

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (2): 319-328.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23019 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23019
• SPECIAL TOPICS • Previous Articles
Jiahang Che1,2,3, Weinan Li1,2,3, Yingzhi Qin1,2,3, Jinhuan Chen1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-02-11
Accepted:2024-01-30
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-10
Contact:
E-mail: Jiahang Che, Weinan Li, Yingzhi Qin, Jinhuan Chen. Research Progress of Leaf Color Variation Mechanism in Woody Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 319-328.
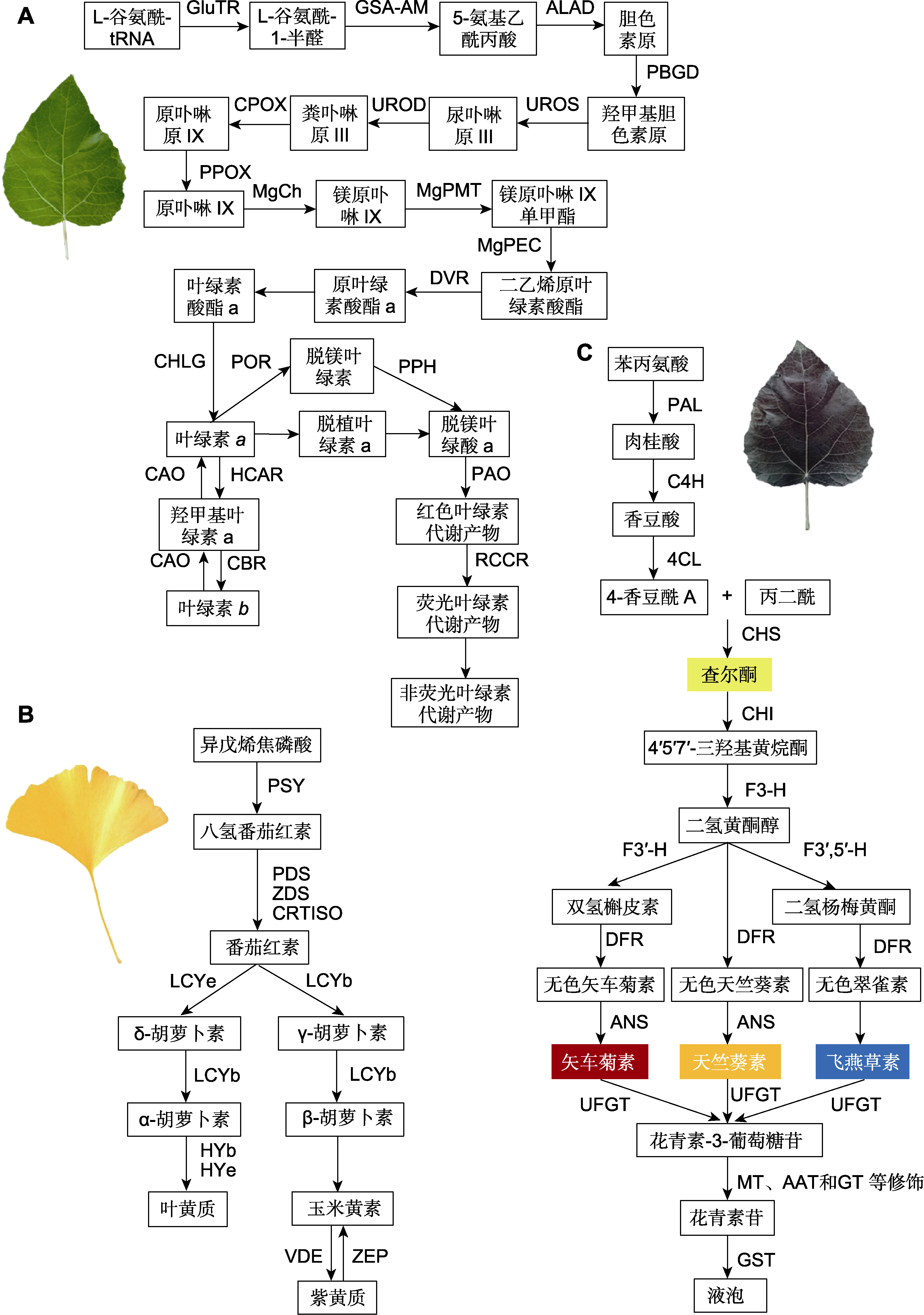
Figure 1 Chlorophyll, carotenoid, and anthocyanin synthesis pathways (A) Chlorophyll biosynthetic pathway; (B) Carotenoid biosynthetic pathway; (C) Anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway. GluTR: Glutamyl-tRNA reductase; GSA-AM: Glutamate-1-semialdehyde 2,1-aminomutase; ALAD: 5-aminolevulinic acid dehydrase; PBGD: Porphobilinogen deaminase; UROS: Uroporphyrinogen III synthase; UROD: Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase; CPOX: Coproporphyrinogen III oxidase; PPOX: Protoporphyrinogen oxidase; MgCh: Magnesium chelatase; MgPMT: Magnesium proto IX methyltransferase; MgPEC: Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester cyclase; DVR: Vinyl reductase; POR: Protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase; CHLG: Chlorophyll synthase; CAO: Chlorophyllide a oxygenase; CBR: Chlorophyll b reductase; HCAR: 7-hydroxymethyl chlorophyll reductase; PPH: Mg-dechelatase; PAO: Pheophorbide a oxygenase; RCCR: Red metabolite reductase; PSY: Phytoene synthase; PDS: Phytoene desaturase; ZDS: ζ-carotene desaturase; CRTISO: Carotene isomerase; LCYb: Lycopene β-cyclase; LCYe: Lycopene ε-cyclase; HYb: β-carotene hydroxylase; HYe: ε-carotene hydroxylase; ZEP: Zeaxanthin cyclase; VDE: Violaxanthin de-epoxidase; PAL: Phenylalanine lyase; C4H: Cinnamate hydroxylase; 4CL: 4-coumaric acid CoA ligase; CHS: Chalcone synthetase; CHI: Chalcone isomerase; F3-H: Flavanone 3-hydroxylase; F3'-H: Flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase; F3',5'-H: Flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase; DFR: Dihydroflavonol-4-reductase; ANS: Anthocyanin synthetase; UFGT: Flavonoside transferase; GST: Glutathione mercaptotransferase
| [1] |
陈柯伊, 李朝娜, 成敏敏, 赵扬辉, 周明兵, 杨海芸 (2018). 不同叶色矢竹叶绿体结构和光系统特性差异. 植物学报 53, 509-518.
DOI |
| [2] | 郭婷 (2021). 栾树彩叶突变体叶色变异机理的初步探究. 硕士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 79. |
| [3] | 韩辉, 宫伟 (2010). 不同土壤酸碱度对紫花槭秋季叶色变化的影响. 吉林农业 6, 76-80. |
| [4] | 姜生辉 (2020). DNA甲基化修饰MdMYB1启动子调控苹果花青苷转运的机理. 博士论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学. pp. 114. |
| [5] | 沈馨, 王开勇, 周晓杰, 刘勇 (2022). 不同土壤pH对银红槭叶色变化的影响. 西北林学院学报 37(2), 29-36. |
| [6] | 司钰苇 (2020). 黄金芽遮阴绿化与返黄生理生化特性研究. 硕士论文. 长沙: 湖南农业大学. pp. 78. |
| [7] |
宋雪薇, 魏解冰, 狄少康, 庞永珍 (2019). 花青素转录因子调控机制及代谢工程研究进展. 植物学报 54, 133-156.
DOI |
| [8] | 王安喜 (2017). 彩叶植物资源在园林中的应用. 农业与技术 37( 18), 219. |
| [9] | 王冬雪, 孙海菁, 德永军, 史久西 (2019). 不同光质处理对枫香幼苗叶色的影响. 林业科学研究 32(4), 158-164. |
| [10] |
王改萍, 张磊, 姚雪冰, 祝遵凌 (2020). 金叶银杏叶色变化特性分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版) 44(5), 41-48.
DOI |
| [11] | 王晓娟, 杨东生, 先锐, 王光剑, 马光良, 周兰英 (2018). 干旱胁迫对红花檵木叶片色素含量及光合特性的影响. 四川林业科技 39(5), 82-86. |
| [12] | 王艳琳 (2010). 2种彩叶植物光合生理特性研究. 硕士论文. 成都: 四川农业大学. pp. 54. |
| [13] | 吴飞洋, 柳新红, 王成龙, 吕江波, 张丽芳, 李因刚 (2021). 土壤水分对乌桕秋叶生理指标及观赏效果的影响. 东北林业大学学报 49(5), 19-23, 44. |
| [14] | 吴驭帆, 于萍, 祝遵凌 (2016). 春季不同叶色鹅耳枥叶片生理生化特性的研究. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版) 44(5), 120-126, 132. |
| [15] | 杨继生 (2020). 枫香变色过程中叶片结构及其生理特征的研究. 硕士论文. 南宁: 广西大学. pp. 82. |
| [16] |
杨露, 于晓跃, 刘煜光, 史宝胜 (2016). 遮阴对2种彩叶风箱果叶色及光合特性的影响. 河北农业大学学报 39(5), 75-81.
DOI |
| [17] | 张少露 (2017). 红叶石楠叶色变化过程中叶结构和生理特征研究. 硕士论文. 成都: 四川农业大学. pp. 50. |
| [18] | 张淑珍 (2019). 芽变突变体金叶杨CLH基因的克隆及功能鉴定. 硕士论文. 成都: 四川农业大学. pp. 74. |
| [19] | 张向娜, 熊立瑰, 温贝贝, 王坤波, 刘仲华, 黄建安, 李娟 (2020). 茶树叶色变异研究进展. 植物生理学报 56, 643-653. |
| [20] | 张鑫, 肖婷婷, 李艰, 王玉涛, 刘广林 (2016). 水分胁迫对美国红枫幼苗生长及叶色变化的影响. 江苏农业科学 44, 224-227. |
| [21] | 郑恬静, 王克凤, 桑瀚旭, 董然 (2017). 两种海棠秋季叶色变化的生理机制研究. 湖北农业科学 56, 2908-2912. |
| [22] | 朱璐, 闻婧, 马秋月, 颜坤元, 杜一鸣, 李淑顺, 李倩中 (2022). 鸡爪槭金陵丹枫和金陵黄枫叶片呈色分析. 江苏农业学报 38, 521-527. |
| [23] | 朱延林, 王念, 程相军, 周春生 (2012). 杨树新品种‘全红杨’. 林业科学 48(2), 188, 191. |
| [24] |
Al Sane KO, Hesham AEL (2015). Biochemical and genetic evidences of anthocyanin biosynthesis and accumulation in a selected tomato mutant. Rend Lincei Sci Fis Nat 26, 293-306.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Albert NW, Davies KM, Lewis DH, Zhang HB, Montefiori M, Brendolise C, Boase MR, Ngo H, Jameson PE, Schwinn KE (2014). A conserved network of transcriptional activators and repressors regulates anthocyanin pig- mentation in eudicots. Plant Cell 26, 962-980.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Cazzonelli CI, Pogson BJ (2010). Source to sink: regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Trends Plant Sci 15, 266-274.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Chen X, Li MH, Ni J, Hou JY, Shu X, Zhao WW, Su PF, Wang DC, Shah FA, Huang SW, Liu ZJ, Wu LF (2021). The R2R3-MYB transcription factor SsMYB1 positively regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis and determines leaf color in Chinese tallow (Sapium sebiferum Roxb.). Ind Crops Prod 164, 113335.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Cho JS, Nguyen VP, Jeon HW, Kim MH, Eom SH, Lim YJ, Kim WC, Park EJ, Choi YI, Ko JH (2016). Overexpres-sion of PtrMYB119, a R2R3-MYB transcription factor from Populus trichocarpa, promotes anthocyanin production in hybrid poplar. Tree Physiol 36, 1162-1176.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Córdoba J, Molina-Cano JL, Martínez-Carrasco R, Mor-cuende R, Pérez P (2016). Functional and transcriptional characterization of a barley mutant with impaired photo-synthesis. Plant Sci 244, 19-30. |
| [30] |
Fan MC, Lian WJ, Li TT, Fan YH, Rao ZM, Li Y, Qian HF, Zhang H, Wu GC, Qi XG, Wang L (2020). Metabolomics approach reveals discriminatory metabolites associating with the blue pigments from Vaccinium bracteatum thunb. Leaves at different growth stages. Ind Crops Prod 147, 112252.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Fu XM, Chen JM, Li JL, Dai GY, Tang JC, Yang ZY (2022). Mechanism underlying the carotenoid accumulation in sha- ded tea leaves. Food Chem X 14, 100323.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
James AM, Ma DW, Mellway R, Gesell A, Yoshida K, Walker V, Tran L, Stewart D, Reichelt M, Suvanto J, Salminen JP, Gershenzon J, Séguin A, Constabel CP (2017). Poplar myb115 and myb134 transcription factors regulate proanthocyanidin synthesis and structure. Plant Physiol 174, 154-171.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Jing YJ, Lin RC (2020). Transcriptional regulatory network of the light signaling pathways. New Phytol 227, 683-697. |
| [34] |
Kräutler B (2016). Breakdown of chlorophyll in higher plants—phyllobilins as abundant, yet hardly visible signs of ripening, senescence, and cell death. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 55, 4882-4907.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Li CF, Xu YX, Ma JQ, Jin JQ, Huang DJ, Yao MZ, Ma CL, Chen L (2016a). Biochemical and transcriptomic analyses reveal different metabolite biosynthesis profiles among three color and developmental stages in ‘Anji Baicha’ (Ca- mellia sinensis). BMC Plant Biol 16, 195.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Li W, Tang S, Zhang S, Shan JG, Tang CJ, Chen QN, Jia GQ, Han YH, Zhi H, Diao XM (2016b). Gene mapping and functional analysis of the novel leaf color gene Si-YGL1 in foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv). Physiol Plant 157, 24-37. |
| [37] | Li WX, Yang SB, Lu ZG, He ZC, Ye YL, Zhao BB, Wang L, Jin B (2018). Cytological, physiological, and transcript-tomic analyses of golden leaf coloration in Ginkgo biloba L. Hortic Res 5, 12. |
| [38] |
Li Y, Zhang ZY, Wang P, Wang SA, Ma LL, Li LF, Yang RT, Ma YZ, Wang Q (2015). Comprehensive transcript-tome analysis discovers novel candidate genes related to leaf color in a Lagerstroemia indica yellow leaf mutant. Genes Genomics 37, 851-863.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Li YH, Wang BH, Dai ZY, Li AH, Liu GQ, Zuo SM, Zhang HX, Pan XB (2012). Morphological structure and genetic mapping of new leaf-color mutant gene in rice (Oryza sa-tiva). Rice Sci 19, 79-85.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Lu YF, Zhang ML, Meng XN, Wan HH, Zhang J, Tian J, Hao SX, Jin KN, Yao YC (2015). Photoperiod and shading regulate coloration and anthocyanin accumulation in the leaves of Malus crabapples. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 121, 619-632. |
| [41] |
Niu Y, Chen G, Peng DL, Song B, Yang Y, Li ZM, Sun H (2014). Grey leaves in an alpine plant: a cryptic colouration to avoid attack? New Phytol 203, 953-963.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Schelbert S, Aubry S, Burla B, Agne B, Kessler F, Krupinska K, Hortensteiner S (2009). Pheophytin pheophorbide hydrolase (pheophytinase) is involved in chlorophyll breakdown during leaf senescence in Arabidop-sis. Plant Cell 21, 767-785.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Sinkkonen A, Somerkoski E, Paaso U, Holopainen JK, Rousi M, Mikola J (2012). Genotypic variation in yellow autumn leaf colours explains aphid load in silver birch. New Phytol 195, 461-469. |
| [44] |
Sun TH, Rao S, Zhou XS, Li L (2022). Plant carotenoids: recent advances and future perspectives. Mol Hortic 2, 3.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Tian YR, Li QQ, Rao SP, Wang AK, Zhang HC, Wang LS, Li Y, Chen JH (2021a). Metabolic profiling and gene ex-pression analysis provides insights into flavonoid and anthocyanin metabolism in poplar. Tree Physiol 41, 1046-1064.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Tian YR, Rao SP, Li QQ, Xu M, Wang AK, Zhang HC, Chen JH (2021b). The coloring mechanism of a novel golden variety in Populus deltoides based on the RGB color mode. Forest Res 1, 5. |
| [47] |
Wang HH, Wang XQ, Song WM, Bao Y, Jin YL, Jiang CM, Wang CT, Li B, Zhang HX (2019). Pdmyb118, isolated from a red leaf mutant of Populus deltoids, is a new tran-scription factor regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in poplar. Plant Cell Rep 38, 927-936.
DOI |
| [48] | Wang LX, Pan DZ, Liang M, Abubakar YS, Li J, Lin JK, Chen SP, Chen W (2017). Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple leaves of Zijuan tea (Camellia sinensis var. kitamura). Int J Mol Sci 18, 833. |
| [49] |
Wang XC, Wu J, Guan ML, Zhao CH, Geng P, Zhao Q (2020a). Arabidopsis MYB4 plays dual roles in flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant J 101, 637-652.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Wang YM, Liu WW, Wang XW, Yang RJ, Wu ZY, Wang H, Wang L, Hu ZB, Guo SY, Zhang HL, Lin JX, Fu CX (2020b). MiR156 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis through SPL targets and other microRNAs in poplar. Hortic Res 7, 118.
DOI |
| [51] | Wu YQ, Guo J, Wang TL, Cao FL, Wang GB (2019). Transcriptional profiling of long noncoding RNAs associated with leaf-color mutation in Ginkgo biloba L. BMC Plant Biol 19, 527. |
| [52] | Wu ZM, Zhang X, He B, Diao LP, Sheng SL, Wang JL, Guo XP, Su N, Wang LF, Jiang L, Wang CM, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2007). A chlorophyll-deficient rice mutant with impaired chlorophyllide esterification in chlorophyll bio-synthesis. Plant Physiol 145, 29-40. |
| [53] |
Yang WZ, Yoon J, Choi H, Fan YL, Chen RM, An G (2015a). Transcriptome analysis of nitrogen-starvation-responsive genes in rice. BMC Plant Biol 15, 31.
DOI URL |
| [54] | Yang YX, Chen XX, Xu B, Li YX, Ma YH, Wang GG (2015b). Phenotype and transcriptome analysis reveals chloroplast development and pigment biosynthesis together influenced the leaf color formation in mutants of Anthurium andraeanum ‘Sonate’. Front Plant Sci 6, 139. |
| [55] |
Yonekura-Sakakibara K, Higashi Y, Nakabayashi R (2019). The origin and evolution of plant flavonoid metabolism. Front Plant Sci 10, 943.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Yu LJ, Sun YY, Zhang X, Chen MC, Wu T, Zhang J, Xing YF, Tian J, Yao YC (2022). ROS1 promotes low tem-perature-induced anthocyanin accumulation in apple by demethylating the promoter of anthocyanin-associated ge- nes. Hortic Res 9, uhac007.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Yudina PK, Ivanova LA, Ronzhina DA, Zolotareva NV, Ivanov LA (2017). Variation of leaf traits and pigment content in three species of steppe plants depending on the climate aridity. Russ J Plant Physiol 64, 410-422
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Zhu XY, Guo S, Wang ZW, Du Q, Xing YD, Zhang TQ, Shen WQ, Sang XC, Ling YH, He GH (2016). Map-based cloning and functional analysis of YGL8, which controls leaf colour in rice (Oryza sativa). BMC Plant Biol 16, 134.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | wei xin, JIANG Lan, Chen-Cheng Zheng, ZHU Jing Jing, Bo Chen, Wen zhou Li, Shu Yv Lai, Jinfu Liu, HE Zhong-Sheng. Distribution and influencing factors of woody plant sexual systems on the altitude gradient of Daiyun Mountain [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(预发表): 0-. |
| [2] | Song Yuanhao, Gong Lü, Li Ben, Hu Yang, Li Xiuzhen. Impacts of different pond-to-wetland restoration methods on macrofauna in the Liao River Estuary, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [3] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [4] | Weiwei Wang, Xiangcheng Mi, Ningning Wang, Haibao Ren, Zhixi Tang, Zhuning Zhang, Keping Ma, Lei Chen. Plant diversity dataset of the 24-ha Zhejiang Gutianshan subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest dynamics plot (2005-2020) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24417-. |
| [5] | WANG Ni, LI Zhao-Na, ZHENG Xu-Li, JIANG Si-Cheng, YANG Hai-Yun. Pigment synthesis and photosynthetic characteristics of leaves in Pseudosasa japonica f. akebonosuji [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(11): 1536-1546. |
| [6] | Yali Zhang, Bingchang Zhang, Kang Zhao, Kaikai Li, Yanjin Liu. Variation of bacterial communities and their driving factors in different types of biological soil crusts in Mu Us sandy land [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23027-. |
| [7] | Xiaofeng Wang, Jiesheng Rao, Tao Yang, Wencong Liu, Xi Tian, Xi Chen, Qiming Liu, Yanxiao Xu, Qiuyu Zhang, Hongqiang Zhang, Xu Zhang, Xiaokun Ou, Zehao Shen. Spatial variation and determinants of woody plant species diversity in a semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [8] | Shaofan Luo, Kai Jiang, Weichang Huang. Advances in the convergent evolution of phenotypes and diversification of developmental mechanisms of floral spurs [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23249-. |
| [9] | Ting Wang, Lizhi Zhou. The spatial-temporal patterns of bird diversity and its determinants in the small wetlands in Hefei City [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21445-. |
| [10] | Wenkai Xue, Huadanshang Meng, Yanhong Wang, Pan Zhu, Ji De, Xiaofang Guo. Relationship between culturable filamentous fungal diversity and environmental factors in Nam Co Lake [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21473-. |
| [11] | Kairu Yang, Qiwei Jia, Jiayi Jin, Hanfei Ye, Sheng Wang, Qianyu Chen, Yian Guan, Chenyang Pan, Dedong Xin, Yuan Fang, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Rice Yellow Green Leaf Regulatory Gene YGL18 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 276-287. |
| [12] | Luyao Wang, Jian Chen, Shouqing Zhao, Huili Yan, Wenxiu Xu, Ruoxi Liu, Mi Ma, Yijun Yu, Zhenyan He. Research Progress of the Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Cadmium Accumulation in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 236-249. |
| [13] | Moxu Wu, Mingtai An, Li Tian, Feng Liu. Effects of environmental factors on quantitative characteristics of woody plant sexual system in Maolan karst forest [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(11): 22025-. |
| [14] | HUANG Jie, LI Xiao-Ling, WANG Xue-Song, YANG Jin, HUANG Cheng-Ming. Characteristics of Distylium chinense communities and their relationships with soil environmental factors in different water level fluctuation zones of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2021, 45(8): 844-859. |
| [15] | Zhenbin Jiao, Yibo Luo. Effects of environmental and genetic factors on phenotypic traits and species classification of Dendrobium huoshanense [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(8): 1073-1086. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||