

植物学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 669-679.DOI: 10.11983/CBB16204 cstr: 32102.14.CBB16204
• 专题论坛 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2016-10-24
接受日期:2017-01-05
出版日期:2017-09-01
发布日期:2017-07-10
通讯作者:
刘春林
基金资助:Jia Hu1, Chunlin Liu2*
Received:2016-10-24
Accepted:2017-01-05
Online:2017-09-01
Published:2017-07-10
Contact:
Chunlin Liu
摘要: 油体是生物体细胞中一种重要的细胞器结构, 由单层磷脂酸膜包裹中性脂肪酸形成, 膜上镶嵌有决定油体性质的多种膜蛋白。油体在能量储存、细胞生殖分化、抗病抗寒和发育调控等多种生命活动中起重要作用。该文对植物油体的结构、生物学功能、不同组织中油体的形成情况以及油体膜蛋白的研究进展进行了多方位概述和总结, 以期为后续研究提供有益的参考。
胡佳, 刘春林. 植物油体研究进展. 植物学报, 2017, 52(5): 669-679.
Jia Hu, Chunlin Liu. Research Advances in Plant Oil Body. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(5): 669-679.
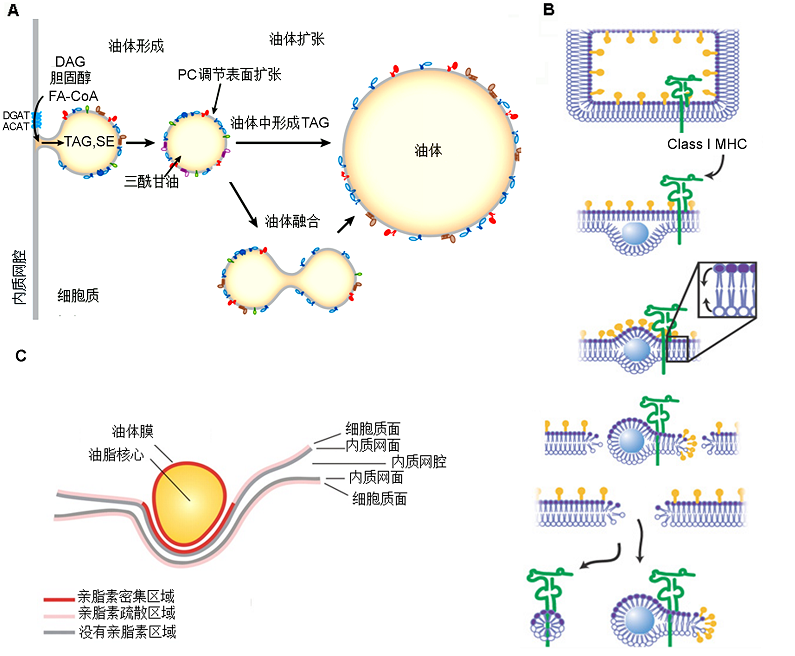
图1 油体形成模式图 (A) 油脂在内质网中通过脂肪酸合成酶DGAT (acyl-CoA: diacylglycerol acyltransferase)和ACAT (acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltrans- ferase)合成后被细胞质面内质网膜包裹, 随着包裹体积的增大, 逐渐形成一个完全封闭的质体——油体, 随后油体与内质网分离或者继续黏结在一起, 通过内部三酰甘油的继续合成或者相互融合进行扩张(Walther and Farese, 2012)。(B) 合成的中性油脂进入内质网腔以后形成一种类似镜头的结构, 该结构为油体中间体。中间体的特殊结构被MHC家族的1类分子体(发卡状所示)识别后开始对中间体部位进行切割, 分别形成油体+MHC分子(右端所示)和磷脂酸+MHC分子(左端所示) 2种不同结构(Ploegh, 2007)。(C) 油体形成的蛋杯模式。内质网上存在的亲脂素能够将内质网膜上的中性油脂集合在一起, 形成一个油脂的核心, 然后内质网以蛋杯裹蛋的形式将含有磷脂单层膜的油脂核心包裹起来, 形成一个蛋杯样的结构。亲脂素存在部位与内质网上油脂部位密切相关。亲脂素在油体膜以及与油体膜接触的细胞质面内质网膜上大量积累, 质面内质网也有少量的亲脂素存在, 腔面内质网基本不含亲脂素(Robenek et al., 2006)。DAG: 二酰甘油; FA-CoA: 脂酰基辅酶A; TAG: 三酰甘油; SE: 甾醇酯; PC: 磷脂酰胆碱
Figure 1 Models of oil body formation (A) Neutral lipids are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by the synthesis enzymes DGAT and ACAT and then covered with cytoplasmic face of the ER membrane. With the expansion of the membrane, a closed plastid called oil body is formed, and then the oil body discharges from the ER or remains adjacent with the ER membrane. The synthesis of neutral lipid in the oil body and the fusion of the oil body lead to the oil body expansion. (B) Neutral lipids enter the ER lumen and form a ‘lens’ structure between the two sheets of phospholipids which is called intermediate. Oil body intermediates are discharged by the recognition of bicelle (hairpin shown). The discharged parts either become part of oil body (right) or a structure composed solely of the class I MHC molecule and phospholipid (left). (C) The egg cup model of oil body synthesis. The adipophilin existing on the ER membrane can recruit the neutral lipid and form a lipid core, and then the ER membranes partially wrap the oil body and form an egg-cup like construct as egg cup wrapping egg. The location of adipophilin is closely related with the lipid existing. Large amounts of adipophilin accumulate on the membrane of oil body and the ER membrane contacting with oil body, low amounts at the cytoplasmic face of the ER, and almost does not exist at the lumen face of the ER (Robenek et al., 2006). DAG: Diacylglycerol; FA-CoA: Fatty acyl-coenzyme A; TAG: Triacylglycerol; SE: Sterol ester; PC: Phosphatidylcholine
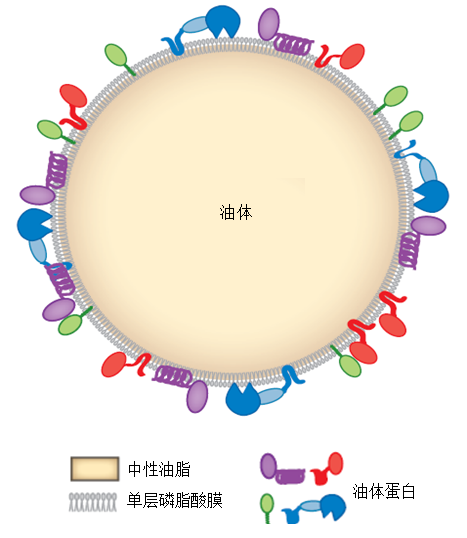
图2 油体分子结构模式图(Walther and Farese, 2012)油体由磷脂酰胆碱、磷脂酰乙醇胺和磷脂酰肌醇等主要磷脂形成的单分子层膜包裹。磷脂膜上镶嵌着各类与油体合成和其生物学性质相关的油体蛋白。磷脂膜内为中性脂肪酸, 包括甾醇酯和三酰甘油等。
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of oil body architecture (Wal- ther and Farese, 2012)Oil body is covered with single layer membrane mainly con- stituted with phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylinositol. The membrane is embedded with different kinds of oil body proteins that related with oil body synthesis and its bio-perspective. Inner the oil body, neural lipids including steroid esters and triacylglycerol are covered by the phospholipids membrane.
| 主要油体膜蛋白 | 主要存在部位 | 生物学功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 油体蛋白(OLEs) | 花粉和整个发育时期的种子 | 阻止/促进油体融合, 维持油体稳定/抗寒/保证种子正常萌发 | Shimada et al., 2008; Krahmer et al., 2012 |
| 油体钙蛋白(Cals) | 营养生长和生殖生长阶段 | 促进油体降解/维持油体稳定/抵抗生物胁迫/参与植物开花调节 | Hara-Nishimura and Hatsugai, 2011; Shen et al., 2016 |
| 脂肪调控蛋白(SEIPIN) | 营养生长和生殖生长阶段 | 控制油体体积和数量 | Cai et al., 2015 |
| 油体协助蛋白1 (OBAP1) | 种子胚 | 抑制油体降解?/保证种子正常萌发 | Ghelis et al., 2008; López-Ribera et al., 2014 |
| α-双加氧酶(α-DOX1) | 营养生长和生殖生长阶段 | 抵抗真菌感染 | Hara-Nishimura and Hatsugai, 2011 |
| 脂滴协助蛋白(LDAP) | 营养生长和生殖生长阶段 | 参与植物昼夜循环/抗胁迫/TAG降解/种子萌发后生长调节 | Gidda et al., 2016 |
| 糖依赖蛋白-1 (SDP1) | 种子 | 种子萌发后降解TAG | Thazar-Poulot et al., 2015 |
| NAD(P)H脱氢酶C1 (NDC1) | 叶绿体 | 参与电子流途径和苯基醌的降解 | Eugeni et al., 2011 |
| 固醇蛋白(Steroleosins) | 种子和含油丰富的营养器官 | 参与甾醇酯的合成? | Shimada and Hara-Nishimura, 2010 |
表1 主要油体膜蛋白及其特点一览表
Table 1 Mainly oil body membrane proteins and their properties
| 主要油体膜蛋白 | 主要存在部位 | 生物学功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 油体蛋白(OLEs) | 花粉和整个发育时期的种子 | 阻止/促进油体融合, 维持油体稳定/抗寒/保证种子正常萌发 | Shimada et al., 2008; Krahmer et al., 2012 |
| 油体钙蛋白(Cals) | 营养生长和生殖生长阶段 | 促进油体降解/维持油体稳定/抵抗生物胁迫/参与植物开花调节 | Hara-Nishimura and Hatsugai, 2011; Shen et al., 2016 |
| 脂肪调控蛋白(SEIPIN) | 营养生长和生殖生长阶段 | 控制油体体积和数量 | Cai et al., 2015 |
| 油体协助蛋白1 (OBAP1) | 种子胚 | 抑制油体降解?/保证种子正常萌发 | Ghelis et al., 2008; López-Ribera et al., 2014 |
| α-双加氧酶(α-DOX1) | 营养生长和生殖生长阶段 | 抵抗真菌感染 | Hara-Nishimura and Hatsugai, 2011 |
| 脂滴协助蛋白(LDAP) | 营养生长和生殖生长阶段 | 参与植物昼夜循环/抗胁迫/TAG降解/种子萌发后生长调节 | Gidda et al., 2016 |
| 糖依赖蛋白-1 (SDP1) | 种子 | 种子萌发后降解TAG | Thazar-Poulot et al., 2015 |
| NAD(P)H脱氢酶C1 (NDC1) | 叶绿体 | 参与电子流途径和苯基醌的降解 | Eugeni et al., 2011 |
| 固醇蛋白(Steroleosins) | 种子和含油丰富的营养器官 | 参与甾醇酯的合成? | Shimada and Hara-Nishimura, 2010 |
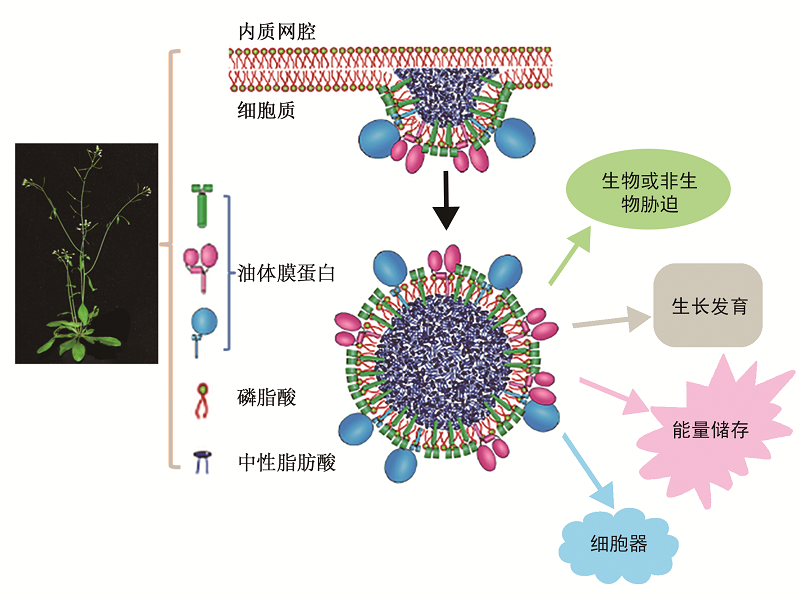
图3 油体的形成及其生物学功能植物营养和生殖器官中形成的中性油脂在内质网上被单层磷脂酸膜包裹形成油体后, 在油体膜蛋白的辅助下参与植物多种生理活动。
Figure 3 The formation of oil body and its corresponding bio-functions The oil body, in both vegetative and reproductive organs, is formed by the neural lipid synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum, and covered by the monolayer phospholipid and oil-body proteins. It play important roles in the physiological activities.
| [1] | 程红焱, 宋松泉 (2006). 种子的贮油细胞器--油体及其蛋白. 植物学通报 23, 418-430. |
| [2] | 戴晓峰, 肖玲, 武玉花, 吴刚, 卢长明 (2007). 植物脂肪酸去饱和酶及其编码基因研究进展. 植物学通报 24, 105-113. |
| [3] | 丁勇, 徐春雷, 甘莉 (2008). 植物油体及其相关蛋白的研究进展. 华中农业大学学报 27, 558-563. |
| [4] | 付三雄, 戚存扣 (2009). 不同海拔地区(南京和拉萨)种植的甘蓝型油菜的种子基因差异表达. 植物学报 44, 178-184. |
| [5] | 虢婷婷, 刘祥华, 邢超, 刘春林, 阮颖 (2012). 蓖麻栽培品种的遗传多样性及蓖麻籽脂肪酸组分分析. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版) 38, 373-376. |
| [6] | 仇键, 谭晓风 (2005). 植物种子油体及相关蛋白研究综述. 中南林学院学报 25, 96-100. |
| [7] | 彭琦, 胡燕, 杜培粉, 谢青轩, 阮颖, 刘春林 (2009). 甘蓝型油菜种子不同发育时期SSH文库的构建. 作物学报 35, 1576-1583. |
| [8] | 王晓茹, 刘文哲 (2011). 黄连木果实中油体的发育. 植物学报 46, 665-674. |
| [9] | Alvarez HM, Steinbüchel A (2002). Triacylglycerols in prokaryotic micro-organisms.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60, 367-376. |
| [10] | Athenstaedt K, Zweytick D, Jandrositz A, Kohlwein S, Daum G (1999). Identification and characterization of ma- jor lipid particle proteins of the yeast Saccharomyces cere- visiae.J Bacteriol 181, 6441-6448. |
| [11] | Bartz R, Li WH, Venables B, Zehmer JK, Roth MR, Welti R, Anderson RGW, Liu PS, Chapman KD (2007). Lipidomics reveals that adiposomes store ether lipids and mediate phospholipid traffic.J Lipid Res 48, 837-847. |
| [12] | Baud S, Lepiniec L (2010). Physiological and developmental regulation of seed oil production.Prog Lipid Res 49, 235-249. |
| [13] | Binns D, Januszewski T, Chen Y, Hill J, Markin VS, Zhao YM, Gilpin C, Chapman KD, Anderson RG, Goodman JM (2006). An intimate collaboration between peroxiso- mes and lipid bodies.J Cell Biol 173, 719-731. |
| [14] | Binns D, Lee S, Hilton CL, Jiang QX, Goodman JM (2010). Seipin is a discrete homooligomer.Biochemistry 49, 10747-10755. |
| [15] | Blée E, Boachon B, Burcklen M, Le Guédard M, Hanano A, Heintz D, Ehlting J, Herrfurth C, Feussner I, Bessoule JJ (2014). The reductase activity of the Arabidopsis caleosin RESPONSIVE TO DESSICATION20 mediates gibberellin-dependent flowering time, abscisic acid sensitivity, and tolerance to oxidative stress.Plant Physiol 166, 109-124. |
| [16] | Brown LA, Larson TR, Graham IA, Hawes C, Paudyal R, Warriner SL, Baker A (2013). An inhibitor of oil body mobilization in Arabidopsis.New Phytol 200, 641-649. |
| [17] | Buhman KK, Chen HC, Farese RV Jr (2001). The enzymes of neutral lipid synthesis.J Biol Chem 276, 40369-40372. |
| [18] | Cai YQ, Goodman JM, Pyc M, Mullen RT, Dyer JM, Chapman KD (2015). Arabidopsis SEIPIN proteins modu- late triacylglycerol accumulation and influence lipid droplet proliferation.Plant Cell 27, 2616-2636. |
| [19] | Cartwright BR, Goodman JM (2012). Seipin: from human disease to molecular mechanism.J Lipid Res 53, 1042-1055. |
| [20] | Chapman KD, Dyer JM, Mullen RT (2012). Biogenesis and functions of lipid droplets in plants: thematic review series: lipid droplet synthesis and metabolism: from yeast to man.J Lipid Res 53, 215-226. |
| [21] | Chapman KD, Ohlrogge JB (2012). Compartmentation of triacylglycerol accumulation in plants.J Biol Chem 287, 2288-2294. |
| [22] | Chen DH, Molitor A, Liu CL, Shen WH (2010). The Arabidopsis PRC1-like ring-finger proteins are necessary for repression of embryonic traits during vegetative growth.Cell Res 20, 1332-1344. |
| [23] | Deruyffelaere C, Bouchez I, Morin H, Guillot A, Miquel M, Froissard M, Chardot T, D'Andrea S (2015). Ubiquitin- mediated proteasomal degradation of oleosins is involved in oil body mobilization during post-germinative seedling growth in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol 56, 1374-1387. |
| [24] | Eastmond PJ (2006).SUGAR-DEPENDENT1 encodes a patatin domain triacylg lycerol lipase that initiates storage oil breakdown in germinating Arabidopsis seeds.Plant Cell 18, 665-675. |
| [25] | Eugeni Piller L, Besagni C, Ksas B, Rumeau D, Bréhélin C, Glauser G, Kessler F, Havaux M (2011). Chloroplast lipid droplet type II NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase is essential for prenylquinone metabolism and vitamin K1 accumulation.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 14354-14359. |
| [26] | Feeney M, Frigerio L, Cui YH, Menassa R (2013). Following vegetative to embryonic cellular changes in leaves of Ara- bidopsis overexpressing LEAFY COTYLEDON2.Plant Phy- siol 162, 1881-1896. |
| [27] | Fei WH, Shui GH, Gaeta B, Du XM, Kuerschner L, Li P, Brown AJ, Wenk MR, Parton RG, Yang HY (2008). Fld1p, a functional homologue of human seipin, regulates the size of lipid droplets in yeast.J Cell Biol 180, 473-482. |
| [28] | Fei WH, Wang H, Fu X, Bielby C, Yang HY (2009). Conditions of endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulate lipid droplet formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem J 424, 61-67. |
| [29] | Frandsen GI, Mundy J, Tzen JTC (2001). Oil bodies and their associated proteins, oleosin and caleosin.Physiol Plant 112, 301-307. |
| [30] | Ghelis T, Bolbach G, Clodic G, Habricot Y, Miginiac E, Sotta B, Jeannette E (2008). Protein tyrosine kinases and protein tyrosine phosphatases are involved in abscisic acid-dependent processes in Arabidopsis seeds and suspension cells.Plant Physiol 148, 1668-1680. |
| [31] | Gidda SK, Park S, Pyc M, Yurchenko O, Cai YQ, Wu P, Andrews DW, Chapman KD, Dyer JM, Mullen RT (2016). Lipid droplet-associated proteins (LDAPs) are required for the dynamic regulation of neutral lipid compartmentation in plant cells.Plant Physiol 170, 2052-2071. |
| [32] | Graham IA (2008). Seed storage oil mobilization.Annu Rev Plant Biol 59, 115-142. |
| [33] | Hara-Nishimura I, Hatsugai N (2011). The role of vacuole in plant cell death.Cell Death Differ 18, 1298-1304. |
| [34] | Huang NL, Huang MD, Chen TL, Huang AHC (2013). Oleosin of subcellular lipid droplets evolved in green algae.Plant Physiol 161, 1862-1874. |
| [35] | Jacquier N, Choudhary V, Mari M, Toulmay A, Reggiori F, Schneiter R (2011). Lipid droplets are functionally con- nected to the endoplasmic reticulum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Cell Sci 124, 2424-2437. |
| [36] | James CN, Horn PJ, Case CR, Gidda SK, Zhang DY, Mullen RT, Dyer JM, Anderson RGW, Chapman KD (2010). Disruption of the Arabidopsis CGI-58 homologue produces Chanarin-Dorfman-like lipid droplet accumula- tion in plants.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 17833-17838. |
| [37] | Jolivet P, Boulard C, Bellamy A, Larré C, Barre M, Rogniaux H, d’Andréa S, Chardot T, Nesi N (2009). Protein composition of oil bodies from mature Brassica napus seeds.Proteomics 9, 3268-3284. |
| [38] | Kelly AA, Quettier AL, Shaw E, Eastmond PJ (2011). Seed storage oil mobilization is important but not essential for germination or seedling establishment in Arabidopsis.Pla- nt Physiol 157, 866-875. |
| [39] | Krahmer N, Guo Y, Wilfling F, Hilger M, Lingrell S, Heger K, Newman HW, Schmidt-Supprian M, Vance DE, Mann M, Farese RV Jr, Walther TC (2011). Phosphatidylch- oline synthesis for lipid droplet expansion is mediated by localized activation of CTP: phosphocholine cytidylyltrans- ferase.Cell Metab 14, 504-515. |
| [40] | Kuerschner L, Moessinger C, Thiele C (2008). Imaging of lipid biosynthesis: how a neutral lipid enters lipid droplets.Traffic 9, 338-352. |
| [41] | Lévesque-Lemay M, Chabot D, Hubbard K, Chan JK, Miller S, Robert LS (2016). Tapetal oleosins play an essential role in tapetosome formation and protein relocation to the pollen coat.New Phytol 209, 691-704. |
| [42] | López-Ribera I, La Paz JL, Repiso C, García N, Miquel M, Hernández ML, Martínez-Rivas JM, Vicient CM (2014). The evolutionary conserved oil body associated protein OBAP1 participates in the regulation of oil body size.Plant Physiol 164, 1237-1249. |
| [43] | Miquel M, Trigui G, d’Andréa S, Kelemen Z, Baud S, Berger A, Deruyffelaere C, Trubuil A, Lepiniec L, Dubreucq B (2014). Specialization of oleosins in oil body dynamics during seed development in Arabidopsis seeds.Plant Physiol 164, 1866-1878. |
| [44] | Murphy DJ (2011). Plants, Biotechnology and Agriculture. Oxford: CABI Press. |
| [45] | Murphy DJ (2012). The dynamic roles of intracellular lipid droplets: from archaea to mammals.Protoplasma 249, 541-585. |
| [46] | Nalam VJ, Keeretaweep J, Sarowar S, Shah J (2012). Root-derived oxylipins promote green peach aphid performance on Arabidopsis foliage.Plant Cell 24, 1643-1653. |
| [47] | Park S, Gidda SK, James CN, Horn PJ, Khuu N, Seay DC, Keereetaweep J, Chapman KD, Mullen RT, Dyer JM (2013). The α/β hydrolase CGI-58 and peroxisomal trans- port protein PXA1 coregulate lipid homeostasis and signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 25, 1726-1739. |
| [48] | Partridge M, Murphy DJ (2009). Roles of a membrane- bound caleosin and putative peroxygenase in biotic and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol Bio- chem 47, 796-806. |
| [49] | Pasaribu B, Chung TY, Chen CS, Wang SL, Jiang PL, Tzen JTC (2014). Identification of caleosin and two oleosin isoforms in oil bodies of pine megagametophytes.Plant Physiol Biochem 82, 142-150. |
| [50] | Penfield S, Pinfield-Wells HM, Graham IA (2006). Storage reserve mobilisation and seedling establishment in Arabidopsis.Arabidopsis Book 4, e0100. |
| [51] | Peng Q, Hu Y, Wei R, Zhang Y, Guan CY, Ruan Y, Liu CL (2010). Simultaneous silencing of FAD2 and FAE1 genes affects both oleic acid and erucic acid contents in Brassica napus seeds.Plant Cell Rep 29, 317-325. |
| [52] | Ploegh HL (2007). A lipid-based model for the creation of an escape hatch from the endoplasmic reticulum.Nature 448, 435-438. |
| [53] | Porta H, Rocha-Sosa M (2002). Plant lipoxygenases. Phy- siological and molecular features.Plant Physiol 130, 15-21. |
| [54] | Poxleitner M, Rogers SW, Samuels AL, Browse J, Rogers JC (2006). A role for caleosin in degradation of oil-body storage lipid during seed germination.Plant J 47, 917-933. |
| [55] | Purkrtová Z, Chardot T, Froissard M (2015). N-terminus of seed caleosins is essential for lipid droplet sorting but not for lipid accumulation.Arch Biochem Biophys 579, 47-54. |
| [56] | Robenek H, Hofnagel O, Buers I, Robenek MJ, Troyer D, Severs NJ (2006). Adipophilin-enriched domains in the ER membrane are sites of lipid droplet biogenesis.J Cell Sci 119, 4215-4224. |
| [57] | Savage MJ, Goldberg DJ, Schacher S (1987). Absolute specificity for retrograde fast axonal transport displayed by lipid droplets originating in the axon of an identified Aplysia neuron in vitro.Brain Res 406, 215-223. |
| [58] | Shen Y, Liu MZ, Wang LL, Li ZW, Taylor DC, Li ZX, Zhang M (2016). Identification, duplication, evolution and expre- ssion analyses of caleosins in Brassica plants and Arabidopsis subspecies.Mol Genet Genomics 291, 971-988. |
| [59] | Shimada TL, Hara-Nishimura I (2010). Oil-body-membrane proteins and their physiological functions in plants.Biol Pharm Bull 33, 360-363. |
| [60] | Shimada TL, Shimada T, Takahashi H, Fukao Y, Hara- Nishimura I (2008). A novel role for oleosins in freezing tolerance of oilseeds in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J 55, 798-809. |
| [61] | Shimada TL, Takano Y, Shimada T, Fujiwara M, Fukao Y, Mori M, Okazaki Y, Saito K, Sasaki R, Aoki K, Hara- Nishimura I (2014). Leaf oil body functions as a subcellular factory for the production of a phytoalexin in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 164, 105-118. |
| [62] | Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Novak I, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Cuervo AM, Czaja MJ (2009). Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism.Nature 458, 1131-1135. |
| [63] | Stone SJ, Levin MC, Zhou P, Han JY, Walther TC, Farese RV Jr (2009). The endoplasmic reticulum enzyme DGAT2 is found in mitochondria-associated membranes and has a mitochondrial targeting signal that promotes its association with mitochondria.J Biol Chem 284, 5352-5361. |
| [64] | Szymanski KM, Binns D, Bartz R, Grishin NV, Li WP, Agarwal AK, Garg A, Anderson RGW, Goodman JM (2007). The lipodystrophy protein seipin is found at endoplasmic reticulum lipid droplet junctions and is important for droplet morphology.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 20890-20895. |
| [65] | Thazar-Poulot N, Miquel M, Fobis-Loisy I, Gaude T (2015). Peroxisome extensions deliver the Arabidopsis SDP1 lipase to oil bodies.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 4158-4163. |
| [66] | Tzen JTC, Cao YZ, Laurent P, Ratnayake C, Huang AHC (1993). Lipids, proteins, and structure of seed oil bodies from diverse species.Plant Physiol 101, 267-276. |
| [67] | Vermachova M, Purkrtova Z, Santrucek J, Jolivet P, Chardot T, Kodicek M (2011). New protein isoforms identified within Arabidopsis thaliana seed oil bodies combining chymotrypsin/trypsin digestion and peptide fragmen- tation analysis.Proteomics 11, 3430-3434. |
| [68] | Walther TC, Farese RV Jr (2012). Lipid droplets and cellular lipid metabolism.Annu Rev Biochem 81, 687-714. |
| [69] | Warakanont J, Tsai CH, Michel EJ, Murphy III GR, Hsueh PY, Roston RL, Sears BB, Benning C (2015). Chloro- plast lipid transfer processes in Chlamydomonas rein- hardtii involving a TRIGALACTOSYLDIA CYLGLYCEROL 2 (TGD2) orthologue.Plant J 84, 1005-1020. |
| [70] | Welte MA, Gross SP, Postner M, Block SM, Wieschaus EF (1998). Developmental regulation of vesicle transport in Drosophila embryos: forces and kinetics.Cell 92, 547-557. |
| [71] | Yamamoto K, Takahara K, Oyadomari S, Okada T, Sato T, Harada A, Mori K (2010). Induction of liver steatosis and lipid droplet formation in ATF6α-knockout mice burdened with pharmacological endoplasmic reticulum stress.Mol Biol Cell 21, 2975-2986. |
| [72] | Yang HY, Galea A, Sytnyk V, Crossley M (2012). Controlling the size of lipid droplets: lipid and protein factors.Curr Opin Cell Biol 24, 509-516. |
| [73] | Zehmer JK, Huang YG, Peng G, Pu J, Anderson RGW, Liu PS (2009). A role for lipid droplets in inter-membrane lipid traffic.Proteomics 9, 914-921. |
| [1] | 胡海涛, 武越, 杨玲. 植物NAD(P)+的生物合成及其生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 114-131. |
| [2] | 李艳艳, 齐艳华. 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [3] | 贺祯媚,李东明,齐艳华. 植物ABCB亚家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 688-698. |
| [4] | 魏铭,王鑫伟,陈博,宋程威,杜亮,肖建伟,林金星. 植物紫色酸性磷酸酶基因家族功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(1): 93-101. |
| [5] | 席红梅, 徐文忠, 麻密. 拟南芥双功能酶SAL1生物学功能的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(3): 377-386. |
| [6] | 俞乐, 刘拥海, 袁伟超, 周丽萍, 彭长连. 植物抗坏血酸积累及其分子机制的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(3): 396-410. |
| [7] | 刘林娅, 黄亚成, 黄小龙, 黄东益. 薯蓣植物块茎特异蛋白Dioscorin的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(2): 274-280. |
| [8] | 刘海娇, 杜立群, 林金星, 李瑞丽. 植物环核苷酸门控离子通道及其功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(6): 779-789. |
| [9] | 翟开恩, 潘伟槐, 叶晓帆, 潘建伟. 高等植物局部生长素合成的生物学功能及其调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(2): 149-158. |
| [10] | 李明, 李长生, 赵传志, 李爱芹, 王兴军. 植物SPL转录因子研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2013, 48(1): 107-116. |
| [11] | 王晓茹, 刘文哲. 黄连木果实中油体的发育[J]. 植物学报, 2011, 46(6): 665-674. |
| [12] | 刘润华;江文波;余迪求. 植物鞘脂的结构、代谢途径及其功能[J]. 植物学报, 2009, 44(05): 619-628. |
| [13] | 董劲松;石东乔;高建芹;李成磊;刘洁;戚存扣*;杨维才*. 甘蓝型油菜油体数量及面积之和与含油量的相关性[J]. 植物学报, 2009, 44(01): 79-85. |
| [14] | 程红焱 宋松泉. 种子的贮油细胞器——油体及其蛋白[J]. 植物学报, 2006, 23(4): 418-430. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
