

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (4): 433-442.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20185 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20185
张雅楠1, 黄蕾1, 李佳彬1, 张雷2,3, 党振华1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-11-20
接受日期:2021-05-27
出版日期:2021-07-01
发布日期:2021-06-30
通讯作者:
党振华
作者简介:*E-mail: zhdang_1982@aliyun.com基金资助:
Yanan Zhang1, Lei Huang1, Jiabin Li1, Lei Zhang2,3, Zhenhua Dang1,*( )
)
Received:2020-11-20
Accepted:2021-05-27
Online:2021-07-01
Published:2021-06-30
Contact:
Zhenhua Dang
摘要: 基因内部的简单重复序列(Genic-SSR)可在植物适应环境变化中发挥重要作用。通过对阿拉善5个样点多枝柽柳(Tamarix ramosissima)的转录组进行测序、组装和比较, 经CandiSSR软件分析, 共鉴定出代表157个基序类型的1 185个多态性Genic-SSR位点, 位于1 123个转录本中。其中, 三核苷酸重复序列(596, 50.30%)最多, 其次是二核苷酸重复序列(486, 41.01%)。定位分析表明, 分别有411、239和163个Genic-SSRs位于相应基因的CDSs、5′UTRs和3′UTRs; 78.47%的三核苷酸重复SSRs位于基因的CDSs, 94.07%的二核苷酸重复SSRs位于基因的UTRs; 在CDS中, AGC/GCT、AGG/CCT、AAG/CTT、CCG/CGG和ATC/GAT重复相对丰富, 占所有Genic-SSRs的64.48%; AG/CT和AT/AT是UTRs中最丰富的重复类型, 占UTR中所有Genic-SSRs的55.22%。功能注释表明, 含有多态Genic-SSRs的基因可注释到多个与植物逆境应答相关的GO条目和KEGG通路中。在随机选取的15个多态性SSR位点中, 14个被成功扩增, 共检测到64个等位基因。遗传多态性估算表明, 它们的期望杂合度(He)、观测杂合度(Ho)和多态性信息含量(PIC)平均值分别为0.553、0.421和0.493, 均属于中、高多态SSR标记, 表明利用RNA-seq技术开发SSR标记可行。
张雅楠, 黄蕾, 李佳彬, 张雷, 党振华. 基于转录组的阿拉善地区多枝柽柳多态Genic-SSRs的识别与开发. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 433-442.
Yanan Zhang, Lei Huang, Jiabin Li, Lei Zhang, Zhenhua Dang. Identification and Development of Polymorphic Genic-SSRs in Tamarix ramosissima in Alxa Region Based on Transcriptome. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(4): 433-442.
| Population | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) | Altitude (m) | Habitats |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR1 | 101°00′06″ | 41°52′16″ | 939 | Wetland |
| TR2 | 101°11′44″ | 41°57′27″ | 927 | Sandy land |
| TR3 | 101°03′36″ | 42°07′02″ | 915 | Wetland |
| TR4 | 101°12′26″ | 41°58′45″ | 924 | Wetland |
| TR5 | 101°16′25″ | 42°01′55″ | 921 | Wetland |
表1 采样点具体信息
Table 1 Detailed information of the sampling locations
| Population | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) | Altitude (m) | Habitats |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR1 | 101°00′06″ | 41°52′16″ | 939 | Wetland |
| TR2 | 101°11′44″ | 41°57′27″ | 927 | Sandy land |
| TR3 | 101°03′36″ | 42°07′02″ | 915 | Wetland |
| TR4 | 101°12′26″ | 41°58′45″ | 924 | Wetland |
| TR5 | 101°16′25″ | 42°01′55″ | 921 | Wetland |
| Sample | CR (No.) | Q30 (%) | GC (%) | Ug (No.) | ML (bp) | N50 (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR1 | 47893646 | 93.12 | 41.95 | 37790 | 1053.09 | 1953 |
| TR2 | 43861774 | 93.06 | 41.96 | 35818 | 1083.87 | 1983 |
| TR3 | 46194046 | 93.04 | 42.33 | 39252 | 995.67 | 1812 |
| TR4 | 44817976 | 93.17 | 42.87 | 32175 | 1099.48 | 1899 |
| TR5 | 44190698 | 92.92 | 42.49 | 34364 | 1082.91 | 1930 |
| All-unigene | 81728 | 823.46 | 1364 |
表2 测序与组装结果统计
Table 2 Statistics of sequencing and assembly results
| Sample | CR (No.) | Q30 (%) | GC (%) | Ug (No.) | ML (bp) | N50 (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR1 | 47893646 | 93.12 | 41.95 | 37790 | 1053.09 | 1953 |
| TR2 | 43861774 | 93.06 | 41.96 | 35818 | 1083.87 | 1983 |
| TR3 | 46194046 | 93.04 | 42.33 | 39252 | 995.67 | 1812 |
| TR4 | 44817976 | 93.17 | 42.87 | 32175 | 1099.48 | 1899 |
| TR5 | 44190698 | 92.92 | 42.49 | 34364 | 1082.91 | 1930 |
| All-unigene | 81728 | 823.46 | 1364 |
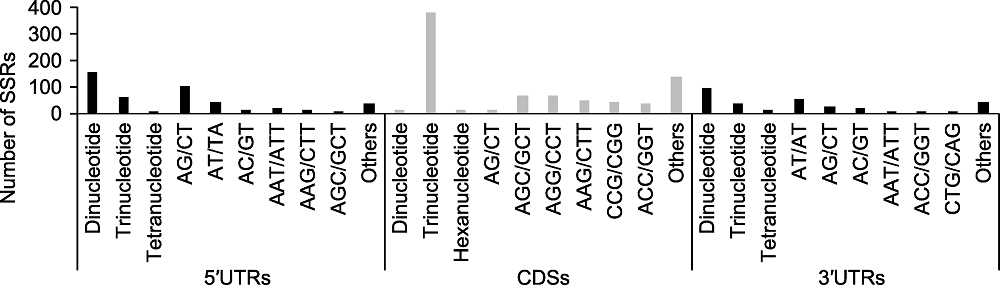
图1 基因内部简单重复序列(Genic-SSRs)的分布 x轴表示多态性Genic-SSRs的分布和motif序列类型; y轴表示Genic-SSRs的数目。
Figure 1 Distribution of the identified Genic-SSRs The x-axis represents the distribution and motif types of polymorphic Genic-SSRs; The y-axis represents the number of Genic- SSRs.
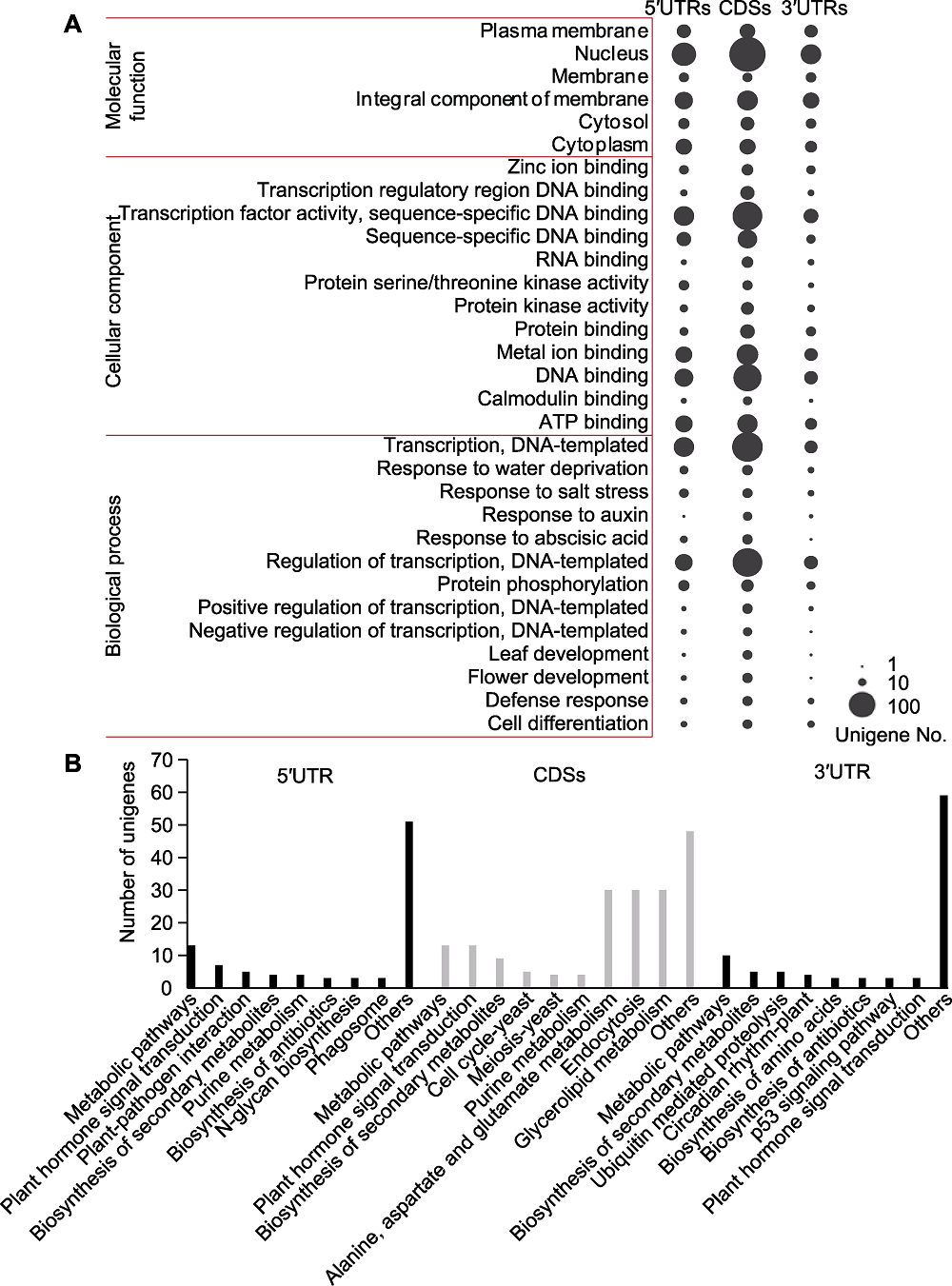
图2 含Genic-SSR序列基因的GO和KEGG富集分析 (A) GO分析, 3列气泡分别代表5′UTRs、CDSs和3′UTRs含有Genic-SSRs基因的GO富集分析结果, GO条目的基因数目由气泡大小表示; 每个基因区域显示基因数目≥10的GO条目; (B) KEGG富集分析, x轴表示5′UTRs、CDSs和3′UTRs含有Genic-SSRs基因富集的代谢通路; y轴表示富集在KEGG通路中的基因数目。
Figure 2 GO and KEGG enrichment of the Genic-SSR-containing sequences (A) GO analysis, the three columns of the bubbles represent GO enrichment analysis of transcripts that containing Genic-SSRs in the 5′UTRs, CDSs and 3′UTRs, respectively, and the number of unigenes assigned to each term is indicated by the size of each bubble; GO terms that contained unigenes more than or equal to ten in one of the gene regions are shown; (B) KEGG enrichment analysis, the x-axis indicates the enriched pathways assigned to the 5°UTRs, CDSs and 3°UTRs Genic-SSR-containing sequences; the y-axis represents the number of unigenes enriched in KEGG pathways.
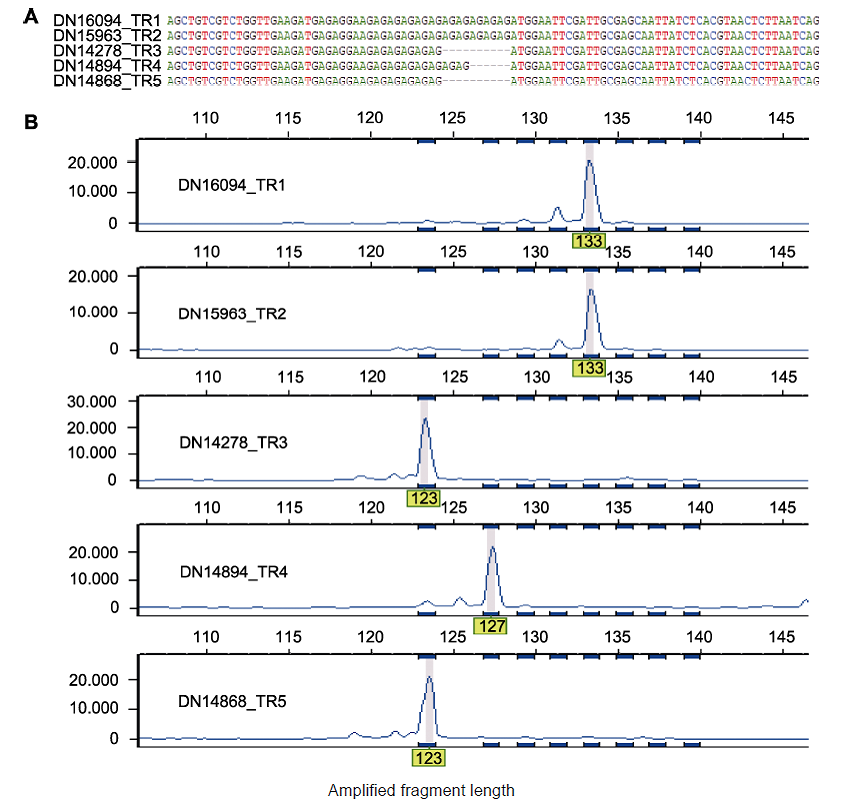
图3 多态Genic-SSR序列比对及毛细管电泳分析 (A) TR1-TR5转录组中多态Genic-SSR 104关联基因序列的比对结果; (B) 图(A)中多态Genic-SSRs的毛细管电泳结果
Figure 3 Multiple sequence alignment of polymorphic Genic-SSR and capillary electrophoresis analysis (A) Multiple sequence alignment for five transcripts assembled in the TR1-TR5 transcriptomes that correspond to polymorphic Genic-SSR 104; (B) The polymorphism of Genic-SSRs in (A) revealed by capillary electrophoresis
| SSR ID | PS (5′→3′) | RM | Tm (°C) | AS (bp) | Na | PIC | Ho | He | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104 | F: CAAGGAGGAGCTGTCGTCTG | AG | 59.9 | 123-139 | 8 | 0.516 | 0.286 | 0.558 | |
| R: GCAGACACGAAGTTTGCGAT | |||||||||
| 221 | F: TGAAGCAGCTGTGTTGGTGA | AT | 53.4 | 158-162 | 3 | 0.562 | 0.321 | 0.645 | |
| R: TCCTCCTCGATTCCCTACTGA | |||||||||
| 300 | F: GAAGGGTTTGGGTGTTTTCAGA | AT | 59.5 | 155-161 | 4 | 0.641 | 0.643 | 0.708 | |
| R: AAAACGCACCCTCTCAGCAG | |||||||||
| 392 | F: CGCAACAAGCACAACATCCA | CAG | 57.9 | 100-109 | 4 | 0.407 | 0.608 | 0.489 | |
| R: GTTAACCGGTCGCACAACTG | |||||||||
| 438 | F: GGCACCGATACACAAGGACA | CCTT | 55.4 | 192-204 | 4 | 0.512 | 0.500 | 0.593 | |
| R: CCCACAGGCTTACACCCATT | |||||||||
| 441 | F: GCCACCGCCACATTTATCTT | CGAG | 50.8 | 106-122 | 5 | 0.520 | 0.286 | 0.570 | |
| R: GGAGCTTGACAGGTACAGCA | |||||||||
| 563 | F: TCCTGTGCAACGAACTGAGT | GA | 51.7 | 176-186 | 6 | 0.593 | 0.536 | 0.666 | |
| R: GGGTTTAGCCATGGGTGACA | |||||||||
| 668 | F: ATGGCGATGATGGAGCAACA | GAG | 59.9 | 146-173 | 7 | 0.711 | 0.429 | 0.758 | |
| R: AGGGATTGGCGGAAGTGAAG | |||||||||
| 670 | F: GAAGACACAGCACCAAGGGA | GAG | 56.7 | 186-201 | 5 | 0.546 | 0.714 | 0.627 | |
| R: CGTCTTCCCCAAGTCCGATC | |||||||||
| 947 | F: TCCCCACACGTAATCCCTTC | TC | 50.8 | 139-149 | 5 | 0.445 | 0.607 | 0.488 | |
| R: GCGGATGGAAGGAGAAGAGG | |||||||||
| 1024 | F: TGCGCATTTCTTGATTGCCA | TCT | 52.1 | 168-180 | 5 | 0.476 | 0.464 | 0.516 | |
| R: GGGTTGATGCGGCTTGATTG | |||||||||
| 1053 | F: GTCGACACTGCAAGCATCAC | TG | 56.7 | 202-204 | 2 | 0.293 | 0.036 | 0.363 | |
| R: GCACGTACGAGCACATCTCT | |||||||||
| 1093 | F: GAATAGTGGTGGCGGGAGTC | TGC | 54.7 | 117-126 | 2 | 0.195 | 0.250 | 0.223 | |
| R: GCTTGGCATCGTACCCCTAT | |||||||||
| 1114 | F: GGTCCTCAGTGTGGCCATAG | TGG | 54.1 | 156-171 | 4 | 0.487 | 0.214 | 0.543 | |
| R: GTGTTAGAGATGGCGGGCAA | |||||||||
| Mean | 4.5 | 0.493 | 0.421 | 0.553 | |||||
表3 14个多态Genic-SSRs标记的基本信息及遗传学参数
Table 3 Basic information and genetic parameters of the 14 polymorphic Genic-SSRs
| SSR ID | PS (5′→3′) | RM | Tm (°C) | AS (bp) | Na | PIC | Ho | He | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104 | F: CAAGGAGGAGCTGTCGTCTG | AG | 59.9 | 123-139 | 8 | 0.516 | 0.286 | 0.558 | |
| R: GCAGACACGAAGTTTGCGAT | |||||||||
| 221 | F: TGAAGCAGCTGTGTTGGTGA | AT | 53.4 | 158-162 | 3 | 0.562 | 0.321 | 0.645 | |
| R: TCCTCCTCGATTCCCTACTGA | |||||||||
| 300 | F: GAAGGGTTTGGGTGTTTTCAGA | AT | 59.5 | 155-161 | 4 | 0.641 | 0.643 | 0.708 | |
| R: AAAACGCACCCTCTCAGCAG | |||||||||
| 392 | F: CGCAACAAGCACAACATCCA | CAG | 57.9 | 100-109 | 4 | 0.407 | 0.608 | 0.489 | |
| R: GTTAACCGGTCGCACAACTG | |||||||||
| 438 | F: GGCACCGATACACAAGGACA | CCTT | 55.4 | 192-204 | 4 | 0.512 | 0.500 | 0.593 | |
| R: CCCACAGGCTTACACCCATT | |||||||||
| 441 | F: GCCACCGCCACATTTATCTT | CGAG | 50.8 | 106-122 | 5 | 0.520 | 0.286 | 0.570 | |
| R: GGAGCTTGACAGGTACAGCA | |||||||||
| 563 | F: TCCTGTGCAACGAACTGAGT | GA | 51.7 | 176-186 | 6 | 0.593 | 0.536 | 0.666 | |
| R: GGGTTTAGCCATGGGTGACA | |||||||||
| 668 | F: ATGGCGATGATGGAGCAACA | GAG | 59.9 | 146-173 | 7 | 0.711 | 0.429 | 0.758 | |
| R: AGGGATTGGCGGAAGTGAAG | |||||||||
| 670 | F: GAAGACACAGCACCAAGGGA | GAG | 56.7 | 186-201 | 5 | 0.546 | 0.714 | 0.627 | |
| R: CGTCTTCCCCAAGTCCGATC | |||||||||
| 947 | F: TCCCCACACGTAATCCCTTC | TC | 50.8 | 139-149 | 5 | 0.445 | 0.607 | 0.488 | |
| R: GCGGATGGAAGGAGAAGAGG | |||||||||
| 1024 | F: TGCGCATTTCTTGATTGCCA | TCT | 52.1 | 168-180 | 5 | 0.476 | 0.464 | 0.516 | |
| R: GGGTTGATGCGGCTTGATTG | |||||||||
| 1053 | F: GTCGACACTGCAAGCATCAC | TG | 56.7 | 202-204 | 2 | 0.293 | 0.036 | 0.363 | |
| R: GCACGTACGAGCACATCTCT | |||||||||
| 1093 | F: GAATAGTGGTGGCGGGAGTC | TGC | 54.7 | 117-126 | 2 | 0.195 | 0.250 | 0.223 | |
| R: GCTTGGCATCGTACCCCTAT | |||||||||
| 1114 | F: GGTCCTCAGTGTGGCCATAG | TGG | 54.1 | 156-171 | 4 | 0.487 | 0.214 | 0.543 | |
| R: GTGTTAGAGATGGCGGGCAA | |||||||||
| Mean | 4.5 | 0.493 | 0.421 | 0.553 | |||||
| [1] | 毕江涛, 马萍, 杨志伟, 关晓庆 (2013). 药用植物柽柳内生真菌分离及其抑菌活性初步研究. 草业学报 22(3), 132-138. |
| [2] |
陈敏, 刘林德, 张莉, 王丽娟 (2012). 黑河中游和烟台海滨中国柽柳的传粉生态学研究. 植物学报 47, 264-270.
DOI |
| [3] | 陈雨, 潘大建, 曲延英, 范芝兰, 陈建酉, 李晨 (2008). 广东高州7个普通野生稻居群遗传结构的SSR分析. 植物学通报 25, 430-436. |
| [4] | 蒋志敏, 陈玉霞, 包颖 (2011). 黄河三角洲柽柳居群的遗传结构和遗传分化. 植物分类与资源学报 33, 403-408. |
| [5] | 李珊, 周天华, 赵桂仿, 朱云国, 杨晓伶, 程舟 (2010). 马蹄香表达序列标签资源的SSR信息分析. 中草药 41, 464-468. |
| [6] | 李永涛, 王霞, 魏海霞, 杨庆山, 周健, 刘德玺, 刘忠杰, 魏文千 (2017). 盐碱生境模拟下两种柽柳的生理特性研究. 山东农业科学 49, 53-58. |
| [7] | 刘林, 李进斌, 张悦, 苏源, 杨静, 陈梦琪, 李成云 (2010). 灰色大角间座壳菌(稻瘟病菌)蛋白激酶编码基因中SSR变异及其对蛋白结构的潜在影响. 菌物学报 29, 698-706. |
| [8] | 王慧, 刘宁, 刘金龙, 姚延梼, 王林 (2020). 晋北干旱区盐碱地柽柳形态特征及其与土壤养分的关系. 中南林业科技大学学报 40, 37-48. |
| [9] | 温月仙, 甘红豪, 史胜青, 江泽平, 吴利禄, 褚建民 (2020). 基于叶绿体和核基因片段序列的甘蒙柽柳谱系地理研究. 林业科学 56, 55-64. |
| [10] | 伍明江, 张德芹, 李盼, 石旭柳, 刘璐 (2020). 柽柳黄素对3T3-L1脂肪细胞胰岛素抵抗的影响及AMPK信号通路的作用机制. 天然产物研究与开发 32, 953-960. |
| [11] | 杨成君, 王军 (2008). 人参EST资源的SSR信息分析. 植物生理学通讯 44, 69-73. |
| [12] | 姚秋阳 (2015). 利用RNA-seq技术在云南山茶中解析重要分子通路与开发多态性EST-SSR. 博士论文. 昆明: 云南大学. pp. 38-96. |
| [13] | 叶春秀, 姜继元, 董鹏, 庄振刚, 陈奇凌, 谢宗铭 (2015). 基于SSR标记的新疆塔里木河流域柽柳指纹图谱构建及遗传多样性分析. 分子植物育种 13, 2566-2571. |
| [14] |
Bräutigam A, Gowik U (2010). What can next generation sequencing do for you? Next generation sequencing as a valuable tool in plant research. Plant Biol 12, 831-841.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Cardle L, Ramsay L, Milbourne D, Macaulay M, Marshall D, Waugh R (2000). Computational and experimental characterization of physically clustered simple sequence repeats in plants. Genetics 156, 847-854.
PMID |
| [16] |
Chen CX, Zhou P, Choi YA, Huang S, Gmitter FG Jr (2006). Mining and characterizing microsatellites from citrus ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 112, 1248-1257.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Chen YN, Zhou HH, Chen YP (2013). Adaptation strategies of desert riparian forest vegetation in response to drought stress. Ecohydrology 6, 956-973.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Dang ZH, Huang L, Jia YY, Lockhart PJ, Fong Y, Tian YY (2020). Identification of Genic SSRs provide a perspective for studying environmental adaptation in the endemic shrub Tetraena mongolica. Genes 11, 322.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Fraser LG, Harvey CF, Crowhurst RN, Silva HN (2004). EST-derived microsatellites from Actinidia species and their potential for mapping. Theor Appl Genet 108, 1010-1016.
PMID |
| [20] |
Gao LF, Tang JF, Li HW, Jia JZ (2003). Analysis of microsatellites in major crops assessed by computational and experimental approaches. Mol Breed 12, 245-261.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Gou XJ, Shi HR, Yu SF, Wang ZQ, Li CX, Liu SH, Ma J, Chen GD, Liu T, Liu YX (2020). SSRMMD: a rapid and accurate algorithm for mining SSR feature loci and candidate polymorphic SSRs based on assembled sequences. Front Genet 11, 706.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Han ZZ, Ma XY, Wei M, Zhao T, Zhan RT, Chen WW (2018). SSR marker development and intraspecific genetic divergence exploration of Chrysanthemum indicum based on transcriptome analysis. BMC Genomics 19, 291.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Beiles A, Nevo E (2002). Microsatellites: genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: a review. Mol Ecol 11, 2453-2465.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Nevo E (2004). Microsatellites within genes: structure, function, and evolution. Mol Biol Evol 21, 991-1007.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Li ZT, Zhong YD, Yu FX, Xu M (2018). Novel SSR marker development and genetic diversity analysis of Cinnamomum camphora based on transcriptome sequencing. Plant Genet Res 16, 568-571.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Liu KJ, Muse SV (2005). PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21, 2128-2129.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Liu LY, Fan XF, Tan PH, Wu JY, Zhang H, Han C, Chen C, Xun LL, Guo WE, Chang ZH, Teng K (2021). The development of SSR markers based on RNA-sequencing and its validation between and within Carex L. species. BMC Plant Biol 21, 17.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Lynch M, Lande R (1993). Biotic Interactions and Global Change. Sunderland MA: Sinauer Assocs.Inc. pp. 234-250. |
| [29] |
Morgante M, Hanafey M, Powell W (2002). Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nat Genet 30, 194-200.
PMID |
| [30] |
Natale E, Zalba SM, Oggero A, Reinoso H (2010). Establishment of Tamarix ramosissima under different conditions of salinity and water availability: implications for its management as an invasive species. J Arid Environ 74, 1399-1407.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Qin LP, Wang LQ, Guo Y, Li Y, Ümüt H, Wang YC (2017). An ERF transcription factor from Tamarix hispida, ThCRF1, can adjust osmotic potential and reactive oxygen species scavenging capability to improve salt tolerance. Plant Sci 265, 154-166.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Ranathunge C, Wheeler GL, Chimahusky ME, Perkins AD, Pramod S, Welch ME (2020). Transcribed microsatellite allele lengths are often correlated with gene expression in natural sunflower populations. Mol Ecol 29, 1704-1716.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Santi L, Wang YM, Stile MR, Berendzen K, Wanke D, Roig C, Pozzi C, Müller K, Müller J, Rohde W, Salamini F (2003). The GA octodinucleotide repeat binding factor BBR participates in the transcriptional regulation of the homeobox gene Bkn3. Plant J 34, 813-826.
PMID |
| [34] |
Sawaya S, Bagshaw A, Buschiazzo E, Kumar P, Chowdhury S, Black MA, Gemmell N (2013). Microsatellite tandem repeats are abundant in human promoters and are associated with regulatory elements. PLoS One 8, e54710.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Trifonov EN (1995). Segmented structure of protein sequences and early evolution of genome by combinatorial fusion of DNA elements. J Mol Evol 40, 337-342.
PMID |
| [1] | 张向歌, 陈晨, 程珊, 李春鑫, 朱雅婧, 许欣然, 王会伟. 油莎豆块茎特异性表达基因鉴定及分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 33-48. |
| [2] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [3] | 程可心, 杜尧, 李凯航, 王浩臣, 杨艳, 金一, 何晓青. 玉米与叶际微生物组的互作遗传机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(2): 215-228. |
| [4] | 祖姆热提•于苏甫江, 董正武, 成鹏, 叶茂, 刘隋赟昊, 李生宇, 赵晓英. 多枝柽柳水分利用策略对沙堆堆积过程的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(1): 113-126. |
| [5] | 魏和平, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 邓飞, 朱浩, 岂泽华, 王玉玺, 叶涵斐, 殷文晶, 方媛, 穆丹, 饶玉春. 水稻抽穗期QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 588-595. |
| [6] | 蔡新宇, 毛晓伟, 赵毅强. 家养动物驯化起源的研究方法与进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21457-. |
| [7] | 徐海霞, 何静, 易航, 王丽. 镉胁迫下地钱转录组的性别特异性响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 182-196. |
| [8] | 张茜, 裘天航, 王安安, 周华健, 袁敏, 李利, 白素兰, 崔素霞. 北京地区芦苇资源状态及其多样性[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 693-704. |
| [9] | 莫日根高娃, 商辉, 刘保东, 康明, 严岳鸿. 一个种还是多个种? 简化基因组及其形态学证据揭示中国白桫椤植物的物种多样性分化[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(11): 1196-1204. |
| [10] | 杨艳, 张海琴, 凡星, 沙莉娜, 康厚扬, 王益, 周永红. 偃麦草属植物醇溶蛋白和谷蛋白多态性及系统学研究[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(5): 579-589. |
| [11] | 黄建峰, 李朗, 李捷. 樟属植物ITS序列多态性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(5): 609-619. |
| [12] | 刘勉, 张彩飞, 黄建勋, 马红. 利用低拷贝核基因重建菊科紫菀亚科族间系统发育关系[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(5): 549-564. |
| [13] | 范文, 徐颖, 许汀, 徐晶, 高继银, 张文驹. 香港红山茶个体内ITS多态性及物种鉴定的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(2): 217-226. |
| [14] | 王纳纳, 陈颖, 应娇妍, 高勇生, 白永飞. 内蒙古草原典型植物对土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(2): 201-208. |
| [15] | 鱼腾飞, 冯起, 司建华. 极端干旱区多枝柽柳叶片气孔导度的环境响应模拟[J]. 植物生态学报, 2012, 36(6): 483-490. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||