

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (5): 760-769.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22141 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22141
• TECHNIQUES AND METHODS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yu Xiaomin1, Wang Yaqin1, Liu Yuhan1, Yi Qingping2, Cheng Wenhan2, Zhu Yu1, Duan Feng1, Zhang Lixue1, He Yanhong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-02
Accepted:2022-12-02
Online:2023-09-01
Published:2023-09-21
Contact:
*E-mail: hyh2010@mail.hzau.edu.cn
Yu Xiaomin, Wang Yaqin, Liu Yuhan, Yi Qingping, Cheng Wenhan, Zhu Yu, Duan Feng, Zhang Lixue, He Yanhong. Establishment of Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated Genetic Transformation System of Marigold (Tagetes erecta)[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 760-769.
| Culture medium types | Formula |
|---|---|
| MS | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+30 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar |
| Regeneration medium | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+40 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ+0.5 mg·L-1 IBA |
| Co-culture medium | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+40 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ+0.5 mg·L-1 IBA+0.5 g·L-1 MES+ 100 μmol·L-1 AS |
| Screening medium | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+40 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ+0.5 mg·L-1 IBA+0.5 g·L-1 MES+10 mg·L-1 Kan+100 mg·L-1 Cef |
| Elongation medium/ rooting medium | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+30 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar+0.5 g·L-1 MES+10 mg·L-1 Kan+100 mg·L-1 Cef |
Table 1 Medium used for genetic transformation of marigold Milestone Yellow
| Culture medium types | Formula |
|---|---|
| MS | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+30 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar |
| Regeneration medium | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+40 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ+0.5 mg·L-1 IBA |
| Co-culture medium | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+40 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ+0.5 mg·L-1 IBA+0.5 g·L-1 MES+ 100 μmol·L-1 AS |
| Screening medium | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+40 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar+0.2 mg·L-1 TDZ+0.5 mg·L-1 IBA+0.5 g·L-1 MES+10 mg·L-1 Kan+100 mg·L-1 Cef |
| Elongation medium/ rooting medium | 4.405 g·L-1 MS+30 g·L-1 sucrose+8 g·L-1 agar+0.5 g·L-1 MES+10 mg·L-1 Kan+100 mg·L-1 Cef |
| Kan concentration (mg·L-1) | Callus induction rate (%) | Regeneration rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100.00±0.00 a | 72.50±5.00 a |
| 2 | 100.00±0.00 a | 67.50±12.58 a |
| 4 | 100.00±0.00 a | 50.00±14.14 b |
| 6 | 97.50±5.00 a | 15.00±10.00 c |
| 8 | 95.00±5.77 ab | 7.50±5.00 d |
| 10 | 92.50±5.00 b | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 15 | 65.00±5.77 c | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 20 | 37.50±12.58 d | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 30 | 27.50±5.00 d | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 40 | 15.00±5.77 e | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 50 | 0.00±0.00 f | 0.00±0.00 e |
Table 2 Effect of Kan concentration on leaflet regeneration of marigold
| Kan concentration (mg·L-1) | Callus induction rate (%) | Regeneration rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100.00±0.00 a | 72.50±5.00 a |
| 2 | 100.00±0.00 a | 67.50±12.58 a |
| 4 | 100.00±0.00 a | 50.00±14.14 b |
| 6 | 97.50±5.00 a | 15.00±10.00 c |
| 8 | 95.00±5.77 ab | 7.50±5.00 d |
| 10 | 92.50±5.00 b | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 15 | 65.00±5.77 c | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 20 | 37.50±12.58 d | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 30 | 27.50±5.00 d | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 40 | 15.00±5.77 e | 0.00±0.00 e |
| 50 | 0.00±0.00 f | 0.00±0.00 e |
| Cef concentration (mg·L-1) | Callus induction rate (%) | Regeneration rate (%) | Growth of bacteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100.00±0.00 a | 60.00±8.16 a | Grow well |
| 100 | 97.50±5.00 a | 47.50±12.58 ab | Completely inhibited |
| 200 | 97.50±5.00 a | 40.00±8.16 abc | Completely inhibited |
| 300 | 65.00±5.77 b | 35.00±12.91 bc | Completely inhibited |
| 400 | 37.50±12.58 c | 37.50±17.08 bc | Completely inhibited |
| 500 | 27.50±5.00 c | 27.50±12.58 c | Completely inhibited |
Table 3 Effect of Cef concentration on leaflet regeneration of marigold and bacteria growth
| Cef concentration (mg·L-1) | Callus induction rate (%) | Regeneration rate (%) | Growth of bacteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100.00±0.00 a | 60.00±8.16 a | Grow well |
| 100 | 97.50±5.00 a | 47.50±12.58 ab | Completely inhibited |
| 200 | 97.50±5.00 a | 40.00±8.16 abc | Completely inhibited |
| 300 | 65.00±5.77 b | 35.00±12.91 bc | Completely inhibited |
| 400 | 37.50±12.58 c | 37.50±17.08 bc | Completely inhibited |
| 500 | 27.50±5.00 c | 27.50±12.58 c | Completely inhibited |
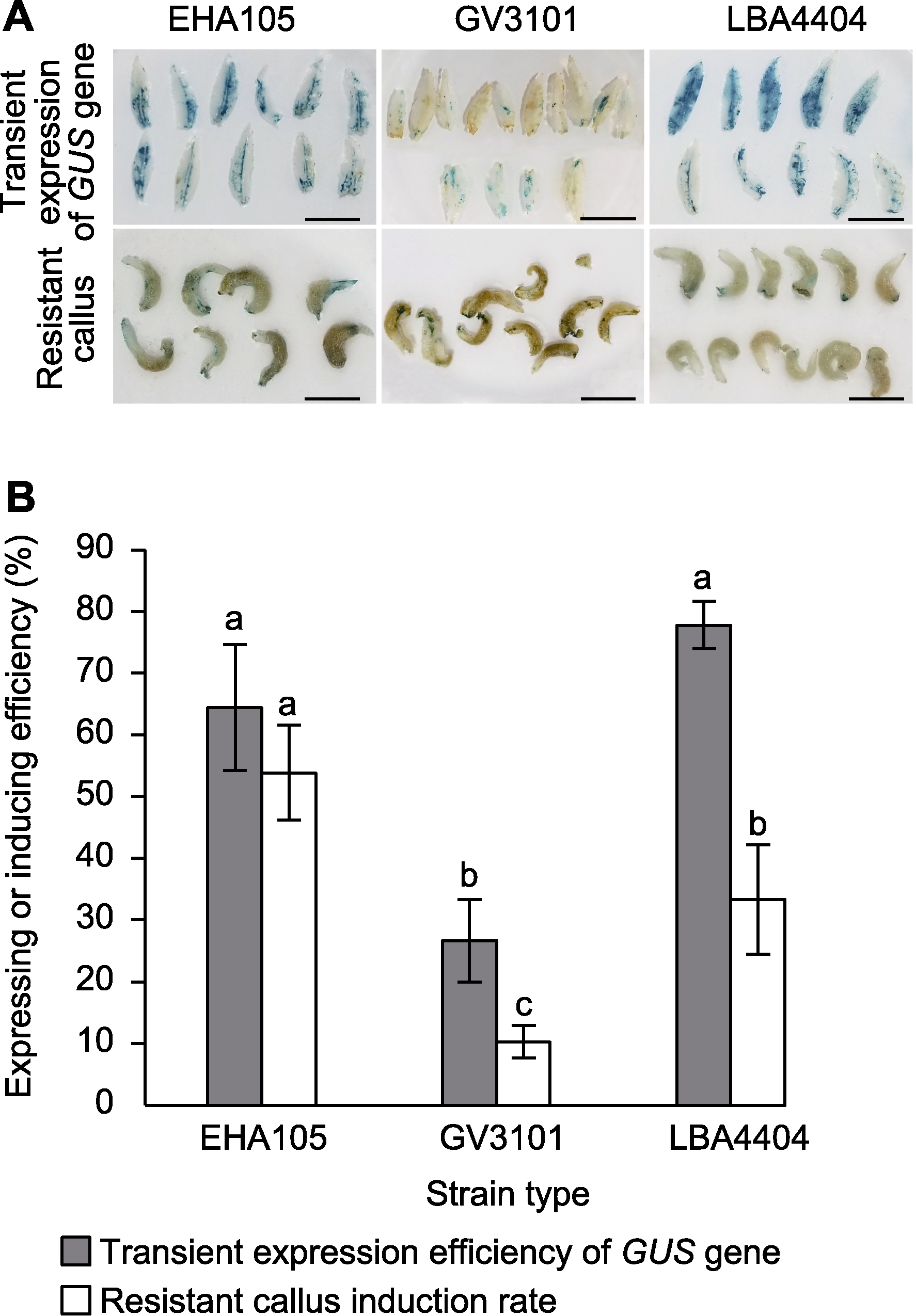
Figure 1 Effects of strain types on genetic transformation efficiency of marigold (A) Schematic diagram of transient expression of GUS gene and resistant callus in three strains (bars=1 cm); (B) Effect of strain types on transient expression efficiency of GUS gene and induction rate of resistant calli (different lowercase letters on the same color histogram indicate significant differences at 0.05 level)
| No. | OD600 | Infection time (d) | Co-culture time (d) | Transient expression rate of GUS gene (%) | Callus induction rate (%) | Resistance bud rate (%) | PCR positive rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 | 5 | 1 | 100 | 90.67±2.31 abcd | 45.33 | 4.00 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 10 | 2 | 100 | 91.85±7.83 abcd | 27.55 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 20 | 3 | 100 | 77.11±6.99 e | 20.25 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 30 | 4 | 100 | 86.20±11.95 cde | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 5 | 2 | 100 | 96.67±2.88 abc | 28.33 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 0.5 | 10 | 1 | 100 | 86.67±0.00 bcde | 22.22 | 3.33 |
| 7 | 0.5 | 20 | 4 | 100 | 93.62±6.45 abc | 3.16 | 0.00 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 30 | 3 | 100 | 96.30±3.21 abc | 0.93 | 0.00 |
| 9 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 100 | 97.10±2.51 ab | 23.53 | 0.00 |
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 4 | 100 | 91.61±4.93 abcd | 13.51 | 0.00 |
| 11 | 1 | 20 | 1 | 100 | 81.25±6.25 de | 28.57 | 0.00 |
| 12 | 1 | 30 | 2 | 100 | 86.03±1.27 cde | 9.00 | 0.00 |
| 13 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 100 | 95.45±7.87 abc | 17.65 | 1.96 |
| 14 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 100 | 100.00±0.00 a | 5.71 | 0.00 |
| 15 | 2 | 20 | 2 | 100 | 86.18±3.66 cde | 12.64 | 0.00 |
| 16 | 2 | 30 | 1 | 100 | 86.11±4.34 cde | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Table 4 Effects of different infection conditions on transformation efficiency of marigold
| No. | OD600 | Infection time (d) | Co-culture time (d) | Transient expression rate of GUS gene (%) | Callus induction rate (%) | Resistance bud rate (%) | PCR positive rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 | 5 | 1 | 100 | 90.67±2.31 abcd | 45.33 | 4.00 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 10 | 2 | 100 | 91.85±7.83 abcd | 27.55 | 0.00 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 20 | 3 | 100 | 77.11±6.99 e | 20.25 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 0.1 | 30 | 4 | 100 | 86.20±11.95 cde | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 5 | 2 | 100 | 96.67±2.88 abc | 28.33 | 0.00 |
| 6 | 0.5 | 10 | 1 | 100 | 86.67±0.00 bcde | 22.22 | 3.33 |
| 7 | 0.5 | 20 | 4 | 100 | 93.62±6.45 abc | 3.16 | 0.00 |
| 8 | 0.5 | 30 | 3 | 100 | 96.30±3.21 abc | 0.93 | 0.00 |
| 9 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 100 | 97.10±2.51 ab | 23.53 | 0.00 |
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 4 | 100 | 91.61±4.93 abcd | 13.51 | 0.00 |
| 11 | 1 | 20 | 1 | 100 | 81.25±6.25 de | 28.57 | 0.00 |
| 12 | 1 | 30 | 2 | 100 | 86.03±1.27 cde | 9.00 | 0.00 |
| 13 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 100 | 95.45±7.87 abc | 17.65 | 1.96 |
| 14 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 100 | 100.00±0.00 a | 5.71 | 0.00 |
| 15 | 2 | 20 | 2 | 100 | 86.18±3.66 cde | 12.64 | 0.00 |
| 16 | 2 | 30 | 1 | 100 | 86.11±4.34 cde | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Factor | OD600 | Infection time (d) | Co-culture time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 4.00 | 5.96 | 7.33 |
| K2 | 3.33 | 3.33 | 0.00 |
| K3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| K4 | 1.96 | 0.00 | 1.96 |
| K1 | 1.00 | 1.49 | 1.83 |
| K2 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.00 |
| K3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| K4 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 0.49 |
| R | 1.00 | 1.49 | 1.83 |
Table 5 Range analysis of PCR positive rate under different infection conditions
| Factor | OD600 | Infection time (d) | Co-culture time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 4.00 | 5.96 | 7.33 |
| K2 | 3.33 | 3.33 | 0.00 |
| K3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| K4 | 1.96 | 0.00 | 1.96 |
| K1 | 1.00 | 1.49 | 1.83 |
| K2 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.00 |
| K3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| K4 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 0.49 |
| R | 1.00 | 1.49 | 1.83 |
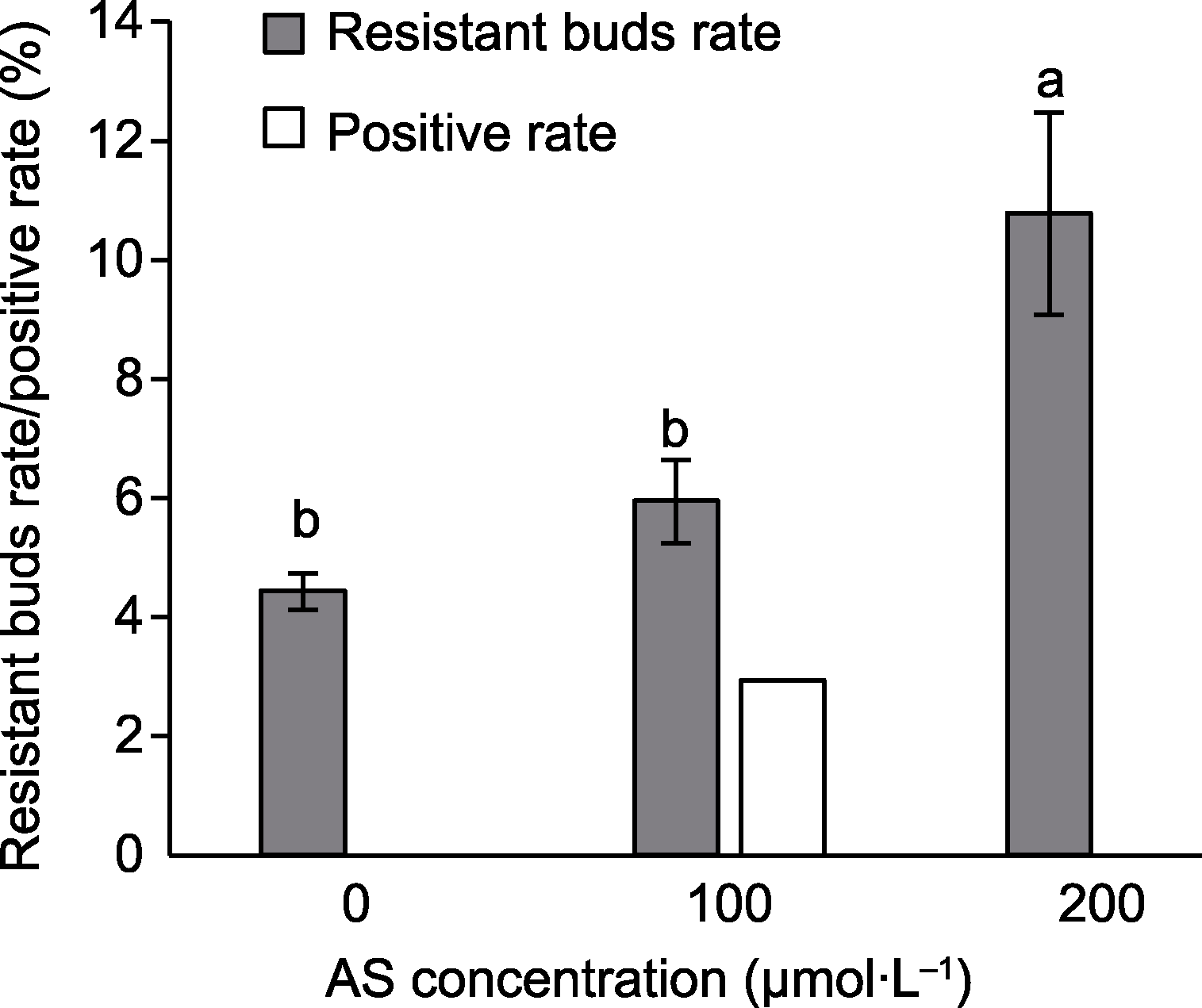
Figure 2 Effect of acetosyringone (AS) on transformation efficiency of marigold Different lowercase letters on the same color histogram indicate significant differences at 0.05 level.
| Anti-browning agent and concentration | No. of resistant buds | Resistance buds rate (%) | No. of positive seedlings | PCR positive rate (%) | Description of budding state |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4 | 4.00 | 0 | 0.00 | Grow well |
| 0.2 g·L-1 CA | 6 | 6.45 | 0 | 0.00 | Hard texture, more clustered buds, basically no main stem |
| 0.4 g·L-1 CA | 9 | 9.00 | 0 | 0.00 | Hard texture, more clustered buds, basically no main stem |
| 0.6 g·L-1 CA | 12 | 12.00 | 0 | 0.00 | Hard texture, more clustered buds, basically no main stem |
| 0.2 g·L-1 PVP | 12 | 12.00 | 4 | 4.00 | Grow well |
| 0.4 g·L-1 PVP | 7 | 7.00 | 0 | 0.00 | Grow well |
| 0.6 g·L-1 PVP | 7 | 7.37 | 1 | 1.11 | Grow well |
Table 6 Effects of citric acid (CA) and polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) on transformation efficiency of marigold
| Anti-browning agent and concentration | No. of resistant buds | Resistance buds rate (%) | No. of positive seedlings | PCR positive rate (%) | Description of budding state |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 4 | 4.00 | 0 | 0.00 | Grow well |
| 0.2 g·L-1 CA | 6 | 6.45 | 0 | 0.00 | Hard texture, more clustered buds, basically no main stem |
| 0.4 g·L-1 CA | 9 | 9.00 | 0 | 0.00 | Hard texture, more clustered buds, basically no main stem |
| 0.6 g·L-1 CA | 12 | 12.00 | 0 | 0.00 | Hard texture, more clustered buds, basically no main stem |
| 0.2 g·L-1 PVP | 12 | 12.00 | 4 | 4.00 | Grow well |
| 0.4 g·L-1 PVP | 7 | 7.00 | 0 | 0.00 | Grow well |
| 0.6 g·L-1 PVP | 7 | 7.37 | 1 | 1.11 | Grow well |

Figure 3 Genetic transformation process diagram of marigold (A) Marigold compound leaves; (B) Leaflet culture; (C) Leaflet-induced calli; (D) GUS staining of transiently transformed leaves; (E) Resistance buds; (F) Resistant seedlings; (G) Rooting culture of resistant seedlings; (H) Positive seedlings; (I) Transplantation of positive seedlings. (A)-(D), (G)-(I) Bars=1 cm; (E), (F) Bars=0.5 cm
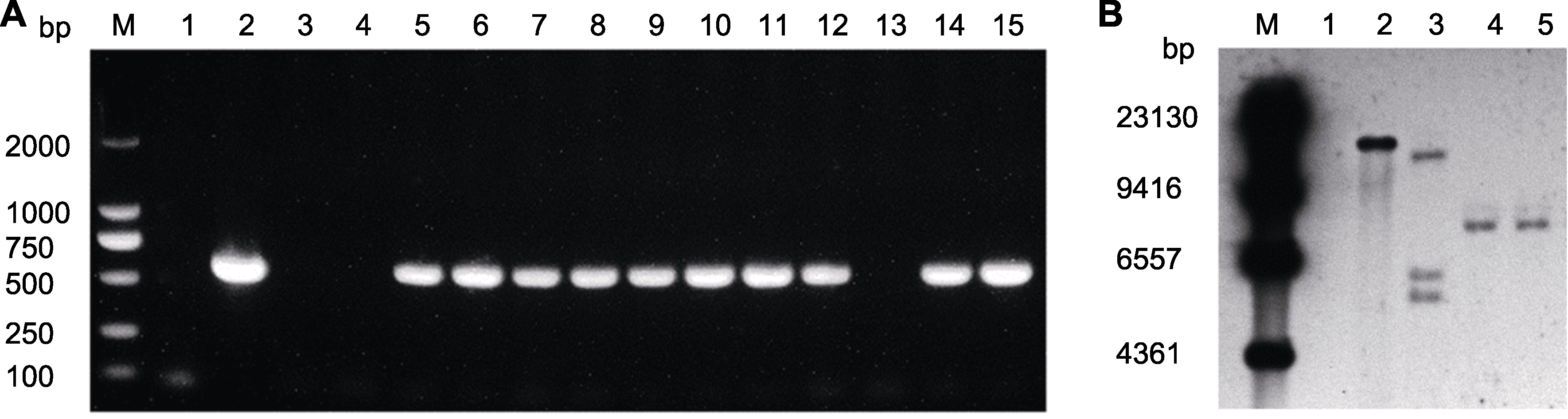
Figure 5 PCR amplification detection and Southern blot results of marigold resistant seedlings (A) PCR amplification detection of resistant seedlings (M: 2000 DNA marker; 1: ddH2O; 2: Plasmid; 3, 4: Negative control, DNA of uninfected leaf; 5-15: DNA of resistant seedlings); (B) Southern blot results of positive seedlings (the NPT-II probe was digested with HindIII. M: DNA marker; 1: Negative control, DNA of uninfected leaf; 2: Positive control, plasmid; 3-5: DNA of positive seedlings).
| [1] | 陈利文, 唐楠 (2021). 不同品种色素万寿菊主要农艺性状评价. 安徽农业科学 49(4), 53-55. |
| [2] |
付洪冰, 崔崇士, 赵曦, 刘琦 (2010). 农杆菌介导南瓜遗传转化体系的建立. 植物学报 45, 472-478.
DOI |
| [3] | 符勇耀, 杨利平, 郑开敏, 徐文姬 (2021). 药用万寿菊多倍体的诱导与特征分析. 热带作物学报 42, 1318-1325. |
| [4] | 郭彩珍 (2021). 响应面法优化紫丁香愈伤组织诱导条件及防褐化研究. 种子 40(8), 141-145, 148. |
| [5] | 梁艳, 赵雪莹, 白雪, 刘德强, 张妍, 潘朋 (2021). PVP处理对黑皮油松外植体酚类物质形成及酶活性的影响. 林业科学 57(10), 166-174. |
| [6] | 刘翰升, 赵春莉, 刘玥, 国伟强 (2019). 镉胁迫对万寿菊属植物幼苗生理及富集的影响. 福建农业学报 34, 1221-1227. |
| [7] | 刘香利, 赵惠贤, 郭蔼光 (2011). 农杆菌介导的小麦遗传转化研究进展. 安徽农业科学 39, 19065-19066. |
| [8] | 王关林, 方宏筠 (2002). 植物基因工程(第2版). 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 393. |
| [9] | 王亚琴, 韦陆丹, 王文静, 刘宝骏, 张春玲, 张俊卫, 何燕红 (2020). 万寿菊再生体系的建立及优化. 植物学报 55, 749-759. |
| [10] | 杨帆 (2011). 色素万寿菊psy双边界载体及遗传转化体系建立和SSR-PCR体系的优化. 硕士论文. 上海: 上海交通大学. pp. 14-23. |
| [11] | 曾益, 李婧怡, 周明康, 曹栋才, 娄琳琳, 何恒, 何梦雪, 邹俊杰, 殷中琼 (2021). 万寿菊茎叶醇提物的镇痛抗炎活性研究. 四川农业大学学报 39, 451-458. |
| [12] | 张海霞, 张少英, 付增娟 (2013). 乙酰丁香酮对甜菜遗传转化的影响. 广东农业科学 40(22), 22-24. |
| [13] | 张嫔 (2012). 万寿菊属植物染色体核型分析及万寿菊psy基因遗传转化体系影响因素的研究. 硕士论文. 上海: 上海交通大学. pp. 36-47. |
| [14] |
Amoah BK, Wu H, Sparks C, Jones HD (2001). Factors influencing Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression of uidA in wheat inflorescence tissue. J Exp Bot 52, 1135-1142.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Cervera M, López MM, Navarro L, Peña L (1998). Virulence and supervirulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciensin woody fruit plants. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 52, 67-78.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Chintakovid W, Visoottiviseth P, Khokiattiwong S, Lauengsuchonkul S (2008). Potential of the hybrid marigolds for arsenic phytoremediation and income generation of remediators in Ron Phibun District, Thailand. Chemosphere 70, 1532-1537.
PMID |
| [17] |
Chitrakar B, Zhang M, Bhandari B (2019). Edible flowers with the common name “Marigold”: their therapeutic values and processing. Trends Food Sci Technol 89, 76-87.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Godoy-Hernández G, Berzunza EA, Concha LC, Miranda- Ham MDL (2006). Agrobacterium-mediated transient transformation of marigold (Tagetes erecta). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 84, 365-368.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Gupta V, Rahman LU (2015). An efficient plant regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Tagetes erecta. Protoplasma 252, 1061-1070.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987). GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6, 3901-3907.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Lacatusu I, Badea G, Popescu M, Bordei N, Istrati D, Moldovan L, Seciu AM, Panteli MI, Rasit I, Badea N (2017). Marigold extract, azelaic acid and black caraway oil into lipid nanocarriers provides a strong anti-inflammatory effect in vivo. Ind Crops Prod 109, 141-150.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Maleki SS, Mohammadi K, Ji KS (2018). Study on factors influencing transformation efficiency in Pinus massoniana using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 133, 437-445.
DOI |
| [23] |
Manivannan A, Narasegowda S, Prakash T (2021). Comparative study on color coordinates, phenolics, flavonoids, carotenoids, and antioxidant potential of marigold (Tagetes sp.) with diverse colored petals. J Food Meas Charact 15, 4343-4353.
DOI |
| [24] |
Mir RA, Argal S, Ahanger MA, Tomar NS, Agarwal RM (2022). Variation in phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and osmotica of different cultivars of Tagetes erecta L. at different growth stages and effect of its leachates on germination and growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Plant Growth Regul 41, 907-921.
DOI |
| [25] |
Nuoendagula, Narushima M, Uesugi M, Murai Y, Katayama Y, Iimura Y, Kajita S (2017). In vitro regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of male- sterile marigold (Tagetes erecta L.). Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo) 34, 125-129.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Sessitsch A, Hardoim P, Döring J, Weilharter A, Krause A, Woyke T, Mitter B, Hauberg-Lotte L, Friedrich F, Rahalkar M, Hurek T, Sarkar A, Bodrossy L, Van Overbeek L, Brar D, Van Elsas JD, Reinhold-Hurek B (2012). Functional characteristics of an endophyte community colonizing rice roots as revealed by metagenomic analysis. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 25, 28-36.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Shabbir M, Rather LJ, Mohammad F (2018). Economically viable UV-protective and antioxidant finishing of wool fabric dyed with Tagetes erecta flower extract: valorization of marigold. Ind Crops Prod 119, 277-282.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Stachel SE, Messens E, Van Montagu M, Zambryski P (1985). Identification of the signal molecules produced by wounded plant cells that activate T-DNA transfer in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nature 318, 624-629.
DOI |
| [29] |
Vanegas PE, Valdez-Morales M, Valverde ME, Cruz-Hernández A, Paredes-López O (2006). Particle bombardment, a method for gene transfer in marigold. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 84, 359-363.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Jingjing Li, Yanfei Li, Anqi Wang, Jiaying Wang, Chengyan Deng, Min Lu, Jianying Ma, Silan Dai. Establishment of Regeneration and Genetic Transformation System for Chrysanthemum Cultivar ‘Wandai Fengguang’ [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | Zeng Wendan, Yan Huabing, Wu Zhengdan, Shang Xiaohong, Cao Sheng, Lu Liuying, Xiao Liang, Shi Pingli, Cheng Dong, Long Ziyuan, Li Jieyu. Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated Transformation System of Pueraria lobata Hairy Roots [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 425-434. |
| [3] | Yuchen Li, Haixia Zhao, Xiping Jiang, Xintian Huang, Yaling Liu, Zhenying Wu, Yan Zhao, Chunxiang Fu. Establishment of Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation System for Agropyron mongolicum [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 600-612. |
| [4] | Lan Yang, Ya Liu, Yang Xiang, Xiujuan Sun, Jingwei Yan, Aying Zhang. Establishment and Optimization of a Shoot Tip-based Genetic Transformation System for Foxtail Millet [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 71-79. |
| [5] | Yaqin Wang, Ludan Wei, Wenjing Wang, Baojun Liu, Chunling Zhang, Junwei Zhang, Yanhong He. The Establishment and Optimization of a Regeneration System for Marigold (Tagetes erecta) [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(6): 749-759. |
| [6] | Junhua Li,Shiyu Liu,Chenglong Li,Linlin Han,Yahui Dong,Xiaoli Zhang,Xiting Zhao,Mingjun Li. Establishment of a Genetic Transformation System for Dioscorea opposita Using Microtuber [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(1): 72-80. |
| [7] | Lijun Guo, Bingshan Zeng, Ying Liu. Agrobacterium-mediated High-efficient Transformation of Eucalyptus grandis Clone Eg5 [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2013, 48(1): 87-93. |
| [8] | Guimei Cui, Yi Sun, Yaoshan Hao, Jianzhong Du, Yixue Wang. The Improvement of Maize Pollen In Vitro Germination Method and Its Role in Pollen-mediated Plant Genetic Transformation [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2012, 47(2): 155-161. |
| [9] | Xuanyu Liu, Qingyun Wang, Shujun Liu, Songquan Song. Advances in the Genetic Transformation of Sorghum bicolor [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2011, 46(2): 216-223. |
| [10] | Hongbing Fu;Chongshi Cui;Xi Zhao;Qi Liu. Establishment of Cucurbita moschata Genetic Transformation System by Agrobacterium tumefaciens Transfection [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2010, 45(04): 472-478. |
| [11] | Daojie Wang, Cuiling Yang, Ming Lu. Transformation of Brassica napus by Vacuum Infiltration [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2009, 44(02): 216-222. |
| [12] | Kaifa Wei*;Yiping Liu;Ziying Lin;Yafang Yang;Zehong Zhang;Wensuo Jia. Problems and Solutions in Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated Genetic Transformation of Monocotyledons [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(04): 491-496. |
| [13] | Tingbo Jiang*;Xinhua Tang;Fengjuan Li;Baojian Ding;Hong Chen. Effects of Ferritin Gene Expression on Transgenic Tobacco for Low Iron Tolerance [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(02): 167-175. |
| [14] | Jianbin Hu*;Jun Liu. Progress in Tissue Culture and Genetic Transformation of Amorphophallus Blume [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2008, 25(01): 14-19. |
| [15] | JI Feng_Yuan, WANG Ge_Liang, XU Yi_Nong. THE EFFECTS OF ANTIOXIDANTS ON THE TRANSIENT EXPRESSION OF GUS GENE IN SOYBEAN HYPOCOTYLS MEDIATED BY AGROBACTERIUM TUMEFACIENS [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2006, 30(2): 330-334. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||