

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 652-661.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19089 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19089
苗青霞1,2,3,方燕1,2,*( ),陈应龙1,2,4,*(
),陈应龙1,2,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-05-14
接受日期:2019-07-26
出版日期:2019-09-01
发布日期:2020-03-10
通讯作者:
方燕,陈应龙
基金资助:
Qingxia Miao1,2,3,Yan Fang1,2,*( ),Yinglong Chen1,2,4,*(
),Yinglong Chen1,2,4,*( )
)
Received:2019-05-14
Accepted:2019-07-26
Online:2019-09-01
Published:2020-03-10
Contact:
Yan Fang,Yinglong Chen
摘要: 干旱胁迫时, 小麦(Triticum aestivum)根系率先产生应激响应, 同时向地上部发出信号, 诱导地上部发生生理反应, 从而提高植株抗旱能力。根系构型包括平面几何性状和立体几何结构(即拓扑构型), 具有遗传稳定性和可塑性。干旱胁迫影响根系理化特性, 如根源化学信号、根系细胞酶类和根系渗透作用的响应。根系通过调整其解剖学结构和水分吸收动力等来适应干旱胁迫。该文从根系构型、理化特性和解剖学结构3个方面, 系统阐述了小麦根系特征对干旱胁迫的响应, 并探讨了其与干旱胁迫的关系和当前研究中存在的问题, 以期为相关研究提供参考。
苗青霞,方燕,陈应龙. 小麦根系特征对干旱胁迫的响应. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 652-661.
Qingxia Miao,Yan Fang,Yinglong Chen. Studies in the Responses of Wheat Root Traits to Drought Stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(5): 652-661.
| 根系构型指标 | 干旱胁迫下的响应 | 原因 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 二维 | |||
| 根长 | 轻度干旱下增加, 重度干旱下减少 | 轻度干旱下根系伸长利用深层水, 重度干旱下根系生长受到抑制 | Barraclough et al., 1989; Siopongco et al., 2005 |
| 根数 | 减少 | 受到干旱胁迫抑制 | 马富举等, 2012; Vandoorne et al., 2012 |
| 根系表面积 | 减少 | 受到干旱胁迫抑制 | 马富举等, 2012; Vandoorne et al., 2012 |
| 根系生物量 | 轻度干旱下增加, 重度干旱下减少 | 轻度干旱下增加有利于维持根系吸水能力 | Kano et al., 2011; 马富举等, 2012 |
| 根长密度 | 表层减少, 深层增加 | 增加对深层储蓄水的利用 | Barraclough et al., 1989; Uga et al., 2011; Wasson et al., 2012; Becker et al., 2016; Fang et al., 2017 |
| 根毛 | 增加 | 增加根系与土壤接触面积, 减少水分吸收阻力 | Passioura, 1991; Segal et al., 2008; White and Kirkegaard, 2010 |
| 三维 | |||
| 根系拓扑构型 | 由叉状向鱼尾形发展 | 鱼尾形结构根系下扎较深, 分支结构可有效利用水分 | 谈峰等, 2011; 单立山等, 2012 |
表1 根系构型对干旱胁迫的响应
Table 1 Responses of root system architecture to drought stress
| 根系构型指标 | 干旱胁迫下的响应 | 原因 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 二维 | |||
| 根长 | 轻度干旱下增加, 重度干旱下减少 | 轻度干旱下根系伸长利用深层水, 重度干旱下根系生长受到抑制 | Barraclough et al., 1989; Siopongco et al., 2005 |
| 根数 | 减少 | 受到干旱胁迫抑制 | 马富举等, 2012; Vandoorne et al., 2012 |
| 根系表面积 | 减少 | 受到干旱胁迫抑制 | 马富举等, 2012; Vandoorne et al., 2012 |
| 根系生物量 | 轻度干旱下增加, 重度干旱下减少 | 轻度干旱下增加有利于维持根系吸水能力 | Kano et al., 2011; 马富举等, 2012 |
| 根长密度 | 表层减少, 深层增加 | 增加对深层储蓄水的利用 | Barraclough et al., 1989; Uga et al., 2011; Wasson et al., 2012; Becker et al., 2016; Fang et al., 2017 |
| 根毛 | 增加 | 增加根系与土壤接触面积, 减少水分吸收阻力 | Passioura, 1991; Segal et al., 2008; White and Kirkegaard, 2010 |
| 三维 | |||
| 根系拓扑构型 | 由叉状向鱼尾形发展 | 鱼尾形结构根系下扎较深, 分支结构可有效利用水分 | 谈峰等, 2011; 单立山等, 2012 |
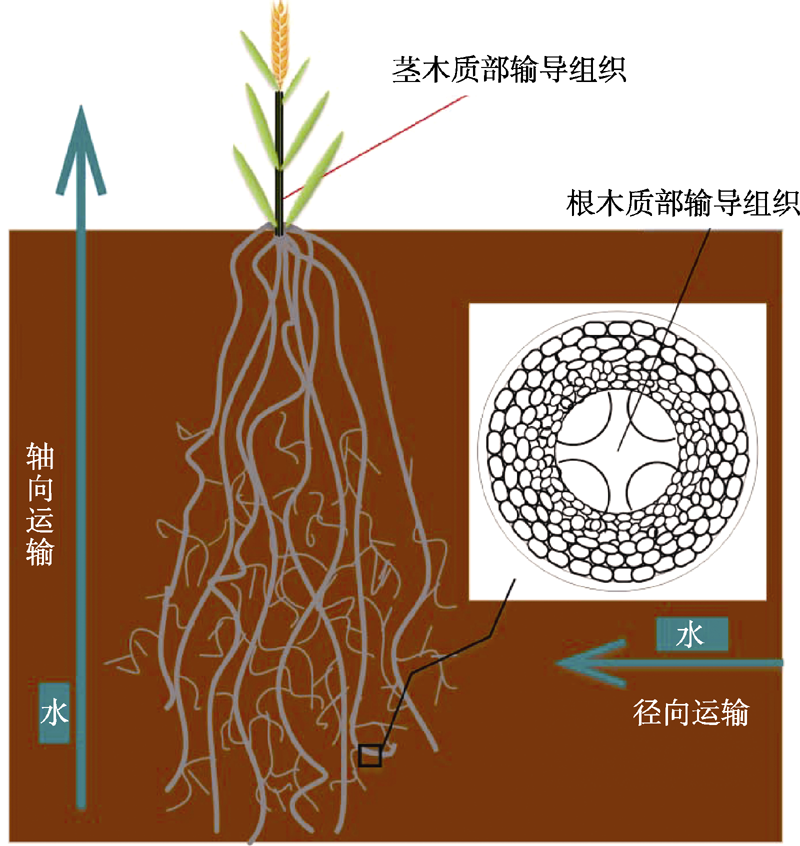
图2 小麦根系解剖结构及其水分运输途径示意图(Wasson et al., 2012)
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of wheat root anatomy and its water transport pathway (modified from Wasson et al., 2012)
| 根源化学信号 | 干旱胁迫下响应 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 脱落酸 | 干旱条件下增加, 传递根源信号和控制气孔导度, 减弱蒸腾作用 | Tardieu et al., 1992; Saradadevi et al., 2015; 马超等, 2017; 谢静静等, 2018 |
| 生长素 | 干旱条件下降低, IAA/ CTK降低, 与脱落酸呈拮抗作用 | Eckert and Kaldenh- off, 2000; Xu et al., 2013; Han et al., 2015 |
| 细胞分裂素(玉米素, 玉 米素核苷) | 干旱条件下降低, 与生长素呈拮抗作用 | Dodd, 2003; Kudoyarova et al., 2007; Han et al., 2015 |
| 木质部pH值 | 干旱条件下增加, 与脱落酸共同作用引起气孔关闭 | Gollan et al., 1992 |
| 钙离子 | 干旱胁迫下脱落酸诱导气孔关闭过程中的第二信使 | Parcy and Giraudat, 1997; Snedden and Fromm, 2001; Bothwell and Ng, 2005; Case et al., 2007 |
表2 干旱胁迫下根源化学信号的响应
Table 2 Responses of root-source chemical signals to drought stress
| 根源化学信号 | 干旱胁迫下响应 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 脱落酸 | 干旱条件下增加, 传递根源信号和控制气孔导度, 减弱蒸腾作用 | Tardieu et al., 1992; Saradadevi et al., 2015; 马超等, 2017; 谢静静等, 2018 |
| 生长素 | 干旱条件下降低, IAA/ CTK降低, 与脱落酸呈拮抗作用 | Eckert and Kaldenh- off, 2000; Xu et al., 2013; Han et al., 2015 |
| 细胞分裂素(玉米素, 玉 米素核苷) | 干旱条件下降低, 与生长素呈拮抗作用 | Dodd, 2003; Kudoyarova et al., 2007; Han et al., 2015 |
| 木质部pH值 | 干旱条件下增加, 与脱落酸共同作用引起气孔关闭 | Gollan et al., 1992 |
| 钙离子 | 干旱胁迫下脱落酸诱导气孔关闭过程中的第二信使 | Parcy and Giraudat, 1997; Snedden and Fromm, 2001; Bothwell and Ng, 2005; Case et al., 2007 |
| 1 | 蔡昆争, 吴学祝, 骆世明 (2008). 不同生育期水分胁迫对水稻根叶渗透调节物质变化的影响. 植物生态学报 32, 491-500. |
| 2 | 陈伟立, 李娟, 朱红慧, 陈杰忠, 姚青 (2016). 根际微生物调控植物根系构型研究进展. 生态学报 36, 5285-5297. |
| 3 | 黄义春, 李建民, 段留生, 李召虎 (2011). 甜菜碱对玉米幼苗抗旱性的诱导效应. 玉米科学 19, 95-100. |
| 4 | 孔妤, 王忠, 熊飞, 顾蕴洁, 邓亚萍 (2008). PEG胁迫下水稻根外皮层厚壁细胞的解剖学研究. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版) 29, 61-65. |
| 5 | 李春香, 王玮, 李德全 (2001). 长期水分胁迫对小麦生育中后期根叶渗透调节能力、渗透调节物质的影响. 西北植物学报 21, 924-930. |
| 6 | 李德全, 邹琦, 程炳嵩 (1992). 土壤干旱下不同抗旱性小麦品种的渗透调节和渗透调节物质. 植物生理学报 18, 37-44. |
| 7 | 李冀南, 李朴芳, 孔海燕, 熊俊兰, 王绍明, 熊友才 (2011). 干旱胁迫下植物根源化学信号研究进展. 生态学报 31, 2610-2620. |
| 8 | 李明, 王根轩 (2002). 干旱胁迫对甘草幼苗保护酶活性及脂质过氧化作用的影响. 生态学报 22, 503-507. |
| 9 | 李淑钰, 李传友 (2016). 植物根系可塑性发育的研究进展与展望. 中国基础科学 18(2), 14-21. |
| 10 | 李迎春, 张超英, 庞启华, 任茂琼 (2008). 干旱胁迫下小麦在不同生育时期的耐旱性研究. 西南农业学报 21, 621-624. |
| 11 | 梁泉, 廖红, 严小龙 (2007). 植物根构型的定量分析. 植物学通报 24, 695-702. |
| 12 | 梁新华, 徐兆桢, 许兴, 马宏玮 (2001). 小麦抗旱生理研究现状与思考. 甘肃农业科技 ( 2), 24-27. |
| 13 | 梁峥, 赵原, 汤岚, 骆爱玲 (1994). 甜菜碱对呼吸酶的保护效应. 植物学报 36, 947-951. |
| 14 | 廖红, 严小龙 (2000). 菜豆根构型对低磷胁迫的适应性变化及基因型差异. 植物学报 42, 158-163. |
| 15 | 卢少云, 黎用朝, 郭振飞, 李宝盛, 李明启 (1999). 钙提高水稻幼苗抗旱性的研究. 中国水稻科学 13, 161-164. |
| 16 | 马超, 冯雅岚, 张均, 王贺正, 原佳乐, 李友军 (2017). 外源茉莉酸甲酯对干旱胁迫下小麦花后内源激素含量及产量形成的影响. 植物生理学报 53, 1051-1058. |
| 17 | 马富举, 李丹丹, 蔡剑, 姜东, 曹卫星, 戴廷波 (2012). 干旱胁迫对小麦幼苗根系生长和叶片光合作用的影响. 应用生态学报 23, 724-730. |
| 18 | 单立山, 李毅, 董秋莲, 耿东梅 (2012). 红砂根系构型对干旱的生态适应. 中国沙漠 32, 1283-1290. |
| 19 | 谭冬梅, 许雪锋, 李天忠, 王忆, 韩振海 (2007). 干旱胁迫诱导新疆野苹果细胞程序性死亡的细胞形态学研究. 华北农学报 22, 50-55. |
| 20 | 谈峰, 汤亮, 胡军成, 姜海燕, 曹卫星, 朱艳 (2011). 小麦根系三维形态建模及可视化. 应用生态学报 22, 137-143. |
| 21 | 唐玉婧, 马猛, 邓西平, 唐春强, 邓荣, 杨淑慎 (2014). 干旱胁迫下小麦抗旱能力与其根系特征间的关系. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版) 42(4), 48-54, 60. |
| 22 | 王川, 谢惠民, 王娜, 王宏礼 (2011). 小麦品种可溶性糖和保护性酶与抗旱性关系研究. 干旱地区农业研究 29(5), 94-99. |
| 23 | 王俊刚, 陈国仓, 张承烈 (2002). 水分胁迫对2种生态型芦苇(Phragmites communis)的可溶性蛋白含量、SOD、POD、CAT活性的影响. 西北植物学报 22, 561-565. |
| 24 | 王敏, 姚维传, 张从宇, 吴晓亮 (2002). 小麦抗旱性的形态性状及初生根解剖结构研究. 种子 ( 6), 14-18. |
| 25 | 王玮, 李德全, 杨兴洪, 邹琦, 周燮, 杨军 (2000). 水分胁迫对不同抗旱性小麦品种芽根生长过程中IAA、ABA含量的影响. 作物学报 26, 738-742. |
| 26 | 王燕, 王洪峰 (2013). 细根皮层的研究进展. 吉林林业科技 42(2), 6-11. |
| 27 | 王振林 (1989). 麦类作物产量形成与激素的关系. 麦类作物学报 ( 6), 35-38. |
| 28 | 魏云霞, 王晓庆, 黄洁 (2016). PEG胁迫对木薯叶片形态、生理及根系解剖结构的影响. 热带作物学报 37, 292-297. |
| 29 | 吴永成, 周顺利, 王志敏 (2004). 小麦与抗旱性有关的根系遗传改良研究进展. 麦类作物学报 24(3), 101-104. |
| 30 | 肖玲, 赵先贵 (1995). 干旱条件下小麦根系的形态解剖学研究. 西北植物学报 15(2), 117-119. |
| 31 | 谢静静, 王笑, 蔡剑, 周琴, 戴廷波, 姜东 (2018). 苗期外源脱落酸和茉莉酸缓减小麦花后干旱胁迫的效应及其生理机制. 麦类作物学报 38, 221-229. |
| 32 | 杨书运, 严平, 梅雪英 (2007). 水分胁迫对冬小麦抗性物质可溶性糖与脯氨酸的影响. 中国农学通报 23, 229-233. |
| 33 | 袁冰剑, 张森磊, 曹萌萌, 王志娟, 李霞 (2014). 脱落酸通过影响生长素合成及分布抑制拟南芥主根伸长. 中国生态农业学报 22, 1341-1347. |
| 34 | 张立新, 李生秀 (2005). 氮、钾、甜菜碱对减缓夏玉米水分胁迫的效果. 中国农业科学 38, 1401-1407. |
| 35 | 张岁岐, 李金虎, 山仑 (2001). 干旱下植物气孔运动的调控. 西北植物学报 21, 1263-1270. |
| 36 | 张旭东, 王智威, 韩清芳, 王子煜, 闵安成, 贾志宽, 聂俊峰 (2016). 玉米早期根系构型及其生理特性对土壤水分的响应. 生态学报 36, 2969-2977. |
| 37 | 张正斌 (2003). 作物抗旱节水的生理遗传育种基础. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 23-23. |
| 38 | 左文博, 吴静利, 杨奇, 张嘉楠, 刘桂茹 (2010). 干旱胁迫对小麦根系活力和可溶性糖含量的影响. 华北农学报 25(6), 191-193. |
| 39 | Anjum SA, Xie XY, Wang LC, Saleem MF, Man C, Lei W (2011). Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress. Afr J Agric Res 6, 2026-2032. |
| 40 | Armengaud P, Breitling R, Amtmann A (2004). The potassium-dependent transcriptome of Arabidopsis reveals a prominent role of jasmonic acid in nutrient signaling. Plant Physiol 136, 2556-2576. |
| 41 | Band LR, Wells DM, Fozard JA, Ghetiu T, French AP, Pound MP, Wilson MH, Yu L, Li WD, Hijazi HI, Oh J, Pearce SP, Perez-Amador MA, Yun J, Kramer E, Alonso JM, Godin C, Vernoux T, Hodgman TC, Pridmore TP, Swarup R, King JR, Bennett MJ (2014). Systems analysis of auxin transport in the Arabidopsis root apex. Plant Cell 26, 862-875. |
| 42 | Bao F, Shen JJ, Brady SR, Muday GK, Asami T, Yang ZB (2004). Brassinosteroids interact with auxin to promote lateral root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134, 1624-1631. |
| 43 | Barraclough PB, Kuhlmann H, Weir AH (1989). The effects of prolonged drought and nitrogen fertilizer on root and shoot growth and water uptake by winter wheat. J Agron Crop Sci 163, 352-360. |
| 44 | Becker SR, Byrne PF, Reid SD, Bauerle WL, McKay JK, Haley SD (2016). Root traits contributing to drought tolerance of synthetic hexaploid wheat in a greenhouse study. Euphytica 207, 213-224. |
| 45 | Berntson GM (1997). Topological scaling and plant root system architecture: developmental and functional hierarchies. New Phytol 135, 621-634. |
| 46 | Bothwell JHF, Ng CKY (2005). The evolution of Ca 2+ signaling in photosynthetic eukaryotes . New Phytol 166, 21-38. |
| 47 | Case RM, Eisner D, Gurney A, Jones O, Muallem S, Verkhratsky A (2007). Evolution of calcium homeostasis: from birth of the first cell to an omnipresent signaling system. Cell Calcium 42, 345-350. |
| 48 | Chen Q, Sun JQ, Zhai QZ, Zhou WK, Qi LL, Xu L, Wang B, Chen R, Jiang HL, Qi J, Li XG, Palme K, Li CY (2011). The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor MYC2 directly represses PLETHORA expression during jasmonate-mediated modulation of the root stem cell niche in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23, 3335-3352. |
| 49 | de Carvalho MHC (2008). Drought stress and reactive oxygen species: production, scavenging and signaling. Plant Signal Behav 3, 156-165. |
| 50 | Deak KI, Malamy J (2005). Osmotic regulation of root system architecture. Plant J 43, 17-28. |
| 51 | Dodd IC (2003). Hormonal interactions and stomatal responses. J Plant Growth Regul 22, 32-46. |
| 52 | Echevarría-Machado I, Escobedo-GM RM, Larqué- Saavedra A (2007). Responses of transformed Catharanthus roseus roots to femtomolar concentrations of salicylic acid. Plant Physiol Biochem 45, 501-507. |
| 53 | Eckert M, Kaldenhoff R (2000). Light-induced stomatal movement of selected Arabidopsis thaliana mutants. J Exp Bot 51, 1435-1442. |
| 54 | Fang B, Shen JJ, Brady SR, Muday GK, Tadao A, Yang ZB (2004). Brassinosteroids interact with auxin to promote lateral root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134, 1624-1631. |
| 55 | Fang Y, Du YL, Wang J, Wu AJ, Qiao S, Xu BC, Zhang SQ, Siddique KHM, Chen YL (2017). Moderate drought stress affected root growth and grain yield in old, modern and newly released cultivars of winter wheat. Front Plant Sci 8, 672. |
| 56 | Fitter AH (1987). An architectural approach to the comparative ecology of plant root systems. New Phytol 106, 61-77. |
| 57 | Gao JQ, Strauss SH, Tsai CJ, Fang K, Chen YR, Jiang XN, Busov VB (2010). Gibberellins regulate lateral root formation in Populus through interactions with auxin and other hormones. Plant Cell 22, 623-639. |
| 58 | Gollan T, Schurr U, Schulze ED (1992). Stomatal response to drying soil in relation to changes in the xylem sap composition of Helianthus annuus. I. The concentration of cations, anions, amino acids in, and pH of, the xylem sap. Plant Cell Environ 15, 551-559. |
| 59 | Gowda VRP, Henry A, Yamauchi A, Shashidhar HE, Serraj R (2011). Root biology and genetic improvement for drought avoidance in rice. Field Crops Res 122, 1-13. |
| 60 | Han HM, Tian ZW, Fan YH, Cui YK, Cai J, Jiang D, Cao WX, Dai TB (2015). Water-deficit treatment followed by re-watering stimulates seminal root growth associated with hormone balance and photosynthesis in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 77, 201-210. |
| 61 | Hartung W, Sauter A, Hose E (2002). Abscisic acid in the xylem: where does it come from, where does it go to? J Exp Bot 53, 27-32. |
| 62 | He XJ, Mu RL, Cao WH, Zhang ZG, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2005). AtNAC2, a transcription factor downstream of ethylene and auxin signaling pathways, is involved in salt stress response and lateral root development. Plant J 44, 903-916. |
| 63 | Ioio RD, Linhares FS, Scacchi E, Casamitjana-Martinez E, Heidstra R, Costantino P, Sabatini S (2007). Cytokinins determine Arabidopsis root-meristem size by controlling cell differentiation. Curr Biol 17, 678-682. |
| 64 | Ivanov II (2009). Endogenous auxins and branching of wheat roots gaining nutrients from isolated compartments. Russ J Plant Physiol 56, 219-223. |
| 65 | Kano M, Inukai Y, Kitano H, Yamauchi A (2011). Root plasticity as the key root trait for adaptation to various intensities of drought stress in rice. Plant Soil 342, 117-128. |
| 66 | Krome K, Rosenberg K, Dickler C, Kreuzer K, Ludwig- Müller J, Ullrich-Eberius C, Scheu S, Bonkowski M (2010). Soil bacteria and protozoa affect root branching via effects on the auxin and cytokinin balance in plants. Plant Soil 328, 191-201. |
| 67 | Kudoyarova GR, Vysotskaya LB, Cherkozyanova A, Dodd IC (2007). Effect of partial rootzone drying on the concentration of zeatin-type cytokinins in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) xylem sap and leaves. J Exp Bot 58, 161-168. |
| 68 | Laplaze L, Benkova E, Casimiro I, Maes L, Vanneste S, Swarup R, Weijers D, Calvo V, Parizot B, Herrera- Rodriguez MB, Offringa R, Graham N, Doumas P, Friml J, Bogusz D, Beeckman T, Bennett M (2007). Cytokinins act directly on lateral root founder cells to inhibit root initiation. Plant Cell 19, 3889-3900. |
| 69 | Linkohr BI, Williamson LC, Fitter AH, Leyser HMO (2002). Nitrate and phosphate availability and distribution have different effects on root system architecture of Arabidopsis. Plant J 29, 751-760. |
| 70 | Liu HY, Sun WN, Su WA, Tang ZC (2006). Co-regulation of water channels and potassium channels in rice. Physiol Plant 128, 58-69. |
| 71 | Ljung K, Bhalerao RP, Sandberg G (2001). Sites and homeostatic control of auxin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis during vegetative growth. Plant J 28, 465-474. |
| 72 | Ludlow MM, Muchow RC (1990). A critical evaluation of traits for improving crop yields in water-limited environments. Adv Agron 43, 107-153. |
| 73 | Lynch J (1995). Root architecture and plant productivity. Plant Physiol 109, 7-13. |
| 74 | Macfall JS, Johnson GA, Kramer PJ (1991). Comparative water uptake by roots of different ages in seedlings of loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). New Phytol 119, 551-560. |
| 75 | Mahouachi J, Arbona V, Gómez-Cadenas A (2007). Hormonal changes in papaya seedlings subjected to progressive water stress and re-watering. Plant Growth Regul 53, 43-51. |
| 76 | Nibau C, Gibbs DJ, Coates JC (2008). Branching out in new directions: the control of root architecture by lateral root formation. New Phytol 179, 595-614. |
| 77 | Osmont KS, Sibout R, Hardtke CS (2007). Hidden branches: developments in root system architecture. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58, 93-113. |
| 78 | Parcy F, Giraudat J (1997). Interactions between the ABI1 and the ectopically expressed ABI3 genes in controlling abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis vegetative tissues. Plant J 11, 693-702. |
| 79 | Passioura JB (1991). Soil structure and plant growth. Aust J Soil Res 29, 717-728. |
| 80 | Quint M, Barkawi LS, Fan KT, Cohen JD, Gray WM (2009). Arabidopsis IAR4 modulates auxin response by regulating auxin homeostasis. Plant Physiol 150, 748-758. |
| 81 | Reddy AR, Chaitanya KV, Jutur PP, Sumithra K (2004). Differential antioxidative responses to water stress among five mulberry (Morus alba L.) cultivars. Environ Exp Bot 52, 33-42. |
| 82 | Richards RA, Passioura JB (1989). A breeding program to reduce the diameter of the major xylem vessel in the seminal roots of wheat and its effect on grain yield in rain-fed environments. Aust J Agric Res 40, 943-950. |
| 83 | Saradadevi R, Bramley H, Palta JA, Edwards E, Siddique KHM (2015). Root biomass in the upper layer of the soil profile is related to the stomatal response of wheat as the soil dries. Funct Plant Biol 43, 62-74. |
| 84 | Schachtman DP, Goodger JQD (2008). Chemical root to shoot signaling under drought. Trends Plant Sci 13, 281-287. |
| 85 | Segal E, Kushnir T, Mualem Y, Shani U (2008). Water uptake and hydraulics of the root hair rhizosphere. Vadose Zone J 7, 1027-1034. |
| 86 | Sharma P, Dubey RS (2005). Drought induces oxidative stress and enhances the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 46, 209-221. |
| 87 | Siopongco JDLC, Yamauchi A, Salekdeh H, Bennett J, Wade LJ (2005). Root growth and water extraction response of doubled-haploid rice lines to drought and rewatering during the vegetative stage. Plant Prod Sci 8, 497-508. |
| 88 | Snedden WA, Fromm H (2001). Calmodulin as a versatile calcium signal transducer in plants. New Phytol 151, 35-66. |
| 89 | Steudle E, Peterson CA (1998). How does water get through roots? J Exp Bot 49, 775-788. |
| 90 | Tardieu F, Zhang J, Davies WJ (1992). What information is conveyed by an ABA signal from maize roots in drying field soil? Plant Cell Environ 15, 185-191. |
| 91 | Türkan T, Bor M, Özdemir F, Koca H (2005). Differential responses of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in the leaves of drought-tolerant P. acutifolius Gray and drought- sensitive P. vulgaris L. subjected to polyethylene glycol mediated water stress. Plant Sci 168, 223-231. |
| 92 | Turner NC (1986). Adaptation to water deficits: a changing perspective. Funct Plant Biol 13, 175-190. |
| 93 | Uga Y, Okuno K, Yano M (2011). Dro1, a major QTL involved in deep rooting of rice under upland field conditions. J Exp Bot 62, 2485-2494. |
| 94 | Uga Y, Sugimoto K, Ogawa S, Rane J, Ishitani M, Hara N, Kitomi Y, Inukai Y, Ono K, Kanno N, Inoue H, Takehisa H, Motoyama R, Nagamura Y, Wu JZ, Matsumoto T, Takai T, Okuno K, Yano M (2013). Control of root system architecture by DEEPER ROOTING 1 increases rice yield under drought conditions. Nat Genet 45, 1097-1102. |
| 95 | Vandoorne B, Mathieu AS, van den Ende W, Vergauwen R, Périlleux C, Javaux M, Lutts S (2012). Water stress drastically reduces root growth and inulin yield in Cichorium intybus(var. sativum) independently of photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 63, 4359-4373. |
| 96 | Wang L, Hua DP, He JN, Duan Y, Chen ZZ, Hong XH, Gong ZZ (2011). Auxin Response Factor2 (ARF2) and its regulated homeodomain gene HB33 mediate abscisic acid response in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 7, e1002172. |
| 97 | Wasson AP, Richards RA, Chatrath R, Misra SC, Prasad SVS, Rebetzke GJ, Kirkegaard JA, Christopher J, Watt M (2012). Traits and selection strategies to improve root systems and water uptake in water-limited wheat crops. J Exp Bot 63, 3485-3498. |
| 98 | White RG, Kirkegaard JA (2010). The distribution and abundance of wheat roots in a dense, structured subsoil-implications for water uptake. Plant Cell Environ 33, 133-148. |
| 99 | Wu QS, He XH, Zou YN, Liu CY, Xiao J, Li Y (2012). Arbuscular mycorrhizas alter root system architecture of Citrus tangerine through regulating metabolism of endogenous polyamines. Plant Growth Regul 68, 27-35. |
| 100 | Xu WF, Jia LG, Shi WM, Liang JS, Zhou F, Li QF, Zhang JH (2013). Abscisic acid accumulation modulates auxin transport in the root tip to enhance proton secretion for maintaining root growth under moderate water stress. New Phytol 197, 139-150. |
| 101 | Zhang HM, Han W, De Smet I, Talboys P, Loya R, Hassan A, Rong H, Jürgens G, Paul KJ, Wang MH (2010). ABA promotes quiescence of the quiescent centre and suppresses stem cell differentiation in the Arabidopsis primary root meristem. Plant J 64, 764-774. |
| [1] | 许庭旸, 刘雨辰, 王万鹏, 苏航, 苏昆龙, 吴振映, 吕明, 李福利, 王小山, 付春祥. 喷施不同植物生长调节剂对盐碱地小麦生长发育的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 354-362. |
| [2] | 刘笑, 杜琬莹, 张云秀, 唐成名, 李华伟, 夏海勇, 樊守金, 孔令安. NO3-缓解小麦根部NH4+毒性机理(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 397-413. |
| [3] | 武棒棒, 郝宇琼, 杨淑斌, 黄雨茜, 关攀锋, 郑兴卫, 赵佳佳, 乔玲, 李晓华, 刘维仲, 郑军. 山西小麦籽粒叶黄素含量变异及遗传特性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 535-547. |
| [4] | 白明义, 彭金荣, 傅向东. 赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号通路双重调控助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 194-198. |
| [5] | 孔令让. 另辟蹊径破解小麦条锈病的基因密码[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 405-408. |
| [6] | 熊淑萍, 曹文博, 曹锐, 张志勇, 付新露, 徐赛俊, 潘虎强, 王小纯, 马新明. 水平结构配置对冬小麦冠层垂直结构、微环境及产量的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(2): 188-196. |
| [7] | 孙佳欢, 刘冬, 朱家祺, 张书宁, 高梅香. 小麦-玉米轮作农田土壤螨多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22292-. |
| [8] | 周俭民. 小麦抗赤霉病利器——他山之石[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 123-125. |
| [9] | 张淑辉,王红,王文茹,吴雪莲,肖元松,彭福田. 蔗糖对桃幼苗生长发育及其SnRK1酶活性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 744-752. |
| [10] | 祝维, 余立璇, 赵德海, 贾黎明. 基于根系发育分级的砂壤土下成熟林木根系构型分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(2): 119-130. |
| [11] | 郭瑞, 周际, 杨帆, 李峰. 小麦根系在碱胁迫下的生理代谢反应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(6): 683-692. |
| [12] | 徐静馨, 郑有飞, 麦博儒, 赵辉, 储仲芳, 黄积庆, 袁月. 基于涡度相关法的麦田O3干沉降及不同沉降通道分配的特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(6): 670-682. |
| [13] | 高林, 王晓菲, 顾行发, 田庆久, 焦俊男, 王培燕, 李丹. 植冠下土壤类型差异对遥感估算冬小麦叶面积指数的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(12): 1273-1288. |
| [14] | 郑成岩, 邓艾兴, LATIFMANESHHojatollah, 宋振伟, 张俊, 王利, 张卫建. 增温对青藏高原冬小麦干物质积累转运及氮吸收利用的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(10): 1060-1068. |
| [15] | 郭瑞, 周际, 杨帆, 李峰, 李昊如, 夏旭, 刘琪. 拔节孕穗期小麦干旱胁迫下生长代谢变化规律[J]. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(12): 1319-1327. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||