

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (6): 903-911.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24085 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24085
所属专题: 玉米生物学与分子设计(2024年59卷6期)
于晓琳, 李西雅, 夏冰玉洁, 李昊, 谭保才, 王勇*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-01
接受日期:2024-08-20
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-08-28
通讯作者:
*王勇, 博士, 副研究员, 硕士生导师。其研究团队主要从事玉米种子发育关键基因克隆、功能解析和RNA加工机制研究, 系统解析了多个基因的功能, 并明确了这些基因参与细胞器RNA加工以及玉米种子发育的分子机制。相关成果以第一作者身份发表在Plant Cell、Plant Commun、PLoS Genet、Plant J和Front Plant Sci等学术期刊; 以合作者身份在Nat Commun、Proc Natl Acad Sci USA、New Phytol、Plant Physiol、J Integr Plant Biol和J Exp Bot等国际主流学术期刊发表论文10余篇。主持国家自然科学基金等项目多项。E-mail: wangy07@sdu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xiaolin Yu, Xiya Li, Bingyujie Xia, Hao Li, Baocai Tan, Yong Wang*( )
)
Received:2024-06-01
Accepted:2024-08-20
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-08-28
Contact:
*E-mail: wangy07@sdu.edu.cn
摘要: 植物体中线粒体和叶绿体是半自主细胞器, 具有自己的基因组。RNA编辑对于细胞器基因的正确表达至关重要, 最常见的RNA编辑是C→U。RNA C→U编辑需要多种编辑因子参与, 其中PPR蛋白中的PPR基序阵列特异性地靶向编辑位点, PPR-DYW蛋白DYW结构域是催化C→U编辑的脱氨酶。该文综述了PPR蛋白参与RNA C→U编辑机制的最新研究进展, 并讨论了人工合成PPR编辑因子的潜在应用价值。
于晓琳, 李西雅, 夏冰玉洁, 李昊, 谭保才, 王勇. PPR蛋白参与细胞器RNA C→U编辑机制研究进展. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 903-911.
Xiaolin Yu, Xiya Li, Bingyujie Xia, Hao Li, Baocai Tan, Yong Wang. Research Advance of PPR Proteins Involved in the Mechanism of Organelle RNA C→U Editing. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 903-911.
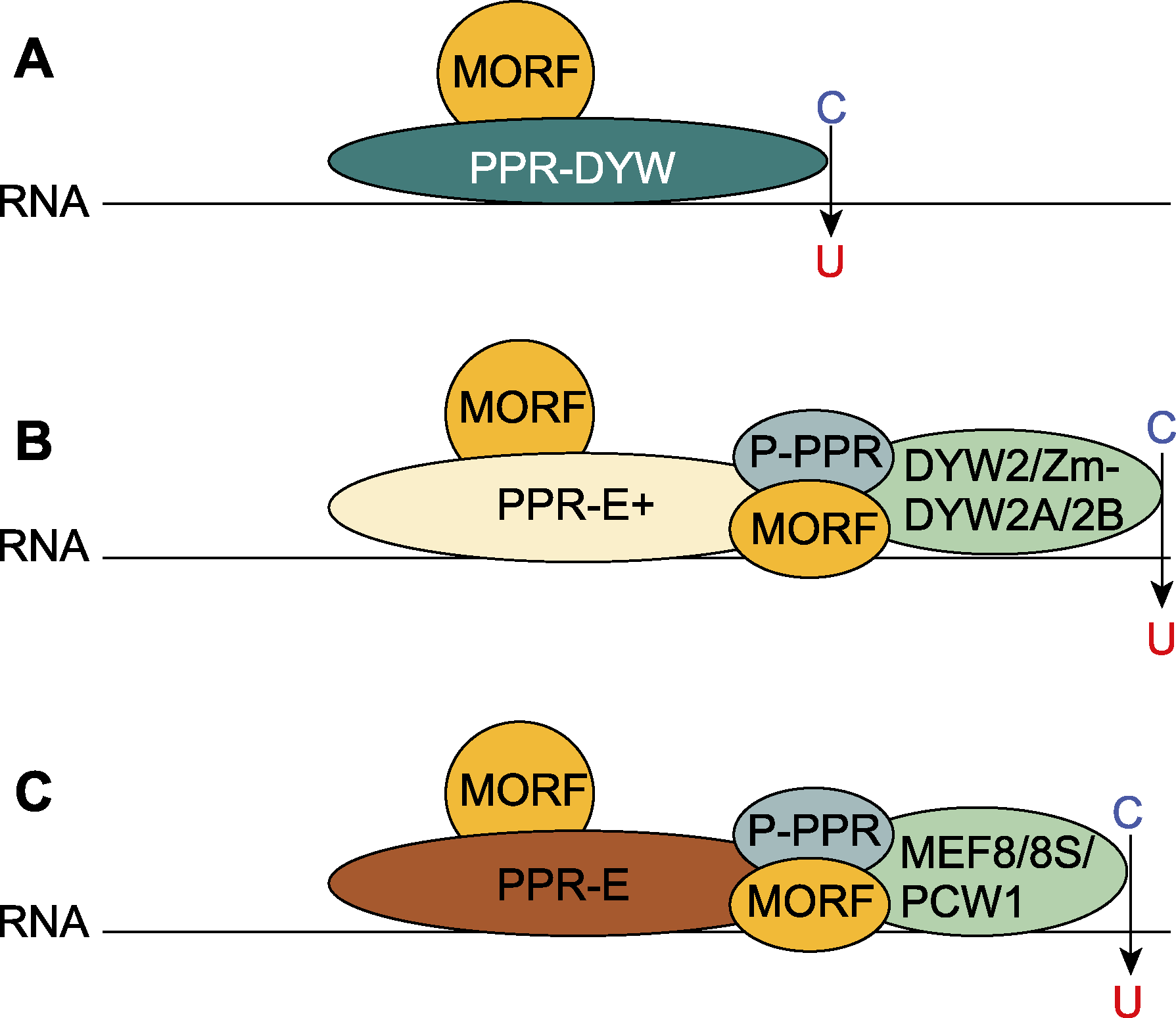
图1 PPR蛋白参与RNA C→U编辑的工作模型 (A) PPR-DYW; (B) PPR-E+; (C) PPR-E
Figure 1 Models of PPR proteins involved in RNA C→U edi- ting (A) PPR-DYW; (B) PPR-E+; (C) PPR-E
| [1] |
Andrés-Colás N, Zhu Q, Takenaka M, De Rybel B, Weijers D, Van Der Straeten D (2017). Multiple PPR protein interactions are involved in the RNA editing system in Arabidopsis mitochondria and plastids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 8883-8888.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Barkan A, Rojas M, Fujii S, Yap A, Chong YS, Bond CS, Small I (2012). A combinatorial amino acid code for RNA recognition by pentatricopeptide repeat proteins. PLoS Genet 8, e1002910. |
| [3] |
Barkan A, Small I (2014). Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65, 415-442.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Bentolila S, Heller WP, Sun T, Babina AM, Friso G, van Wijk KJ, Hanson MR (2012). RIP1, a member of an Arabidopsis protein family, interacts with the protein RARE1 and broadly affects RNA editing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, E1453-E1461. |
| [5] | Bentolila S, Oh J, Hanson MR, Bukowski R (2013). Comprehensive high-resolution analysis of the role of an Arabidopsis gene family in RNA editing. PLoS Genet 9, e1003584. |
| [6] | Bernath-Levin K, Schmidberger J, Honkanen S, Gutmann B, Sun YK, Pullakhandam A, des Francs-Small CC, Bond CS, Small I (2022). Cofactor-independent RNA editing by a synthetic S-type PPR protein. Synth Biol 7, ysab034. |
| [7] |
Blanc V, Litvak S, Araya A (1995). RNA editing in wheat mitochondria proceeds by a deamination mechanism. FEBS Lett 373, 56-60.
PMID |
| [8] |
Boussardon C, Avon A, Kindgren P, Bond CS, Challenor M, Lurin C, Small I (2014). The cytidine deaminase signature HxE(x)nCxxC of DYW1 binds zinc and is necessary for RNA editing of ndhD-1. New Phytol 203, 1090-1095.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Boussardon C, Salone V, Avon A, Berthome R, Hammani K, Okuda K, Shikanai T, Small I, Lurin C (2012). Two interacting proteins are necessary for the editing of the NdhD-1 site in Arabidopsis plastids. Plant Cell 24, 3684-3694. |
| [10] |
Brown GG, des Francs-Small CC, Ostersetzer-Biran O (2014). Group II intron splicing factors in plant mitochondria. Front Plant Sci 5, 35.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Cheng SF, Gutmann B, Zhong X, Ye YT, Fisher MF, Bai FQ, Castleden I, Song Y, Song B, Huang JY, Liu X, Xu X, Lim BL, Bond CS, Yiu SM, Small I (2016). Redefining the structural motifs that determine RNA binding and RNA editing by pentatricopeptide repeat proteins in land plants. Plant J 85, 532-547. |
| [12] | Deng LK, Li Y, Yu JN (2012). RNA editing sites in chloroplast protein-coding genes in leaf white mutant of Triticum aestivum. Chin Bull Bot 47, 581-593. (in Chinese) |
|
邓李坤, 李妍, 俞嘉宁 (2012). 小麦叶绿体蛋白质编码基因RNA编辑位点的测定及与返白现象的关系. 植物学报 47, 581-593.
DOI |
|
| [13] | Diaz MF, Bentolila S, Hayes ML, Hanson MR, Mulligan RM (2017). A protein with an unusually short PPR domain, MEF8, affects editing at over 60 Arabidopsis mitochondrial C targets of RNA editing. Plant J 92, 638-649. |
| [14] | Ding YH, Liu NY, Tang ZS, Liu J, Yang WC (2006). Arabidopsis GLUTAMINE-RICH PROTEIN23 is essential for early embryogenesis and encodes a novel nuclear PPR motif protein that interacts with RNA polymerase II subunit III. Plant Cell 18, 815-830. |
| [15] |
Fey J, Weil JH, Tomita K, Cosset A, Dietrich A, Small I, Maréchal-Drouard L (2002). Role of editing in plant mitochondrial transfer RNAs. Gene 286, 21-24.
PMID |
| [16] |
Guillaumot D, Lopez-Obando M, Baudry K, Avon A, Rigaill G, de Longevialle AF, Broche B, Takenaka M, Berthomé R, De Jaeger G, Delannoy E, Lurin C (2017). Two interacting PPR proteins are major Arabidopsis editing factors in plastid and mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 8877-8882.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Hayes ML, Santibanez PI (2020). A plant pentatricopeptide repeat protein with a DYW-deaminase domain is sufficient for catalyzing C-to-U RNA editing in vitro. J Biol Chem 295, 3497-3505. |
| [18] | He ZS, Zhu AD, Yang JB, Fan WS, Li DZ (2021). Organelle genomes and transcriptomes of Nymphaea reveal the interplay between intron splicing and RNA editing. Int J Mol Sci 22, 9842. |
| [19] |
Huang J, Lu G, Liu L, Raihan MS, Xu JT, Jian LM, Zhao LX, Tran TM, Zhang QH, Liu J, Li WQ, Wei CX, Braun DM, Li Q, Fernie AR, Jackson D, Yan JB (2020). The kernel size-related quantitative trait locus qKW9 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein that affects photosynthesis and grain filling. Plant Physiol 183, 1696-1709.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Kadowaki KI, Ozawa K, Kazama S, Kubo N, Akihama T (1995). Creation of an initiation codon by RNA editing in the coxl transcript from tomato mitochondria. Curr Genet 28, 415-422.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Kotera E, Tasaka M, Shikanai T (2005). A pentatricopeptide repeat protein is essential for RNA editing in chloroplasts. Nature 433, 326-330. |
| [22] |
Lesch E, Schilling MT, Brenner S, Yang YY, Gruss OJ, Knoop V, Schallenberg-Rüdinger M (2022). Plant mitochondrial RNA editing factors can perform targeted C-to-U editing of nuclear transcripts in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 50, 9966-9983.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Li XJ, Zhang YF, Hou MM, Sun F, Shen Y, Xiu ZH, Wang XM, Chen ZL, Sun SSM, Small I, Tan BC (2014). Small kernel 1 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein required for mitochondrial nad7 transcript editing and seed development in maize (Zea mays) and rice (Oryza sativa). Plant J 79, 797-809. |
| [24] |
Liu R, Cao SK, Sayyed A, Yang HH, Zhao J, Wang XM, Jia RX, Sun F, Tan BC (2020). The DYW-subgroup pentatricopeptide repeat protein PPR27 interacts with ZmMORF1 to facilitate mitochondrial RNA editing and seed development in maize. J Exp Bot 71, 5495-5505.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Liu XY, Jiang RC, Wang Y, Tang JJ, Sun F, Yang YZ, Tan BC (2021). ZmPPR26, a DYW-type pentatricopeptide repeat protein, is required for C-to-U RNA editing at AtpA- 1148 in maize chloroplasts. J Exp Bot 72, 4809-4821. |
| [26] | Liu YJ, Xiu ZH, Meeley R, Tan BC (2013). Empty pericarp5 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein that is required for mitochondrial RNA editing and seed development in maize. Plant Cell 25, 868-883. |
| [27] | Lurin C, AndrEés C, Aubourg S, Bellaoui M, Bitton F, Bruyère C, Caboche M, Debast C, Gualberto J, Hoffmann B, Lecharny A, Le Ret M, Martin-Magniette ML, Mireau H, Peeters N, Renou JP, Szurek B, Taconnat L, Small I (2004). Genome-wide analysis of Arabidopsis pentatricopeptide repeat proteins reveals their essential role in organelle biogenesis. Plant Cell 16, 2089-2103. |
| [28] | Ma YL, Chen HY, Wang JG, Yu JN (2011). Analysis of edi- ting sites for chloroplast ndhF in Ginkgo biloba and the editing efficiency at C290 in response to different stresses. Chin Bull Bot 46, 1-10. (in Chinese) |
|
马艳莉, 陈海燕, 王继刚, 俞嘉宁 (2011). 银杏叶绿体ndhF RNA编辑现象分析及C290位编辑对胁迫处理的响应. 植物学报 46, 1-10.
DOI |
|
| [29] |
McDowell R, Small I, Bond CS (2022). Synthetic PPR proteins as tools for sequence-specific targeting of RNA. Methods 208, 19-26.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Miyata Y, Sugita M (2004). Tissue- and stage-specific RNA editing of rps14 transcripts in moss (Physcomitrella patens) chloroplasts. J Plant Physiol 161, 113-115. |
| [31] | Mower JP, Palmer JD (2006). Patterns of partial RNA editing in mitochondrial genes of Beta vulgaris. Mol Genet Genomics 276, 285-293. |
| [32] |
Murayama M, Hayashi S, Nishimura N, Ishide M, Kobayashi K, Yagi Y, Asami T, Nakamura T, Shinozaki K, Hirayama T (2012). Isolation of Arabidopsis ahg11, a weak ABA hypersensitive mutant defective in nad4 RNA editing. J Exp Bot 63, 5301-5310.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Notsu Y, Masood S, Nishikawa T, Kubo N, Akiduki G, Nakazono M, Hirai A, Kadowaki K (2002). The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa L.) mitochondrial genome: frequent DNA sequence acquisition and loss during the evolution of flowering plants. Mol Genet Genomics 268, 434-445.
PMID |
| [34] |
Okuda K, Nakamura T, Sugita M, Shimizu T, Shikanai T (2006). A pentatricopeptide repeat protein is a site recognition factor in chloroplast RNA editing. J Biol Chem 281, 37661-37667.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Oldenkott B, Yang YY, Lesch E, Knoop V, Schallenberg-Rüdinger M (2019). Plant-type pentatricopeptide repeat proteins with a DYW domain drive C-to-U RNA editing in Escherichia coli. Commun Biol 2, 85.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
O’toole N, Hattori M, Andres C, Iida K, Lurin C, Schmitz- Linneweber C, Sugita M, Small I (2008). On the expansion of the pentatricopeptide repeat gene family in plants. Mol Biol Evol 25, 1120-1128.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Royan S, Gutmann B, des Francs-Small CC, Honkanen S, Schmidberger J, Soet A, Sun YK, Sanglard LVP, Bond CS, Small I (2021). A synthetic RNA editing factor edits its target site in chloroplasts and bacteria. Commun Biol 4, 545.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Rüdinger M, Funk HT, Rensing SA, Maier UG, Knoop V (2009). RNA editing: only eleven sites are present in the Physcomitrella patens mitochondrial transcriptome and a universal nomenclature proposal. Mol Genet Genomics 281, 473-481.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Sandoval R, Boyd RD, Kiszter AN, Mirzakhanyan Y, Santibańez P, Gershon PD, Hayes ML (2019). Stable native RIP9 complexes associate with C-to-U RNA editing activity, PPRs, RIPs, OZ1, ORRM1 and ISE2. Plant J 99, 1116-1126.
DOI |
| [40] | Shen C, Xu H, Huang WZ, Zhao Q, Zhu RL (2024). Is RNA editing truly absent in the complex thalloid liverworts (Marchantiopsida)? Evidence of extensive RNA editing from Cyathodium cavernarum. New Phytol 242, 2817-2831. |
| [41] | Small ID, Peeters N (2000). The PPR motif—a TPR-related motif prevalent in plant organellar proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 25, 45-47. |
| [42] |
Small ID, Schallenberg-Rüdinger M, Takenaka M, Mireau H, Ostersetzer-Biran O (2020). Plant organellar RNA editing: what 30 years of research has revealed. Plant J 101, 1040-1056.
DOI |
| [43] | Sosso D, Mbelo S, Vernoud V, Gendrot G, Dedieu A, Chambrier P, Dauzat M, Heurtevin L, Guyon V, Takenaka M, Rogowsky PM (2012). PPR2263, a DYW-subgroup pentatricopeptide repeat protein, is required for mitochondrial nad5 and cob transcript editing, mitochondrion biogenesis, and maize growth. Plant Cell 24, 676-691. |
| [44] |
Sun T, Bentolila S, Hanson MR (2016). The unexpected diversity of plant organelle RNA editosomes. Trends Plant Sci 21, 962-973.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Takenaka M, Takenaka S, Barthel T, Frink B, Haag S, Verbitskiy D, Oldenkott B, Schallenberg-Rüdinger M, Feiler CG, Weiss MS, Palm GJ, Weber G (2021). DYW domain structures imply an unusual regulation principle in plant organellar RNA editing catalysis. Nat Catal 4, 510-522.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Toma-Fukai S, Sawada Y, Maeda A, Shimizu H, Shikanai T, Takenaka M, Shimizu T (2023). Structural insight into the activation of an Arabidopsis organellar C-to-U RNA editing enzyme by active site complementation. Plant Cell 35, 1888-1900. |
| [47] | Wang Y, Huang ZQ, Tian KD, Li H, Xu CH, Xia BYJ, Tan BC (2024). Multiple factors interact in editing of PPR-E+- targeted sites in maize mitochondria and plastids. Plant Commun 5, 100836. |
| [48] | Wang Y, Li H, Huang ZQ, Ma B, Yang YZ, Xiu ZH, Wang L, Tan BC (2023). Maize PPR-E proteins mediate RNA C-to- U editing in mitochondria by recruiting the transdeaminase PCW1. Plant Cell 35, 529-551. |
| [49] | Wang Y, Liu XY, Huang ZQ, Li YY, Yang YZ, Sayyed A, Sun F, Gu ZQ, Wang XM, Tan BC (2021). PPR-DYW protein EMP17 is required for mitochondrial RNA editing, complex III biogenesis, and seed development in maize. Front Plant Sci 12, 693272. |
| [50] | Wang Y, Liu XY, Yang YZ, Huang J, Sun F, Lin JS, Gu ZQ, Sayyed A, Xu CH, Tan BC (2019). Empty Pericarp21 encodes a novel PPR-DYW protein that is required for mitochondrial RNA editing at multiple sites, complexes I and V biogenesis, and seed development in maize. PLoS Genet 15, e1008305. |
| [51] | Wei KF, Han P (2016). Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins in maize. Mol Breeding 36, 170. |
| [52] | Xu CH, Song S, Yang YZ, Lu F, Zhang MD, Sun F, Jia RX, Song RL, Tan BC (2020). DEK46 performs C-to-U editing of a specific site in mitochondrial nad7 introns that is critical for intron splicing and seed development in maize. Plant J 103, 1767-1782. |
| [53] | Yan JJ, Zhang QX, Guan ZY, Wang Q, Li L, Ruan FY, Lin RC, Zou TT, Yin P (2017). MORF9 increases the RNA- binding activity of PLS-type pentatricopeptide repeat protein in plastid RNA editing. Nat Plants 3, 17037. |
| [54] | Yang DL, Cao SK, Yang HH, Liu R, Sun F, Wang L, Wang MD, Tan BC (2022a). DEK48 is required for RNA editing at multiple mitochondrial sites and seed development in maize. Int J Mol Sci 23, 3064. |
| [55] | Yang YZ, Liu XY, Tang JJ, Wang Y, Xu CH, Tan BC (2022b). GRP23 plays a core role in E-type editosomes via interacting with MORFs and atypical PPR-DYWs in Arabidopsis mitochondria. Proc NatI Acad Sci USA 119, e2210978119. |
| [56] | Yin P, Li QX, Yan CY, Liu Y, Liu JJ, Yu F, Wang Z, Long JF, He JH, Wang HW, Wang JW, Zhu JK, Shi YG, Yan NE (2013). Structural basis for the modular recognition of single-stranded RNA by PPR proteins. Nature 504, 168-171. |
| [57] |
Yu W, Schuster W (1995). Evidence for a site-specific cytidine deamination reaction involved in C to U RNA editing of plant mitochondria. J Biol Chem 270, 18227-18233.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Yuan H, Liu D (2012). Functional disruption of the pentatricopeptide protein SLG1 affects mitochondrial RNA editing, plant development, and responses to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 70, 432-444. |
| [59] | Zang J, Zhang TF, Zhang ZG, Liu J, Chen HB (2024). DEFECTIVE KERNEL 56 functions in mitochondrial RNA editing and maize seed development. Plant Physiol 194, 1593-1610. |
| [60] |
Zehrmann A, van der Merwe J, Verbitskiy D, Härtel B, Brennicke A, Takenaka M (2012). The DYW-class PPR protein MEF7 is required for RNA editing at four sites in mitochondria of Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA Biol 9, 155-161.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 谢涛, 章一帆, 刘云辉, 游慧玉, 夏季奔奔, 马蓉, 张春妮, 华学军. 植物线粒体铁硫簇合成系统及其调控的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 王传永, 庄典, 宋正达, 翟恒华, 李乃伟, 张凡. 黑果腺肋花楸叶绿体全基因组的结构和比较分析及系统进化推断[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [3] | 殷斯, 杨依婷, 卢瑞玲, 念蕊, 郝转, 高永. 滇魔芋中国种群的谱系地理研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(2): 308-319. |
| [4] | 林珍, 向家宝, 蔡何佳奕, 高贝, 杨金涛, 李俊毅, 周青松, 黄晓磊, 邓鋆. 七种半翅目昆虫线粒体基因组数据[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24434-. |
| [5] | 邓洪, 钟占友, 寇春妮, 朱书礼, 李跃飞, 夏雨果, 武智, 李捷, 陈蔚涛. 基于线粒体全基因组揭示斑鳠的种群遗传结构与演化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24241-. |
| [6] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [7] | 褚振州, 古丽巴哈尔·依斯拉木, 屈泽众, 田新民. 同域分布的3种木蓼属植物叶绿体基因组比较[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 417-432. |
| [8] | 包金波, 丁志杰, 苗浩宇, 李雪丽, 任书贤, 焦若岩, 李浩, 邓茜茜, 李英姿, 田新民. 石栗叶绿体基因组研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 248-260. |
| [9] | 卢聪聪, 刘倩, 黄晓磊. 三种蚜虫的线粒体基因组数据[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22204-. |
| [10] | 李晨, 刘建廷, 樊永信, 赵雪惠, 肖伟, 陈修德, 付喜玲, 李玲, 李冬梅. UV-B对设施桃叶片光合功能及叶绿体超微结构的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 434-443. |
| [11] | 翟俊杰, 赵慧峰, 商光申, 孙振钧, 张玉峰, 王兴. 蚯蚓基因组学的研究进展: 基于全基因组及线粒体基因组[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22257-. |
| [12] | 陆奇丰, 黄至欢, 骆文华. 极小种群濒危植物广西火桐、丹霞梧桐的叶绿体基因组特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 586-595. |
| [13] | 张梦华, 张宪春. 中国薄叶卷柏复合群的物种划分[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1607-1619. |
| [14] | 王春成, 马松梅, 张丹, 王绍明. 柴达木野生黑果枸杞的空间遗传结构[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(6): 661-668. |
| [15] | 李潮,金锦锦,罗锦桢,王春晖,王俊杰,赵俊. 唐鱼养殖种群与广州附近4个野生种群的遗传关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 474-484. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||