

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 693-704.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20006 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xi Zhang, Tianhang Qiu, Anan Wang, Huajian Zhou, Min Yuan, Li Li, Sulan Bai, Suxia Cui*( )
)
Received:2020-01-14
Accepted:2020-08-26
Online:2020-11-01
Published:2020-11-11
Contact:
Suxia Cui
Xi Zhang, Tianhang Qiu, Anan Wang, Huajian Zhou, Min Yuan, Li Li, Sulan Bai, Suxia Cui. Morphology and Genetic Diversity of Phragmites australis in Beijing[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(6): 693-704.
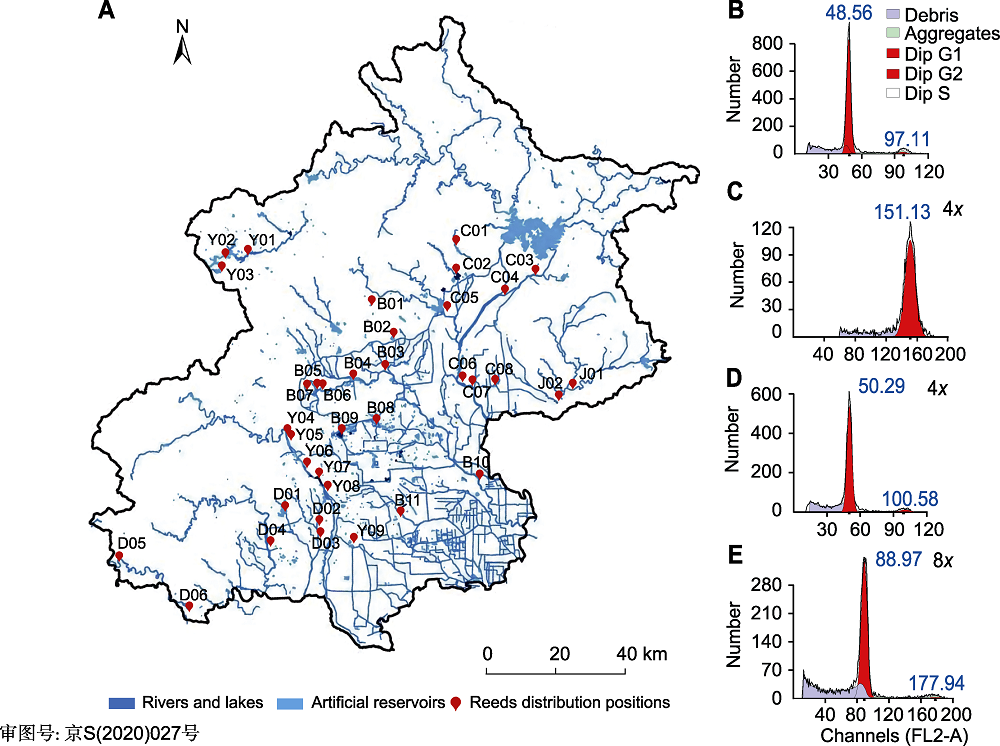
Figure 1 Distribution and chromosome ploidy of Phragmites australis in Beijing (A) Distribution of reeds in Beijing (The main distribution areas of reeds are marked by red dots and numbered according to the water system: Yongding River System (Y), Chaobai River System (C), North Canal System (B), Grand Canal System (D), Ji Canal System (J); Blue indicates rivers, lakes or artificial reservoirs); (B)-(E) Detection of reed chromosome ploidy by flow cytometry (The abscissa is the fluorescence intensity of the channel, and the ordinate is the number of nuclei; G1 and G2 phases are indicated by dark red and light red, respectively; fragments and aggregates are indicated by gray-purple and green, respectively). Figures (B) and (C) detected the tetraploid reeds using rice as the internal reference; Figures (D) and (E) detected the octaploid reeds using the tetraploid reeds as the internal reference.
| Water system | Distribution location | Distribution description | Area (hm2) | Proportion (%) | Ploidy level | Origin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yongding River System | 304.11 | 47.16 | |||||||
| Y01 | Weishui River | Distributed at both sides of the west of the Weishui River Tunnel passes th- rough the World Horticultural, exposition to Yankang Road | 5.14 | 0.80 | NA | 115.95°E, 40.45°N | |||
| Y02 | Guanting Reservoir (in Beijing) | Scattered along the bank about 15 km west of the Guanting Bridge | 0.21 | 0.03 | 8x/4x | 115.87°E, 40.44°N | |||
| Y03 | Wild Duck Lake National Wetland Park | Distributed in patches in the core area, buffer zone, and test area | 257.40 | 39.92 | 8x | 115.86°E, 40.41°N | |||
| Water system | Distribution location | Distribution description | Area (hm2) | Proportion (%) | Ploidy level | Origin | |||
| Y04 | Shanxia Section of Yongding River | Distributed along the river bank | 8.31 | 1.29 | NA | 116.09°E, 39.99°N | |||
| Y05 | Sanjiadian Rush Wetland Park | Distributed in patches | 4.60 | 0.71 | 8x | 116.10°E, 39.97°N | |||
| Y06 | Lianshi Lake Park | Distributed along both banks of the river | 2.12 | 0.33 | 8x | 116.15°E, 39.90°N | |||
| Y07 | Yuanbo Lake Wetland | Distributed in patches | 16.30 | 2.53 | NA | 116.21°E, 39.87°N | |||
| Y08 | Ludi Park | Distributed in patches along the coast | 9.71 | 1.51 | NA | 116.22°E, 39.84°N | |||
| Y09 | Niantan Park | Distributed around the shore of a lake in the park | 0.32 | 0.05 | NA | 116.31°E, 39.71°N | |||
| Daqing River System | 58.63 | 9.09 | |||||||
| D01 | Chongqing Reservoir | Distributed in patches in the southwest corner of the reservoir | 13.17 | 2.04 | NA | 116.08°E, 39.79°N | |||
| D02 | Jiuzi River | Distributed in the upper reaches of Xiaoqing River | 5.42 | 0.84 | 8x | 116.19°E, 39.75°N | |||
| D03 | Xiaoqing River | Distributed in patches along the river from the south of Shuisi Road to the junction of Hedgehog River | 20.02 | 3.10 | 8x/4x | 116.20°E, 39.72°N | |||
| D04 | Dashi River | Distributed along the north and south rivers of Jingzhou Road | 16.41 | 2.54 | NA | 116.03°E, 39.70°N | |||
| D05 | Juma River | Sporadic distribution from Shidu to Yesanpo | 0.31 | 0.05 | 8x | 115.51°E, 39.66°N | |||
| D06 | Beijuma River | Distributed in patches at the Beijing border of the North Juma River Estuary | 3.30 | 0.51 | NA | 115.76°E, 39.53°N | |||
| Chaobai River System | 196.83 | 30.52 | |||||||
| C01 | Qinglong Gorge | Sporadically distributed from the upper reaches of Qinglong Gorge to Baiquan Mountain | 0.06 | 0.01 | 4x | 116.66°E, 40.48°N | |||
| C02 | Yanqi Lake | Artificial reed landscape at the northwest corner of the lake | 0.83 | 0.13 | 8x | 116.60°E, 40.40°N | |||
| C03 | Chao River | Distributed in patches about 7 km along the river near Miyun Service Area of Dachang Expressway | 38.23 | 5.93 | 8x/4x | 116.94°E, 40.40°N | |||
| C04 | The estuary of Chaobai River | Upper reaches of Chao River and Bai River cross estuary | 7.08 | 1.10 | 8x | 116.83°E, 40.35°N | |||
| C05 | Huai River | About 4.5 km from Huairou Reservoir to Yanqi River junction | 10.83 | 1.68 | 8x | 116.63°E, 40.31°N | |||
| C06 | Chaobai River Bridge | Piled up along the bank of Fuxing Bridge/Fengbo Bridge/Chaobai River Bridge in Shunping Road | 18.94 | 2.94 | NA | 116.69°E, 40.12°N | |||
| C07 | Hanshiqiao Wetland Park | Distributed in pieces of the core area, buffer zone and recovery area | 83.95 | 13.02 | 8x | 116.80°E, 40.12°N | |||
| C08 | Binhe Forest Park | Distributed along the north and south banks of Chaobai River | 36.91 | 5.72 | NA | 116.72°E, 40.11°N | |||
| North Canal Water System | 82.91 | 12.86 | |||||||
| B01 | Lily Reservoir | Distributed in upstream area of the reservoir | 0.05 | 0.01 | 8x | 116.38°E, 40.32°N | |||
| B02 | Taoyukou Reservoir | Distributed in periphery and upstream areas of the east and west sides of the reservoir | 9.46 | 1.47 | 8x | 116.45°E, 40.24°N | |||
| B03 | Wenyu River | Scattered along the middle and upper banks of Wenyu River | 0.21 | 0.03 | NA | 116.42°E, 40.15°N | |||
| B04 | Shahezha Park | Distributed in patches in the west bank of the lake in the park | 0.34 | 0.05 | 8x | 116.31°E, 40.13°N | |||
| Water system | Distribution location | Distribution description | Area (hm2) | Proportion (%) | Ploidy level | Origin | |||
| B05 | Cuihu Wetland Park | Uneven distribution on the wet land in protected areas and open areas | 45.38 | 7.04 | 8x | 116.19°E, 40.11°N | |||
| B06 | Shangzhuang Reservoir | Evenly distributed along the bank of Shangzhuang Reservoir and scattered along the downstream bank | 0.81 | 0.13 | 8x/4x | 116.21°E, 40.11°N | |||
| B07 | Nansha River | Discontinuous distribution in the 10 km section near Daoxiang Lake | 8.29 | 1.29 | 8x | 116.15°E, 40.10°N | |||
| B08 | Olympic Forest Park | Distributed at the west side of Wetland in Southern District and the east side around the lake | 5.04 | 0.78 | 8x/4x | 116.39°E, 40.01°N | |||
| B09 | Summer Palace | Mixed distribution of calamus on the shore near Zaojiantang site | 0.12 | 0.02 | NA | 116.27°E, 39.99°N | |||
| B10 | Grand Canal Forest Park | Distributed on the semi-arid coastal wetlands in popular reeds | 6.51 | 1.01 | NA | 116.75°E, 39.87°N | |||
| B11 | Nanhaizi Park | Distribution of small pieces of lakeshore in the park | 6.70 | 1.04 | 8x/4x | 116.47°E, 39.77°N | |||
| Jiyun River System | 2.37 | 0.37 | |||||||
| J01 | Ju River and Ru River | Sporadically distributed at the confluence of the Ru River and the Ju River | 2.03 | 0.31 | NA | 117.06°E, 40.11°N | |||
| J02 | Jinji River | The junction of Jinji River and Yanghe River to the vicinity of Yingcheng Village | 0.34 | 0.05 | NA | 117.02°E, 40.08°N | |||
Table 1 The distribution, area and ploidy level of Phragmites australis in Beijing
| Water system | Distribution location | Distribution description | Area (hm2) | Proportion (%) | Ploidy level | Origin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yongding River System | 304.11 | 47.16 | |||||||
| Y01 | Weishui River | Distributed at both sides of the west of the Weishui River Tunnel passes th- rough the World Horticultural, exposition to Yankang Road | 5.14 | 0.80 | NA | 115.95°E, 40.45°N | |||
| Y02 | Guanting Reservoir (in Beijing) | Scattered along the bank about 15 km west of the Guanting Bridge | 0.21 | 0.03 | 8x/4x | 115.87°E, 40.44°N | |||
| Y03 | Wild Duck Lake National Wetland Park | Distributed in patches in the core area, buffer zone, and test area | 257.40 | 39.92 | 8x | 115.86°E, 40.41°N | |||
| Water system | Distribution location | Distribution description | Area (hm2) | Proportion (%) | Ploidy level | Origin | |||
| Y04 | Shanxia Section of Yongding River | Distributed along the river bank | 8.31 | 1.29 | NA | 116.09°E, 39.99°N | |||
| Y05 | Sanjiadian Rush Wetland Park | Distributed in patches | 4.60 | 0.71 | 8x | 116.10°E, 39.97°N | |||
| Y06 | Lianshi Lake Park | Distributed along both banks of the river | 2.12 | 0.33 | 8x | 116.15°E, 39.90°N | |||
| Y07 | Yuanbo Lake Wetland | Distributed in patches | 16.30 | 2.53 | NA | 116.21°E, 39.87°N | |||
| Y08 | Ludi Park | Distributed in patches along the coast | 9.71 | 1.51 | NA | 116.22°E, 39.84°N | |||
| Y09 | Niantan Park | Distributed around the shore of a lake in the park | 0.32 | 0.05 | NA | 116.31°E, 39.71°N | |||
| Daqing River System | 58.63 | 9.09 | |||||||
| D01 | Chongqing Reservoir | Distributed in patches in the southwest corner of the reservoir | 13.17 | 2.04 | NA | 116.08°E, 39.79°N | |||
| D02 | Jiuzi River | Distributed in the upper reaches of Xiaoqing River | 5.42 | 0.84 | 8x | 116.19°E, 39.75°N | |||
| D03 | Xiaoqing River | Distributed in patches along the river from the south of Shuisi Road to the junction of Hedgehog River | 20.02 | 3.10 | 8x/4x | 116.20°E, 39.72°N | |||
| D04 | Dashi River | Distributed along the north and south rivers of Jingzhou Road | 16.41 | 2.54 | NA | 116.03°E, 39.70°N | |||
| D05 | Juma River | Sporadic distribution from Shidu to Yesanpo | 0.31 | 0.05 | 8x | 115.51°E, 39.66°N | |||
| D06 | Beijuma River | Distributed in patches at the Beijing border of the North Juma River Estuary | 3.30 | 0.51 | NA | 115.76°E, 39.53°N | |||
| Chaobai River System | 196.83 | 30.52 | |||||||
| C01 | Qinglong Gorge | Sporadically distributed from the upper reaches of Qinglong Gorge to Baiquan Mountain | 0.06 | 0.01 | 4x | 116.66°E, 40.48°N | |||
| C02 | Yanqi Lake | Artificial reed landscape at the northwest corner of the lake | 0.83 | 0.13 | 8x | 116.60°E, 40.40°N | |||
| C03 | Chao River | Distributed in patches about 7 km along the river near Miyun Service Area of Dachang Expressway | 38.23 | 5.93 | 8x/4x | 116.94°E, 40.40°N | |||
| C04 | The estuary of Chaobai River | Upper reaches of Chao River and Bai River cross estuary | 7.08 | 1.10 | 8x | 116.83°E, 40.35°N | |||
| C05 | Huai River | About 4.5 km from Huairou Reservoir to Yanqi River junction | 10.83 | 1.68 | 8x | 116.63°E, 40.31°N | |||
| C06 | Chaobai River Bridge | Piled up along the bank of Fuxing Bridge/Fengbo Bridge/Chaobai River Bridge in Shunping Road | 18.94 | 2.94 | NA | 116.69°E, 40.12°N | |||
| C07 | Hanshiqiao Wetland Park | Distributed in pieces of the core area, buffer zone and recovery area | 83.95 | 13.02 | 8x | 116.80°E, 40.12°N | |||
| C08 | Binhe Forest Park | Distributed along the north and south banks of Chaobai River | 36.91 | 5.72 | NA | 116.72°E, 40.11°N | |||
| North Canal Water System | 82.91 | 12.86 | |||||||
| B01 | Lily Reservoir | Distributed in upstream area of the reservoir | 0.05 | 0.01 | 8x | 116.38°E, 40.32°N | |||
| B02 | Taoyukou Reservoir | Distributed in periphery and upstream areas of the east and west sides of the reservoir | 9.46 | 1.47 | 8x | 116.45°E, 40.24°N | |||
| B03 | Wenyu River | Scattered along the middle and upper banks of Wenyu River | 0.21 | 0.03 | NA | 116.42°E, 40.15°N | |||
| B04 | Shahezha Park | Distributed in patches in the west bank of the lake in the park | 0.34 | 0.05 | 8x | 116.31°E, 40.13°N | |||
| Water system | Distribution location | Distribution description | Area (hm2) | Proportion (%) | Ploidy level | Origin | |||
| B05 | Cuihu Wetland Park | Uneven distribution on the wet land in protected areas and open areas | 45.38 | 7.04 | 8x | 116.19°E, 40.11°N | |||
| B06 | Shangzhuang Reservoir | Evenly distributed along the bank of Shangzhuang Reservoir and scattered along the downstream bank | 0.81 | 0.13 | 8x/4x | 116.21°E, 40.11°N | |||
| B07 | Nansha River | Discontinuous distribution in the 10 km section near Daoxiang Lake | 8.29 | 1.29 | 8x | 116.15°E, 40.10°N | |||
| B08 | Olympic Forest Park | Distributed at the west side of Wetland in Southern District and the east side around the lake | 5.04 | 0.78 | 8x/4x | 116.39°E, 40.01°N | |||
| B09 | Summer Palace | Mixed distribution of calamus on the shore near Zaojiantang site | 0.12 | 0.02 | NA | 116.27°E, 39.99°N | |||
| B10 | Grand Canal Forest Park | Distributed on the semi-arid coastal wetlands in popular reeds | 6.51 | 1.01 | NA | 116.75°E, 39.87°N | |||
| B11 | Nanhaizi Park | Distribution of small pieces of lakeshore in the park | 6.70 | 1.04 | 8x/4x | 116.47°E, 39.77°N | |||
| Jiyun River System | 2.37 | 0.37 | |||||||
| J01 | Ju River and Ru River | Sporadically distributed at the confluence of the Ru River and the Ju River | 2.03 | 0.31 | NA | 117.06°E, 40.11°N | |||
| J02 | Jinji River | The junction of Jinji River and Yanghe River to the vicinity of Yingcheng Village | 0.34 | 0.05 | NA | 117.02°E, 40.08°N | |||
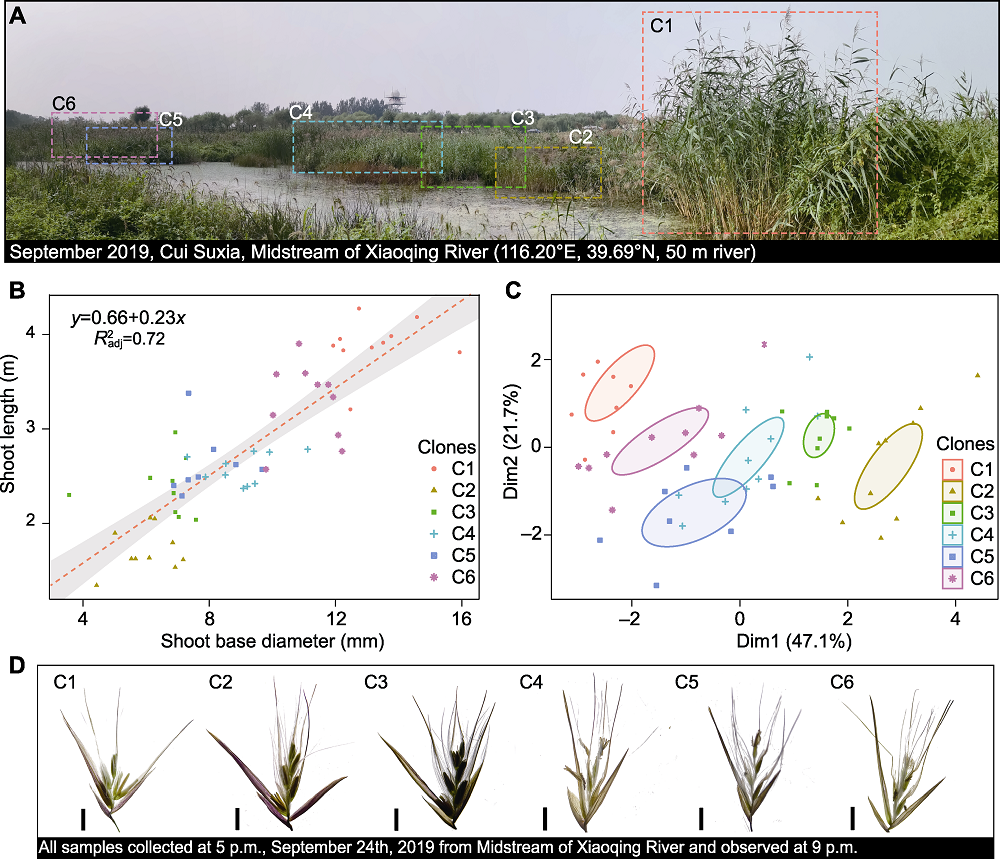
Figure 2 Polymorphism analysis of Phragmites australis in the Xiaoqing River plot (A) Panoramic view of the Xiaoqing River plot (six different reed clones C1-C6 are marked by rectangular dashed boxes of different colors); (B) Correlation analysis of height and base diameter of six different reed clones (The gray shaded part is the regression interval, and the red dotted line is the best regression curve); (C) Principal component analysis of polymorphism in the reed plot of Xiaoqing River (based on eight morphological indicators of six species of reed clones in Table 2), selecting each reed clone according to 95% confidence probability; (D) Representative photos of spikelets (bars=5 mm)
| Phenotype | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Standard deviation | Variation coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (m) | 2.74 | 4.25 | 1.34 | 0.75 | 27.48 |
| Diameter (mm) | 9.02 | 15.93 | 3.56 | 2.77 | 30.76 |
| Inflorescences length (cm) | 24.21 | 36.20 | 10.40 | 5.77 | 23.85 |
| Inflorescences width (cm) | 5.92 | 17.08 | 1.39 | 3.70 | 62.55 |
| Length of flag leaf (cm) | 31.57 | 53.10 | 15.40 | 7.06 | 22.37 |
| Width of flag leaf (cm) | 1.46 | 2.51 | 0.51 | 0.46 | 31.31 |
| Length of the sixth leaf (cm) | 39.41 | 62.30 | 15.30 | 14.19 | 36.02 |
| Width of the sixth leaf (cm) | 2.82 | 4.98 | 1.31 | 0.86 | 30.63 |
Table 3 Morphological polymorphism and variation coefficient in Phragmites australis clone populations in Xiaoqing River plot, Beijing (n=59)
| Phenotype | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Standard deviation | Variation coefficient (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (m) | 2.74 | 4.25 | 1.34 | 0.75 | 27.48 |
| Diameter (mm) | 9.02 | 15.93 | 3.56 | 2.77 | 30.76 |
| Inflorescences length (cm) | 24.21 | 36.20 | 10.40 | 5.77 | 23.85 |
| Inflorescences width (cm) | 5.92 | 17.08 | 1.39 | 3.70 | 62.55 |
| Length of flag leaf (cm) | 31.57 | 53.10 | 15.40 | 7.06 | 22.37 |
| Width of flag leaf (cm) | 1.46 | 2.51 | 0.51 | 0.46 | 31.31 |
| Length of the sixth leaf (cm) | 39.41 | 62.30 | 15.30 | 14.19 | 36.02 |
| Width of the sixth leaf (cm) | 2.82 | 4.98 | 1.31 | 0.86 | 30.63 |
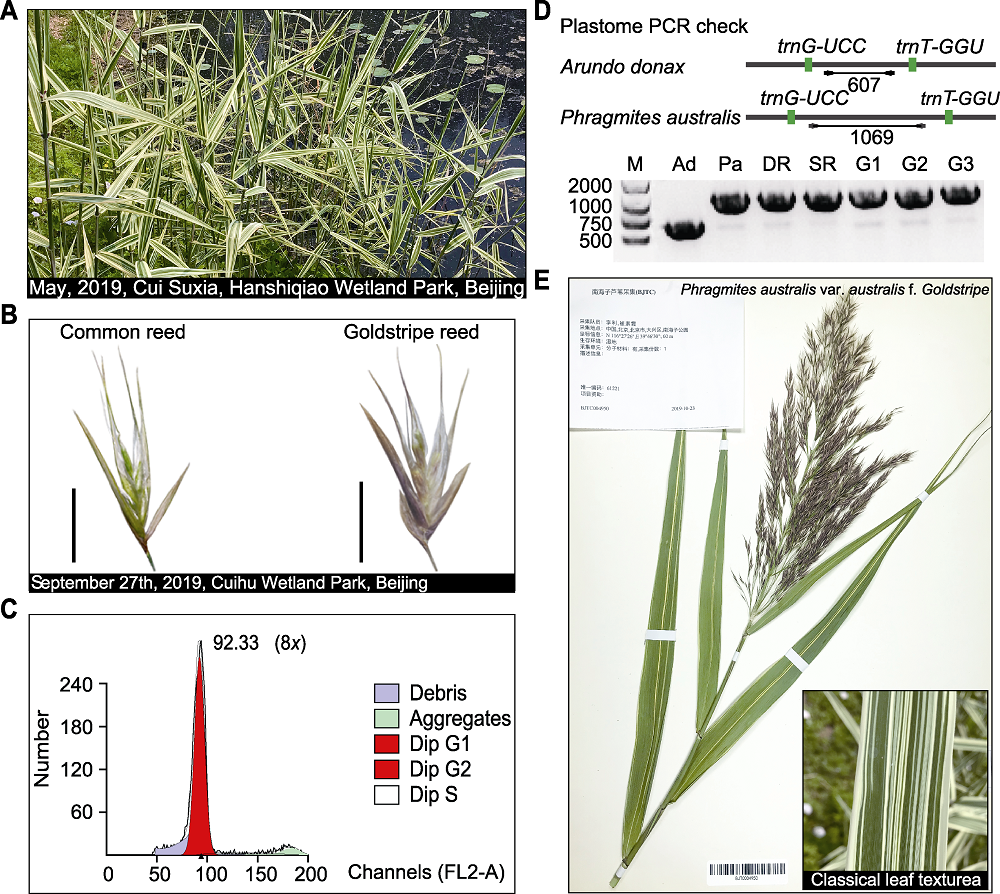
Figure 3 Identification of a new form of Phragmites australis (A) Phragmites australis f. Goldstripe in natural habitats; (B) Spikelets of goldstripe reed (bars=5 mm); (C) Identification of ploidy level by the flow cytometric analysis on the goldstripe reed nuclei; (D) The size difference of a DNA fragment (from trnG-UCC to trnT-GGU) as revealed by PCR between goldstripe reed and Arundo donax var. versicolor, A. donax (Ad) produced a 607 bp band; common reeds and goldstripe reed produced 1069 bp bands (Pa indicates Xiaoqinghe reed C6, DR and SR indicate desert dune reeds and swamp reeds growing in the Hexi Corridor, and G1-G3 are all goldstripe reeds)(M: Molecular marker); (E) A type specimen of goldstripe reed
| Sample | Height (m) | Diameter (mm) | Seed setting rate (%) | Flowering time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common reed | 3.6±0.2 | 8.70±0.80 | 16.8±7.1 | Mid-August |
| Goldstripe reed | 2.8±0.2 | 7.42±0.75 | 0.6±0.2 | Early September |
Table 4 Phenotype comparison of common reed and goldstripe reed in Cuihu Wetland Park, Beijing (means±SD, n≥16)
| Sample | Height (m) | Diameter (mm) | Seed setting rate (%) | Flowering time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common reed | 3.6±0.2 | 8.70±0.80 | 16.8±7.1 | Mid-August |
| Goldstripe reed | 2.8±0.2 | 7.42±0.75 | 0.6±0.2 | Early September |
| [1] | 程杰 (2013). 论中国古代芦苇资源的自然分布、社会利用和文化反映. 阅江学刊 5, 119-134. |
| [2] | 郭春秀, 李发明, 张莹花, 刘淑娟, 朱淑娟, 张大彪 (2012). 河西走廊芦苇草地资源特征及其保护利用. 草原与草坪 32(4), 93-96. |
| [3] | 李建国, 李贵宝, 刘芳, 王殿武, 陈桂珅 (2004). 白洋淀芦苇资源及其生态功能与利用. 南水北调与水利科技 2(5), 37-40. |
| [4] | 张兵 (2008). 谈芦苇湿地的价值. 现代农业科技 (12), 347. |
| [5] | 张承烈, 陈国仓 (1991). 河西走廊不同生态类型芦苇的气体交换特点的研究. 生态学报 11(3), 250-255. |
| [6] | Ahmed MJ (2017). Application of raw and activated Phragmites australis as potential adsorbents for wastewater treatments. Ecol Eng 102, 262-269. |
| [7] | An JX, Wang Q, Yang J, Liu JQ (2012). Phylogeographic analyses of Phragmites australis in China: native distribution and habitat preference of the haplotype that invaded North America. J Syst Evol 50, 334-340. |
| [8] | Burdick DM, Konisky RA (2003). Determinants of expansion for Phragmites australis, common reed, in natural and impacted coastal marshes. Estuaries 26, 407-416. |
| [9] | Clayton WD (1967). Studies in the Gramineae: XIV. Kew Bull 21, 111-117. |
| [10] | Clevering OA, Lissner J (1999). Taxonomy, chromosome numbers, clonal diversity and population dynamics of Phragmites australis. Aquat Bot 64, 185-208. |
| [11] |
Cui SX, Hu J, Yang B, Shi L, Huang F, Tsai SN, Ngai SM, He YK, Zhang JH (2009). Proteomic characterization of Phragmites communis in ecotypes of swamp and desert dune. Proteomics 9, 3950-3967.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] | Cui SX, Wang W, Zhang CL (2002). Plant regeneration from callus cultures in two ecotypes of reed ( Phragmites communis Trinius). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 38, 325-329. |
| [13] |
Doležel J, Greilhuber J, Suda J (2007). Estimation of nuclear DNA content in plants using flow cytometry. Nat Protoc 2, 2233-2244.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Dykyjová D, Pazourková Z (1979). A diploid form of Phragmites communis, as a possible result of cytogenetical response to ecological stress. Folia Geobot Phytotax 14, 113-120. |
| [15] |
Eller F, Skálová H, Caplan JS, Bhattarai GP, Burger MK, Cronin JT, Guo WY, Guo X, Hazelton ELG, Kettenring KM, Lambertini C, McCormick MK, Meyerson LA, Mozdzer TJ, Pyšek P, Sorrell BK, Whigham DF, Brix H (2017). Cosmopolitan species as models for ecophysiological responses to global change: the common reed Phragmites australis. Front Plant Sci 8, 1833.
URL PMID |
| [16] | Gorenflot R (1986). Degrés et niveaux de la variation du nombre chromosomique chez Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. Veröff. Geobot. Inst. ETH, Stiftung Rübel. Zürich 87, 53-65. |
| [17] | Haslam SM (1970). Variation of population type in Phragmites communis Trin. Ann Bot 34, 147-158. |
| [18] | Haslam SM (1971). Community regulation in Phragmites communis Trin. I. monodominant stands. J Ecol 59, 65-73. |
| [19] |
Li L, Chen XD, Shi L, Wang CJ, Fu B, Qiu TH, Cui SX (2017). A proteome translocation response to complex desert stress environments in perennial Phragmites sympatric ecotypes with contrasting water availability. Front Plant Sci 8, 511.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Meyerson LA, Cronin JT, Bhattarai GP, Brix H, Lambertini C, Lučanová M, Rinehart S, Suda J, Pyšek P (2016). Do ploidy level and nuclear genome size and latitude of origin modify the expression of Phragmites australis traits and interactions with herbivores? Biol Invasions 18, 2531-2549. |
| [21] | Meyerson LA, Saltonstall K, Chambers RM, Silliman BR, Bertness MD, Strong D (2009). Phragmites australis in eastern North America: a historical and ecological perspective In: Silliman BR, Grosholz ED, Bertness MD, eds. Human Impacts on Salt Marshes: A Global Perspective. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 57-82. |
| [22] | Porebski S, Bailey LG, Baum BR (1997). Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Mol Biol Rep 15, 8-15. |
| [23] | Raicu P, Staicu S, Stoian V, Roman T (1972). The Phragmites communis Trin. chromosome complement in the Danube delta. Hydrobiologia 39, 83-89. |
| [24] | Saltonstall K (2001). A set of primers for amplification of noncoding regions of chloroplast DNA in the grasses. Mol Ecol Notes 1, 76-78. |
| [25] |
Saltonstall K (2002). Cryptic invasion by a non-native genotype of the common reed, Phragmites australis, into North America. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 2445-2449.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] |
Saltonstall K (2003). Microsatellite variation within and among North American lineages of Phragmites australis. Mol Ecol 12, 1689-1702.
URL PMID |
| [27] | Saltonstall K (2016). The naming of Phragmites haplotypes. Biol Invasions 18, 2433-2441. |
| [28] |
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991). Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17, 1105-1109.
URL PMID |
| [29] | Tanaka TST, Irbis C, Inamura T (2017). Phylogenetic analyses of Phragmites spp. in southwest China identified two lineages and their hybrids. Plant Syst Evol 303, 699-707. |
| [30] |
Wang WS, Mauleon R, Hu ZQ, Chebotarov D, Tai SS, Wu ZC, Li M, Zheng TQ, Fuentes RR, Zhang F, Mansueto L, Copetti D, Sanciangco M, Palis KC, Xu JL, Sun C, Fu BY, Zhang HL, Gao YM, Zhao XQ, Shen F, Cui X, Yu H, Li ZC, Chen ML, Detras J, Zhou YL, Zhang XY, Zhao Y, Kudrna D, Wang CC, Li R, Jia B, Lu JY, He XC, Dong ZT, Xu JB, Li YH, Wang M, Shi JX, Li J, Zhang DB, Lee S, Hu WS, Poliakov A, Dubchak I, Ulat VJ, Borja FN, Mendoza JR, Ali J, Li J, Gao Q, Niu YC, Yue Z, Naredo MEB, Talag J, Wang XQ, Li JJ, Fang XD, Yin Y, Glaszmann JC, Zhang JW, Li JY, Hamilton RS, Wing RA, Ruan J, Zhang GY, Wei CC, Alexandrov N, McNally KL, Li ZK, Leung H (2018). Genomic variation in 3,010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice. Nature 557, 43-49.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | CHENG Ke-Xin, DU Yao, LI Kai-Hang, WANG Hao-Chen, YANG Yan, JIN Yi, HE Xiao-Qing. Genetic mechanism of interaction between maize and phyllospheric microbiome [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(2): 215-228. |
| [2] | Jingci Meng, Guodong Wang, Guanglan Cao, Nanlin Hu, Meiling Zhao, Yantong Zhao, Zhenshan Xue, Bo Liu, Wenhua Piao, Ming Jiang. Patterns and drivers of plant species richness in Phragmites australis marshes in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [3] | Qiu Tianhang, Wang An’an, Li Li, Wang Yingchun, Cui Jipeng, Wang Ziyao, Wang Rui, Cui Suxia. Characteristics and Expression Specificity of RCA Genes in Two Ecotypes of Phragmites australis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 687-700. |
| [4] | Hui Zhang, Hongkai Liang, Hui Zhi, Linlin Zhang, Xianmin Diao, Guanqing Jia. Analyses on the Transcription and Structure Variation of β-carotene Isomerase Gene Family in Foxtail Millet [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 34-50. |
| [5] | Wei Heping, Lu Tao, Jia Qiwei, Deng Fei, Zhu Hao, Qi Zehua, Wang Yuxi, Ye Hanfei, Yin Wenjing, Fang Yuan, Mu Dan, Rao Yuchun. QTL Mapping of Candidate Genes for Heading Date in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 588-595. |
| [6] | Jia Song, Mingyang Zhi, Qiang Chen, Yueying Li, Longkun Wu, Baoxuan Nong, Danting Li, Hongbo Pang, Xiaoming Zheng. Nucleotide diversity and adaptation of CTB4a gene related to cold tolerance in rice [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 21258-. |
| [7] | Yanan Zhang, Lei Huang, Jiabin Li, Lei Zhang, Zhenhua Dang. Identification and Development of Polymorphic Genic-SSRs in Tamarix ramosissima in Alxa Region Based on Transcriptome [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 433-442. |
| [8] | Gang Ren, En Li, Shiye Zhao, Yanqiong Jiang, Shasha Wang, Sixian Tang, Huijian Hu. Correlation between color polymorphism and the MC1R gene of Lanius schach [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(6): 688-694. |
| [9] | GUO Rui, ZHOU Ji, LIU Qi, GU Feng-Xue. Characterization of nutrient elements at different leaf positions in Phragmites australis in Songnen degraded grassland [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2018, 42(7): 734-740. |
| [10] | Qun LI, Cheng-Zhang ZHAO, Lian-Chun ZHAO, Jian-Liang WANG, Wei-Tao ZHANG, Wen-Xiu YAO. Empirical relationship between specific leaf area and thermal dissipation of Phragmites australis in salt marshes of Qinwangchuan [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2017, 41(9): 985-994. |
| [11] | Yan Yang, Haiqin Zhang, Xing Fan, Lina Sha, Houyang Kang, Yi Wang, Yonghong Zhou. Polymorphism of Gliadin and Glutelin and Systematics Studies in Elytrigia [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(5): 579-589. |
| [12] | Jianfeng Huang, Lang Li, Jie Li. Polymorphism of the Internal Transcribed Spacer of nrDNA in Cinnamomum Schaeffer (Lauraceae) [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(5): 609-619. |
| [13] | LIU Bo,LÜ Xian-Guo,JIANG Ming,ZHANG Wen-Guang,WU Hai-Tao. Effects of light and water depth on seed germination of Phragmites australis in the wetlands of Songnen Plain [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2015, 39(6): 616-620. |
| [14] | Wen Fan, Ying Xu, Ting Xu, Jing Xu, Takahiro Yonezawa, Jiyin Gao, Wenju Zhang. Intragenomic Polymorphism of the Internal Transcribed Spacer Region of Ribosomal DNA in Camellia hongkongensis (Theaceae) and Species Identification [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(2): 217-226. |
| [15] | CHEN Qing,WANG Yi-Dong,GUO Chang-Cheng,WANG Zhong-Liang. Foliar stable carbon isotope ratios of Phragmites australis and the relevant environmental factors in marsh wetlands in Tianjin [J]. Chin J Plan Ecolo, 2015, 39(11): 1044-1052. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||