

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 51-61.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22149 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22149
Special Issue: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuan Li, Yujie Chang, Lanfen Wang, Shumin Wang, Jing Wu*( )
)
Received:2022-07-12
Accepted:2023-02-09
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-02-10
Contact:
*E-mail: wujing@caas.cn
Yuan Li, Yujie Chang, Lanfen Wang, Shumin Wang, Jing Wu. Screening of Resistance Germplasm Resources and Genome-wide Association Study of Fusarium Wilt in Common Bean[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 51-61.
| Rating scale | System description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No symptom |
| 1 | <20% lesions or discoloration of hypocotyledonary axis |
| 3 | 20%-50% lesions or some discoloration of hypocotyledonary axis |
| 5 | 50%-100% lesions or heavy discoloration of hypocotyledonary axis |
| 7 | >100% lesions or severe discoloration of hypo- cotyledonary axis |
| 9 | Plants wilted and died |
Table 1 Disease grading standard of common bean fusarium wilt inoculated by hypocotyl double-hole injection
| Rating scale | System description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No symptom |
| 1 | <20% lesions or discoloration of hypocotyledonary axis |
| 3 | 20%-50% lesions or some discoloration of hypocotyledonary axis |
| 5 | 50%-100% lesions or heavy discoloration of hypocotyledonary axis |
| 7 | >100% lesions or severe discoloration of hypo- cotyledonary axis |
| 9 | Plants wilted and died |
| Mean | Max | Min | Standard deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 1.00 | 0.18 | 0.19 | -0.10 | -0.62 |
Table 2 Phenotype description of fusarium wilt resistance levels in natural populations of common bean
| Mean | Max | Min | Standard deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.65 | 1.00 | 0.18 | 0.19 | -0.10 | -0.62 |
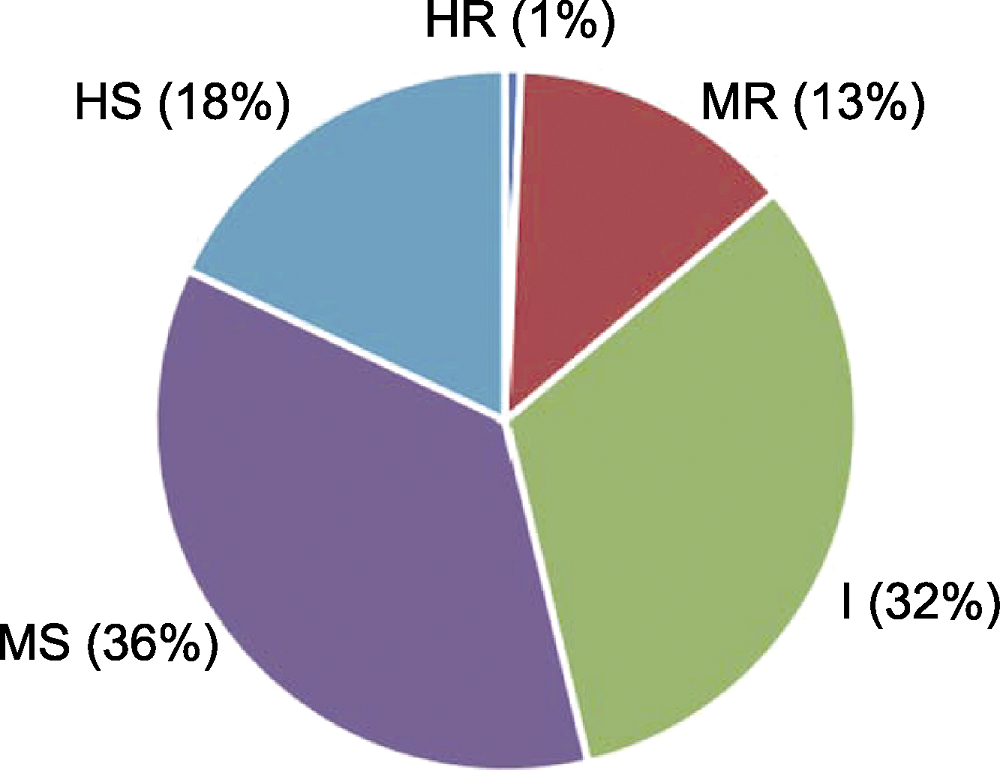
Figure 3 Distribution of common bean germplasm resources for resistance to fusarium wilt HR: Highly resistant; MR: Medium resistant; I: Intermediate; MS: Medium susceptible; HS: Highly susceptible
| Region | Chr. | Interval locationa | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2583702-2807552 | 2.18E-07 |
| 2 | 1 | 50017907-50231907 | 4.11E-06 |
| 3 | 2 | 26253984-26467984 | 5.72E-06 |
| 4 | 2 | 29642890-29856890 | 7.61E-06 |
| 5 | 6 | 26400983-26614983 | 8.82E-06 |
| 6 | 8 | 58863473-59077488 | 5.40E-06 |
| 7 | 11 | 46491343-46705343 | 6.48E-06 |
| 8 | 11 | 49598097-49814082 | 7.73E-06 |
Table 3 Loci related with common bean fusarium wilt by genome-wide association study
| Region | Chr. | Interval locationa | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2583702-2807552 | 2.18E-07 |
| 2 | 1 | 50017907-50231907 | 4.11E-06 |
| 3 | 2 | 26253984-26467984 | 5.72E-06 |
| 4 | 2 | 29642890-29856890 | 7.61E-06 |
| 5 | 6 | 26400983-26614983 | 8.82E-06 |
| 6 | 8 | 58863473-59077488 | 5.40E-06 |
| 7 | 11 | 46491343-46705343 | 6.48E-06 |
| 8 | 11 | 49598097-49814082 | 7.73E-06 |
| Gene ID | Chr. | Start base-end basea (bp) | Predicted function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phvul.001G240400 | 1 | 50026833-50031313 | RNI-like superfamily protein |
| Phvul.001G241500 | 1 | 50126351-50130393 | Transmembrane amino acid transporter family protein |
| Phvul.001G242200 | 1 | 50180058-50185697 | Cytochrome P450 superfamily protein |
| Phvul.002G133400 | 2 | 26437427-26440702 | NB-ARC domain-containing disease resistance protein |
| Phvul.002G133600 | 2 | 26447784-26451915 | NB-ARC domain-containing disease resistance protein |
| Phvul.002G154800 | 2 | 29644994-29651836 | PAS domain-containing protein tyrosine kinase family protein |
| Phvul.006G150900 | 6 | 26403392-26405713 | Protein kinase superfamily protein |
| Phvul.008G285400 | 8 | 59055451-59060614 | Heat shock protein 89.1 |
| Phvul.011G212100 | 11 | 49695779-49697294 | Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) family protein |
Table 4 Candidate genes and annotation
| Gene ID | Chr. | Start base-end basea (bp) | Predicted function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phvul.001G240400 | 1 | 50026833-50031313 | RNI-like superfamily protein |
| Phvul.001G241500 | 1 | 50126351-50130393 | Transmembrane amino acid transporter family protein |
| Phvul.001G242200 | 1 | 50180058-50185697 | Cytochrome P450 superfamily protein |
| Phvul.002G133400 | 2 | 26437427-26440702 | NB-ARC domain-containing disease resistance protein |
| Phvul.002G133600 | 2 | 26447784-26451915 | NB-ARC domain-containing disease resistance protein |
| Phvul.002G154800 | 2 | 29644994-29651836 | PAS domain-containing protein tyrosine kinase family protein |
| Phvul.006G150900 | 6 | 26403392-26405713 | Protein kinase superfamily protein |
| Phvul.008G285400 | 8 | 59055451-59060614 | Heat shock protein 89.1 |
| Phvul.011G212100 | 11 | 49695779-49697294 | Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) family protein |
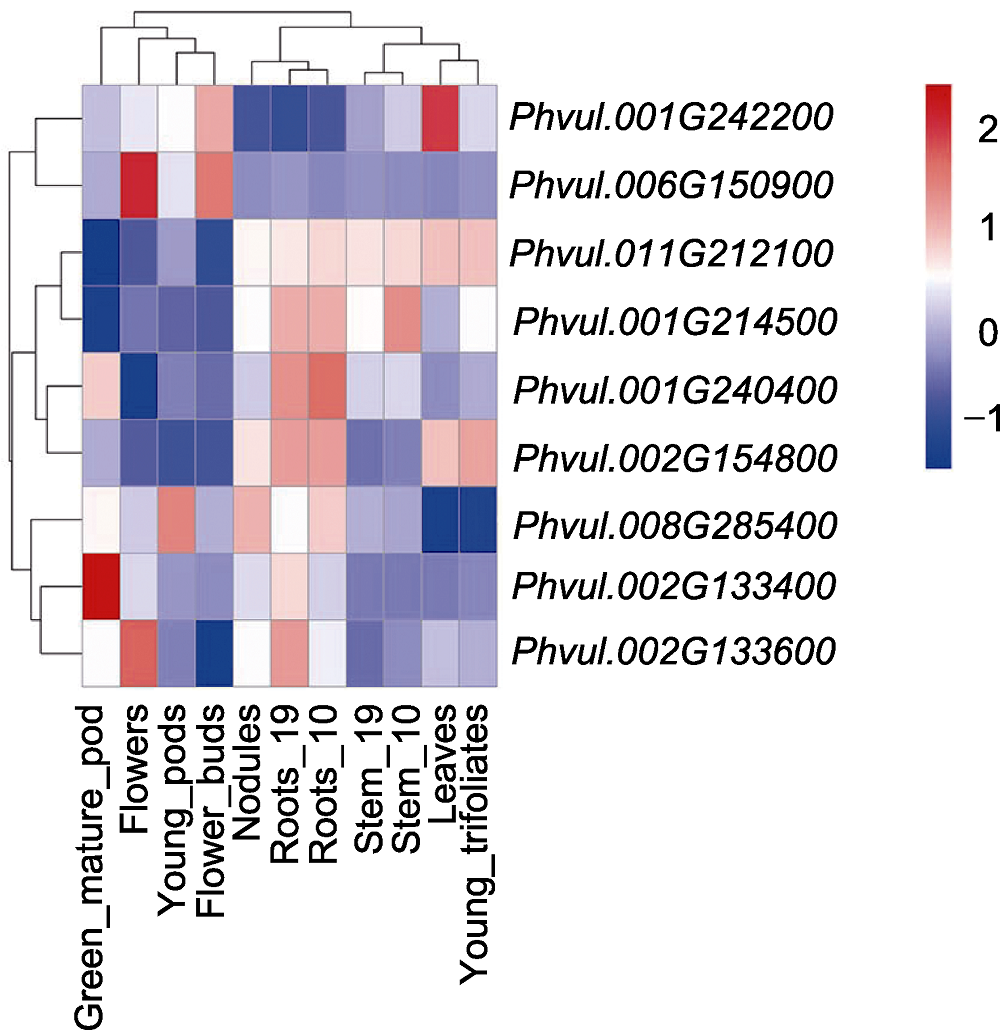
Figure 5 Expression patterns of 9 resistance candidate ge- nes in common bean different tissues Stem_10 is to take samples from the stem 10 days after planting, Stem_19 is to take samples from the stem 19 days after planting, Roots_10 is to take samples from the root 10 days after planting, Roots_19 is to take samples from the root 19 days after planting. Data is from https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/info/Pvulgaris_v2_1.
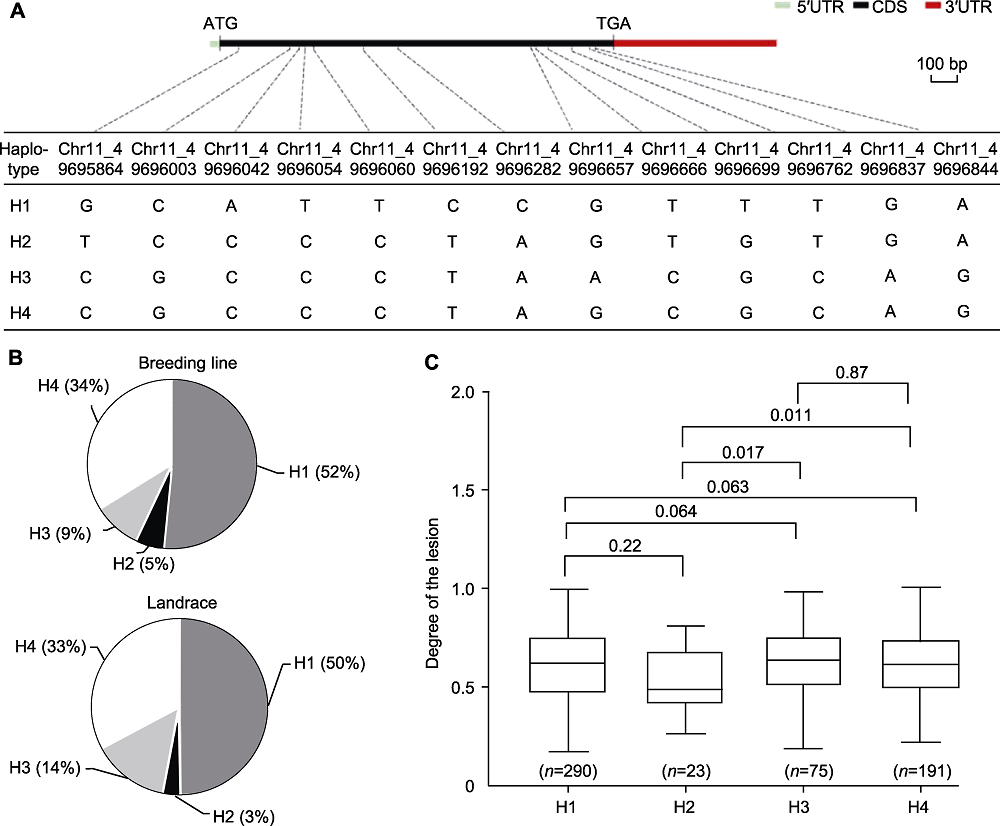
Figure 6 Haplotype analysis of Phvul.001G212100 (A) The genome structure and haplotypes of the Phvul.001G212100 (the linear gene structure showing 5'UTR (cyan rectangle), CDS region (black rectangle), 3'UTR (red rectangle); the black dotted line indicate the position of the SNP in the gene); (B) Occurrence frequencies of 4 haplotypes in breeding lines and landraces; (C) Significant differences in the degree of lesions between haplotypes (the numbers above the boxplot are P-values, P<0.05 indicate significant differences. n represent the number of germplasm recourses. The significance was tested with two-tailed T-tests). CDS: Coding sequence; UTR: Untranslated region
| [1] | 程须珍 (2016). 普通菜豆生产技术. 北京: 北京教育出版社. pp. 83-84. |
| [2] | 薛仁风 (2012). 普通菜豆镰孢菌枯萎病抗病种质鉴定及抗病机理研究. 博士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 37-40. |
| [3] | 薛仁风, 丰明, 赵阳, 陈剑, 李韬, 葛维德 (2019). 普通菜豆生长素调节蛋白基因PvARP1的克隆及表达分析. 河南农业科学 48(9), 82-89. |
| [4] | 薛仁风, 朱振东, 王晓鸣, 王兰芬, 武小菲, 王述民 (2012). 普通菜豆镰孢菌枯萎病抗病相关基因PvCaM1的克隆及表达. 作物学报 38, 606-613. |
| [5] |
Alves-Santos FM, Cordeiro-Rodrigues L, Sayagués JM, Martín-Domínguez R, García-Benavides P, Crespo MC, Díaz-Mínguez JM, Eslava AP (2002). Pathogenicity and race characterization of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli isolates from Spain and Greece. Plant Pathol 51, 605-611.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Bancoş S, Nomura T, Sato T, Molnár G, Bishop GJ, Koncz C, Yokota T, Nagy F, Szekeres M (2002). Regulation of transcript levels of the Arabidopsis cytochrome p450 genes involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 130, 504-513.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Batista RO, Silva LC, Moura LM, Souza MH, Carneiro PCS, Filho JLSC, de Souza Carneiro JE (2017). Inheritance of resistance to fusarium wilt in common bean. Euphytica 213, 133.
DOI |
| [8] |
Belkhadir Y, Subramaniam R, Dangl JL (2004). Plant disease resistance protein signaling: NBS-LRR proteins and their partners. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7, 391-399.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Bent AF, Kunkel BN, Dahlbeck D, Brown KL, Schmidt R, Giraudat J, Leung J, Staskawicz BJ (1994). RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265, 1856-1860.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Bolwell GP, Bozak K, Zimmerlin A (1994). Plant cytochrome P450. Phytochemistry 37, 1491-1506.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Boyes DC, Nam J, Dangl JL (1998). The Arabidopsis thaliana RPM1 disease resistance gene product is a peripheral plasma membrane protein that is degraded coincident with the hypersensitive response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 15849-15854.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Brick MA, Ogg JB, Schwartz HF, Byrne PF, Kelly JD (2006). Resistance to multiple races of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli in common bean. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 47, 131-132. |
| [13] |
Chen YC, Wong CL, Muzzi F, Vlaardingerbroek I, Kidd BN, Schenk PM (2014). Root defense analysis against Fusarium oxysporum reveals new regulators to confer resistance. Sci Rep 4, 5584.
DOI |
| [14] |
Cross H, Brick MA, Schwartz HF, Panella LW, Byrne PF (2000). Inheritance of resistance to Fusarium wilt in two common bean races. Crop Sci 40, 954-958.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Deng Y, Chen H, Zhang C, Cai T, Zhang B, Zhou S, Fountain JC, Pan RL, Guo B, Zhuang WJ (2018). Evolution and characterisation of the AhRAF4 NB-ARC gene family induced by Aspergillus flavus inoculation and abiotic stresses in peanut. Plant Biol 20, 737-750.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Fall AL, Byrne PF, Jung G, Coyne DP, Brick MA, Schwartz HF (2001). Detection and mapping of a major locus for Fusarium wilt resistance in common bean. Crop Sci 41, 1494-1498.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Gao ZY, Chen YF, Randlett MD, Zhao XC, Findell JL, Kieber JJ, Schaller GE (2003). Localization of the Raf-like kinase CTR1 to the endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis through participation in ethylene receptor signaling complexes. J Biol Chem 278, 34725-34732.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Grant MR, Godiard L, Straube E, Ashfield T, Lewald J, Sattler A, Innes RW, Dangl JL (1995). Structure of the Arabidopsis RPM1 gene enabling dual specificity disease resistance. Science 269, 843-846.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Harter LL (1929). A Fusarium disease of beans. Phytopathology 19, 82. |
| [20] |
Huang Y, Li H, Hutchison CE, Laskey J, Kieber JJ (2003). Biochemical and functional analysis of CTR1, a protein kinase that negatively regulates ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J 33, 221-233.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Kieber JJ, Rothenberg M, Roman G, Feldmann KA, Ecker JR (1993). CTR1, a negative regulator of the ethylene response pathway in Arabidopsis, encodes a member of the Raf family of protein kinases. Cell 72, 427-441.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Leitão ST, Malosetti M, Song QJ, van Eeuwijk F, Rubiales D, Vaz Patto MC (2020). Natural variation in portuguese common bean germplasm reveals new sources of resistance against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli and resistance-associated candidate genes. Phytopath-ology 110, 633-647. |
| [23] |
Li YX, Wei KF (2020). Comparative functional genomics analysis of cytochrome P450 gene superfamily in wheat and maize. BMC Plant Biol 20, 93.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Manzo D, Ferriello F, Puopolo G, Zoina A, D'Esposito D, Tardella L, Ferrarini A, Ercolano MR (2016). Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici induces distinct transcriptome reprogramming in resistant and susceptible isogenic tomato lines. BMC Plant Biol 16, 53.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Martin GB, Bogdanove AJ, Sessa G (2003). Understanding the functions of plant disease resistance proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54, 23-61. |
| [26] |
McCarthy RL, Zhong RQ, Ye ZH (2009). MYB83 is a direct target of SND1 and acts redundantly with MYB46 in the regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 1950-1964.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Mindrinos M, Katagiri F, Yu GL, Ausubel FM (1994). The A. thaliana disease resistance gene RPS2 encodes a protein containing a nucleotide-binding site and leucine- rich repeats. Cell 78, 1089-1099.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, van Breusegem F (2004). Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9, 490-498.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Nakashita H, Yasuda M, Nitta T, Asami T, Fujioka S, Arai Y, Sekimata K, Takatsuto S, Yamaguchi I, Yoshida S (2003). Brassinosteroid functions in a broad range of disease resistance in tobacco and rice. Plant J 33, 887-898.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Nakayama N, Takemae A, Shoun H (1996). Cytochrome P450foxy, a catalytically self-sufficient fatty acid hydroxylase of the fungus Fusarium oxysporum. J Biochem 119, 435-440.
PMID |
| [31] |
Nie YB, Ji WQ (2019). Cloning and characterization of disease resistance protein RPM1 genes against powdery mildew in wheat line N9134. Cereal Res Commun 47, 473-483.
DOI |
| [32] |
Ribeiro RLD, Hagedorn DJ (1979). Inheritance and nature of resistance in beans to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli. Phytopathology 69, 859-861.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Salgado MO, Schwartz HF, Brick MA (1995). Inheritance of resistance to a Colorado race of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli in common beans. Plant Dis 79, 279-281.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Schmutz J, McClean PE, Mamidi S, Wu GA, Cannon SB, Grimwood J, Jenkins J, Shu SQ, Song QJ, Chavarro C, Torres-Torres M, Geffroy V, Moghaddam SM, Gao D, Abernathy B, Barry K, Blair M, Brick MA, Chovatia M, Gepts P, Goodstein DM, Gonzales M, Hellsten U, Hyten DL, Jia GF, Kelly JD, Kudrna D, Lee R, Richard MMS, Miklas PN, Osorno JM, Rodrigues J, Thareau V, Urrea CA, Wang M, Yu Y, Zhang M, Wing RA, Cregan PB, Rokhsar DS, Jackson SA (2014). A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat Genet 46, 707-713.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Sun JH, Huang GZ, Fan FG, Wang SF, Zhang YY, Han YF, Zou YM, Lu DP (2017). Comparative study of Arabidopsis PBS1 and a wheat PBS1 homolog helps understand the mechanism of PBS1 functioning in innate immunity. Sci Rep 7, 5487.
DOI |
| [36] |
Swiderski MR, Innes RW (2001). The Arabidopsis PBS1 resistance gene encodes a member of a novel protein kinase subfamily. Plant J 26, 101-112.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Wang AJ, Shu XY, Jing X, Jiao CZ, Chen L, Zhang JF, Ma L, Jiang YQ, Yamamoto N, Li SC, Deng QM, Wang SQ, Zhu J, Liang YY, Zou T, Liu HN, Wang LZ, Huang YB, Li P, Zheng AP (2021). Identification of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genes involved in sheath blight resistance via a genome- wide association study. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 1553-1566.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B (1994). The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: similarity to toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 78, 1101-1115.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Woo SL, Zoina A, Del Sorbo G, Lorito M, Nanni B, Scala F, Noviello C (1996). Characterization of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli by pathogenic races, VCGs, RFLPs, and RAPD. Phytopathology 86, 966-973.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wu J, Wang LF, Fu JJ, Chen JB, Wei SH, Zhang SL, Zhang J, Tang YS, Chen ML, Zhu JF, Lei L, Geng QH, Liu Cl, Wu L, Li XM, Wang Xl, Wang Q, Wang Zl, Xing Sl, Zhang HK, Blair MW, Wang SM (2020). Resequencing of 683 common bean genotypes identifies yield component trait associations across a north-south cline. Nat Genet 52, 118-125.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Xue RF, Wu J, Wang LF, Blair MW, Wang XM, Ge WD, Zhu Z, Wang SM (2014). Salicylic acid enhances resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli in common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Plant Growth Regul 33, 470-476.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Xue RF, Wu J, Zhu ZD, Wang LF, Wang XM, Wang SM, Blair MW (2015). Differentially expressed genes in resistant and susceptible common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes in response to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli. PLoS One 10, e0127698. |
| [43] |
Xue RF, Wu XB, Wang YJ, Zhuang Y, Chen J, Wu J, Ge WD, Wang LF, Wang SM, Blair MW (2017). Hairy root transgene expression analysis of a secretory peroxidase (PvPOX1) from common bean infected by Fusarium wilt. Plant Sci 260, 1-7.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Yang DL, Yang YN, He ZH (2013). Roles of plant hormones and their interplay in rice immunity. Mol Plant 6, 675-685.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Yuan SK, Zhou MG (2005). A major gene for resistance to carbendazim, in field isolates of Gibberella zeae. Can J Plant Pathol 27, 58-63.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Zhong RQ, Ye ZH (2012). MYB46 and MYB83 bind to the SMRE sites and directly activate a suite of transcription factors and secondary wall biosynthetic genes. Plant Cell Physiol 53, 368-380.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | Bangbang Wu, Yuqiong Hao, Shubin Yang, Yuxi Huang, Panfeng Guan, Xingwei Zheng, Jiajia Zhao, Ling Qiao, Xiaohua Li, Weizhong Liu, Jun Zheng. Evaluation and Genetic Variation of Grain Lutein Contents in Common Wheat From Shanxi [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 535-547. |
| [2] | Qi Zhang, Wenjing Zhang, Xiankai Yuan, Ming Li, Qiang Zhao, Yanli Du, Jidao Du. The Regulatory Mechanism of Melatonin on Nucleic Acid Repairing of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) at the Sprout Stage Under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 108-121. |
| [3] | Xiaoming Li, Lanfen Wang, Yongsheng Tang, Yujie Chang, Juxiang Zhang, Shumin Wang, Jing Wu. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Resistance to Acanthoscelides obtectus in Common Bean [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 77-89. |
| [4] | Wei Xuan, Guohua Xu. Genomic Basis of Rice Adaptation to Soil Nitrogen Status [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 1-5. |
| [5] | Yuhui Zhao, Xiuxiu Li, Zhuo Chen, Hongwei Lu, Yucheng Liu, Zhifang Zhang, Chengzhi Liang. An Overview of Genome-wide Association Studies in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(6): 715-732. |
| [6] | Hongru Wang, Chengcai Chu. Underlying Mechanism of Heterosis Unveiled by -Omics [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(1): 4-9. |
| [7] | Xinghai Yang, Baoxuan Nong, Xiuzhong Xia, Zongqiong Zhang, Yu Zeng, Kaiqiang Liu, Guofu Deng, Danting Li. Genome-wide Association Study of Genes Related to Waxiness in Oryza sativa [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2016, 51(6): 737-742. |
| [8] | Mei Yan, Xinyou Zhang, Suoyi Han, Bingyan Huang, Wenzhao Dong, Hua Liu, Ziqi Sun. Genome-wide Association Study of Agronomic and Yield Traits in a Worldwide Collection of Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) Germplasm [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(4): 460-472. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||