

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 341-352.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17103 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17103
所属专题: 药用植物专辑 (2018年53卷3期)
李璐1, 安叶娟1, 乔春雷1, 杨晓华2,*( ), 张华峰1,*(
), 张华峰1,*( ), 薛梦莹1
), 薛梦莹1
收稿日期:2017-05-23
接受日期:2017-08-30
出版日期:2018-05-01
发布日期:2018-09-11
通讯作者:
杨晓华,张华峰
基金资助:
Li Lu1, An Yejuan1, Qiao Chunlei1, Yang Xiaohua2,*( ), Zhang Huafeng1,*(
), Zhang Huafeng1,*( ), Xue Mengying1
), Xue Mengying1
Received:2017-05-23
Accepted:2017-08-30
Online:2018-05-01
Published:2018-09-11
Contact:
Yang Xiaohua,Zhang Huafeng
摘要: 建立了药用植物心叶淫羊藿(Epimedium brevicornum)生物碱的超声波-微波协同提取工艺, 探讨了提取机理, 分析了生物碱的化学组成及其对人宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖的抑制作用。采用正交试验法优化得到了淫羊藿生物碱的超声波-微波协同提取工艺: 浸泡时间为40分钟, 超声波-微波协同作用18分钟, 微波功率250 J∙s-1, 液固比为30 mL∙g-1, 乙醇溶液浓度为70%。超声波-微波协同提取法的提取率可达16.146 mg∙g-1, 显著高于超声波提取法、微波提取法和加热提取法。扫描电子显微镜观察结果表明, 超声波-微波协同作用可使淫羊藿叶片样品表面出现大量裂隙。激光粒度分析显示, 超声波-微波协同提取后, 中、低粒度范围的样品量明显增多, 而高粒度范围的样品量明显减少。薄层色谱和高效液相色谱分析结果表明, 淫羊藿生物碱含有木兰花碱, 不含小檗碱或含量很低。淫羊藿生物碱对HeLa细胞的增殖具有明显的抑制作用, 并且呈现出剂量依赖性。研究结果为药用植物淫羊藿资源的开发利用提供理论依据。
李璐, 安叶娟, 乔春雷, 杨晓华, 张华峰, 薛梦莹. 淫羊藿生物碱的超声波-微波协同提取及其 对HeLa细胞的抑制作用. 植物学报, 2018, 53(3): 341-352.
Li Lu, An Yejuan, Qiao Chunlei, Yang Xiaohua, Zhang Huafeng, Xue Mengying. Ultrasound-microwave-assisted Extraction of Alkaloids from Epimedium brevicornum and Their Inhibitory Effect on HeLa Cells. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(3): 341-352.
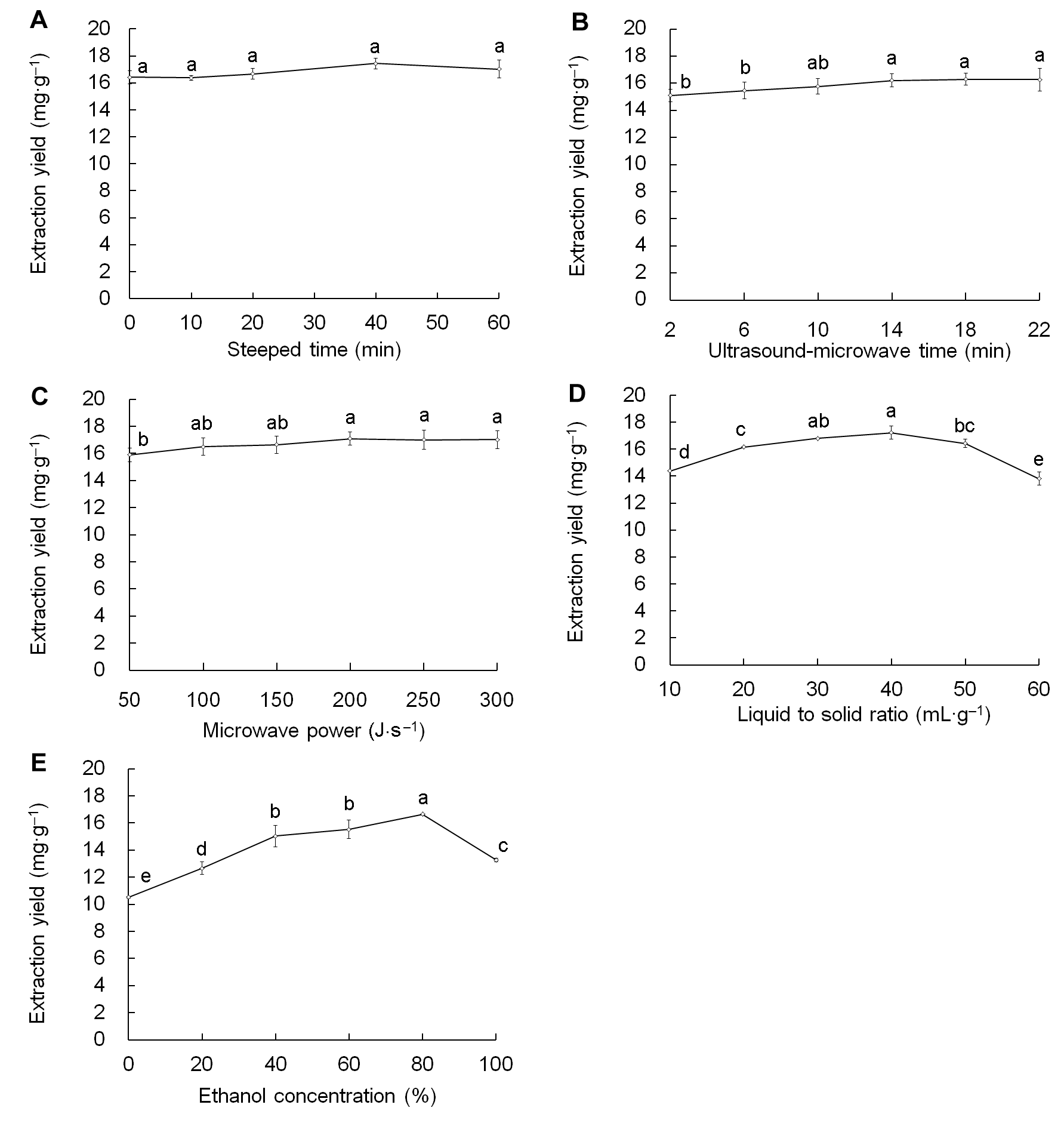
图1 浸泡时间(A)、超声波-微波协同作用时间(B)、微波功率(C)、液固比(D)与乙醇溶液浓度(E)对淫羊藿生物碱提取率的影响不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 1 Effects of steeped time (A), ultrasound- microwave time (B), microwave power (C), liquid to solid ratio (D), and ethanol concentration (E) on extraction yield of Epimedium brevicornum alkaloidsDifferent lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05).
| Test No. | Factor | Mean extraction yield (mg∙g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Steeped time (min) | (B) Ultrasound- microwave time (min) | (C) Microwave power (J∙s-1) | Blank | (D) Liquid to solid ratio (mL∙g-1) | (E) Ethanol concentration (%) | ||
| 1 | A1 16 | B1 2 | C1 50 | 1 | D1 30 | E1 50 | 14.361 |
| 2 | A1 16 | B2 6 | C2 100 | 2 | D2 35 | E2 60 | 13.343 |
| 3 | A1 16 | B3 10 | C3 150 | 3 | D3 40 | E3 70 | 12.015 |
| 4 | A1 16 | B4 14 | C4 200 | 4 | D4 45 | E4 80 | 10.966 |
| 5 | A1 16 | B5 18 | C5 250 | 5 | D5 50 | E5 90 | 9.221 |
| 6 | A2 24 | B1 2 | C2 100 | 3 | D4 45 | E5 90 | 9.430 |
| 7 | A2 24 | B2 6 | C3 150 | 4 | D5 50 | E1 50 | 9.696 |
| 8 | A2 24 | B3 10 | C4 200 | 5 | D1 30 | E2 60 | 15.878 |
| 9 | A2 24 | B4 14 | C5 250 | 1 | D2 35 | E3 70 | 14.259 |
| 10 | A2 24 | B5 18 | C1 50 | 2 | D3 40 | E4 80 | 11.946 |
| 11 | A3 32 | B1 2 | C3 150 | 5 | D2 35 | E4 80 | 12.869 |
| 12 | A3 32 | B2 6 | C4 200 | 1 | D3 40 | E5 90 | 11.181 |
| 13 | A3 32 | B3 10 | C5 250 | 2 | D4 45 | E1 50 | 10.934 |
| 14 | A3 32 | B4 14 | C1 50 | 3 | D5 50 | E2 60 | 9.948 |
| 15 | A3 32 | B5 18 | C2 100 | 4 | D1 30 | E3 70 | 15.833 |
| 16 | A4 40 | B1 2 | C4 200 | 2 | D5 50 | E3 70 | 9.967 |
| 17 | A4 40 | B2 6 | C5 250 | 3 | D1 30 | E4 80 | 15.758 |
| 18 | A4 40 | B3 10 | C1 50 | 4 | D2 35 | E5 90 | 12.806 |
| 19 | A4 40 | B4 14 | C2 100 | 5 | D3 40 | E1 50 | 12.022 |
| 20 | A4 40 | B5 18 | C3 150 | 1 | D4 45 | E2 60 | 11.251 |
| 21 | A5 48 | B1 2 | C5 250 | 4 | D3 40 | E2 60 | 11.895 |
| 22 | A5 48 | B2 6 | C1 50 | 5 | D4 45 | E3 70 | 10.764 |
| 23 | A5 48 | B3 10 | C2 100 | 1 | D5 50 | E4 80 | 9.765 |
| 24 | A5 48 | B4 14 | C3 150 | 2 | D1 30 | E5 90 | 14.588 |
| 25 | A5 48 | B5 18 | C4 200 | 3 | D2 35 | E1 50 | 13.640 |
| T1 | 59.906 | 58.522 | 59.824 | 60.817 | 76.417 | 60.652 | |
| T2 | 61.209 | 60.741 | 60.393 | 60.779 | 66.917 | 62.315 | |
| T3 | 60.766 | 61.398 | 60.418 | 60.791 | 59.059 | 62.839 | |
| T4 | 61.803 | 61.784 | 61.632 | 61.196 | 53.345 | 61.303 | |
| T5 | 60.652 | 61.891 | 62.086 | 60.753 | 48.598 | 57.226 | |
| K1 | 11.981 | 11.704 | 11.965 | 12.163 | 15.284 | 12.131 | |
| K2 | 12.242 | 12.148 | 12.079 | 12.156 | 13.383 | 12.463 | |
| K3 | 12.153 | 12.280 | 12.084 | 12.158 | 11.812 | 12.568 | |
| K4 | 12.361 | 12.357 | 12.326 | 12.239 | 10.669 | 12.261 | |
| K5 | 12.131 | 12.378 | 12.414 | 12.151 | 9.720 | 11.445 | |
| R | 0.379 | 0.674 | 0.449 | 0.089 | 5.564 | 1.123 | |
表1 正交试验设计、结果与极差分析
Table 1 Design, result and extreme difference of orthogonal test
| Test No. | Factor | Mean extraction yield (mg∙g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Steeped time (min) | (B) Ultrasound- microwave time (min) | (C) Microwave power (J∙s-1) | Blank | (D) Liquid to solid ratio (mL∙g-1) | (E) Ethanol concentration (%) | ||
| 1 | A1 16 | B1 2 | C1 50 | 1 | D1 30 | E1 50 | 14.361 |
| 2 | A1 16 | B2 6 | C2 100 | 2 | D2 35 | E2 60 | 13.343 |
| 3 | A1 16 | B3 10 | C3 150 | 3 | D3 40 | E3 70 | 12.015 |
| 4 | A1 16 | B4 14 | C4 200 | 4 | D4 45 | E4 80 | 10.966 |
| 5 | A1 16 | B5 18 | C5 250 | 5 | D5 50 | E5 90 | 9.221 |
| 6 | A2 24 | B1 2 | C2 100 | 3 | D4 45 | E5 90 | 9.430 |
| 7 | A2 24 | B2 6 | C3 150 | 4 | D5 50 | E1 50 | 9.696 |
| 8 | A2 24 | B3 10 | C4 200 | 5 | D1 30 | E2 60 | 15.878 |
| 9 | A2 24 | B4 14 | C5 250 | 1 | D2 35 | E3 70 | 14.259 |
| 10 | A2 24 | B5 18 | C1 50 | 2 | D3 40 | E4 80 | 11.946 |
| 11 | A3 32 | B1 2 | C3 150 | 5 | D2 35 | E4 80 | 12.869 |
| 12 | A3 32 | B2 6 | C4 200 | 1 | D3 40 | E5 90 | 11.181 |
| 13 | A3 32 | B3 10 | C5 250 | 2 | D4 45 | E1 50 | 10.934 |
| 14 | A3 32 | B4 14 | C1 50 | 3 | D5 50 | E2 60 | 9.948 |
| 15 | A3 32 | B5 18 | C2 100 | 4 | D1 30 | E3 70 | 15.833 |
| 16 | A4 40 | B1 2 | C4 200 | 2 | D5 50 | E3 70 | 9.967 |
| 17 | A4 40 | B2 6 | C5 250 | 3 | D1 30 | E4 80 | 15.758 |
| 18 | A4 40 | B3 10 | C1 50 | 4 | D2 35 | E5 90 | 12.806 |
| 19 | A4 40 | B4 14 | C2 100 | 5 | D3 40 | E1 50 | 12.022 |
| 20 | A4 40 | B5 18 | C3 150 | 1 | D4 45 | E2 60 | 11.251 |
| 21 | A5 48 | B1 2 | C5 250 | 4 | D3 40 | E2 60 | 11.895 |
| 22 | A5 48 | B2 6 | C1 50 | 5 | D4 45 | E3 70 | 10.764 |
| 23 | A5 48 | B3 10 | C2 100 | 1 | D5 50 | E4 80 | 9.765 |
| 24 | A5 48 | B4 14 | C3 150 | 2 | D1 30 | E5 90 | 14.588 |
| 25 | A5 48 | B5 18 | C4 200 | 3 | D2 35 | E1 50 | 13.640 |
| T1 | 59.906 | 58.522 | 59.824 | 60.817 | 76.417 | 60.652 | |
| T2 | 61.209 | 60.741 | 60.393 | 60.779 | 66.917 | 62.315 | |
| T3 | 60.766 | 61.398 | 60.418 | 60.791 | 59.059 | 62.839 | |
| T4 | 61.803 | 61.784 | 61.632 | 61.196 | 53.345 | 61.303 | |
| T5 | 60.652 | 61.891 | 62.086 | 60.753 | 48.598 | 57.226 | |
| K1 | 11.981 | 11.704 | 11.965 | 12.163 | 15.284 | 12.131 | |
| K2 | 12.242 | 12.148 | 12.079 | 12.156 | 13.383 | 12.463 | |
| K3 | 12.153 | 12.280 | 12.084 | 12.158 | 11.812 | 12.568 | |
| K4 | 12.361 | 12.357 | 12.326 | 12.239 | 10.669 | 12.261 | |
| K5 | 12.131 | 12.378 | 12.414 | 12.151 | 9.720 | 11.445 | |
| R | 0.379 | 0.674 | 0.449 | 0.089 | 5.564 | 1.123 | |
| Source | Sum of squares | dƒ | Mean square | F | P | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Steeped time (min) | 0.394 | 4 | 0.099 | 14.375 | 0.012 | * |
| (B) Ultrasound-microwave time (min) | 1.537 | 4 | 0.384 | 56.051 | 0.001 | ** |
| (C) Microwave power (J∙s-1) | 0.708 | 4 | 0.177 | 25.825 | 0.004 | ** |
| Blank | 0.027 | 4 | 0.007 | |||
| (D) Liquid to solid ratio (mL∙g-1) | 97.760 | 4 | 24.440 | 3564.343 | 0.0001 | ** |
| (E) Ethanol concentration (%) | 3.896 | 4 | 0.974 | 142.039 | 0.0001 | ** |
| Error | 0.027 | 4 | 0.007 | |||
| Total | 104.323 | 28 |
表2 正交试验方差分析
Table 2 Variance analysis of orthogonal test
| Source | Sum of squares | dƒ | Mean square | F | P | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Steeped time (min) | 0.394 | 4 | 0.099 | 14.375 | 0.012 | * |
| (B) Ultrasound-microwave time (min) | 1.537 | 4 | 0.384 | 56.051 | 0.001 | ** |
| (C) Microwave power (J∙s-1) | 0.708 | 4 | 0.177 | 25.825 | 0.004 | ** |
| Blank | 0.027 | 4 | 0.007 | |||
| (D) Liquid to solid ratio (mL∙g-1) | 97.760 | 4 | 24.440 | 3564.343 | 0.0001 | ** |
| (E) Ethanol concentration (%) | 3.896 | 4 | 0.974 | 142.039 | 0.0001 | ** |
| Error | 0.027 | 4 | 0.007 | |||
| Total | 104.323 | 28 |
| Method | Extraction yield (mg∙g-1) | RSD (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replicate 1 | Replicate 2 | Replicate 3 | Mean | ||
| Ultrasound-microwave assisted extraction | 15.915 | 16.262 | 16.262 | 16.146 a | 0.197 |
| Ultrasound assisted extraction | 15.780 | 15.453 | 14.972 | 15.402 bc | 0.401 |
| Microwave assisted extraction | 15.626 | 15.357 | 15.626 | 15.536 bc | 0.154 |
| Heating extraction | 15.472 | 14.952 | 15.472 | 15.299 c | 0.296 |
表3 不同提取方法的提取效果比较
Table 3 Comparison of extraction yields between ultrasound-microwave assisted extraction and other extraction methods
| Method | Extraction yield (mg∙g-1) | RSD (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replicate 1 | Replicate 2 | Replicate 3 | Mean | ||
| Ultrasound-microwave assisted extraction | 15.915 | 16.262 | 16.262 | 16.146 a | 0.197 |
| Ultrasound assisted extraction | 15.780 | 15.453 | 14.972 | 15.402 bc | 0.401 |
| Microwave assisted extraction | 15.626 | 15.357 | 15.626 | 15.536 bc | 0.154 |
| Heating extraction | 15.472 | 14.952 | 15.472 | 15.299 c | 0.296 |
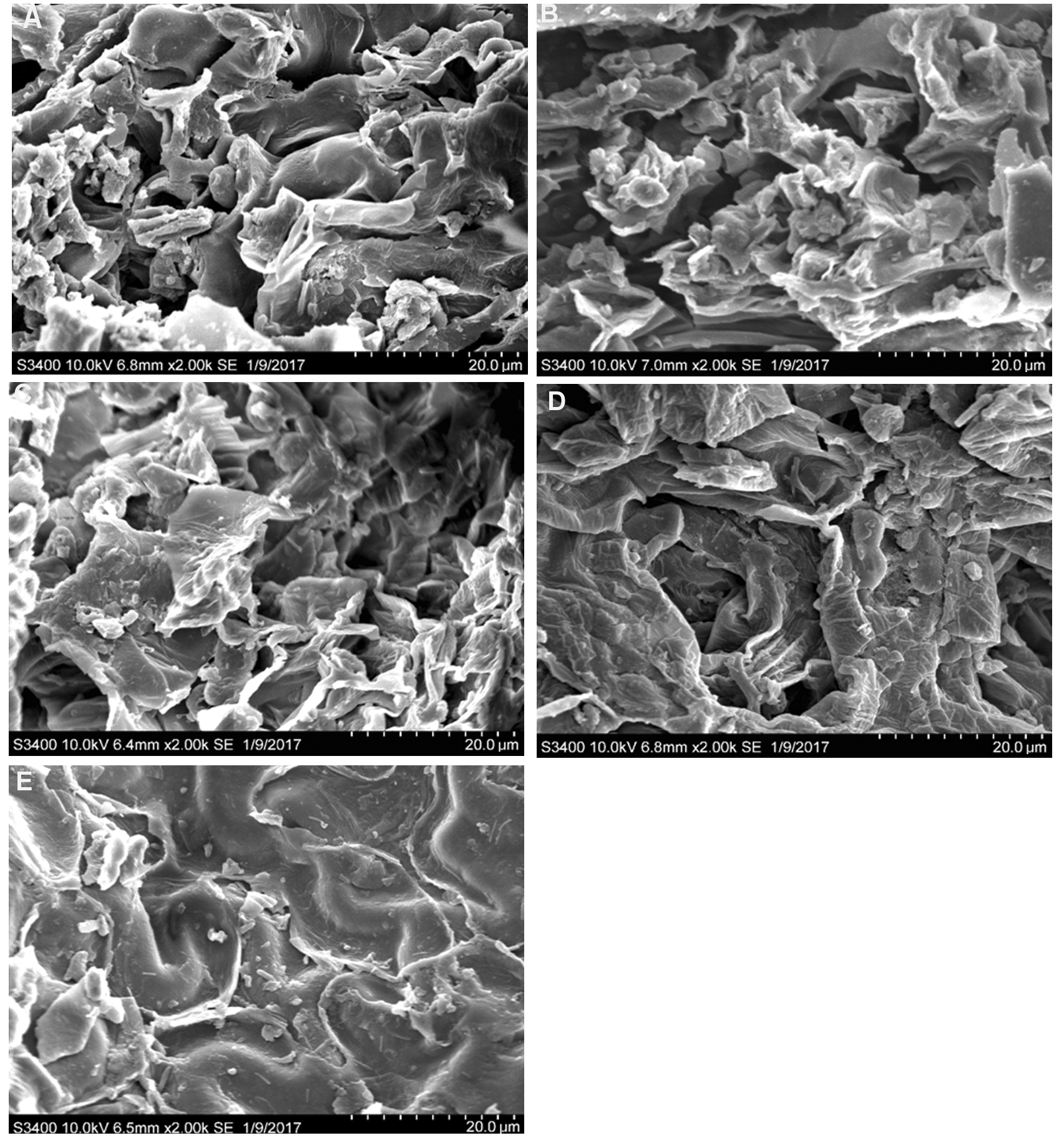
图2 不同提取方法处理后淫羊藿样品的扫描电子显微图像(A) 超声波-微波协同提取法; (B) 超声波提取法; (C) 微波提取法; (D) 加热提取法; (E) 未处理
Figure 2 Scanning electron micrographs of Epime- dium brevicornum leaf samples processed by different extraction methods(A) Ultrasound-microwave assisted extraction; (B) Ultrasound assisted extraction; (C) Microwave assisted extraction; (D) Heating extraction; (E) Untre- ated
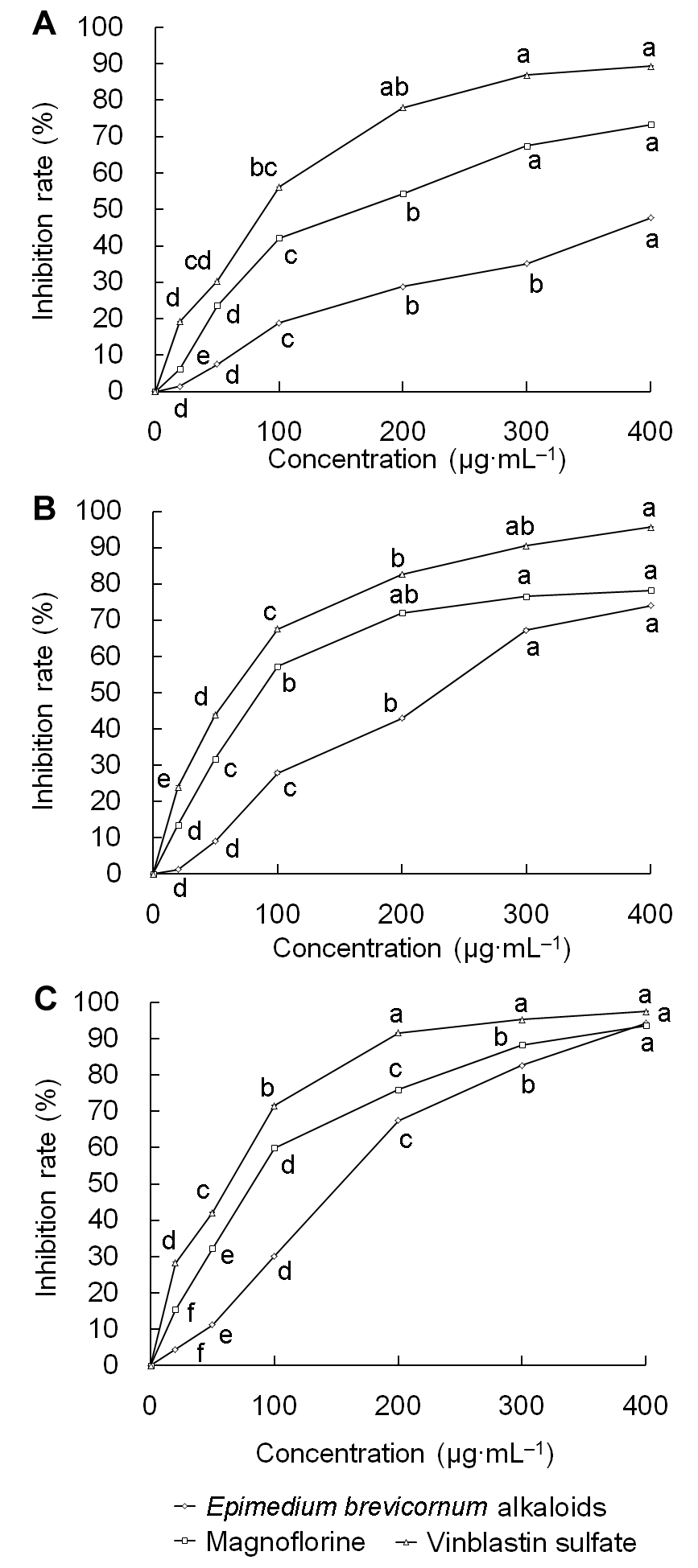
图4 淫羊藿生物碱对人宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖的抑制率(A) 24小时; (B) 48小时; (C) 72小时。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 4 Inhibition rate of Epimedium brevicornum alkaloids on human cervical cancer HeLa cells(A) 24 h; (B) 48 h; (C) 72 h. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05).
| Concentration (μg∙mL-1) | Inhibition rate (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epimedium brevicornum alkaloids | Magnoflorine | Vinblastin sulfate | |||||||||
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||
| 0 | 0.000± 0.024 | 0.000± 0.140 | 0.000± 0.048 | 0.000± 0.015 | 0.000± 0.242 | 0.000± 0.035 | 0.000± 0.534 | 0.000± 0.101 | 0.000± 0.111 | ||
| 20 | 1.354± 0.048 | 1.239± 0.109 | 4.435± 0.077 | 6.150± 0.005 | 13.541± 0.504 | 15.408± 0.133 | 19.142± 0.075 | 23.967± 0.288 | 28.283± 0.316 | ||
| 50 | 7.472± 0.024 | 9.010± 0.298 | 11.156± 0.128 | 23.583± 0.071 | 31.737± 0.440 | 32.191± 0.105 | 30.362± 0.007 | 43.853± 0.273 | 42.140± 0.193 | ||
| 100 | 18.811± 0.025 | 27.799± 0.454 | 30.129± 0.162 | 42.173± 0.049 | 57.217± 0.426 | 59.882± 0.162 | 56.205± 0.102 | 67.590± 0.322 | 71.598± 0.177 | ||
| 200 | 28.827± 0.036 | 42.880± 0.283 | 67.410± 0.079 | 54.315± 0.094 | 72.024± 0.058 | 75.961± 0.061 | 77.961± 0.044 | 82.618± 0.061 | 91.609± 0.074 | ||
| 300 | 35.134± 0.084 | 67.263± 0.372 | 82.682± 0.208 | 67.496± 0.032 | 76.609± 0.181 | 88.300± 0.024 | 86.866± 0.045 | 90.539± 0.133 | 95.317± 0.100 | ||
| 400 | 47.724± 0.048 | 74.015± 0.058 | 94.238± 0.016 | 73.354± 0.125 | 78.255± 0.122 | 93.591± 0.011 | 89.346± 0.035 | 95.637± 0.110 | 97.515± 0.094 | ||
| IC50 | >400 | 193.301 ±0.245 | 121.816 ±0.103 | 147.478 ±0.056 | 93.513± 0.282 | 77.672± 0.076 | 78.571± 0.120 | 57.159± 0.184 | 50.468± 0.152 | ||
| IC25 | 130.490 ±0.041 | 71.873 ±0.245 | 56.048 ±0.103 | 48.857 ±0.056 | 31.541± 0.282 | 31.103± 0.076 | 29.803± 0.120 | 20.712± 0.184 | 18.863± 0.152 | ||
表4 淫羊藿生物碱对人宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖的抑制作用(平均值±标准误)
Table 4 Inhibitory effect of Epimedium brevicornum alkaloids on human cervical cancer HeLa cells (means±SD)
| Concentration (μg∙mL-1) | Inhibition rate (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epimedium brevicornum alkaloids | Magnoflorine | Vinblastin sulfate | |||||||||
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||
| 0 | 0.000± 0.024 | 0.000± 0.140 | 0.000± 0.048 | 0.000± 0.015 | 0.000± 0.242 | 0.000± 0.035 | 0.000± 0.534 | 0.000± 0.101 | 0.000± 0.111 | ||
| 20 | 1.354± 0.048 | 1.239± 0.109 | 4.435± 0.077 | 6.150± 0.005 | 13.541± 0.504 | 15.408± 0.133 | 19.142± 0.075 | 23.967± 0.288 | 28.283± 0.316 | ||
| 50 | 7.472± 0.024 | 9.010± 0.298 | 11.156± 0.128 | 23.583± 0.071 | 31.737± 0.440 | 32.191± 0.105 | 30.362± 0.007 | 43.853± 0.273 | 42.140± 0.193 | ||
| 100 | 18.811± 0.025 | 27.799± 0.454 | 30.129± 0.162 | 42.173± 0.049 | 57.217± 0.426 | 59.882± 0.162 | 56.205± 0.102 | 67.590± 0.322 | 71.598± 0.177 | ||
| 200 | 28.827± 0.036 | 42.880± 0.283 | 67.410± 0.079 | 54.315± 0.094 | 72.024± 0.058 | 75.961± 0.061 | 77.961± 0.044 | 82.618± 0.061 | 91.609± 0.074 | ||
| 300 | 35.134± 0.084 | 67.263± 0.372 | 82.682± 0.208 | 67.496± 0.032 | 76.609± 0.181 | 88.300± 0.024 | 86.866± 0.045 | 90.539± 0.133 | 95.317± 0.100 | ||
| 400 | 47.724± 0.048 | 74.015± 0.058 | 94.238± 0.016 | 73.354± 0.125 | 78.255± 0.122 | 93.591± 0.011 | 89.346± 0.035 | 95.637± 0.110 | 97.515± 0.094 | ||
| IC50 | >400 | 193.301 ±0.245 | 121.816 ±0.103 | 147.478 ±0.056 | 93.513± 0.282 | 77.672± 0.076 | 78.571± 0.120 | 57.159± 0.184 | 50.468± 0.152 | ||
| IC25 | 130.490 ±0.041 | 71.873 ±0.245 | 56.048 ±0.103 | 48.857 ±0.056 | 31.541± 0.282 | 31.103± 0.076 | 29.803± 0.120 | 20.712± 0.184 | 18.863± 0.152 | ||
| [1] | 陈翠萍, 沙明, 杨松松, 张振学 (1996). 朝鲜淫羊藿中木兰碱的定量研究. 中国中药杂志 21, 681-682, 704. |
| [2] | 高敏, 刘京晶, 孙欣光, 黄文华, 郭宝林, 肖培根 (2011). 中药淫羊藿主要资源种类木兰花碱含量的研究. 中国中药杂志 36, 16-18. |
| [3] | 国家药典委员会 (2015). 中华人民共和国药典(四部). 北京: 中国医药科技出版社. pp. 57-59, 322. |
| [4] | 郝淼, 张华峰, 陈乐, 李璐 (2015). 淫羊藿生物碱定量分析方法的建立与应用. 中国食品学报 15(4), 201-207. |
| [5] | 李璐, 胡欢欢, 张华峰, 杨善慧, 乔春雷, 郝淼 (2016). 淫羊藿生物碱对大肠杆菌的抑菌作用. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版) 44(6), 74-79. |
| [6] | 李艳, 杜蕾蕾, 张小灵, 刘川, 赖先荣, 张艺, 范刚 (2014). 藏药小檗花的质量标准研究. 中药与临床 5(6), 6-8, 12. |
| [7] | 刘春明, 刘志强, 窦建鹏, 李丽, 刘淑莹 (2003). 朝鲜淫羊藿中生物碱类新成分的分离提取及结构鉴定. 高等学校化学学报 24, 2215-2217. |
| [8] | 牛丽丽, 张华峰, 陈乐, 杨晓华, 李璐 (2014). 基于近红外漫反射光谱快速测定淫羊藿蛋白质含量. 植物学报 49, 611-617. |
| [9] | 孙晨倩, 陈乐, 张华峰, 杨晓华, 杨娟 (2015). 一种快速定量分析药用植物淫羊藿生物碱的方法. 植物学报 50, 746-753. |
| [10] | 薛耀碧, 张华峰, 杨晓华, 牛丽丽, 张翔, 刘冬, 李建科 (2013). 近红外漫反射光谱法快速测定药用植物淫羊藿总黄酮含量. 植物学报 48, 65-71. |
| [11] | 袁航, 曹树萍, 陈抒云, 过立农, 郑健, 林瑞超 (2014). RRLC-DAD-ESI-MS2分析天平山淫羊藿中的11个化学成分. 药物分析杂志 34, 1156-1160. |
| [12] | 张华峰, 杨晓华, 郭玉蓉, 王瑛 (2009). 药用植物淫羊藿资源可持续利用现状与展望. 植物学报 44, 363-370. |
| [13] | Alonso-Carrillo N, De Los Ángeles Aguilar-Santamaría M, Vernon-Carter EJ, Jiménez-Alvarado R, Cruz-Sosa F, Román-Guerrero A (2017). Extraction of phenolic compounds from Satureja macrostema using microwave- ultrasound assisted and reflux methods and evaluation of their antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity. Ind Crops Prod 103, 213-221. |
| [14] | Blom TJM, Sierra M, Van Vliet TB, Franke-van Dijk MEI, De Koning P, Van Iren F, Verpoorte R, Libbenga KR (1991). Uptake and accumulation of ajmalicine into isolated vacuoles of cultured cells of Catharanthus roseus(L.) G. Don. and its conversion into serpentine. Planta 183, 170-177. |
| [15] | Chen FL, Zhang XL, Zhang Q, Du XQ, Yang L, Zu YG, Yang FJ (2016). Simultaneous synergistic microwave- ultrasonic extraction and hydrolysis for preparation of trans-resveratrol in tree peony seed oil-extracted residues using imidazolium-based ionic liquid. Ind Crops Prod 94, 266-280. |
| [16] | Fidaleo M, Miele NA, Mainardi S, Armini V, Nardi R, Cavella S (2017). Effect of refining degree on particle size, sensory and rheological characteristics of anhydrous paste for ice creams produced in industrial stirred ball mill.LWT- Food Sci Technol 79, 242-250. |
| [17] | Kou Y, Li L, Li H, Tan YH, Li B, Wang K, Du BY (2016). Berberine suppressed epithelial mesenchymal transition through cross-talk regulation of PI3K/AKT and RARα/RARβ in melanoma cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun 479, 290-296. |
| [18] | Li CM, Wang MH (2014). Potential biological activities of magnoflorine—a compound from Aristolochia debilis Sieb. et Zucc. Korean J Plant Resour 27, 223-228. |
| [19] | Liew SQ, Ngoh GC, Yusoff R, Teoh WH (2016). Sequential ultrasound-microwave assisted acid extraction (UMAE) of pectin from pomelo peels.Int J Biol Macromol 93, 426-435. |
| [20] | Lopez-Acevedo M, Grace L, Teoh D, Whitaker R, Adams DJ, Jia JQ, Nixon AB, Secord AA (2014). Dasatinib (BMS-35482) potentiates the activity of gemcitabine and docetaxel in uterine leiomyosarcoma cell lines.Gynecol Oncol Res Pract 1, 2. |
| [21] | Luque-Garcı?a JL, De Castro MDL (2003). Ultrasound: a powerful tool for leaching.Trends Analyt Chem 22, 41-47. |
| [22] | Nikoloff N, Ponzinibbio MV, Padula G, De Luca JC, Golijow CD, Seoane A (2016). Folic acid enhances the apop- totic and genotoxic activity of carboplatin in HeLa cell line.Toxicol Vitro 37, 142-147. |
| [23] | Patil DM, Akamanchi KG (2017). Ultrasound-assisted rapid extraction and kinetic modelling of influential factors: extraction of camptothecin from Nothapodytes nimmoniana plant. Ultrason Sonochem 37, 582-591. |
| [24] | Shitan N, Yazaki K (2007). Accumulation and membrane transport of plant alkaloids.Curr Pharm Biotechnol 8, 244-252. |
| [25] | Van De Velde ME, Kaspers GL, Abbink FCH, Wilhelm AJ, Ket JCF, Van Den Berg MH (2017). Vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy in children with cancer: a systematic review.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 114, 114-130. |
| [26] | Verma P, Mathur AK, Srivastava A, Mathur A (2012). Emerging trends in research on spatial and temporal organization of terpenoid indole alkaloid pathway in Catharanthus roseus: a literature update. Protoplasma 249, 255-268. |
| [27] | Vinatoru M (2001). An overview of the ultrasonically assisted extraction of bioactive principles from herbs.Ultrason So- nochem 8, 303-313. |
| [28] | Zhang HF, Yang XH (2012). Asian medicine: protect rare plants.Nature 482, 35. |
| [29] | Zhang HF, Yang XH, Wang Y (2011). Microwave assisted extraction of secondary metabolites from plants: current status and future directions.Trends Food Sci Technol 22, 672-688. |
| [30] | Zhang HF, Yang XH, Zhao LD, Wang Y (2009). Ultrasonic- assisted extraction of epimedin C from fresh leaves of Epimedium and extraction mechanism. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 10, 54-60. |
| [31] | Zhang HF, Zhang X, Yang XH, Qiu NX, Wang Y, Wang ZZ (2013a). Microwave assisted extraction of flavonoids from cultivated Epimedium sagittatum: extraction yield and me- chanism, antioxidant activity and chemical composition. Ind Crops Prod 50, 857-865. |
| [32] | Zhang XD, Oh M, Kim S, Kim J, Kim H, Kim S, Houghton PJ, Whang W (2013b). Epimediphine, a novel alkaloid from Epimedium koreanum inhibits acetylcholinesterase. Nat Prod Res 27, 1067-1074. |
| [33] | Zhou HY, Liu CZ (2006). Rapid determination of solanesol in tobacco by high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection following microwave-assisted extraction.J Chromatogr B 835, 119-122. |
| [1] | 刘旭鹏, 王敏, 韩守安, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 潘明启, 张雯. 植物器官脱落调控因素及分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [2] | 吴锁伟, 安学丽, 万向元. 玉米雄性不育机理及其在工程核不育制种中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [3] | 董云伟, 鲍梦幻, 程娇, 陈义永, 杜建国, 高养春, 胡利莎, 李心诚, 刘春龙, 秦耿, 孙进, 王信, 杨光, 张崇良, 张雄, 张宇洋, 张志新, 战爱斌, 贺强, 孙军, 陈彬, 沙忠利, 林强. 中国海洋生物地理学研究进展和热点: 物种分布模型及其应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23453-. |
| [4] | 王复标, 叶子飘. 植物电子传递速率光响应模型的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(3): 287-305. |
| [5] | 苏金源, 燕语, 李冲, 李丹, 杜芳. 通过遗传多样性探讨极小种群野生植物的致濒机理及保护策略: 以裸子植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 376-384. |
| [6] | 蒙文萍, 戴全厚, 冉景丞. 苔藓植物岩溶作用研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(5): 396-407. |
| [7] | 刘佳怡,王嘉欣,宋海超,张正科,徐祥彬,吉训聪,史学群. 纳他霉素对芒果采后胶孢炭疽菌的抑菌效果及机理[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 455-463. |
| [8] | 叶子飘, 段世华, 安婷, 康华靖. 最大电子传递速率的确定及其对电子流分配的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(4): 498-507. |
| [9] | 李荣改, 陆艳梅, 王月影, 王宝强, 宋炜, 张文英. 玉米粗缩病的分子研究新进展[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(3): 375-387. |
| [10] | 张玲玲, 吴丹, 赵子捷, 赵立群. 植物一氧化氮信号分子的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(3): 337-345. |
| [11] | 叶子飘, 胡文海, 闫小红. 光系统II实际光化学量子效率对光的响应模型的比较[J]. 植物生态学报, 2016, 40(11): 1208-1217. |
| [12] | 孙晨倩, 陈乐, 张华峰, 杨晓华, 杨娟. 一种快速定量分析药用植物淫羊藿生物碱的方法[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(6): 746-753. |
| [13] | 程巧, 曾建国, 乐捷. 异喹啉类生物碱生物合成、运输、储藏相关细胞生物学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(6): 720-728. |
| [14] | 叶子飘,胡文海,肖宜安,樊大勇,尹建华,段世华,闫小红,贺俐,张斯斯. 光合电子流对光响应的机理模型及其应用[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(11): 1241-1249. |
| [15] | 贺纪正, 李晶, 郑袁明. 土壤生态系统微生物多样性-稳定性关系的思考[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(4): 411-420. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||