

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (5): 691-708.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23171 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23171
• INVITED REVIEWS • Next Articles
Xiang Song†, Luyao Wang†, Boxiao Fu, Shuangda Li, Yuanyuan Wei, Yan Hong*( ), Silan Dai*(
), Silan Dai*( )
)
Received:2023-12-22
Accepted:2024-03-18
Online:2024-09-10
Published:2024-08-19
Contact:
Yan Hong, Silan Dai
About author:First author contact: These authors contributed equally to this paper
CLC Number:
Xiang Song, Luyao Wang, Boxiao Fu, Shuangda Li, Yuanyuan Wei, Yan Hong, Silan Dai. Advances in Identification and Synthesis of Promoter Elements in Higher Plants[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 691-708.
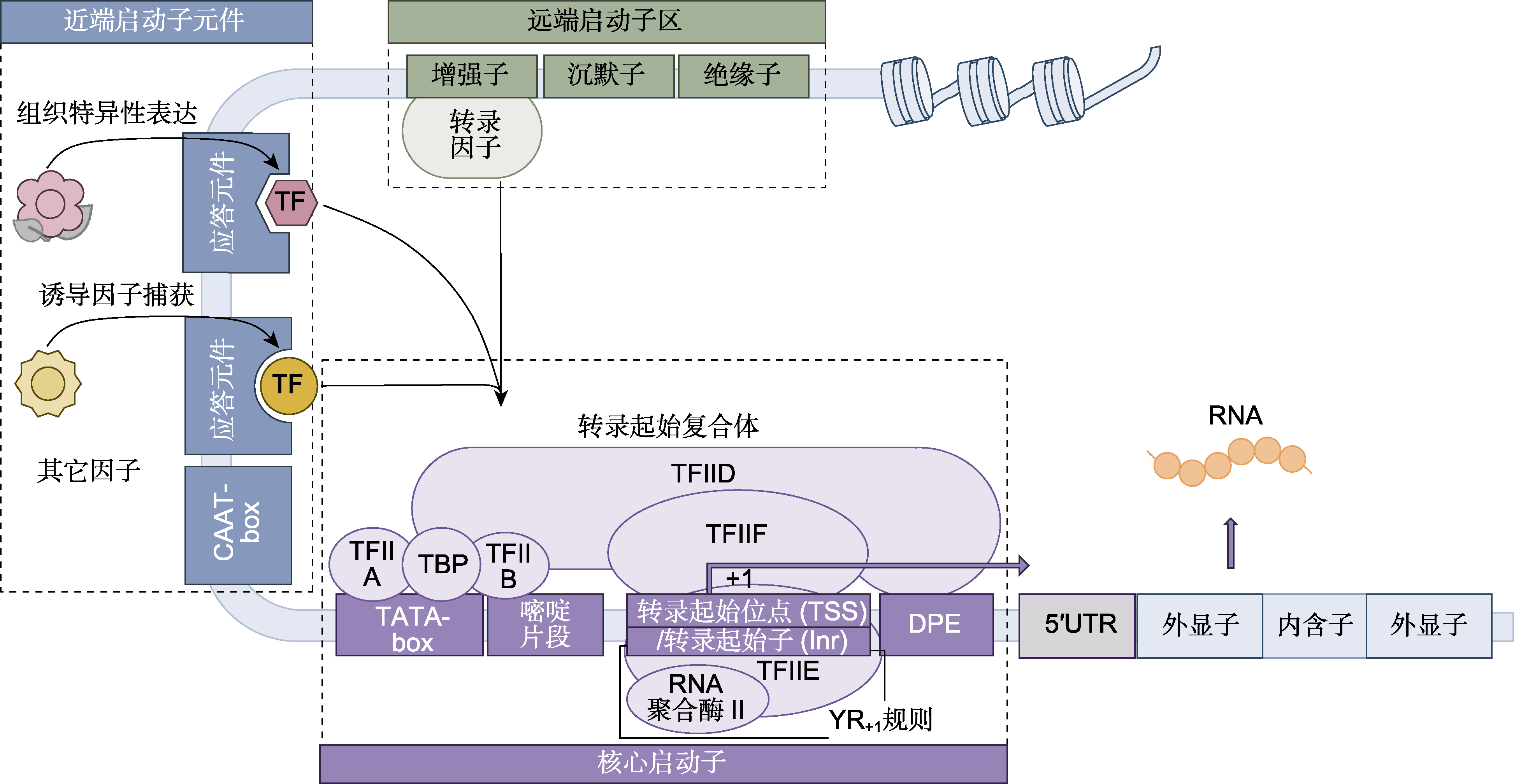
Figure 1 The structure and mode of actions of plant promoters (Chen and Xu, 2022; Yasmeen et al., 2023; Brooks et al., 2023) The promoter region of plants and RNA polymerase II are at the center of transcriptional regulation in plants. In the core promoter region, The TBP region of the general transcription factor TFIID recognizes the TATA-box and assembles with proteins such as TFIIF, TFIIE, and RNA polymerase II to form the transcription initiation complex that recognizes and binds TATA-box or downstream core promoter elements (DPE) to regulate the initiation of transcription together with transcription initiation sites (TSS) and other core elements. Some elements such as Y patch can enhance or stabilize promoter activity. Regulatory upstream elements and responsive elements (such as CAAT-box) bind to the regulated transcription factors and participate in the regulation of gene expression. Cis-acting elements such as enhancers exist on the upstream and downstream of genes which regulate gene expression through the synergistic effect of specific transcription factors.
| 元件类型 | 时空响应因子 | 元件名称 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 诱导型 | 生物因子 | 病原体 | W-box、S-box、D-box、EIRE、GCC-box、H-box、G-box、GST1、PRE2PRE4E-box、SARE、PR-1基序、ERE、NPR-1基序、JERE、E17元件、F元件、FELEMENT1 (大豆根瘤菌)、TDBA12NTCHN50 (TMV)和OSE1ROOTNODULE (根瘤菌) | |
| 创伤 | 20NTNTNOS、W-box、WIN、WRE、WUN-box和as-1-like | |||
| 物理因子 | 光 | 光质 | 10PEHVPSBD (蓝光、白光或UV-A光)、ACE (UV-B和UV-1/蓝光)和ELRE1 (UV) | |
| 光强 | 3AF1-box、AT-1 box、BOX-C、BOX-I、CPRF、CYTO位点、DE1、DRE (高光强胁迫)、G-box、GT2、HY5、I-box、LRE-box、MNF1、PAL-box、PI、PII、PRE、SITE1、SORLIPs、T-box、Z-DNA-forming序列和GT1基序 | |||
| 光周期 | EVENING | |||
| 温度 | 低温 | DRE、CARGATCONSENSUS、CBF、CRT、LTRE、TCA-like、CAT-box、HSE | ||
| 高温 | 和GAATTC | |||
| 干旱和盐胁迫 | ABAD、ABRE、ACGT、DRE、EMBP1、MYB1、MYB2和SRENTTTO1、NACR/HDZFR、MYBR/MYR、MBS、Erd1、TC-rich重复、GT1基序、E-box和STRE | |||
| 化学因子 | 激素 | 生长素 | RE、AuxRE、TGA元件、偶联元件CE1和CE3 | |
| 脱落酸 | ABRE、ABRC、ABRERATCAL、ABRELATERD1、偶联元件CEs和STRE | |||
| 细胞分裂素 | CANBNNAPA、MYBGAHV和CARG1 | |||
| 赤霉素 | GARE基序和as-1-like | |||
| 茉莉酸 | 20NTNTNOS、JASE1、JERE、T/G-box、ACG基序和as-1-like | |||
| 乙烯 | EIN3、EREGCC、ERE、GCCCORE、YREGIONNTPRB1B和Y区 | |||
| 水杨酸 | AS1、LS5、LS7、SARECAMV和TCA1基序 | |||
| 糖 | 284MOTIF、314MOTIF、ACGTABOX、TATCCAY基序、BBOXSITE1STPATS-box、CMSRE1和SREATMSD | |||
| 氮 | EM和GLMHVCHORD | |||
| 其它物质 | PAS (镉)、IDE1 (缺铁)、IRO (缺铁)和SURECORE (硫) | |||
| 组织特 异性 | 根 | RSE、ROOTMOTIFTAPOX1、RHERPATEXPA7、tef-box、TGA1a、MYCCONSENSUSAT、SORLIP1AT、RAV1AAT、LEAFYATAG、SURECOREATSULTR11、P1BS (根毛)、SP8BFIBSP8AIB (块根)、141NTG13 (根尖)、AUXREPSIAA4 (根尖)、OSE1ROOTNODULE (根瘤感染细胞)、OSE2ROOTNODULE (根瘤感染细胞)、WUSATAg (根尖分生组织)和XYLAT (核心木质部) | ||
| 茎 | ABF、as-2-box、BBOXSITE1STPAT (块茎)和TSSR (块茎) | |||
| 叶 | GATFLK、LPSE1、LSE1、GRA、RAV1 (莲座叶)和TCCAAAA基序(抑制基因在叶片表达) | |||
| 绿色组织 | GEAT、GSE1和GSE2 | |||
| 其它组织 | ACIIIPVPAL2 (维管束)、BS1 (维管束)、DOF结合位点(保卫细胞)和LPRSE1 (抑制基因在茎和种子中表达) | |||
| 花 | AGAMOUSAT、AGL1、CArG-box、TACPyAT和CHS启动子核心片段(PCHS、LCHS) GATA-box、CACT-box、CACG-box、MYBPLANT (花茎)和MYB26PS (花蕾) | |||
| 花粉 | PS区、POLLEN1LELAT52、POLLEN1、5256-box、定量元件、GTGANTG10、VOZ 结合序列、GTGA-box、telo-box、A9和TA29启动子片段(绒毡层)及anther box (花药) | |||
| 果实 | TAAAG基序、E-box、SEF结合位点、AGTTAGG、TGTCACA和SlHDC-A核心启动子区 | |||
| 种子 | Skn-1、RY基序、O2位点、E-box、AACACORE、ABAD、AMYBOX1、CAREOSREP1、EM、ESP、GLMHVCHORD、Sph元件、TGACGT基序、A27zn、Glb1、GCN4基序、CANBNNAPA和CATGTAA (大麦糊粉层) | |||
Table1 Cis-acting elements of promoters in higher plants
| 元件类型 | 时空响应因子 | 元件名称 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 诱导型 | 生物因子 | 病原体 | W-box、S-box、D-box、EIRE、GCC-box、H-box、G-box、GST1、PRE2PRE4E-box、SARE、PR-1基序、ERE、NPR-1基序、JERE、E17元件、F元件、FELEMENT1 (大豆根瘤菌)、TDBA12NTCHN50 (TMV)和OSE1ROOTNODULE (根瘤菌) | |
| 创伤 | 20NTNTNOS、W-box、WIN、WRE、WUN-box和as-1-like | |||
| 物理因子 | 光 | 光质 | 10PEHVPSBD (蓝光、白光或UV-A光)、ACE (UV-B和UV-1/蓝光)和ELRE1 (UV) | |
| 光强 | 3AF1-box、AT-1 box、BOX-C、BOX-I、CPRF、CYTO位点、DE1、DRE (高光强胁迫)、G-box、GT2、HY5、I-box、LRE-box、MNF1、PAL-box、PI、PII、PRE、SITE1、SORLIPs、T-box、Z-DNA-forming序列和GT1基序 | |||
| 光周期 | EVENING | |||
| 温度 | 低温 | DRE、CARGATCONSENSUS、CBF、CRT、LTRE、TCA-like、CAT-box、HSE | ||
| 高温 | 和GAATTC | |||
| 干旱和盐胁迫 | ABAD、ABRE、ACGT、DRE、EMBP1、MYB1、MYB2和SRENTTTO1、NACR/HDZFR、MYBR/MYR、MBS、Erd1、TC-rich重复、GT1基序、E-box和STRE | |||
| 化学因子 | 激素 | 生长素 | RE、AuxRE、TGA元件、偶联元件CE1和CE3 | |
| 脱落酸 | ABRE、ABRC、ABRERATCAL、ABRELATERD1、偶联元件CEs和STRE | |||
| 细胞分裂素 | CANBNNAPA、MYBGAHV和CARG1 | |||
| 赤霉素 | GARE基序和as-1-like | |||
| 茉莉酸 | 20NTNTNOS、JASE1、JERE、T/G-box、ACG基序和as-1-like | |||
| 乙烯 | EIN3、EREGCC、ERE、GCCCORE、YREGIONNTPRB1B和Y区 | |||
| 水杨酸 | AS1、LS5、LS7、SARECAMV和TCA1基序 | |||
| 糖 | 284MOTIF、314MOTIF、ACGTABOX、TATCCAY基序、BBOXSITE1STPATS-box、CMSRE1和SREATMSD | |||
| 氮 | EM和GLMHVCHORD | |||
| 其它物质 | PAS (镉)、IDE1 (缺铁)、IRO (缺铁)和SURECORE (硫) | |||
| 组织特 异性 | 根 | RSE、ROOTMOTIFTAPOX1、RHERPATEXPA7、tef-box、TGA1a、MYCCONSENSUSAT、SORLIP1AT、RAV1AAT、LEAFYATAG、SURECOREATSULTR11、P1BS (根毛)、SP8BFIBSP8AIB (块根)、141NTG13 (根尖)、AUXREPSIAA4 (根尖)、OSE1ROOTNODULE (根瘤感染细胞)、OSE2ROOTNODULE (根瘤感染细胞)、WUSATAg (根尖分生组织)和XYLAT (核心木质部) | ||
| 茎 | ABF、as-2-box、BBOXSITE1STPAT (块茎)和TSSR (块茎) | |||
| 叶 | GATFLK、LPSE1、LSE1、GRA、RAV1 (莲座叶)和TCCAAAA基序(抑制基因在叶片表达) | |||
| 绿色组织 | GEAT、GSE1和GSE2 | |||
| 其它组织 | ACIIIPVPAL2 (维管束)、BS1 (维管束)、DOF结合位点(保卫细胞)和LPRSE1 (抑制基因在茎和种子中表达) | |||
| 花 | AGAMOUSAT、AGL1、CArG-box、TACPyAT和CHS启动子核心片段(PCHS、LCHS) GATA-box、CACT-box、CACG-box、MYBPLANT (花茎)和MYB26PS (花蕾) | |||
| 花粉 | PS区、POLLEN1LELAT52、POLLEN1、5256-box、定量元件、GTGANTG10、VOZ 结合序列、GTGA-box、telo-box、A9和TA29启动子片段(绒毡层)及anther box (花药) | |||
| 果实 | TAAAG基序、E-box、SEF结合位点、AGTTAGG、TGTCACA和SlHDC-A核心启动子区 | |||
| 种子 | Skn-1、RY基序、O2位点、E-box、AACACORE、ABAD、AMYBOX1、CAREOSREP1、EM、ESP、GLMHVCHORD、Sph元件、TGACGT基序、A27zn、Glb1、GCN4基序、CANBNNAPA和CATGTAA (大麦糊粉层) | |||
| [1] | 曹译文, 宋阳, 渠可心, 王丕武 (2017). 大豆组织特异启动子的克隆与功能分析. 中国油料作物学报 39, 771-777. |
| [2] | 崔文文, 迟婧, 冯艳芳, 耿丽丽, 刘荣梅 (2020). 人工合成根特异启动子SRSP的功能分析. 生物工程学报 36, 700-706. |
| [3] | 邓泽宜, 宋想, 洪艳, 戴思兰 (2021). 启动子在观赏植物基因工程中的应用综述. 园艺学报 48, 1250-1264. |
| [4] | 方彦昊, 南文斌, 梁永书, 张汉马 (2015). 植物组织特异性基因表达技术及其应用. 植物生理学报 51, 797-805. |
| [5] | 胡朝阳, 唐培培, 邓炎春, 孙伟娟, 姚勤 (2019). 转录水平调控中的负调控元件——沉默子. 生命科学 31, 686-692. |
| [6] | 黄珂, 黄格格, 薛满德, 龙艳, 袁潜华, 裴新梧 (2018). 普通野生稻根特异启动子的克隆与鉴定. 生物技术通报 34(8), 87-92. |
| [7] | 康丹, 方小艳, 游腾飞, 王婷婷, 眭安平, 杨星勇 (2013). 染色体步移技术克隆已知序列侧翼启动子的研究进展. 农业生物技术学报 21, 355-366. |
| [8] | 李季, 黄天带, 华玉伟, 黄华孙 (2015). 启动子陷阱技术在植物启动子克隆研究中的应用. 热带农业科学 35(9), 46-50. |
| [9] | 梁晋刚, 张开心, 张旭冬, 王颢潜, 陈子言, 刘鹏程, 张秀杰 (2021). 中国农业转基因生物环境安全检测标准体系现状与展望. 中国油料作物学报 43, 1-14. |
| [10] | 刘晓娜, 付畅, 黄永芬 (2007). 种子特异性启动子研究进展. 植物学通报 24, 218-225. |
| [11] | 刘玉瑛, 张江丽 (2007). 真核生物启动子预测相关数据库资源概述. 安徽农业科学 35, 7418-7419. |
| [12] | 王海, 张倩, 方向东 (2011). 绝缘子调控基因的表达. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报 27, 493-498. |
| [13] | 王婧, 李冰, 刘翠翠, 朱阵, 张继瑜 (2014). 启动子结构和功能研究进展. 生物技术通报 (8), 40-45. |
| [14] | 王美华, 高洁, 李玉莲, 张淑娟, 宋国琦, 张荣志, 李玮, 李吉虎, 李根英 (2021). 籽粒高效特异性表达启动子的克隆与表达分析. 山东农业科学 53(5), 45-50. |
| [15] | 王睿, 朱梦琳, 高方远, 任鄄胜, 陆贤军, 任光俊, 林拥军 (2017). 水稻组织特异型人工合成启动子的设计、构建及功能鉴定. 作物学报 43, 789-794. |
| [16] | 夏江东, 程在全, 黄兴奇, 季鹏章, 熊华斌 (2006). 矮牵牛花色CHS-A基因启动子(Pchsa)的克隆及序列分析. 西南农业学报 19, 676-678. |
| [17] | 杨鹏芳, 段国琴, 胡晓炜, 缪秀梅, 南淑珍, 张丽静 (2018). 高等植物启动子研究概述. 分子植物育种 16, 1482-1493. |
| [18] | 昝新丽, 高英, 陈玉玲, 赵开军 (2013). 病原菌诱导型启动子顺式作用元件及其互作的转录因子. 植物学报 48, 219-229. |
| [19] | 曾晓玲, 赵昶灵, 文国松, 丁灿, 张洪玲, 徐率, 古朝山 (2018). 启动子结构、功能预测和验证方法的研究进展. 分子植物育种 16, 3915-3925. |
| [20] | 张春晓, 王文棋, 蒋湘宁, 陈雪梅 (2004). 植物基因启动子研究进展. 遗传学报 31, 1455-1464. |
| [21] | 张玺丽, 殷学仁, 李方, 陈昆松, 刘晓芬 (2017). MrMYB1- MrbHLH1: 一个有潜力的园艺植物转基因可视化报告基因. 园艺学报 44, 2296-2304. |
| [22] | 张雄飞, 刘雅莉, 娄倩, 祁银燕, 杜灵娟 (2013). 通过重叠PCR构建2个增强型植物花特异双向启动子. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版) 39, 34-41. |
| [23] | 张雪, 程荔书, 张军, 魏爽, 赵艳 (2023). 高等植物不同类型启动子及其相关顺式元件研究进展. 高师理科学刊 43(4), 60-67. |
| [24] | 郑少缘, 范燕萍 (2011). 花器官特异启动子的研究进展. 安徽农业科学 39, 19067-19069. |
| [25] | 智联腾, 赵倩, 敖光明, 于静娟 (2011). 天然彩色棉纤维特异表达启动子LTP3的克隆及其在烟草中的表达特异性. 热带生物学报 2, 133-137. |
| [26] | Alvarado MC, Zsigmond LM, Kovács I, Cséplö Á, Koncz C, Szabados LM (2004). Gene trapping with firefly luciferase in Arabidopsis. Tagging of stress-responsive genes. Plant Physiol 134, 18-27. |
| [27] | Amack SC, Antunes M (2020). CaMV35S promoter—a plant biology and biotechnology workhorse in the era of synthetic biology. Curr Plant Biol 24, 100179. |
| [28] | Amen RD (1968). A model of seed dormancy. Bot Rev 34, 1-31. |
| [29] | Annadana S, Beekwilder MJ, Kuipers G, Visser PB, Outchkourov N, Pereira A, Udayakumar M, De Jong J, Jongsma MA (2002). Cloning of the chrysanthemum UEP1promoter and comparative expression in florets and leaves of Dendranthema grandiflora.Transgenic Res 11, 437-445. |
| [30] | Antunes MS, Morey KJ, Smith JJ, Albrecht KD, Bowen TA, Zdunek JK, Troupe JF, Cuneo MJ, Webb CT, Hellinga HW, Medford JI (2011). Programmable ligand detection system in plants through a synthetic signal transduction pathway. PLoS One 6, e16292. |
| [31] | Araceli OA, Alfredo CR, Javier MM, Luis HE (2017). A phosphate starvation-driven bidirectional promoter as a potential tool for crop improvement and in vitro plant biotechnology. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 558-567. |
| [32] | Arnold CD, Gerlach D, Stelzer C, Boryń ŁM, Rath M, Stark A (2013). Genome-wide quantitative enhancer activity maps identified by STARR-seq. Science 339, 1074-1077. |
| [33] | Aysha J, Noman M, Wang FW, Liu WC, Zhou YG, Li HY, Li XW (2018). Synthetic promoters: designing the cis regulatory modules for controlled gene expression. Mol Biotechnol 60, 608-620. |
| [34] | Bade J, van Grinsven E, Custers J, Hoekstra S, Ponstein A (2003). T-DNA tagging in Brassica napus as an efficient tool for the isolation of new promoters for selectable marker genes. Plant Mol Biol 52, 53-68. |
| [35] | Bai JY, Wang X, Wu H, Ling F, Zhao Y, Lin YJ, Wang R (2020). Comprehensive construction strategy of bidirectional green tissue-specific synthetic promoters. Plant Bio-technol J 18, 668-678. |
| [36] | Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren JY, Li WW, Noble WS (2009). MEMESUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37, W202-W208. |
| [37] | Bartlett A, O’Malley RC, Huang SSC, Galli M, Nery JR, Gallavotti A, Ecker JR (2017). Mapping genome-wide transcription-factor binding sites using DAP-seq. Nat Protoc 12, 1659-1672. |
| [38] | Belcher MS, Vuu KM, Zhou A, Mansoori N, Ramos AA, Thompson MG, Scheller HV, Loqué D, Shih PM (2020). Design of orthogonal regulatory systems for modulating gene expression in plants. Nat Chem Biol 16, 857-865. |
| [39] | Beliaev DV, Yourieva NO, Tereshonok DV, Derevyagina MK, Meleshin AA (2023). Early blight resistance of transgenic potato plants expressing the ProSmAMP1gene for antimicrobial peptides under the control of a lightinducible cab promoter. Russ J Plant Physiol 70, 57. |
| [40] | Bernard V, Brunaud V, Lecharny A (2010). TC-motifs at the TATA-box expected position in plant genes: a novel class of motifs involved in the transcription regulation. BMC Genomics 11,166. |
| [41] | Blake MC, Jambou RC, Swick AG, Kahn JW, Azizkhan JC (1990). Transcriptional initiation is controlled by upstream GC-box interactions in a TATAA-less promoter. Mol Cell Biol 10, 6632-6641. |
| [42] | Brackmann K, Qi JY, Gebert M, Jouannet V, Schlamp T, Grünwald K, Wallner ES, Novikova DD, Levitsky VG, Agustí J, Sanchez P, Lohmann JU, Greb T (2018). Spatial specificity of auxin responses coordinates wood formation. Nat Commun 9, 875. |
| [43] | Brázda V, Bartas M, Bowater RP (2021). Evolution of diverse strategies for promoter regulation. Trends Genet 37, 730-744. |
| [44] | Brooks EG, Elorriaga E, Liu Y, Duduit JR, Yuan GL, Tsai CJ, Tuskan GA, Ranney TG, Yang XH, Liu WS (2023). Plant promoters and terminators for high-precision bioengineering. Biodes Res 5, 0013. |
| [45] | Butler JEF, Kadonaga JT (2002). The RNA polymerase II core promoter: a key component in the regulation of gene expression. Genes Dev 16, 2583-2592. |
| [46] | Chaturvedi CP, Sawant SV, Kiran K, Mehrotra R, Lodhi N, Ansari SA, Tuli R (2006). Analysis of polarity in the expression from a multifactorial bidirectional promoter designed for high-level expression of transgenes in plants. J Biotechnol 123, 1-12. |
| [47] | Che DS, Jensen S, Cai LM, Liu JS (2005). BEST: binding- site estimation suite of tools. Bioinformatics 21, 2909-2911. |
| [48] | Chen X, Guo LQ, Fan ZC, Jiang T (2008). W-AlignACE: an improved Gibbs sampling algorithm based on more accurate position weight matrices learned from sequence and gene expression/ChIP-chip data. Bioinformatics 24, 1121-1128. |
| [49] | Chen XZ, Xu YH (2022). Structural insights into assembly of transcription preinitiation complex. Curr Opin Struct Biol 75, 102404. |
| [50] | Chen YR, Yordanov YS, Ma C, Strauss S, Busov VB (2013). DR5 as a reporter system to study auxin response in Populus. Plant Cell Rep 32, 453-463. |
| [51] | Chow CN, Lee TY, Hung YC, Li GZ, Tseng KC, Liu YH, Kuo PL, Zheng HQ, Chang WC (2019). PlantPAN3. 0: a new and updated resource for reconstructing transcriptional regulatory networks from ChIP-seq experiments in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 47, D1155-D1163. |
| [52] | Dey N, Sarkar S, Acharya S, MaitiI B (2015). Synthetic promoters in planta. Planta 242, 1077-1094. |
| [53] | Diehl AG, Boyle AP (2018). Conserved and species-specific transcription factor co-binding patterns drive divergent gene regulation in human and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res 46, 1878-1894. |
| [54] | Du LJ, Lou Q, Zhang XF, Jiao SZ, Liu YL, Wang YJ (2014). Construction of flower-specific chimeric promoters and analysis of their activities in transgenicTorenia. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32, 234-245. |
| [55] | Efremova LN, Strelnikova SR, Gazizova GR, Minkina EA, Komakhin RA (2020). A synthetic strong and constitutive promoter derived from the Stellaria media pro-SmAMP1 and pro-SmAMP2 promoters for effective transgene expression in plants. Genes 11, 1407. |
| [56] | Fornes O, Castro-Mondragon JA, Khan A, van der Lee R, Zhang X, Richmond PA, Modi BP, Correard S, Gheorghe M, Baranasic D, Santana-Garcia W, Tan G, Chèneby J, Ballester B, Parcy F, Sandelin A, Lenhard B, Wasserman WW, Mathelier A (2020). JASPAR 2020: update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 48, D87-D92. |
| [57] | Gasch P, Fundinger M, Müller JT, Lee T, Bailey-Serres J, Mustroph A (2016). Redundant ERF-VII transcription factors bind to an evolutionarily conserved cis-motif to regulate hypoxia-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 28, 160-180. |
| [58] | Gupta D, Dey N, Leelavathi S, Ranjan R (2021). Development of efficient synthetic promoters derived from pararetrovirus suitable for translational research. Planta 253, 42. |
| [59] | Hamma lF, deLangen P, Bergon A, Lopez F, Ballester B (2022). ReMap 2022: a database of human, mouse, drosophila and Arabidopsis regulatory regions from an integrative analysis of DNA-binding sequencing experiments. Nucleic Acids Res 50, D316-D325. |
| [60] | Han ML, Yin J, Zhao YH, Sun XW, Meng JX, Zhou J, Shen T, Li HH, Zhang F (2020). How the color fades from Malus halliana flowers: transcriptome sequencing and DNA methylation analysis. Front Plant Sci 11, 576054. |
| [61] | He SF, Zhang ZW, Lu WY (2023). Natural promoters and promoter engineering strategies for metabolic regulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 50, kuac029. |
| [62] | He YB, Zhang T, Sun H, Zhan HD, Zhao YD (2020). A reporter for noninvasively monitoring gene expression and plant transformation. Hortic Res 7, 152. |
| [63] | Hemberg T (1949). Growth-inhibiting substances in terminal buds of Fraxinus. Physiol Plant 2, 37-44. |
| [64] | Hernández-Rodríguez CS, Ferré J, Herrero S (2009). Genomic structure and promoter analysis of pathogen- induced repat genes from Spodoptera exigua. Insect Mol Biol 18, 77-85. |
| [65] | Hiratsuka T, Makita Y, Yamamoto YY (2022). Sequence-based evaluation of promoter context for prediction of transcription start sites in Arabidopsis and rice. Sci Rep 12, 6976. |
| [66] | Hou L, Chen LJ, Wang JY, Xu DF, Dai LX, Zhang H, Zhao YX (2012). Construction of stress responsive synthetic promoters and analysis of their activity in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30, 1496-1506. |
| [67] | Huang WB, Wong JM, Bateman E (1996). TATA elements direct bi-directional transcription by RNA polymerases II and III. Nucleic Acids Res 24, 1158-1163. |
| [68] | In S, Lee HA, Woo J, Park E, Choi D (2020). Molecular characterization of apathogen-inducible bidirectional promoter from hot pepper (Capsicum annuum). Mol Plant Mic- robe Interact 33, 1330-1339. |
| [69] | Inukai S, Kock KH, Bulyk ML (2017). Transcription factor-DNA binding: beyond binding site motifs. Curr Opin Genet Dev 43, 110-119. |
| [70] | Jameel A, Noman M, Liu WC, Ahmad N, Wang FW, Li XW, Li HY (2020). Tinkering cis motifs jigsaw puzzle led to root-specific drought-inducible novel synthetic promoters. Int J Mol Sci 21, 1357. |
| [71] | Jopcik M, Moravcikova J, Matusikova I, Libantova J (2014). Spacer length-dependent protection of specific activity of pollen and/or embryo promoters from influence of CaMV35S promoter/enhancer in transgenic plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 118, 507-518. |
| [72] | Jores T, Tonnies J, Wrightsman T, Buckler ES, Cuperus JT, Fields S, Queitsch C (2021). Synthetic promoter designs enabled by a comprehensive analysis of plant core promoters. Nat Plants 7, 842-855. |
| [73] | Kar S, Bordiya Y, Rodriguez N, Kim J, Gardner EC, Gollihar JD, Sung S, Ellington AD (2022). Orthogonal control of gene expression in plants using synthetic promoters and CRISPR-based transcription factors. Plant Methods 18, 42. |
| [74] | Khan ZH, Dang S, Memaya MB, Bhadouriya SL, Agarwal S, Mehrotra S, Gupta D, Mehrotra R (2022). Genome-wide analysis of AAAG and ACGT cis-elements in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals their involvement with genes downregulated under jasmonic acid response in an orientation independent manner. G3-Genes Genom Genet 12, jkac057. |
| [75] | Kim HM, Park SH, Park SY, Ma SH, Do JH, Kim AY, Jeon MJ, Shim JS, Joung YH (2022). Identification of essential element determining fruit-specific transcriptional activity in the tomato HISTIDINE DECARBOXYLASE A gene promoter. Plant Cell Rep 41, 1721-1731. |
| [76] | Ksouri N, Castro-Mondragón JA, Montardit-Tarda F, vanHelden J, Contreras-Moreira B, Gogorcena Y (2021). Tuning promoter boundaries improves regulatory motif discovery in nonmodel plants: the peach example. Plant Physiol 185, 1242-1258. |
| [77] | Kumar D, Patro S, Ghosh J, Das A, Maiti IB, Dey N (2012). Development of asalicylic acid inducible minimal sub-genomic transcript promoter from Figwort mosaic virus with enhanced root- and leaf-activity using TGACG motif rearrangement. Gene 503, 36-47. |
| [78] | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 325-327. |
| [79] | Lieberman-Lazarovich M, Yahav C, Israeli A, Efroni I (2019). Deep conservation of cis-element variants regulating plant hormonal responses. Plant Cell 31, 2559-2572. |
| [80] | Liu L, Gallagher J, Arevalo ED, Chen R, Skopelitis T, Wu QY, Bartlett M, Jackson D (2021). Enhancing grain- yield-related traits by CRISPR-Cas9 promoter editing of maize CLE genes. Nat Plants 7, 287-294. |
| [81] | Liu WS, Mazarei M, Peng YH, Fethe MH, Rudis MR, Lin JY, Millwood RJ, Arelli PR, Stewart CN Jr (2014). Computational discovery of soybean promoter cis-regulatory elements for the construction of soybean cyst nematode-inducible synthetic promoters. Plant Biotechnol J 12, 1015-1026. |
| [82] | Liu WS, Mazarei M, Rudis MR, Fethe MH, Stewart CN Jr (2011). Rapid in vivo analysis of synthetic promoters for plant pathogen phytosensing. BMC Biotechnol 11, 108. |
| [83] | Liu WS, Stewart CN Jr (2016). Plant synthetic promoters and transcription factors. Curr Opin Biotechnol 37, 36-44. |
| [84] | Liu XS, Brutlag DL, Liu JS (2002). An algorithm for finding protein-DNA binding sites with applications to chromatin-immunoprecipitation microarray experiments. Nat Biotechnol 20, 835-839. |
| [85] | Lu ZF, Hofmeister BT, Vollmers C, DuBois RM, Schmitz RJ (2017). Combining ATAC-seq with nuclei sorting for discovery of cis-regulatory regions in plant genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 45, e41. |
| [86] | Lucibelli F, Valoroso MC, Aceto S (2022). Plant DNA methylation: an epigenetic mark in development, environmental interactions, and evolution. Int J Mol Sci 23, 8299. |
| [87] | Mehrotra R, Gupta G, Sethi R, Bhalothia P, Kumar N, Mehrotra S (2011). Designer promoter: an artwork of cis engineering. Plant Mol Biol 75, 527-536. |
| [88] | Misra S, Ganesan M (2021). The impact of inducible promoters in transgenic plant production and crop improvement. Plant Gene 27, 100300. |
| [89] | Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012). AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1819, 86-96. |
| [90] | Molina C, Grotewold E (2005). Genome wide analysis of Arabidopsis core promoters. BMC Genomics 6, 25. |
| [91] | Nakamura M, Tsunoda T, Obokata J (2002). Photosynthesis nuclear genes generally lack TATA-boxes: a tobacco photosystem I gene responds to light through an initiator. Plant J 29, 1-10. |
| [92] | Noda N, Aida R, Kishimoto S, Ishiguro K, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Tanaka Y, Ohmiya A (2013). Genetic engineering of novel bluer-colored chrysanthemums produced by accumulation of delphinidin-based anthocyanins. Plant Cell Physiol 54, 1684-1695. |
| [93] | Noda N, Yoshioka S, Kishimoto S, Nakayama M, Douzono M, Tanaka Y, Aida R (2017). Generation of blue chrysanthemums by anthocyanin B-ring hydroxylation and glucosylation and its coloration mechanism. Sci Adv 3, e1602785. |
| [94] | Nutiu R, Friedman RC, Luo SJ, Khrebtukova I, Silva D, Li RB, Zhang L, Schroth GP, Burge CB (2011). Direct measurement of DNA affinity landscapes on a high-throughput sequencing instrument. Nat Biotechnol 29, 659-664. |
| [95] | Oldfield AJ, Henriques T, Kumar D, Burkholder AB, Cinghu S, Paulet D, Bennett BD, Yang PY, Scruggs BS, Lavender CA, Rivals E, Adelman K, Jothi R (2019). NF-Y controls fidelity of transcription initiation at gene pro- moters through maintenance of the nucleosome-depleted region. Nat Commun 10, 3072. |
| [96] | Oliva R, Ji CH, Atienza-Grande G, Huguet-Tapia JC, Perez-Quintero A, Li T, Eom JS, Li CH, Nguyen H, Liu B, Auguy F, Sciallano C, Luu VT, Dossa GS, Cunnac S, Schmidt SM, Slamet-Loedin IH, Cruz CV, Szurek B, Frommer WB, White FF, Yang B (2019). Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 37, 1344-1350. |
| [97] | Peremarti A, Twyman RM, Gómez-Galera S, Naqvi S, Farré G, Sabalza M, Miralpeix B, Dashevskaya S, Yuan DW, Ramessar K, Christou P, Zhu CF, Bassie L, Capell T (2010). Promoter diversity in multigene transformation. Plant Mol Biol 73, 363-378. |
| [98] | Persad-Russell R, Mazarei M, Schimel TM, Howe L, Schmid MJ, Kakeshpour T, Barnes CN, Brabazon H, Seaberry EM, Reuter DN, Lenaghan SC, Stewart CN Jr (2022). Specific bacterial pathogen phytosensing is enabled by a synthetic promoter-transcription factor system in potato. Front Plant Sci 13, 873480. |
| [99] | Porto MS, Pinheiro MPN, Batista VGL, dos Santos RC, de Albuquerque Melo Filho P, de Lima LM (2014). Plant promoters: an approach of structure and function. Mol Bio- technol 56, 38-49. |
| [100] | Ranjan R, Dey N (2012). Development of vascular tissue and stress inducible hybrid-synthetic promoters through DOF-1 motifs rearrangement. Cell Biochem Biophys 63, 235-245. |
| [101] | Rao GS, Jiang WJ, Mahfouz M (2021). Synthetic directed evolution in plants: unlocking trait engineering and improvement. Synth Biol 6, ysab025. |
| [102] | Rodriguez-Leal D, Xu C, Kwon CT, Soyars C, Demesa-Arevalo E, Man J, Liu L, Lemmon ZH, Jones DS, Van Eck J, Jackson DP, Bartlett ME, Nimchuk ZL, Lippman ZB (2019). Evolution of buffering in a genetic circuit controlling plant stem cell proliferation. Nat Genet 51, 786-792. |
| [103] | Rozière J, Guichard C, Brunaud V, Martin ML, Coursol S (2022). A comprehensive map of preferentially located motifs reveals distinct proximal cis-regulatory sequences in plants. Front Plant Sci 13, 976371. |
| [104] | Rushton PJ (2016). What have we learned about synthetic promoter construction? Methods Mol Biol 1482, 1-13. |
| [105] | Santos E, Remy S, Thiry E, Windelinckx S, Swennen R, Sági L (2009). Characterization and isolation of a T-DNA tagged banana promoter active during in vitro culture and low temperature stress. BMC Plant Biol 9, 77. |
| [106] | Schmitz RJ, Grotewold E, Stam M (2022). Cis-regulatory sequences in plants: their importance, discovery, and future challenges. Plant Cell 34, 718-741. |
| [107] | Selma S, Bernabé-Orts JM, Vazquez-Vilar M, Diego- Martin B, Ajenjo M, Garcia-Carpintero V, Granell A, Orzaez D (2019). Strong gene activation in plants with genome-wide specificity using a new orthogonal CRISPR/ Cas9-based programmable transcriptional activator. Plant Biotechnol J 17, 1703-1705. |
| [108] | Shahmuradov IA, Gammerman AJ, Hancock JM, Bramley PM, Solovyev VV (2003). PlantProm: a database of plant promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 31, 114-117. |
| [109] | Shahmuradov IA, Umarov RK, Solovyev VV (2017). TSSPlant: a new tool for prediction of plant Pol II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res 45, e65. |
| [110] | Shi L, Su J, Cho MJ, Song H, Dong XO, Liang Y, Zhang ZY (2023). Promoter editing for the genetic improvement of crops. J Exp Bot 74, 4349-4366. |
| [111] | Sun M, Ding JY, Li DL, Yang GP, Cheng ZN, Zhu QB (2017). NUDT21 regulates 3′-UTR length and microRNA- mediated gene silencing in hepatocellular carcinoma. Can- cer Lett 410, 158-168. |
| [112] | Uygun S, Azodi CB, Shiu SH (2019). Cis-regulatory code for predicting plant cell-type transcriptional response to high salinity. Plant Physiol 181, 1739-1751. |
| [113] | Wang R, Zhu ML, Ye RJ, Liu ZX, Zhou F, Chen H, Lin YJ (2015). Novel green tissue-specific synthetic promoters and cis-regulatory elements in rice. Sci Rep 5, 18256. |
| [114] | Wei B, Jolma A, Sahu B, Orre LM, Zhong F, Zhu FJ, Kivioja T, Sur I, Lehtiö J, Taipale M, Taipale J (2018). A protein activity assay to measure global transcription factor activity reveals determinants of chromatin accessibility. Nat Biotechnol 36, 521-529. |
| [115] | Weirauch MT, Yang A, Albu M, Cote AG, Montenegro- Montero A, Drewe P, Najafabadi HS, Lambert SA, Mann I, Cook K, Zheng H, Goity A, van Bakel H, Lozano JC, Galli M, Lewsey MG, Huang EY, Mukherjee T, Chen XT, Reece-Hoyes JS, Govindarajan S, Shaulsky G, Walhout AJM, Bouget FY, Ratsch G, Larrondo LF, Ecker JR, Hughes TR (2014). Determination and inference of eukaryotic transcription factor sequence specificity. Cell 158, 1431-1443. |
| [116] | Wen CJ, Yuan Z, Zhang XT, Chen H, Luo L, Li WY, Li T, Ma NN, Mao F, Lin DM, Lin ZX, Lin CT, Xu TD, Lü PT, Lin JC, Zhu FJ (2023). Sea-ATI unravels novel vocabularies of plant active cistrome. Nucleic Acids Res 51, 11568-11583. |
| [117] | Wu B, Meng JH, Liu HB, Mao DH, Yin HR, Zhang ZY, Zhou XC, Zhang B, Sherif A, Liu HY, Li XH, Xiao JH, Yan WH, Wang L, Li XW, Chen W, Xie WB, Yin P, Zhang QF, Xing YZ (2023). Suppressing a phosphohydrolase of cytokinin nucleotide enhances grain yield in rice. Nat Genet 55, 1381-1389. |
| [118] | Xue GP, Rae AL, White RG, Drenth J, Richardson T, McIntyre CL (2016). A strong root-specific expression system for stable transgene expression in bread wheat. Plant Cell Rep 35, 469-481. |
| [119] | Yamamoto YY, Ichida H, Matsui M, Obokata J, Sakurai T, Satou M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Abe T (2007). Identification of plant promoter constituents by analysis of local distribution of shorts equences. BMC Genom 8, 67. |
| [120] | Yamamoto YY, Obokata J (2008). PPDB: a plant promoter database. Nucleic Acids Res 36, D977-D981. |
| [121] | Yang MM, Zhang WW, Ji SY, Cao PH, Chen YL, Zhao X (2013). Generation of an artificial double promoter for pro- tein expression in Bacillus subtilis through a promoter trap system. PLoS One 8, e56321. |
| [122] | Yang YL, Lee JH, Poindexter MR, Shao YH, Liu WS, Lenaghan SC, Ahkami AH, Blumwald E, Stewart CN Jr (2021). Rational design and testing of abiotic stress-inducible synthetic promoters from poplar cis-regulatory elements. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 1354-1369. |
| [123] | Yang ZF, Yan HD, Wang JP, Nie G, Feng GY, Xu XH, Li DD, Huang LK, Zhang XQ (2022). DNA hypermethylation promotes the flowering of orchard grass during vernalization. Plant Physiol 190, 1490-1505. |
| [124] | Yasmeen E, Wang J, Riaz M, Zhang LD, Zuo KJ (2023). Designing artificial synthetic promoters for accurate, smart, and versatile gene expression in plants. Plant Commun 4, 100558. |
| [125] | Yuan X, Ma KF, Zhang M, Wang J, Zhang QX (2021). Integration of transcriptome and methylome analyses provides insight into the pathway of floralscent biosynthesis in Prunus mume. Front Genet 12, 779557. |
| [126] | Zhang CX, Gai Y, Wang WQ, Zhu YY, Chen XM, Jiang XN (2008). Construction and analysis of a plant transformation binary vector pBDGG harboring a bi-directional promoter fusing dual visible reporter genes. J Genet Genomics 35, 245-249. |
| [127] | Zhang F, Lu CF, Qi S, Dai SL (2022). Difference analysis of ClCYC2-like genes expression and DNA methylation between the two types of florets in Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium. J Plant Growth Regul 41, 1316-1330. |
| [128] | Zhang PC, Wang HC, Xu HW, Wei L, Liu LY, Hu ZR, Wang XW (2023). Deep flanking sequence engineering for efficient promoter design using DeepSEED. Nat Commun 14, 6309. |
| [129] | Zhou JP, Liu GQ, Zhao YX, Zhang R, Tang X, Li L, Jia XY, Guo YC, Wu YC, Han YS, Bao Y, He Y, Han QQ, Yang H, Zheng XL, Qi YP, Zhang T, Zhang Y (2023). An efficient CRISPR-Cas12a promoter editing system for crop improvement. Nat Plants 9, 588-604. |
| [130] | Zrimec J, Börlin CS, Buric F, Muhammad AS, Chen R, Siewers V, Verende lV, Nielsen J, Töpe lM, Zelezniak A (2020). Deep learning suggests that gene expression is encoded in all parts of a co-evolving interacting gene regulatory structure. Nat Commun 11, 6141. |
| [1] | Fei Zhao, Liuyi Dang, Minhui Wei, Chunying Liu, Wei Leng, Chenjing Shang. Expression of Amaranthin-like Lectins Gene and Responses to Abiotic Stresses in Cucumber [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(2): 183-190. |
| [2] | Huijin Fan, Kangming Jin, Renying Zhuo, Guirong Qiao. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Different Truncated U3 Promoters in Phyllostachys edulis [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(3): 299-307. |
| [3] | Min Song,Yao Zhang,Liying Wang,Xiangyong Peng. Genome-wide Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Zinc Finger Homeodomain Family Genes in Brassica napus [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 699-710. |
| [4] | Shaoshuai Yu, Caili Lin, Shengjie Wang, Wenxin Zhang, Guozhong Tian. Structures of the tuf gene and its upstream part genes and characteristic analysis of conserved regions and activity from related gene promoters of a phytoplasma [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(7): 738-748. |
| [5] | Xinli Zan, Ying Gao, Yuling Chen, Kaijun Zhao. Pathogen-responsive Cis-acting Elements and Their Interactive Transcription Factors [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(2): 219-229. |
| [6] | Weiwei Liu, Hailei Zhang, Caifeng Liu, Xiaochun Ge. Construction and Activity Analysis of an Antibiotic-inducible Promoter [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(5): 560-568. |
| [7] | Xuanyu Liu, Qingyun Wang, Shujun Liu, Songquan Song. Advances in the Genetic Transformation of Sorghum bicolor [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(2): 216-223. |
| [8] | Xiaobo Qin;Jihai Gao;Ying Xu*;Jinping Zhang;Caixia Shao;Sha Lin;Shuwen Zhang;Luding Jiang;Yueqin Li;Fang Chen . Isolation of Curcin Promoter from Jatropha curcas and Analysis in Transgenic Tobacco Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(04): 407-414. |
| [9] | Wei Xie Chaoyin Yue Zhenghong Guo Zhipeng Dai Min Liu Wei Yao. Transient Expression of GUS Gene Controlled by Different Regulator Sequences of Tobacco [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2007, 24(04): 452-458. |
| [10] | Xiaona Liu;Chang Fu;Yongfen Huang*. Advances in Studies of Seed-specific Gene Promoters [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2007, 24(02): 218-225. |
| [11] | I Xin-Qi YUAN Long-PingDENG Qi-Yun XIAO Jin-Hua. Potential Ways to Use Spontaneous Genic Male Sterility in the Molecular Breeding of Hybrid Crops [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2003, 20(05): 625-631. |
| [12] | SU NingSUN Meng LI Yi-Nü NI Pi-Chong SHEN Gui-Fang. Isolation and Modification of Rice Chloroplast 16S Promoter,Construction of Expression Vector and Transformation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2003, 20(03): 295-301. |
| [13] | LI Li ZHANG Jing-Yu DU Gui-Sen SONG Yan-Ru. Isolation of Seed Specific Promoter (napinB promoter),Construction of Expression Vector and Obtainmentof Transgenic Tobacco Plants [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2001, 18(02): 216-220. |
| [14] | LI Yi-Kun and WANG Jin-Fa. Advances of the Studies on Plant Promoter [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 1998, 15(增刊): 1-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||