

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 468-478.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21181 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21181
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuan Rongzhen1,2, Wang Guohong1,*( ), Tang Zhiyao3, Wang Qinggui4
), Tang Zhiyao3, Wang Qinggui4
Received:2021-10-19
Revised:2022-04-24
Online:2022-07-01
Published:2022-07-14
Contact:
Wang Guohong
Yuan Rongzhen, Wang Guohong, Tang Zhiyao, Wang Qinggui. The Vegetation Classification on Picea koraiensis Forest Alliance and Its Environmental Interpretation[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 468-478.
| Plot | Place | Latitude (º) | Longitude (º) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20105 | Amuer, Heilongjiang province | 52.6236 | 123.1739 | 561 |
| 20063 | Daqing mountain, Dailing district, Heilongjiang province | 46.9669 | 129.0389 | 361 |
| 03LS3-1 | Liangshui national nature reserve, Heilongjiang province | 47.1833 | 128.8981 | 430 |
| 03LS4-1 | Liangshui national nature reserve, Heilongjiang province | 47.1933 | 128.8877 | 344 |
| XXAL09070710 | Dailing district, Heilongjiang province | 47.1900 | 128.8800 | 319 |
| XXAL09070711 | Dailing district, Heilongjiang province | 47.0917 | 129.1469 | 283 |
| XXAL09070204 | Hongxing district, Heilongjiang province | 48.2700 | 129.3300 | 326 |
| XXAL09070305 | Hongxing district, Heilongjiang province | 48.1100 | 129.1900 | 303 |
| XXAL09070508 | Meixi district, Heilongjiang province | 47.7600 | 129.4600 | 322 |
| 20076 | Dawusu, Mohe town, Heilongjiang province | 51.8019 | 124.4992 | 491 |
| 20078 | Dawusu, Mohe town, Heilongjiang province | 51.8014 | 124.5042 | 491 |
| 20079 | Dawusu, Mohe town, Heilongjiang province | 51.8033 | 124.5053 | 491 |
| 20080 | Dawusu, Mohe town, Heilongjiang province | 51.8119 | 124.4975 | 511 |
| XXAL09070812 | Shuangfeng district, Heilongjiang province | 46.6800 | 128.0500 | 247 |
| XXAL09082701 | Mengke mountain, Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.6300 | 124.2300 | 775 |
| 20070 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3364 | 124.6583 | 421 |
| 20071 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3367 | 124.6581 | 421 |
| 20072 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3378 | 124.6592 | 421 |
| Plot | Place | Latitude (º) | Longitude (º) | Altitude (m) |
| 20073 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3381 | 124.6581 | 421 |
| 20074 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3386 | 124.6569 | 431 |
| 20075 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3389 | 124.6556 | 420 |
| XXAL09083011 | Talin forest, Heilongjiang province | 52.3200 | 124.5200 | 382 |
| 20052 | Tangwanghe district, Heilongjiang province | 48.5047 | 129.4814 | 411 |
| 20053 | Tangwanghe district, Heilongjiang province | 48.5028 | 129.4825 | 401 |
| 20054 | Tangwanghe district, Heilongjiang province | 48.5006 | 129.4847 | 401 |
| XXAL09070103 | Tangwanghe district, Heilongjiang province | 48.5000 | 129.7000 | 387 |
| XXAL09070609 | Wumahe district, Heilongjiang province | 47.6300 | 128.7700 | 309 |
| XXAL09062901 | Wuyiling district, Heilongjiang province | 48.7400 | 129.4100 | 319 |
| 20036 | Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.5075 | 128.4831 | 381 |
| 20037 | Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.5056 | 128.4858 | 391 |
| 20038 | Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.6211 | 128.5831 | 343 |
| 20039 | Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.6208 | 128.5842 | 346 |
| 20040 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7028 | 128.9108 | 311 |
| 20041 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7019 | 128.8956 | 341 |
| 20042 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7022 | 128.8981 | 371 |
| 20043 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7028 | 128.8953 | 321 |
| 20047 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7014 | 128.8878 | 351 |
| 20048 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7028 | 128.8875 | 331 |
| 20049 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.6947 | 128.8972 | 497 |
| XXAL09070407 | Youhao district, Heilongjiang province | 48.1200 | 128.6600 | 322 |
| XXAL09070406 | Sanhe forest, Youhao district, Heilongjiang province | 48.0200 | 128.5400 | 289 |
| 20022 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.3278 | 128.1228 | 861 |
| 20023 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.3303 | 128.1214 | 861 |
| 20024 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.3306 | 128.1217 | 851 |
| 00CB-19 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.1871 | 128.1700 | 1140 |
| 00CB-20 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.2203 | 128.1714 | 1075 |
| 20010 | Fusong, Jilin province | 42.0644 | 127.6583 | 881 |
| 20011 | Fusong, Jilin province | 42.0628 | 127.6600 | 861 |
| 20012 | Fusong, Jilin province | 42.0625 | 127.6592 | 851 |
Table 1 Locations of 49 plots of Picea koraiensis Forest Alliance
| Plot | Place | Latitude (º) | Longitude (º) | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20105 | Amuer, Heilongjiang province | 52.6236 | 123.1739 | 561 |
| 20063 | Daqing mountain, Dailing district, Heilongjiang province | 46.9669 | 129.0389 | 361 |
| 03LS3-1 | Liangshui national nature reserve, Heilongjiang province | 47.1833 | 128.8981 | 430 |
| 03LS4-1 | Liangshui national nature reserve, Heilongjiang province | 47.1933 | 128.8877 | 344 |
| XXAL09070710 | Dailing district, Heilongjiang province | 47.1900 | 128.8800 | 319 |
| XXAL09070711 | Dailing district, Heilongjiang province | 47.0917 | 129.1469 | 283 |
| XXAL09070204 | Hongxing district, Heilongjiang province | 48.2700 | 129.3300 | 326 |
| XXAL09070305 | Hongxing district, Heilongjiang province | 48.1100 | 129.1900 | 303 |
| XXAL09070508 | Meixi district, Heilongjiang province | 47.7600 | 129.4600 | 322 |
| 20076 | Dawusu, Mohe town, Heilongjiang province | 51.8019 | 124.4992 | 491 |
| 20078 | Dawusu, Mohe town, Heilongjiang province | 51.8014 | 124.5042 | 491 |
| 20079 | Dawusu, Mohe town, Heilongjiang province | 51.8033 | 124.5053 | 491 |
| 20080 | Dawusu, Mohe town, Heilongjiang province | 51.8119 | 124.4975 | 511 |
| XXAL09070812 | Shuangfeng district, Heilongjiang province | 46.6800 | 128.0500 | 247 |
| XXAL09082701 | Mengke mountain, Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.6300 | 124.2300 | 775 |
| 20070 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3364 | 124.6583 | 421 |
| 20071 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3367 | 124.6581 | 421 |
| 20072 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3378 | 124.6592 | 421 |
| Plot | Place | Latitude (º) | Longitude (º) | Altitude (m) |
| 20073 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3381 | 124.6581 | 421 |
| 20074 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3386 | 124.6569 | 431 |
| 20075 | Tahe, Heilongjiang province | 52.3389 | 124.6556 | 420 |
| XXAL09083011 | Talin forest, Heilongjiang province | 52.3200 | 124.5200 | 382 |
| 20052 | Tangwanghe district, Heilongjiang province | 48.5047 | 129.4814 | 411 |
| 20053 | Tangwanghe district, Heilongjiang province | 48.5028 | 129.4825 | 401 |
| 20054 | Tangwanghe district, Heilongjiang province | 48.5006 | 129.4847 | 401 |
| XXAL09070103 | Tangwanghe district, Heilongjiang province | 48.5000 | 129.7000 | 387 |
| XXAL09070609 | Wumahe district, Heilongjiang province | 47.6300 | 128.7700 | 309 |
| XXAL09062901 | Wuyiling district, Heilongjiang province | 48.7400 | 129.4100 | 319 |
| 20036 | Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.5075 | 128.4831 | 381 |
| 20037 | Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.5056 | 128.4858 | 391 |
| 20038 | Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.6211 | 128.5831 | 343 |
| 20039 | Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.6208 | 128.5842 | 346 |
| 20040 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7028 | 128.9108 | 311 |
| 20041 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7019 | 128.8956 | 341 |
| 20042 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7022 | 128.8981 | 371 |
| 20043 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7028 | 128.8953 | 321 |
| 20047 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7014 | 128.8878 | 351 |
| 20048 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.7028 | 128.8875 | 331 |
| 20049 | Xing’an park, Yichun, Heilongjiang province | 47.6947 | 128.8972 | 497 |
| XXAL09070407 | Youhao district, Heilongjiang province | 48.1200 | 128.6600 | 322 |
| XXAL09070406 | Sanhe forest, Youhao district, Heilongjiang province | 48.0200 | 128.5400 | 289 |
| 20022 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.3278 | 128.1228 | 861 |
| 20023 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.3303 | 128.1214 | 861 |
| 20024 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.3306 | 128.1217 | 851 |
| 00CB-19 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.1871 | 128.1700 | 1140 |
| 00CB-20 | Changbai mountain, Jilin province | 42.2203 | 128.1714 | 1075 |
| 20010 | Fusong, Jilin province | 42.0644 | 127.6583 | 881 |
| 20011 | Fusong, Jilin province | 42.0628 | 127.6600 | 861 |
| 20012 | Fusong, Jilin province | 42.0625 | 127.6592 | 851 |
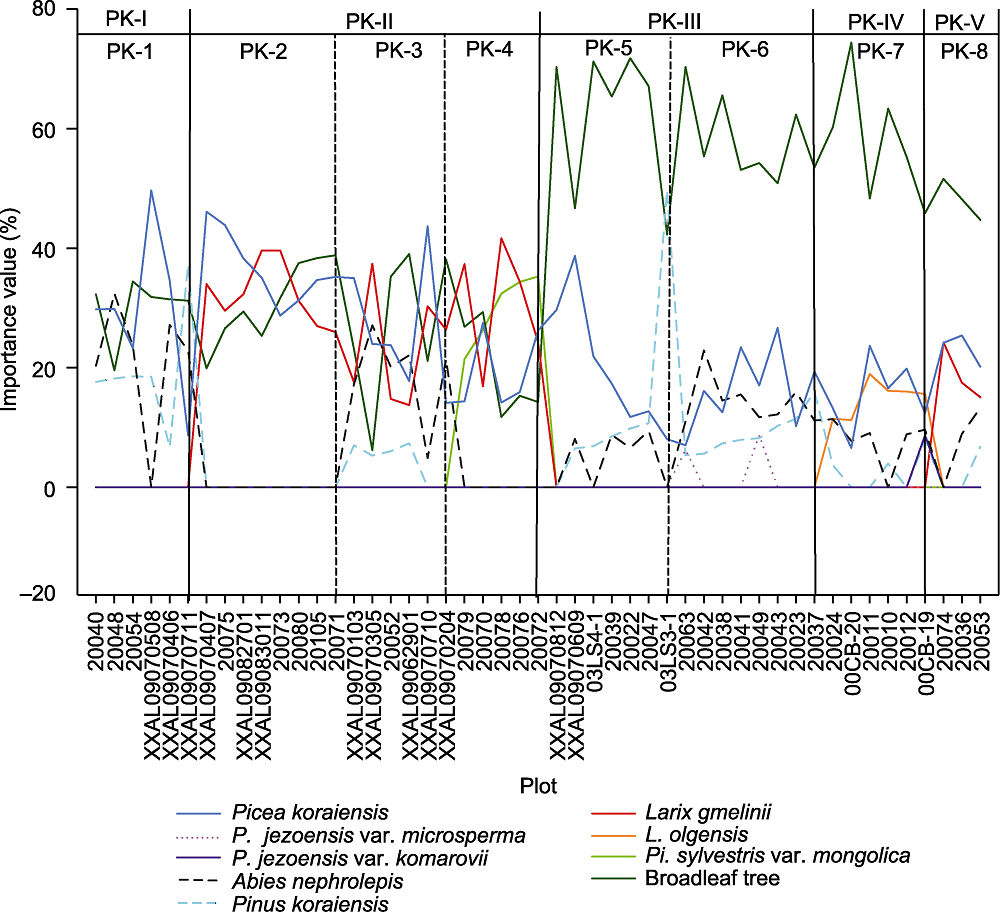
Figure 1 Importance values of needleleaf trees and the layer of broadleaf trees of tree stratum in Picea koraiensis Forest Alliance PK-1-PK-8 represent the 8 associations; PK-I-PK-V represent the 5 association groups.
| Association groups | Associations | Number of plots |
|---|---|---|
| PK-I: Picea koraiensis + Abies nephrolepis + Pinus koraiensis - Shrub - Herb Evergreen Need- leleaf Forest | PK-1: Picea koraiensis + Abies nephrolepis + Pinus koraiensis - Lonicera chrysantha - Trigonotis radicans Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | 6 |
| PK-II: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii - Shurb - Herb Mixed Deciduous and Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | PK-2: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii - Rosa acicularis - Vaccinium vitis-idaea - Deyeuxia purpurea Mixed Deciduous and Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | 8 |
| PK-3: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii + Abies nephrolepis - Corylus mandshurica - Polygonatum humile Mixed Deciduous and Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | 6 | |
| PK-4: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii + Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica - Rosa acicularis - Vaccinium vitis-idaea - Carex lanceolata Mixed Deciduous and Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | 5 | |
| PK-III: Picea koraiensis + Pinus koraiensis - Broadleaf Tree - Shrub - Herb Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | PK-5: Picea koraiensis + Pinus koraiensis - Tilia amurensis - Eleutherococcus senticosus - Carex siderosticta Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | 7 |
| PK-6: Picea koraiensis + Pinus koraiensis + Abies nephrolepis - Fraxinus mandshurica - Eleutherococcus senticosus - Dryopteris crassirhizoma Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | 8 | |
| PK-IV: Picea koraiensis + Larix olgensis - Broadleaf Tree - Shrub - Herb Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | PK-7: Picea koraiensis + Larix olgensis - Acer ukurunduense - Rubus sachalinensis - Athyrium brevifrons Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | 6 |
| PK-V: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii - Betula platyphylla - Herb Mixed Needleleaf and Broad- leaf Forest | PK-8: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii - Betula platyphylla - Ostericum maximowiczii Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | 3 |
Table 2 A vegetation classification scheme of association groups and associations in Picea koraiensis Forest Alliance
| Association groups | Associations | Number of plots |
|---|---|---|
| PK-I: Picea koraiensis + Abies nephrolepis + Pinus koraiensis - Shrub - Herb Evergreen Need- leleaf Forest | PK-1: Picea koraiensis + Abies nephrolepis + Pinus koraiensis - Lonicera chrysantha - Trigonotis radicans Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | 6 |
| PK-II: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii - Shurb - Herb Mixed Deciduous and Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | PK-2: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii - Rosa acicularis - Vaccinium vitis-idaea - Deyeuxia purpurea Mixed Deciduous and Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | 8 |
| PK-3: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii + Abies nephrolepis - Corylus mandshurica - Polygonatum humile Mixed Deciduous and Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | 6 | |
| PK-4: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii + Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica - Rosa acicularis - Vaccinium vitis-idaea - Carex lanceolata Mixed Deciduous and Evergreen Needleleaf Forest | 5 | |
| PK-III: Picea koraiensis + Pinus koraiensis - Broadleaf Tree - Shrub - Herb Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | PK-5: Picea koraiensis + Pinus koraiensis - Tilia amurensis - Eleutherococcus senticosus - Carex siderosticta Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | 7 |
| PK-6: Picea koraiensis + Pinus koraiensis + Abies nephrolepis - Fraxinus mandshurica - Eleutherococcus senticosus - Dryopteris crassirhizoma Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | 8 | |
| PK-IV: Picea koraiensis + Larix olgensis - Broadleaf Tree - Shrub - Herb Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | PK-7: Picea koraiensis + Larix olgensis - Acer ukurunduense - Rubus sachalinensis - Athyrium brevifrons Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | 6 |
| PK-V: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii - Betula platyphylla - Herb Mixed Needleleaf and Broad- leaf Forest | PK-8: Picea koraiensis + Larix gmelinii - Betula platyphylla - Ostericum maximowiczii Mixed Needleleaf and Broadleaf Forest | 3 |
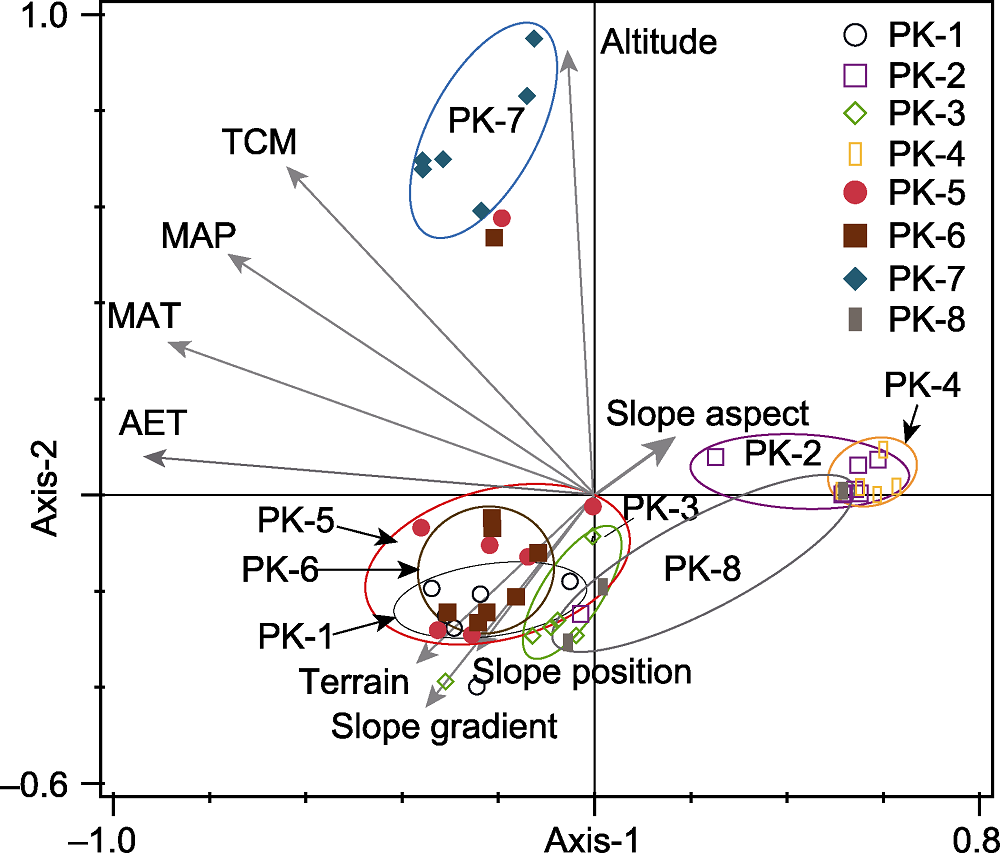
Figure 2 A redundancy analysis (RDA) biplot defined by the first two axes showing the relationship between the plots of Picea koraiensis Forest Alliance and environmental variables PK-1-PK-8 represent the 8 associations. AET: Actual evapotranspiration; MAP: Mean annual precipitation; MAT: Mean annual temperature; TCM: Mean temperature of the coldest month
| [1] | 陈灵芝 (1963). 长白山西南坡鱼鳞云杉林结构的初步研究. 植物生态学与地植物学丛刊 1, 69-80. |
| [2] | 陈灵芝, 鲍显诚, 李才贵 (1964). 吉林省长白山北坡各垂直带内主要植物群落的某些结构特征. 植物生态学与地植物学丛刊 2, 207-225. |
| [3] |
段晓梅, 白玉芳, 张钦弟, 张金屯 (2016). 山西太岳山脱皮榆群落的生态梯度分析及环境解释. 植物学报 51, 40-48.
DOI |
| [4] |
方精云, 郭柯, 王国宏, 唐志尧, 谢宗强, 沈泽昊, 王仁卿, 强胜, 梁存柱, 达良俊, 于丹 (2020). 《中国植被志》的植被分类系统、植被类型划分及编排体系. 植物生态学报 44, 96-110.
DOI |
| [5] |
郭柯, 方精云, 王国宏, 唐志尧, 谢宗强, 沈泽昊, 王仁卿, 强胜, 梁存柱, 达良俊, 于丹 (2020). 中国植被分类系统修订方案. 植物生态学报 44, 111-127.
DOI |
| [6] | 侯向阳, 韩进轩 (1997). 长白山西坡风灾干扰区的恢复和保护. 自然资源学报 12, 29-34. |
| [7] | 侯学煜 (1960). 中国的植被. 北京: 人民教育出版社. pp. 68-71. |
| [8] | 黄大明, 韩铁成, 侯世昌, 范德清, 吴力文, 史广飞 (1998). 长白山区白山市的森林资源与林业可持续发展研究. 清华大学学报(自然科学版) 38, 123-127. |
| [9] | 沈泽昊, 张新时 (2000). 三峡大老岭地区森林植被的空间格局分析及其地形解释. 植物学报 42, 1089-1095. |
| [10] | 沈泽昊, 张新时, 金义兴 (2000). 地形对亚热带山地景观尺度植被格局影响的梯度分析. 植物生态学报 24, 430-435. |
| [11] | 王国宏 (2017). 中国云杉林. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 254-284. |
| [12] |
王国宏, 方精云, 郭柯, 谢宗强, 唐志尧, 沈泽昊, 王仁卿, 王襄平, 王德利, 强胜, 于丹, 彭少麟, 达良俊, 刘庆, 梁存柱 (2020). 《中国植被志》研编内容与规范. 植物生态学报 44, 128-178.
DOI |
| [13] |
王国宏, 郭柯, 谢宗强, 唐志尧, 蒋延玲, 方精云 (2022). 《中国植被志》研编规范的若干说明、补充与修订. 植物生态学报 46, 368-372.
DOI |
| [14] | 张新时 (1993). 研究全球变化的植被-气候分类系统. 第四纪研究 (2), 157-169. |
| [15] | 中国科学院中国植被图编辑委员会 (2007). 中国植被及其地理格局——中华人民共和国植被图(1:1000000) 说明书. 北京: 地质出版社. pp. 127-145. |
| [16] | 中国森林编辑委员会 (1997). 中国森林-第1卷-总论. 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 519-528. |
| [17] | 中国森林编辑委员会 (1999). 中国森林-第2卷-针叶林. 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 698-703. |
| [18] | 中国植被编辑委员会 (1980). 中国植被. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 159-210. |
| [19] | 周以良 (1991). 中国大兴安岭植被. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 49-87. |
| [20] | 周以良 (1994). 中国小兴安岭植被. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 54-116. |
| [21] | Whittaker RH 周纪纶译 (1985). 植物群落分类. 北京: 科学出版社. pp. 250-270. |
| [22] |
Barkman JJ, Moravec J, Rauschert S (1986). Special issue-code of phytosociological nomenclature. Vegetatio 67, 145-195.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Fang JY, Song YC, Liu HY, Piao SL (2002). Vegetation-climate relationship and its application in the division of vegetation zone in China. Acta Bot Sin 44, 1105-1122. |
| [24] | Federal Geographic Data Committee (2008). National Vegetation Classification Standard, Version 2. http://www.fgdc.gov/standards/projects/FGDC-standards-projects/vegetation/NVCS_V2_FINAL_2008-02.pdf. 2019-10-10. |
| [25] |
Kolbek J, Jarolímek I, Valachovič M (2003). Forest vegetation of the northern Korean Peninsula. In: Kolbek J, Šrůtek M, Box EO, eds. Forest Vegetation of Northeast Asia. Dordrecht: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-0143-3_8.
DOI |
| [26] |
Krestov PV (2003). Forest vegetation of easternmost Russia (Russian Far East). In: Kolbek J, Šrůtek M, Box EO, eds. Forest Vegetation of Northeast Asia. Dordrecht: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-0143-3_5.
DOI |
| [27] |
Krestov PV, Nakamura Y (2002). Phytosociological study of the Picea jezoensis forests of the Far East. Folia Geobot 37, 441-473.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Lockwood JD, Aleksić JM, Zou JB, Wang J, Liu JQ, Renner SS (2013). A new phylogeny for the genus Picea from plastid, mitochondrial, and nuclear sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 69, 717-727.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Song JS (1991). Phytosociology of subalpine coniferous forests in Korea 1. Syntaxonomical interpretation. Ecol Res 6, 1-19. |
| [30] |
Song JS (1992). A comparative phytosociological study of the subalpine coniferous forests in northeastern Asia. Vegetatio 98, 175-186.
DOI URL |
| [31] | ter Braak CJF, Smilauer P (2012). CANOCO Reference Manual and User’s Guide: Software for Ordination, Version 5.0. Ithaca: Microcomputer Power. |
| [32] |
Tichý L (2002), JUICE, software for vegetation classification. J Vegetation Sci 13, 451-453.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Tichý L, Holt J (2006). JUICE: program for management, analysis and classification of ecological data. https://www.sci.muni.cz/botany/juice/JC_man1.pdf. 2019-10-10. |
| [34] | Whittaker RH (1978). Classification of Plant Communities. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 287-399. |
| [35] | Woodward EI (1987). Climate and Plant Distribution. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 62-155. |
| [1] | . Community types and characteristics of Keteleeria pubescens forests in China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(植被): 1-0. |
| [2] | Peng-Bin Han Kang-Di PEI Bin He Shu-Li XIAO Cindy Q.TANG. Community composition and characteristics of Tsuga dumosa forests in China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(植被): 1-0. |
| [3] | Bin He Peng-Bin Han Shu-Li XIAO Kang-Di PEI Cindy Q.TANG. Community types and characteristics of Keteleeria davidiana forests [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(植被): 1-0. |
| [4] | XIONG Gao-Ming, SHEN Guo-Zhen, ZHAO Chang-Ming, WANG Yang, XIE Zong-Qiang, Li Jiaxiang, XU Yao-Zhan, LI Yue-Lin, CHEN Fang-Qing 无. Vegetation types and community characteristics of Loropetalum chinense Shrubland in China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(植被): 1-. |
| [5] | ZHENG Li-Yuan, XU Xi-Zhu, Yin JiaQi, SUN Xiao-Wen, Wang Yan. Niche characteristics and interspecific associations of Glycine soja community on recessional farmland near river in suburban Shenyang, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 1-. |
| [6] |
Juan Cui, Xiaoyu Yu, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun, Wenfu Chen.
Analysis of Texture Factors and Genetic Basis Influencing the Differences in Eating Quality between Northeast China and Japanese Japonica Rice [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [7] | WAN Jia-Min, ZHANG Cai-Cai, DENG Yun, GU Rong, SINA Qu-Zong, WU Jun-Hua, LOU Qi-Yan, CHEN Mei, ZHANG Zhi-Ming, LIN Lu-Xiang. Spatial distribution patterns and intraspecific and interspecific associations of dominant species in subalpine cold-temperate coniferous forests of Shangri-La, Yunnan, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(2): 268-281. |
| [8] | Xiaolong Huang, Bingshun Meng, Haibo Li, Wei Ran, Wei Yang, Cheng Wang, Bo Xie, Xu Zhang, Jingcheng Ran, Mingming Zhang. Interspecific associations between Rhinopithecus brelichi and its sympatric species using infrared cameras [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [9] | WANG Li-Ping, WU Jun-Jie, CHAI Yong, LI Jia-Hua, YANG Chang-Ji, ZHAO Shi-Jie. Spatial patterns and associations of dominant species in a subtropical mid-mountain moist evergreen broadleaf forest in Gaoligong Mountains, Southwest China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2024, 48(2): 180-191. |
| [10] | Churan Zhang, Shengfa Li, Fengchang Li, Zhizhong Tang, Huiyan Liu, Lihong Wang, Rong Gu, Yun Deng, Zhiming Zhang, Luxiang Lin. Habitat association and community classification of woody plants in the 20 ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical semi-humid evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Jizu Mountains, Yunnan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23393-. |
| [11] | Minghui Wang, Zhaoquan Chen, Shuaifeng Li, Xiaobo Huang, Xuedong Lang, Zihan Hu, Ruiguang Shang, Wande Liu. Spatial pattern of dominant species with different seed dispersal modes in a monsoon evergreen broad-leaved forest in Pu’er, Yunnan Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [12] | Jiaojiao Wu, Guanting Guo, Dong Chen, Xin Zhao, Mingzhong Long, Dengfu Wang, Xiaona Li. Review of diversity and nitrogen fixation potential of bryophyte-cyanobacteria associations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23081-. |
| [13] | Bangbang Wu, Yuqiong Hao, Shubin Yang, Yuxi Huang, Panfeng Guan, Xingwei Zheng, Jiajia Zhao, Ling Qiao, Xiaohua Li, Weizhong Liu, Jun Zheng. Evaluation and Genetic Variation of Grain Lutein Contents in Common Wheat From Shanxi [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 535-547. |
| [14] | LI Xiao-Tian, WANG Tie-Juan, HAN Wen-Juan, ZHANG Li, ZHANG Hui, LIU Xiao-Ting, LIU Ya-Jie. Population structure and point pattern analysis of rare and endangered plant Potaninia mongolica in eastern Alxa, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2023, 47(4): 506-514. |
| [15] | Xiaoming Li, Lanfen Wang, Yongsheng Tang, Yujie Chang, Juxiang Zhang, Shumin Wang, Jing Wu. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Resistance to Acanthoscelides obtectus in Common Bean [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 77-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||