

植物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (3): 358-374.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22007 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22007
王韫慧, 王一帆, 蔺佳雨, 李金红, 姚士恩, 冯湘池, 曹振林, 王俊, 李美娜( )
)
收稿日期:2022-01-12
接受日期:2022-02-25
出版日期:2022-05-01
发布日期:2022-05-18
通讯作者:
李美娜
作者简介:* E-mail: limeina@gzhu.edu.cn基金资助:
Yunhui Wang, Yifan Wang, Jiayu Lin, Jinhong Li, Shien Yao, Xiangchi Feng, Zhenlin Cao, Jun Wang, Meina Li( )
)
Received:2022-01-12
Accepted:2022-02-25
Online:2022-05-01
Published:2022-05-18
Contact:
Meina Li
摘要: 驱动蛋白(kinesin)是以微管为轨道的分子马达, 其催化ATP水解为ADP, 将贮藏在ATP分子中的化学能高效地转化为机械能, 在细胞形态建成、细胞分裂、细胞运动、胞内物质运输和信号转导等多种生命活动中发挥重要作用。对植物驱动蛋白的研究落后于动物和真菌, 其原因不仅由于植物进化出独有的驱动蛋白家族, 而且其家族成员数量远多于动物驱动蛋白。该文主要总结了驱动蛋白在微管阵列动态组织, 包括周质微管和有丝分裂早前期微管带、纺锤体及成膜体中的角色和功能, 以及其对植物生理活动的调控作用。同时对重要经济作物大豆(Glycine max)中的驱动蛋白进行了系统分析、分类及功能预测, 发现大豆驱动蛋白数量庞大。结合公共数据库中大豆转录组数据, 对部分大豆驱动蛋白进行功能预测, 以期对大豆及其它作物驱动蛋白功能研究提供线索和启示。
王韫慧, 王一帆, 蔺佳雨, 李金红, 姚士恩, 冯湘池, 曹振林, 王俊, 李美娜. 植物驱动蛋白: 从微管阵列到生理活动调控. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 358-374.
Yunhui Wang, Yifan Wang, Jiayu Lin, Jinhong Li, Shien Yao, Xiangchi Feng, Zhenlin Cao, Jun Wang, Meina Li. Plant Kinesin: from Microtubule Arrays to Physiological Regulation. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 358-374.
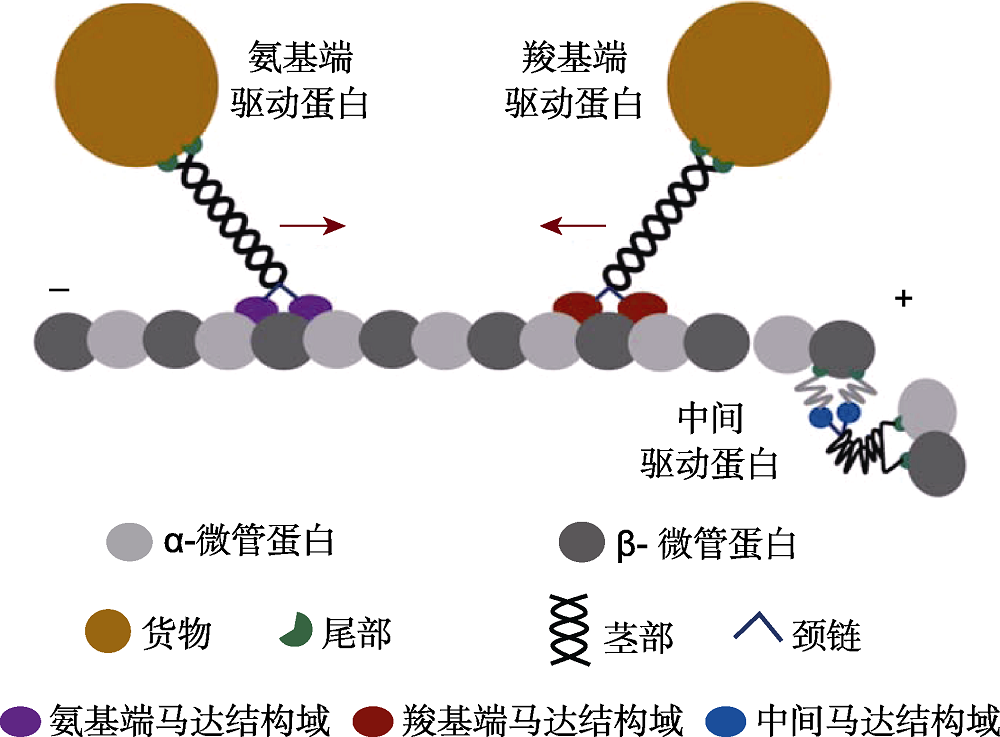
图1 氨基端驱动蛋白、羧基端驱动蛋白及中间驱动蛋白结构模型 箭头代表运动方向。
Figure 1 Domain organization of N terminal kinesin, C terminal kinesin and internal kinesin The arrows represent the direction of movement.
| 蛋白家族 | 物种 | 基因名 | 基因登录号 | 细胞学功能 | 生理学功能 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KIN1 | 拟南芥 | AtKin-1/AtPSS1 | AT3G63480 | 减数分裂调控纺锤 体形态 | 育性控制 | Wang et al., | |
| 水稻 | OsPSS1 | Os08g0117000 | 育性控制 | Zhou et al., | |||
| KIN4 | 拟南芥 | AtKinesin-4A/FRA1 | AT5G47820 | 合成细胞壁 | Zhu et al., | ||
| 水稻 | BC2/GDD1 | Os09g0114500 | 合成细胞壁; 调控细胞延伸 | Li et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | Kin4-Ia | Pp3c25_8700 | 抑制成膜体中间区 的微管生长 | de Keijzer et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | Kin4-Ic | Pp3c10_9510 | |||||
| KIN5 | 拟南芥 | RSW7/AtKRP125c | AT2g28620 | 有丝分裂间期交联 微管, 前中期稳定纺 锤体两极间微管阵列 | Bannigan et al., | ||
| KIN7 | 拟南芥 | AtNACK1/HINKEL | AT1G18370 | 有丝分裂及减数分裂II末期促进成膜体解聚 | 育性控制 | Strompen et al., | |
| 拟南芥 | STUD/TES/AtNACK2 | AT3G43210 | 育性控制 | Yang et al., | |||
| 烟草 | NACK1 | LOC107780313 | 育性控制 | Nishihama et al., | |||
| 烟草 | NACK2 | LOC107775653 | 育性控制 | ||||
| 大豆 | GmNACK2 | Glyma.13G114200 | 育性控制 | Fang et al., | |||
| 蛋白家族 | 物种 | 基因名 | 基因登录号 | 细胞学功能 | 生理学功能 | 参考文献 | |
| 拟南芥 | Kinesin7 | AT3g12020 | 有丝分裂间期促进微管组装 | Moschou et al., | |||
| 拟南芥 | MKRP1 | AT1G21730 | 与线粒体共定位 | Itoh et al., | |||
| 拟南芥 | MKRP2 | AT4G39050 | |||||
| KIN10 | 拟南芥 | AtPAKRP2 | AT4g14330 | 组装细胞板 | Lee et al., | ||
| 苔藓 | KINID1a | AB434497 | 交联成膜体反向平行微管阵列 | Hiwatashi et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | KINID1b | AB434498 | |||||
| KIN12 | 拟南芥 | PAKRP1/Kinesin-12A | AT4G14150 | 稳定成膜体反向平行微管阵列 | Lee and Liu, | ||
| 拟南芥 | PAKRP1L/Kinesin-12B | AT3G23670 | |||||
| 拟南芥 | POK1 | AT3G17360 | 标识周质分裂位点 | Müller et al., | |||
| 拟南芥 | POK2 | AT3G19050 | |||||
| 拟南芥 | Kinesin-12E | AT3G44050 | 有丝分裂组装纺锤体 | Herrmann et al., | |||
| KIN13 | 拟南芥 | AtKinesin-13A/AtMACK | AT3G16630 | 有丝分裂间期解聚微管 | Oda and Fukuda, | ||
| KIN14 | 拟南芥 | KATA/ATK1 | AT4G21270 | 有丝分裂向纺锤体两极拉动微管 | Chen et al., | ||
| 拟南芥 | ATK5 | AT4G05190 | 有丝分裂纺锤体中间区交联微管 | Ambrose and Cyr, | |||
| 拟南芥 | ATKP1 | AT3G44730 | 沿微管运输微丝 | 与线粒体共定位 | Yang et al., | ||
| 水稻 | OsKCH1 | Os12g0547500 | Frey et al., | ||||
| 水稻 | OsKCH2 | 未公布 | Tseng et al., | ||||
| 拟南芥 | KAC1 | AT5G10470 | 介导光驱动叶绿体 | Suetsugu et al., | |||
| 拟南芥 | KAC2 | AT5G65460 | |||||
| 棉花 | GhKCH1 | AY695833 | Preuss et al., | ||||
| 棉花 | GhKCH2 | EF432568 | Xu et al., | ||||
| 拟南芥 | KCBP/ZWI | AT5G65930 | 有丝分裂间期交联微管微丝, 后期将成膜体外围微管拉向中间区 | Tian et al., | |||
| 玉米 | VSK1 | Zm00001d018624 | 有丝分裂组装纺锤体 | Huang et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | KINDR | KX759199- KX759203 | 激活着丝粒 | Dawe et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | GTRC | Pp3c2_9150 | 调控微丝极性 | 参与重力感受 | Li et al., | ||
| KINU | 拟南芥 | ARK1/AtKINUc | AT3G54870 | 有丝分裂间期促进微管灾变 | Yang et al., | ||
| 拟南芥 | ARK3/AtKINUa | AT1G12430 | 有丝分裂促进早前期微管带的形成与稳定 | Malcos and Cyr, | |||
表1 植物驱动蛋白的主要功能
Table1 Main functions of plant kinesin
| 蛋白家族 | 物种 | 基因名 | 基因登录号 | 细胞学功能 | 生理学功能 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KIN1 | 拟南芥 | AtKin-1/AtPSS1 | AT3G63480 | 减数分裂调控纺锤 体形态 | 育性控制 | Wang et al., | |
| 水稻 | OsPSS1 | Os08g0117000 | 育性控制 | Zhou et al., | |||
| KIN4 | 拟南芥 | AtKinesin-4A/FRA1 | AT5G47820 | 合成细胞壁 | Zhu et al., | ||
| 水稻 | BC2/GDD1 | Os09g0114500 | 合成细胞壁; 调控细胞延伸 | Li et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | Kin4-Ia | Pp3c25_8700 | 抑制成膜体中间区 的微管生长 | de Keijzer et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | Kin4-Ic | Pp3c10_9510 | |||||
| KIN5 | 拟南芥 | RSW7/AtKRP125c | AT2g28620 | 有丝分裂间期交联 微管, 前中期稳定纺 锤体两极间微管阵列 | Bannigan et al., | ||
| KIN7 | 拟南芥 | AtNACK1/HINKEL | AT1G18370 | 有丝分裂及减数分裂II末期促进成膜体解聚 | 育性控制 | Strompen et al., | |
| 拟南芥 | STUD/TES/AtNACK2 | AT3G43210 | 育性控制 | Yang et al., | |||
| 烟草 | NACK1 | LOC107780313 | 育性控制 | Nishihama et al., | |||
| 烟草 | NACK2 | LOC107775653 | 育性控制 | ||||
| 大豆 | GmNACK2 | Glyma.13G114200 | 育性控制 | Fang et al., | |||
| 蛋白家族 | 物种 | 基因名 | 基因登录号 | 细胞学功能 | 生理学功能 | 参考文献 | |
| 拟南芥 | Kinesin7 | AT3g12020 | 有丝分裂间期促进微管组装 | Moschou et al., | |||
| 拟南芥 | MKRP1 | AT1G21730 | 与线粒体共定位 | Itoh et al., | |||
| 拟南芥 | MKRP2 | AT4G39050 | |||||
| KIN10 | 拟南芥 | AtPAKRP2 | AT4g14330 | 组装细胞板 | Lee et al., | ||
| 苔藓 | KINID1a | AB434497 | 交联成膜体反向平行微管阵列 | Hiwatashi et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | KINID1b | AB434498 | |||||
| KIN12 | 拟南芥 | PAKRP1/Kinesin-12A | AT4G14150 | 稳定成膜体反向平行微管阵列 | Lee and Liu, | ||
| 拟南芥 | PAKRP1L/Kinesin-12B | AT3G23670 | |||||
| 拟南芥 | POK1 | AT3G17360 | 标识周质分裂位点 | Müller et al., | |||
| 拟南芥 | POK2 | AT3G19050 | |||||
| 拟南芥 | Kinesin-12E | AT3G44050 | 有丝分裂组装纺锤体 | Herrmann et al., | |||
| KIN13 | 拟南芥 | AtKinesin-13A/AtMACK | AT3G16630 | 有丝分裂间期解聚微管 | Oda and Fukuda, | ||
| KIN14 | 拟南芥 | KATA/ATK1 | AT4G21270 | 有丝分裂向纺锤体两极拉动微管 | Chen et al., | ||
| 拟南芥 | ATK5 | AT4G05190 | 有丝分裂纺锤体中间区交联微管 | Ambrose and Cyr, | |||
| 拟南芥 | ATKP1 | AT3G44730 | 沿微管运输微丝 | 与线粒体共定位 | Yang et al., | ||
| 水稻 | OsKCH1 | Os12g0547500 | Frey et al., | ||||
| 水稻 | OsKCH2 | 未公布 | Tseng et al., | ||||
| 拟南芥 | KAC1 | AT5G10470 | 介导光驱动叶绿体 | Suetsugu et al., | |||
| 拟南芥 | KAC2 | AT5G65460 | |||||
| 棉花 | GhKCH1 | AY695833 | Preuss et al., | ||||
| 棉花 | GhKCH2 | EF432568 | Xu et al., | ||||
| 拟南芥 | KCBP/ZWI | AT5G65930 | 有丝分裂间期交联微管微丝, 后期将成膜体外围微管拉向中间区 | Tian et al., | |||
| 玉米 | VSK1 | Zm00001d018624 | 有丝分裂组装纺锤体 | Huang et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | KINDR | KX759199- KX759203 | 激活着丝粒 | Dawe et al., | |||
| 苔藓 | GTRC | Pp3c2_9150 | 调控微丝极性 | 参与重力感受 | Li et al., | ||
| KINU | 拟南芥 | ARK1/AtKINUc | AT3G54870 | 有丝分裂间期促进微管灾变 | Yang et al., | ||
| 拟南芥 | ARK3/AtKINUa | AT1G12430 | 有丝分裂促进早前期微管带的形成与稳定 | Malcos and Cyr, | |||
| [1] |
沈锦波, 姜里文 (2018). 中国科学家在植物细胞骨架研究领域取得突破性进展. 植物学报 53, 741-744.
DOI |
| [2] | 岳剑茹, 赫云建, 邱天麒, 郭南南, 韩雪萍, 王显玲 (2021). 植物微管骨架参与下胚轴伸长调节机制研究进展. 植物学报 56, 363-371. |
| [3] |
Albertsen MC, Palmer RG (1979). A comparative light- and electron-microscopic study of microsporogenesis in male sterile (MS1) and male fertile soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Am J Bot 66, 253-265.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Ambrose JC, Cyr R (2007). The kinesin ATK5 functions in early spindle assembly in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 226- 236.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Ambrose JC, Li WX, Marcus A, Ma H, Cyr R (2005). A minus-end-directed kinesin with plus-end tracking protein activity is involved in spindle morphogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 16, 1584-1592. |
| [6] |
Asada T, Kuriyama R, Shibaoka H (1997). TKRP125, a kinesin-related protein involved in the centrosome-independent organization of the cytokinetic apparatus in tobacco BY-2 cells. J Cell Sci 110, 179-189.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Bannigan A, Scheible WR, Lukowitz W, Fagerstrom C, Wadsworth P, Somerville C, Baskin TI (2007). A conserved role for kinesin-5 in plant mitosis. J Cell Sci 120, 2819-2827.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Bieling P, Telley IA, Surrey T (2010). A minimal midzone protein module controls formation and length of antiparallel microtubule overlaps. Cell 142, 420-432.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Blancaflor EB (2013). Regulation of plant gravity sensing and signaling by the actin cytoskeleton. Am J Bot 100, 143-152.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Brady ST (1985). A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor. Nature 317, 73-75.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Brim CA, Young MF (1971). Inheritance of a male-sterile character in soybeans. Crop Sci 11, 564-566.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Buschmann H, Dols J, Kopischke S, Peña EJ, Andrade- Navarro MA, Heinlein M, Szymanski DB, Zachgo S, Doonan JH, Lloyd CW (2015). Arabidopsis KCBP interacts with AIR9 but stays in the cortical division zone throughout mitosis via its MyTH4-FERM domain. J Cell Sci 128, 2033-2046. |
| [13] |
Chandrasekaran G, Tátrai P, Gergely F (2015). Hitting the brakes: targeting microtubule motors in cancer. Br J Cancer 113, 693-698.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Chen CB, Marcus A, Li WX, Hu Y, Calzada JPV, Grossniklaus U, Cyr JR, Ma H (2002). The Arabidopsis ATK1 gene is required for spindle morphogenesis in male meiosis. Development 129, 2401-2409.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Dawe RK, Lowry EG, Gent JI, Stitzer MC, Swentowsky KW, Higgins DM, Ross-Ibarra J, Wallace JG, Kanizay LB, Alabady M, Qiu WH, Tseng KF, Wang N, Gao Z, Birchler JA, Harkess AE, Hodges AL, Hiatt EN (2018). A kinesin-14 motor activates neocentromeres to promote meiotic drive in maize. Cell 173, 839-850.
DOI |
| [16] |
de Cuevas M, Tao T, Goldstein LSB (1992). Evidence that the stalk of Drosophila kinesin heavy chain is an α-helical coiled coil. J Cell Biol 116, 957-965.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
de Keijzer J, Kieft H, Ketelaar T, Goshima G, Janson ME (2017). Shortening of microtubule overlap regions defines membrane delivery sites during plant cytokinesis. Curr Biol 27, 514-520.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Desai A, Verma S, Mitchison TJ, Walczak CE (1999). Kin I kinesins are microtubule-destabilizing enzymes. Cell 96, 69-78.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Duroc Y, Lemhemdi A, Larchevêque C, Hurel A, Cuacos M, Cromer L, Horlow C, Armstrong SJ, Chelysheva L, Mercier R (2014). The kinesin AtPSS1 promotes synapsis and is required for proper crossover distribution in meiosis. PLoS Genet 10, e1004674. |
| [20] |
Eng RC, Wasteneys GO (2014). The microtubule plus-end tracking protein ARMADILLO-REPEAT KINESIN 1 promotes microtubule catastrophe in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 3372-3386.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Fang XL, Sun XY, Yang XD, Li Q, Lin CJ, Xu J, Gong WJ, Wang YF, Liu L, Zhao LM, Liu BH, Qin J, Zhang MC, Zhang CB, Kong FJ, Li MN (2021). MS1 is essential for male fertility by regulating the microsporocyte cell plate expansion in soybean. Sci China Life Sci 64, 1533-1545.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Frey N, Klotz J, Nick P (2009). Dynamic bridges—a calponin-domain kinesin from rice links actin filaments and microtubules in both cycling and non-cycling cells. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 1493-1506.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Fu Y, Li H, Yang ZB (2002). The ROP2 GTPase controls the formation of cortical fine F-actin and the early phase of directional cell expansion during Arabidopsis organogenesis. Plant Cell 14, 777-794.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Ganguly A, DeMott L, Zhu CM, McClosky DD, Anderson CT, Dixit R (2018). Importin-β directly regulates the motor activity and turnover of a Kinesin-4. Dev Cell 44, 642-651.
DOI |
| [25] |
Ganguly A, Zhu CM, Chen WZ, Dixit R (2020). FRA1 kinesin modulates the lateral stability of cortical microtubules through cellulose synthase-microtubule uncoupling proteins. Plant Cell 32, 2508-2524.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Gicking AM, Wang P, Liu C, Mickolajczyk KJ, Guo LJ, Hancock WO, Qiu WH (2019). The orphan kinesin PAKRP2 achieves processive motility via a noncanonical stepping mechanism. Biophys J 116, 1270-1281.
DOI |
| [27] | Hamada T (2014). Microtubule organization and microtubule-associated proteins in plant cells. Int Rev Cel Mol Biol 312, 1-52. |
| [28] |
Hedden P, Phillips AL (2000). Gibberellin metabolism: new insights revealed by the genes. Trends Plant Sci 5, 523- 530.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Herrmann A, Livanos P, Zimmermann S, Berendzen K, Rohr L, Lipka E, Müller S (2021). KINESIN-12E regulates metaphase spindle flux and helps control spindle size in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 33, 27-43. |
| [30] |
Higgins DM, Nannas NJ, Dawe RK (2016). The maize divergent spindle-1 (dv1) gene encodes a Kinesin-14A motor protein required for meiotic spindle pole organization. Front Plant Sci 7, 1277.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Hiwatashi Y, Obara M, Sato Y, Fujita T, Murata T, Hasebe M (2008). Kinesins are indispensable for interdigitation of phragmoplast microtubules in the Moss Physcomitrella pa-tens. Plant Cell 20, 3094-3106.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Hiwatashi Y, Sato Y, Doonan JH (2014). Kinesins have a dual function in organizing microtubules during both tip growth and cytokinesis in Physcomitrella patens. Plant Cell 26, 1256-1266.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Ho CMK, Hotta T, Guo FL, Roberson RW, Lee YRJ, Liu B (2011). Interaction of antiparallel microtubules in the phragmoplast is mediated by the microtubule-associated pro- tein MAP65-3 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23, 2909-2923.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Hu CK, Coughlin M, Field CM, Mitchison TJ (2011). KIF4 regulates midzone length during cytokinesis. Curr Biol 21, 815-824.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Huang YC, Wang HH, Huang X, Wang Q, Wang JC, An D, Li JQ, Wang WQ, Wu YR (2019). Maize VKS1 regulates mitosis and cytokinesis during early endosperm development. Plant Cell 31, 1238-1256.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Itoh R, Fujiwara M, Yoshida S (2001). Kinesin-related proteins with a mitochondrial targeting signal. Plant Physiol 127, 724-726.
PMID |
| [37] | Iwata S, Morikawa M, Takei Y, Hirokawa N (2020). An activity-dependent local transport regulation via degradation and synthesis of KIF17 underlying cognitive flexibility. Sci Adv 6, eabc8355. |
| [38] |
Jones MA, Raymond MJ, Smirnoff N (2006). Analysis of the root-hair morphogenesis transcriptome reveals the molecular identity of six genes with roles in root-hair development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 45, 83-100.
PMID |
| [39] |
Kadota A, Yamada N, Suetsugu N, Hirose M, Saito C, Shoda K, Ichikawa S, Kagawa T, Nakano A, Wada M (2009). Short actin-based mechanism for light-directed chloroplast movement in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 13106-13111.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Kasahara M, Kagawa T, Oikawa K, Suetsugu N, Miyao M, Wada M (2002). Chloroplast avoidance movement reduces photodamage in plants. Nature 420, 829-832.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Kong ZS, Ioki M, Braybrook S, Li SD, Ye ZH, Lee YRJ, Hotta T, Chang A, Tian J, Wang GD, Liu B (2015). Kinesin-4 functions in vesicular transport on cortical micro- tubules and regulates cell wall mechanics during cell elongation in plants. Mol Plant 8, 1011-1023.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Lane J, Allan V (1998). Microtubule-based membrane movement. Biochim Biophys Acta 1376, 27-55.
PMID |
| [43] |
Lawrence CJ, Dawe RK, Christie KR, Cleveland DW, Dawson SC, Endow SA, Goldstein LSB, Goodson HV, Hirokawa N, Howard J, Malmberg RL, McIntosh JR, Miki H, Mitchison TJ, Okada Y, Reddy ASN, Saxton WM, Schliwa M, Scholey JM, Vale RD, Walczak CE, Wordeman L (2004). A standardized kinesin nomenclature. J Cell Biol 167, 19-22.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Lee YRJ, Giang HM, Liu B (2001). A novel plant kinesin-related protein specifically associates with the phragmoplast organelles. Plant Cell 13, 2427-2439.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Lee YRJ, Li Y, Liu B (2007). Two Arabidopsis phragmoplast-associated kinesins play a critical role in cytokinesis during male gametogenesis. Plant Cell 19, 2595-2605.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Lee YRJ, Liu B (2000). Identification of a phragmoplast- associated kinesin-related protein in higher plants. Curr Biol 10, 797-800.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Lee YRJ, Liu B (2004). Cytoskeletal motors in Arabidopsis. Sixty-one kinesins and seventeen myosins. Plant Physiol 136, 3877-3883.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Lee YRJ, Qiu WH, Liu B (2015). Kinesin motors in plants: from subcellular dynamics to motility regulation. Curr Opin Plant Biol 28, 120-126.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Li J, Jia JF, Qian Q, Yun YY, Zhang C, Xiao J, Du C, Luo W, Zou GX, Chen ML, Huang YQ, Feng YQ, Cheng ZK, Yuan M, Chong K (2011). Mutation of rice BC12/GDD1, which encodes a kinesin-like protein that binds to a GA biosynthesis gene promoter, leads to dwarfism with impaired cell elongation. Plant Cell 23, 628-640.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Li YF, Deng ZG, Kamisugi Y, Chen ZR, Wang JJ, Han X, Wei YX, He H, Terzaghi W, Cove DJ, Cuming AC, Chen HD (2021). A minus-end directed kinesin motor directs gravitropism in Physcomitrella patens. Nat Commun 12, 4470.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Malcos JL, Cyr RJ (2011). An ungrouped plant kinesin accumulates at the preprophase band in a cell cycle- dependent manner. Cytoskeleton 68, 247-258.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Marcus AI, Li W, Ma H, Cyr RJ (2003). A kinesin mutant with an atypical bipolar spindle undergoes normal mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 14, 1717-1726.
DOI PMID |
| [53] |
McFarlane HE, Döring A, Persson S (2014). The cell biology of cellulose synthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65, 69-94.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Miki H, Okada Y, Hirokawa N (2005). Analysis of the kinesin superfamily: insights into structure and function. Trends Cell Biol 15, 467-476.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Mineyuki Y (1999). The preprophase band of microtubules: its function as a cytokinetic apparatus in higher plants. Int Rev Cytol 187, 1-49. |
| [56] |
Moschou PN, Gutierrez-Beltran E, Bozhkov PV, Smertenko A (2016). Separase promotes microtubule polymerization by activating CENP-E-related kinesin Kin7. Dev Cell 37, 350-361.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Moschou PN, Smertenko AP, Minina EA, Fukada K, Savenkov EI, Robert S, Hussey PJ, Bozhkov PV (2013). The caspase-related protease separase (EXTRA SPINDLE POLES) regulates cell polarity and cytokinesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 2171-2186.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Müller S, Han SC, Smith LG (2006). Two kinesins are involved in the spatial control of cytokinesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 16, 888-894.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Myers SM, Collins I (2016). Recent findings and future directions for interpolar mitotic kinesin inhibitors in cancer therapy. Future Med Chem 8, 463-489.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Nakamura M, Toyota M, Tasaka M, Morita MT (2011). An Arabidopsis E3 ligase, SHOOT GRAVITROPISM 9, modu- lates the interaction between statoliths and F-actin in gravity sensing. Plant Cell 23, 1830-1848.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Nebenführ A, Dixit R (2018). Kinesins and myosins: molecular motors that coordinate cellular functions in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69, 329-361.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Ni CZ, Wang HQ, Xu T, Qu Z, Liu GQ (2005). AtKP1, a kinesin-like protein, mainly localizes to mitochondria in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell Res 15, 725-733.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Nishihama R, Ishikawa M, Araki S, Soyano T, Asada T, Machida Y (2001). The NPK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is a regulator of cell-plate formation in plant cytokinesis. Genes Dev 15, 352-363.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Nishihama R, Soyano T, Ishikawa M, Araki S, Tanaka H, Asada T, Irie K, Ito M, Terada M, Banno H, Yamazaki Y, Machida Y (2002). Expansion of the cell plate in plant cytokinesis requires a kinesin-like protein/MAPKKK complex. Cell 109, 87-99.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
Oda Y, Fukuda H (2013). Rho of plant Gtpase signaling regulates the behavior of Arabidopsis kinesin-13A to establish secondary cell wall patterns. Plant Cell 25, 4439- 4450.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Oh SA, Allen T, Kim GJ, Sidorova A, Borg M, Park SK, Twell D (2012). Arabidopsis fused kinase and the Kinesin-12 subfamily constitute a signaling module required for phragmoplast expansion. Plant J 72, 308-319.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Oh SA, Bourdon V, Das 'Pal M, Dickinson H, Twell D (2008). Arabidopsis kinesins HINKEL and TETRASPORE act redundantly to control cell plate expansion during cytokinesis in the male gametophyte. Mol Plant 1, 794-799.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Olszewski N, Sun TP, Gubler F (2002). Gibberellin signaling: biosynthesis, catabolism, and response pathways. Plant Cell 14, S61-S80.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Pan RQ, Lee YRJ, Liu B (2004). Localization of two homologous Arabidopsis kinesin-related proteins in the phragmoplast. Planta 220, 156-164.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Preuss ML, Kovar DR, Lee YRJ, Staiger CJ, Delmer DP, Liu B (2004). A plant-specific kinesin binds to actin microfilaments and interacts with cortical microtubules in cotton fibers. Plant Physiol 136, 3945-3955.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Rath O, Kozielski F (2012). Kinesins and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12, 527-539.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Sasabe M, Machida Y (2012). Regulation of organization and function of microtubules by the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade during plant cytokinesis. Cytoskeleton 69, 913-918.
DOI URL |
| [73] | Song Y, Li G, Nowak J, Zhang XQ, Xu DB, Yang XJ, Huang GQ, Liang WQ, Yang LT, Wang CH, Bulone V, Nikoloski Z, Hu JP, Persson S, Zhang DB (2019). The rice actin-binding protein RMD regulates light-dependent shoot gravitropism. Plant Physiol 181, 630-644. |
| [74] |
Strompen G, El Kasmi F, Richter S, Lukowitz W, Assaad FF, Jürgens G, Mayer U (2002). The Arabidopsis HINKEL gene encodes a kinesin-related protein involved in cytokinesis and is expressed in a cell cycle-dependent manner. Curr Biol 12, 153-158.
DOI PMID |
| [75] |
Suetsugu N, Yamada N, Kagawa T, Yonekura H, Uyeda TQP, Kadota A, Wada M (2010). Two kinesin-like proteins mediate actin-based chloroplast movement in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 8860-8865.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Tian J, Han LB, Feng ZD, Wang GD, Liu WW, Ma YP, Yu YJ, Kong ZS (2015). Orchestration of microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton in trichome cell shape determination by a plant-unique kinesin. eLife 4, e09351.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Tseng KF, Wang P, Lee YRJ, Bowen J, Gicking AM, Guo LJ, Liu B, Qiu WH (2018). The preprophase band-associated Kinesin-14 OsKCH2 is a processive minus-end- directed microtubule motor. Nat Commun 9, 1067.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Vale RD (2003). The molecular motor toolbox for intracellular transport. Cell 112, 467-480.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Vale RD, Fletterick RJ (1997). The design plan of kinesin motors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13, 745-777.
PMID |
| [80] |
Vale RD, Reese TS, Sheetz MP (1985). Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell 42, 39-50.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Walker KL, Müller S, Moss D, Ehrhardt DW, Smith LG (2007). Arabidopsis TANGLED identifies the division plane throughout mitosis and cytokinesis. Curr Biol 17, 1827- 1836.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Wang HQ, Liu RJ, Wang JW, Wang P, Shen PWY, Liu GQ (2014). The Arabidopsis kinesin gene AtKin-1 plays a role in the nuclear division process during megagametogenesis. Plant Cell Rep 33, 819-828.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Wick SM, Seagull RW, Osborn M, Weber K, Gunning BES (1981). Immunofluorescence microscopy of organized mic- rotubule arrays in structurally stabilized meristematic plant cells. J Cell Biol 89, 685-690.
PMID |
| [84] |
Xu XM, Zhao Q, Rodrigo-Peiris T, Brkljacic J, He CS, Müller S, Meier I (2008). RanGAP1 is a continuous marker of the Arabidopsis cell division plane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 18637-18642.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Yamada M, Tanaka-Takiguchi Y, Hayashi M, Nishina M, Goshima G (2017). Multiple Kinesin-14 family members drive microtubule minus end-directed transport in plant cells. J Cell Biol 216, 1705-1714.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Yang CY, Spielman M, Coles JP, Li Y, Ghelani S, Bourdon V, Brown RC, Lemmon BE, Scott RJ, Dickinson HG (2003). TETRASPORE encodes a kinesin required for male meiotic cytokinesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 34, 229- 240.
DOI PMID |
| [87] |
Yang GH, Gao P, Zhang H, Huang SJ, Zheng ZL (2007). A mutation in MRH2 kinesin enhances the root hair tip growth defect caused by constitutively activated ROP2 small GTPase in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 2, e1074.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Yang XY, Chen ZW, Xu T, Qu Z, Pan XD, Qin XH, Ren DT, Liu GQ (2011). Arabidopsis kinesin KP1 specifically interacts with VDAC3, a mitochondrial protein, and regulates respiration during seed germination at low temperature. Plant Cell 23, 1093-1106.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
Yin XL, Takei Y, Kido MA, Hirokawa N (2011). Molecular motor KIF17 is fundamental for memory and learning via differential support of synaptic NR2A/2B levels. Neuron 70, 310-325.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
Yuan M, Shaw PJ, Warn RM, Lloyd CW (1994). Dynamic reorientation of cortical microtubules, from transverse to longitudinal, in living plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91, 6050-6053.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
Zhang M, Zhang BC, Qian Q, Yu YC, Li R, Zhang JW, Liu XL, Zeng DL, Li JY, Zhou YH (2010). Brittle Culm 12, a dual-targeting Kinesin-4 protein, controls cell-cycle progression and wall properties in rice. Plant J 63, 312-328.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
Zhong RQ, Burk DH, Morrison III WH, Ye ZH (2002). A kinesin-like protein is essential for oriented deposition of cellulose microfibrils and cell wall strength. Plant Cell 14, 3101-3117.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
Zhou SR, Wang Y, Li WC, Zhao ZG, Ren YL, Wang Y, Gu SH, Lin QB, Wang D, Jiang L, Su N, Zhang X, Liu LL, Cheng ZJ, Lei CL, Wang JL, Guo XP, Wu FQ, Ikehashi H, Wang HY, Wan JM (2011). Pollen Semi-Sterility 1 encodes a kinesin-1-like protein important for male meiosis, anther dehiscence, and fertility in rice. Plant Cell 23, 111-129.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
Zhu CM, Dixit R (2012). Functions of the Arabidopsis kinesin superfamily of microtubule-based motor proteins. Protoplasma 249, 887-899.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Zhu CM, Ganguly A, Baskin TI, McClosky DD, Anderson CT, Foster C, Meunier KA, Okamoto R, Berg H, Dixit R (2015). The Fragile Fiber 1 kinesin contributes to cortical microtubule-mediated trafficking of cell wall components. Plant Physiol 167, 780-792.
DOI |
| [96] |
Zou JJ, Zheng ZY, Xue S, Li HH, Wang YR, Le J (2016). The role of Arabidopsis Actin-Related Protein 3 in amyloplast sedimentation and polar auxin transport in root gravitropism. J Exp Bot 67, 5325-5337.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 郑立媛, 徐茜竹, 尹嘉淇, 孙小雯, 王艳. 沈阳城郊近河农田退耕地野大豆群落生态位和种间联结研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 1-. |
| [2] | 曹婕, 卢秋连, 翟健平, 刘宝辉, 方超, 李世晨, 苏彤. 大豆TPS基因家族在盐胁迫下的表达变化及单倍型选择规律分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 172-185. |
| [3] | 陈佳欣, 梅浩, 黄彩翔, 梁宗原, 全依桐, 李东鹏, 布威麦尔耶姆·赛麦提, 李欣欣, 廖红. 利用转基因毛状根高效培育大豆嵌合植株的方法[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 89-98. |
| [4] | 杜梦柯, 连文婷, 张晓, 李欣欣. 氮处理对大豆根瘤固氮能力及GmLbs基因表达的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 391-403. |
| [5] | 张慧, 刘倩, 黄晓磊. 社会性昆虫级型和行为分化机制研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 507-516. |
| [6] | 夏正俊, 李玉卓, 朱金龙, 吴红艳, 徐坤, 翟红. 快速、无损大豆种子连续取样技术及其DNA制备[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 56-61. |
| [7] | 王研, 贾博为, 孙明哲, 孙晓丽. 野生大豆耐逆分子调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 104-115. |
| [8] | 祝光涛,黄三文. 360度群体遗传变异扫描——大豆泛基因组研究[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 403-406. |
| [9] | 冯锋,战勇,田志喜. 新疆地区发展大豆生产的可行性和初步建议[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 199-204. |
| [10] | 唐康,杨若林. 大豆蛋白编码基因起源与进化[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 316-327. |
| [11] | 叶子飘, 段世华, 安婷, 康华靖. 最大电子传递速率的确定及其对电子流分配的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(4): 498-507. |
| [12] | 艾文琴, 姜瀚原, 李欣欣, 廖红. 一种高效研究大豆根瘤共生固氮的营养液栽培体系[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(4): 519-527. |
| [13] | 吴国栋, 修宇, 王华芳. 优化子叶节转化法培育大豆MtDREB2A转基因植株[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 59-71. |
| [14] | 李艳, 盖钧镒. 大豆向热带地区发展的遗传基础[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(4): 389-393. |
| [15] | 夏正俊. 大豆基因组解析与重要农艺性状基因克隆研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(2): 148-158. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||