

植物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (6): 742-755.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22156 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22156
所属专题: 饲草生物学专辑 (2023年58卷2期、2022年57卷6期)
赵洪1,*( ), 宋丽珍2, 张玉娥1, 程佑发2, 薛勇彪1,*(
), 宋丽珍2, 张玉娥1, 程佑发2, 薛勇彪1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-16
接受日期:2022-08-22
出版日期:2022-11-01
发布日期:2022-11-18
通讯作者:
赵洪,薛勇彪
作者简介:ybxue@genetics.ac.cn基金资助:
Hong Zhao1,*( ), Lizhen Song2, Yu’e Zhang1, Youfa Cheng2, Yongbiao Xue1,*(
), Lizhen Song2, Yu’e Zhang1, Youfa Cheng2, Yongbiao Xue1,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-16
Accepted:2022-08-22
Online:2022-11-01
Published:2022-11-18
Contact:
Hong Zhao,Yongbiao Xue
摘要: 显花植物自交不亲和性(self-incompatibility, SI)是一种广泛分布的种内生殖障碍, 在防止植物近交衰退并促进其异交中发挥重要作用。然而, 该性状也严重限制了自交制种与杂交育种进程, 而包含绝大多数饲草种类的豆科、菊科与禾本科植物自交不亲和的分子机制尚不明确, 因此饲草自交不亲和性成为制约我国乃至世界饲草产业发展的主要原因之一。现有研究已经揭示五类自交不亲和性的分子机制, 并对其生化与演化机制有了比较深入的了解, 为解析豆科、菊科与禾本科饲草自交不亲和性的分子机制奠定了基础。该文简要综述五类自交不亲和机制, 以及豆科、菊科与禾本科饲草自交不亲和性及其近交衰退的研究进展。
赵洪, 宋丽珍, 张玉娥, 程佑发, 薛勇彪. 饲草自交不亲和性与近交衰退. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 742-755.
Hong Zhao, Lizhen Song, Yu’e Zhang, Youfa Cheng, Yongbiao Xue. Self-incompatibility and Inbreeding Depression of Forage Crops. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(6): 742-755.
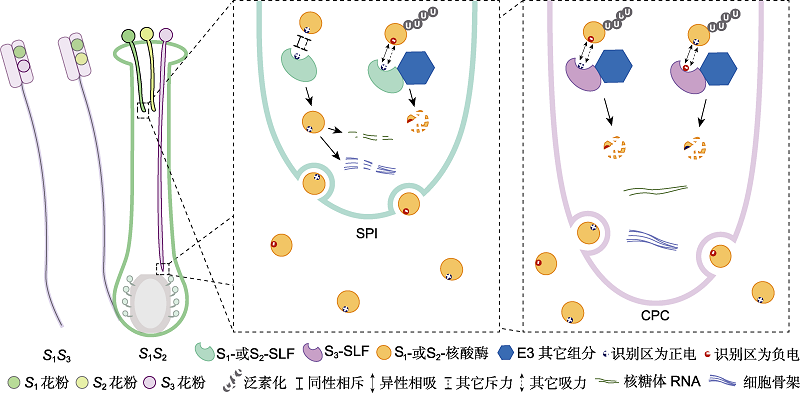
图1 1类自交不亲和性(SI)的分子与生化机制 图示车前科、茄科、蔷薇科和芸香科1类自交不亲和性的分子与生化机制。S表示S基因。图片左侧表示花药、花粉及授粉花柱, 右侧虚线框中分别表示花粉管中发生的自交不亲和反应(self-pollen incompatibility, SPI)和异交亲和反应(cross-pollen compatibility, CPC)。
Figure 1 Molecular and biochemical mechanisms of Type 1 self-incompatibility (SI) Schematic diagram illustrating the molecular and biochemical mechanisms of the Type 1 SI in Plantaginaceae, Solanaceae, Rosaceae and Rutaceae. S indicates the S gene. The anther, pollen and pollinated pistils are shown on the left, with self-pollen incompatibility (SPI) and cross-pollen compatibility (CPC) reactions occurring in pollen tubes on the right dashed boxes.
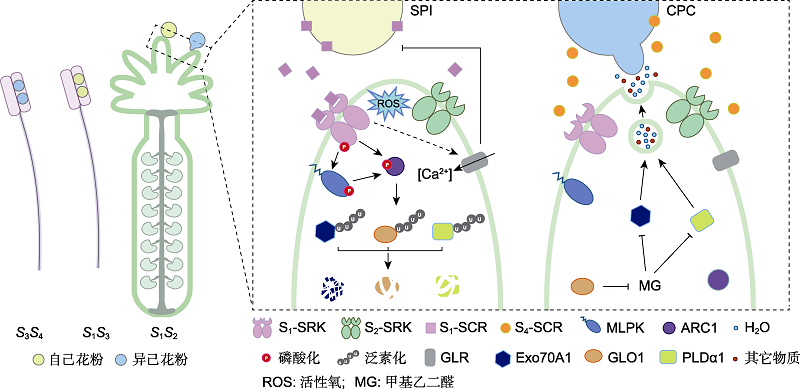
图2 2类自交不亲和性(SI)的分子与生化机制 图示十字花科2类自交不亲和性的分子与生化机制。图片右侧虚线框中表示柱头乳突细胞中分别发生的SPI和CPC反应。S、SPI和CPC含义同图1。
Figure 2 Molecular and biochemical mechanisms of Type 2 self-incompatibility (SI) Schematic diagram illustrating the molecular and biochemical mechanisms of Type 2 SI in Brassicaceae with SPI and CPC reactions occurring in stigma papillae cells shown on the right dashed box. The meanings of S, SPI and CPC are identical to those described in Figure 1.
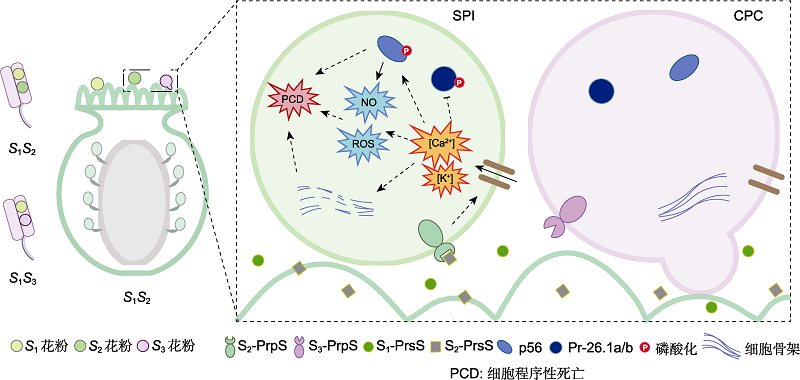
图3 3类自交不亲和性(SI)的分子与生化机制 图示罂粟科3类自交不亲和性的分子与生化机制。图片右侧虚线框表示自己和异己花粉中分别发生的SPI和CPC反应。SPI和CPC同图1, ROS同图2。
Figure 3 Molecular and biochemical mechanisms of Type 3 self-incompatibility (SI) Schematic diagram illustrating the molecular and biochemical mechanisms of Type 3 SI in Papaveraceae with SPI and CPC reactions occurring in self and cross pollen cells shown on the right dashed box. The meanings of SPI and CPC are identical to those described in Figure 1, and ROS is the same as shown in Figure 2.
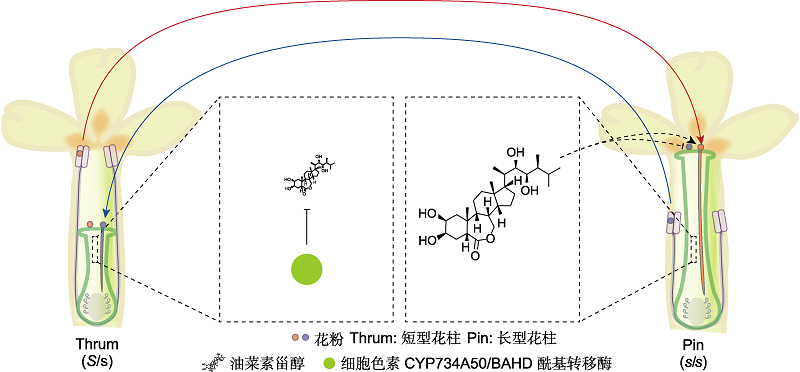
图4 4类和5类自交不亲和性(SI)的分子与生化机制 图示报春花科和时钟花科4类和5类自交不亲和性的分子机制。图片左右两侧分别表示短型花柱(短花柱和长花药)与长型花柱(长花柱和短花药)。红色和蓝色箭头指示授粉方向。黑色虚线箭头及其平末端形式分别表示油菜素甾醇(BR)对异交和自交花粉的促进和抑制作用。黑色实线平末端箭头表示CYP734A50/BAHD对BR含量的抑制作用。
Figure 4 Molecular and biochemical mechanisms of Type 4 and Type 5 self-incompatibility (SI) Schematic diagram of Type 4 and Type 5 SI in Primulaceae and Turneraceae. Short style with long anther and long style with short anther are separately shown on the left and right sides. Red and blue arrows indicate the pollination direction. The black dotted arrow and its flat terminal form represent the promotion and inhibition effects of brassinosteroid (BR) on the cross and self pollen, respectively. The black solid arrow with a flat end indicates the inhibition on BR content by CYP734A50/BAHD.
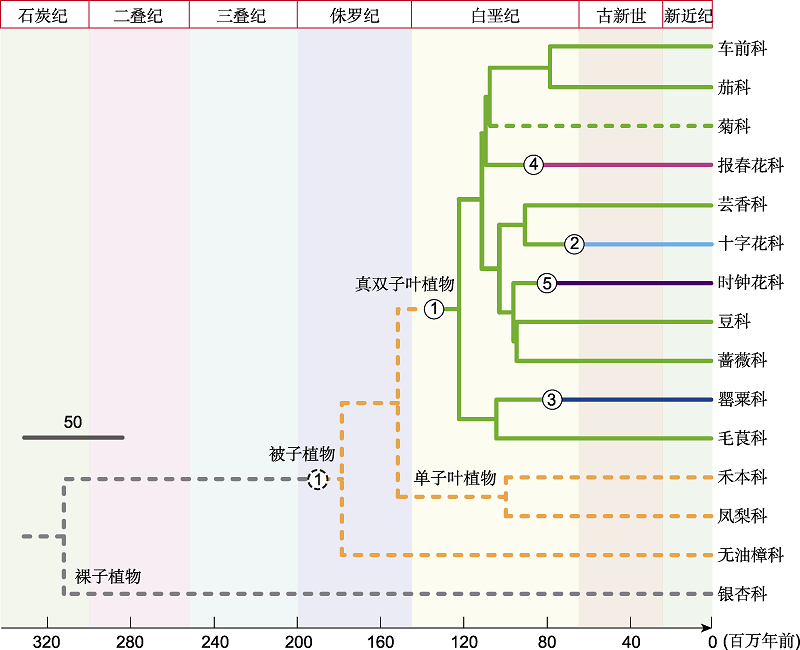
图5 1-5类自交不亲和性(SI)的起源与演化机制 图示1-5类自交不亲和代表物种的科水平物种进化树。进化树由TimeTree (http://www.timetree.org/)网站生成, 下方数轴为演化时间轴。圆圈中的序号分别表示1-5类SI。绿色、浅蓝色、深蓝色、玫红色和深紫色实线分别指示1-5类S位点。灰色虚线表示不具有T2 RNase与FBA/FBK连锁位点, 橙色虚线表示具有能够编码Class I/II T2 RNase和FBA/FBK结构域蛋白的Type 1 S-like结构, 绿色虚线代表不具有Class III T2 RNase/S-RNase与FBA/FBK紧密连锁形成的Type 1 S位点。
Figure 5 Origin and evolution of Type 1-5 self-incompatibility (SI) Phylogenetic tree constructed with TimeTree (http://www.timetree.org/) showing several representative families/species separately possessing Type 1-5 SI. The axis under the tree indicates the evolutionary time. The serial numbers in the circles represent the five SI types. Green, light blue, dark blue, rose, and dark purple lines indicate Type 1-5 S-locus, respectively. The gray dotted line represents no T2 RNase linked to FBA/FBK, the orange dotted line represents Type 1 S-like structure encoding Class I/II T2 RNase and FBA/FBK domain proteins and the green dotted line represents no Type 1 S-locus containing Class III T2 RNase/S-RNase tightly linked to FBA/FBK.
| [1] | 何咏松, 吴仁润 (1987). 苜蓿自交不亲和性研究. 中国草业科学 (4), 6-12. |
| [2] |
Aguiar B, Vieira J, Cunha AE, Vieira CP (2015). No evidence for Fabaceae gametophytic self-incompatibility being determined by Rosaceae, Solanaceae, and Plantaginaceae S-RNase lineage genes. BMC Plant Biol 15, 129.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Allen AM, Thorogood CJ, Hegarty MJ, Lexer C, Hiscock SJ (2011). Pollen-pistil interactions and self-incompatibility in the Asteraceae: new insights from studies of Senecio squalidus (Oxford ragwort). Ann Bot 108, 687-698. |
| [4] | Anderson MA, Cornish EC, Mau SL, Williams EG, Hoggart R, Atkinson A, Bonig I, Grego B, Simpson R, Roche PJ, Haley JD, Penschow JD, Niall HD, Tregear GW, Coghlan JP, Crawford RJ, Clarke AE (1986). Cloning of cDNA for a stylar glycoprotein associated with expression of self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata. Nature 321, 38-44. |
| [5] | Arroyo MTK (1981). Breeding systems and pollination biology in Leguminosae. In: Polhill RM, Raven PH, eds. Advances in Legume Systematics. Kew: Royal Botanic Gardens. pp. 723-769. |
| [6] | Atwood SS (1940). Genetics of cross-incompatibility among self-incompatible plants of Trifolium repens. Agron J 32, 955-968. |
| [7] | Baumann U, Juttner J, Bian XY, Langridge P (2000). Self-incompatibility in the grasses. Ann Bot 85, 203-209. |
| [8] |
Brewbaker JL (1954). Incompatibility in autotetraploid Trifolium repens L. I. Competition and self-compatibility. Genetics 39, 307-316.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Brewbaker JL (1957). Pollen cytology and self-incompatibility systems in plants. J Hered 48, 271-277. |
| [10] |
Brink RA, Cooper DC (1938). Partial self-incompatibility in Medicago sativa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 24, 497-499.
PMID |
| [11] | Cabrillac D, Cock JM, Dumas C, Gaude T (2001). The S-locus receptor kinase is inhibited by thioredoxins and activated by pollen coat proteins. Nature 410, 220-223. |
| [12] |
Casey NM, Milbourne D, Barth S, Febrer M, Jenkins G, Abberton MT, Jones C, Thorogood D (2010). The genetic location of the self-incompatibility locus in white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Theor Appl Genet 121, 567-576.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Chen JQ, Wang P, de Graaf BHJ, Zhang H, Jiao HJ, Tang C, Zhang SL, Wu JY (2018). Phosphatidic acid counteracts S-RNase signaling in pollen by stabilizing the actin cytoskeleton. Plant Cell 30, 1023-1039. |
| [14] | Chen SY, Jia JT, Cheng LQ, Zhao PC, Qi DM, Yang WG, Liu H, Dong XB, Li XX, Liu GS (2019). Transcriptomic analysis reveals a comprehensive calcium- and phytohormone-dominated signaling response in Leymus chinensis self-incompatibility. Int J Mol Sci 20, 2356. |
| [15] | Cornish MA, Hayward MD, Lawrence MJ (1980). Self- incompatibility in ryegrass. Heredity 44, 55-62. |
| [16] | de Graaf BHJ, Rudd JJ, Wheeler MJ, Perry RM, Bell EM, Osman K, Franklin FCH, Franklin-Tong VE (2006). Self-incompatibility in Papaver targets soluble inorganic pyrophosphatases in pollen. Nature 444, 490-493. |
| [17] | de Nettancourt D (2001). Incompatibility and Incongruity in Wild and Cultivated Plants, 2nd edn. Berl in: Springer. pp. 1-356. |
| [18] | Delaney LE, Igić B (2022). The phylogenetic distribution and frequency of self-incompatibility in Fabaceae. Int J Plant Sci 183, 30-42. |
| [19] |
Do Canto J, Studer B, Frei U, Lübberstedt T (2018). Fine mapping a self-fertility locus in perennial ryegrass. Theor Appl Genet 131, 817-827.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Duvick DN (2005). The contribution of breeding to yield advances in maize (Zea mays L.). Adv Agron 86, 83-145. |
| [21] |
Enciso-Rodriguez F, Manrique-Carpintero NC, Nadakuduti SS, Buell CR, Zarka D, Douches D (2019). Overcoming self-incompatibility in diploid potato using CRISPR-Cas9. Front Plant Sci 10, 376.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Entani T, Kubo KI, Isogai S, Fukao Y, Shirakawa M, Isogai A, Takayama S (2014). Ubiquitin-proteasome- mediated degradation of S-RNase in a Solanaceous cross- compatibility reaction. Plant J 78, 1014-1021. |
| [23] |
Ferrer MM, Good-Avila SV (2007). Macrophylogenetic analyses of the gain and loss of self-incompatibility in the Asteraceae. New Phytol 173, 401-414.
PMID |
| [24] |
Foote HC, Ride JP, Franklin-Tong VE, Walker EA, Lawrence MJ, Franklin FC (1994). Cloning and expression of a distinctive class of self-incompatibility (S) gene from Papaver rhoeas L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91, 2265-2269.
PMID |
| [25] | Franklin-Tong VE (2008). Self-incompatibility in Flowering Plants. Berlin: Springer. pp. 1-313. |
| [26] |
Fujii S, Kubo KI, Takayama S (2016). Non-self- and self-recognition models in plant self-incompatibility. Nat Plants 2, 16130.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Gertz A, Wricke G (1989). Linkage between the incompatibility locus Z and β-glucosidase locus in rye. Plant Breed 102, 255-259. |
| [28] |
Gonthier L, Blassiau C, Mörchen M, Cadalen T, Poiret M, Hendriks T, Quillet MC (2013). High-density genetic maps for loci involved in nuclear male sterility (NMS1) and sporophytic self-incompatibility (S-locus) in chicory (Cichorium intybus L., Asteraceae). Theor Appl Genet 126, 2103-2121.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Gu TS, Mazzurco M, Sulaman W, Matias DD, Goring DR (1998). Binding of an arm repeat protein to the kinase domain of the S-locus receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 382-387.
PMID |
| [30] | Gu ZY, Meng D, Yang Q, Yuan H, Wang AD, Li W, Chen QJ, Zhang Y, Wang DM, Li TZ (2015). A CBL gene, MdCBL5, controls the calcium signal and influences pollen tube growth in apple. Tree Genet Genomes 11, 27. |
| [31] | Hayman DL (1956). The genetical control of incompatibility in Phalaris coerulescens Desf. Aust J Biol Sci 9, 321-331. |
| [32] | Heslop-Harrison Y, Shivanna KR (1977). The receptive surface of the angiosperm stigma. Ann Bot 41, 1233-1258. |
| [33] | Hiscock SJ (2000). Genetic control of self-incompatibility in Senecio squalidus L. (Asteraceae): a successful colonizing species. Heredity 85, 10-19. |
| [34] |
Hiscock SJ, McInnis SM, Tabah DA, Henderson CA, Brennan AC (2003). Sporophytic self-incompatibility in Senecio squalidus L. (Asteraceae)—the search for S. J Exp Bot 54, 169-174.
PMID |
| [35] | Hosaka K, Hanneman RE Jr (1998a). Genetics of self- compatibility in a self-incompatible wild diploid potato species Solanum chacoense. 1. Detection of an S locus inhibitor (Sli) gene. Euphytica 99, 191-197. |
| [36] | Hosaka K, Hanneman RE Jr (1998b). Genetics of self- compatibility in a self-incompatible wild diploid potato species Solanum chacoense. 2. Localization of an S locus inhibitor (Sli) gene on the potato genome using DNA markers. Euphytica 103, 265-271. |
| [37] |
Huang J, Zhao L, Yang QY, Xue YB (2006). AhSSK1, a novel SKP1-like protein that interacts with the S-locus F-box protein SLF. Plant J 46, 780-793.
PMID |
| [38] | Huang WJ, Liu HK, McCormick S, Tang WH (2014). Tomato pistil factor STIG1 promotes in vivo pollen tube growth by binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and the extracellular domain of the pollen receptor kinase LePRK2. Plant Cell 26, 2505-2523. |
| [39] | Huu CN, Kappel C, Keller B, Sicard A, Takebayashi Y, Breuninger H, Nowak MD, Bäurle I, Himmelbach A, Burkart M, Ebbing-Lohaus T, Sakakibara H, Altschmied L, Conti E, Lenhard M (2016). Presence versus absence of CYP734A50 underlies the style-length dimorphism in primroses. eLife 5, e17956. |
| [40] | Huu CN, Keller B, Conti E, Kappel C, Lenhard M (2020). Supergene evolution via stepwise duplications and neofunctionalization of a floral-organ identity gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117, 23148-23157. |
| [41] | Huu CN, Plaschil S, Himmelbach A, Kappel C, Lenhard M (2022). Female self-incompatibility type in heterostylous Primula is determined by the brassinosteroid-inactivating cytochrome P450 CYP734A50. Curr Biol 32, 671-676. |
| [42] | Iwano M, Ito K, Fujii S, Kakita M, Asano-Shimosato H, Igarashi M, Kaothien-Nakayama P, Entani T, Kanatani A, Takehisa M, Tanaka M, Komatsu K, Shiba H, Nagai T, Miyawaki A, Isogai A, Takayama S (2015). Calcium signaling mediates self-incompatibility response in the Brassicaceae. Nat Plants 1, 15128. |
| [43] | Kakeda K (2009). S locus-linked F-box genes expressed in anthers of Hordeum bulbosum. Plant Cell Rep 28, 1453-1460. |
| [44] | Kakita M, Murase K, Iwano M, Matsumoto T, Watanabe M, Shiba H, Isogai A, Takayama S (2007). Two distinct forms of M-locus protein kinase localize to the plasma membrane and interact directly with S-locus receptor kinase to transduce self-incompatibility signaling in Brassica rapa. Plant Cell 19, 3961-3973. |
| [45] | Klaas M, Yang BC, Bosch M, Thorogood D, Manzanares C, Armstead IP, Franklin FCH, Barth S (2011). Progress towards elucidating the mechanisms of self-incompatibility in the grasses: further insights from studies in Lolium. Ann Bot 108, 677-685. |
| [46] | Lai Z, Ma WS, Han B, Liang LZ, Zhang YS, Hong GF, Xue YB (2002). An F-box gene linked to the self-incompatibility (S) locus of Antirrhinum is expressed specifically in pollen and tapetum. Plant Mol Biol 50, 29-41. |
| [47] | Lao XT, Suwabe K, Niikura S, Kakita M, Iwano M, Takayama S (2014). Physiological and genetic analysis of CO2-induced breakdown of self-incompatibility in Brassica rapa. J Exp Bot 65, 939-951. |
| [48] | Lewis D, Jones DA (1992). The genetics of heterostyly. In: Barrett SCH, ed. Evolution and Function of Heterostyly. Berlin: Springer. pp. 129-150. |
| [49] | Li JH, Cocker JM, Wright J, Webster MA, McMullan M, Dyer S, Swarbreck D, Caccamo M, Oosterhout CV, Gil- martin PM (2016). Genetic architecture and evolution of the S locus supergene in Primula vulgaris. Nat Plants 2, 16188. |
| [50] | Li JH, Zhang Y, Song YZ, Zhang H, Fan JB, Li Q, Zhang DF, Xue YB (2017). Electrostatic potentials of the S-locus F-box proteins contribute to the pollen S specificity in self-incompatibility in Petunia hybrida. Plant J 89, 45-57. |
| [51] | Li ST, Šamaj J, Franklin-Tong VE (2007). A mitogen-activated protein kinase signals to programmed cell death induced by self-incompatibility in Papaver pollen. Plant Physiol 145, 236-245. |
| [52] |
Li XM, Nield J, Hayman D, Langridge P (1994). Cloning a putative self-incompatibility gene from the pollen of the grass Phalaris coerulescens. Plant Cell 6, 1923-1932.
PMID |
| [53] |
Li XM, Nield J, Hayman D, Langridge P (1995). Thioredoxin activity in the C terminus of Phalaris S protein. Plant J 8, 133-138.
PMID |
| [54] | Lian XP, Zhang SL, Huang GF, Huang LY, Zhang J, Hu FY (2021). Confirmation of a gametophytic self-incompatibility in Oryza longistaminata. Front Plant Sci 12, 576340. |
| [55] |
Liang M, Cao ZH, Zhu AD, Liu YL, Tao MQ, Yang HY, Xu Q Jr, Wang SH, Liu JJ, Li YP, Chen CW, Xie ZZ, Deng CL, Ye JL, Guo WW, Xu Q, Xia R, Larkin RM, Deng XX, Bosch M, Franklin-Tong VE, Chai LJ (2020). Evolution of self-compatibility by a mutant Sm-RNase in citrus. Nat Plants 6, 131-142.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | Lundqvist A (1954). Studies on self-sterility in rye, Secale cereale L. Hereditas 40, 278-294. |
| [57] |
Manzanares C, Barth S, Thorogood D, Byrne SL, Yates S, Czaban A, Asp T, Yang BC, Studer B (2016). A gene encoding a DUF247 domain protein cosegregates with the S self-incompatibility locus in perennial ryegrass. Mol Biol Evol 33, 870-884.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Matzke CM, Hamam HJ, Henning PM, Dougherty K, Shore JS, Neff MM, McCubbin AG (2021). Pistil mating type and morphology are mediated by the brassinosteroid inactivating activity of the S-locus gene BAHD in heterostylous Turnera species. Int J Mol Sci 22, 10603. |
| [59] | Matzke CM, Shore JS, Neff MM, McCubbin AG (2020). The Turnera style S-locus gene TsBAHD possesses brassinosteroid-inactivating activity when expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 9, 1566. |
| [60] | McClure BA, Gray JE, Anderson MA, Clarke AE (1990). Self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata involves degradation of pollen rRNA. Nature 347, 757-760. |
| [61] | McClure BA, Haring V, Ebert PR, Anderson MA, Simpson RJ, Sakiyama F, Clarke AE (1989). Style self-incompatibility gene products of Nicotiana alata are ribonucleases. Nature 342, 955-957. |
| [62] | Mcinnis SM, Costa LM, Gutiérrez-Marcos JF, Henderson CA, Hiscock SJ (2005). Isolation and characterization of a polymorphic stigma-specific class III peroxidase gene from Senecio squalidus L. (Asteraceae). Plant Mol Biol 57, 659-677. |
| [63] | Parajuli A, Yu LX, Peel M, See D, Wagner S, Norberg S, Zhang ZW (2021). Self-incompatibility, inbreeding depression, and potential to develop inbred lines in alfalfa. In: Yu LX, Kole C, eds. The Alfalfa Genome. Cham: Springer pp. 255-269. |
| [64] | Phumichai C, Mori M, Kobayashi A, Kamijima O, Hosaka K (2005). Toward the development of highly homozygous diploid potato lines using the self-compatibility controlling Sli gene. Genome 48, 977-984. |
| [65] |
Price JH, Raduski AR, Brandvain Y, Van Tassel DL, Smith KP (2022). Development of first linkage map for Silphium integrifolium (Asteraceae) enables identification of sporophytic self-incompatibility locus. Heredity 128, 304-312.
DOI PMID |
| [66] | Qiao H, Wang F, Zhao L, Zhou JL, Lai Z, Zhang YS, Robbins TP, Xue YB (2004a). The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 controls the pollen function of S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant Cell 16, 2307-2322. |
| [67] | Qiao H, Wang HY, Zhao L, Zhou JL, Huang J, Zhang YS, Xue YB (2004b). The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 physically interacts with S-RNases that may be inhibited by the ubiquitin/26S proteasome pathway of protein degradation during compatible pollination in Antirrhinum. Plant Cell 16, 582-595. |
| [68] | Qu HY, Guan YQ, Wang YZ, Zhang SL (2017). PLC-mediated signaling pathway in pollen tubes regulates the gametophytic self-incompatibility of Pyrus species. Front Plant Sci 8, 1164. |
| [69] | Samuel MA, Chong YT, Haasen KE, Aldea-Brydges MG, Stone SL, Goring DR (2009). Cellular pathways regulating responses to compatible and self-incompatible pollen in Brassica and Arabidopsis stigmas intersect at Exo70A1, a putative component of the exocyst complex. Plant Cell 21, 2655-2671. |
| [70] | Samuel MA, Mudgil Y, Salt JN, Delmas F, Ramachandran S, Chilelli A, Goring DR (2008). Interactions between the S-domain receptor kinases and AtPUB-ARM E3 ubiquitin ligases suggest a conserved signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 147, 2084-2095. |
| [71] | Sankaranarayanan S, Jamshed M, Kumar A, Skori L, Scandola S, Wang TN, Spiegel D, Samuel MA (2017). Glyoxalase goes green: the expanding roles of glyoxalase in plants. Int J Mol Sci 18, 898. |
| [72] |
Sankaranarayanan S, Jamshed M, Samuel MA (2015). Degradation of glyoxalase I in Brassica napus stigma leads to self-incompatibility response. Nat Plants 1, 15185.
DOI PMID |
| [73] | Sassa H, Kakui H, Miyamoto M, Suzuki Y, Hanada T, Ushijima K, Kusaba M, Hirano H, Koba T (2007). S locus F-box brothers: multiple and pollen-specific F-box genes with S haplotype-specific polymorphisms in apple and Japanese pear. Genetics 175, 1869-1881. |
| [74] | Sassa H, Nishio T, Kowyama Y, Hirano H, Koba T, Ikehashi H (1996). Self-incompatibility (S) alleles of the Rosaceae encode members of a distinct class of the T2/S ribonuclease superfamily. Mol Gen Genet 250, 547-557. |
| [75] |
Scandola S, Samuel MA (2019). A flower-specific phospholipase D is a stigmatic compatibility factor targeted by the self-incompatibility response in Brassica napus. Curr Biol 29, 506-512.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
Schopfer CR, Nasrallah ME, Nasrallah JB (1999). The male determinant of self-incompatibility in Brassica. Science 286, 1697-1700.
PMID |
| [77] |
Shinozuka H, Cogan NOI, Smith KF, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2010). Fine-scale comparative genetic and physical mapping supports map-based cloning strategies for the self-incompatibility loci of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Plant Mol Biol 72, 343-355.
DOI PMID |
| [78] |
Shore JS, Hamam HJ, Chafe PDJ, Labonne JDJ, Henning PM, McCubbin AG (2019). The long and short of the S-locus in Turnera (Passifloraceae). New Phytol 224, 1316-1329.
DOI PMID |
| [79] | Sijacic P, Wang X, Skirpan AL, Wang Y, Dowd PE, McCubbin AG, Huang S, Kao TH (2004). Identification of the pollen determinant of S-RNase-mediated self-incompatibility. Nature 429, 302-305. |
| [80] | Stone SL, Anderson EM, Mullen RT, Goring DR (2003). ARC1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase and promotes the ubiquitination of proteins during the rejection of self-incompatible Brassica pollen. Plant Cell 15, 885-898. |
| [81] |
Suzuki T, Kusaba M, Matsushita M, Okazaki K, Nishio T (2000). Characterization of Brassica S-haplotypes lacking S-locus glycoprotein. FEBS Lett 482, 102-108.
PMID |
| [82] | Tabah DA, Mcinnis SM, Hiscock SJ (2004). Members of the S-receptor kinase multigene family in Senecio squalidus L (Asteraceae), a species with sporophytic self-incompatibility. Sex Plant Reprod 17, 131-140. |
| [83] | Takasaki T, Hatakeyama K, Suzuki G, Watanabe M, Isogai A, Hinata K (2000). The S receptor kinase determines self-incompatibility in Brassica stigma. Nature 403, 913-916. |
| [84] |
Takayama S, Isogai A (2005). Self-incompatibility in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 56, 467-489.
PMID |
| [85] | Takayama S, Shimosato H, Shiba H, Funato M, Che FS, Watanabe M, Iwano M, Isogai A (2001). Direct ligand- receptor complex interaction controls Brassica self-incompatibility. Nature 413, 534-538. |
| [86] | Thomas SG, Franklin-Tong VE (2004). Self-incompatibility triggers programmed cell death in Papaver pollen. Nature 429, 305-309. |
| [87] |
Thomas SG, Huang SJ, Li ST, Staiger CJ, Franklin-Tong VE (2006). Actin depolymerization is sufficient to induce programmed cell death in self-incompatible pollen. J Cell Biol 174, 221-229.
PMID |
| [88] |
Thorogood D, Armstead IP, Turner LB, Humphreys MO, Hayward MD (2005). Identification and mode of action of self-compatibility loci in Lolium perenne L. Heredity 94, 356-363.
DOI PMID |
| [89] |
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Tao R, Hirano H (2003). Structural and transcriptional analysis of the self-incompatibility locus of almond: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with haplotype-specific polymorphism. Plant Cell 15, 771-781.
DOI PMID |
| [90] | Wehling P, Hackauf B, Wricke G (1994). Phosphorylation of pollen proteins in relation to self-incompatibility in rye (Secale cereale L.). Sex Plant Reprod 7, 67-75. |
| [91] | Wheeler MJ, de Graaf BHJ, Hadjiosif N, Perry RM, Poulter NS, Osman K, Vatovec S, Harper A, Franklin FCH, Franklin-Tong VE (2009). Identification of the pollen self-incompatibility determinant in Papaver rhoeas. Nature 459, 992-995. |
| [92] |
Wilkins KA, Bancroft J, Bosch M, Ings J, Smirnoff N, Franklin-Tong VE (2011). Reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide mediate actin reorganization and programmed cell death in the self-incompatibility response of Papaver. Plant Physiol 156, 404-416.
DOI PMID |
| [93] |
Wricke G, Wehling P (1985). Linkage between an incompatibility locus and a peroxidase isozyme locus (Prx 7) in rye. . Theor Appl Genet 71, 289-291.
DOI PMID |
| [94] | Xu C, Li MF, Wu JK, Guo H, Li Q, Zhang YE, Chai JJ, Li TZ, Xue YB (2013). Identification of a canonical SCFSLF complex involved in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility of Pyrus (Rosaceae). Plant Mol Biol 81, 245-257. |
| [95] |
Xue YB, Carpenter R, Dickinson HG, Coen ES (1996). Origin of allelic diversity in Antirrhinum S locus RNases. Plant Cell 8, 805-814.
PMID |
| [96] |
Yang BC, Thorogood D, Armstead I, Barth S (2008). How far are we from unravelling self-incompatibility in grasses? New Phytol 178, 740-753.
DOI PMID |
| [97] | Yang Q, Meng D, Gu ZY, Li W, Chen QJ, Li Y, Yuan H, Yu J, Liu CS, Li TZ (2018). Apple S-RNase interacts with an actin-binding protein, MdMVG, to reduce pollen tube growth by inhibiting its actin-severing activity at the early stage of self-pollination induction. Plant J 95, 41-56. |
| [98] | Ye MW, Peng Z, Tang D, Yang ZM, Li DW, Xu YM, Zhang CZ, Huang SW (2018). Generation of self-compatible diploid potato by knockout of S-RNase. Nat Plants 4, 651-654. |
| [99] | Zhang LL, Huang JB, Su SQ, Wei XC, Yang L, Zhao HH, Yu JQ, Wang J, Hui JY, Hao SY, Song SS, Cao YY, Wang MS, Zhang XW, Zhao YY, Wang ZY, Zeng WQ, Wu HM, Yuan YX, Zhang XS, Cheung AY, Duan QH (2021). FERONIA receptor kinase-regulated reactive oxygen species mediate self-incompatibility in Brassica rapa. Curr Biol 31, 3004-3016. |
| [100] |
Zhang YJ, Zhao ZH, Xue YB (2009). Roles of proteolysis in plant self-incompatibility. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60, 21-42.
DOI PMID |
| [101] | Zhao H, Song YZ, Li JH, Zhang Y, Huang HQ, Li Q, Zhang Y, Xue YB (2021). Primary restriction of S-RNase cytotoxicity by a stepwise ubiquitination and degradation pathway in Petunia hybrida. New Phytol 231, 1249-1264. |
| [102] | Zhao H, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Song YZ, Zhao F, Zhang Y, Zhu SH, Zhang HK, Zhou ZD, Guo H, Li MM, Li JH, Gao Q, Han QQ, Huang HQ, Copsey L, Li Q, Chen H, Coen E, Zhang YJ, Xue YB (2022). Origin, loss, and regain of self-incompatibility in angiosperms. Plant Cell 34, 579-596. |
| [103] | Zhao L, Huang J, Zhao ZH, Li Q, Sims TL, Xue YB (2010). The Skp1-like protein SSK1 is required for cross-pollen compatibility in S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant J 62, 52-63. |
| [1] | 邱锐, 何峰, 李瑞, 王亚梅, 邢思年, 曹英萍, 刘叶飞, 周昕越, 赵彦, 付春祥. 柳枝稷木质素基因F5H的高效编辑[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 298-307. |
| [2] | 邓娴, 李彤, 曹晓风. 基因编辑在饲草育种中的应用与展望[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 233-240. |
| [3] | 林克剑, 刘志鹏, 罗栋, 武自念. 饲草种质资源研究现状、存在问题与发展建议[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 241-247. |
| [4] | 景海春, 王台, 林荣呈, 曹晓风, 种康. 加强饲草基础生物学研究,保障饲草种业与国家大粮食安全[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 719-724. |
| [5] | 孔照胜, 杨文强, 王柏臣, 林荣呈. 豆科饲草碳氮高效固定、转运和同化利用研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 764-773. |
| [6] | 金京波, 梁承志. 饲草基因组学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 732-741. |
| [7] | 曹丽雯, 卢蕊, 范吉标, 胡龙兴, 陈良. 新型饲草开发利用的基础生物学问题[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 826-836. |
| [8] | 王甜甜, 曹丽雯, 刘智全, 杨庆山, 陈良, 陈敏, 景海春. 黄河三角洲滨海草带建设的饲草基础生物学问题[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 837-847. |
| [9] | 李强, 黄迎新, 周道玮, 丛山. 土壤氮磷添加下豆科草本植物生物固氮与磷获取策略的权衡机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(3): 286-297. |
| [10] | 郝祎祺, 赵鑫峰. 被子植物早期近交衰退与晚期自交不亲和[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(1): 106-112. |
| [11] | 刘敏, 孙杉, 李庆军. 两种姜科花柱卷曲性植物柱头的位置与其可授性的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2007, 15(6): 639-644. |
| [12] | 张一婧 薛勇彪. 基于S- 核酸酶的自交不亲和性的分子机制[J]. 植物学报, 2007, 24(03): 372-388. |
| [13] | 于晓敏 蓝兴国 李玉花. 泛素/26S蛋白酶体途径与显花植物自交不亲和反应[J]. 植物学报, 2006, 23(2): 197-206. |
| [14] | 白伟宁, 张大勇. 雌雄同体植物的性别干扰及其进化意义[J]. 植物生态学报, 2005, 29(4): 672-679. |
| [15] | 陈晓流;束怀瑞;陈学森. 核果类果树自交不亲和性研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2004, 21(06): 755-764. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||