

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 519-527.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18007 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18007
• TECHNIQUES AND METHODS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ai Wenqin1, Jiang Hanyuan1, Li Xinxin2, Liao Hong2,*( )
)
Received:2018-01-09
Accepted:2018-02-12
Online:2018-07-01
Published:2018-09-11
Contact:
Liao Hong
About author:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
Ai Wenqin, Jiang Hanyuan, Li Xinxin, Liao Hong. An Efficient Nutrient Solution System to Study Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Soybean[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(4): 519-527.
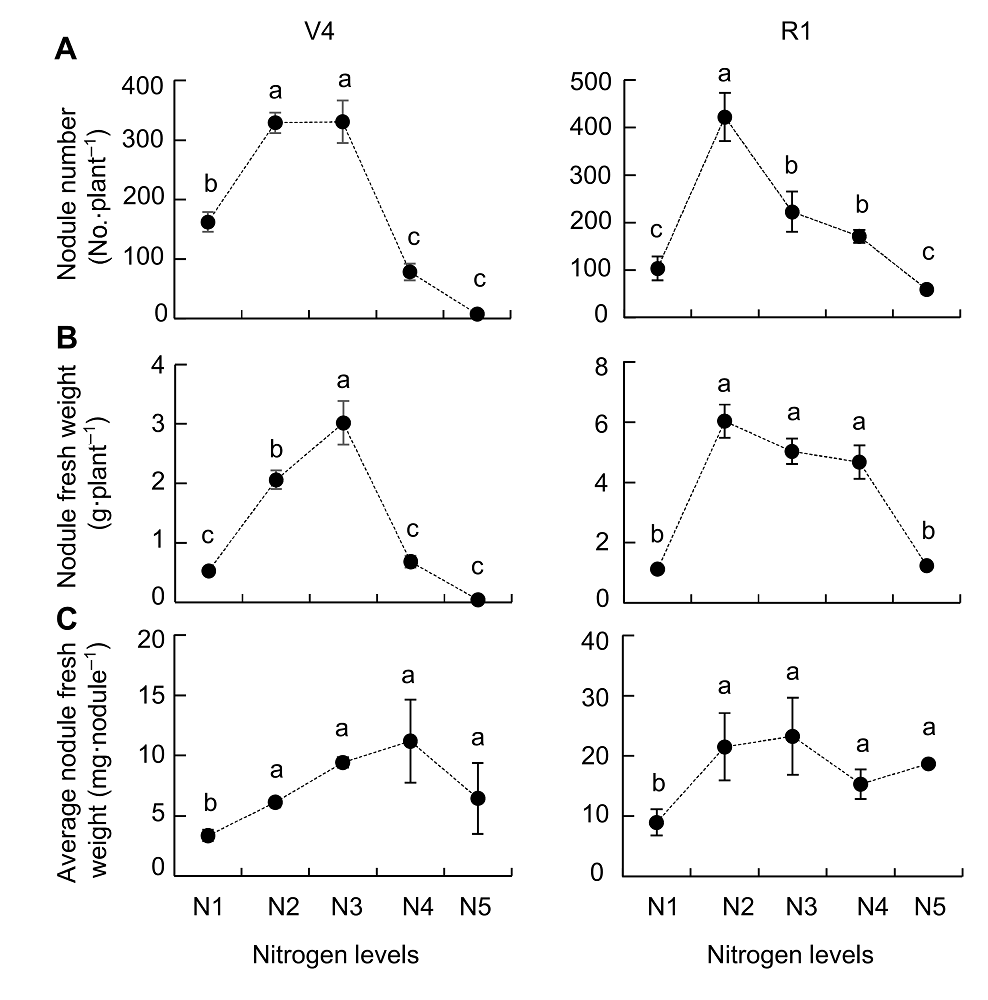
Figure 1 Effects of nitrogen supply on soybean nodulation(A) Nodule number; (B) Nodules fresh weight; (C) Average nodules fresh weight. V4 and R1 represent different growth stages of soybean. N1-N5 indicate 300 μmol·L-1, 900 μmol·L-1, 2 400 μmol·L-1, 4 800 μmol·L-1 and 7 200 μmol·L-1 nitrogen level, respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different N supply levels (P<0.05).
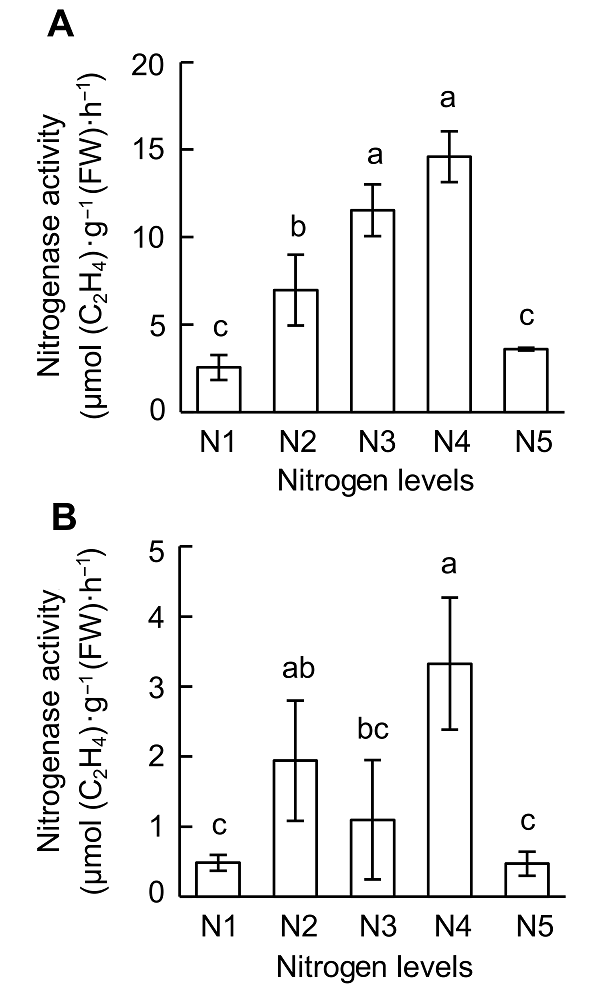
Figure 2 Effects of nitrogen supply on nitrogenase activity at different growth stages of soybean(A) V4 stage; (B) R1 stage. N1-N5 see Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different N supply levels (P<0.05).
| F value | Shoot dry weight | Root dry weight | Grain weight | Hundred grain weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 67.15*** | 134.57*** | 50.75*** | 36.33*** |
| R | 0.89* | 2.11* | 49.53*** | 0.398 |
| N×R | 4.31* | 14.80*** | 8.31*** | 4.45** |
Table 1 Effect of nitrogen supply levels and inoculation of rhizobium on soybean growth and yield
| F value | Shoot dry weight | Root dry weight | Grain weight | Hundred grain weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 67.15*** | 134.57*** | 50.75*** | 36.33*** |
| R | 0.89* | 2.11* | 49.53*** | 0.398 |
| N×R | 4.31* | 14.80*** | 8.31*** | 4.45** |
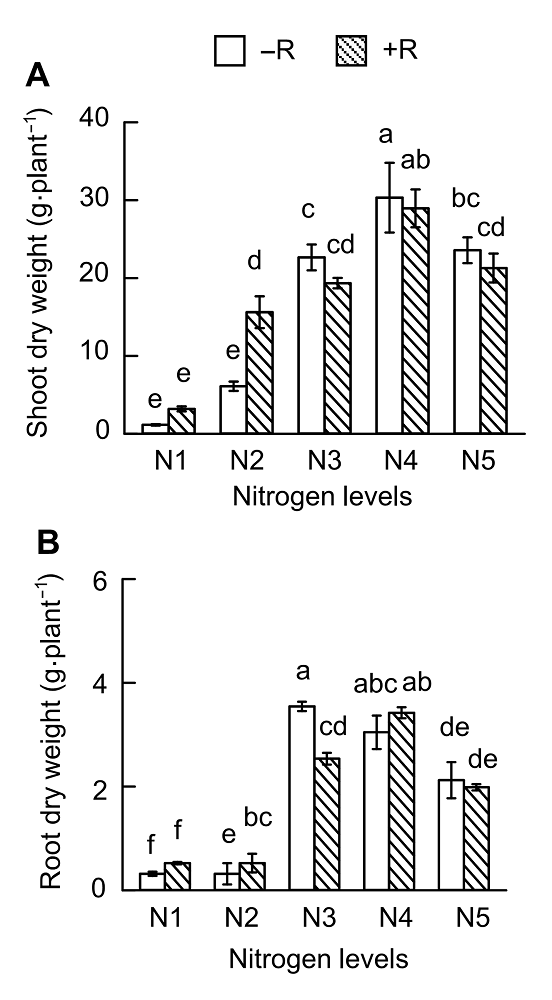
Figure 3 Effects of nitrogen supply on soybean growth(A) Up-ground dry weight; (B) Root dry weight. N1-N5 see Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different N supply levels (P<0.05).
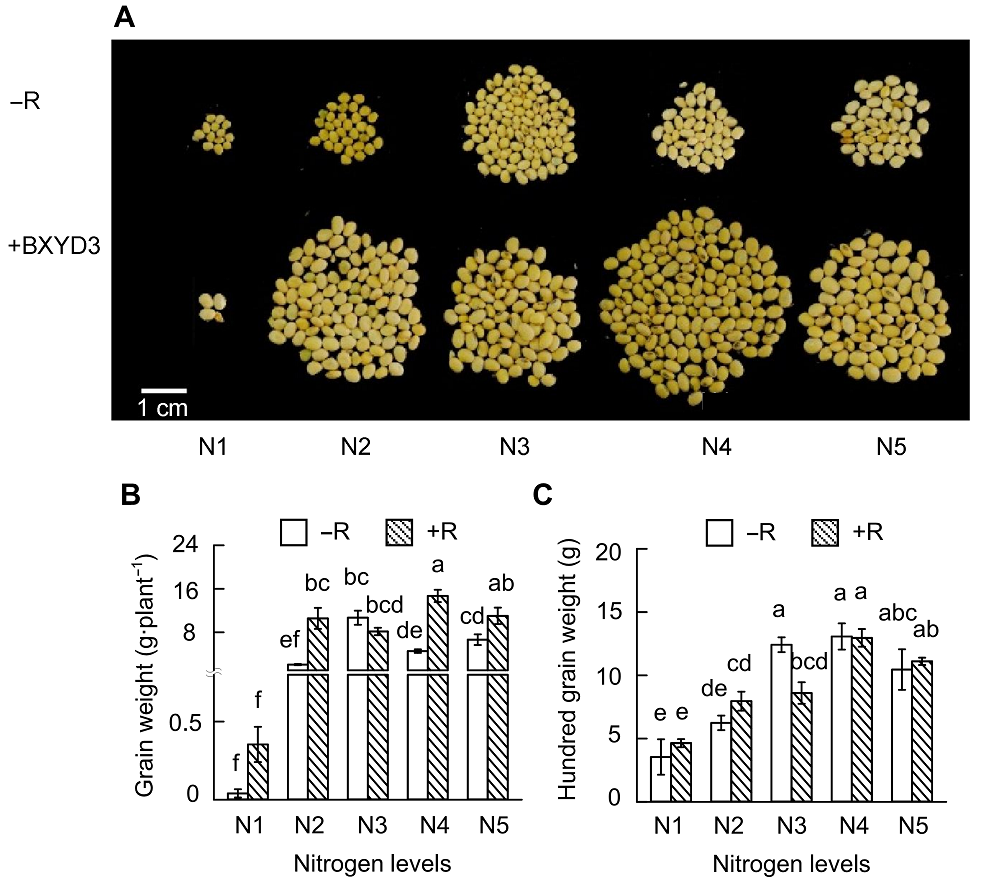
Figure 4 Effects of nitrogen supply levels on soybean yield(A) Pictures of soybean seeds; (B) Grain weight; (C) Hundred grain weight. N1-N5 see Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different N supply levels (P<0.05).
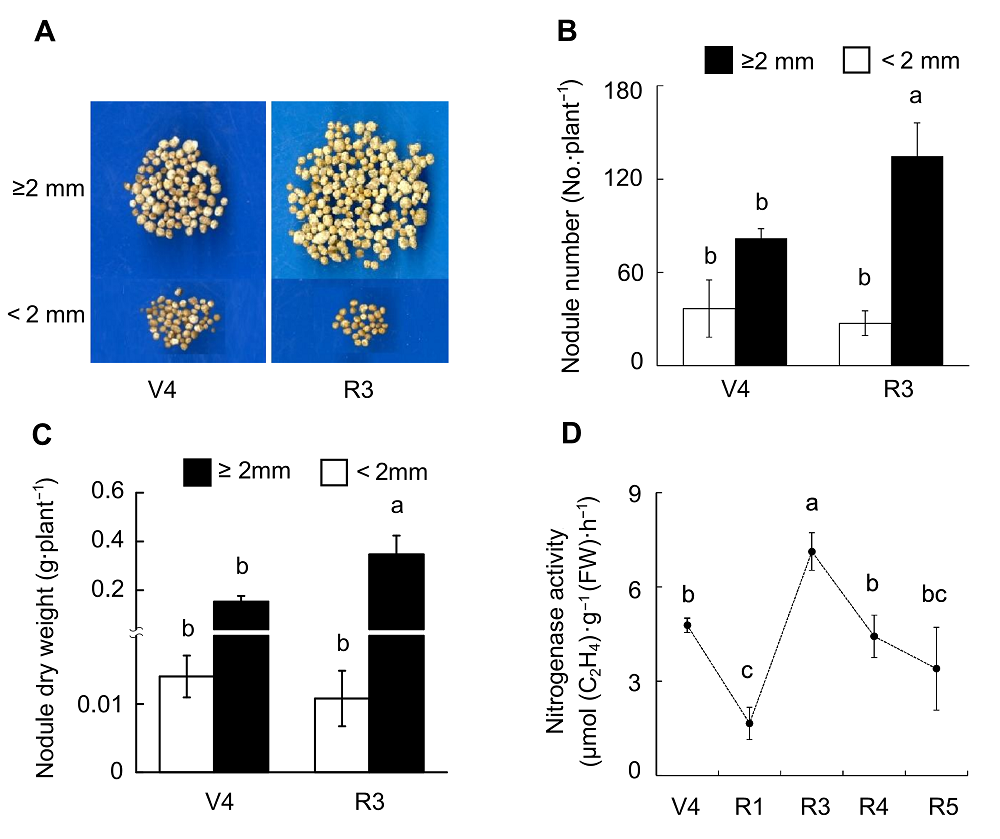
Figure 5 Effects of rhizobium inoculation on soybean nodule growth and nitrogenase activity(A) Pictures of nodules; (B) Nodule number; (C) Nodule dry weight; (D) Nitrogenase activity. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different growth stages of soybean (P<0.05).
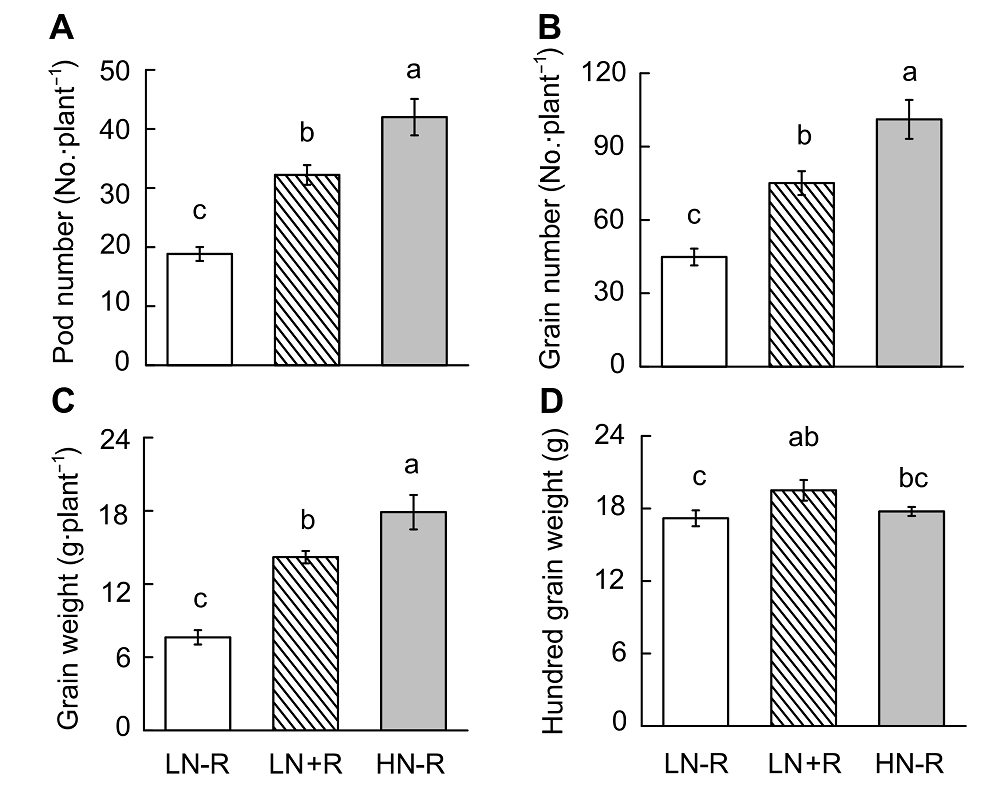
Figure 6 Soybean yield as affected by different nitrogen or rhizobia inoculation treatments(A) Pod number; (B) Grain number; (C) Grain weight; (D) Hundred grain weight. LN-R: Low N without inoculation treatment; LN+R: Low N with inoculation treatment; HN-R: High N without inoculation treatment. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
| 1 | 陈文新, 陈文峰 (2004). 发挥生物固氮作用减少化学氮肥用量. 中国农业科技导报 6(6), 3-6. |
| 2 | 程凤娴, 曹桂芹, 王秀荣, 赵静, 严小龙, 廖红 (2008). 华南酸性低磷土壤中大豆根瘤菌高效株系的发现及应用. 科学通报 53, 2903-2910. |
| 3 | 邸伟, 金喜军, 马春梅, 龚振平, 董守坤, 张磊 (2010). 施氮水平对大豆氮素积累与产量影响的研究. 核农学报 24, 612-617. |
| 4 | 胡浩南, 敖俊华, 黄晓财, 李欣欣, 廖红 (2017). 甘蔗不同组织联合固氮能力评价. 植物生理学报 53, 437-444. |
| 5 | 李欣欣, 许锐能, 廖红 (2016). 大豆共生固氮在农业减肥增效中的贡献及应用潜力. 大豆科学 35, 531-535. |
| 6 | 李艳, 盖钧镒 (2017). 大豆向热带地区发展的遗传基础. 植物学报 52, 389-393. |
| 7 | 李宗盛, 李展辉, 邓建军 (1986). 不同时期施氮对大豆产量影响的研究. 土壤肥料 (6), 46-47. |
| 8 | 罗进, 曹智 (2017). 2016年国内外大豆市场回顾及2017年展望. 中国畜牧杂志 53(4), 160-165, 178. |
| 9 | 彭玉新 (2009). 施肥对大豆产量及品质的影响研究. 现代农业科技(18), 19, 21. |
| 10 | 王庆胜 (2010). 根瘤菌对大豆产量及品质的影响. 黑龙江农业科学(9), 138, 147. |
| 11 | Alam F, Bhuiyan MAH, Alam SS, Waghmode TR, Kim PJ, Lee YB (2015). Effect of Rhizobium sp. BARIRGm901 ino- culation on nodulation, nitrogen fixation and yield of soybean(Glycine max) genotypes in gray terrace soil. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 79, 1660-1668. |
| 12 | Alves BJR, Boddey RM, Urquiaga S (2003). The success of BNF in soybean in Brazil.Plant Soil 252, 1-9. |
| 13 | Brewin NJ (1991). Development of the legume root nodule.Annu Rev Cell Biol 7, 191-226. |
| 14 | Daimon H, Hori K, Shimizu A, Nakagawa M (1999). Nitrate-induced inhibition of root nodule formation and nitrogenase activity in the peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Prod Sci 2, 81-86. |
| 15 | Fujikake H, Yamazaki A, Ohtake N, Sueyoshi K, Matsuhashi S, Ito T, Mizuniwa C, Kume T, Hashimoto S, Ishioka NS, Watanabe S, Osa A, Sekine T, Uchida H, Tsuji A, Ohyama T (2003). Quick and reversible inhibition of soybean root nodule growth by nitrate involves a decrease in sucrose supply to nodules.J Exp Bot 54, 1379-1388. |
| 16 | Gan YB, Stulen I, van Keulen H, Kuiper PJC (2004). Low concentrations of nitrate and ammonium stimulate nodulation and N2 fixation while inhibiting specific nodulation (nodule DW·g-1 root dry weight) and specific N2 fixation (N2 fixed·g-1 root dry weight) in soybean.Plant Soil 258, 281-292. |
| 17 | Hungria M, Campo RJ, Mendes IC (2005). Reinoculation increasing soybean grain yield in Brazil. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Nitrogen Fixation Congress. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 315-315. |
| 18 | Hungria M, Franchini JC, Campo RJ, Crispino CC, Mor- aes JZ, Sibaldelli RNR, Mendes IC, Arihara J (2006). Nitrogen nutrition of soybean in Brazil: contributions of biological N2 fixation and N fertilizer to grain yield.Can J Plant Sci 86, 927-939. |
| 19 | Li XX, Zhao J, Tan ZY, Zeng RS, Liao H (2015). GmEXPB2, a cell wall β-expansin, affects soybean nodulation through modifying root architecture and promoting nodule formation and development.Plant Physiol 169, 2640-2653. |
| 20 | Qin L, Jiang H, Tian J, Zhao J, Liao H (2011). Rhizobia enhance acquisition of phosphorus from different sources by soybean plants.Plant Soil 349, 25-36. |
| 21 | Qin L, Zhao J, Tian J, Chen LY, Sun ZA, Guo YX, Lu X, Gu M, Xu GH, Liao H (2012). The high-affinity phosphate transporter GmPT5 regulates phosphate transport to nodu- les and nodulation in soybean.Plant Physiol 159, 1634-1643. |
| 22 | Saito A, Tanabata S, Tanabata T, Tajima S, Ueno M, Ishikawa S, Ohtake N, Sueyoshi K, Ohyama T (2014). Effect of nitrate on nodule and root growth of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Int J Mol Sci 15, 4464-4480. |
| 23 | Tang F, Yang SM, Liu JG, Zhu HY (2016). Rj4, a gene controlling nodulation specificity in soybeans, encodes a thau- matin-like protein but not the one previously reported. Plant Physiol 170, 26-32. |
| 24 | Wang D, Yang SM, Tang F, Zhu HY (2012). Symbiosis specificity in the legume-rhizobial mutualism.Cell Microbiol 14, 334-342. |
| [1] | WANG Xiu-Yuan, SHEN Lei, LIU Ting-Ting, WEI Wen-Wen, ZHANG Shuai, ZHANG Wei. Spatial and temporal distribution of root system and interspecific competition strategy in Malus pumila ‘Saiwaihong’ - Glycine max agroforestry system [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(5): 748-759. |
| [2] | TANG Yuan-Xiang, XIONG Shi-Chen, ZHU Hong-Feng, ZHANG Xin-Sheng, YOU Cheng-Ming, LIU Si-Ning, TAN Bo, XU Zhen-Feng. Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on leaf litter production and carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus return of the dominant tree species in broadleaf evergreen forests on the western margin of Sichuan Basin [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(5): 720-731. |
| [3] | Xu Tingyang, Liu Yuchen, Wang Wanpeng, Su Hang, Su Kunlong, Wu Zhenying, Lϋ Ming, Li Fuli, Wang Xiaoshan, Fu Chunxiang. Effects of Different Plant Growth Regulators on Wheat Growth and Development in the Saline-alkali Land [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 354-362. |
| [4] | Jie Cao, Qiulian Lu, Jianping Zhai, Baohui Liu, Chao Fang, Shichen Li, Tong Su. Changes in the Expression of the Soybean TPS Gene Family Under Salt Stress and Haplotype Selection Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(2): 172-185. |
| [5] | Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Zhenan Zhu, Zhining Zhang, Lihai Wang, Jun Chen, Sanfeng Li, Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Qianqian Zhong, Wenjing Yin, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTLs Associated with Rice Panicle Traits and Candidate Gene Analysis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [6] | LI Lin, SUN Yi, YANG Xiao-Qiong, FANG Hai-Dong, YAN Bang-Guo. Response of endophytes in root nodules of Arachis hypogaea ‘Qicai’ to nitrogen addition and its relationship with plant stoichiometry characteristics [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(10): 1374-1384. |
| [7] | Jiaxin Chen, Hao Mei, Caixiang Huang, Zongyuan Liang, Yitong Quan, Dongpeng Li, Buweimaieryemu·Saimaiti , Xinxin Li, Hong Liao. A Highly Efficient Method to Generate Chimeric Soybean Plant with Transgenic Hairy Roots [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 89-98. |
| [8] | Yuping Yan, Xiaoqi Yu, Deyong Ren, Qian Qian. Genetic Mechanisms and Breeding Utilization of Grain Number Per Panicle in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 359-372. |
| [9] | LIU Jian-Xin, LIU Rui-Rui, LIU Xiu-Li, JIA Hai-Yan, BU Ting, LI Na. Regulation of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on photosynthetic carbon metabolism in Avena nude under saline-alkaline stress [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2023, 47(3): 374-388. |
| [10] | Xiaomin Feng, Xiang Gao, Huadong Zang, Yuegao Hu, Changzhong Ren, Zhiping Hao, Huiqing Lü, Zhaohai Zeng. Intercropping Effect and Nitrogen Transfer Characteristics of Oat-Mungbean Intercrop [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 122-131. |
| [11] | Weijun Ye, Yin Zhang, Peiran Wang, Lingling Zhang, Dongfeng Tian, Zejiang Wu, Bin Zhou. QTLs Analysis for Five Yield-related Traits in Mungbean [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 150-158. |
| [12] | YU Shui-Jin, WANG Juan, ZHANG Chun-Yu, ZHAO Xiu-Hai. Impact and mechanism of maintaining biomass stability in a temperate coniferous and broadleaved mixed forest [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2022, 46(6): 632-641. |
| [13] | Liu Xiaolong, Ji Ping, Yang Hongtao, Ding Yongdian, Fu Jialing, Liang Jiangxia, Yu Congcong. Priming Effect of Abscisic Acid on High Temperature Stress During Rice Heading-flowering Stage [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 596-610. |
| [14] | Wang Lei, Chong Kang. Choice of both Ways: Variations of Reverted Repeats Balance Environmental Adaptation and Yield in Maize [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(5): 555-558. |
| [15] | Yunhui Wang, Yifan Wang, Jiayu Lin, Jinhong Li, Shien Yao, Xiangchi Feng, Zhenlin Cao, Jun Wang, Meina Li. Plant Kinesin: from Microtubule Arrays to Physiological Regulation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(3): 358-374. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||