

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 391-403.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21037 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21037
• 研究报告 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2021-02-13
接受日期:2021-05-07
出版日期:2021-07-01
发布日期:2021-06-30
通讯作者:
李欣欣
作者简介:*E-mail: xxli@fafu.edu.cn基金资助:
Mengke Du, Wenting Lian, Xiao Zhang, Xinxin Li*( )
)
Received:2021-02-13
Accepted:2021-05-07
Online:2021-07-01
Published:2021-06-30
Contact:
Xinxin Li
摘要: 共生根瘤的固氮效率受外界氮素的严格调控。除固氮酶活性外, 豆血红蛋白(Lb)浓度亦是反应固氮能力的重要指标。为明确氮水平对生物固氮作用的影响, 以大豆(Glycine max)为材料, 在低氮(0.53 mmol·L-1)条件下接种根瘤菌, 30天后再进行高氮(5.3、10、20、30和40 mmol·L-1)处理7天, 分析Lb浓度、固氮酶活性及类菌体发育状态。结果表明, 随着外界氮浓度的增加, 根瘤由红变绿, 且红色Lb明显减少而绿色Lb急剧增加; 固氮酶活性显著被抑制, 类菌体中侵染细胞数目和面积显著下降, 表明高氮引起Lb形态的改变与固氮能力关系密切。利用生物信息学及公开表达谱等数据进行分析, 发现大豆根瘤中主要含有4个共生Lb基因, 即GmLb1、GmLb2、GmLb3和GmLb4。4个GmLbs亲缘关系很近且位于进化树的同一分支。进一步分析GmLb1-4转录水平对氮的响应, 结果表明, GmLb1-4的表达显著受高氮抑制。研究结果可为揭示氮介导根瘤衰老机制及生物固氮的应用提供依据。
杜梦柯, 连文婷, 张晓, 李欣欣. 氮处理对大豆根瘤固氮能力及GmLbs基因表达的影响. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 391-403.
Mengke Du, Wenting Lian, Xiao Zhang, Xinxin Li. Effects of Nitrogen Application on Nitrogen Fixation Capacity and GmLbs Expression in Soybean. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 391-403.
| Name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| GmLb1-qF | CCTCGATACTGGAGAAAGCACC |
| GmLb1-qR | CAAGTGCGGCATCAATCACC |
| GmLb2-qF | AATGGAACAGTGGTGGCTGA |
| GmLb2-qR | AGCACTGCTCAATTCGTCAC |
| GmLb3-qF | CCGCACTTGGTTCTGTTCAT |
| GmLb3-qR | TGCTGCCAATTCATCGTAGG |
| GmLb4-qF | GATCTACTATTGCCGTCAA |
| GmLb4-qR | GCATCGATTATGATTCACA |
表1 用于qRT-PCR分析的基因特异性引物
Table 1 Gene-specific primers used for qRT-PCR analysis
| Name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| GmLb1-qF | CCTCGATACTGGAGAAAGCACC |
| GmLb1-qR | CAAGTGCGGCATCAATCACC |
| GmLb2-qF | AATGGAACAGTGGTGGCTGA |
| GmLb2-qR | AGCACTGCTCAATTCGTCAC |
| GmLb3-qF | CCGCACTTGGTTCTGTTCAT |
| GmLb3-qR | TGCTGCCAATTCATCGTAGG |
| GmLb4-qF | GATCTACTATTGCCGTCAA |
| GmLb4-qR | GCATCGATTATGATTCACA |
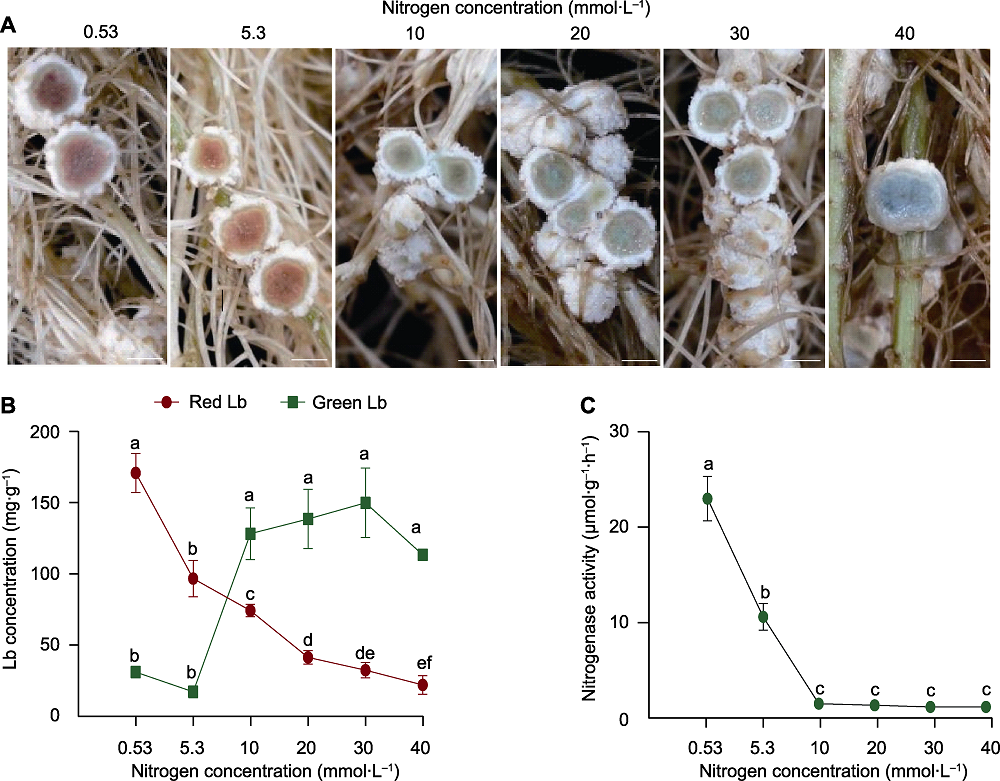
图1 供氮水平对大豆根瘤豆血红蛋白(Lb)浓度及固氮能力的影响 (A) 根瘤横切图; (B) 豆血红蛋白浓度; (C) 固氮酶活性。实验设置4个生物学重复, 每个重复随机取2或3个根瘤测定豆血红蛋白浓度和固氮酶活性。数据为10个根瘤的平均值±标准误。不同小写字母代表不同供氮水平间差异显著(P<0.05)。Bars=2 mm
Figure 1 Effects of nitrogen supply on leghemoglobin (Lb) concentration and nitrogenase activity of soybean nodules (A) Cross section of nodules; (B) Leghemoglobin concentration; (C) Nitrogenase activity. There were 4 biological replicates, 2 or 3 nodules were randomly harvested for Lb concentration and nitrogenase activity analysis. Data are means±SE from 10 nodules. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different N supply levels (P<0.05). Bars=2 mm
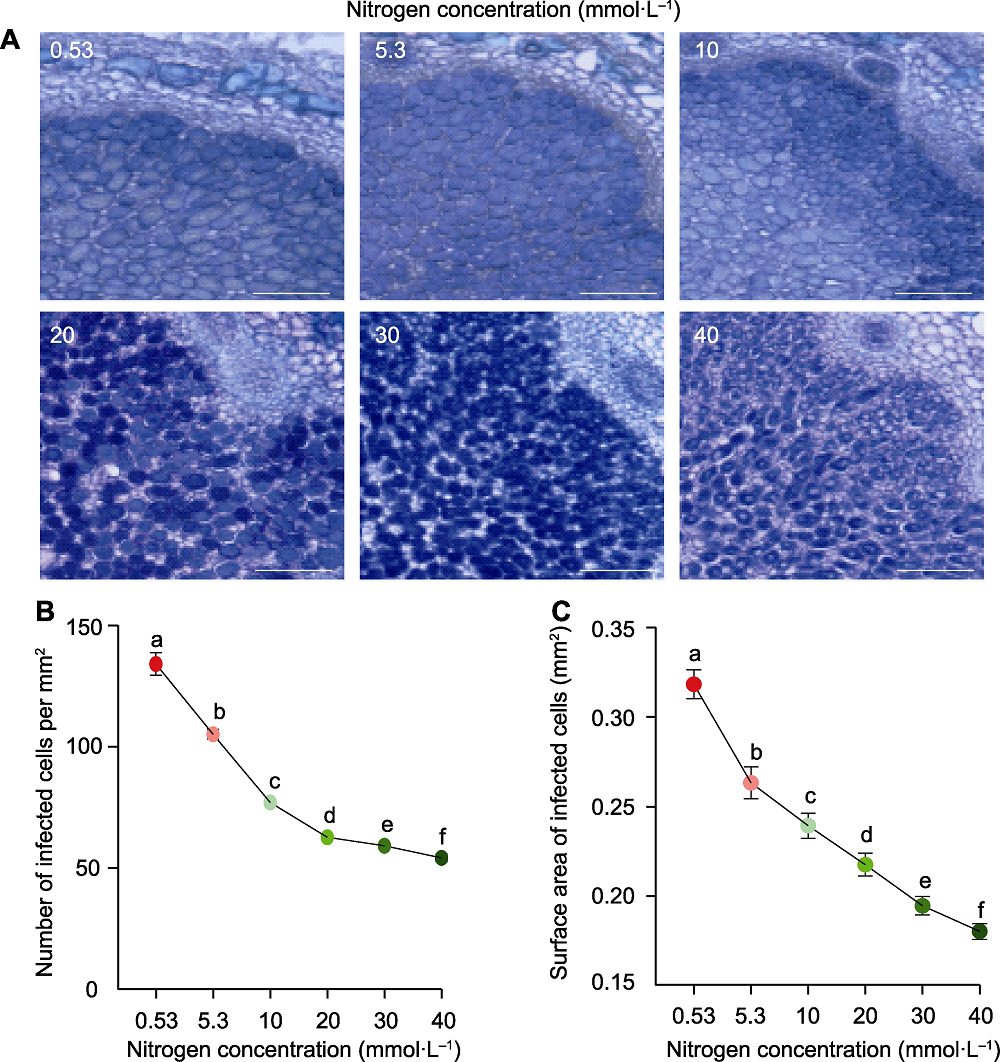
图2 供氮水平对根瘤侵染细胞发育的影响 (A) 甲苯胺蓝染色的根瘤横切面; (B) 侵染细胞数目; (C) 侵染细胞表面积。数据为40个根瘤横切面的平均值±标准误。不同小写字母代表不同供氮水平间差异显著(P<0.05)。Bars=200 µm
Figure 2 Effects of nitrogen supply on the infected cell development in nodules (A) Toluidine blue-stained nodule cross-sections; (B) Number of infected cells; (C) Surface area of infected cells. Data are means±SE from 40 cross of nodules. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different N supply levels (P<0.05). Bars=200 µm
| Gene name | Phytozome locus9.1 | Phytozome locus12.0 | NCBI number | Accession number | Location coordinates (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GmLb1 | Glyma10g34260 | Glyma.10G198800.1 | NM_001248494.2 | BT092230 | 42996028-42997092 |
| GmLb2 | Glyma10g34280 | Glyma.10G199000.1 | NM_001358072.1 | FK026737 | 43004554-43005947 |
| GmLb3 | Glyma10g34290 | Glyma.10G199100.1 | NM_001248999.3 | BT092268 | 43009363-43011021 |
| GmLb4 | Glyma20g33290 | Glyma.20G191200.1 | NM_001248319.3 | BT092218 | 42993081-42994203 |
| GmLb5 | Glyma10g34275 | Glyma.10G198900.1 | - | - | 43000045-43003378 |
| GmHb1 | Glyma11g12960 | Glyma.11G121700.1 | NM_001255274.2 | BT098807 | 9299437-9300752 |
| GmHb2 | Glyma11g12980 | Glyma.11G121800.1 | NM_001357481.1 | BT096529 | 9303967-9305430 |
表2 大豆GmLbs/GmHbs基因信息
Table 2 Information of GmLbs/GmHbs genes in soybean
| Gene name | Phytozome locus9.1 | Phytozome locus12.0 | NCBI number | Accession number | Location coordinates (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GmLb1 | Glyma10g34260 | Glyma.10G198800.1 | NM_001248494.2 | BT092230 | 42996028-42997092 |
| GmLb2 | Glyma10g34280 | Glyma.10G199000.1 | NM_001358072.1 | FK026737 | 43004554-43005947 |
| GmLb3 | Glyma10g34290 | Glyma.10G199100.1 | NM_001248999.3 | BT092268 | 43009363-43011021 |
| GmLb4 | Glyma20g33290 | Glyma.20G191200.1 | NM_001248319.3 | BT092218 | 42993081-42994203 |
| GmLb5 | Glyma10g34275 | Glyma.10G198900.1 | - | - | 43000045-43003378 |
| GmHb1 | Glyma11g12960 | Glyma.11G121700.1 | NM_001255274.2 | BT098807 | 9299437-9300752 |
| GmHb2 | Glyma11g12980 | Glyma.11G121800.1 | NM_001357481.1 | BT096529 | 9303967-9305430 |
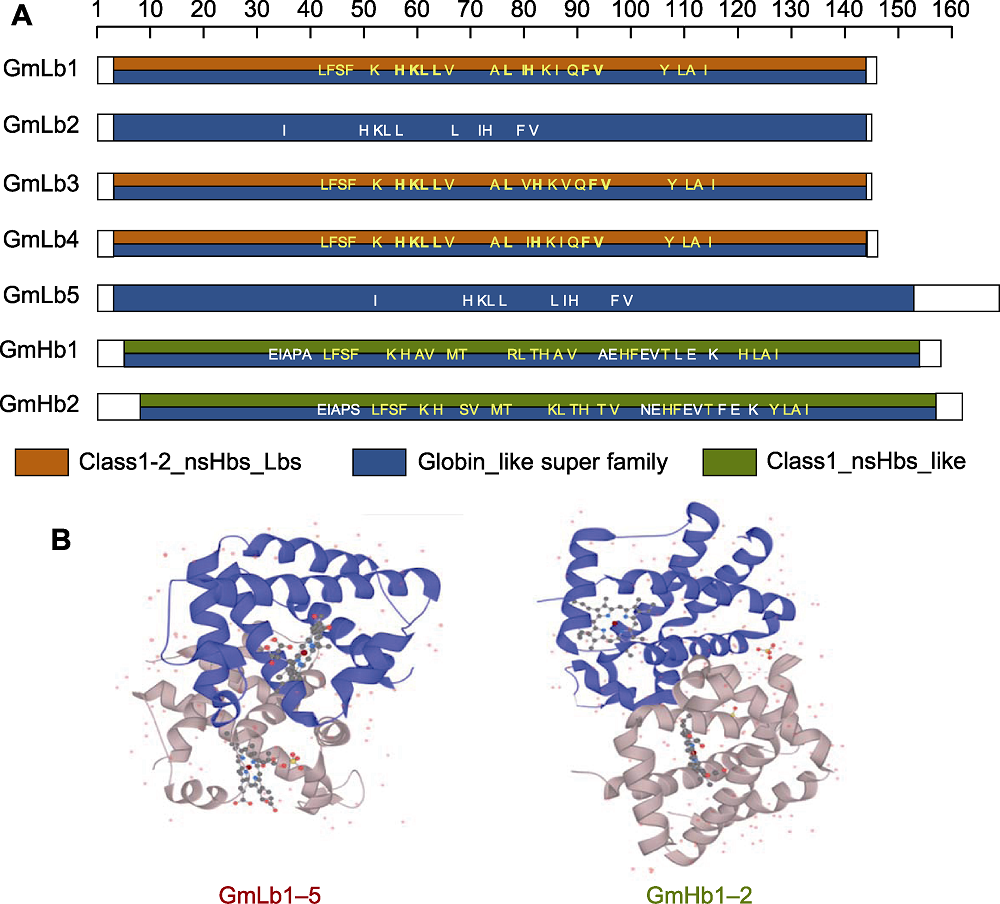
图3 豆血红蛋白功能域和3D结构预测 (A) 保守功能域预测(黄色字体为血红素结合位点, 黑色字体为辅助因子结合位点, 白色字体为多肽结合位点); (B) 蛋白3D结构预测
Figure 3 Prediction of the conserved domain and 3D protein structure of leghemoglobin (A) Prediction of the conserved domains (the yellow font represents the heme binding site, the black font represents the cofactor binding site, and the white font represents polypeptide binding site); (B) Prediction of 3D protein structure
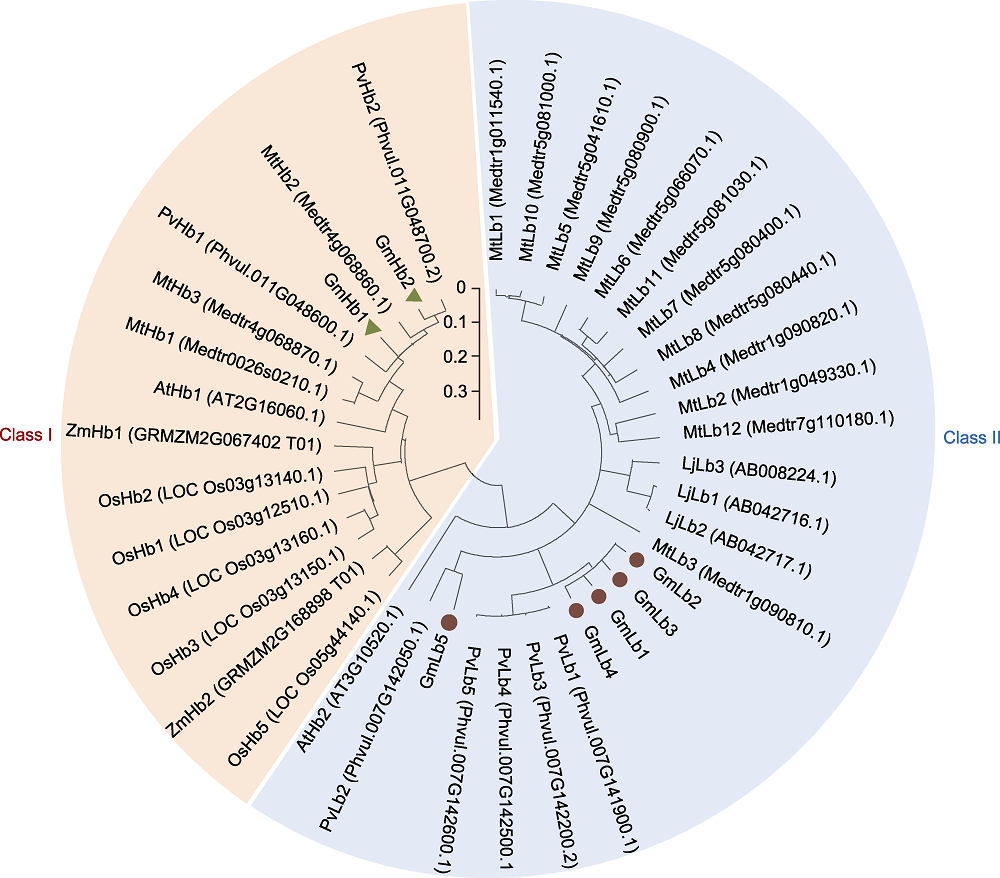
图4 血红蛋白系统进化树 利用MEGA 6.1软件中的邻接法构建系统进化树。
Figure 4 Phylogenetic tree of hemoglobin This phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method in the MEGA 6.1 program.
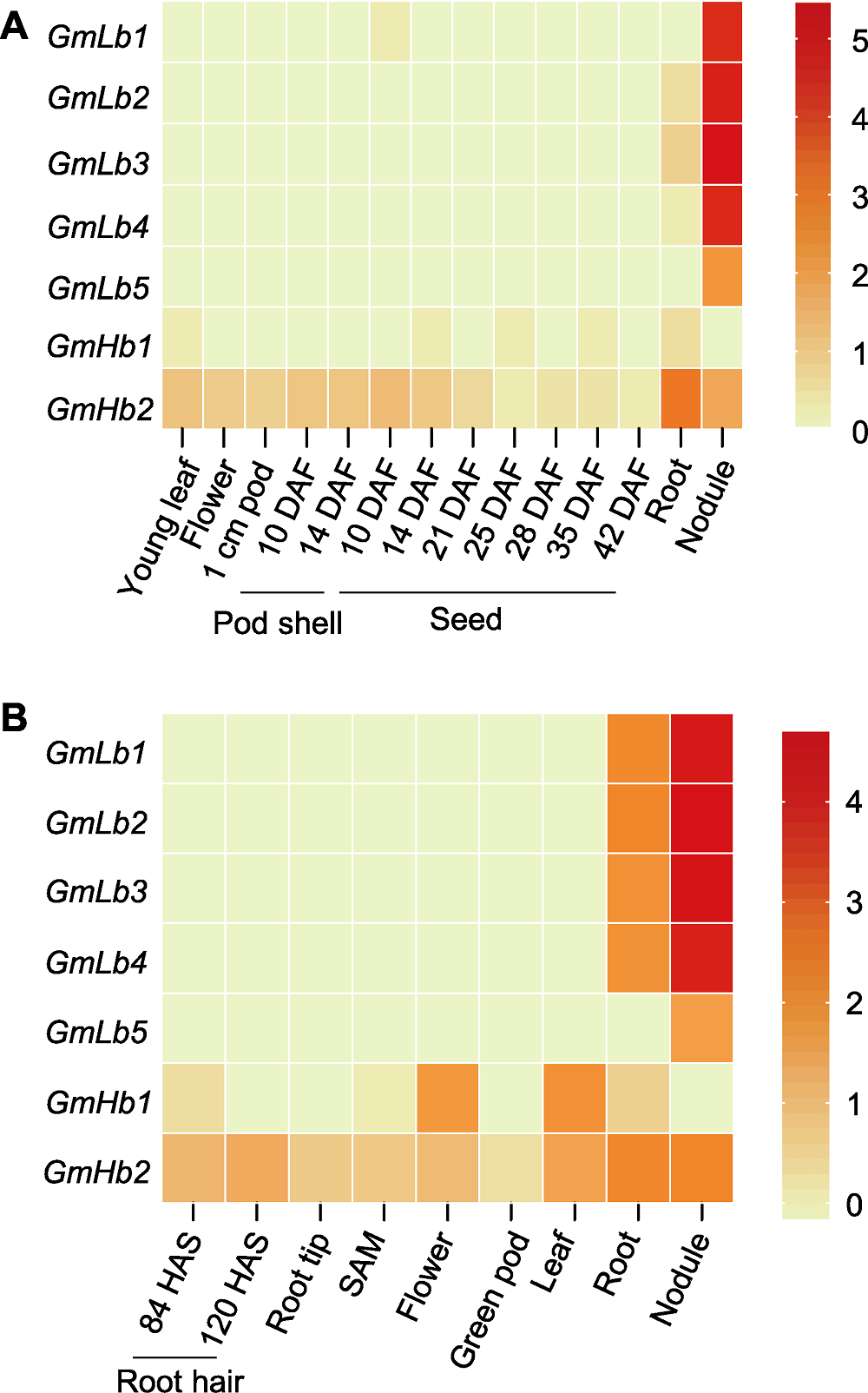
图5 大豆GmLbs和GmHbs基因表达热图 (A) RNA-seq数据来源于Soybase网站(https://www.soybase.org); (B) RNA-seq数据来自Libault等(2010)。不同来源的RNA-seq数据通过log10 (FPKM+1)计算后进行热图分析。DAF: 开花后天数; HAS: 播种后小时数; SAM: 顶端分生组织
Figure 5 Heatmaps of GmLbs and GmHbs gene expression in soybean (A) The RNA-seq data obtained from Soybase website (https://www.soybase.org); (B) The RNA-seq data obtained from Libault et al. (2010). RNA-seq data of different sources were calculated with log10(FPKM+1) and further used to generate the heatmaps. DAF: Days after flowering; HAS: Hours after sowing; SAM: Shoot apical meristem
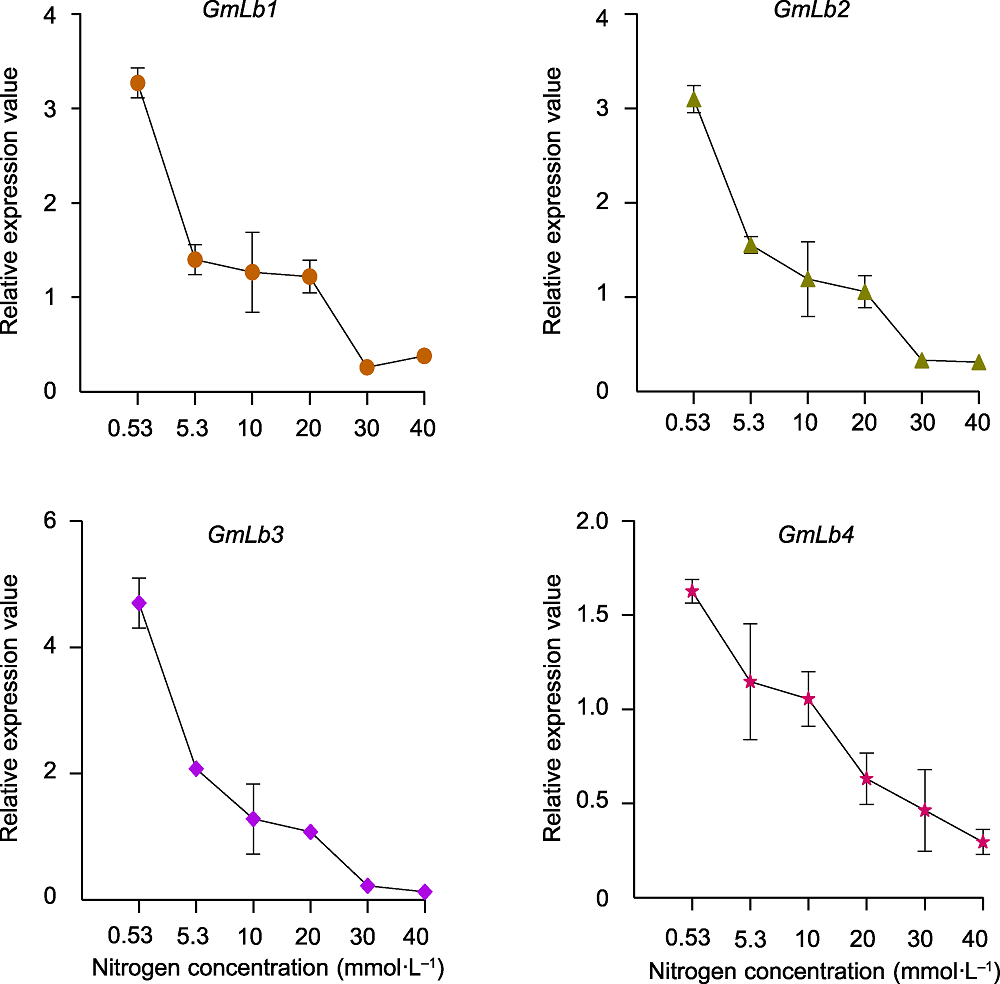
图6 GmLb1-4在不同氮浓度下的相对表达量 数据为3个生物学重复的平均值±标准误。
Figure 6 Relative expression value of GmLb1-4 in soybean nodules under different nitrogen concentrations Data are means±SE of 3 biological replicates.
| [1] | 艾文琴, 姜瀚原, 李欣欣, 廖红 (2018). 一种高效研究大豆根瘤共生固氮的营养液栽培体系. 植物学报 53, 519-527. |
| [2] | 程凤娴, 曹桂芹, 王秀荣, 赵静, 严小龙, 廖红 (2008). 华南酸性低磷土壤中大豆根瘤菌高效株系的发现及应用. 科学通报 53, 2903-2910. |
| [3] | 黎健龙, 涂攀峰, 陈娜, 唐劲驰, 王秀荣, 年海, 廖红, 严小龙 (2008). 茶树与大豆间作效应分析. 中国农业科学 41, 2040-2047. |
| [4] | 李欣欣, 杨永庆, 钟永嘉, 廖红 (2019). 豆科作物适应酸性土壤的养分高效根系遗传改良. 华南农业大学学报 40(5), 186-194. |
| [5] | 农玉琴, 黄少欣, 刘振洋, 廖春文, 韦锦坚, 陆金梅, 陈远权, 覃潇敏 (2019). 茶豆间作体系氮素对茶叶营养成分的影响. 安徽农业科学 47(21), 160-162. |
| [6] |
Appleby CA (1984). Leghemoglobin and rhizobium respiration. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35, 443-478.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Berger A, Guinand S, Boscari A, Puppo A, Brouquisse R (2020). Medicago truncatula Phytoglobin 1.1 controls symbiotic nodulation and nitrogen fixation via the regulation of nitric oxide concentration. New Phytol 227, 84-98.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Bergersen FJ, Goodchild DJ (1973). Cellular location and concentration of leghaemoglobin in soybean root nodules. Aust J BioI Sci 26, 741-756. |
| [9] |
Brisson N, Verma DP (1982). Soybean leghemoglobin gene family: normal, pseudo, and truncated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79, 4055-4059.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Chen LY, Qin L, Zhou LL, Li XX, Chen ZC, Sun LL, Wang WF, Lin ZH, Zhao J, Yamaji N, Ma JF, Gu M, Xu GH, Liao H (2019a). A nodule-localized phosphate transporter GmPT7 plays an important role in enhancing symbiotic N2 fixation and yield in soybean. New Phytol 221, 2013-2025.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Chen P, Song C, Liu XM, Zhou L, Yang H, Zhang XN, Zhou Y, Du Q, Pang T, Fu ZD, Wang XC, Liu WG, Yang F, Shu K, Du JB, Liu J, Yang WY, Yong TW (2019b). Yield advantage and nitrogen fate in an additive maize- soybean relay intercropping system. Sci Total Environ 657, 987-999.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Dakora FD (1995). A functional relationship between leghaemoglobin and nitrogenase based on novel measurements of the two proteins in legume root nodules. Ann Bot 75, 49-54.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Dakora FD, Appleby CA, Atkins CA (1991). Effect of pO2 on the formation and status of leghemoglobin in nodules of cowpea and soybean. Plant Physiol 95, 723-730.
PMID |
| [14] |
Du MK, Gao Z, Li XX, Liao H (2020). Excess nitrate induces nodule greening and reduces transcript and protein expression levels of soybean leghaemoglobins. Ann Bot 126, 61-72.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Fuchsman WH, Appleby CA (1979). Separation and determination of the relative concentrations of the homogeneous components of soybean leghemoglobin by isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta-Protein Struct 579, 314-324.
PMID |
| [16] |
Fujikake H, Yamazaki A, Ohtake N, Sueyoshi K, Matsuhashi S, Ito T, Mizuniwa C, Kume T, Hashimoto S, Ishioka NS, Watanabe S, Osa A, Sekine T, Uchida H, Tsuji A, Ohyama T (2003). Quick and reversible inhibition of soybean root nodule growth by nitrate involves a decrease in sucrose supply to nodules. J Exp Bot 54, 1379-1388.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Gan YB, Stulen I, van Keulen H, Kuiper PJC (2004). Low concentrations of nitrate and ammonium stimulate nodulation and N2 fixation while inhibiting specific nodulation (nodule DW·g-1 root dry weight) and specific N2 fixation (N2 fixed·g-1 root dry weight) in soybean. Plant Soil 258, 281-292.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Garrocho-Villegas V, Gopalasubramaniam SK, Arredondo- Peter R (2007). Plant hemoglobins: what we know six decades after their discovery. Gene 398, 78-85.
PMID |
| [19] |
Gautrat P, Laffont C, Frugier F, Ruffel S (2021). Nitrogen systemic signaling: from symbiotic nodulation to root acquisition. Trends Plant Sci 26, 392-406.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Hargrove MS, Brucker EA, Stec B, Sarath G, Arredondo-Peter R, Klucas RV, Olson JS, Phillips GN Jr (2000). Crystal structure of a nonsymbiotic plant hemoglobin. Structure 8, 1005-1014.
PMID |
| [21] |
Herridge DF, Peoples MB, Boddey RM (2008). Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 311, 1-18.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Hoy JA, Hargrove MS (2008). The structure and function of plant hemoglobins. Plant Physiol Biochem 46, 371-379.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Khan AA, Khan AA (1981). Effects of nitrate nitrogen on growth, nodulation and distribution of 14C-labelled photosynthates in cowpea. Plant Soil 63, 141-147.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LaRue TA, Child JJ (1979). Sensitive fluorometric assay for leghemoglobin. Anal Biochem 92, 11-15.
PMID |
| [25] |
Li X, Feng H, Wen JQ, Dong JL, Wang T (2018a). MtCAS31 aids symbiotic nitrogen fixation by protecting the leghemoglobin MtLb120-1 under drought stress in Medicago truncatula. Front Plant Sci 9, 633.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Li XX, Zhao J, Tan ZY, Zeng RS, Liao H (2015). GmEXPB2, a cell wall β-expansin, affects soybean nodulation through modifying root architecture and promoting nodule formation and development. Plant Physiol 169, 2640-2653. |
| [27] |
Li XX, Zheng JK, Yang YQ, Liao H (2018b). INCREASING NODULE SIZE 1 expression is required for normal rhizobial symbiosis and nodule development. Plant Physiol 178, 1233-1248.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Libault M, Farmer A, Joshi T, Takahashi K, Langley RJ, Franklin LD, He J, Xu D, May G, Stacey G (2010). An integrated transcriptome atlas of the crop model Glycine max, and its use in comparative analyses in plants. Plant J 63, 86-99. |
| [29] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
PMID |
| [30] |
Marcker A, Lund M, Jensen EØ, Marcker KA (1984). Transcription of the soybean leghemoglobin genes during nodule development. EMBO J 3, 1691-1695.
PMID |
| [31] |
Minchin FR, Minguez MI, Sheehy JE, Witty JF, Skøt L (1986). Relationships between nitrate and oxygen supply in symbiotic nitrogen fixation by white clover. J Exp Bot 37, 1103-1113.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Navascués J, Pérez-Rontomé C, Gay M, Marcos M, Yang F, Walker FA, Desbois A, Abián J, Becana M (2012). Leghemoglobin green derivatives with nitrated hemes evidence production of highly reactive nitrogen species during aging of legume nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 2660-2665.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Ott T, Sullivan J, James EK, Flemetakis E, Günther C, Gibon Y, Ronson C, Udvardi M (2009). Absence of symbiotic leghemoglobins alters bacteroid and plant cell differentiation during development of Lotus japonicus root nodules. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22, 800-808.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Ott T, van Dongen JT, Günther C, Krusell L, Desbrosses G, Vigeolas H, Bock V, Czechowski T, Geigenberger P, Udvardi MK (2005). Symbiotic leghemoglobins are crucial for nitrogen fixation in legume root nodules but not for general plant growth and development. Curr Biol 15, 531-535.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Prudent M, Vernoud V, Girodet S, Salon C (2016). How nitrogen fixation is modulated in response to different water availability levels and during recovery: a structural and functional study at the whole plant level. Plant Soil 399, 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Sainz M, Calvo-Begueria L, Pérez-Rontomé C, Wienkoop S, Abián J, Staudinger C, Bartesaghi S, Radi R, Becana M (2015). Leghemoglobin is nitrated in functional legume nodules in a tyrosine residue within the heme cavity by a nitrite/peroxide-dependent mechanism. Plant J 81, 723-735.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Sinclair TR, Serraj R (1995). Legume nitrogen fixation and drought. Nature 378, 344.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Stasolla C, Hill RD (2017). Determining cellular responses: phytoglobins may direct the traffic. Trends Plant Sci 22, 820-822.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Vázquez-Limón C, Hoogewijs D, Vinogradov SN, Arredondo-Peter R (2012). The evolution of land plant hemoglobins. Plant Sci 191-192, 71-81.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Virtanen AI, Laine T (1946). Red, brown and green pigments in leguminous root nodules. Nature 157, 25-26.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Xia X, Ma CM, Dong SK, Xu Y, Gong ZP (2017). Effects of nitrogen concentrations on nodulation and nitrogenase activity in dual root systems of soybean plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 63, 470-482.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Xu HY, Li YJ, Zhang KF, Li MJ, Fu SY, Tian YZ, Qin TF, Li XX, Zhong YJ, Liao H (2021). miR169c-NFYA-C-ENOD40 modulates nitrogen inhibitory effects in soybean nodulation. New Phytol 229, 3377-3392.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Zhang H, Zeng FP, Zou ZG, Zhang ZQ, Li YZ (2017). Nitrogen uptake and transfer in a soybean/maize intercropping system in the karst region of southwest China. Ecol Evol 7, 8419-8426.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 郑立媛, 徐茜竹, 尹嘉淇, 孙小雯, 王艳. 沈阳城郊近河农田退耕地野大豆群落生态位和种间联结研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 1-. |
| [2] | 曹婕, 卢秋连, 翟健平, 刘宝辉, 方超, 李世晨, 苏彤. 大豆TPS基因家族在盐胁迫下的表达变化及单倍型选择规律分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 172-185. |
| [3] | 陈佳欣, 梅浩, 黄彩翔, 梁宗原, 全依桐, 李东鹏, 布威麦尔耶姆·赛麦提, 李欣欣, 廖红. 利用转基因毛状根高效培育大豆嵌合植株的方法[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 89-98. |
| [4] | 王韫慧, 王一帆, 蔺佳雨, 李金红, 姚士恩, 冯湘池, 曹振林, 王俊, 李美娜. 植物驱动蛋白: 从微管阵列到生理活动调控[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 358-374. |
| [5] | 王研, 贾博为, 孙明哲, 孙晓丽. 野生大豆耐逆分子调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 104-115. |
| [6] | 王银柳, 耿倩倩, 黄建辉, 王常慧, 李磊, 哈斯木其尔, 牛国祥. 氮肥和种植密度对达乌里胡枝子的生长与生物固氮的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(1): 13-22. |
| [7] | 夏正俊, 李玉卓, 朱金龙, 吴红艳, 徐坤, 翟红. 快速、无损大豆种子连续取样技术及其DNA制备[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 56-61. |
| [8] | 刘承武, 赵忠. 豆科植物SHR-SCR模块——根瘤“奠基细胞”的命运推手[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 661-665. |
| [9] | 祝光涛,黄三文. 360度群体遗传变异扫描——大豆泛基因组研究[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 403-406. |
| [10] | 冯锋,战勇,田志喜. 新疆地区发展大豆生产的可行性和初步建议[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 199-204. |
| [11] | 王雪梅, 闫帮国, 史亮涛, 刘刚才. 车桑子幼苗生物量分配与叶性状对氮磷浓度的响应差异[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(12): 1247-1261. |
| [12] | 唐康,杨若林. 大豆蛋白编码基因起源与进化[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 316-327. |
| [13] | 艾文琴, 姜瀚原, 李欣欣, 廖红. 一种高效研究大豆根瘤共生固氮的营养液栽培体系[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(4): 519-527. |
| [14] | 叶子飘, 段世华, 安婷, 康华靖. 最大电子传递速率的确定及其对电子流分配的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(4): 498-507. |
| [15] | 吴国栋, 修宇, 王华芳. 优化子叶节转化法培育大豆MtDREB2A转基因植株[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 59-71. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||