

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 457-467.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22040 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22040
• EXPERIMENTAL COMMUNICATIONS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Shi Shuiqin1, Qin Huaguang1, Zhang Jingjing1, Han Yu1, Yu Hao1, Peng Yining2, Yang Shao1, Wang Jiayi1, He Guangyu1, Qi Zehua1, Wu Wenjie2, Zhu Xingyu1, Rao Yuchun2,*( ), Mu Dan1,*(
), Mu Dan1,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-07
Revised:2022-05-30
Online:2022-07-01
Published:2022-07-14
Contact:
Rao Yuchun,Mu Dan
About author:First author contact:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
Shi Shuiqin, Qin Huaguang, Zhang Jingjing, Han Yu, Yu Hao, Peng Yining, Yang Shao, Wang Jiayi, He Guangyu, Qi Zehua, Wu Wenjie, Zhu Xingyu, Rao Yuchun, Mu Dan. Characteristics and Function Analysis of Rhizosphere Bacterial Community of Endangered Plant Pinus dabeshanensis[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 457-467.
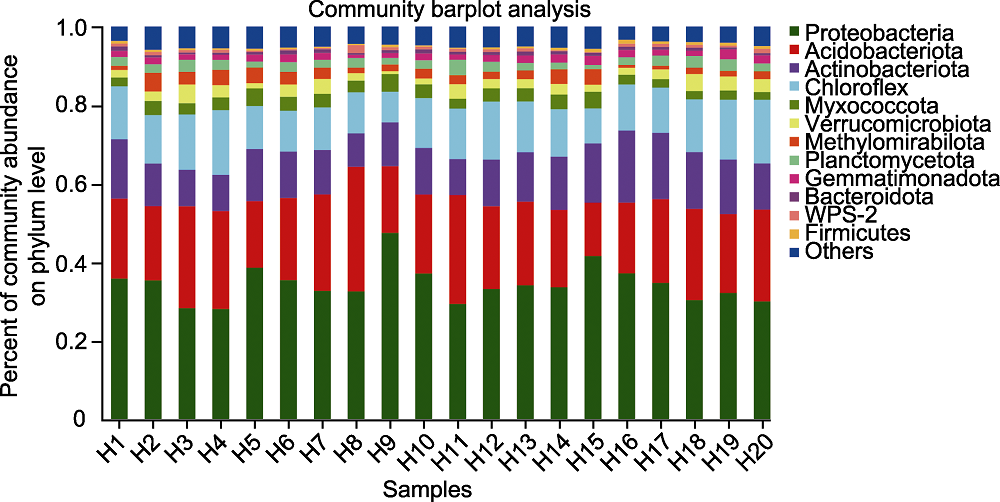
Figure 1 Species composition of rhizosphere microorganisms of Pinus dabeshanensis at phylum level The abscissa is the sample number, and the ordinate is the proportion of different species in the sample at phylum level. Columns in different colors represent different species in the sample, and the height of columns represents the proportion of the species.
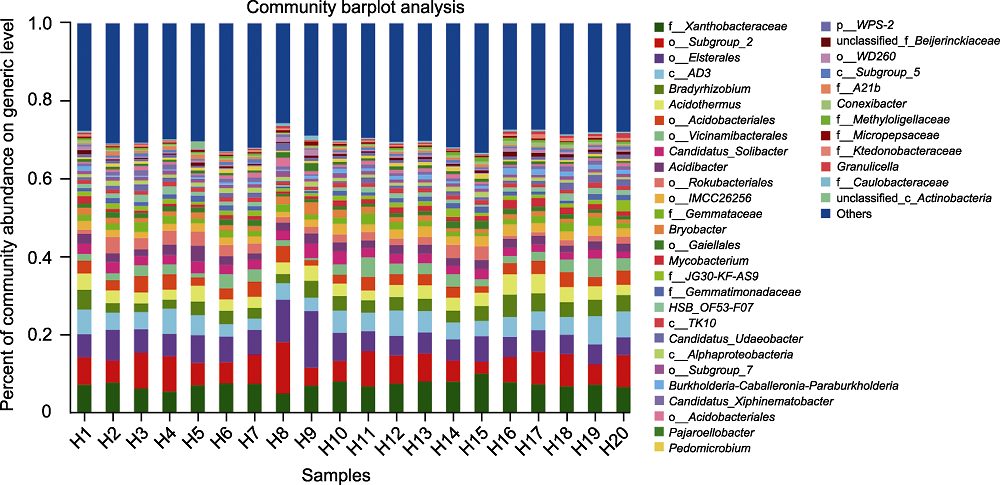
Figure 2 Species composition of rhizosphere microorganisms of Pinus dabeshanensis at generic level The abscissa is the sample number, and the ordinate is the proportion of different species in the sample at generic level. Columns in different colors represent different species in the sample, and the height of columns represents the proportion of the species.
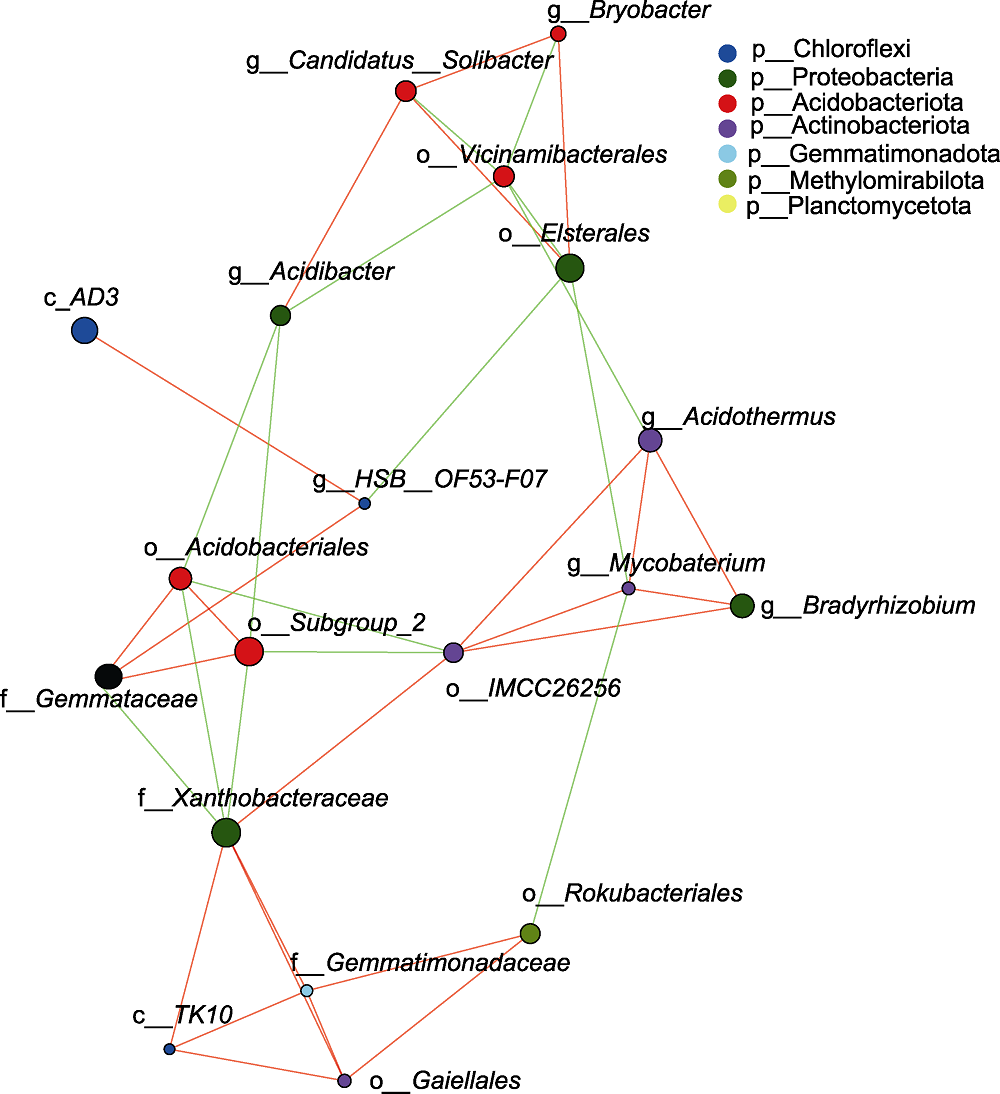
Figure 3 Network analysis of rhizosphere microorganisms of Pinus dabeshanensis The size of nodes correlated with the proportion of species abundance annotated. The red line indicates positive correlations and the green line indicates negative correlations. The thicker the connecting line, the higher the correlation between species. The more connecting lines between species, the closer the relationship between species.
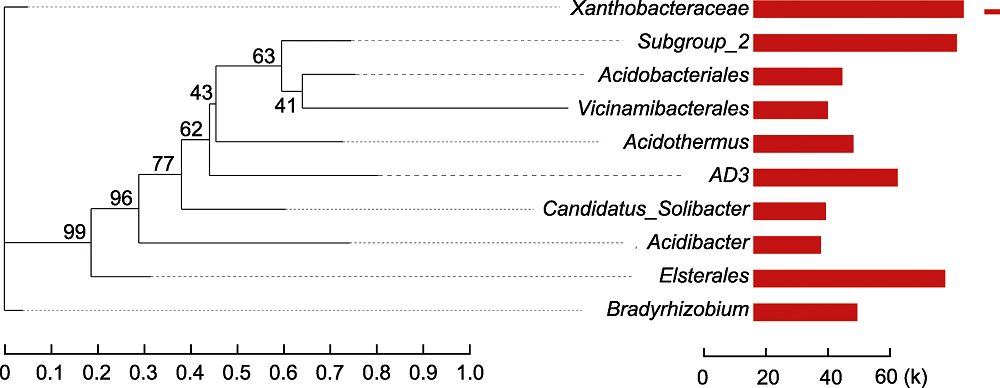
Figure 4 Phylogenetic analysis of rhizosphere microorganisms of Pinus dabeshanensis Each branch of phylogenetic evolutionary tree represents a species. The branches are colored according to the high taxonomic level of the species. The branch length is the phylogenetic distance between the two species, that is, the degree of species difference. The bar chart shows the proportion of reads of species in different groups.
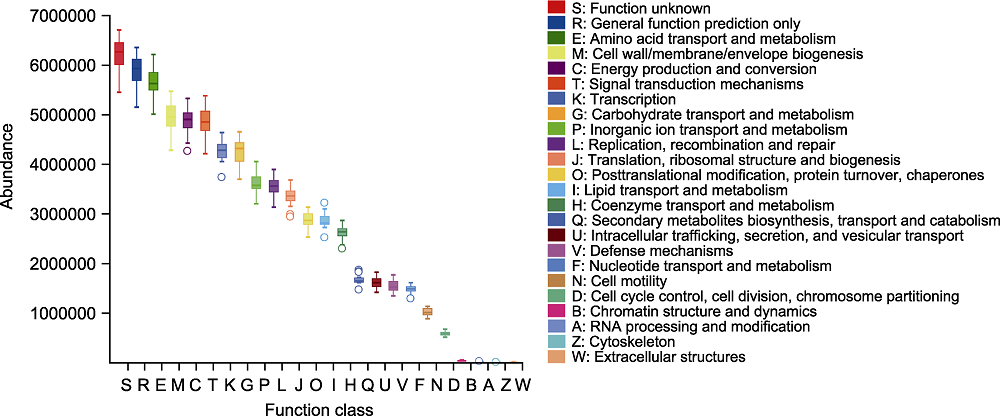
Figure 5 Classification and statistical analysis of cluster of orthologous groups of proteins (COG) function of rhizosphere microbiome of Pinus dabeshanensis The abscissa represents COG secondary function number, and the ordinate represents function abundance.
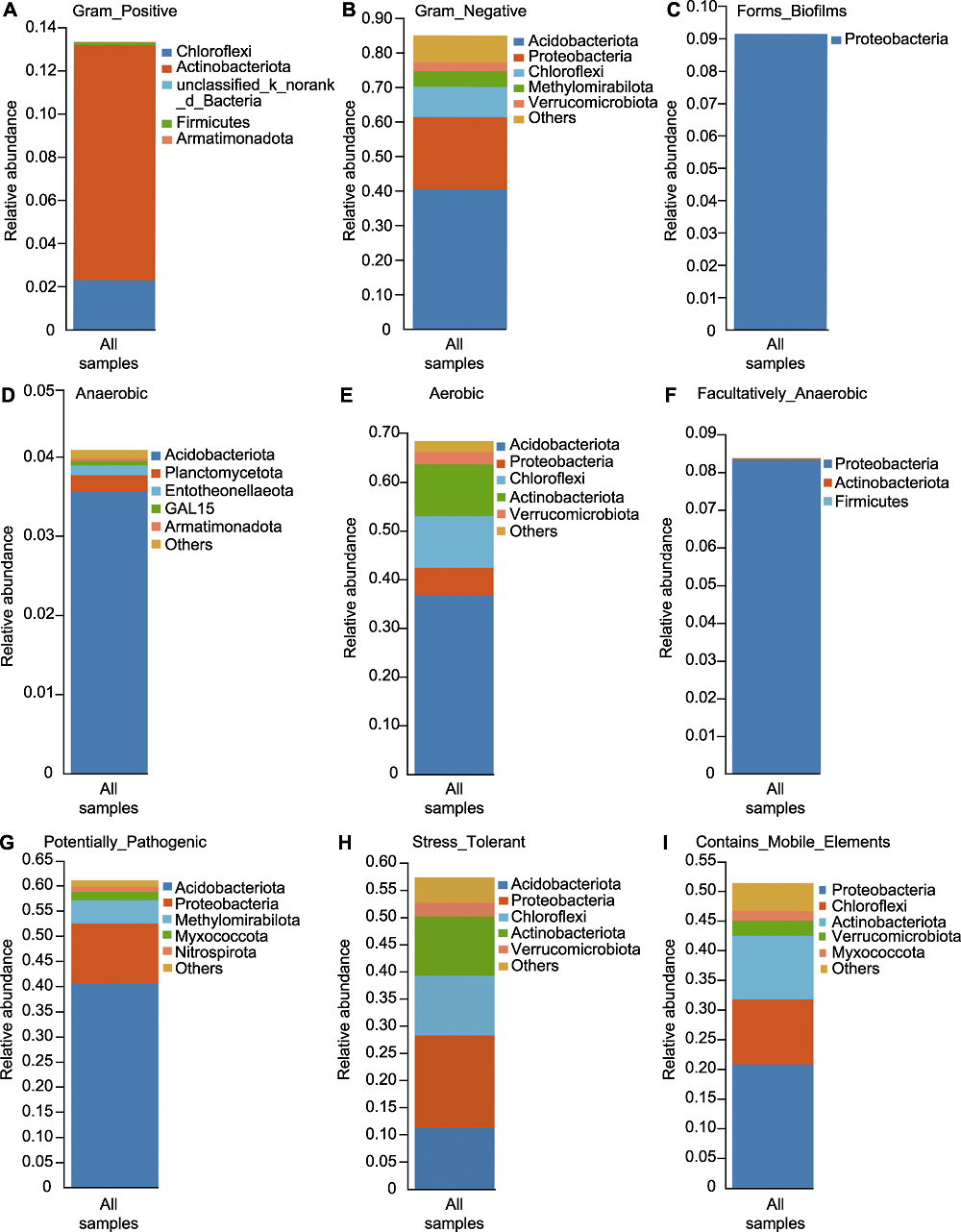
Figure 6 Species-phenotype contribution of rhizosphere microbiome of Pinus dabeshanensis (A) Gram positive phenotype; (B) Gram negative phenotype; (C) Biofilm forming phenotype; (D) Anaerobic phenotype; (E) Aerobic phenotype; (F) Facultatively anaerobic phenotype; (G) Pathogenic phenotype; (H) Stress tolerant phenotype; (I) Mobile element containing phenotype. The species-phenotype contribution shows the main species composition of a specific phenotype, it reflects the corresponding relationship between species and phenotype. The abscissa represents all samples, different color represents different species, and the ordinate is the contribution of different species in the sample to this phenotype.
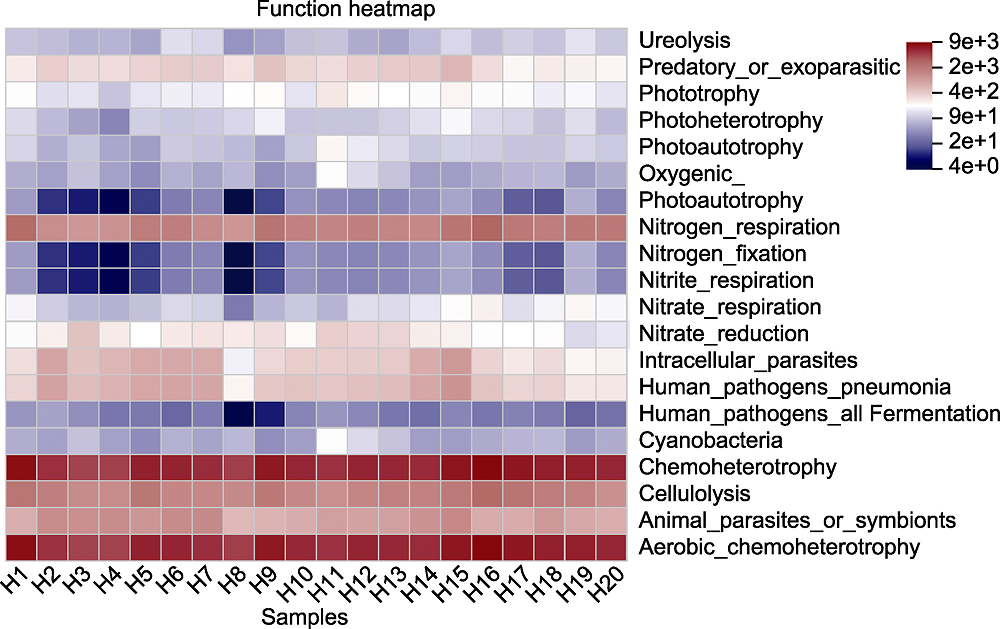
Figure 7 Functional heatmap of main species of rhizosphere microorganisms of Pinus dabeshanensis The abscissa is the sample number, the ordinate is the function name, and the color block gradient shows the abundance changes of different functions in the sample. The right side is the value represented by the color gradient.
| [1] | 宋健, 张海剑, 刘莉, 杜立新, 柳健虎, 曹伟平 (2020). 高通量测序分析高温覆膜对韭菜根际微生物多样性的影响. 中国生物防治学报 36, 938-945. |
| [2] | 滕泽栋, 李敏, 朱静, 宋明阳 (2017). 野鸭湖湿地芦苇根际微生物多样性与磷素形态关系. 环境科学 38, 4589-4597. |
| [3] |
王孝林, 王二涛 (2019). 根际微生物促进水稻氮利用的机制. 植物学报 54, 285-287.
DOI |
| [4] | 王亚茹, 田宝玉, 张碧尧, 范競文, 戈峰, 王国红 (2021). 饵料蛋白水平对德国小蠊肠道细菌群落的影响. 生态学报 41, 5495-5505. |
| [5] | Agler MT, Ruhe J, Kroll S, Morhenn C, Kim ST, Weigel D, Kemen EM (2016). Microbial hub taxa link host and abiotic factors to plant microbiome variation. PLoS Biol 14, e1002352. |
| [6] |
Babalola OO, Emmanuel OC, Adeleke BS, Odelade KA, Nwachukwu BC, Ayiti OE, Adegboyega TT, Igiehon NO (2021). Rhizosphere microbiome cooperations: strategies for sustainable crop production. Curr Microbiol 78, 1069-1085.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Bano S, Wu XG, Zhang XJ (2021). Towards sustainable agriculture: rhizosphere microbiome engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 7141-7160.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Berendsen RL, Pieterse CMJ, Bakker PAHM (2012). The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci 17, 478-486.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Bulgarelli D, Garrido-Oter R, Münch PC, Weiman A, Dröge J, Pan Y, McHardy AC, Schulze-Lefert P (2015). Structure and function of the bacterial root microbiota in wild and domesticated barley. Cell Host Microbe 17, 392-403.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Campbell BJ, Engel AS, Porter ML, Takai K (2006). The versatile ε-proteobacteria: key players in sulphidic habitats. Nat Rev Microbiol 4, 458-468.
PMID |
| [11] |
Dai ZM, Su WQ, Chen HH, Barberán A, Zhao HC, Yu MJ, Yu L, Brookes PC, Schadt CW, Chang SX, Xu JM (2018). Long-term nitrogen fertilization decreases bacterial diversity and favors the growth of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria in agro-ecosystems across the globe. Glob Chang Biol 24, 3452-3461.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Grinyer J, Reich PB, Singh BK, Allen E (2016). Relative importance of soil properties and microbial community for soil functionality: insights from a microbial swap experiment. Funct Ecol 30, 1862-1873.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Durán P, Thiergart T, Garrido-Oter R, Agler M, Kemen E, Schulze-Lefert P, Hacquard S (2018). Microbial interkingdom interactions in roots promote Arabidopsis survival. Cell 175, 973-983.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Edgar RC (2010). Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26, 2460-2461.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Eren AM, Vineis JH, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2013). A filtering method to generate high quality short reads using illumina paired-end technology. PLoS One 8, e66643. |
| [16] |
Fierer N (2017). Embracing the unknown: disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 15, 579-590.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Fu LK, Chin CM (1992). China Plant Red Data Book:Rare and Endangered Plants. Beijing: Science Press. pp. 46-47. |
| [18] |
Jacoby RP, Chen L, Schwier M, Koprivova A, Kopriva S (2020). Recent advances in the role of plant metabolites in shaping the root microbiome. F1000Res 9, 151.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Keswani C, Prakash O, Bharti N, Vilchez JI, Sansinenea E, Lally RD, Borriss R, Singh SP, Gupta VK, Fraceto LF, de Lima R, Singh HB (2019). Re-addressing the biosafety issues of plant growth promoting rizobacteria. Sci Total Environ 690, 841-852.
DOI |
| [20] |
Li YB, Li Q, Chen SF (2021). Diazotroph Paenibacillus triticisoli BJ-18 drives the variation in bacterial, diazotrophic and fungal communities in the rhizosphere and root/shoot endosphere of maize. Int J Mol Sci 22, 1460.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Ling N, Song Y, Raza W, Huang QW, Guo SW, Shen QR (2015). The response of root-associated bacterial commu- nity to the grafting of watermelon. Plant Soil 391, 253-264.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Lucas G, Synge H (1978). The IUCN Plant Red Data Book: Comprising Red Data Sheets on Two Hundred-fifty Selected Plants Threatened on a World Scale. Gland: IUCN. pp. 365-366. |
| [23] |
Lundberg DS, Lebeis SL, Paredes SH, Yourstone S, Geh- ring J, Malfatti S, Tremblay J, Engelbrektson A, Kunin V, del Rio TG, Edgar RC, Eickhorst T, Ley RE, Hugenholtz P, Tringe SG, Dangl JL (2012). Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature 488, 86-90.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Mendes LW, Kuramae EE, Navarrete AA, van Veen JA, Tsai SM (2014). Taxonomical and functional microbial community selection in soybean rhizosphere. ISME J 8, 1577-1587.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Nihorimbere V, Ongena M, Smargiassi M, Thonart P (2011). Beneficial effect of the rhizosphere microbial community for plant growth and health. Biotechnol Agron Soc Environ 15, 327-337. |
| [26] |
Noman M, Ahmed T, Ijaz U, Shahid M, Azizullah, Li DY, Manzoor I, Song FM (2021). Plant-microbiome crosstalk: dawning from composition and assembly of microbial community to improvement of disease resilience in plants. Int J Mol Sci 22, 6852.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Qu Q, Zhang ZY, Peijnenburg WJGM, Liu WY, Lu T, Hu BL, Chen JM, Chen J, Lin ZF, Qian HF (2020). Rhizosphere microbiome assembly and its impact on plant growth. J Agric Food Chem 68, 5024-5038.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Reinhold-Hurek B, Bϋnger W, Burbano CS, Sabale M, Hurek T (2015). Roots shaping their microbiome: global hotspots for microbial activity. Annu Rev Phytopathol 53, 403-424.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Sarkar J, Chakraborty B, Chakraborty U (2018). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria protect wheat plants against temperature stress through antioxidant signaling and reducing chloroplast and membrane injury. J Plant Growth Regul 37, 1396-1412.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Tang HM, Xiao XP, Li C, Pan XC, Cheng KK, Li WY, Wang K (2020). Microbial carbon source utilization in rice rhizosphere and nonrhizosphere soils with short-term manure N input rate in paddy field. Sci Rep 10, 6487.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Tian L, Chang JJ, Shi SH, Ji L, Zhang JF, Sun Y, Li XJ, Li XJ, Xie HW, Cai YH, Chen DZ, Wang JL, van Veen JA, Kuramae EE, Tran LSP, Tian CJ (2022). Comparison of methane metabolism in the rhizomicrobiomes of wild and related cultivated rice accessions reveals a strong impact of crop domestication. Sci Total Environ 803, 150131.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Tiepo AN, Hertel MF, Rocha SS, Calzavara AK, De Oliveira ALM, Pimenta JA, Oliveira HC, Bianchini E, Stolf-Moreira R (2018). Enhanced drought tolerance in seedlings of Neotropical tree species inoculated with plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Physiol Biochem 130, 277-288.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Trivedi P, Leach JE, Tringe SG, Sa TM, Singh BK (2021). Plant-microbiome interactions: from community assembly to plant health. Nat Rev Microbiol 18, 607-621.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Ward NL, Challacombe JF, Janssen PH, Henrissat B, Coutinho PM, Wu M, Xie G, Haft DH, Sait M, Badger J, Barabote RD, Bradley B, Brettin TS, Brinkac LM, Bruce D, Creasy T, Daugherty SC, Davidsen TM, DeBoy RT, Detter JC, Dodson RJ, Durkin AS, Ganapathy A, Gwinn-Giglio M, Han CS, Khouri H, Kiss H, Kothari SP, Madupu R, Nelson KE, Nelson WC, Paulsen I, Penn K, Ren QH, Rosovitz MJ, Selengut JD, Shrivastava S, Sullivan SA, Tapia R, Thompson LS, Watkins KL, Yang Q, Yu CH, Zafar N, Zhou LW, Kuske CR (2009). Three genomes from the phylum Acidobacteria provide insight into the lifestyles of these microorganisms in soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 75, 2046-2056.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Warrad M, Hassan YM, Mohamed MSM, Hagagy N, Al- Maghrabi OA, Selim S, Saleh AM, AbdElgawad H (2020). A bioactive fraction from Streptomyces sp. enhances maize tolerance against drought stress. J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 1156-1168.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Xu J, Zhang YZ, Zhang PF, Trivedi P, Riera N, Wang YY, Liu X, Fan GY, Tang JL, Coletta-Filho HD, Cubero J, Deng XL, Ancona V, Lu ZJ, Zhong BL, Roper MC, Capote N, Catara V, Pietersen G, Vernière C, Al-Sadi AM, Li L, Yang F, Xu X, Wang J, Yang HM, Jin T, Wang N (2018). The structure and function of the global citrus rhizosphere microbiome. Nat Commun 9, 4894.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Zhu ZK, Ge TD, Hu YJ, Zhou P, Wang TT, Shibistova O, Guggenberger G, Su YR, Wu JS (2017). Fate of rice shoot and root residues, rhizodeposits, and microbial assimilated carbon in paddy soil-part 2: turnover and microbial utilization. Plant Soil 416, 243-257.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Zhu ZK, Ge TD, Liu SL, Hu YJ, Ye RZ, Xiao ML, Tong CL, Kuzyakov Y, Wu JS (2018). Rice rhizodeposits affect organic matter priming in paddy soil: the role of N fertilization and plant growth for enzyme activities, CO2 and CH4 emissions. Soil Biol Biochem 116, 369-377.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Zhou xin-yu, huiliang liu, GAO Bei, LU Yuting, TAO Lingqing, WEN Xiaohu, ZHANG Lan, ZHANG Yuan-Ming. Reproductive Biology of the Endangered and Endemic Species Nymphaea candida C. Presl in Xinjiang [J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [2] | JIA Yan-Yan, LIU Hua-Qing, XIE Xin-Ran, WANG Bo, ZHANG Wei, YANG Yun-Fei. Age structure and population dynamics of rare and endangered Fraxinus sogdiana, China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2025, 49(5): 760-772. |
| [3] | Murong Yi, Ping Lu, Yong Peng, Yong Tang, Jiuheng Xu, Haoping Yin, Luyang Zhang, Xiaodong Weng, Mingxiao Di, Juan Lei, Chenqi Lu, Rujun Cao, Nianhua Dai, Deyang Zhan, Mei Tong, Zhiming Lou, Yonggang Ding, Jing Chai, Jing Che. Population status and habitat of Critically Endangered Jiangxi giant salamander (Andrias jiangxiensis) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24145-. |
| [4] | Yang Ding, Yingqun Feng, Jinyu Zhang, Bo Wang. Seed predation and dispersal by animals of an endangered endemic species Pinus dabeshanensis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23401-. |
| [5] | Yunrui Ji, Xuelei Wei, Guofeng Zhang, Minggui Xiang, Yongchao Wang, Renhu Gong, Yang Hu, Diqiang Li, Fang Liu. Diversity and composition of bird species in the Hubei Wufeng Houhe National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 21475-. |
| [6] | Yanyan Liu, Chang Liu, Xiaoxin Wei. Current status of taxonomy, systematics and conservation of the white pines in China and adjacent regions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 21344-. |
| [7] | Chengqiang Xia, Yi Li, Yanru Dang, Qianqian Cha, Xiaoyan He, Qilong Qin. Diversity of culturable and in situ bacteria in surface seawater from the central Indian Ocean and the western South China Sea [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(1): 21407-. |
| [8] | Wenting Wang, Tingting Yang, Lei Jin, Jiamin Jiang. Vulnerability of two Rhodiola species under climate change in the future [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(12): 1620-1628. |
| [9] | Yong Yang, Chao Tan, Zhi Yang. Conservation of gymnosperms in China: Perspectives from the List of National Key Protected Wild Plants [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(12): 1591-1598. |
| [10] | Zhongcheng Liu, Zhong Zhang, Yong Lan, Wanyi Zhao, Jia Liu, Chunquan Chen, Wenbo Liao, Lei Wang. Status and management strategy for rare and endangered key protected wild plants in the Luoxiao Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(7): 867-875. |
| [11] | Xinying Jin, Xiaochong Zhang, Duo Jin, Yun Chen, Jingyu Li. Diversity and seasonal dynamics of bacteria among different biological soil crusts in the southeast Tengger Desert [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(6): 718-726. |
| [12] | Zhigang Jiang, Jianping Jiang, Yuezhao Wang, E Zhang, Yanyun Zhang, Bo Cai. Significance of country red lists of endangered species for biodiversity conservation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(5): 558-565. |
| [13] | Jun Liu, Ning Wang, Daizong Cui, Lei Lu, Min Zhao. Community structure and diversity of soil bacteria in different habitats of Da Liangzihe National Forest Park in the Lesser Khinggan Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(8): 911-918. |
| [14] | Liu Shanlin. DNA barcoding and emerging reference construction and data analysis technologies [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(5): 526-533. |
| [15] | Qiujie Zhou, Yacheng Cai, Wei Lun Ng, Wei Wu, Seping Dai, Feng Wang, Renchao Zhou. Molecular evidence for natural hybridization between two Melastoma species endemic to Hainan and their widespread congeners [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(6): 638-646. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||