

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 759-772.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25098 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25098
• INVITED REVIEWS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wu Aian, Tao Yifei, Fang Siqi, Xu Xinyue, Zhu Shanshan, Chen Shiying, Wang Tingchao, Guo Wei,*( )
)
Received:2025-05-30
Accepted:2025-09-02
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-09-02
Contact:
*E-mail: weiguo817@zjnu.cn
Wu Aian, Tao Yifei, Fang Siqi, Xu Xinyue, Zhu Shanshan, Chen Shiying, Wang Tingchao, Guo Wei. Research Progress on Pathogenesis of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola and Rice Resistance Mechanisms[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 759-772.
| 中国稻作区 | BLS主要发病区 | BLS严重发病区 |
|---|---|---|
| 华南双季稻稻作区 | 海南; 广东和广西北部; 云南和福建南部 | 广东和广西南部; 福建北部 |
| 华中双单季稻稻作区 | 四川东北部; 安徽和江苏北部; 湖南和江西南部 | 湖北; 浙江; 上海; 湖南东北部; 江西北部; 安徽和江苏南部 |
| 华北单季稻稻作区 | 几乎无 | 几乎无 |
| 东北早熟单季稻稻作区 | 几乎无 | 几乎无 |
| 西南高原单双季稻稻作区 | 贵州; 云南西部和南部 | 湖南西北部; 四川西南部 |
| 西北干燥区单季稻稻作区 | 几乎无 | 几乎无 |
Table 1 Spatial coupling relationship between rice planting ecoregions and bacterial leaf streak (BLS) epidemic areas in China
| 中国稻作区 | BLS主要发病区 | BLS严重发病区 |
|---|---|---|
| 华南双季稻稻作区 | 海南; 广东和广西北部; 云南和福建南部 | 广东和广西南部; 福建北部 |
| 华中双单季稻稻作区 | 四川东北部; 安徽和江苏北部; 湖南和江西南部 | 湖北; 浙江; 上海; 湖南东北部; 江西北部; 安徽和江苏南部 |
| 华北单季稻稻作区 | 几乎无 | 几乎无 |
| 东北早熟单季稻稻作区 | 几乎无 | 几乎无 |
| 西南高原单双季稻稻作区 | 贵州; 云南西部和南部 | 湖南西北部; 四川西南部 |
| 西北干燥区单季稻稻作区 | 几乎无 | 几乎无 |
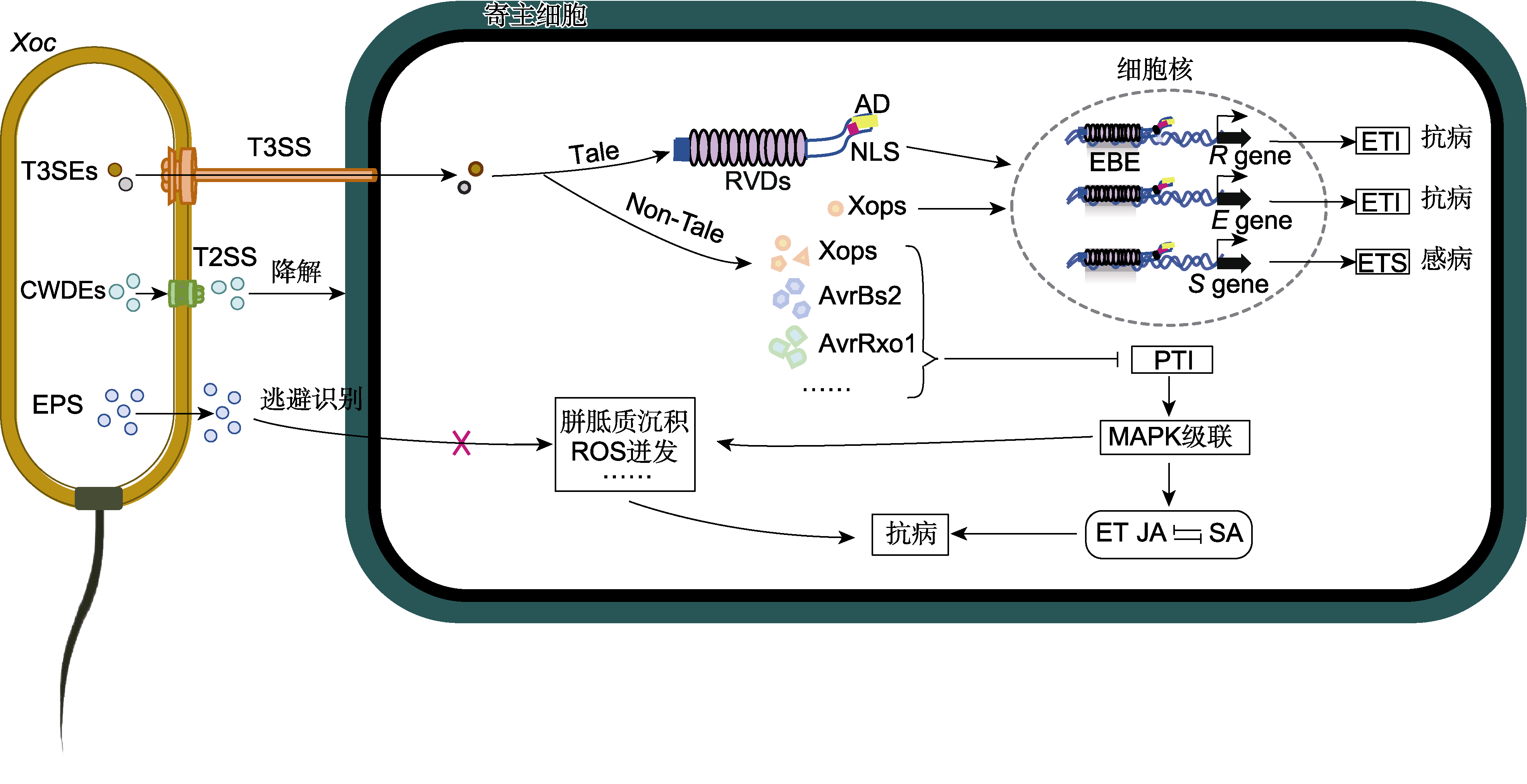
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the interaction between Xoc and host rice Xoc employs the T2SS to secrete CWDEs that hydrolyze rice cell wall components, facilitating its invasion and colonization; concurrently, it utilizes the T3SS to inject T3SEs (TALEs and non-TALEs) into rice cells. TALEs target the EBE region of host gene promoters through nuclear localization, specifically activating R/E/S gene expression to trigger ETI or ETS, while non-TALEs cooperatively suppress PTI that regulates hormone synthesis. Xoc secretes EPS to form a mucoid layer encapsulating bacterial cells, thereby evading host immune recognition including ROS burst and callose deposition. Xoc: Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola; T2SS: Type II secretion system; CWDEs: Cell wall-degrading enzymes; T3SS: Type III secretion system; T3SEs: Type III secretion effectors; TALEs: Transcription activator-like effectors; non-TALEs: Non transcription activator-like effectors; EBE: Effector-binding element; R gene: Resistance gene; E gene: Executor gene; S gene: Susceptibility gene; ETI: Effector-triggered immunity; ETS: Effector-triggered susceptibility; PTI: Pattern-triggered immunity; EPS: Extracellular polysaccharides; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; Xops: Xanthomonas outer proteins; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; SA: Salicylic acid; JA: Jasmonic acid; ET: Ethylene; RVDs: Repeat-variable diresidues; NLS: Nuclear localization signal; AD: Acidic activation domain. Lines with arrows mean activation while blunt lines mean repression.
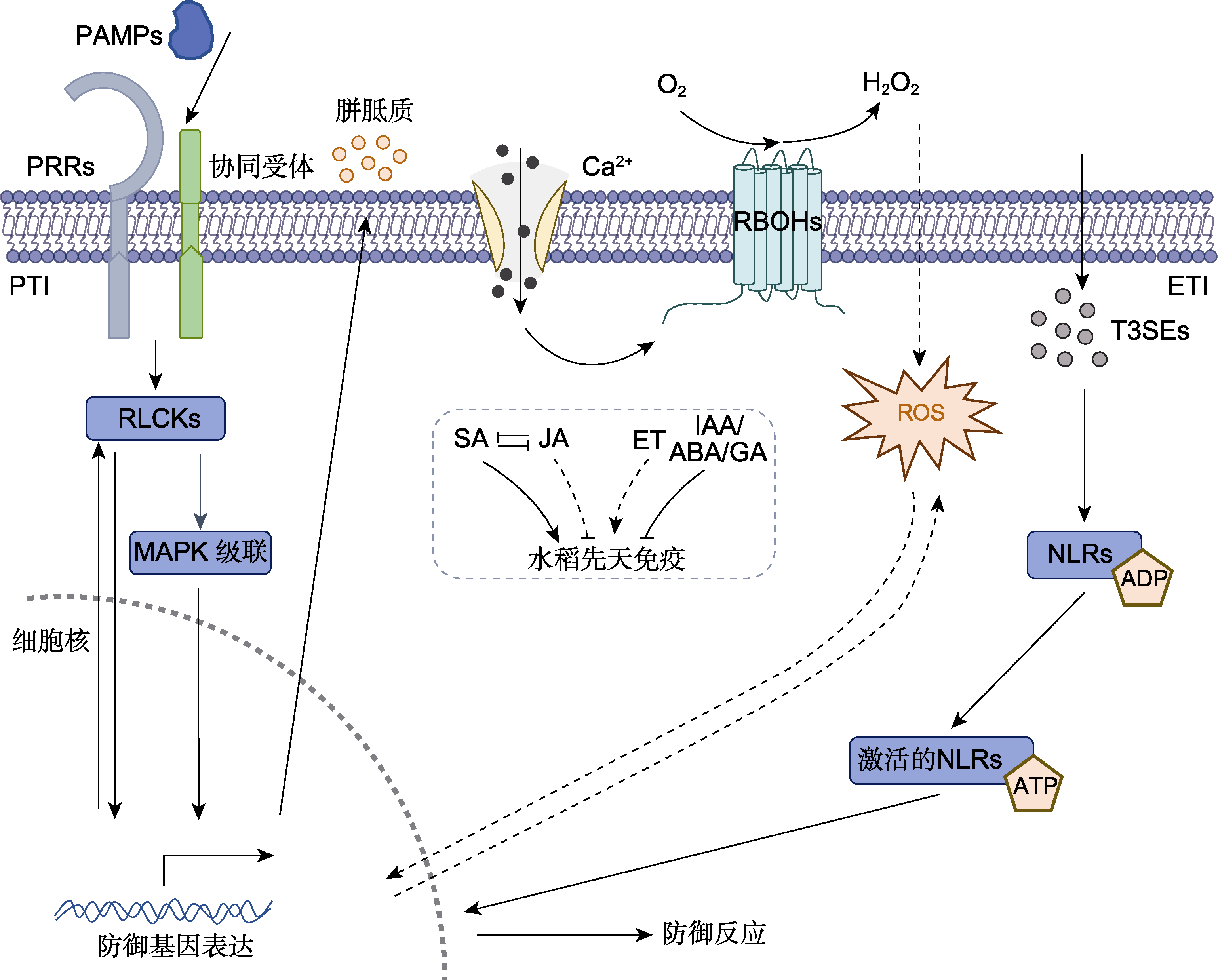
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of rice innate immune system During Xoc-rice interactions, PRRs recognize PAMPs to activate RLCKs, inducing defense signals including Ca2+ influx, MAPK activation, and transcriptional reprogramming. RLCKs phosphorylate the N-terminus of RBOHs. The activated RBOHs convert O2 to H2O2, causing ROS burst and promoting defense gene expression. The MAPK cascade regulates the synthesis of plant hormones SA, JA, and ET, forming a hormone cross-regulatory network that modulates rice resistance. NLRs recognize T3SEs and integrate intracellular signaling events to trigger defense responses such as HR. PTI and ETI act synergistically to collectively enhance immune responses. Xoc: Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola; PRRs: Pattern recognition receptors; PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; RLCKs: Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; RBOHs: Respiratory burst oxidase homologs; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SA: Salicylic acid; JA: Jasmonic acid; ET: Ethylene; NLRs: Nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat containing receptors; T3SEs: Type III secretion effectors; HR: Hypersensitive response; PTI: Pattern-triggered immunity; ETI: Effector-triggered immunity; IAA: Auxin; GA: Gibberellin; ABA: Abscisic acid. Arrows indicate direct (solid) or indirect (dashed) activation, flathead arrows indicate inhibition.
| 来源 | 位点与基因 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 玉米 | Rxo1 | Zhao et al., |
| Minghui 63 | OsWRKY45-2 | Tao et al., |
| ZH11 | OsMPK6 | Shen et al., |
| Acc8558 | qBlsr5a: 5号染色体ID73-ID79 (30 kb) | Xie et al., |
| Carolina Gold Select | Xo1: 1090 kb | Triplett et al., |
| ZH11 | AtNPR1 | Xu et al., |
| TP309 | XCRK: 1号染色体上 | 张玉霞等, |
| Acc8558 | qBlsr3d: LOC_Os3g03570 (81 kb) | Wang et al., |
| DP3 | bls1: 6号染色体上(21 kb) | Ma et al., |
| DY19 | bls2: 2号染色体RM13592-RM13599 (240 kb) | 罗登杰等, |
| X455 | Xo2: 2号染色体RM12941-M6-1 (110 kb) | Chen et al., |
| WP1, 9311 | qBLS4.1: 4号染色体上(521 kb) | 韦敏益等, |
Table 2 Resistance (R) loci and genes for bacterial leaf streak (BLS) in rice
| 来源 | 位点与基因 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 玉米 | Rxo1 | Zhao et al., |
| Minghui 63 | OsWRKY45-2 | Tao et al., |
| ZH11 | OsMPK6 | Shen et al., |
| Acc8558 | qBlsr5a: 5号染色体ID73-ID79 (30 kb) | Xie et al., |
| Carolina Gold Select | Xo1: 1090 kb | Triplett et al., |
| ZH11 | AtNPR1 | Xu et al., |
| TP309 | XCRK: 1号染色体上 | 张玉霞等, |
| Acc8558 | qBlsr3d: LOC_Os3g03570 (81 kb) | Wang et al., |
| DP3 | bls1: 6号染色体上(21 kb) | Ma et al., |
| DY19 | bls2: 2号染色体RM13592-RM13599 (240 kb) | 罗登杰等, |
| X455 | Xo2: 2号染色体RM12941-M6-1 (110 kb) | Chen et al., |
| WP1, 9311 | qBLS4.1: 4号染色体上(521 kb) | 韦敏益等, |
| 来源 | 基因 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| Mudanjiang 8, Dongjin | OsWRKY45-1 | Tao et al., |
| Nipponbare | OsSULTR3;6 | Cernadas et al., |
| Nipponbare | Os09g29100 | Cai et al., |
| ZH11 | OsTFIIAγ5, OsTFIIAγ5V39E | Hui et al., |
| Guihong 1, ZH11 | OsSULTR3;6 | Ni et al., |
| IRBB10 | OsSULRT3;6 | Xu et al., |
| ZH11 | OsF3H03g | Wu et al., |
| ZH11 | OsBLS6.2 | Xie et al., |
| Nipponbare, ZH11 | OsHXK5, OsSULRT3;6 | Wang et al., |
Table 3 Susceptibility (S) genes for bacterial leaf streak (BLS) in rice
| 来源 | 基因 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|
| Mudanjiang 8, Dongjin | OsWRKY45-1 | Tao et al., |
| Nipponbare | OsSULTR3;6 | Cernadas et al., |
| Nipponbare | Os09g29100 | Cai et al., |
| ZH11 | OsTFIIAγ5, OsTFIIAγ5V39E | Hui et al., |
| Guihong 1, ZH11 | OsSULTR3;6 | Ni et al., |
| IRBB10 | OsSULRT3;6 | Xu et al., |
| ZH11 | OsF3H03g | Wu et al., |
| ZH11 | OsBLS6.2 | Xie et al., |
| Nipponbare, ZH11 | OsHXK5, OsSULRT3;6 | Wang et al., |
| [1] | Caarls L, Pieterse CMJ, Van Wees SCM (2015). How salicylic acid takes transcriptional control over jasmonic acid signaling. Front Plant Sci 6,170. |
| [2] | Cai LL, Cao YY, Xu ZY, Ma WX, Zakria M, Zou LF, Cheng ZQ, Chen GY (2017). A transcription activator-like effector Tal7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola activates rice gene Os09g29100 to suppress rice immunity. Sci Rep 7, 5089. |
| [3] | Cai LL, Ma WX, Zou LF, Xu XM, Xu ZY, Deng CY, Qian W, Chen XB, Chen GY (2022). Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola response regulator VemR is co-opted by the sensor kinase CheA for phosphorylation of multiple pathogenicity-related targets. Front Microbiol 13, 928551. |
| [4] | Cernadas RA, Doyle EL, Niño-Liu DO, Wilkins KE, Bancroft T, Wang L, Schmidt CL, Caldo R, Yang B, White FF, Nettleton D, Wise RP, Bogdanove AJ (2014). Code- assisted discovery of TAL effector targets in bacterial leaf streak of rice reveals contrast with bacterial blight and a novel susceptibility gene. PLoS Pathog 10, e1003972. |
| [5] | Chaloner TM, Gurr SJ, Bebber DP (2021). Plant pathogen infection risk tracks global crop yields under climate chan- ge. Nat Clim Change 11, 710-715. |
| [6] | Chen K, Shi ZQ, Zhang SW, Wang YX, Xia X, Jiang Y, Gull S, Chen L, Guo H, Wu TK, Zhang HY, Liu JL, Kong WW (2022a). Methylation and expression of rice NLR genes after low temperature stress. Gene 845, 146830. |
| [7] | Chen S, Feng AQ, Wang CY, Zhao JL, Feng JQ, Chen B, Yang JY, Wang WJ, Zhang MY, Chen KL, Chen WQ, Su J, Liu B, Zhu XY (2022b). Identification and fine-mapping of Xo2, a novel rice bacterial leaf streak resistance gene. Theor Appl Genet 135, 3195-3209. |
| [10] | Chen X, Tang B, Zhao YC, Liu FQ (2025). Research advance on bacterial leaf streak of rice. J Nanjing Agric Univer 48, 46-57. (in Chinese) |
| 陈贤, 汤宝, 赵延存, 刘凤权 (2025). 水稻细菌性条斑病的研究进展. 南京农业大学学报 48, 46-57. | |
| [11] | Chen ZY, Liu YF, Liu FQ, Luo CP, Nie YF (2009). Resistant evaluation of rice bacterial leaf streak and virulence differentiation of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola in Jiang- su. Acta Phytophy Sin 36, 315-318. (in Chinese) |
| 陈志谊, 刘永峰, 刘凤权, 罗楚平, 聂亚峰 (2009). 江苏省水稻品种细菌性条斑病抗性评价与病原菌致病力分化. 植物保护学报 36, 315-318. | |
| [10] | Deb S, Ghosh P, Patel HK, Sonti RV (2020). Interaction of the Xanthomonas effectors XopQ and XopX results in induction of rice immune responses. Plant J 104, 332-350. |
| [11] | Ding F, Tang M, Deng ZQ, Yuan L, Peng LL, Huang JY, Wei X, Liu F (2023). Effect of exogenous methyl jasmonate on resistance to bacterial leaf stripe in rice. Guangdong Agric Sci 50(12), 131-139. (in Chinese) |
| 丁法, 唐敏, 邓子秋, 袁霖, 彭莉莉, 黄洁怡, 韦璇, 刘芳 (2023). 外源茉莉酸甲酯对水稻细菌性条斑病抗性的影响. 广东农业科学 50(12), 131-139. | |
| [12] | Fang Y, Ding D, Gu YJ, Jia QW, Zheng QL, Qian Q, Wang YX, Rao YC, Mao YJ (2023). Identification of QTLs conferring resistance to bacterial diseases in rice. Plants (Basel) (Basel) 12, 2853. |
| [13] | Fang YL, Tian CY, Su RY, Liu YP, Wang CL, Chen XF, Guo W, Ji ZY (2024). Mining and preliminary mapping of rice resistance genes against bacterial leaf streak. Chin Bull Bot 59, 1-9. (in Chinese) |
|
方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远 (2024). 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位. 植物学报 59, 1-9.
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Fu J, Liu HB, Li Y, Yu HH, Li XH, Xiao JH, Wang SP (2011). Manipulating broad-spectrum disease resistance by suppressing pathogen-induced auxin accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol 155, 589-602.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Guo YH, Xu ZG, Hu BS, Shen XP, Chen ZY, Liu YF (2004). Virulence differentiation of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzi- cola in southern region of China. Chin J Rice Sci 18, 83-85. (in Chinese) |
| 郭亚辉, 许志刚, 胡白石, 沈秀萍, 陈志谊, 刘永峰(2004). 中国南方水稻条斑病菌小种分化研究. 中国水稻科学 18, 83-85. | |
| [16] | He T, Yu JH, Zhang LX, Tan GJ (2014). Isolation and pathotype monitoring of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola population in Anhui province. Chin Agric Sci Bull 30(10)299-302. |
| 何涛, 于建红, 张立新, 檀根甲 (2014). 安徽省水稻条斑病菌种群的分离及其致病型监测. 中国农学通报 30(10)299-302. | |
| [17] |
Hui SG, Liu HL, Zhang M, Chen D, Li QQ, Tian JJ, Xiao JH, Li XH, Wang SP, Yuan M (2019). The host basal transcription factor IIA subunits coordinate for facilitating infection of TALEs-carrying bacterial pathogens in rice. Plant Sci 284, 48-56.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Hummel AW, Wilkins KE, Wang L, Cernadas RA, Bogdanove AJ (2017). A transcription activator-like effector from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola elicits dose-dependent resistance in rice. Mol Plant Pathol 18, 55-66.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Ji ZY, Ji CH, Liu B, Zou LF, Chen GY, Yang B (2016). Interfering TAL effectors of Xanthomonas oryzae neutralize R-gene-mediated plant disease resistance. Nat Commun 7, 13435. |
| [20] | Ji ZY, Zakria M, Zou LF, Xiong L, Li Z, Ji GH, Chen GY (2014). Genetic diversity of transcriptional activator-like effector genes in Chinese isolates of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Phytopathology 104, 672-682. |
| [21] | Jin HB, Wang DW, Wang XF (2023). A novel module regulating ROS in NLR-mediated immunity. Trends Plant Sci 28, 512-514. |
| [22] | Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323-329. |
| [23] |
Jones JDG, Staskawicz BJ, Dangl JL (2024). The plant immune system: from discovery to deployment. Cell 187, 2095-2116.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Li S, Wang YP, Wang SZ, Fang AF, Wang JY, Liu LJ, Zhang K, Mao YL, Sun WX (2015). The type III effector AvrBs2 in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola suppresses rice immunity and promotes disease development. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28, 869-880. |
| [25] | Li XB, Niu GQ, Fan YH, Liu WY, Wu Q, Yu C, Wang J, Xiao YH, Hou L, Jin D, Chen S, Hu RY, Yang YM, Pei Y (2023). Synthetic dual hormone-responsive promoters enable engineering of plants with broad-spectrum resistance. Plant Commun 4, 100596. |
| [26] | Li XQ, Zhang SJ, Wang CY, Ren B, Yan F, Li SF, Spetz C, Huang JG, Zhou XP, Zhou HB (2025). Efficient in situ epitope tagging of rice genes by nuclease-mediated prime editing. Plant Cell 37, koae316. |
| [27] | Li XS, Zou LF, Cai YH, Huang RR, Hua JL (2017). Pathotype monitoring of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola and resistance identification of rice varieties to bacterial leaf streak in Jiangxi province. Acta Phytopathol Sin 47, 808-815. (in Chinese) |
|
李信申, 邹丽芳, 蔡耀辉, 黄瑞荣, 华菊玲 (2017). 江西省细菌性条斑病菌的致病型划分和水稻抗性资源的鉴定. 植物病理学报 47, 808-815.
DOI |
|
| [28] | Li YR, Che YZ, Zou HS, Cui YP, Guo W, Zou LF, Biddle EM, Yang CH, Chen GY (2011). Hpa2 required by HrpF to translocate Xanthomonas oryzae transcriptional activator-like effectors into rice for pathogenicity. Appl Environ Microbiol 77, 3809-3818. |
| [29] | Liang CY, Li DC, Yi JP, Xu ZG (1994). Studies on virulence types of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola collected from diseased area in China. J Nanjing Agric Univer 17, 48-52. |
| [30] | Liang D, Yang DY, Li T, Zhu Z, Yan BX, He Y, Li XY, Zhai KR, Liu JY, Kawano Y, Deng YW, Wu XN, Liu JZ, He ZH (2025). A PRA-Rab trafficking machinery modulates NLR immune receptor plasma membrane microdomain anchoring and blast resistance in rice. Sci Bull 70, 733-747. |
| [31] | Liao ZX, Li JY, Mo XY, Ni Z, Jiang W, He YQ, Huang S (2020). Type III effectors xopN and avrBS2 contribute to the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola strain GX01. Res Microbiol 171, 102-106. |
| [32] | Liu HF, Lu CC, Li Y, Wu T, Zhang BG, Liu BY, Feng WJ, Xu Q, Dong HS, He SY, Chu ZH, Ding XH (2022a). The bacterial effector AvrRxo1 inhibits vitamin B6 biosynthesis to promote infection in rice. Plant Commun 3, 100324. |
| [33] | Liu LY, Li Y, Xu ZY, Chen H, Zhang JY, Manion B, Liu FQ, Zou LF, Fu ZQ, Chen GY (2022b). The Xanthomonas type III effector XopAP prevents stomatal closure by interfering with vacuolar acidification. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 1994-2008. |
| [34] | Liu W, Liu FD, Lu ZH, Lu DB, Wang SG, Wang XF, Xue J, He XY (2022). Rice bacterial leaf streak: research progress on occurrence and development and resistance genes. J Agric 12(10), 15-20. (in Chinese) |
|
刘维, 刘芳丹, 陆展华, 卢东柏, 王石光, 王晓飞, 薛皦, 何秀英 (2022). 水稻细条病的发生发展及抗病基因研究进展. 农学学报 12(10), 15-20.
DOI |
|
| [35] | Liu YX, Cheng GY, Tu LC, Sun XC, Hu ML, Li YH (2004). Comparison of the pathogenicity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola causing streak blight of rice in four provinces in central South China. J Huazhong Agric Univer 23, 504-506. (in Chinese) |
| 刘友勋, 成国英, 涂立超, 孙新城, 胡明亮, 李耀洪 (2004). 中南4省水稻细菌性条斑病菌致病型的比较. 华中农业大学学报 23, 504-506. | |
| [36] | Liu YY, Chen XF, Qian Q, Gao ZY (2025). Advances in molecular mechanisms regulating panicle development in rice. Biotechnol Bull 41(5), 1-13. (in Chinese) |
|
刘园园, 陈析丰, 钱前, 高振宇 (2025). 水稻穗发育调控的分子机制研究进展. 生物技术通报 41(5), 1-13.
DOI |
|
| [37] | Liu YY, Ding Y, Zheng JQ, Wan BJ, Cao T, Liu XH (2023). Research progress on PRRs and NLRs mediated immune signaling pathways in plants. Jiangsu Agric Sci 51(8), 43-50. (in Chinese) |
| 刘艳艳, 丁颖, 郑佳秋, 宛柏杰, 曹婷, 刘兴华 (2023). 植物PRRs和NLRs介导的免疫信号通路研究进展. 江苏农业科学 51(8), 43-50. | |
| [38] | Lu H, Patil P, Van Sluys MA, White FF, Ryan RP, Dow JM, Rabinowicz P, Salzberg SL, Leach JE, Sonti R, Brendel V, Bogdanove AJ (2008). Acquisition and evolution of plant pathogenesis-associated gene clusters and candidate determinants of tissue-specificity in Xanthomonas. PLoS One 3, e3828. |
| [39] | Luo DJ, Wan Y, Qin XM, Shi LJ, Zhang H, Li RB, Liu F (2021). Development of SSR molecular markers for bacterial leaf streak resistance gene bls2 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Southern Agric 52, 1167-1173. (in Chinese) |
| 罗登杰, 万瑶, 覃雪梅, 施力军, 张慧, 李容柏, 刘芳 (2021). 水稻细菌性条斑病抗性基因bls2 SSR分子标记开发. 南方农业学报 52, 1167-1173. | |
| [40] | Ma HG, Chen J, Zhang ZZ, Ma L, Yang ZY, Zhang QL, Li XH, Xiao JH, Wang SP (2017). MAPK kinase 10.2 promotes disease resistance and drought tolerance by activating different MAPKs in rice. Plant J 92, 557-570. |
| [41] | Ma ZF, Qin G, Zhang YX, Chi L, Wei MY, Cen ZL, Yan Y, Luo TP, Li ZJ, Liang HF, Huang DH, Deng GF (2021). Bacterial Leaf Streak 1 encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase confers resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Plant J 107, 1084-1101. |
| [42] | Mei FQ, Wu XZ, Yao CX, Li LP, Wang L, Chen QY (1988). Rice croppinng regionalization in China. Chin J Rice Sci 2, 97-110. (in Chinese) |
| 梅方权, 吴宪章, 姚长溪, 李路平, 王磊, 陈秋云 (1988). 中国水稻种植区划. 中国水稻科学 2, 97-110. | |
| [43] | Mukherjee R, Ghosh A, Chakraborty C, De JN, Mishra DP (2025). Rice leaf disease identification and classification using machine learning techniques: a comprehensive review. Eng Appl Artif Intell 139, 109639. |
| [44] |
Naskar S, Hohl M, Tassinari M, Low HH (2021). The structure and mechanism of the bacterial type II secretion system. Mol Microbiol 115, 412-424.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Ni Z, Cao YQ, Jin X, Fu ZM, Li JY, Mo XY, He YQ, Tang JL, Huang S (2021). Engineering resistance to bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak in rice. Rice 14, 38.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Niño-Liu DO, Ronald PC, Bogdanove AJ (2006). Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: model pathogens of a model crop. Mol Plant Pathol 7, 303-324.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Pfeilmeier S, Werz A, Ote M, Bortfeld-Miller M, Kirner P, Keppler A, Hemmerle L, Gäbelein CG, Petti GC, Wolf S, Pestalozzi CM, Vorholt JA (2024). Leaf microbiome dysbiosis triggered by T2SS-dependent enzyme secretion from opportunistic Xanthomonas pathogens. Nat Microbiol 9, 136-149.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Qian GL, Zhou YJ, Zhao YC, Song ZW, Wang SY, Fan JQ, Hu BS, Venturi V, Liu FQ (2013). Proteomic analysis reveals novel extracellular virulence-associated proteins and functions regulated by the diffusible signal factor (DSF) in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. J Proteome Res 12, 3327-3341. |
| [49] | Read AC, Hutin M, Moscou MJ, Rinaldi FC, Bogdanove AJ (2020). Cloning of the rice Xo1 resistance gene and interaction of the Xo1 protein with the defense-suppressing Xanthomonas effector Tal2h. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 33, 1189-1195. |
| [50] | Read AC, Rinaldi FC, Hutin M, He YQ, Triplett LR, Bogdanove AJ (2016). Suppression of Xo1-mediated disease resistance in rice by a truncated, Non-DNA-binding TAL effector of Xanthomonas oryzae. Front Plant Sci 7, 1516. |
| [51] | Sattayachiti W, Wanchana S, Arikit S, Nubankoh P, Patarapuwadol S, Vanavichit A, Darwell CT, Toojinda T (2020). Genome-wide association analysis identifies resistance loci for bacterial leaf streak resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants (Basel) 9, 1673. |
| [52] |
Scholze H, Boch J (2011). TAL effectors are remote controls for gene activation. Curr Opin Microbiol 14, 47-53.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Sharada K, Choudhary SL, Harikrishna T, Dixit RS, Suman SK, Chakravarthi MA, Bhagyalakshmi L (2025). GeoAgriGuard: AI-driven pest and disease management with remote sensing for global food security. Remote Sens Earth Syst Sci 8, 409-422. |
| [54] | Shen XL, Yuan B, Liu HB, Li XH, Xu CG, Wang SP (2010). Opposite functions of a rice mitogen-activated protein kinase during the process of resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant J 64, 86-99. |
| [55] | Shi LJ, Luo DJ, Zhao Y, Cen ZL, Liu F, Li RB (2019). Genetic analysis and mapping of bacterial leaf streak resistance genes in Oryzae rufipogon Griff. J South China Agric Univer 40(2), 1-5. (in Chinese) |
| 施力军, 罗登杰, 赵严, 岑贞陆, 刘芳, 李容柏 (2019). 普通野生稻抗细菌性条斑病基因的遗传分析与定位. 华南农业大学学报 40(2), 1-5. | |
| [56] | Tan NW, Huang YC, Miao WG, Zhang QX, Wu T (2024). Type III secretion effectors of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola: the arsenal to attack equivalent rice defense for invasion. Agronomy (Basel) 14, 1881. |
| [57] | Tang DZ, Wu WR, Li WM, Lu H, Worland AJ (2000). Mapping of QTLs conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Theor Appl Genet 101, 286-291. |
| [58] |
Tao Z, Liu HB, Qiu DY, Zhou Y, Li XH, Xu CG, Wang SP (2009). A pair of allelic WRKY genes play opposite roles in rice-bacteria interactions. Plant Physiol 151, 936-948.
DOI PMID |
| [59] | Teper D, Pandey SS, Wang N (2021). The HrpG/HrpX regulon of xanthomonads—an insight to the complexity of regulation of virulence traits in phytopathogenic bacteria. Microorganisms 9, 187. |
| [60] |
Timilsina S, Potnis N, Newberry EA, Liyanapathiranage P, Iruegas-Bocardo F, White FF, Goss EM, Jones JB (2020). Xanthomonas diversity, virulence and plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 18, 415-427.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Triplett LR, Cohen SP, Heffelfinger C, Schmidt CL, Huerta AI, Tekete C, Verdier V, Bogdanove AJ, Leach JE (2016). A resistance locus in the American heirloom rice variety Carolina Gold Select is triggered by TAL effectors with diverse predicted targets and is effective against African strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzicola Plant J 87, 472-483. |
| [62] | Wang JX, Liao ZX, Jin X, Liao LD, Zhang YQ, Zhang RB, Zhao XY, Qin HJ, Chen JH, He YQ, Zhuang CX, Tang JL, Huang S (2024). Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola effector Tal10a directly activates rice OsHXK5 expression to facilitate pathogenesis. Plant J 119, 2423-2436. |
| [63] | Wang S, Xie XF, Zhang Z, Guan HZ, Mao DM, Wu WR, Chen ZW (2020a). Fine mapping of qBlsr3d, a quantitative trait locus conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Crop Sci 60, 1854-1862. |
| [64] | Wang SX, Ma GZ, Wei LF, Ji GH (2010). Virulence differentiation of strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola in southwest of China. J Hunan Agric Univer (Nat Sci) 36, 188-191. (in Chinese) |
| 王绍雪, 马改转, 魏兰芳, 姬广海(2010). 西南地区水稻细菌性条斑病菌致病力的分化. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版) 36, 188-191. | |
| [65] | Wang W, Feng BM, Zhou JM, Tang DZ (2020b). Plant immune signaling: advancing on two frontiers. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 2-24. |
| [66] | Wang YB, Wang HF, Peng ZH (2021). Rice diseases detection and classification using attention based neural network and bayesian optimization. Exper Syst Appl 178, 114770. |
| [67] |
Wei MY, Ma ZF, Huang DH, Qin YY, Liu C, Lu YP, Luo TP, Li ZJ, Zhang YX, Qin G (2023). QTL-Seq analysis for identification of resistance locus to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Chin J Rice Sci 37, 133-141. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
韦敏益, 马增凤, 黄大辉, 秦媛媛, 刘驰, 卢颖萍, 罗同平, 李振经, 张月雄, 秦钢 (2023). 基于QTL-Seq的水稻抗细菌性条斑病QTL定位. 中国水稻科学 37, 133-141.
DOI |
|
| [68] | Wilkins KE, Booher NJ, Wang L, Bogdanove AJ (2015). TAL effectors and activation of predicted host targets distinguish Asian from African strains of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola while strict conservation suggests universal importance of five TAL effectors. Front Plant Sci 6, 536. |
| [69] | Wu T, Zhang HM, Yuan B, Liu HF, Kong LG, Chu ZH, Ding XH (2022). Tal2b targets and activates the expression of OsF3H03g to hijack OsUGT74H4 and synergistically interfere with rice immunity. New Phytol 233, 1864-1880. |
| [70] | Xie HB, Lin CZ, Lu WY, Han ZK, Wei DH, Huo X, Li TJ, Zhang J, He YQ, Chen C, Wang H, Guo T, Wang JF (2023). OsBLS6.2: a rice bacterial leaf streak resistance gene identified by GWAS and RNA-seq. Crop J 11, 1862-1871. |
| [71] | Xie XF, Chen ZW, Cao JL, Guan HZ, Lin DG, Li CL, Lan T, Duan YL, Mao DM, Wu WR (2014). Toward the positional cloning of qBlsr5a, a QTL underlying resistance to bacterial leaf streak, using overlapping sub-CSSLs in rice. PLoS One 9, e95751. |
| [72] | Xu GY, Yuan M, Ai CR, Liu LJ, Zhuang E, Karapetyan S, Wang SP, Dong XN (2017). uORF-mediated translation allows engineered plant disease resistance without fitness costs. Nature 545, 491-494. |
| [73] | Xu XM, Li Y, Xu ZY, Yan JL, Wang Y, Wang YJ, Cheng GY, Zou LF, Chen GY (2022). TALE-induced immunity against the bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Phytopathol Res 4, 47. |
| [74] | Xu XM, Shen LL, Yan JL, Wang Y, Xu ZY, Chen GY (2023). Advances in the occurrence and control of rice bacterial leaf blight and bacterial leaf streak in China. Plant Prot 49(5), 43-49. (in Chinese) |
| 徐夏萌, 沈丽丽, 闫佳丽, 王勇, 徐正银, 陈功友 (2023). 我国水稻白叶枯病和条斑病发生与防控研究进展. 植物保护 49(5), 43-49. | |
| [75] | Xu XM, Xu ZY, Li ZY, Zakria M, Zou LF, Chen GY (2021). Increasing resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice by editing the promoter of susceptibility gene OsSULRT3;6. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 1101-1103. |
| [76] |
Xu ZY, Xu XM, Gong Q, Li ZY, Li Y, Wang S, Yang YY, Ma WX, Liu LY, Zhu B, Zou LF, Chen GY (2019). Engineering broad-spectrum bacterial blight resistance by simultaneously disrupting variable TALE-binding elements of multiple susceptibility genes in rice. Mol Plant 12, 1434-1446.
DOI PMID |
| [77] |
Yamada K, Yamaguchi K, Yoshimura S, Terauchi A, Kawasaki T (2017). Conservation of chitin-induced MAPK signaling pathways in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 58, 993-1002.
DOI PMID |
| [78] | Yang J, Wang X, Wang YF, Liu Q, Wang YT, Zhang JH, Wei LF, Ji GH (2020). Pathotypes differentiation of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola and identification of rice varieties resistant to bacterial leaf streak in Yunnan province. Acta Phytopathol Sin 50, 218-227. (in Chinese) |
|
杨俊, 王星, 王彦芳, 刘棋, 汪娅婷, 张晋豪, 魏兰芳, 姬广海 (2020). 云南省水稻细菌性条斑病菌的致病型划分和水稻抗性资源的鉴定. 植物病理学报 50, 218-227.
DOI |
|
| [79] | Yu XQ, Niu HQ, Liu C, Wang HL, Yin WL, Xia XL (2024). PTI-ETI synergistic signal mechanisms in plant immunity. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 2113-2128. |
| [80] | Yun MH, Torres PS, El Oirdi M, Rigano LA, Gonzalez- Lamothe R, Marano MR, Castagnaro AP, Dankert MA, Bouarab K, Vojnov AA (2006). Xanthan induces plant susceptibility by suppressing callose deposition. Plant Phy- siol 141, 178-187. |
| [81] | Zhang RS, Chen ZY, Liu YF (2011). Virulence differentiation of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola in rice at seedling and adult stages. Jiangsu J Agric Sci 27, 996-999. (in Chinese) |
| 张荣胜, 陈志谊, 刘永锋 (2011). 细菌性条斑病菌致病力分化及其对水稻幼苗和成株的致病力差异. 江苏农业学报 27, 996-999. | |
| [82] | Zhang YB, Wei C, Jiang WD, Wang L, Li CR, Wang YY, Dow JM, Sun WX (2013). The HD-GYP domain protein RpfG of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola regulates synthesis of extracellular polysaccharides that contribute to biofilm formation and virulence on rice. PLoS One 8, e59428. |
| [83] | Zhang YX, Cui YC, Li Y, Zhou D, Chen L (2018). Functional analysis of XCRK gene in the interaction between rice and bacterial leaf streak strain. J Xiamen Univer 57, 201-207. (in Chinese) |
| 张玉霞, 崔玉超, 李燕, 周丹, 陈亮 (2018). XCRK基因在水稻与细菌性条斑病菌互作中的功能解析. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版) 57, 201-207. | |
| [84] |
Zhao BY, Lin XH, Poland J, Trick H, Leach J, Hulbert S (2005). A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak disease in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 15383-15388.
DOI PMID |
| [85] | Zheng Q, Huang WJ, Xia Q, Dong YY, Ye HC, Jiang H, Chen SS, Huang SY (2023). Remote sensing monitoring of rice diseases and pests from different data sources: a review. Agronomy 13, 1851. |
| [86] | Zhou D, Zou LF, Zou HS, Chen GY (2011). Identification of extracellular polysaccharide-associated genes in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Acta Microbiol Sin 51, 1334-1341. (in Chinese) |
| 周丹, 邹丽芳, 邹华松, 陈功友(2011). 水稻条斑病菌胞外多糖相关基因的鉴定. 微生物学报 51, 1334-1341. | |
| [87] | Zhou LH, Yang J, Li M, Ji GH (2014). A study on the genetic diversity of rice leaf blight pathogen. Acta Agric Univer Jiangxiensis 36, 750-759. (in Chinese) |
| 周丽洪, 杨俊, 李淼, 姬广海 (2014). 水稻条斑病菌遗传多样性研究. 江西农业大学学报 36, 750-759. | |
| [88] |
Zhu TT, Wu XF, Yuan GX, Wang DL, Bhadauria V, Peng YL, Liu JF, Zhang X (2025). A resurfaced sensor NLR confers new recognition specificity to non-MAX effectors. J Integr Plant Biol 67, 11-14.
DOI |
| [89] |
Zhu XY, Chen L, Zhang ZY, Li JJ, Zhang HL, Li ZC, Pan YH, Wang XQ (2023). Genetic-based dissection of resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice by GWAS. BMC Plant Biol 23, 396.
DOI PMID |
| [90] | Zou HS, Song X, Zou LF, Yuan L, Li YR, Guo W, Che YZ, Zhao WX, Duan YP, Chen GY (2012). EcpA, an extracellular protease, is a specific virulence factor required by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola but not by X. oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Microbiology (Reading) 158, 2372-2383. |
| [1] | Yanli Fang, Chuanyu Tian, Ruyi Su, Yapei Liu, Chunlian Wang, Xifeng Chen, Wei Guo, Zhiyuan Ji. Mining and Preliminary Mapping of Rice Resistance Genes Against Bacterial Leaf Streak [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [2] | Ma Lu, Fang Yuan, Xiao Saqing, Zhou Chun, Jin Zhelun, Ye Wenlan, Rao Yuchun. QTL Exploration of Bacterial Leaf Streak and Their Gene Expression in Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(4): 468-476. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||