

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 77-89.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22138 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22138
Special Issue: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoming Li1, Lanfen Wang1, Yongsheng Tang2, Yujie Chang1, Juxiang Zhang2, Shumin Wang1, Jing Wu1,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-30
Accepted:2022-09-19
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: wujing@caas.cn
About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
Xiaoming Li, Lanfen Wang, Yongsheng Tang, Yujie Chang, Juxiang Zhang, Shumin Wang, Jing Wu. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Resistance to Acanthoscelides obtectus in Common Bean[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 77-89.
| Gene pool | Outside of Chinaa | Inside of Chinab | All | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | L | BL | L | ||
| Andean | 33 | 16 | 27 | 206 | 282 |
| Mesoamerican | 64 | 11 | 20 | 248 | 343 |
| All | 97 | 27 | 47 | 454 | 625 |
Table 1 Origin and classification of 625 common bean germplasm resources
| Gene pool | Outside of Chinaa | Inside of Chinab | All | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | L | BL | L | ||
| Andean | 33 | 16 | 27 | 206 | 282 |
| Mesoamerican | 64 | 11 | 20 | 248 | 343 |
| All | 97 | 27 | 47 | 454 | 625 |
| Rating scale | PDS (%) | Resistant evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ≤10 | Highly resistance (HR) |
| 3 | 10<PDS≤35 | Resistance (R) |
| 5 | 35<PDS≤65 | Medium resistance (MR) |
| 7 | 65<PDS≤90 | Susceptible (S) |
| 9 | >90 | Highly susceptible (HS) |
Table 2 Evaluation standard of resistance grade of common bean germplasm resources
| Rating scale | PDS (%) | Resistant evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ≤10 | Highly resistance (HR) |
| 3 | 10<PDS≤35 | Resistance (R) |
| 5 | 35<PDS≤65 | Medium resistance (MR) |
| 7 | 65<PDS≤90 | Susceptible (S) |
| 9 | >90 | Highly susceptible (HS) |
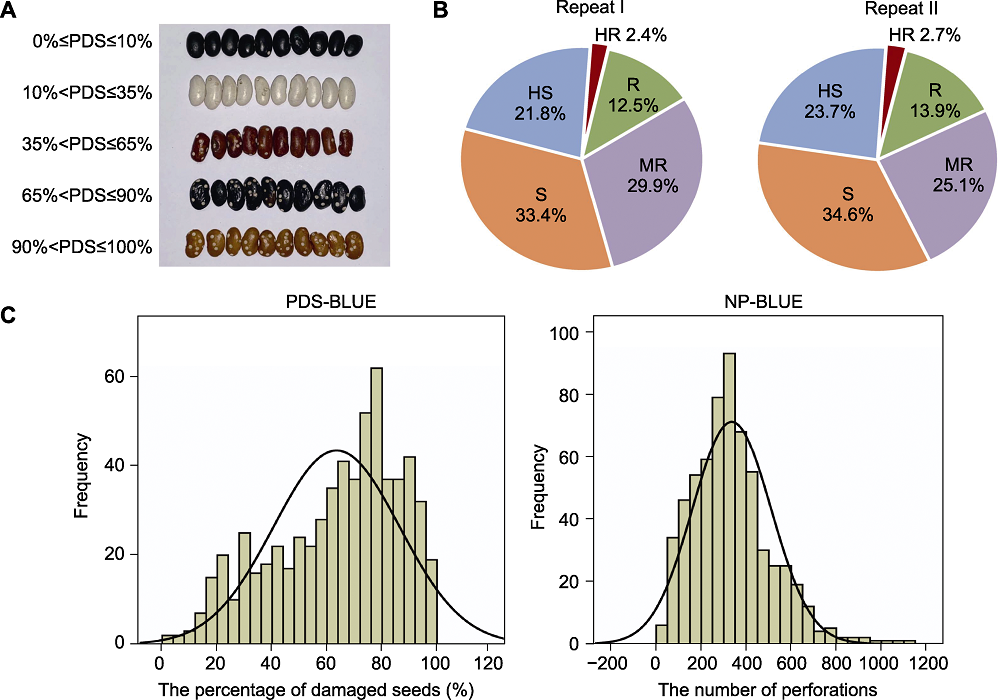
Figure 1 Results of two repeated identification of the resistance of common bean germplasm resources to Acanthoscelides obtectus (A) Infestation by A. obtectus of common beans with different resistance levels; (B) Results of bruchid resistance in two repeated identifications; (C) Distribution histogram of the best linear unbiased estimators (BLUE) values of PDS and NP in 625 common beans of two repeated identifications. Repeat I: The first repeated identification; Repeat II: The second repeated identification; PDS: The percentage of damaged seeds; NP: The number of perforations
| Traits | Min | Median | Max | Mean | SD (%) | Kurtosis | Skewness | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS I (%) | 1.00 | 67.50 | 100 | 64.14 | 25.65 | -0.71 | -0.45 | 40.00 |
| NP I | 3.00 | 263.50 | 1224 | 294.12 | 181.20 | 1.48 | 0.96 | 61.61 |
| PDS II (%) | 0.00 | 72.00 | 100 | 66.44 | 27.17 | -0.76 | -0.62 | 40.89 |
| NP II | 0.00 | 329.00 | 1816 | 376.20 | 254.91 | 3.12 | 1.37 | 67.76 |
| PDS-BLUE (%) | 4.00 | 70.00 | 100 | 65.44 | 0.23 | -0.63 | -0.58 | 35.07 |
| NP-BLUE | 0.56 | 318.00 | 1126 | 335.55 | 174.94 | 1.56 | 0.92 | 52.02 |
Table 3 Phenotypic characteristics of PDS and NP in 625 common beans
| Traits | Min | Median | Max | Mean | SD (%) | Kurtosis | Skewness | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS I (%) | 1.00 | 67.50 | 100 | 64.14 | 25.65 | -0.71 | -0.45 | 40.00 |
| NP I | 3.00 | 263.50 | 1224 | 294.12 | 181.20 | 1.48 | 0.96 | 61.61 |
| PDS II (%) | 0.00 | 72.00 | 100 | 66.44 | 27.17 | -0.76 | -0.62 | 40.89 |
| NP II | 0.00 | 329.00 | 1816 | 376.20 | 254.91 | 3.12 | 1.37 | 67.76 |
| PDS-BLUE (%) | 4.00 | 70.00 | 100 | 65.44 | 0.23 | -0.63 | -0.58 | 35.07 |
| NP-BLUE | 0.56 | 318.00 | 1126 | 335.55 | 174.94 | 1.56 | 0.92 | 52.02 |
| Accession No. | Origin | 100 seeds weight (g) | Repeat I | Repeat II | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS (%) | NP | PDS (%) | NP | |||
| Longyundou7 | China-Heilongjiang | 17.29 | 4 | 21 | 4 | 11 |
| I2K03033 | USA | 17.34 | 10 | 30 | 6 | 24 |
Table 4 Two germplasms of common beans with stable high resistance in two repeated identifications
| Accession No. | Origin | 100 seeds weight (g) | Repeat I | Repeat II | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS (%) | NP | PDS (%) | NP | |||
| Longyundou7 | China-Heilongjiang | 17.29 | 4 | 21 | 4 | 11 |
| I2K03033 | USA | 17.34 | 10 | 30 | 6 | 24 |
| Traits | Min | Median | Max | Mean | SD (%) | Kurtosis | Skewness | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW I (g) | 10.80 | 34.21 | 80.40 | 34.95 | 12.93 | -0.57 | 0.36 | 37.00 |
| SW II (g) | 7.08 | 31.62 | 70.23 | 33.18 | 12.35 | -0.44 | 0.42 | 37.22 |
| SL I (mm) | 6.30 | 12.20 | 17.80 | 12.30 | 2.51 | -1.01 | 0.05 | 20.40 |
| SL II (mm) | 6.25 | 13.89 | 15.25 | 14.94 | 3.02 | -0.93 | -0.06 | 20.19 |
| SWI I (mm) | 4.20 | 7.10 | 15.60 | 7.11 | 1.13 | 9.79 | 1.59 | 15.91 |
| SWI II (mm) | 4.88 | 8.70 | 13.50 | 8.66 | 1.40 | -0.25 | 0.19 | 16.20 |
| SH I (mm) | 3.80 | 5.50 | 8.50 | 5.62 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 15.03 |
| SH II (mm) | 3.70 | 5.40 | 8.80 | 5.49 | 0.82 | 0.58 | 0.74 | 14.90 |
Table 5 Characteristics of seeds size in 625 common beans
| Traits | Min | Median | Max | Mean | SD (%) | Kurtosis | Skewness | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW I (g) | 10.80 | 34.21 | 80.40 | 34.95 | 12.93 | -0.57 | 0.36 | 37.00 |
| SW II (g) | 7.08 | 31.62 | 70.23 | 33.18 | 12.35 | -0.44 | 0.42 | 37.22 |
| SL I (mm) | 6.30 | 12.20 | 17.80 | 12.30 | 2.51 | -1.01 | 0.05 | 20.40 |
| SL II (mm) | 6.25 | 13.89 | 15.25 | 14.94 | 3.02 | -0.93 | -0.06 | 20.19 |
| SWI I (mm) | 4.20 | 7.10 | 15.60 | 7.11 | 1.13 | 9.79 | 1.59 | 15.91 |
| SWI II (mm) | 4.88 | 8.70 | 13.50 | 8.66 | 1.40 | -0.25 | 0.19 | 16.20 |
| SH I (mm) | 3.80 | 5.50 | 8.50 | 5.62 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 15.03 |
| SH II (mm) | 3.70 | 5.40 | 8.80 | 5.49 | 0.82 | 0.58 | 0.74 | 14.90 |
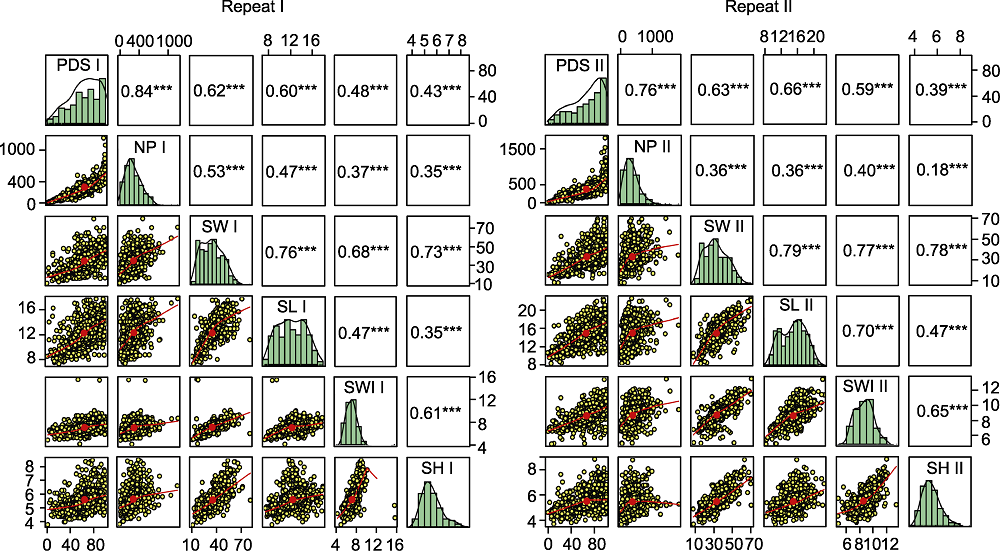
Figure 2 Correlation analysis for seeds size and bruchid resistance of germplasm resources in two repeated identifications PDS I, NP I, PDS II and NP II see Table 3. SW I, SW II, SL I, SL II, SWI I, SWI II, SH I and SH II see Table 5. *** P<0.001

Figure 4 Manhattan plot of PDS and NP by genome-wide association study (A) Manhattan plot (left) and Q-Q plot (right) of PDS-BLUE by mixed linear model (MLM); (B) Manhattan plot (left) and Q-Q plot (right) of NP-BLUE by the MLM. The abscissa is the chromosome, and the ordinate is the LOD effect value. The black dotted line is the threshold value (-Log10 p=6), and the points exceeding the threshold are the significant association sites, highlighting in red. PDS and NP see Figure 1.
| Traits | Locus | Peak SNP marker | Chromosome | Position (bp) | p-value | R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS | Loc_1 | Pv01_43986475 | Pv01 | 43986475 | 1E-07 | 5.24 |
| Loc_2 | Pv01_49901915 | Pv01 | 49901915 | 8.15E-07 | 4.54 | |
| Loc_3 | Pv03_1235524 | Pv03 | 1235524 | 2.25E-07 | 4.97 | |
| Loc_4 | Pv03_6664019 | Pv03 | 6664019 | 4.46E-07 | 4.74 | |
| Loc_5 | Pv03_11569042 | Pv03 | 11569042 | 2.19E-07 | 4.98 | |
| Loc_6 | Pv03_37792879 | Pv03 | 37792879 | 5.51E-07 | 4.67 | |
| Loc_7 | Pv05_522813 | Pv05 | 522813 | 3.89E-07 | 4.79 | |
| Loc_8 | Pv05_5075510 | Pv05 | 5075510 | 3.54E-07 | 4.82 | |
| Loc_9 | Pv05_22022919 | Pv05 | 22022919 | 3.89E-08 | 5.56 | |
| Loc_10 | Pv06_19260606 | Pv06 | 19260606 | 7.22E-07 | 4.58 | |
| Loc_11 | Pv07_386049 | Pv07 | 386049 | 6.01E-07 | 4.64 | |
| Loc_12 | Pv08_13992928 | Pv08 | 13992928 | 6.42E-07 | 4.62 | |
| Loc_13 | Pv08_43139505 | Pv08 | 43139505 | 5.06E-07 | 4.70 | |
| Loc_14 | Pv10_9574825 | Pv10 | 9574825 | 2.3E-07 | 4.96 | |
| Loc_15 | Pv11_11777960 | Pv11 | 11777960 | 2.62E-07 | 4.92 | |
| NP | Loc_16 | Pv02_36436725 | Pv02 | 36436725 | 5.26E-07 | 4.74 |
| Loc_17 | Pv03_23935240 | Pv03 | 23935240 | 5.31E-07 | 4.74 | |
| Loc_18 | Pv04_9609212 | Pv04 | 9609212 | 2.01E-07 | 5.07 | |
| Loc_19 | Pv04_10133957 | Pv04 | 10133957 | 5.13E-07 | 4.75 | |
| Loc_20 | Pv04_44834996 | Pv04 | 44834996 | 7.56E-07 | 4.62 | |
| Loc_21 | Pv10_8170537 | Pv10 | 8170537 | 6.45E-07 | 4.68 | |
| Loc_22 | Pv11_13013375 | Pv11 | 13013375 | 2.37E-07 | 5.01 | |
| Loc_23 | Pv11_19511385 | Pv11 | 19511385 | 7.45E-07 | 4.63 |
Table 6 All loci related with bruchid resistance detected by genome-wide association study (GWAS)
| Traits | Locus | Peak SNP marker | Chromosome | Position (bp) | p-value | R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS | Loc_1 | Pv01_43986475 | Pv01 | 43986475 | 1E-07 | 5.24 |
| Loc_2 | Pv01_49901915 | Pv01 | 49901915 | 8.15E-07 | 4.54 | |
| Loc_3 | Pv03_1235524 | Pv03 | 1235524 | 2.25E-07 | 4.97 | |
| Loc_4 | Pv03_6664019 | Pv03 | 6664019 | 4.46E-07 | 4.74 | |
| Loc_5 | Pv03_11569042 | Pv03 | 11569042 | 2.19E-07 | 4.98 | |
| Loc_6 | Pv03_37792879 | Pv03 | 37792879 | 5.51E-07 | 4.67 | |
| Loc_7 | Pv05_522813 | Pv05 | 522813 | 3.89E-07 | 4.79 | |
| Loc_8 | Pv05_5075510 | Pv05 | 5075510 | 3.54E-07 | 4.82 | |
| Loc_9 | Pv05_22022919 | Pv05 | 22022919 | 3.89E-08 | 5.56 | |
| Loc_10 | Pv06_19260606 | Pv06 | 19260606 | 7.22E-07 | 4.58 | |
| Loc_11 | Pv07_386049 | Pv07 | 386049 | 6.01E-07 | 4.64 | |
| Loc_12 | Pv08_13992928 | Pv08 | 13992928 | 6.42E-07 | 4.62 | |
| Loc_13 | Pv08_43139505 | Pv08 | 43139505 | 5.06E-07 | 4.70 | |
| Loc_14 | Pv10_9574825 | Pv10 | 9574825 | 2.3E-07 | 4.96 | |
| Loc_15 | Pv11_11777960 | Pv11 | 11777960 | 2.62E-07 | 4.92 | |
| NP | Loc_16 | Pv02_36436725 | Pv02 | 36436725 | 5.26E-07 | 4.74 |
| Loc_17 | Pv03_23935240 | Pv03 | 23935240 | 5.31E-07 | 4.74 | |
| Loc_18 | Pv04_9609212 | Pv04 | 9609212 | 2.01E-07 | 5.07 | |
| Loc_19 | Pv04_10133957 | Pv04 | 10133957 | 5.13E-07 | 4.75 | |
| Loc_20 | Pv04_44834996 | Pv04 | 44834996 | 7.56E-07 | 4.62 | |
| Loc_21 | Pv10_8170537 | Pv10 | 8170537 | 6.45E-07 | 4.68 | |
| Loc_22 | Pv11_13013375 | Pv11 | 13013375 | 2.37E-07 | 5.01 | |
| Loc_23 | Pv11_19511385 | Pv11 | 19511385 | 7.45E-07 | 4.63 |
| Traits | Gene | Chromosome | Locus | Gene annotation or coding protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS | Phvul.001G239200 | Pv01 | Loc_2 | Concanavalin A-like lectin family protein |
| Phvul.003G014200 | Pv03 | Loc_3 | Hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein family protein | |
| Phvul.003G169100 | Pv03 | Loc_6 | Bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein | |
| Phvul.005G005800 | Pv05 | Loc_7 | WRKY DNA-binding protein 2 | |
| Phvul.005G046000 | Pv05 | Loc_8 | Peroxidase superfamily protein | |
| Phvul.006G073200 | Pv06 | Loc_10 | Hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein family protein | |
| Phvul.008G113100 | Pv08 | Loc_12 | Kunitz family trypsin and protease inhibitor protein | |
| Phvul.008G113900 | Pv08 | Bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein | ||
| Phvul.010G057000 | Pv10 | Loc_14 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | |
| Phvul.010G057100 | Pv10 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | ||
| Phvul.010G057300 | Pv10 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | ||
| Phvul.010G057500 | Pv10 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | ||
| Phvul.010G057900 | Pv10 | WRKY DNA-binding protein 70 | ||
| NP | Phvul.002G205700 | Pv02 | Loc_16 | Defensin-like (DEFL) family protein |
| Phvul.002G205900 | Pv02 | Defensin-like (DEFL) family protein | ||
| Phvul.003G099300 | Pv03 | Loc_17 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | |
| Phvul.004G067300 | Pv04 | Loc_18 | Sterol | |
| Phvul.004G068800 | Pv04 | Loc_19 | Bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein | |
| Phvul.011G108700 | Pv11 | Loc_22 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | |
| Phvul.011G119200 | Pv11 | Loc_23 | Concanavalin A-like lectin protein kinase family protein |
Table 7 Information of candidate genes by screening
| Traits | Gene | Chromosome | Locus | Gene annotation or coding protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS | Phvul.001G239200 | Pv01 | Loc_2 | Concanavalin A-like lectin family protein |
| Phvul.003G014200 | Pv03 | Loc_3 | Hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein family protein | |
| Phvul.003G169100 | Pv03 | Loc_6 | Bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein | |
| Phvul.005G005800 | Pv05 | Loc_7 | WRKY DNA-binding protein 2 | |
| Phvul.005G046000 | Pv05 | Loc_8 | Peroxidase superfamily protein | |
| Phvul.006G073200 | Pv06 | Loc_10 | Hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein family protein | |
| Phvul.008G113100 | Pv08 | Loc_12 | Kunitz family trypsin and protease inhibitor protein | |
| Phvul.008G113900 | Pv08 | Bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein | ||
| Phvul.010G057000 | Pv10 | Loc_14 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | |
| Phvul.010G057100 | Pv10 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | ||
| Phvul.010G057300 | Pv10 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | ||
| Phvul.010G057500 | Pv10 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | ||
| Phvul.010G057900 | Pv10 | WRKY DNA-binding protein 70 | ||
| NP | Phvul.002G205700 | Pv02 | Loc_16 | Defensin-like (DEFL) family protein |
| Phvul.002G205900 | Pv02 | Defensin-like (DEFL) family protein | ||
| Phvul.003G099300 | Pv03 | Loc_17 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | |
| Phvul.004G067300 | Pv04 | Loc_18 | Sterol | |
| Phvul.004G068800 | Pv04 | Loc_19 | Bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein | |
| Phvul.011G108700 | Pv11 | Loc_22 | S-locus lectin protein kinase family protein | |
| Phvul.011G119200 | Pv11 | Loc_23 | Concanavalin A-like lectin protein kinase family protein |
| [1] | 江兆春, 张忠民, 耿坤, 余杰颖 (2018). 菜豆象入侵我国的风险性评价. 贵州农业科学 46, 47-50. |
| [2] | 阮期平, 周立, 郑远旗 (2000). PGIP在植物抗病方面的研究进展. 植物学通报 17, 60-63. |
| [3] | 申智慧, 刘春, 杨洪, 郑松, 罗全丽, 徐本刚 (2014). 菜豆象发生规律与防治措施. 耕作与栽培 3, 47-48. |
| [4] | 宋凤鸣, 郑重, 葛起新 (1992). 富含羟脯氨酸糖蛋白在植物-病原物相互作用中的积累、作用及调控. 植物生理学通讯 28, 141-145. |
| [5] | 孙海燕, 罗兵, 喻德跃 (2005). 次生代谢抗虫基因工程研究进展. 安徽农业科学 33, 1906-1907. |
| [6] | 王辉, 李琳, 梁正, 吴一江 (2013). 菜豆象检疫及防治研究进展. 农业灾害研究 3(9), 8-12. |
| [7] | 吴长松, 冯明义, 李海, 姜府文, 赵芳, 龙贵兴, 丁昭兵, 卢云昌, 彭瑶, 廖华刚, 张国升, 颜兴, 陶惠, 文静, 高强 (2019). 毕节市菜豆象疫情发生危害及储存期防控措施初探. 植物检疫 33, 59-61. |
| [8] | 杨璐, 戴仁怀, 杨洪, 江兆春, 李敏, 杨燕琼 (2022). 甲酸乙酯和异硫氰酸甲酯混用对菜豆象的熏蒸活性研究. 山地农业生物学报 41, 79-83. |
| [9] | 杨乃博, 伍苏然, 沈林波, 张树珍, 杨本鹏 (2014). 植物抗虫性研究概况. 热带农业科学 34(9), 61-68, 89. |
| [10] | 周晓宇, 陈杰, 杨敬, 黄海涛, 宋翔 (2010). 植物凝集素及其在抗虫基因工程中的应用. 山地农业生物学报 29, 255-260. |
| [11] | Apostolova ED, Palagacheva NG, Svetleva DL, Mateeva AV (2013). Investigations on the resistance of some Bulgarian common bean genotypes towards bean weevil (Acanthoscelides obtectus Say). J Cent Eur Agric 14, 1547-1557. |
| [12] | Azizoglu U (2018). Biochemical properties of Turkish common beans and their resistance against bean weevil Acanthoscelides obtectus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). Ar-thropod-plant Inte 12, 283-290. |
| [13] |
Blair MW, Muñoz C, Buendía HF, Flower J, Bueno JM, Cardona C (2010a). Genetic mapping of microsatellite markers around the Arcelin bruchid resistance locus in common bean. Theor Appl Genet 121, 393-402.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Blair MW, Prieto S, Díaz LM, Buendía HF, Cardona C (2010b). Linkage disequilibrium at the APA insecticidal seed protein locus of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). BMC Plant Biol 10, 79.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Bradbury PJ, Zhang ZW, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007). TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23, 2633-2635.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Buchler ES, Holland JB, Bradbury PJ, Acharya CB, Brown PJ, Browne C, Ersoz E, Flint-Garcia S, Garcia A, Glaubitz JC, Goodman MM, Harjes C, Guill K, Kroon DE, Larsson S, Lepak NK, Li HH, Mitchell SE, Pressoir G, Peiffer JA, Rosas MO, Rocheford TR, Romay MC, Romero S, Salvo S, Villeda HS, da Silva HS, Sun Q, Tian F, Upadyayula N, Ware D, Yates H, Yu JM, Zhang ZW, Kresovich S, Mcmullen MD (2009). The genetic architecture of maize flowering time. Science 325, 714-718.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Chen KC, Lin CY, Kuan CC, Sung HY, Chen CS (2002). A novel defensin encoded by a mungbean cDNA exhibits insecticidal activity against bruchid. J Agric Food Chem 50, 7258-7263.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Cormier F, Le Gouis J, Dubreuil P, Lafarge S, Praud S (2014). A genome-wide identification of chromosomal re-gions determining nitrogen use efficiency components in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 127, 2679-2693.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
De Andrade EKV, Rodrigues R, da Costa Vieira Bard G, da Silva Pereira L, Baptista KEV, Cavalcanti TFM, Oliveira AEA, Souza TAM, Gomes VM (2020). Identifi-cation, biochemical characterization and biological role of defense proteins from common bean genotypes seeds in response to Callosobruchus maculatus infestation. J Stored Prod Res 87, 101580.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Duan CX, Zhu ZD, Li WC, Bao SY, Wang XM (2017). Ge-netic diversity and differentiation of Acanthoscelides ob-tectus Say (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) populations in China. Agric For Entomol 19, 113-121.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Duarte MAG, Cabral GB, Ibrahim AB, Aragão FJL (2018). An overview of the APA locus and Arcelin proteins and their biotechnological potential in the control of bruchids. Agri Gene 8, 57-62. |
| [22] |
Gautam AK, Shrivastava N, Sharma B, Bhagyawant SS (2018). Current scenario of legume lectins and their prac-tical applications. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 21, 217-227.
DOI |
| [23] |
Goossens A, Quintero C, Dillen W, DeRycke R, Valor JF, De Clercq J, Van Montagu M, Cardona C, Angenon G (2000). Analysis of bruchid resistance in the wild common bean accession G02771: no evidence for insecticidal ac-tivity of Arcelin 5. J Exp Bot 51, 1229-1236.
PMID |
| [24] |
Gupta M, Sharma P, Nath AK (2014). Purification of a novel α-amylase inhibitor from local Himalayan bean (Phaseo-lus vulgaris) seeds with activity towards bruchid pests and human salivary amylase. J Food Sci Technol 51, 1286-1293.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Hategekimana A, Erler F (2020). Fecundity and fertility inhibition effects of some plant essential oils and their major components against Acanthoscelides obtectus Say (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). J Plant Dis Protect 127, 615-623. |
| [26] |
Huang XH, Zhao Y, Wei XH, Li CY, Wang AH, Zhao Q, Li WJ, Guo YL, Deng LW, Zhu CR, Fan DL, Lu YQ, Weng QJ, Liu KY, Zhou TY, Jing YF, Si LZ, Dong GJ, Huang T, Lu TT, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li JY, Han B (2012). Geno-me-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat Genet 44, 32-39.
DOI |
| [27] |
Iturralde-García RD, Castañé C, Wong-corral FJ, Riu-davets J (2020). Biological control of Acanthoscelides obtectus and Zabrotes subfasciatus in stored dried beans. BioControl 65, 693-701.
DOI |
| [28] |
Jia MJ, Yang LJ, Zhang W, Rosewarne G, Li JH, Yang EN, Chen L, Wang WX, Liu YK, Tong HW, He WJ, Zhang YQ, Zhu ZW, Gao CB (2020). Genome-wide as-sociation analysis of stripe rust resistance in modern Chinese wheat. BMC Plant Biol 20, 491.
DOI |
| [29] |
Jiménez JC, de la Fuente M, Ordás B, Domínguez LEG, Malvae RA (2017). Resistance categories to Acanthosce-lides obtectus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius), new sources of resistance for dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) breeding. Crop Prot 98, 255-266.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Joshi J, Pandurangan S, Diapari M, Marsolais F (2017). Comparison of gene families:seed storage and other seed proteins. In: de la Vega MP, Santalla M, Marsolais F, eds. The Common Bean Genome. Cham: Springer. pp. 201-217. |
| [31] |
Kamfwa K, Beaver JS, Cichy KA, Kelly JD (2018). QTL mapping of resistance to bean weevil in common bean. Crop Sci 58, 2370-2378.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Kornegay JL, Cardona C (1991). Inheritance of resistance to Acanthoscelides obtectus in a wild common bean ac-cession crossed to commercial bean cultivars. Euphytica 52, 103-111.
DOI |
| [33] |
Kump KL, Bradbury PJ, Wisser RJ, Buckler ES, Belcher AR, Oropeza-Rosas MA, Zwonitzer JC, Kresovich S, McMullen MD, Ware D, Balint-Kurti PJ, Holland JB (2011). Genome-wide association study of quantitative resistance to southern leaf blight in the maize nested as-sociation mapping population. Nat Genet 43, 163-168.
DOI |
| [34] | Kusolwa PM, Myers JR (2011). Seed storage proteins ARL2 and its variants from the apalocus of wild tepary bean G40199 confers resistance to Acanthoscelides ob-tectus when expressed in common beans. Afr Crop Sci J 19, 255-265. |
| [35] |
Kusolwa PM, Myers JR, Porch TG, Trukhina Y, González-Vélez A, Beaver JS (2016). Registration of AO- 1012-29-3-3A red kidney bean germplasm line with bean weevil, BCMV, and BCMNV resistance. J Plant Regist 10, 149-153.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Li B, Chen SL, Qin C, Xiao J (2016). Research progress on germplasm resources of common bean. Agric Sci Technol 17, 2572-2577. |
| [37] |
Li XM, Tang YS, Wang LF, Chang YJ, Wu J, Wang SM (2022). QTL mapping and identification of genes associated with the resistance to Acanthoscelides obtectus in cultivated common bean using a high-density genetic linkage map. BMC Plant Biol 22, 260.
DOI |
| [38] |
Macedo MLR, das Graças MachadoFreire M, da Silva MBR, Coelho LCB (2007). Insecticidal action of Bauhinia monandra leaf lectin (BmoLL) against Anagasta kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), Zabrotes subfasciatus and Callosobruchus maculatus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 146, 486-498.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Mutungi C, Affognon HD, Njoroge AW, Manono J, Baributsa D, Murdock LL (2015). Triple-layer plastic bags protect dry common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) against damage by Acanthoscelides obtectus (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) during storage. J Econ Entomol 108, 2479-2488.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Oliva MLV, Silva MCC, Sallai RC, Brito MV, Sampaio MU (2010). A novel subclassification for Kunitz proteinase in-hibitors from leguminous seeds. Biochimie 92, 1667-1673.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Oliveira AS, Migliolo L, Aquino RO, Ribeiro JKC, Macedo LLP, Andrade LBS, Bemquerer MP, Santos EA, Kiyota S, de Sales MP (2007). Purification and characterization of a trypsin-papain inhibitor from Pithecelobium dumosum seeds and its in vitro effects towards digestive enzymes from insect pests. Plant Physiol Biochem 45, 858-865.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MAR, Bender D, MallerJ, Sklar P, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007). PLINK: a tool set for whole-ge-nome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81, 559-575.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Rakotoson T, Dusserre J, Letourmy P, Frouin J, Ratsimiala IR, Rakotoarisoa NV, Cao TV, Brocke KV, Ramanantsoanirina A, Ahmadi N, Raboin LM (2021). Genome-wide association study of nitrogen use efficiency and agronomic traits in upland rice. Rice Sci 28, 379-390.
DOI |
| [44] | Santino A, Valsasina B, Lioi L, Vitale A, Bollini R (1991). Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seed lectins: a novel elec-trophoretic variant of Arcelin. Plant Physiol 10, 7-11. |
| [45] |
Schmutz J, McClean PE, Mamidi S, Wu GA, Cannon SB, Grimwood J, Jenkins J, Shu SQ, Song QJ, Chavarro C, Torres-Torres M, Geffroy V, Moghaddam SM, Gao DY, Abernathy B, Barry K, Blair M, Brick MA, Chovatia M, Gepts P, Goodstein DM, Gonzales M, Hellsten U, Hyten DL, Jia GF, Kelly JD, Kudrna D, Lee R, Richard MMS, Miklas PN, Osorno JM, Rodrigues J, Thareau V, Urrea CA, Wang M, Yu Y, Zhang M, Wing RA, Cregan PB, Rokhsar DS, Jackson SA (2014). A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat Genet 46, 707-713.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Schroeder HE, Gollasch S, Moore A, Tabe LM, Craig S, Hardie DC, Chrispeels MJ, Spencer D, Higgins TJV (1995). Bean α-amylase inhibitor confers resistance to the pea weevil (Bruchus pisorum) in transgenic peas (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Physiol 107, 1233-1239.
PMID |
| [47] |
Shade RE, Pratt RC, Pomeroy MA (1987). Development and mortality of the bean weevil, Acanthoscelides obtec-tus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae), on mature seeds of tepary beans, Phaseolus acutifolius, and common beans, Phaseolus vulgaris. Environ Entomol 16, 1067-1070.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Smith MR, Rao IM (2021). Common bean. In: Sadras VO, Calderini DF, eds. Crop Physiology Case Histories for Major Crops. London: Academic Press. pp. 384-406. |
| [49] |
Velten G, Rott AS, Cardona C, Dorn S (2007). The inhibi-tory effect of the natural seed storage protein Arcelin on the development of Acanthoscelides obtectus. J Stored Prod Res 43, 550-557.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Visscher PM, Brown MA, McCarthy MI, Yang J (2012). Five years of GWAS discovery. Am J Hum Genet 90, 7-24.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Wu J, Wang LF, Fu JJ, Chen JB, Wei SH, Zhang SL, Zhang J, Tang YS, Chen ML, Zhu JF, Lei L, Geng QH, Liu CL, Wu L, Li XM, Wang XL, Wang Q, Wang ZL, Xing SL, Zhang HK, Blair MW, Wang SM (2020). Resequencing of 683 common bean genotypes identifies yield component trait associations across a north-south cline. Nat Genet 52, 118-125.
DOI PMID |
| [52] | Yin LL, Zhang HH, Tang ZS, Xu JY, Yin D, Zhang ZW, Yuan XH, Zhu MJ, Zhao SH, Li XY, Liu XL (2021). rMVP: a memory-efficient, visualization-enhanced, and parallel- accelerated tool for genome-wide association study. Ge-nom Proteom Bioinf 19, 619-628. |
| [53] |
Yuste-Lisbona FJ, González AM, Capel C, García-Alcázar M, Capel J, De Ron AM, Lozano R, Santalla M (2014). Genetic analysis of single-locus and epistatic QTLs for seed traits in an adapted × nuña RIL population of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 127, 897-912.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Zaugg I, Magni C, Panzeri D, Daminati MG, Bollini R, Benrey B, Bacher S, Sparvoli F (2013). QUES, a new Phaseolus vulgaris genotype resistant to common bean weevils, contains the Arcelin-8 allele coding for new lectin-related variants. Theor Appl Genet 126, 647-661.
DOI URL |
| [1] |
Juan Cui, Xiaoyu Yu, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun, Wenfu Chen.
Analysis of Texture Factors and Genetic Basis Influencing the Differences in Eating Quality between Northeast China and Japanese Japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | Yuan Li, Yujie Chang, Lanfen Wang, Shumin Wang, Jing Wu. Screening of Resistance Germplasm Resources and Genome-wide Association Study of Fusarium Wilt in Common Bean [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 51-61. |
| [3] | Qi Zhang, Wenjing Zhang, Xiankai Yuan, Ming Li, Qiang Zhao, Yanli Du, Jidao Du. The Regulatory Mechanism of Melatonin on Nucleic Acid Repairing of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) at the Sprout Stage Under Salt Stress [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 108-121. |
| [4] | Jing Bo Jin, Chengzhi Liang. Research Advances in Forage Grass Genomics [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(6): 732-741. |
| [5] | Wenqing Tan, Jun Chen, Hongwei Cai. Recent Progress in Biology of Genus Lolium [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(6): 802-813. |
| [6] | Sunlu Chen, Chengfang Zhan, Hong Jiang, Linhan Li, Hongsheng Zhang. Advances in the Molecular Mechanism and Genetic Regulation of Grain-filling Rate in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 80-89. |
| [7] | Rong Zhou, Bo Wang,Rui Yang, Shu Li, Linlin Fan, Qianchun Zeng, Qiong Luo. Quantitative Trait Loci Analysis of Rice Blast Resistance in Japonica Rice Variety Ziyu44 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2015, 50(6): 691-698. |
| [8] | Lihui Gong, Zhenyu Gao, Bojun Ma, Qian Qian. Progress in Genetic Research into Grain Shape in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(6): 597-605. |
| [9] | SHEN Jin-Xiong YI Bin FU Ting-Dong YANG Guang-Sheng. Overview on Mapping of Quantitative Traits for Plant [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2003, 20(03): 257-263. |
| [10] | ZHOU Li-Ying YANG Li-Tao ZHENG Jian-Yu. Recent Progresses in the Studies of Genetic Engineering for Cold Resistance in Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2001, 18(03): 325-331. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||