

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (2): 308-315.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22184 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22184
任露露1, 张有泽1, 黄克林1, 宛晓春1, 张照亮1,*( ), 朱木兰2,3,*(
), 朱木兰2,3,*( ), 韦朝领1,*(
), 韦朝领1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-03
接受日期:2022-11-15
出版日期:2023-03-01
发布日期:2023-03-15
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Lulu Ren1, Youze Zhang1, Kelin Huang1, Xiaochun Wan1, Zhaoliang Zhang1,*( ), Mulan Zhu2,3,*(
), Mulan Zhu2,3,*( ), Chaoling Wei1,*(
), Chaoling Wei1,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-03
Accepted:2022-11-15
Online:2023-03-01
Published:2023-03-15
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要: 茶树(Camellia sinensis)是重要的经济作物, 杂合度高且变异度大, 其高效离体再生体系鲜见报道。以舒茶早茎段为起始外植体, 进行不定芽高效发生影响因子研究。结果表明, MS+2 mg∙L-1 6-BA为定芽诱导的最适配方, 定芽诱导率为84.44%, 吸收底盘膨大率为80%, 利于后续不定芽诱导; MS+2 mg∙L-1 6-BA+0.2 mg∙L-1 NAA+0.1 mg∙L-1 KT+1 mg∙L-1脯氨酸为不定芽增殖诱导的适宜配方, 不定芽诱导率为88.89%, 平均芽数为7.8。不定根诱导的适宜配方为1/2MS+3 mg∙L-1 IBA, 生根率为85.56%。采用RAPD和ISSR技术对再生植株进行分子检测, 在连续2代离体再生植株中未发现明显变异。
任露露, 张有泽, 黄克林, 宛晓春, 张照亮, 朱木兰, 韦朝领. 茶树茎段不定芽高效发生体系的建立. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 308-315.
Lulu Ren, Youze Zhang, Kelin Huang, Xiaochun Wan, Zhaoliang Zhang, Mulan Zhu, Chaoling Wei. An Efficient System for Regenerating Adventitious Buds in Stem Segments of Tea Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(2): 308-315.
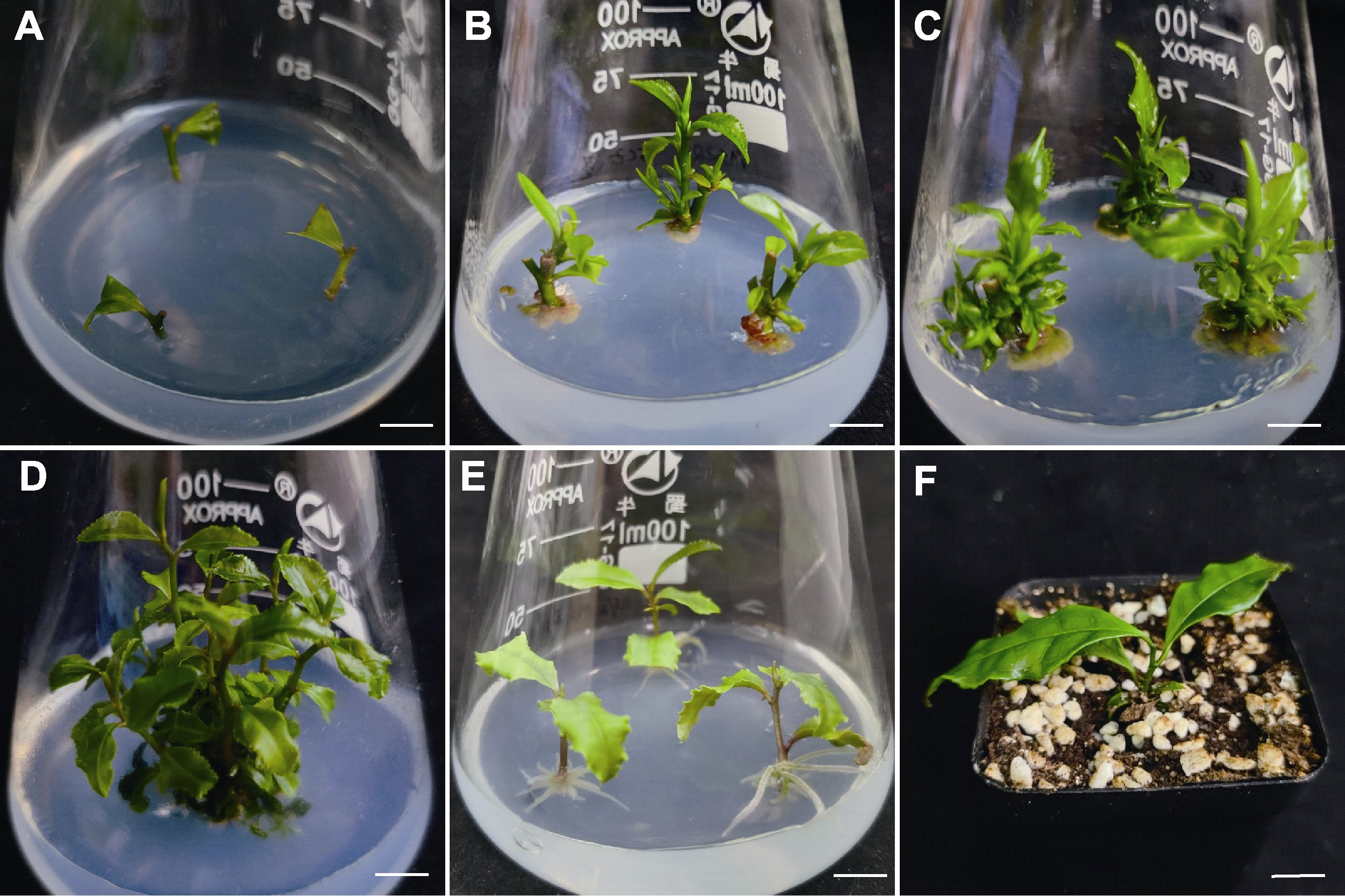

图1 茎段不定芽发生体系 (A) 外植体(bar=1 cm); (B) 定芽诱导(bar=1 cm); (C) 不定芽诱导(bar=1 cm); (D) 不定芽伸长(bar=1 cm); (E) 不定根诱导(bar=1.5 cm); (F) 移栽存活的植株(bar=2 cm)
Figure 1 Adventitious budding system of stem segment (A) Explant (bar=1 cm); (B) Normal bud induction (bar=1 cm); (C) Adventitious bud induction (bar=1 cm); (D) Adventitious bud elongation (bar=1 cm); (E) Adventitious root induction (bar=1.5 cm); (F) Transplanted plants (bar=2 cm)
| Basic medium | State of growth |
|---|---|
| WPM | The bottom callus starts quickly and grows well, the petiole turns red, a small number of normal buds |
| MS | The bottom callus is thickened, the fixed buds are robust, a small number of normal buds, the foliage is emerald green, and the whole culture is viable |
| N6 | The bottom callus starts quickly, the petiole is reddish, and the leaves are thin |
| DCR | There is less callus at the bottom and the leaves are thin and yellowish |
表1 不同基本培养基对茎段诱导的影响
Table 1 Effects of different basic media on stem induction
| Basic medium | State of growth |
|---|---|
| WPM | The bottom callus starts quickly and grows well, the petiole turns red, a small number of normal buds |
| MS | The bottom callus is thickened, the fixed buds are robust, a small number of normal buds, the foliage is emerald green, and the whole culture is viable |
| N6 | The bottom callus starts quickly, the petiole is reddish, and the leaves are thin |
| DCR | There is less callus at the bottom and the leaves are thin and yellowish |
| 6-BA (mg?L-1) | Bud induction rate (%) | Bottom expansion rate (%) | State of growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5.56±1.92 d | 1.11±1.92 d | The growth is weak and the base becomes brown |
| 1 | 51.11±5.09 c | 61.11±3.84 c | The growth is better, with fewer buds and calli form at the base |
| 2 | 77.78±5.09 a | 80.00±3.33 b | The growth is strong, with fixed buds at the axillary buds and callus at the base |
| 3 | 84.44±1.92 a | 78.89±6.93 b | The growth is better, with fixed buds at the axillary buds and more callus at the base |
| 4 | 58.89±3.84 b | 88.89±5.09 a | The growth is weak, the axillary buds are yellow, and the chassis is expanded and partially lobed |
表2 不同浓度6-BA对茎段定芽诱导的影响
Table 2 Effect of different concentrations of 6-BA on the normal bud induction of stem segments
| 6-BA (mg?L-1) | Bud induction rate (%) | Bottom expansion rate (%) | State of growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5.56±1.92 d | 1.11±1.92 d | The growth is weak and the base becomes brown |
| 1 | 51.11±5.09 c | 61.11±3.84 c | The growth is better, with fewer buds and calli form at the base |
| 2 | 77.78±5.09 a | 80.00±3.33 b | The growth is strong, with fixed buds at the axillary buds and callus at the base |
| 3 | 84.44±1.92 a | 78.89±6.93 b | The growth is better, with fixed buds at the axillary buds and more callus at the base |
| 4 | 58.89±3.84 b | 88.89±5.09 a | The growth is weak, the axillary buds are yellow, and the chassis is expanded and partially lobed |
| Number | 6-BA (mg?L-1) | NAA (mg?L-1) | Adventitious bud elongation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2 | 0.02 | 24.44±6.94 c |
| 2 | 0.4 | 0.04 | 30.00±3.33 c |
| 3 | 0.6 | 0.06 | 58.89±1.92 b |
| 4 | 0.8 | 0.08 | 70.00±8.82 a |
| 5 | 1 | 0.1 | 51.11±5.09 b |
表4 植物生长调节剂对不定芽伸长的影响
Table 4 Effects of plant growth regulators on adventitious bud elongation
| Number | 6-BA (mg?L-1) | NAA (mg?L-1) | Adventitious bud elongation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2 | 0.02 | 24.44±6.94 c |
| 2 | 0.4 | 0.04 | 30.00±3.33 c |
| 3 | 0.6 | 0.06 | 58.89±1.92 b |
| 4 | 0.8 | 0.08 | 70.00±8.82 a |
| 5 | 1 | 0.1 | 51.11±5.09 b |
| Number | Medium | IBA (mg?L-1) | Rooting rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/2MS | 1 | 38.89±5.88 b |
| 2 | 2 | 42.22±4.01 b | |
| 3 | 3 | 85.56±2.94 a | |
| 4 | 4 | 46.67±5.77 b | |
| 5 | MS | 1 | 5.56±2.22 c |
| 6 | 2 | 18.89±2.94 c | |
| 7 | 3 | 8.89±4.01 c | |
| 8 | 4 | 11.11±4.01 c |
表5 不同浓度IBA和基本培养基对不定根诱导的影响
Table 5 Effects of different concentration of IBA and basal medium on the induction of adventitious root
| Number | Medium | IBA (mg?L-1) | Rooting rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/2MS | 1 | 38.89±5.88 b |
| 2 | 2 | 42.22±4.01 b | |
| 3 | 3 | 85.56±2.94 a | |
| 4 | 4 | 46.67±5.77 b | |
| 5 | MS | 1 | 5.56±2.22 c |
| 6 | 2 | 18.89±2.94 c | |
| 7 | 3 | 8.89±4.01 c | |
| 8 | 4 | 11.11±4.01 c |
| Primer | Nucleotide sequence (5°-3°) | Number of amplification band | Size range of band (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S29 | GGGTAACGCC | 8 | 750-3000 |
| S30 | CTGCTGGGAC | 12 | 300-5000 |
| S31 | TGTCATCCCC | 9 | 400-3000 |
| S49 | CTCACCGTCC | 7 | 500-3000 |
| S132 | CAGCTCACGA | 8 | 250-2000 |
| S133 | CTCTCCGCCA | 9 | 300-2000 |
| S144 | GGAAGTCGCC | 6 | 500-2000 |
| S169 | TGGAGAGCAG | 4 | 750-3000 |
| S172 | AGAGGGCACA | 5 | 500-2000 |
| S175 | TCATCCGAGG | 6 | 500-3000 |
| S181 | CTACTGCGCT | 9 | 250-3000 |
| S208 | AACGGCGACA | 8 | 300-3000 |
| S221 | TGACGCATGG | 5 | 600-2000 |
| S226 | ACGCCCAGGT | 10 | 500-3000 |
| S230 | GGACCTGCTG | 7 | 500-2000 |
| Total | 113 | ||
表6 随机扩增多态性DNA (RAPD)引物及其扩增谱
Table 6 The random amplification polymorphic DNA (RAPD) primers used in the study and their amplification profile
| Primer | Nucleotide sequence (5°-3°) | Number of amplification band | Size range of band (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S29 | GGGTAACGCC | 8 | 750-3000 |
| S30 | CTGCTGGGAC | 12 | 300-5000 |
| S31 | TGTCATCCCC | 9 | 400-3000 |
| S49 | CTCACCGTCC | 7 | 500-3000 |
| S132 | CAGCTCACGA | 8 | 250-2000 |
| S133 | CTCTCCGCCA | 9 | 300-2000 |
| S144 | GGAAGTCGCC | 6 | 500-2000 |
| S169 | TGGAGAGCAG | 4 | 750-3000 |
| S172 | AGAGGGCACA | 5 | 500-2000 |
| S175 | TCATCCGAGG | 6 | 500-3000 |
| S181 | CTACTGCGCT | 9 | 250-3000 |
| S208 | AACGGCGACA | 8 | 300-3000 |
| S221 | TGACGCATGG | 5 | 600-2000 |
| S226 | ACGCCCAGGT | 10 | 500-3000 |
| S230 | GGACCTGCTG | 7 | 500-2000 |
| Total | 113 | ||
| Primer | Nucleotide sequence (5°-3°) | Number of amplification band | Size range of band (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UBC824 | TCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCG | 4 | 500-2000 |
| UBC835 | CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTYC | 6 | 300-1500 |
| UBC840 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAYT | 2 | 500-1500 |
| UBC844 | CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTRC | 5 | 500-1500 |
| UBC853 | TCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCRT | 5 | 600-1500 |
| UBC854 | TCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCRG | 6 | 500-2000 |
| UBC856 | ACACACACACACACACYA | 5 | 500-1500 |
| UBC859 | TGTGTGTGTGTGTGTGRC | 4 | 500-3000 |
| UBC873 | GACAGACAGACAGACA | 5 | 750-3000 |
| UBC880 | GGAGAGGAGAGGAGA | 6 | 500-2000 |
| Total | 48 | ||
表7 简单重复序列区间(ISSR)引物及其扩增谱
Table 7 The inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) primers used in the study and their amplification profile
| Primer | Nucleotide sequence (5°-3°) | Number of amplification band | Size range of band (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UBC824 | TCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCG | 4 | 500-2000 |
| UBC835 | CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTYC | 6 | 300-1500 |
| UBC840 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAYT | 2 | 500-1500 |
| UBC844 | CTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTRC | 5 | 500-1500 |
| UBC853 | TCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCRT | 5 | 600-1500 |
| UBC854 | TCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCRG | 6 | 500-2000 |
| UBC856 | ACACACACACACACACYA | 5 | 500-1500 |
| UBC859 | TGTGTGTGTGTGTGTGRC | 4 | 500-3000 |
| UBC873 | GACAGACAGACAGACA | 5 | 750-3000 |
| UBC880 | GGAGAGGAGAGGAGA | 6 | 500-2000 |
| Total | 48 | ||
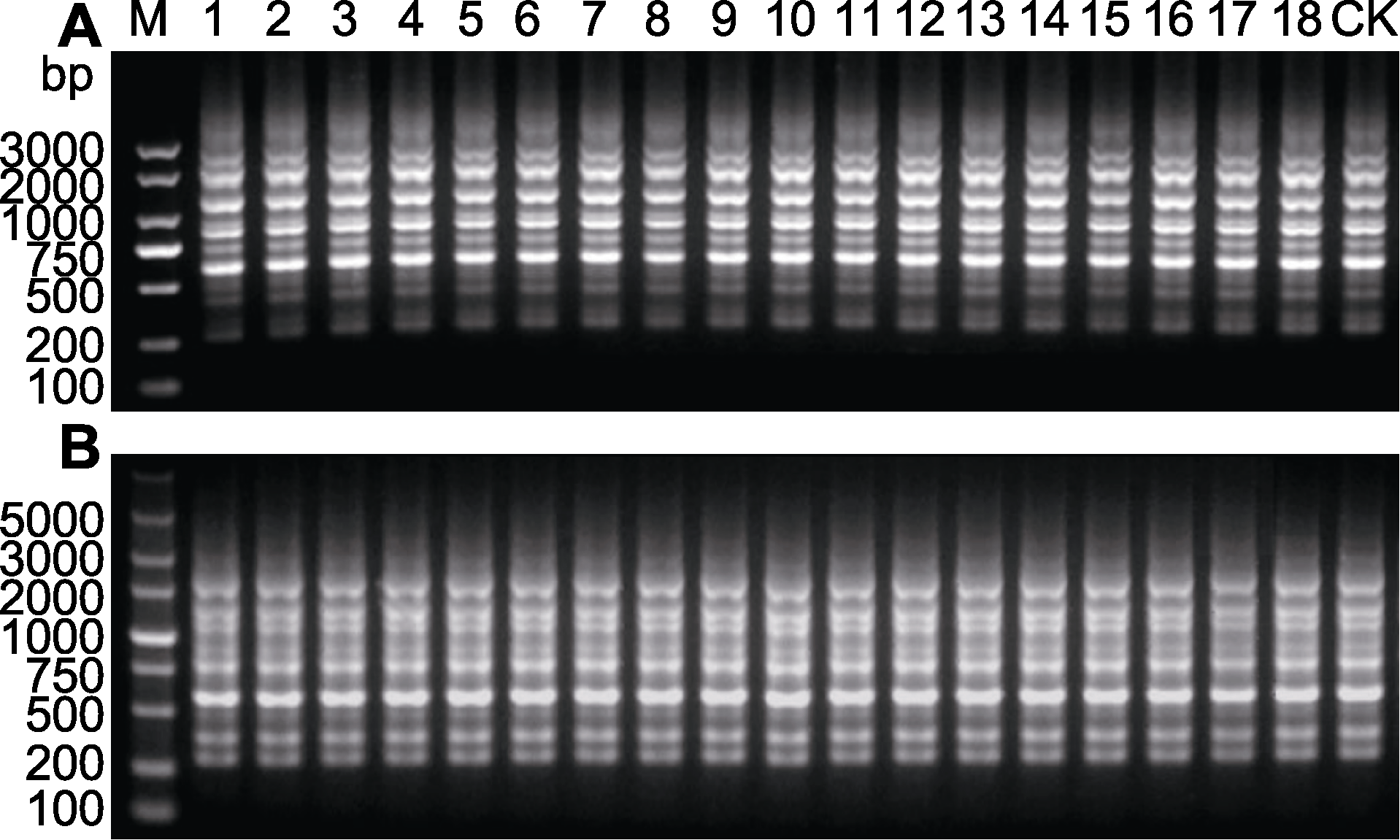
图2 舒茶早再生植株的随机扩增多态性DNA (RAPD)扩增图谱 (A) 引物S132; (B) 引物S133。1-18: 同一茶树茎段的离体再生植株群; 1-6: 舒茶早一代再生植株; 7-12: 舒茶早二代再生植株; 13-18: 舒茶早三代再生植株; CK: 母本材料
Figure 2 Random amplification polymorphic DNA (RAPD) banding profiles of regenerated plants of Shuchazao (A) Primer S132; (B) Primer S133. 1-18: In vitro regenerated plant population of the same tea plant stem segment; 1-6: First generation regenerated plants of Shuchazao; 7-12: Second generation regenerated plants of Shuchazao; 13-18: Third generation regenerated plants of Shuchazao; CK: Mother plant
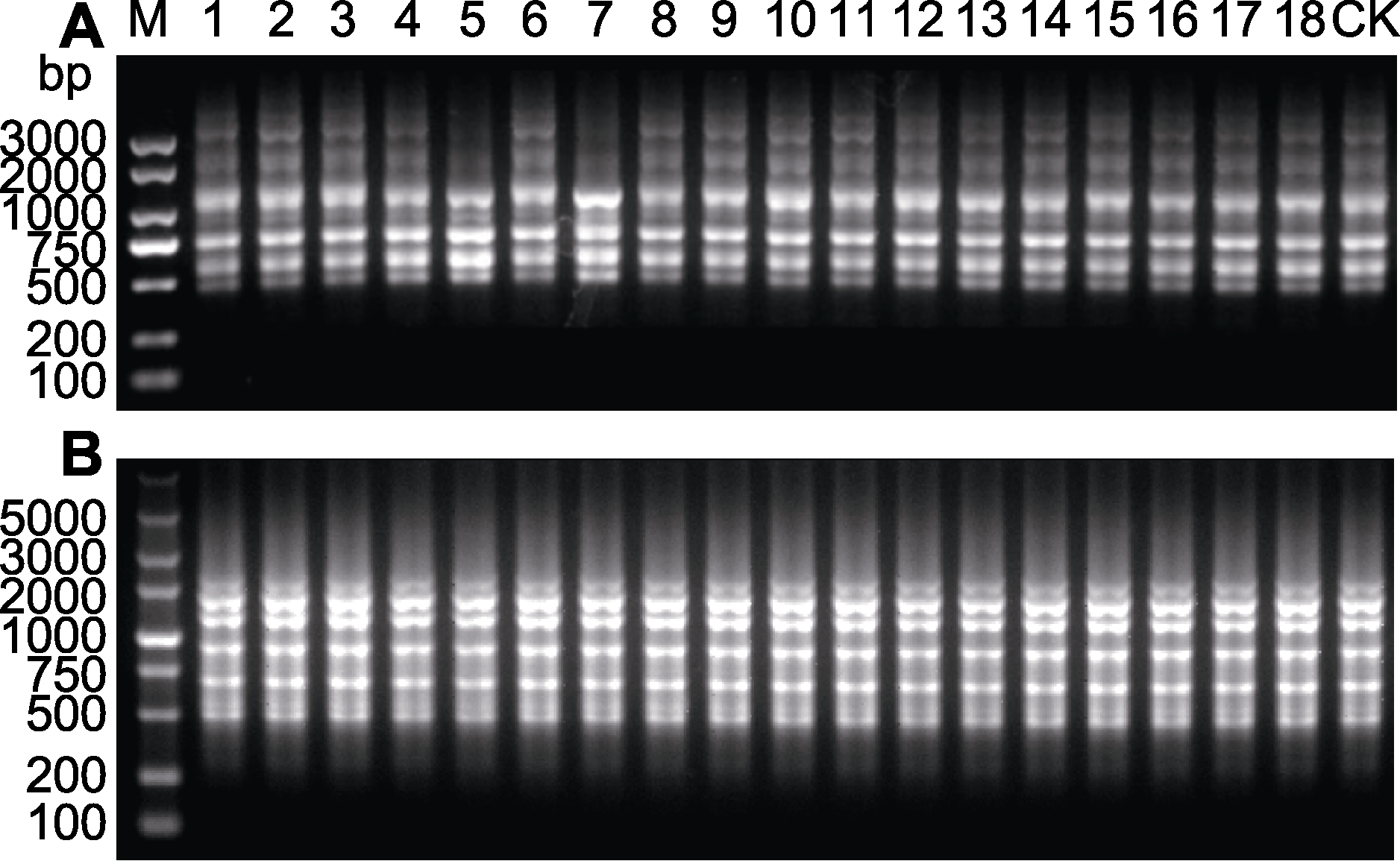
图3 舒茶早再生植株的简单重复序列区间(ISSR)扩增图谱 (A) 引物UBC854; (B) 引物UBC880。1-18: 同一茶树茎段的离体再生植株群; 1-6: 舒茶早一代再生植株; 7-12: 舒茶早二代再生植株; 13-18: 舒茶早三代再生植株; CK: 母本材料
Figure 3 Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) banding pro- files of regenerated plants of Shuchazao (A) Primer UBC854; (B) Primer UBC880. 1-18: In vitro regenerated plant population of the same tea plant stem segment; 1-6: First generation regenerated plants of Shuchazao; 7-12: Second generation regenerated plants of Shuchazao; 13-18: Third generation regenerated plants of Shuchazao; CK: Mother plant
| Number | 6-BA (mg?L-1) | NAA (mg?L-1) | Adventitious bud induction rate (%) | Average number of shoots |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 16.67±5.78 d | 0.33±0.15 d |
| 2 | 1 | 0.1 | 54.44±5.09 c | 1.33±0.08 c |
| 3 | 2 | 0.2 | 88.89±6.93 a | 7.88±0.23 a |
| 4 | 3 | 0.3 | 71.11±6.93 b | 3.48±0.25 b |
表3 植物生长调节剂对不定芽增殖诱导的影响
Table 3 Effects of plant growth regulators on the induction of adventitious bud proliferation
| Number | 6-BA (mg?L-1) | NAA (mg?L-1) | Adventitious bud induction rate (%) | Average number of shoots |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 16.67±5.78 d | 0.33±0.15 d |
| 2 | 1 | 0.1 | 54.44±5.09 c | 1.33±0.08 c |
| 3 | 2 | 0.2 | 88.89±6.93 a | 7.88±0.23 a |
| 4 | 3 | 0.3 | 71.11±6.93 b | 3.48±0.25 b |
| [1] | 陈立杰, 杨霞, 高倩, 李悦, 陈红 (2019). 花溪古茶树离体繁殖技术研究初报. 种业导刊 (8), 10-13. |
| [2] | 陈泽雄, 刘奕清, 黄登艳 (2009). ‘渝茶1号’离体培养及植株再生研究. 西南大学学报(自然科学版) 31(12),67-70. |
| [3] | 陈宗懋 (1994). 中国茶经. 上海: 上海文化出版社. pp. 5. |
| [4] | 陈祖枝 (2018). 福安茶树良种繁育现状及存在问题分析. 福建茶叶 40(2), 1-2. |
| [5] | 成浩, 曾建明, 周健, 王丽鸳, 常杰, 葛滢, 袁海波, 谷保静, 张小飞 (2007). 茶树种苗工厂化快速繁育技术. 茶叶科学 27, 231-235. |
| [6] | 李华锋, 滕杰, 莫岚, 曾雯, 晏嫦妤, 黄亚辉 (2016). 连南县茶树种质资源遗传多样性的RAPD分析. 茶叶学报 57, 166-171. |
| [7] | 李晓东, 向勤锃, 高吉刚, 张丽霞 (2010). 不同成熟度茶籽外植体诱导发生体胚的研究. 中国农学通报 26(18), 54-58. |
| [8] | 李旭云 (2020). 安溪县茶树种苗繁育及种质资源保护利用. 福建茶叶 42(11), 11-12. |
| [9] | 刘静 (2020). 茶树带腋芽茎段组织培养研究. 陕西农业科学 66(10), 43-45. |
| [10] | 刘青, 赵德刚, 赵懿琛 (2021). 古茶树种质资源遗传多样性ISSR分析. 种子 40(5), 7-14. |
| [11] | 罗军武, 施兆鹏, 沈程文, 刘春林, 龚志华, 黄意欢 (2004). 茶树种质资源遗传多样性的RAPD分析. 作物学报 30, 266-269. |
| [12] | 欧少云, 陈珊, 陈春兰, 刘细群 (2012). 不同外源激素对清远笔架茶愈伤组织诱导的影响. 湖北农业科学 51, 3626-3627. |
| [13] | 亓峥, 庞志强, 蓝增全 (2020). 云南小叶种茶树叶片和茎段愈伤组织诱导及继代培养. 科学技术与工程 20, 7206-7212. |
| [14] | 谭和平, 徐利远, 余桂蓉, 杜文平, 王宇星, 钟昌松 (2006). 茶树种质资源ISSR分子标记初步研究. 核农学报 20, 113-115. |
| [15] | 谢恩俊, 田维丽, 陈正武, 李岩, 赵德刚 (2020). ‘中黄1号’茶树带腋芽茎段组培快繁体系建立. 分子植物育种 18, 5071-5080. |
| [16] | 许益娟 (2012). 茶树组织培养再生体系优化与遗传转化的研究. 硕士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 1-64. |
| [17] |
鄢东海, 刘声传, 罗显扬, 魏杰, 陆建良, 范方媛 (2015). 贵州地方茶树品种资源遗传多样性RAPD分析. 中国农学通报 31(19), 30-34.
DOI |
| [18] | 姚明哲, 黄海涛, 余继忠, 陈亮 (2005). ISSR在茶树品种分子鉴别和亲缘关系研究中的适用性分析. 茶叶科学 25, 153-157. |
| [19] | 岳翠男, 王治会, 江新凤, 杨普香 (2018). 茶树组培技术研究进展. 蚕桑茶叶通讯 2(3), 27-31. |
| [20] | Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987). A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19, 11-15. |
| [21] |
Sun J, Lei PD, Zhang ZZ, Shi GH, Tang ZJ, Zhu SY, Jiang CJ, Wan XC (2012). Shoot basal ends as novel explants for in vitro plantlet regeneration in an elite clone of tea. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 87, 71-76.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 冯雯, 王玉国. 栽培薯蓣茎段离体再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 792-799. |
| [2] | 谢纯刚, 刘哲, 章书声, 胡海涛. 手指柠檬茎段离体再生体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 926-934. |
| [3] | 穆丹, 岂泽华, 李沁, 梁可欣, 华绍贵, 朱星雨, 焦梦婕, 饶玉春, 孙廷哲. 茶树花挥发物对叶蝉三棒缨小蜂的引诱增强效应[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 559-572. |
| [4] | 孙廷哲, 岂泽华, 梁可欣, 李沁, 饶玉春, 穆丹. 蚜害茶树挥发物组分变化的聚类分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 422-432. |
| [5] | 刘建福, 陈育才, 王文建, 王河川, 蔡金福, 王明元, 李丹丹, 张斌, 黄昆. 航天搭载对武夷名丛相关生理及生长特性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 564-572. |
| [6] | 杨小青,黄晓琴,韩晓阳,刘腾飞,岳晓伟,伊冉. 外源物质对茶树耐寒及蔗糖代谢关键基因表达的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 21-30. |
| [7] | 张晓玲, 李亦超, 王芸芸, 蔡宏宇, 曾辉, 王志恒. 未来气候变化对不同国家茶适宜分布区的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(6): 595-606. |
| [8] | 刘小妹,孙丽莉,傅向东,廖红. 茶树嫩枝扦插的高效方法[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 531-538. |
| [9] | 吕秀立, 张群, 陈香波, 李圃锦, 吴伟, 关媛. 岩白菜属植物规模化繁殖及遗传稳定性[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(5): 643-652. |
| [10] | 王燕, 牟豪杰, 吕永平, 李海营, 汪一婷, 陈剑平. 寿锦的离体植株再生及组培产业化增殖[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(3): 331-336. |
| [11] | 林郑和, 钟秋生, 陈常颂, 陈志辉, 游小妹. 不同香型茶树鲜叶挥发性组分与β-葡萄糖苷酶的相关性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(6): 713-720. |
| [12] | 李海萍, 张鲁刚, 张静, 茹磊, 刘学成, 孙希禄. 萝卜带柄子叶高频再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2011, 46(3): 331-337. |
| [13] | 孙美莲, 王云生, 杨冬青, 韦朝领, 高丽萍, 夏涛, 单育, 骆洋. 茶树实时荧光定量PCR分析中内参基因的选择[J]. 植物学报, 2010, 45(05): 579-587. |
| [14] | 王曙光 林先贵 董元华 罗质超 施亚琴. 丛枝菌根(AM)对无性繁殖茶苗生长及茶叶品质的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2002, 19(04): 462-468. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||