

植物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (5): 623-634.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22048 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22048
所属专题: 生物安全
收稿日期:2022-03-14
接受日期:2022-06-28
出版日期:2022-09-01
发布日期:2022-09-09
通讯作者:
韩榕
作者简介:*E-mail: hhwrsl@163.com基金资助:
Ye Qing, Yan Xiaoyan, Chen Huize, Feng Jinlin, Han Rong*( )
)
Received:2022-03-14
Accepted:2022-06-28
Online:2022-09-01
Published:2022-09-09
Contact:
Han Rong
About author:*E-mail: hhwrsl@163.com摘要: 石墨烯量子点(GQDs)在电化学生物传感器、生物成像和生物医学等领域具有巨大的应用潜力, 在公众和环境中的暴露程度也越来越高, 近年来其生物安全性备受关注。截至目前, 有关石墨烯量子点对植物生长发育影响的研究较少。该文从细胞和分子水平探究了氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)处理对拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)主根生长方向的影响。结果表明, N-GQDs能够被根摄取, 并通过维管束运输。50-100 mg∙L-1 N-GQDs处理可改变主根的生长方向, 使其朝着远离培养基的方向发生弯曲。研究发现, N-GQDs处理导致根尖小柱细胞中淀粉粒的积累减少, 生长素外排载体PIN3的表达量降低, 小柱细胞中的PIN3重新定位到远离培养基一侧的细胞外侧膜(即朝向空气), 促进根尖生长素的不对称分布, 从而引发主根朝着远离培养基的方向弯曲生长, 以避开较高浓度的N-GQDs环境。研究结果为进一步阐明N-GQDs处理改变根生长方向的机制提供了重要线索, 同时也为N-GQDs的生物安全性评价提供参考依据。
叶青, 闫晓燕, 陈慧泽, 冯金林, 韩榕. 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点对拟南芥主根生长方向的影响. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 623-634.
Ye Qing, Yan Xiaoyan, Chen Huize, Feng Jinlin, Han Rong. Effect of Nitrogen-doped Graphene Quantum Dots on Growth Direction of Primary Root in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 623-634.
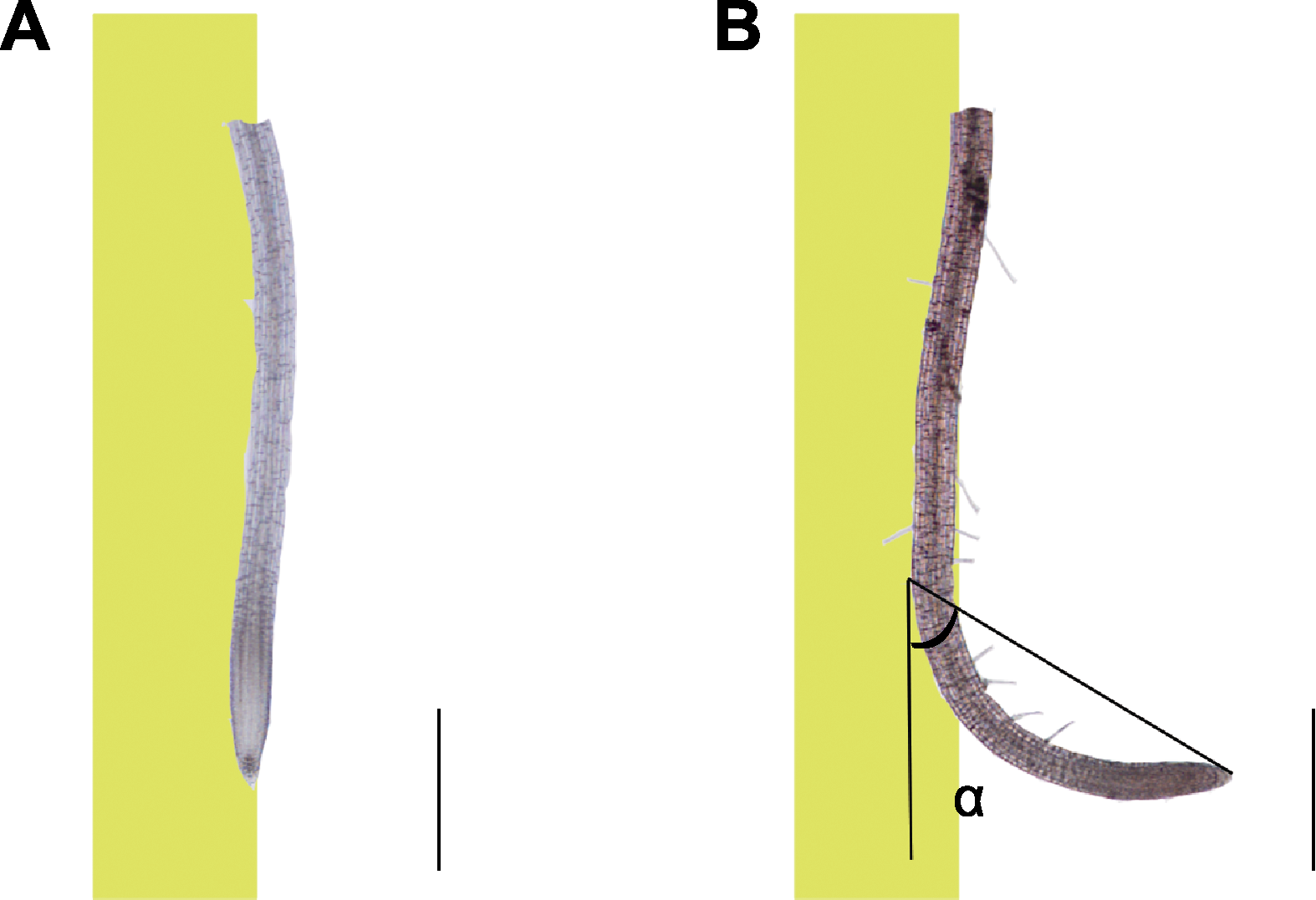
图1 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)处理后拟南芥主根根尖弯曲角度的测量方法 (A) 1/4MS培养基上垂直培养的5日龄拟南芥幼苗主根; (B) 将(A)中的幼苗转移至添加50 mg·L-1 N-GQDs的1/4MS培养基上垂直培养3天, 根沿着远离培养基的方向发生弯曲, 测定主根弯曲角度, 即根的生长方向与重力方向之间的弯曲夹角α。图中左侧的黄色部分表示垂直放置的培养基一侧, 右侧白色部分表示远离培养基的空气一侧。Bars=500 μm
Figure 1 Measurement method for bending angle of Arabidopsis primary root tip after nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) treatment (A) Primary roots of 5-day-old Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings vertically cultured on 1/4MS medium; (B) The seedlings in (A) were transferred to 1/4MS medium containing 50 mg·L-1 N-GQDs, they were cultured vertically for 3 d, the roots were bent towards the direction distant from the medium. The bending angle α of primary roots between root growth direction and gravity direction was determined. The yellow part at the left side in figure meant the seedlings were perpendicularly placed at one side of the medium, and the white part at the right side denoted that the seedlings were placed at the air side distant from the medium. Bars=500 μm
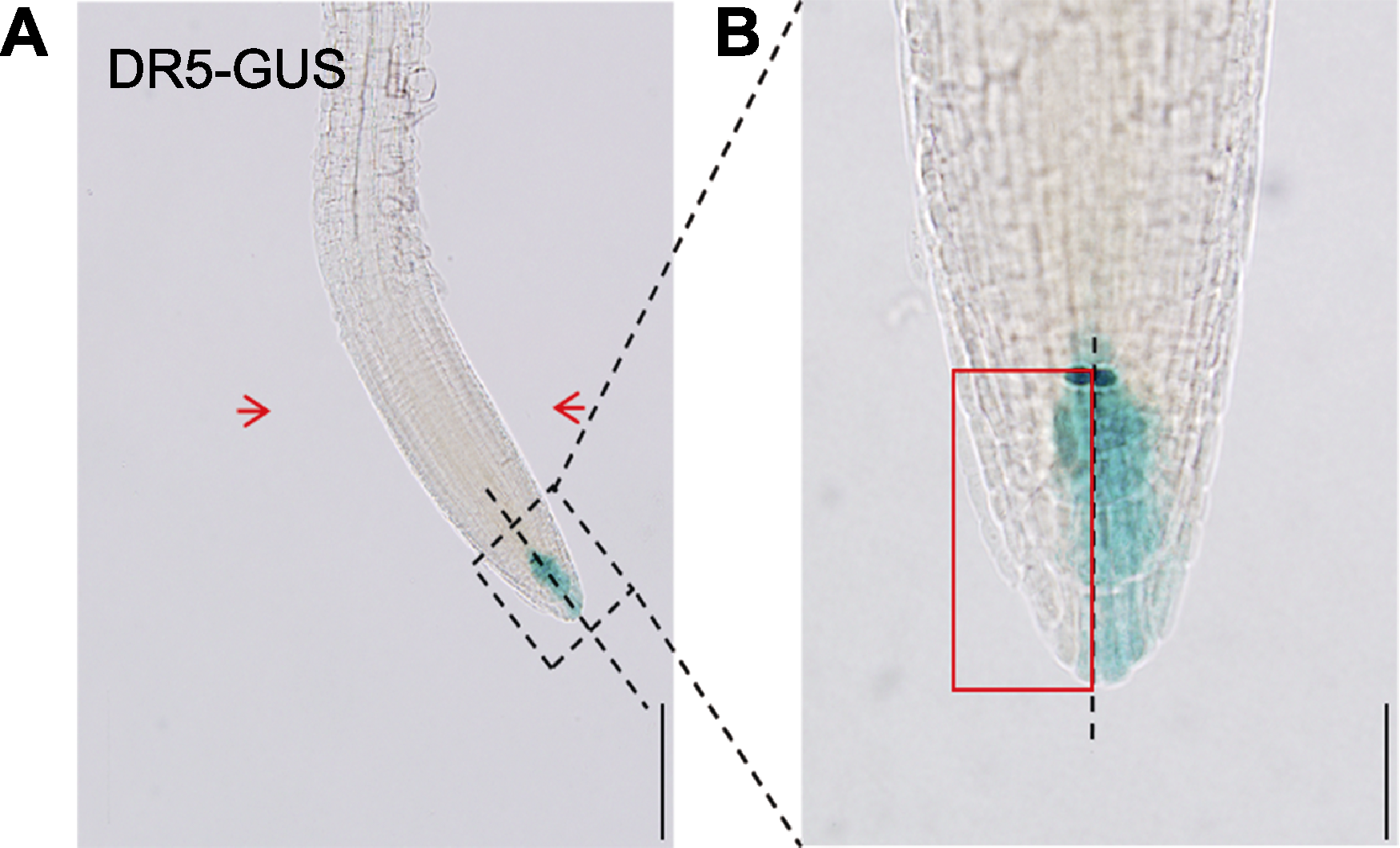
图2 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)处理后拟南芥主根根尖两侧GUS活性的测量方法 (A) 用含50 mg·L-1 N-GQDs的1/4MS培养基垂直培养5日龄拟南芥DR5-GUS株系3天, 根沿着远离培养基的方向发生弯曲, 测定主根根尖左右两侧(靠近培养基一侧/远离培养基一侧)的GUS活性, 其中左侧的红色箭头表示靠近培养基一侧, 右侧的红色箭头表示远离培养基一侧(bar=200 μm); (B) DR5-GUS株系主根根尖左右两侧GUS活性的测量方法, 图中红色方框所选区域即为测定左侧区域(bar=50 μm)。
Figure 2 Measurement method of GUS activity at two sides of Arabidopsis thaliana primary root tip after nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) treatment (A) After 5-day-old Arabidopsis thaliana DR5-GUS plant was perpendicularly cultured in 1/4MS medium containing 50 mg·L-1 N-GQDs for 3 d, the root was bent towards a direction distant from the medium, and the GUS activity value at the left and right sides (close to the culture medium/distant from the medium) of primary root tips were determined, the red arrow at the left side represents the side close to the medium and that at the right side denotes the side distant from the medium (bar=200 μm); (B) Measurement method of GUS activity at the left and right sides of primary root tip of DR5-GUS plant, the red box in the figure was the determined left region (bar=50 μm).

图3 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)的表征 (A) N-GQDs的透射电子显微镜图, 红色箭头示N-GQDs (bar=20 nm); (B) N-GQDs的粒径分布; (C) N-GQDs的PL光谱
Figure 3 The characterization of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) (A) Transmission electron microscope graph of N-GQDs, the red arrows represent N-GQDs (bar=20 nm); (B) Particle size distribution diagram of N-GQDs; (C) Photoluminescence (PL) spectrogram of N-GQDs
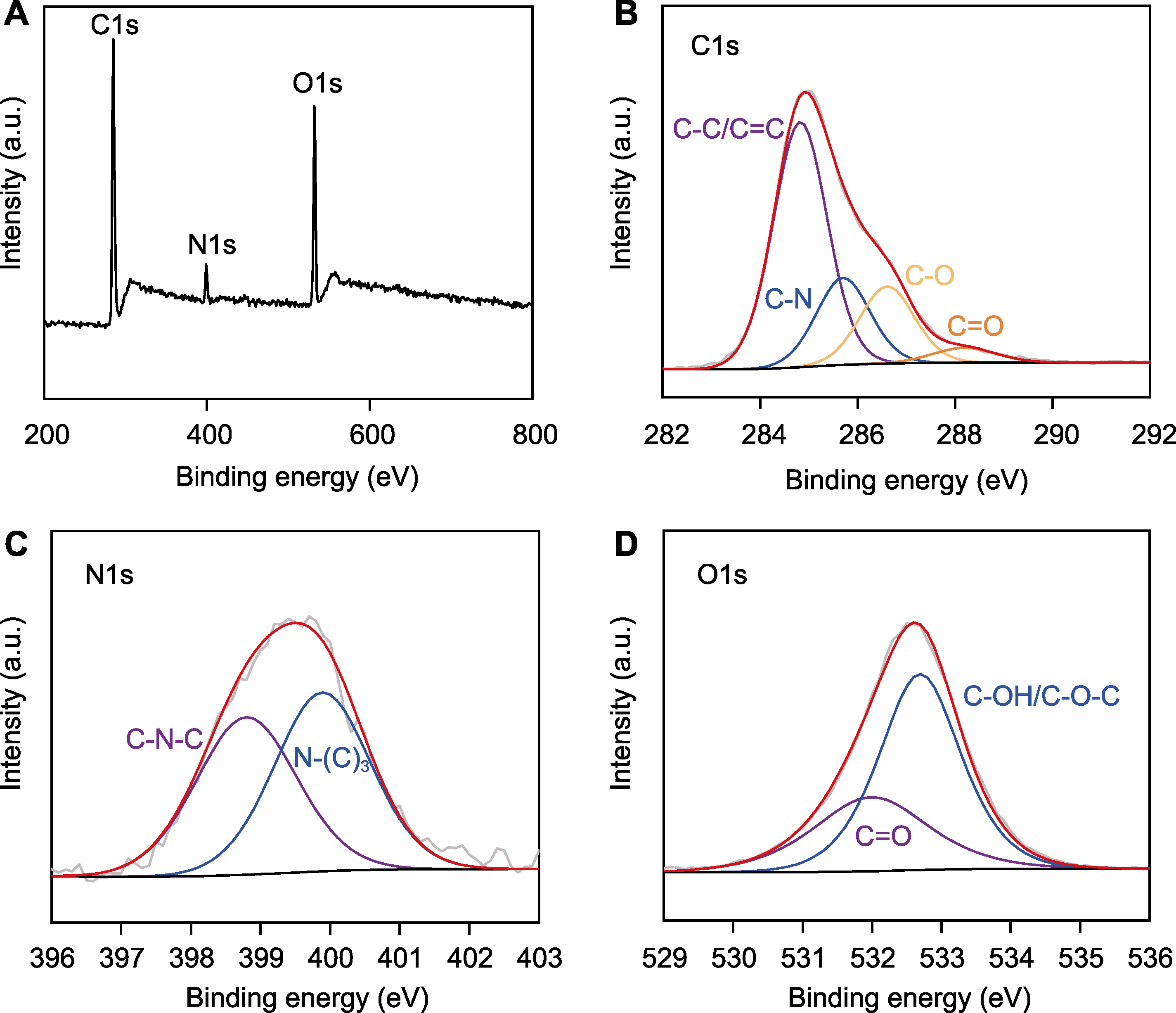
图4 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)的X射线光电子能谱(XPS) (A) N-GQDs的全扫描XPS图谱; (B) 高分辨率C1s光谱; (C) N1s光谱; (D) O1s光谱
Figure 4 X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectrum of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) (A) Full-scan XPS spectrum of N-GQDs; (B) High resolution C1s spectrum; (C) N1s spectrum; (D) O1s spectrum
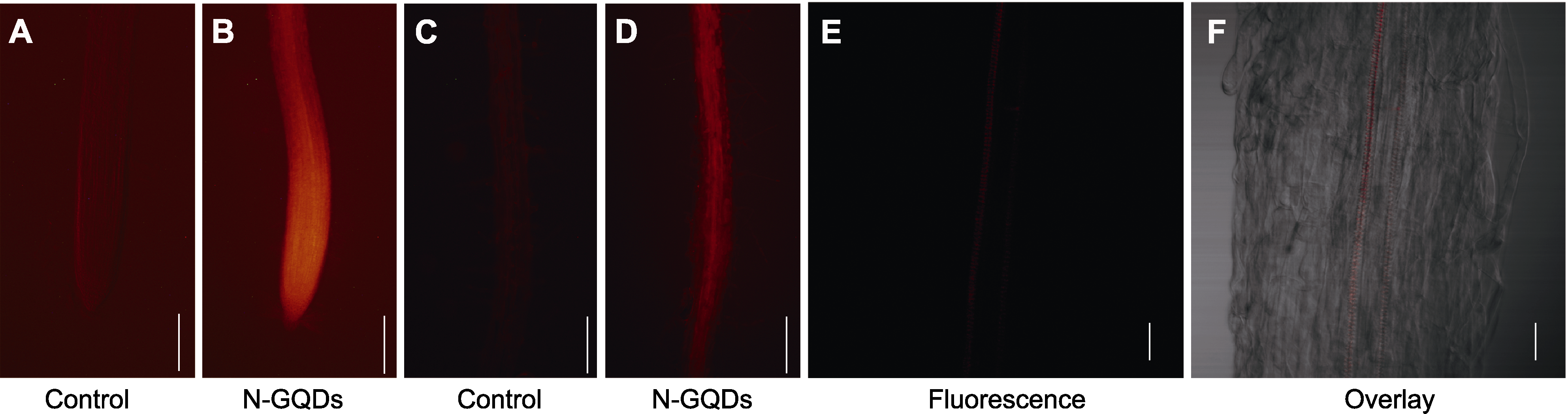
图5 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)在拟南芥幼苗主根中的分布 (A), (C) 未经N-GQDs处理的拟南芥幼苗主根分生区和伸长区(A)及根毛区(C)的荧光显微镜图像(bars=200 μm); (B), (D) N-GQDs处理3天后主根分生区和伸长区(B)及根毛区(D)的荧光显微镜图像(bars=200 μm), N-GQDs在荧光显微镜下呈现红光; (E), (F) N-GQDs处理3天后根毛区维管束的激光共聚焦显微镜图像(bars=30 μm)
Figure 5 Distribution of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) in primary roots of Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings (A), (C) Fluorescence micro images of meristem zone and elongation zone (A), and root hair zone (C) of primary roots in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings untreated with N-GQDs (bars=200 μm); (B), (D) Fluorescence micro images of meristem zone and elongation zone (B), and root hair zone (D) of primary roots under N-GQDs treatment for 3 days (bars=200 μm), the N-GQDs presented red fluorescence under a fluorescence microscope; (E), (F) Confocal images of vascular bundles in the root hair zone under N-GQDs treatment for 3 days (bars=30 μm)
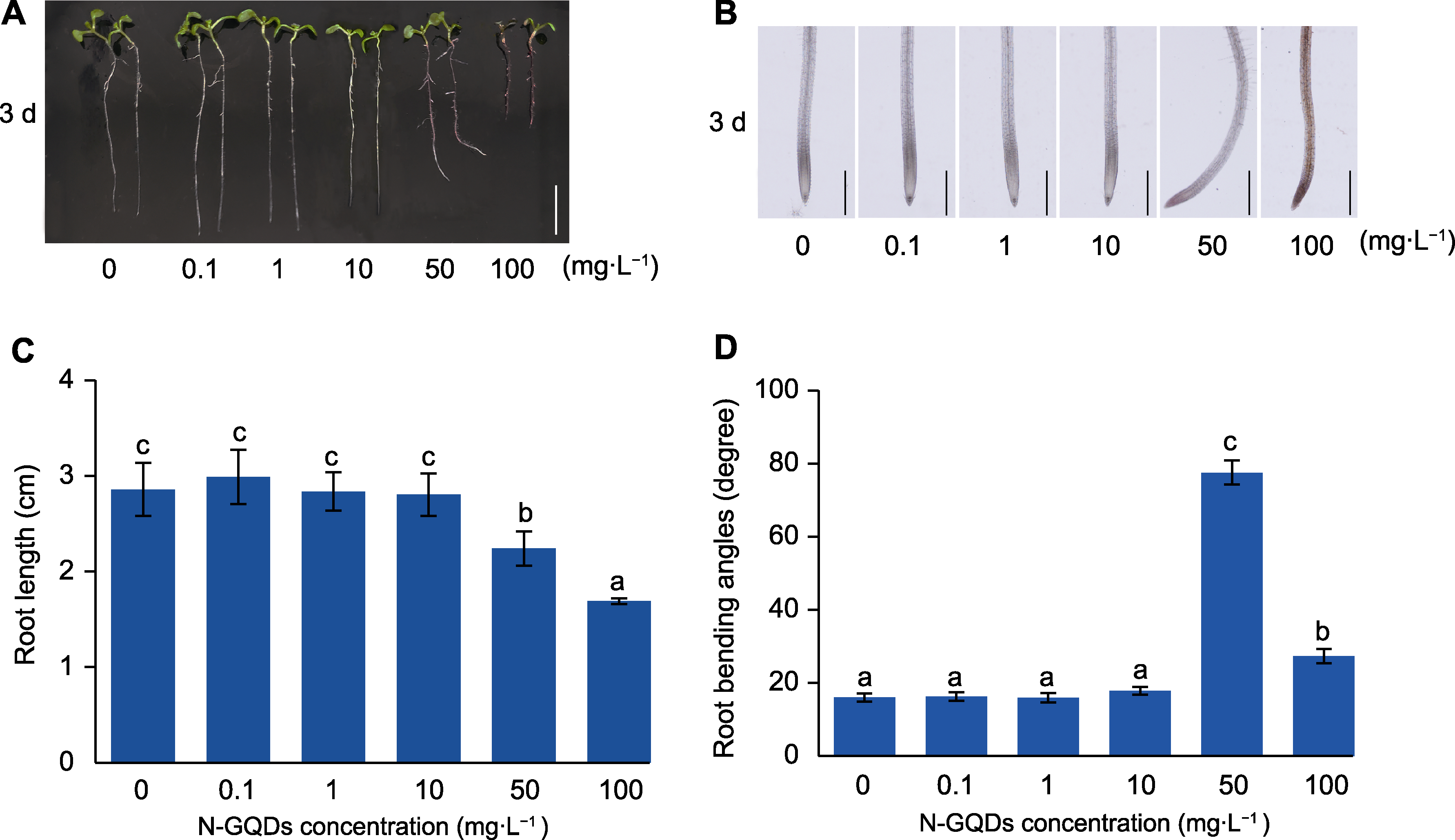
图6 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)处理影响拟南芥幼苗主根的生长方向 (A) 不同浓度N-GQDs处理3天后拟南芥主根表型(bar=1 cm); (B) 光学显微镜下观察主根的生长方向(bars=500 μm); (C) 主根长度统计; (D) 主根弯曲角度统计。数据为3次重复的平均值±标准差(n=30)。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 6 Effects of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) on growth direction of primary root of Arabidopsis thaliana (A) Primary root phenotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana under different concentrations of N-GQDs for 3 days (bar=1 cm); (B) The growth direction of primary roots under optical microscope (bars=500 μm); (C) Statistical analysis of primary roots length; (D) Statistical analysis of primary roots bending angles. The values are presented as means±SD of triplicate samples (n=30). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences (P<0.05).
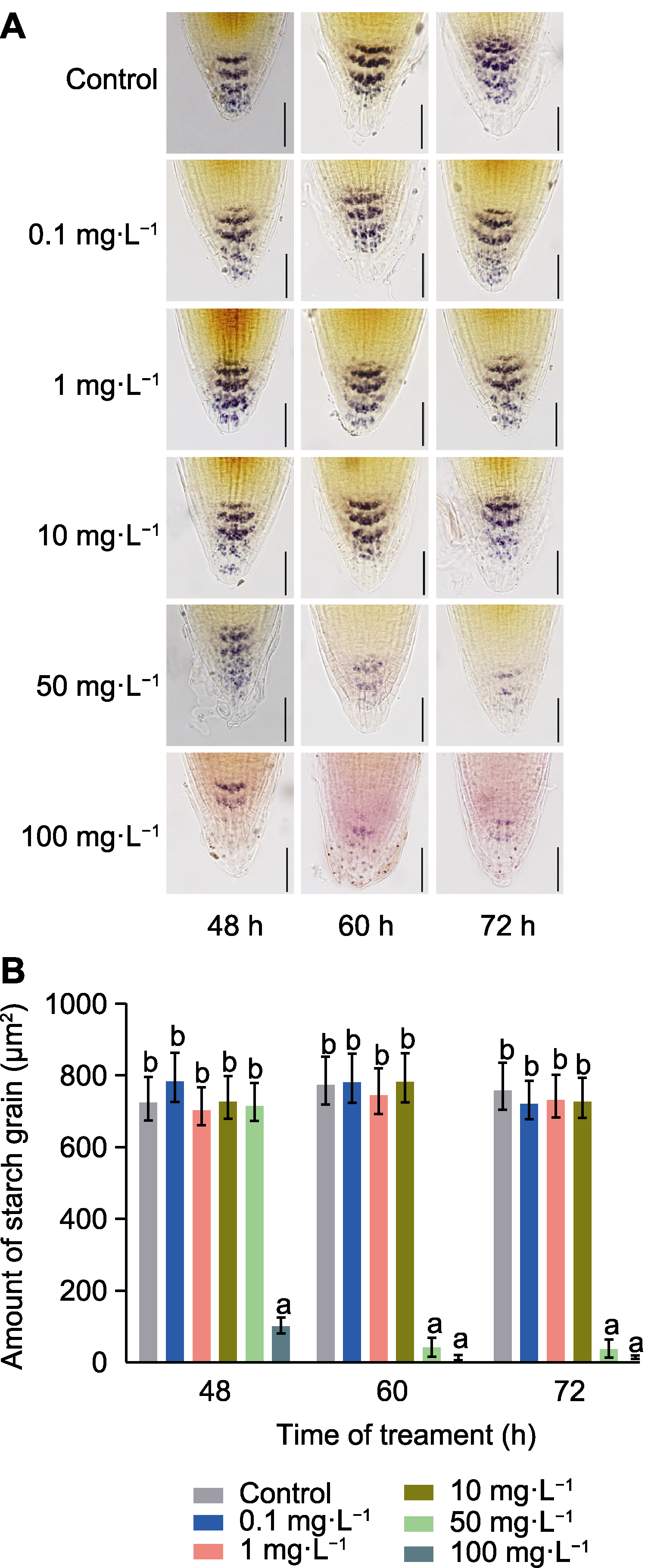
图7 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)降低拟南芥主根根尖淀粉粒的积累 (A) 不同浓度N-GQDs处理不同时间后染色观察拟南芥主根根尖淀粉粒含量变化(bars=50 μm); (B) 根尖淀粉粒含量统计分析。数据为3次重复的平均值±标准差(n=15)。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 7 Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) reduce the accumulation of starch grains in Arabidopsis thaliana primary root tips (A) Changes of starch grains content in A. thaliana primary root tips by staining with different concentrations of N-GQDs treatment for different time (bars=50 μm); (B) Statistical analysis of starch grains amount in primary root tips. The values are presented as means±SD of triplicate samples (n=15). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences (P<0.05).

图8 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)干扰拟南芥根尖生长素的分布 (A) N-GQDs处理不同时间后染色观察主根两侧GUS活性, 左侧的红色箭头均表示靠近培养基一侧(bars=50 μm); (B) 主根左右两侧GUS活性比值统计分析; 左侧对应于(A)中靠近培养基的一侧, 右侧对应于(A)中远离培养基的一侧。数据为3次重复的平均值±标准差(n=15)。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 8 Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) disrupt the auxin distribution in Arabidopsis thaliana root tips (A) The GUS activity on both sides of the primary roots were observed by staining after N-GQDs treatment for different time, the red arrow at the left side represents the side close to the culture medium (bars=50 μm); (B) Statistical analysis of GUS activity ratio at the left and right sides of primary roots; the left side corresponds to one side in (A) close to the culture medium while the right side corresponds to the side in (A) distant from the culture medium. The values are presented as means±SD of triplicate samples (n=15). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences (P<0.05).
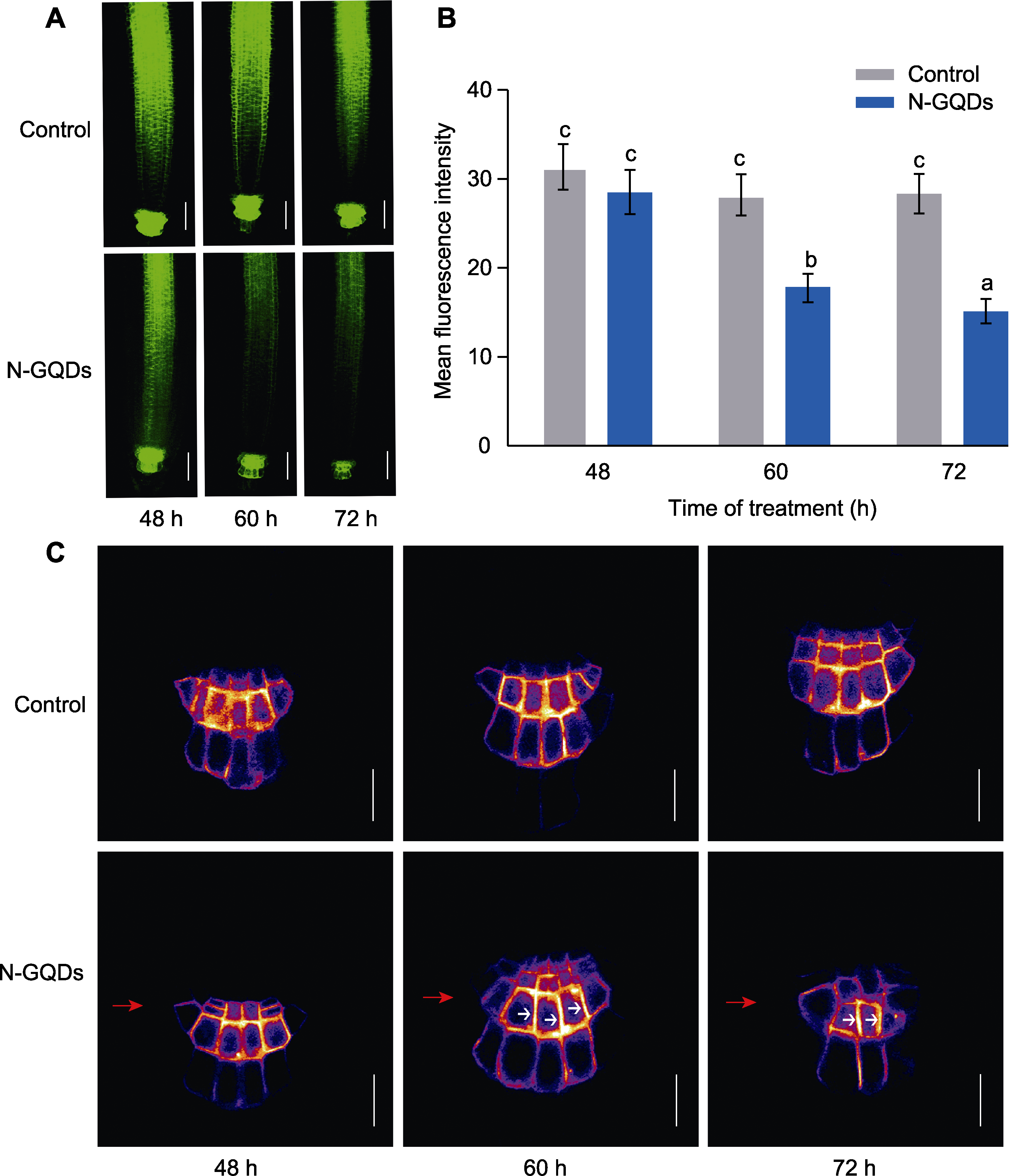
图9 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点(N-GQDs)干扰拟南芥主根PIN3的丰度和分布 (A) N-GQDs处理不同时间后主根中PIN3-GFP的荧光信号(bars=50 μm); (B) 主根中PIN3-GFP荧光强度定量分析; (C) 小柱细胞中PIN3的分布(bars=20 μm)。图中红色箭头表示靠近培养基一侧。白色箭头表示PIN3的偏振方向。数据为3次重复的平均值±标准差(n=15)。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 9 Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) disrupt the abundance and distribution of PIN3 in Arabidopsis thaliana primary roots (A) GFP fluorescence of PIN3-GFP in the primary roots after N-GQDs treatment for different time (bars=50 μm); (B) Quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity of PIN3-GFP in the primary roots; (C) Distribution of PIN3 in columnar cells (bars=20 μm). The red arrows represent the side close to the culture medium. The white arrows in the columnar cells indicate the polarization directions of PIN3. The values are presented as means±SD of triplicate samples (n=15). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences (P<0.05).
| [1] | 高坤, 常金科, 黎家 (2018). 植物根向水性反应研究进展. 植物学报 53, 154-163. |
| [2] | 韩雯, 韩榕 (2015). 不同时间的UV-B辐射对拟南芥幼苗生长的影响. 植物学报 50, 40-46. |
| [3] | 李晓阳, 陈慧泽, 韩榕 (2013). UV-B辐射对拟南芥种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 植物学报 48, 52-58. |
| [4] | Baldwin KL, Strohm AK, Masson PH (2013). Gravity sensing and signal transduction in vascular plant primary roots. Am J Bot 100, 126-142. |
| [5] | Band LR, Wells DM, Larrieu A, Sun JY, Middleton AM, French AP, Brunoud G, Sato EM, Wilson MH, Péret B, Oliva M, Swarup R, Sairanen I, Parry G, Ljung K, Beeckman T, Garibaldi JM, Estelle M, Owen MR, Vissenberg K, Hodgman TC, Pridmore TP, King JR, Vernoux T, Bennett MJ (2012). Root gravitropism is regulated by a transient lateral auxin gradient controlled by a tipping-point mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 4668-4673. |
| [6] | Blancaflor EB, Fasano JM, Gilroy S (1998). Mapping the functional roles of cap cells in the response of Arabidopsis primary roots to gravity. Plant Physiol 116, 213-222. |
| [7] | Brunoud G, Wells DM, Oliva M, Larrieu A, Mirabet V, Burrow AH, Beeckman T, Kepinski S, Traas J, Bennett MJ, Vernoux T (2012). A novel sensor to map auxin response and distribution at high spatio-temporal resolution. Nature 482, 103-106. |
| [8] | Caspar T, Pickard BG (1989). Gravitropism in a starchless mutant of Arabidopsis: implications for the starch-statolith theory of gravity sensing. Planta 177, 185-197. |
| [9] | Chakravarty D, Erande MB, Late DJ (2015). Graphene quantum dots as enhanced plant growth regulators: effects on coriander and garlic plants. J Sci Food Agric 95, 2772-2778. |
| [10] | Deng S, Jia PP, Zhang JH, Junaid M, Niu AP, Ma YB, Fu AL, Pei DS (2018). Transcriptomic response and perturbation of toxicity pathways in zebrafish larvae after exposure to graphene quantum dots (GQDs). J Hazard Mater 357, 146-158. |
| [11] | Ding Y, Cheng HH, Zhou C, Fan YQ, Zhu J, Shao HB, Qu LT (2012). Functional microspheres of graphene quantum dots. Nanotechnology 23, 255605. |
| [12] | Feng P, Geng BJ, Cheng Z, Liao XY, Pan DY, Huang JY (2019). Graphene quantum dots-induced physiological and biochemical responses in mung bean and tomato seedlings. Braz J Bot 42, 29-41. |
| [13] | Friml J, Wiśniewska J, Benková E, Mendgen K, Palme K (2002). Lateral relocation of auxin efflux regulator PIN3 mediates tropism in Arabidopsis. Nature 415, 806-809. |
| [14] | Galvan-Ampudia CS, Julkowska MM, Darwish E, Gandullo J, Korver RA, Brunoud G, Haring MA, Munnik T, Vernoux T, Testerink C (2013). Halotropism is a response of plant roots to avoid a saline environment. Curr Biol 23, 2044-2050. |
| [15] | Galvan-Ampudia CS, Testerink C (2011). Salt stress signals shape the plant root. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14, 296-302. |
| [16] | Grunewald W, Friml J (2010). The march of the PINs: developmental plasticity by dynamic polar targeting in plant cells. EMBO J 29, 2700-2714. |
| [17] | Guo XQ, Mei N (2014). Assessment of the toxic potential of graphene family nanomaterials. J Food Drug Anal 22, 105-115. |
| [18] | Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Alam M, Roychowdhury R, Fujita M (2013). Physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms of heat stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 14, 9643-9684. |
| [19] | Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000). Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51, 463-499. |
| [20] | Hu XG, Zhou QX (2013). Health and ecosystem risks of graphene. Chem Rev 113, 3815-3835. |
| [21] | Ju J, Chen W (2014). Synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for sensitive, label- free detection of Fe (III) in aqueous media. Biosens Bioelectron 58, 219-225. |
| [22] | Kleine-Vehn J, Ding ZJ, Jones AR, Tasaka M, Morita MT, Friml J (2010). Gravity-induced PIN transcytosis for polarization of auxin fluxes in gravity-sensing root cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 22344-22349. |
| [23] | Kong Z, Hu W, Jiao FF, Zhang PZ, Shen JW, Cui B, Wang HB, Liang LJ (2020). Theoretical evaluation of DNA genotoxicity of graphene quantum dots: a combination of density functional theory and molecular dynamics simulations. J Phys Chem B 124, 9335-9342. |
| [24] | Ku TT, Hao F, Yang XX, Rao ZY, Liu QS, Sang N, Faiola F, Zhou QF, Jiang GB (2021). Graphene quantum dots disrupt embryonic stem cell differentiation by interfering with the methylation level of Sox2. Environ Sci Technol 55, 3144-3155. |
| [25] | Leitz G, Kang BH, Schoenwaelder ME, Staehelin LA (2009). Statolith sedimentation kinetics and force transduction to the cortical endoplasmic reticulum in gravity- sensing Arabidopsis columella cells. Plant Cell 21, 843-860. |
| [26] | Li XL, Zhou ZH, Lu DJ, Dong XW, Xu MH, Wei LM, Zhang YF (2014). The effect of pristine carbon-based nanomaterial on the growth of green gram sprouts and pH of water. Nanoscale Res Lett 9, 583. |
| [27] | Li Y, Yuan W, Li LC, Miao R, Dai H, Zhang JH, Xu WF (2020). Light-dark modulates root hydrotropism associated with gravitropism by involving amyloplast response in Arabidopsis. Cell Rep 32, 108198. |
| [28] | Li Y, Zhao Y, Cheng HH, Hu Y, Shi GQ, Dai LM, Qu LT (2012). Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots with oxygen-rich functional groups. J Am Chem Soc 134, 15-18. |
| [29] | Lin YH, Zhuang SX, Wang YL, Lin S, Hong ZW, Liu Y, Xu L, Li FP, Xu BH, Chen MH, He SW, Liao BQ, Fu XP, Jiang ZQ, Wang HL (2019). The effects of graphene quantum dots on the maturation of mouse oocytes and development of offspring. J Cell Physiol 234, 13820-13831. |
| [30] | Morita MT, Tasaka M (2004). Gravity sensing and signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7, 712-718. |
| [31] | Nan WB, Wang XM, Yang L, Hu YF, Wei YT, Liang XL, Mao LN, Bi YR (2014). Cyclic GMP is involved in auxin signaling during Arabidopsis root growth and development. J Exp Bot 65, 1571-1583. |
| [32] | Ottenschläger I, Wolff P, Wolverton C, Bhalerao RP, Sandberg G, Ishikawa H, Evans M, Palme K (2003). Gravity-regulated differential auxin transport from columella to lateral root cap cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 2987-2991. |
| [33] | Su SH, Gibbs NM, Jancewicz AL, Masson PH (2017). Molecular mechanisms of root gravitropism. Curr Biol 27, R964-R972. |
| [34] | Sun HF, Wang M, Wang J, Wang WP (2022). Surface charge affects foliar uptake, transport and physiological effects of functionalized graphene quantum dots in plants. Sci Total Environ 812, 151506. |
| [35] | Swarup R, Kramer EM, Perry P, Knox K, Leyser HMO, Haseloff J, Beemster GTS, Bhalerao R, Bennett MJ (2005). Root gravitropism requires lateral root cap and epidermal cells for transport and response to a mobile auxin signal. Nat Cell Biol 7, 1057-1065. |
| [36] | Tsugeki R, Fedoroff NV (1999). Genetic ablation of root cap cells in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96, 12941-12946. |
| [37] | Ulmasov T, Murfett J, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (1997). Aux/IAA proteins repress expression of reporter genes containing natural and highly active synthetic auxin response elements. Plant Cell 9, 1963-1971. |
| [38] | Wang D, Zhu L, Chen JF, Dai LM (2015a). Can graphene quantum dots cause DNA damage in cells? Nanoscale 7, 9894-9901. |
| [39] | Wang ZG, Zhou R, Jiang D, Song JE, Xu Q, Si J, Chen YP, Zhou X, Gan L, Li JZ, Zhang H, Liu B (2015b). Toxicity of graphene quantum dots in zebrafish embryo. Biomed Environ Sci 28, 341-351. |
| [40] | Wen J, Xu YQ, Li HJ, Lu AP, Sun SG (2015). Recent applications of carbon nanomaterials in fluorescence biosensing and bioimaging. Chem Commun 51, 11346-11358. |
| [41] | Wiśniewska J, Xu J, Seifertová D, Brewer PB, Růžička K, Blilou I, Rouquié D, Benková E, Scheres B, Friml J (2006). Polar PIN localization directs auxin flow in plants. Science 312, 883. |
| [42] | Zheng XT, Ananthanarayanan A, Luo KQ, Chen P (2015). Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 11, 1620-1636. |
| [43] | Zhu JK (2016). Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 167, 313-324. |
| [1] | 周玉滢, 陈辉, 刘斯穆. 植物非典型Aux/IAA蛋白应答生长素研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [2] | 吴晨, 陈心怡, 刘源豪, 黄锦学, 熊德成. 增温对森林细根生长、死亡及周转特征影响的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(8): 1043-1054. |
| [3] | 吴帆, 吴晨, 张宇辉, 余恒, 魏智华, 郑蔚, 刘小飞, 陈仕东, 杨智杰, 熊德成. 增温对成熟杉木人工林不同季节细根生长、形态及生理代谢特征的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(6): 856-866. |
| [4] | 孔祥培, 张蒙悦, 丁兆军. 柳暗花明:胞外生长素信号感受的新突破[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 861-865. |
| [5] | 园园, 恩和巴雅尔, 齐艳华. 植物GH3基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 770-782. |
| [6] | 周淑瑶, 李建明, 毛娟. AtGH3.17调控拟南芥生长素和油菜素甾醇的响应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 373-384. |
| [7] | 李彬琪, 闫佳慧, 李豪, 辛伟, 田云鹤, 杨贞标, 唐文鑫. 黄瓜卷须缠绕过程中小G蛋白活性变化[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 299-307. |
| [8] | 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [9] | 王静文, 王兴军, 马长乐, 李膨呈. 植物核糖体应激响应机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 80-89. |
| [10] | 李艳艳, 齐艳华. 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [11] | 林雨晴, 齐艳华. 生长素输出载体PIN家族研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 151-165. |
| [12] | 黄荣峰, 徐通达. 生长素通过MAPK介导的超长链脂肪酸合成调控侧根发育[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 6-9. |
| [13] | 姚玉婷,马家琦,冯晓莉,潘建伟,王超. 磷酸肌醇激酶FAB1调控拟南芥根毛伸长[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 126-136. |
| [14] | 贺祯媚,李东明,齐艳华. 植物ABCB亚家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 688-698. |
| [15] | 张淑辉,王红,王文茹,吴雪莲,肖元松,彭福田. 蔗糖对桃幼苗生长发育及其SnRK1酶活性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 744-752. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||