

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (2): 302-318.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23035 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23035
收稿日期:2023-03-13
接受日期:2023-11-14
出版日期:2024-03-10
发布日期:2024-03-10
通讯作者:
* 杨永, 南京林业大学教授, 世界自然保护联盟(IUCN)物种生存委员会松柏类专家组主席, 博士生导师。长期从事植物分类、生物地理和濒危物种保护研究。发表论文(著) 150余篇(部), 主持国家自然科学基金和江苏省自然科学基金等项目。主编《世界裸子植物的分类和地理分布》获第十五届“上海图书奖”一等奖。目前其研究团队以裸子植物和樟科为研究对象, 开展整合分类学、生物地理和生物多样性保护等方面研究。E-mail: 基金资助:
Zhi Yang1,2,3, Yong Yang1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-03-13
Accepted:2023-11-14
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-10
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要: 近年来, 随着测序技术的革新、测序成本的降低和生物信息学软件的开发, 植物全基因组研究蓬勃发展。樟科(Lauraceae)隶属被子植物木兰类, 泛热带分布, 物种多样性高, 其中很多物种具有重要的经济和生态价值, 目前已发表包括8个物种的13个基因组。该文从樟科全基因组研究现状、基因组特征、起源和进化以及功能基因和基因家族4个方面进行综述, 着重介绍基于组学数据的木兰类及樟科的系统发生、樟科经历的多倍化事件以及与樟科花器官进化和代谢产物相关的基因鉴定。结合研究现状展望了樟科基因组研究的发展方向, 建议通过增加测序基因组分支的代表性并关注具有特殊价值的物种, 及研究物种特异性功能基因以加深对该家族基因功能和进化的理解。
杨智, 杨永. 重要林木樟科植物全基因组测序研究进展. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 302-318.
Zhi Yang, Yong Yang. Research Advances on Nuclear Genomes of Economically Important Trees of Lauraceae. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 302-318.
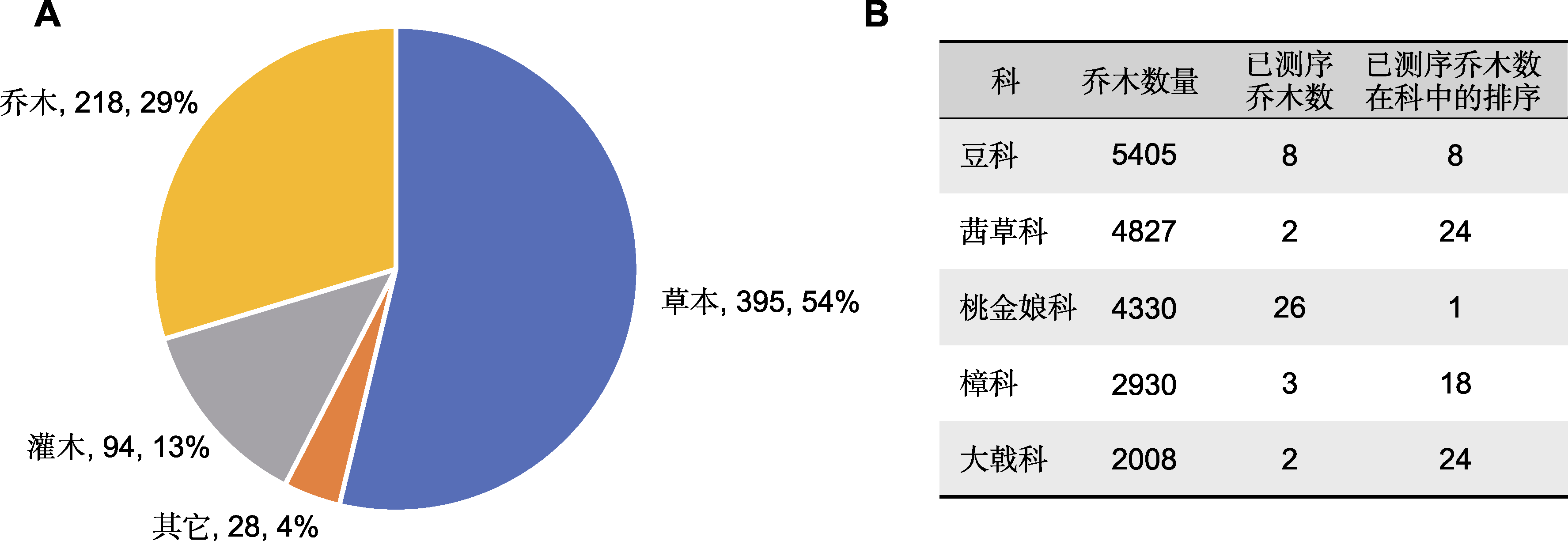
图1 已测序乔木物种概况 (A) 已测序物种的生活型分布, 图中依次标注生活型、数量和占已测序维管植物数量的百分比(附录1); (B) 乔木数量最多的5个科测序情况。已测序物种数据来自Sun等(2022b); 生活型数据来自GIFT数据库(Weigelt et al., 2020)
Figure 1 Overview of sequenced tree species (A) The distribution of the growth form of sequenced species, growth form, species number and the percentage of the number of sequenced vascular plants were indicated (Appendix 1); (B) Overview of sequenced top five families with the largest number of tree species. The datasets of sequenced species were obtained from the paper of Sun et al. (2022b); the corresponding datasets of growth form were obtained from the GIFT database (Weigelt et al., 2020)
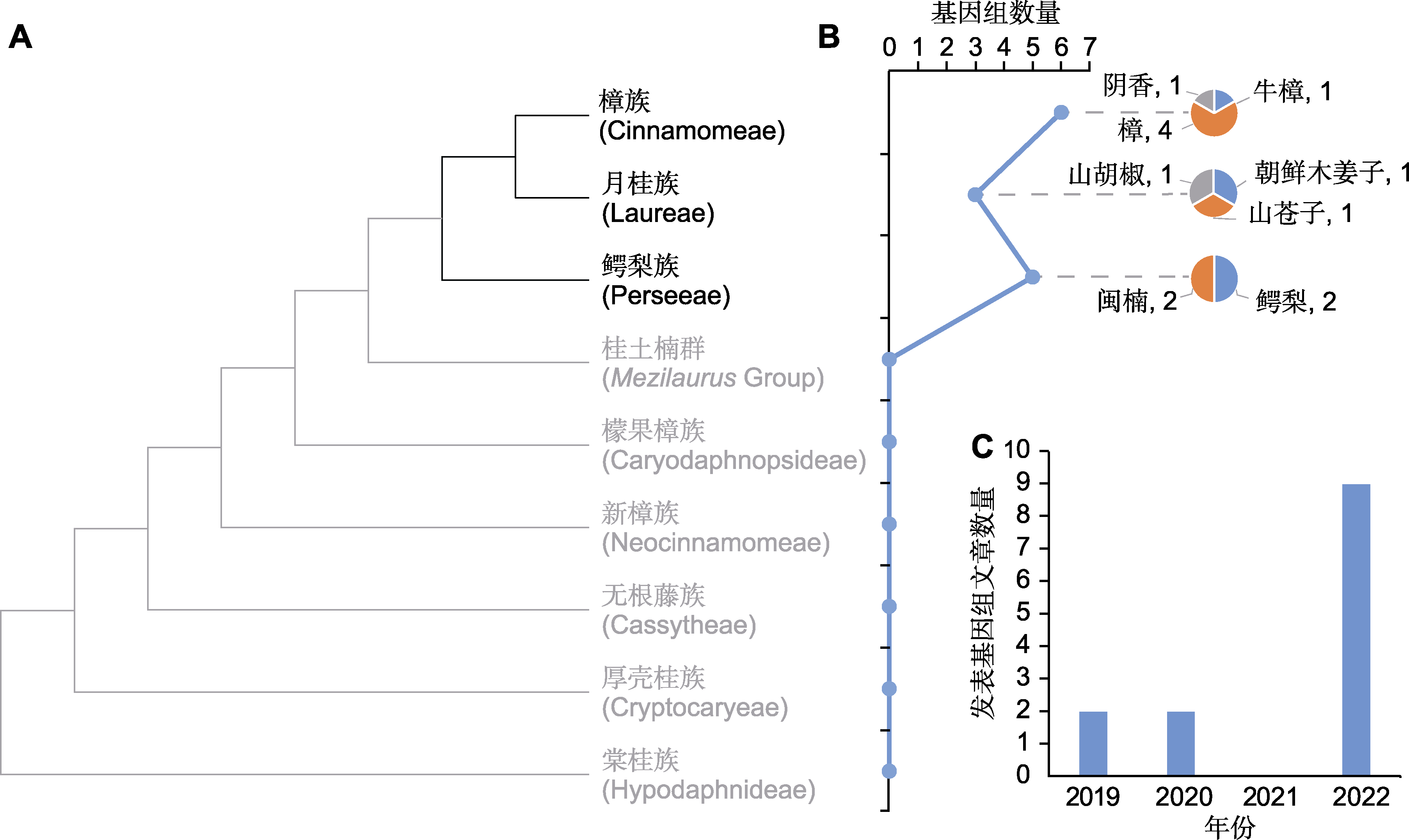
图2 樟科基因组已测序物种概况 (A) 樟科系统发生树(参考Liu et al., 2021); (B) 樟科物种已测序基因组数量折线图和各族测序物种基因组数量的饼图; (C) 近几年发表樟科基因组文章数量
Figure 2 Overview of sequenced species of Lauraceae (A) Phylogenetic tree of Lauraceae (refer to Liu et al., 2021); (B) Line chart of the number of sequenced genome of Lauraceae, and pie charts of numbers of sequenced species of every tribe; (C) Number of articles on Lauraceae genome in recent years
| 序号 | 物种 | 族 | 基因组大小 (Mb) | 染色体 数目 (2n) | 杂合度 (%) | 编码基因数量 | 染色体挂载率 (%) | 组装完 整度 (BUSCO) (%) | 注释完 整度(BUSCO) (%) | 测序方法 | 组装 水平 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 山苍子(Litsea cubeba) | 月桂族(Laureae) | 1325.7 | 24 | - | 31329 | 94.6 | 88.4 | 89.2 | PacBio CLR和Hi-C | 染色体 | Chen et al., |
| 2 | 朝鲜木姜子 (L. coreana) | 1139.5 | 24 | 1.1 | 32445 | 97.1 | 94.0 | - | Illumina、PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Zhang et al., | |
| 3 | 山胡椒(Lindera glauca) | 2092.2 | 24 | 1.4 | 65145 | 94.4 | 94.2 | 92.3 | Illumina、Nanopor和Hi-C | 染色体 | Xiong et al., | |
| 4 | 牛樟(Cinnamomum kanehirae=Camphora kanahirae) | 樟族(Cinnamomeae) | 730.7 | 24 | - | 27899 | - | 89.0 | - | Illumina、PacBio CLR、‘Chicago’和Hi-C | 染色体 | Chaw et al., |
| 5 | 樟(C. camphora=Ca. officinarum) | 755.4 | 24 | - | 24883 | 92.4 | 96.2 | - | PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Jiang et al., | |
| 6 | 723.1 | 24 | 1.2 | 36411 | 97.9 | 95.2 | 90.0 | Illumina、PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Wang et al., | ||
| 7 | 719.9 | 24 | 2.9 | 28789 | 99.9 | 95.3 | 89.8 | Illumina、PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Sun et al., | ||
| 8 | 785.0 | 24 | - | 29919 | 85.4 | 95.2 | 90.8 | PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Shen et al., | ||
| 9 | 阴香(C. burmanni) | 1177.6 | 24 | 0.7 | 41549 | 98.8 | 89.7 | - | Illumina、PacBio CLR和Hi-C | 染色体 | Li et al., | |
| 10 | 闽楠(Phoebe bournei) | 鳄梨族(Perseeae) | 989.2 | 24 | 1.5 | 28198 | - | 95.0 | 81.0 | PacBio CLR | Scaffold | Chen et al., |
| 11 | 941.8 | 24 | 1.4 | 30096 | 99.2 | 92.1 | 91.7 | PacBio CLR、BioNano和Hi-C | 染色体 | Han et al., | ||
| 12 | 鳄梨(Persea americana) | 912.6 | 24 | - | 24616 | 46.2 | 85.0 | - | PacBio CLR | 染色体 | Rendón-Anaya et al., | |
| 13 | 913.0 | 24 | - | 42769 | 98.8 | 98.9 | 96.6 | Illumina和PacBio CCS | 染色体 | Nath et al., |
表1 已测序樟科基因组信息
Table 1 Information of sequenced Lauraceae genomes
| 序号 | 物种 | 族 | 基因组大小 (Mb) | 染色体 数目 (2n) | 杂合度 (%) | 编码基因数量 | 染色体挂载率 (%) | 组装完 整度 (BUSCO) (%) | 注释完 整度(BUSCO) (%) | 测序方法 | 组装 水平 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 山苍子(Litsea cubeba) | 月桂族(Laureae) | 1325.7 | 24 | - | 31329 | 94.6 | 88.4 | 89.2 | PacBio CLR和Hi-C | 染色体 | Chen et al., |
| 2 | 朝鲜木姜子 (L. coreana) | 1139.5 | 24 | 1.1 | 32445 | 97.1 | 94.0 | - | Illumina、PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Zhang et al., | |
| 3 | 山胡椒(Lindera glauca) | 2092.2 | 24 | 1.4 | 65145 | 94.4 | 94.2 | 92.3 | Illumina、Nanopor和Hi-C | 染色体 | Xiong et al., | |
| 4 | 牛樟(Cinnamomum kanehirae=Camphora kanahirae) | 樟族(Cinnamomeae) | 730.7 | 24 | - | 27899 | - | 89.0 | - | Illumina、PacBio CLR、‘Chicago’和Hi-C | 染色体 | Chaw et al., |
| 5 | 樟(C. camphora=Ca. officinarum) | 755.4 | 24 | - | 24883 | 92.4 | 96.2 | - | PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Jiang et al., | |
| 6 | 723.1 | 24 | 1.2 | 36411 | 97.9 | 95.2 | 90.0 | Illumina、PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Wang et al., | ||
| 7 | 719.9 | 24 | 2.9 | 28789 | 99.9 | 95.3 | 89.8 | Illumina、PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Sun et al., | ||
| 8 | 785.0 | 24 | - | 29919 | 85.4 | 95.2 | 90.8 | PacBio CCS和Hi-C | 染色体 | Shen et al., | ||
| 9 | 阴香(C. burmanni) | 1177.6 | 24 | 0.7 | 41549 | 98.8 | 89.7 | - | Illumina、PacBio CLR和Hi-C | 染色体 | Li et al., | |
| 10 | 闽楠(Phoebe bournei) | 鳄梨族(Perseeae) | 989.2 | 24 | 1.5 | 28198 | - | 95.0 | 81.0 | PacBio CLR | Scaffold | Chen et al., |
| 11 | 941.8 | 24 | 1.4 | 30096 | 99.2 | 92.1 | 91.7 | PacBio CLR、BioNano和Hi-C | 染色体 | Han et al., | ||
| 12 | 鳄梨(Persea americana) | 912.6 | 24 | - | 24616 | 46.2 | 85.0 | - | PacBio CLR | 染色体 | Rendón-Anaya et al., | |
| 13 | 913.0 | 24 | - | 42769 | 98.8 | 98.9 | 96.6 | Illumina和PacBio CCS | 染色体 | Nath et al., |

图3 樟科各属染色体数目变化 概率为染色体数目在该属中出现的比例。数据来自染色体数目数据库(CCDB, version 1.66) (Rice et al., 2015)及Oginuma和Tobe (2006) (附录2)
Figure 3 Variation in chromosome number of various genera in Lauraceae Cirde sizes represent the percentage occurrence of chromosome numbers across genera. The data was extracted from chromosome counts database (CCDB, version 1.66) (Rice et al., 2015) and result from Oginuma and Tobe (2006) (Appendix 2)

图4 已测序樟科基因组特征比较 (A) 基因组大小; (B) 基因组杂合度; (C) 重复序列比例; (D) 长末端重复序列比例
Figure 4 Comparison of characters of sequenced Lauraceae genomes (A) Genome sizes; (B) Genomic heterozygosity; (C) Ratio of repeat sequences; (D) Ratio of long terminal repeat
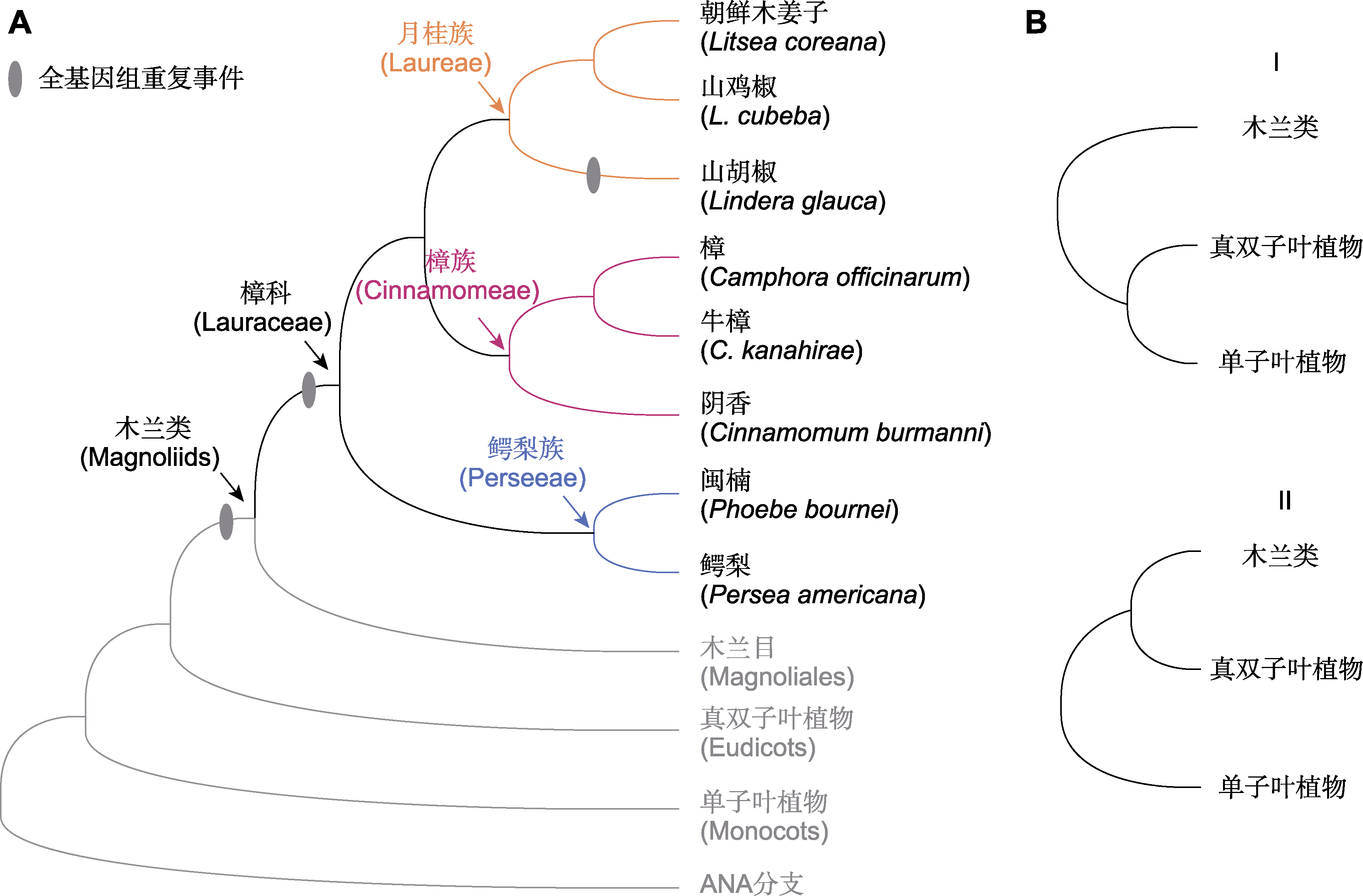
图5 樟科已测序物种系统发生关系 (A) 樟科已测序物种系统发生树(参考Liu et al., 2021; Han et al., 2022) (灰色椭圆形代表樟科经历的全基因组重复事件); (B) 从樟科基因组文献中得到的木兰类、真双子叶植物和单子叶植物系统发生关系的2种拓扑结构。
Figure 5 Phylogenetic relationships of sequenced species of Lauraceae (A) Phylogenetic tree of sequenced species in Lauraceae (refer to Liu et al., 2021; Han et al., 2022) (The grey ovals represent predicted whole genome duplication events in Lauraceae); (B) Two topologies of the relationship of magnoliids, eudicots and monocots in the published papers based on the studies on Lauraceae genomes
| [1] |
Amborella Genome Project (2013). The Amborella genome and the evolution of flowering plants. Science 342, 1241089.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Beech E, Rivers MC, Oldfield S, Smith PP (2017). GlobalTreeSearch: the first complete global database of tree species and country distributions. J Sustain For 36, 454-489. |
| [3] | Blaxter M, Archibald JM, Childers AK, Coddington JA, Crandall KA, Di Palma F, Durbin R, Edwards SV, Graves JAM, Hackett KJ, Hall N, Jarvis ED, Johnson RN, Karlsson EK, Kress WJ, Kuraku S, Lawniczak MKN, Lindblad-Toh K, Lopez JV, Moran NA, Robinson GE, Ryder OA, Shapiro B, Soltis PS, Warnow T, Zhang GJ, Lewin HA (2022). Why sequence all eukaryotes? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119, e2115636118. |
| [4] |
Cai LM, Arnold BJ, Xi ZX, Khost DE, Patel N, Hartmann CB, Manickam S, Sasirat S, Nikolov LA, Mathews S, Sackton TB, Davis CC (2021). Deeply altered genome architecture in the endoparasitic flowering plant Sapria himalayana Griff. (Rafflesiaceae). Curr Biol 31, 1002-1011.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Chanderbali AS, van der Werff H, Renner SS (2001). Phylogeny and historical biogeography of Lauraceae: evidence from the chloroplast and nuclear genomes. Ann Mo Bot Gard 88, 104-134.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Chaw SM, Liu YC, Wu YW, Wang HY, Lin CYI, Wu CS, Ke HM, Chang LY, Hsu CY, Yang HT, Sudianto E, Hsu MH, Wu KP, Wang LN, Leebens-Mack JH, Tsai IJ (2019). Stout camphor tree genome fills gaps in understanding of flowering plant genome evolution. Nat Plants 5, 63-73. |
| [7] |
Chen SP, Sun WH, Xiong YF, Jiang YT, Liu XD, Liao XY, Zhang DY, Jiang SZ, Li Y, Liu B, Ma L, Yu X, He L, Liu B, Feng JL, Feng LZ, Wang ZW, Zou SQ, Lan SR, Liu ZJ (2020a). The Phoebe genome sheds light on the evolution of magnoliids. Hortic Res 7, 146.
DOI |
| [8] |
Chen YC, Li Z, Zhao YX, Gao M, Wang JY, Liu KW, Wang X, Wu LW, Jiao YL, Xu ZL, He WG, Zhang QY, Liang CK, Hsiao YY, Zhang DY, Lan SR, Huang LQ, Xu W, Tsai WC, Liu ZJ, Van de Peer Y, Wang YD (2020b). The Litsea genome and the evolution of the laurel family. Nat Commun 11, 1675.
DOI |
| [9] | Christianson DW (2017). Structural and chemical biology of terpenoid cyclases. Chem Rev 117, 11570-11648. |
| [10] | Chung KF, Hsieh CL (2023). Synopsis of Camphora (Cinnamomeae, Lauraceae) of Taiwan, with two new combinations and one new svnonvm. Taiwania 68, 384-390. |
| [11] | Dong Y, Duan SC, Xia QJ, Liang ZC, Dong X, Margaryan K, Musayev M, Goryslavets S, Zdunić G, Bert PF, Lacombe T, Maul E, Nick P, Bitskinashvili K, Bisztray GD, Drori E, De Lorenzis G, Cunha J, Popescu CF, Arroyo-Garcia R, Arnold C, Ergül A, Zhu YF, Ma C, Wang SF, Liu SQ, Tang L, Wang CP, Li DW, Pan YB, Li JX, Yang L, Li XZ, Xiang GS, Yang ZJ, Chen BZ, Dai ZW, Wang Y, Arakelyan A, Kuliyev V, Spotar G, Girollet N, Delrot S, Ollat N, This P, Marchal C, Sarah G, Laucou V, Bacilieri R, Röckel F, Guan PY, Jung A, Riemann M, Ujmajuridze L, Zakalashvili T, Maghradze D, Höhn M, Jahnke G, Kiss E, Deák T, Rahimi O, Hübner S, Grassi F, Mercati F, Sunseri F, Eiras-Dias J, Dumitru AM, Carrasco D, Rodriguez-Izquierdo A, Muñoz G, Uysal T, Özer C, Kazan K, Xu ML, Wang YY, Zhu SS, Lu J, Zhao MX, Wang L, Jiu S, Zhang Y, Sun L, Yang HM, Weiss E, Wang SP, Zhu YY, Li SH, Sheng J, Chen W (2023). Dual domestications and origin of traits in grapevine evolution. Science 379, 892-901. |
| [12] |
Eckardt NA, Birchler JA, Brady SM, Buell CR, Leebens-Mack JH, Meyers BC (2021). Focus on the biology of plant genomes. Plant Cell 33, 781-782.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Editorial Committee of Flora of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences 1982). Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, Vol. 31. Beijing: Science Press. pp.1-462. (in Chinese) |
| 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会 (1982). 中国植物志, 第31卷. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 1-462. | |
| [14] | Gao SH, Yu HY, Wu SY, Wang S, Geng JN, Luo YF, Hu SN (2018). Advances of sequencing and assembling technologies for complex genomes. Hereditas 40, 944-963. (in Chinese) |
| 高胜寒, 禹海英, 吴双阳, 王森, 耿佳宁, 骆迎峰, 胡松年 (2018). 复杂基因组测序技术研究进展. 遗传 40, 944-963. | |
| [15] |
Ge S (2022). A review of recent studies of plant systematics and evolution in China. Biodiv Sci 30, 22385. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
葛颂 (2022). 中国植物系统和进化生物学研究进展. 生物多样性 30, 22385.
DOI |
|
| [16] |
Guo C, Luo Y, Gao LM, Yi TS, Li HT, Yang JB, Li DZ (2023). Phylogenomics and the flowering plant tree of life. J Integr Plant Biol 65, 299-323.
DOI |
| [17] | Han X, Zhang JH, Han S, Chong SL, Meng GL, Song MY, Wang Y, Zhou SC, Liu CC, Lou LH, Lou XZ, Cheng LJ, Lin EP, Huang HH, Yang Q, Tong ZK (2022). The chromosome-scale genome of Phoebe bournei reveals contrasting fates of terpene synthase (TPS)-a and TPS-b subfamilies. Plant Commun 3, 100410. |
| [18] | Hao CL, Yu XF, Qu MH, Lai EH, Guo SM, Gao L (2022). Current status and prospects of pan-genome studies in plants. Plant Sci J 40, 124-132. (in Chinese) |
| 郝晨路, 於晓芬, 曲明昊, 赖恩惠, 郭素敏, 高磊 (2022). 植物泛基因组研究进展与展望. 植物科学学报 40, 124-132. | |
| [19] |
Hu HY, Sun PC, Yang YZ, Ma JX, Liu JQ (2023a). Genome-scale angiosperm phylogenies based on nuclear, plastome, and mitochondrial datasets. J Integr Plant Biol 65, 1479-1489.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Hu RY, Li XD, Hu Y, Zhang RJ, Lv Q, Zhang M, Sheng XY, Zhao F, Chen ZJ, Ding YH, Yuan H, Wu XF, Xing S, Yan XY, Bao F, Wan P, Xiao LH, Wang XQ, Xiao W, Decker EL, van Gessel N, Renault H, Wiedemann G, Horst NA, Haas FB, Wilhelmsson PKI, Ullrich KK, Neumann E, Lv B, Liang CZ, Du HL, Lu HW, Gao Q, Cheng ZK, You HL, Xin PY, Chu JF, Huang CH, Liu Y, Dong SS, Zhang LS, Chen F, Deng L, Duan FZ, Zhao WJ, Li K, Li ZF, Li XR, Cui HJ, Zhang YE, Ma C, Zhu RL, Jia Y, Wang MZ, Hasebe M, Fu JZ, Goffinet B, Ma H, Rensing SA, Reski R, He YK (2023b). Adaptive evolution of the enigmatic Takakia now facing climate change in Tibet. Cell 186, 3558-3576. |
| [21] | Huang JF, Li L, Li J (2016). Polymorphism of the internal transcribed spacer of nrDNA in Cinnamomum Schaeffer (Lauraceae). Chin Bull Bot 51, 609-619. (in Chinese) |
|
黄建峰, 李朗, 李捷 (2016). 樟属植物ITS序列多态性分析. 植物学报 51, 609-619.
DOI |
|
| [22] | Huang X, Wang WL, Gong T, Wickell D, Kuo LY, Zhang XT, Wen JL, Kim H, Lu FC, Zhao HS, Chen S, Li H, Wu WQ, Yu CJ, Chen S, Fan W, Chen S, Bao XQ, Li L, Zhang D, Jiang LY, Yan XJ, Liao ZY, Zhou GK, Guo YL, Ralph J, Sederoff RR, Wei HR, Zhu P, Li FW, Ming R, Li QZ (2022). The flying spider-monkey tree fern genome provides insights into fern evolution and arborescence. Nat Plants 8, 500-512. |
| [23] |
Jia QD, Brown R, Köllner TG, Fu JY, Chen XL, Wong GKS, Gershenzon J, Peters RJ, Chen F (2022). Origin and early evolution of the plant terpene synthase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119, e2100361119.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Jiang RH, Chen XL, Liao XZ, Peng D, Han XX, Zhu CS, Wang P, Hufnagel DE, Wang L, Li KX, Li C (2022). A chromosome-level genome of the camphor tree and the underlying genetic and climatic factors for its top-geoherbalism. Front Plant Sci 13, 827890.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Jing CY, Zhang FM, Wang XH, Wang MX, Zhou L, Cai Z, Han JD, Geng MF, Yu WH, Jiao ZH, Huang L, Liu R, Zheng XM, Meng QL, Ren NN, Zhang HX, Du YS, Wang X, Qiang CG, Zou XH, Gaut BS, Ge S (2023). Multiple domestications of Asian rice. Nat Plants 9, 1221-1235. |
| [26] | Joshi SC, Padalia RC, Bisht DS, Mathela CS (2009). Terpenoid diversity in the leaf essential oils of Himalayan Lauraceae species. Chem Biodivers 6, 1364-1373. |
| [27] |
Kress WJ, Soltis DE, Kersey PJ, Wegrzyn JL, Leebens-Mack JH, Gostel MR, Liu X, Soltis PS (2022). Green plant genomes: what we know in an era of rapidly expanding opportunities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119, e2115640118.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Lewin HA, Robinson GE, Kress WJ, Baker WJ, Coddington J, Crandall KA, Durbin R, Edwards SV, Forest F, Gilbert MTP, Goldstein MM, Grigoriev IV, Hackett KJ, Haussler D, Jarvis ED, Johnson WE, Patrinos A, Richards S, Castilla-Rubio JC, van Sluys MA, Soltis PS, Xu X, Yang HM, Zhang GJ (2018). Earth BioGenome Project: sequencing life for the future of life. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 4325-4333. |
| [29] |
Li FP, Huang SL, Mei Y, Wu BQ, Hou ZW, Zhan PL, Hou ZH, Huang WJ, Zhao JL, Wang JH (2022). Genome assembly provided new insights into the Cinnamomum burmannii evolution and D-borneol biosynthesis differences between chemotypes. Ind Crops Prod 186, 115181.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Li HT, Luo Y, Gan L, Ma PF, Gao LM, Yang JB, Cai J, Gitzendanner MA, Fritsch PW, Zhang T, Jin JJ, Zeng CX, Wang H, Yu WB, Zhang R, van der Bank M, Olmstead RG, Hollingsworth PM, Chase MW, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Yi TS, Li DZ (2021). Plastid phylogenomic insights into relationships of all flowering plant families. BMC Biol 19, 232.
DOI |
| [31] |
Li HW, Liu B, Davis CC, Yang Y (2020). Plastome phylogenomics, systematics, and divergence time estimation of the Beilschmiedia group (Lauraceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 151, 106901.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Li J, Christophel DC, Conran JG, Li HW (2004). Phylogenetic relationships within the ‘core’ Laureae (Litsea complex, Lauraceae) inferred from sequences of the chloroplast gene matK and nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS regions. Plant Syst Evol 246, 19-34. |
| [33] |
Li J, Conran JG, Christophel DC, Li ZM, Li L, Li HW (2008). Phylogenetic relationships of the Litsea complex and core Laureae (Lauraceae) using ITS and ETS sequences and morphology. Ann Mo Bot Gard 95, 580-599.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Li J, Li XW (2004). Systematic research on the world scale advances in Lauraceae. Acta Bot Yunnan 26, 1-11. (in Chinese) |
| 李捷, 李锡文 (2004). 世界樟科植物系统学研究进展. 云南植物研究 26, 1-11. | |
| [35] | Liu Y, Wang SB, Li LZ, Yang T, Dong SS, Wei T, Wu SD, Liu YB, Gong YQ, Feng XY, Ma JC, Chang GX, Huang JL, Yang Y, Wang HL, Liu M, Xu Y, Liang HP, Yu J, Cai YQ, Zhang ZW, Fan YN, Mu WX, Sahu SK, Liu SC, Lang XA, Yang LL, Li N, Habib S, Yang YQ, Lindstrom AJ, Liang P, Goffinet B, Zaman S, Wegrzyn JL, Li DX, Liu J, Cui J, Sonnenschein EC, Wang XB, Ruan J, Xue JY, Shao ZQ, Song C, Fan GY, Li Z, Zhang LS, Liu JQ, Liu ZJ, Jiao YN, Wang XQ, Wu H, Wang ET, Lisby M, Yang HM, Wang J, Liu X, Xu X, Li N, Soltis PS, Van de Peer Y, Soltis DE, Gong X, Liu H, Zhang SZ (2022). The Cycas genome and the early evolution of seed plants. Nat Plants 8, 389-401. |
| [36] |
Liu ZF, Ma H, Ci XQ, Li L, Song Y, Liu B, Li HW, Wang SL, Qu XJ, Hu JL, Zhang XY, Conran JG, Twyford AD, Yang JB, Hollingsworth PM, Li J (2021). Can plastid genome sequencing be used for species identification in Lauraceae? Bot J Linn Soc 197, 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Moeglein MK, Chatelet DS, Donoghue MJ, Edwards EJ (2020). Evolutionary dynamics of genome size in a radiation of woody plants. Am J Bot 107, 1527-1541. |
| [38] |
Nagegowda DA, Gupta P (2020). Advances in biosynthesis, regulation, and metabolic engineering of plant specialized terpenoids. Plant Sci 294, 110457.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Nath O, Fletcher SJ, Hayward A, Shaw LM, Masouleh AK, Furtado A, Henry RJ, Mitter N (2022). A haplotype resolved chromosomal level avocado genome allows analysis of novel avocado genes. Hortic Res 9, uhac157.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Niu SH, Li J, Bo WH, Yang WF, Zuccolo A, Giacomello S, Chen X, Han FX, Yang JH, Song YT, Nie YM, Zhou B, Wang PY, Zuo Q, Zhang H, Ma JJ, Wang J, Wang L, Zhu QY, Zhao HH, Liu ZM, Zhang XM, Liu T, Pei SR, Li ZM, Hu Y, Yang YH, Li WZ, Zan YJ, Zhou LH, Lin JX, Yuan TQ, Li W, Li Y, Wei HR, Wu HX (2022). The Chinese pine genome and methylome unveil key features of conifer evolution. Cell 185, 204-217. |
| [41] | Oginuma K, Tobe H (2006). Chromosome evolution in the Laurales based on analyses of original and published data. J Plant Res 119, 309-320. |
| [42] | One Thousand Plant Transcriptomes Initiative (2019). One thousand plant transcriptomes and the phylogenomics of green plants. Nature 574, 679-685. |
| [43] |
Pellicer J, Hidalgo O, Dodsworth S, Leitch IJ (2018). Genome size diversity and its impact on the evolution of land plants. Genes (Basel) 9, 88.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Peng YY, Yan HH, Guo LC, Deng C, Wang CL, Wang YB, Kang LP, Zhou PP, Yu KQ, Dong XL, Liu XM, Sun ZY, Peng Y, Zhao J, Deng D, Xu YH, Li Y, Jiang QT, Li Y, Wei LM, Wang JR, Ma J, Hao M, Li W, Kang HY, Peng ZS, Liu DC, Jia JZ, Zheng YL, Ma T, Wei YM, Lu F, Ren CZ (2022). Reference genome assemblies reveal the origin and evolution of allohexaploid oat. Nat Genet 54, 1248-1258.
DOI |
| [45] |
Pichersky E, Raguso RA (2018). Why do plants produce so many terpenoid compounds? New Phytol 220, 692-702.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Qin SY, Zuo ZY, Guo C, Du XY, Liu SY, Yu XQ, Xiang XG, Rong J, Liu B, Liu ZF, Ma PF, Li DZ (2023). Phylogenomic insights into the origin and evolutionary history of evergreen broadleaved forests in East Asia under Cenozoic climate change. Mol Ecol 32, 2850-2868.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Rendón-Anaya M, Ibarra-Laclette E, Méndez-Bravo A, Lan TY, Zheng CF, Carretero-Paulet L, Perez-Torres CA, Chacón-López A, Hernandez-Guzmán G, Chang TH, Farr KM, Barbazuk WB, Chamala S, Mutwil M, Shivhare D, Alvarez-Ponce D, Mitter N, Hayward A, Fletcher S, Rozas J, Sánchez Gracia A, Kuhn D, Barrientos-Priego AF, Salojärvi J, Librado P, Sankoff D, Herrera-Estrella A, Albert VA, Herrera-Estrella L (2019). The avocado genome informs deep angiosperm phylogeny, highlights introgressive hybridization, and reveals pathogen-influenced gene space adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 17081-17089. |
| [48] | Rice A, Glick L, Abadi S, Einhorn M, Kopelman NM, Salman-Minkov A, Mayzel J, Chay O, Mayrose I (2015). The chromosome counts database (CCDB)—a community resource of plant chromosome numbers. New Phytol 206, 19-26. |
| [49] | Rohwer JG (1993). Lauraceae. In: Kubitzki K, Rohwer JG, Bittrich V, eds. Flowering Plants · Dicotyledons: Magnoliid, Hamamelid and Caryophyllid Families. Berlin: Springer. pp. 366-391. |
| [50] |
Rohwer JG (2000). Toward a phylogenetic classification of the Lauraceae: evidence from matK sequences. Syst Bot 25, 60-71.
DOI URL |
| [51] | Rohwer JG, Rudolph B (2005). Jumping genera: the phylogenetic positions of Cassytha, Hypodaphnis, and Neocinnamomum (Lauraceae) based on different analyses of trnK intron sequences. Ann Mo Bot Gard 92, 153-178. |
| [52] |
Shen TF, Qi HR, Luan XY, Xu WL, Yu FX, Zhong YD, Xu M (2022). The chromosome-level genome sequence of the camphor tree provides insights into Lauraceae evolution and terpene biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnol J 20, 244-246.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Steenwyk JL, Li YN, Zhou XF, Shen XX, Rokas A (2023). Incongruence in the phylogenomics era. Nat Rev Genet 24, 834-850.
DOI |
| [54] |
Sun WH, Xiang S, Zhang QG, Xiao L, Zhang DY, Zhang PL, Chen DQ, Hao Y, Liu DK, Ding L, Li YF, Ni H, Wang YF, Wu X, Liu FH, Chen GR, Han GY, Chen JZ, Su BC, Gao JX, Wan XH, Wang ZW, Chen YC, Wang YD, Huang W, Liu BB, Zou XX, Ni L, Liu ZJ, Zou SQ (2022a). The camphor tree genome enhances the understanding of magnoliid evolution. J Genet Genomics 49, 249-253.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Sun YQ, Shang LG, Zhu QH, Fan LJ, Guo LB (2022b). Twenty years of plant genome sequencing: achievements and challenges. Trends Plant Sci 27, 391-401.
DOI URL |
| [56] | The Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (2016). An update of the angiosperm phylogeny group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot J Linn Soc 181, 1-20. |
| [57] | The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000). Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408, 796-815. |
| [58] | Tian YJ, Zhou JB, Zhang YY, Wang S, Wang Y, Liu H, Wang ZS (2021). Research progress in plant molecular systematics of Lauraceae. Biology (Basel) 10, 391. |
| [59] |
Trofimov D, Cadar D, Schmidt-Chanasit J, Rodrigues de Moraes PL, Rohwer JG (2022). A comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genomes of seven Ocotea species (Lauraceae) confirms low sequence divergence within the Ocotea complex. Sci Rep 12, 1120.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
Vogel A, Schwacke R, Denton AK, Usadel B, Hollmann J, Fischer K, Bolger A, Schmidt MHW, Bolger ME, Gundlach H, Mayer KFX, Weiss-Schneeweiss H, Temsch EM, Krause K (2018). Footprints of parasitism in the genome of the parasitic flowering plant Cuscuta campestris. Nat Commun 9, 2515.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Wakabayashi K (2000). Changes in cell wall polysaccharides during fruit ripening. J Plant Res 113, 231-237. |
| [62] |
Wan T, Liu ZM, Leitch IJ, Xin HP, Maggs-Kölling G, Gong YB, Li Z, Marais E, Liao YY, Dai C, Liu F, Wu QJ, Song C, Zhou YD, Huang WC, Jiang K, Wang Q, Yang Y, Zhong ZX, Yang M, Yan X, Hu GW, Hou C, Su YJ, Feng SX, Yang J, Yan JJ, Chu JF, Chen F, Ran JH, Wang XQ, Van de Peer Y, Leitch AR, Wang QF (2021). The Welwitschia genome reveals a unique biology underpinning extreme longevity in deserts. Nat Commun 12, 4247.
DOI |
| [63] |
Wang S, Qian YQ, Zhao RP, Chen LL, Song JM (2023a). Graph-based pan-genomes: increased opportunities in plant genomics. J Exp Bot 74, 24-39.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Wang T, Duan S, Xu C, WangY, Zhang X, Xu X, Chen L, Han Z, Wu T (2023b). Pan-genome analysis of 13 Malus accessions reveals structural and sequence variations associated with fruit traits. Nat Commun 14, 7377.
DOI |
| [65] |
Wang W, Liu Y (2020). The current status, problems, and policy suggestions for reconstructing the plant tree of life. Biodiv Sci 28, 176-188. (in Chinese)
DOI |
| 王伟, 刘阳 (2020). 植物生命之树重建的现状、问题和对策建议. 生物多样性 28, 176-188. | |
| [66] |
Wang XD, Xu CY, Zheng YJ, Wu YF, Zhang YT, Zhang T, Xiong ZY, Yang HK, Li J, Fu C, Qiu FY, Dai XY, Liu XL, He XS, Zhou SS, Li SX, Fu T, Xie H, Chen YL, Zhang QQ, Wang HQ, Wang YD, Zhou C, Jiang XM (2022). Chromosome-level genome assembly and resequencing of camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora) provides insight into phylogeny and diversification of terpenoid and triglyceride biosynthesis of Cinnamomum. Hortic Res 9, uhac216.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Weigelt P, König C, Kreft H (2020). GIFT—a global inventory of floras and traits for macroecology and biogeography. J Biogeogr 47, 16-43.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Wu S, Sun HH, Gao L, Branham S, McGregor C, Renner SS, Xu Y, Kousik C, Wechter WP, Levi A, Fei Z (2023). A Citrullus genus super-pangenome reveals extensive variations in wild and cultivated watermelons and sheds light on watermelon evolution and domestication. Plant Biotechnol J 21, 1926-1928.
DOI PMID |
| [69] |
Wu SD, Han BC, Jiao YN (2020). Genetic contribution of paleopolyploidy to adaptive evolution in angiosperms. Mol Plant 13, 59-71.
DOI PMID |
| [70] |
Xiao TW, Ge XJ (2022). Plastome structure, phylogenomics, and divergence times of tribe Cinnamomeae (Lauraceae). BMC Genomics 23, 642.
DOI |
| [71] |
Xiao TW, Xu Y, Jin L, Liu TJ, Yan HF, Ge XJ (2020). Conflicting phylogenetic signals in plastomes of the tribe Laureae (Lauraceae). PeerJ 8, e10155.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Xiao TW, Yan HF, Ge XJ (2022). Plastid phylogenomics of tribe Perseeae (Lauraceae) yields insights into the evolution of East Asian subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests. BMC Plant Biol 22, 32.
DOI |
| [73] | Xie LJ, Ye CY, Shen EH (2021). Advances in plant genome construction. Plant Sci J 39, 681-691. (in Chinese) |
| 谢玲娟, 叶楚玉, 沈恩惠 (2021). 植物基因组测序研究进展. 植物科学学报 39, 681-691. | |
| [74] |
Xiong B, Zhang LM, Xie L, Li LZ, He XX, Niu Y, Zhang TY, Liao S, Dong SB, Zhang ZX (2022). Genome of Lindera glauca provides insights into the evolution of biosynthesis genes for aromatic compounds. iScience 25, 104761.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Yang Z, Liu B, Yang Y, Ferguson DK (2022a). Phylogeny and taxonomy of Cinnamomum (Lauraceae). Ecol Evol 12, e9378.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Yang Z, Tan C, Wei YM, Rohwer JG, Liu B, Yang Y (2022b). Floral morphology and phenology of Sassafras tzumu (Lauraceae). BMC Plant Biol 22, 327.
DOI |
| [77] |
Yuan JH, Jiang SJ, Jian JB, Liu MY, Yue Z, Xu JB, Li J, Xu CY, Lin LH, Jing Y, Zhang XX, Chen HX, Zhang LJ, Fu T, Yu SY, Wu ZY, Zhang Y, Wang CZ, Zhang X, Huang LB, Wang HQ, Hong DY, Chen XY, Hu YH (2022). Genomic basis of the giga-chromosomes and giga-genome of tree peony Paeonia ostii. Nat Commun 13, 7328.
DOI PMID |
| [78] |
Zhang BH, Yao XZ, Chen HF, Lu LT (2022). High-quality chromosome-level genome assembly of Litsea coreana L. provides insights into Magnoliids evolution and flavonoid biosynthesis. Genomics 114, 110394.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Zhang BY, Zhu WX, Diao S, Wu XJ, Lu JQ, Ding CJ, Su XH (2019). The poplar pangenome provides insights into the evolutionary history of the genus. Commun Biol 2, 215.
DOI PMID |
| [80] | Zhang XT, Wang G, Zhang SC, Chen S, Wang YB, Wen P, Ma XK, Shi Y, Qi R, Yang Y, Liao ZY, Lin J, Lin JS, Xu XM, Chen XQ, Xu XD, Deng F, Zhao LH, Lee YL, Wang R, Chen XY, Lin YR, Zhang JS, Tang HB, Chen J, Ming R (2020). Genomes of the banyan tree and pollinator wasp provide insights into fig-wasp coevolution. Cell 183, 875-889. |
| [1] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [2] | 赵白龙, 李业亮, 王宇飞, 孙斌. 十大功劳属(小檗科)的叶结构分型新体系[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [3] | 夏琳凤, 李瑞, 王海政, 冯大领, 王春阳. 轮藻门植物基因组学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 271-282. |
| [4] | 洪德元. 分类学中的方法论小叙[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24541-. |
| [5] | 孙亚君. 何谓高等或低等生物——澄清《物种起源》所蕴含的生物等级性的涵义及其成立性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [6] | 何花, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 被子植物隐性雌雄异株性系统的多样性、系统演化及进化意义[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24149-. |
| [7] | 陈文娜, 李良涛, 周璐, 姚纲. 太行山近期隆升促进太行花属(蔷薇科)谱系分化[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 763-773. |
| [8] | 杨继轩, 王雪霏, 顾红雅. 西藏野生拟南芥开花时间变异的遗传基础[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 373-382. |
| [9] | 蒋陈焜, 郁文彬, 饶广远, 黎怀成, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. 植物系统发生海报——以演化视角介绍植物多样性的科教资料项目[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [10] | 董小云, 魏家萍, 崔俊美, 武泽峰, 郑国强, 李辉, 王莹, 田海燕, 刘自刚. 植物抗冻蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 966-981. |
| [11] | 景昭阳, 程可光, 舒恒, 马永鹏, 刘平丽. 全基因组重测序方法在濒危植物保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22679-. |
| [12] | 彭焕文, 王伟. 基于分子数据的系统发生树构建[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 261-273. |
| [13] | 金恒镳. 从天择到人择: 在华莱士的肩膀上看地球的未来[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23267-. |
| [14] | 朱华. 地质事件和季风气候影响了云南植物区系和植被的演化[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23262-. |
| [15] | 刘珂, 韩思成, 遇赫, 罗述金. 荒漠猫的演化遗传、分类和保护研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22396-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||