Rubin E, Ophir R, Fluhr R (2004). Intron retention is a major phenomenon in alternative splicing in Arabidopsis. Plant J 39, 877-885. |
| [60] | Nishizawa A, Yabuta Y, Yoshida E, Maruta T, Yoshimura K, Shigeoka S (2006). Arabidopsis heat shock transcription factor A2 as a key regulator in response to several types of environmental stress. Plant J 48, 535-547. |
| [61] | Palusa SG, Reddy ASN (2015). Differential recruitment of splice variants from SR Pre-mRNAs to polysomes during development and in response to stresses. Plant Cell Physiol 56, 421-427. |
| [62] | Paul T, Zhang PC, Zhang ZH, Fargason T, De Silva NIU, Powell E, Ekpenyong E, Jamal S, Yu YB, Prevelige P, Lu R, Zhang J (2024). The U1-70K and SRSF1 interaction is modulated by phosphorylation during the early stages of spliceosome assembly. Protein Sci 33, e5117. |
| [63] | Punzo P, Grillo S, Batelli G (2020). Alternative splicing in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochem Soc Trans 48, 2117-2126. |
| [64] | Remy E, Cabrito TR, Baster P, Batista RA, Teixeira MC, Friml J, Sá-Correia I, Duque P (2013). A major facilitator superfamily transporter plays a dual role in polar auxin transport and drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 901-926. |
| [65] |
Rosenkranz RRE, Vraggalas S, Keller M, Sankaranarayanan S, McNicoll F, Löchli K, Bublak D, Benhamed M, Crespi M, Berberich T, Bazakos C, Feldbrügge M, Schleiff E, Müller-McNicoll M, Zarnack K, Fragkostefanakis S (2024). A plant-specific clade of serine/arginine- rich proteins regulates RNA splicing homeostasis and thermotolerance in tomato. Nucleic Acids Res 52, 11466-11480.
DOI PMID |
| [66] |
Seo PJ, Park MJ, Park CM (2013). Alternative splicing of transcription factors in plant responses to low temperature stress: mechanisms and functions. Planta 237, 1415-1424.
DOI PMID |
| [67] | Song L, Pan ZZ, Chen L, Dai Y, Wan JR, Ye H, Nguyen HT, Zhang GZ, Chen HT (2020). Analysis of whole transcriptome RNA-seq data reveals many alternative splicing events in soybean roots under drought stress conditions. Genes 11, 1520. |
| [68] | Song NN, Wang J, Qin QQ, Su AQ, Cheng YF, Si WN, Cheng BJ, Fan J, Jiang HY (2025). ZmHSFA2B self- regulatory loop is critical for heat tolerance in maize. Plant Biotechnol J 23, 284-301. |
| [69] | Song NX, Xie YF, Li X (2020). Effects of epigenetic mechanisms on C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase transgenic rice (Oryza sativa) seed germination under drought stress. Chin Bull Bot 55, 677-692. (in Chinese) |
| 宋凝曦, 谢寅峰, 李霞 (2020). 干旱胁迫下表观遗传机制对转C4型PEPC基因水稻种子萌发的影响. 植物学报 55, 677-692. | |
| [70] | Staiger D, Brown JWS (2013). Alternative splicing at the intersection of biological timing, development, and stress responses. Plant Cell 25, 3640-3656. |
| [71] | Sun Q, Sun YX, Liu X, Li ML, Li Q, Xiao JL, Xu PF, Zhang SZ, Ding XD (2024). Regulation of plant resistance to salt stress by the SnRK1-dependent splicing factor SRRM1L. New Phytol 242, 2093-2114. |
| [72] | Syed NH, Kalyna M, Marquez Y, Barta A, Brown JWS (2012). Alternative splicing in plants-coming of age. Trends Plant Sci 17, 616-623. |
| [73] | Tanabe N, Yoshimura K, Kimura A, Yabuta Y, Shigeoka S (2007). Differential expression of alternatively spliced mRNAs of Arabidopsis SR protein homologs, AtSR30 and AtSR45a, in response to environmental stress. Plant Cell Physiol 48, 1036-1049. |
| [74] | Tian L, Zhao XY, Liu HH, Ku LX, Wang SX, Han ZP, Wu LC, Shi Y, Song XH, Chen YH (2019). Alternative splicing of ZmCCA1 mediates drought response in tropical maize. PLoS One 14, e0211623. |
| [75] | Wang F, Li Y, Yuan JB, Li C, Lin Y, Gu JB, Wang ZY (2024a). The U1 small nuclear RNA enhances drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 196, 1126-1146. |
| [76] | Wang X, Liu Y, Ouyang L, Yao RN, Yu TT, Yan LY, Chen YN, Huai DX, Zhou XJ, Wang ZH, Kang YP, Wang QQ, Jiang HF, Lei Y, Liao BS (2024b). Full-length transcriptome sequencing provides insights into alternative splicing under cold stress in peanut. Front Plant Sci 15, 1362277. |
| [77] | Wang XX, Wu FM, Xie QG, Wang HM, Wang Y, Yue YL, Gahura O, Ma SS, Liu L, Cao Y, Jiao YL, Puta F, McClung CR, Xu XD, Ma LG (2012). SKIP is a component of the spliceosome linking alternative splicing and the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 3278-3295. |
| [78] | Wang Z, Hong YC, Yao JJ, Huang H, Qian BL, Liu X, Chen YJ, Pang J, Zhan XQ, Zhu JK, Zhu JH (2022). Modulation of plant development and chilling stress responses by alternative splicing events under control of the spliceosome protein SmEb in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 45, 2762-2779. |
| [79] | Wen JJ, Qin Z, Sun L, Zhang YM, Wang DL, Peng HR, Yao YY, Hu ZR, Ni ZF, Sun QX, Xin MM (2023). Alternative splicing of TaHSFA6e modulates heat shock protein-mediated translational regulation in response to heat stress in wheat. New Phytol 239, 2235-2247. |
| [80] | Will CL, Lührmann R (2011). Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3, a003707. |
| [81] |
Wu Z, Liang JH, Wang CP, Ding LP, Zhao X, Cao X, Xu SJ, Teng NJ, Yi MF (2019). Alternative splicing provides a mechanism to regulate LlHSFA3 function in response to heat stress in lily. Plant Physiol 181, 1651-1667.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006). Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tole-rance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57, 781-803.
PMID |
| [83] | Yao H, Li GZ, Gao ZZ, Guo F, Feng JH, Xiao GH, Shen HT, Li HB (2024). Alternative splicing responses to salt stress in Glycyrrhiza uralensis revealed by global profiling of transcriptome RNA-seq datasets. Front Genet 15, 1397502. |
| [84] | Yu ZP, Huang X, Wen SH, Cao HJ, Wang N, Shen SH, Ding MQ (2023). Alternative splicing under cold stress in paper mulberry. Plants 12, 3950. |
| [85] |
Yunus AA, Lima CD (2009). Structure of the Siz/PIAS SUMO E3 ligase Siz1 and determinants required for SUMO modification of PCNA. Mol Cell 35, 669-682.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Zahler AM, Roth MB (1995). Distinct functions of SR proteins in recruitment of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein to alternative 5' splice sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92, 2642-2646.
PMID |
| [87] | Zhang H, Chen W, Zhu D, Zhang BT, Xu Q, Shi CL, He HY, Dai XF, Li YL, He WC, Lv Y, Yang LB, Cao XL, Cui Y, Leng Y, Wei H, Liu XP, Zhang B, Wang XM, Guo ML, Zhang ZP, Li XX, Liu CC, Yuan QL, Wang TY, Yu XM, Qian HG, Zhang QQ, Chen DD, Hu GJ, Qian Q, Shang LG (2024a). Population-level exploration of alternative splicing and its unique role in controlling agronomic traits of rice. Plant Cell 36, 4372-4387. |
| [88] | Zhang WT, Du BJ, Liu D, Qi XT (2014). Splicing factor SR34b mutation reduces cadmium tolerance in Arabidopsis by regulating iron-regulated transporter 1 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 455, 312-317. |
| [89] | Zhang WX, Wang H, Guo YN, Hao XY, Li YX, He WT, Zhao X, Cai SY, Song XB (2024b). Functional validation of different alternative splicing variants of the Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium ClNUM1 gene in tobacco. Curr Issues Mol Biol 46, 5242-5256. |
| [90] | Zhang YL, Chen ZT, Tian HW, Wu YM, Kong Y, Wang XM, Sui N (2024c). Alternative splicing plays a crucial role in the salt tolerance of foxtail millet. J Agric Food Chem 72, 10814-10827. |
| [91] | Zhong YY, Luo YH, Sun JL, Qin XM, Gan P, Zhou ZW, Qian YQ, Zhao RP, Zhao ZY, Cai WG, Luo JJ, Chen LL, Song JM (2024). Pan-transcriptomic analysis reveals alternative splicing control of cold tolerance in rice. Plant Cell 36, 2117-2139. |
| [92] | Zhou HP, Shi HF, Yang YQ, Feng XX, Chen X, Xiao F, Lin HH, Guo Y (2024). Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. J Genet Genomics 51, 16-34. |
| [1] | Tao Xie, Yifan Zhang, Yunhui Liu, Huiyu You, Jibenben Xia, Rong Ma, Chunni Zhang, Xuejun Hua. Research progress of iron-sulfur cluster synthesis system and regulation in plant mitochondria [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | Yaqi Shi, Haishuang Liu, Jin Ke, Qing Ma, Suomin Wang. Research Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide-gated Ion Channels in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 294-306. |
| [3] | Yan Deng, Limin Lu, Qiang Zhang, Zhiduan Chen, Haihua Hu. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Plastid DNA Data Gaps of Vascular Plants in Species and Geographic Area [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 1-16. |
| [4] | Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Gan Xie, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Ze Wei, Mingyue Zhao, Liang Zhi, Huawei Wan, Jixi Gao, Min Li. An Artificial Intelligence Model for Identifying Grassland Plants in Northern China [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 74-80. |
| [5] | Qingguo Du, Wenxue Li. Research Progress in the Regulation of Development and Stress Responses by Long Non-coding RNAs in Maize [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [6] | Wenjie Zhou, Wenhan Zhang, Wei Jia, Zicheng Xu, Wuxing Huang. Advances in Plant miRNAs Responses to Abiotic Stresses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 810-833. |
| [7] | Chunjiao Xia, Yunguang Li, Shu Xia, Wei Pang, Chunli Chen. Flow Cytometric Analysis and Sorting in Plant Genomics [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 774-782. |
| [8] | Lansha Luo, Wenpei Song, Qingzhu Hua, Dawei Li, Hong Liang, Xianzhi Zhang. Research Progress on Plant Sex-determination Genes and Their Epigenetic Regulation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 278-290. |
| [9] | Jiahang Che, Weinan Li, Yingzhi Qin, Jinhuan Chen. Research Progress of Leaf Color Variation Mechanism in Woody Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 319-328. |
| [10] | Zhaoxuan Zhong, Dongrui Zhang, Lu Li, Ying Su, Daining Wang, Zeran Wang, Yang Liu, Ying Chang. Bioinformatic and Expression Pattern Analysis of dfr-miR160a and Target Gene DfARF10 in Dryopteris fragrans [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 22-33. |
| [11] | Yuejing Zhang, Hetian Sang, Hanqi Wang, Zhenzhen Shi, Li Li, Xin Wang, Kun Sun, Ji Zhang, Hanqing Feng. Research Progress of Plant Signaling in Systemic Responses to Abiotic Stresses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [12] | Yi Li, Xi Zhang, Yanhui Yuan, Pichang Gong, Jinxing Lin. Aptamers and Their Applications in Plant Science Researches [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 935-945. |
| [13] | Yanan Xu, Jiarong Yan, Xin Sun, Xiaomei Wang, Yufeng Liu, Zhouping Sun, Mingfang Qi, Tianlai Li, Feng Wang. Red and Far-red Light Regulation of Plant Growth, Development, and Abiotic Stress Responses [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 622-637. |
| [14] | Xiaotong Ren, Ranran Zhang, Shaowei Wei, Xiaofeng Luo, Jiahui Xu, Kai Shu. Research Progress of Spermosphere Microorganisms [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 499-509. |
| [15] | Jia Zhang, Qidong Li, Cui Li, Qinghai Wang, Xincun Hou, Chunqiao Zhao, Shuhe Li, Qiang Guo. Research Progress on MATE Transporters in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 461-474. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||