

Chinese Bulletin of Botany ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 441-454.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18191 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18191
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuemei Zhao1,Zhenyan Yang2,Yongping Zhao1,Xiaoling Li1,Zhixin Zhao1,Guifang Zhao3,*( )
)
Received:2018-09-06
Accepted:2019-04-23
Online:2019-07-01
Published:2020-01-08
Contact:
Guifang Zhao
Yuemei Zhao,Zhenyan Yang,Yongping Zhao,Xiaoling Li,Zhixin Zhao,Guifang Zhao. Chloroplast Genome Structural Characteristics and Phylogenetic Relationships of Oleaceae[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(4): 441-454.
| Species | petD | rps12 | clpP | rpoC1 | rps16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 483/1196 | 372/908 | 591/2047 | 2064/2821 | 267/1132 |
| 2 | 483/1218 | 372/908 | 591/2043 | 2073/2834 | 267/1147 |
| 3 | 483/1230 | 375/911 | 591/2045 | 2052/2820 | 267/1134 |
| 4 | 483/1261 | 381/917 | 591/2043 | 2073/2827 | 267/1153 |
| 5 | 483/1134 | 372/908 | 591/2045 | 2052/2811 | 255/1147 |
| 6 | 483/1148 | 372/908 | 591/2053 | 2073/2830 | 267/1136 |
| 7 | 483/1217 | 372/908 | 591/2039 | 2073/2834 | 267/1142 |
| 8 | 483/1196 | 372/908 | 588/2045 | 2064/2822 | 267/1131 |
| 9 | 483/1196 | 381/917 | 660 | 2076/2844 | 267/1162 |
| 10 | 483/1203 | 387/923 | 786 | 2052/2808 | 267/1154 |
| 11 | 483/1213 | 387/923 | 786 | 2052/2807 | 267/1161 |
| 12 | 483/1215 | 381/917 | 591/2041 | 2073/2833 | 267/1143 |
| 13 | 483/1217 | 372/908 | 591/2043 | 2073/2830 | 267/1143 |
| 14 | 483/1215 | 372/908 | 591/2046 | 2073/2832 | 267/1141 |
| 15 | 483/1213 | 371/907 | 591/2043 | 2073/2831 | 267/1142 |
| 16 | 483/1213 | 372/908 | 591/2044 | 2073/2831 | 267/1142 |
| 17 | 483/1215 | 373/909 | 591/2041 | 2073/2833 | 267/1141 |
| 18 | 483/1203 | 372/908 | 591/2047 | 2073/2834 | 267/1147 |
| 19 | 483/1199 | 372/913 | 591/2041 | 2073/2784 | 237/1115 |
Table 2 Length of coding region and complete gene of intron-contained protein-coding genes of chloroplast genomes
| Species | petD | rps12 | clpP | rpoC1 | rps16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 483/1196 | 372/908 | 591/2047 | 2064/2821 | 267/1132 |
| 2 | 483/1218 | 372/908 | 591/2043 | 2073/2834 | 267/1147 |
| 3 | 483/1230 | 375/911 | 591/2045 | 2052/2820 | 267/1134 |
| 4 | 483/1261 | 381/917 | 591/2043 | 2073/2827 | 267/1153 |
| 5 | 483/1134 | 372/908 | 591/2045 | 2052/2811 | 255/1147 |
| 6 | 483/1148 | 372/908 | 591/2053 | 2073/2830 | 267/1136 |
| 7 | 483/1217 | 372/908 | 591/2039 | 2073/2834 | 267/1142 |
| 8 | 483/1196 | 372/908 | 588/2045 | 2064/2822 | 267/1131 |
| 9 | 483/1196 | 381/917 | 660 | 2076/2844 | 267/1162 |
| 10 | 483/1203 | 387/923 | 786 | 2052/2808 | 267/1154 |
| 11 | 483/1213 | 387/923 | 786 | 2052/2807 | 267/1161 |
| 12 | 483/1215 | 381/917 | 591/2041 | 2073/2833 | 267/1143 |
| 13 | 483/1217 | 372/908 | 591/2043 | 2073/2830 | 267/1143 |
| 14 | 483/1215 | 372/908 | 591/2046 | 2073/2832 | 267/1141 |
| 15 | 483/1213 | 371/907 | 591/2043 | 2073/2831 | 267/1142 |
| 16 | 483/1213 | 372/908 | 591/2044 | 2073/2831 | 267/1142 |
| 17 | 483/1215 | 373/909 | 591/2041 | 2073/2833 | 267/1141 |
| 18 | 483/1203 | 372/908 | 591/2047 | 2073/2834 | 267/1147 |
| 19 | 483/1199 | 372/913 | 591/2041 | 2073/2784 | 237/1115 |
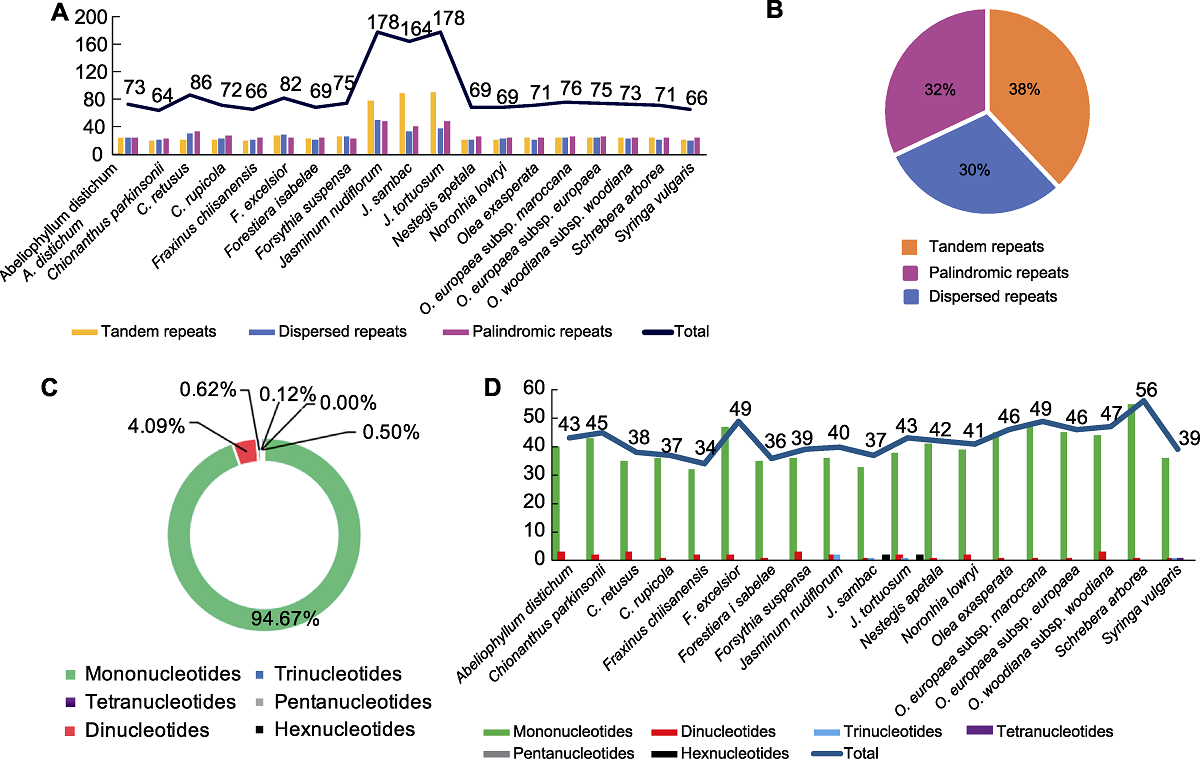
Figure 1 The type and percentage of repeated sequences in the chloroplast genomes of 19 species in Oleaceae (A) Number of three type repeats; (B) Percentage of three type repeats; (C) Percentage of SSR types; (D) Number and types of SSRs
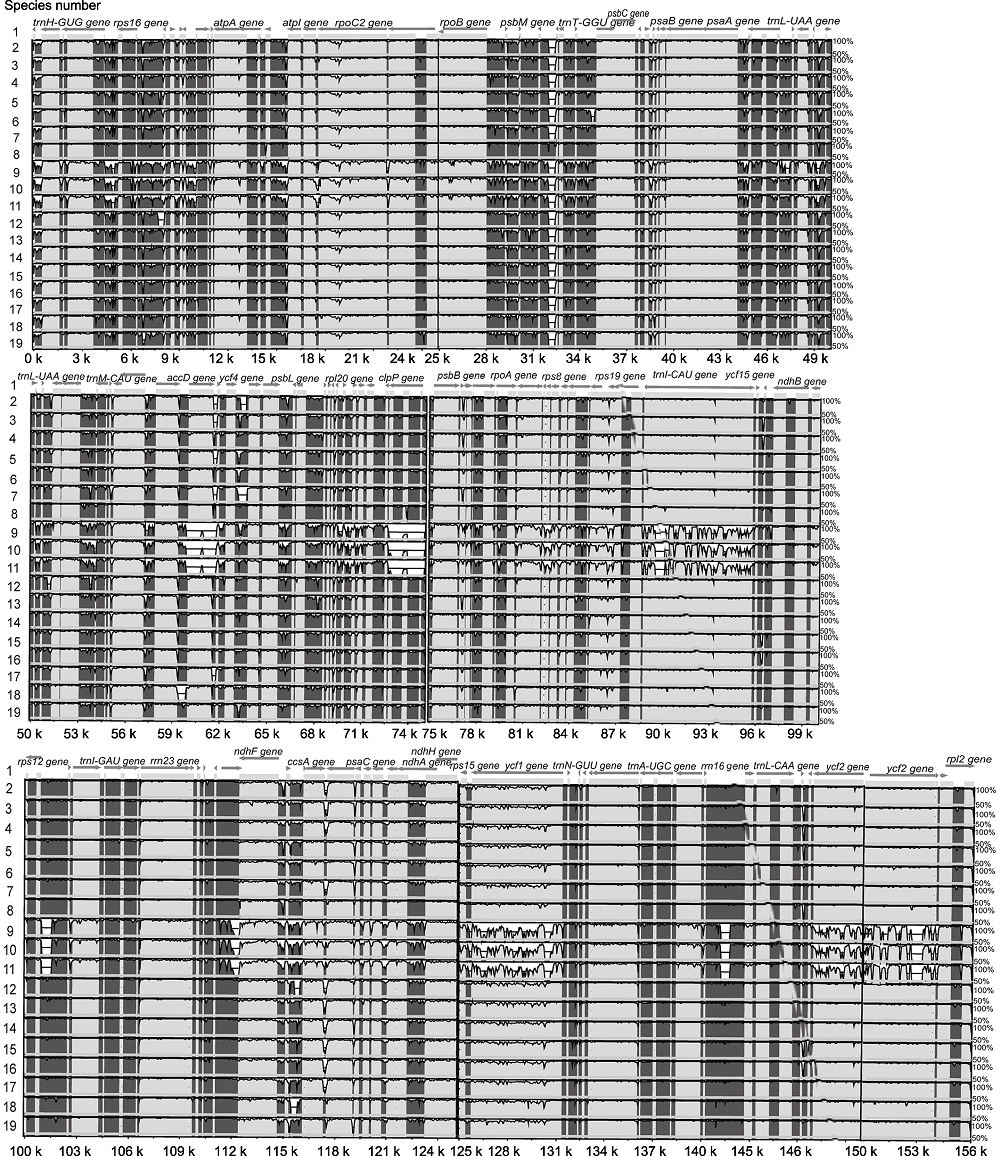
Figure 3 Graphic view of the alignment of chloroplast genomes from 19 species in Oleaceae The species number 1-19 same as Table 1. Sequence identity varying between 50% and 100% are drawn on the y axis of the plot, the x axis corresponds to the coordinates on the Abeliophyllum distichum chloroplast genome. Arrows indicate the annotated genes and their transcriptional direction.
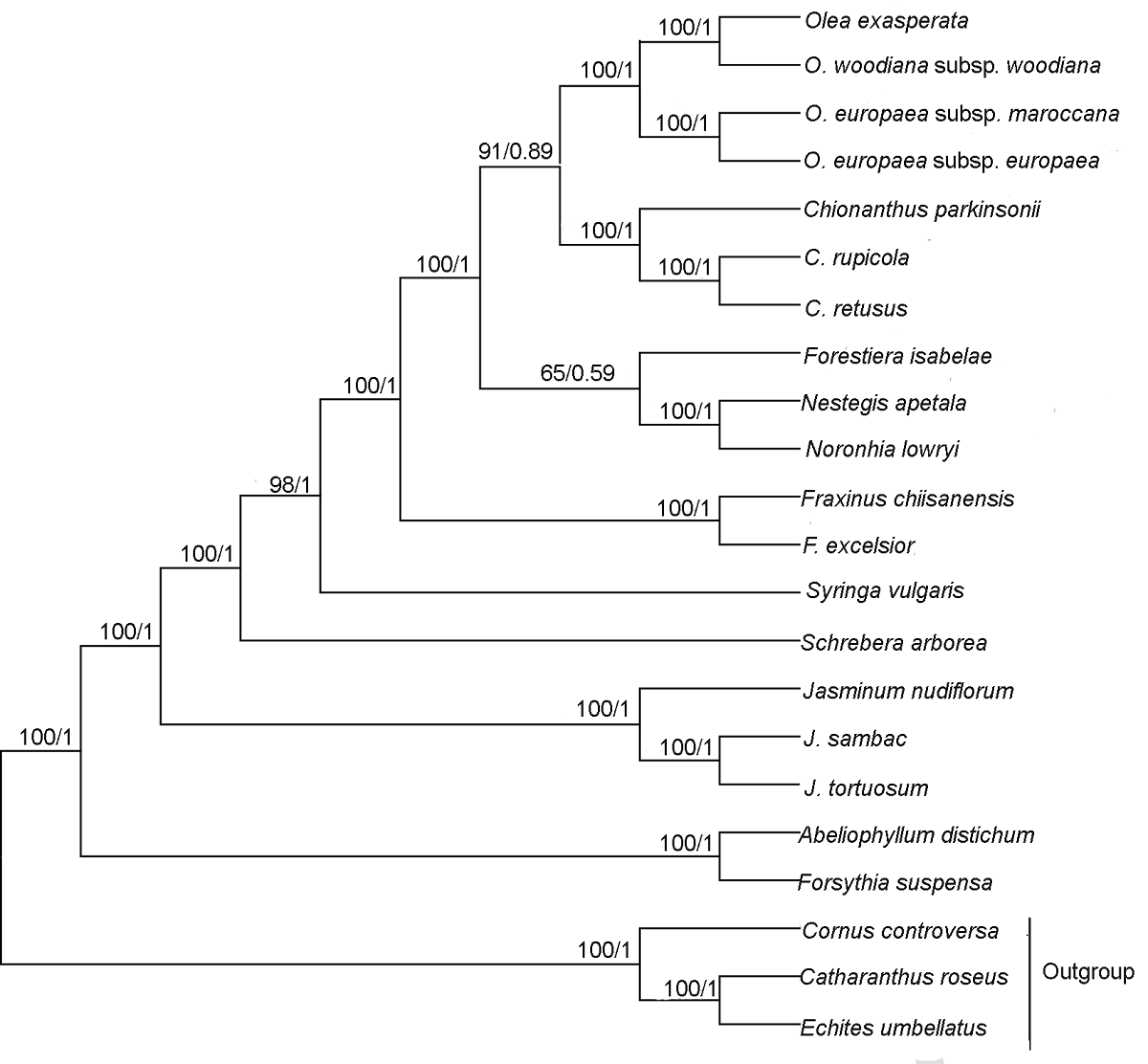
Figure 5 Phylogenetic relationship of 19 species in Oleaceae inferred from ML and BI analyses based on shared protein-coding genes The numbers near each node are bootstrap support values in ML and posterior probability in BI. The outgroups are Cornus controversa, Echites umbellatus and Catharanthus roseus. ML: Maximum likelihood; BI: Bayesian inference
| [1] | 李巧丽, 延娜, 宋琼, 郭军战 ( 2018). 鲁桑叶绿体基因组序列及特征分析. 植物学报 53, 94-103. |
| [2] | 唐萍, 阮秋燕, 彭程 ( 2011). 禾本科植物叶绿体基因组结构的系统进化研究. 中国农学通报 27(30), 17. |
| [3] | Baali-Cherif D, Besnard G ( 2005). High genetic diversity and clonal growth in relict populations of Olea europaea subsp. laperrinei ( Oleaceae) from Hoggar, Algeria. Ann Bot 96, 823-830. |
| [4] | Benson G ( 1999). Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 27, 573-580. |
| [5] | Besnard G, de Casas RR, Christin PA, Vargas P ( 2009). Phylogenetics of Olea( Oleaceae) based on plastid and nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences: tertiary climatic shifts and lineage differentiation times. Ann Bot 104, 143-160. |
| [6] | Besnard G, Hernández P, Khadari B, Dorado G, Savolainen V ( 2011). Genomic profiling of plastid DNA variation in the mediterranean olive tree. BMC Plant Biol 11, 80. |
| [7] | Besnard G, Khadari B, Baradat P, Bervillé A ( 2002). Olea europaea( Oleaceae) phylogeography based on chloroplast DNA polymorphism. Theor Appl Genet 104, 1353-1361. |
| [8] | Blazier JC, Ruhlman TA, Weng ML, Rehman SK, Sabir JSM, Jansen RK ( 2016). Divergence of RNA polymerase α subunits in angiosperm plastid genomes is mediated by genomic rearrangement. Sci Rep 6, 24595. |
| [9] | Chumley TW, Palmer JD, Mower JP, Fourcade HM, Calie PJ, Boore JL, Jansen RK ( 2006). The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Pelargonium x hortorum: organization and evolution of the largest and most highly rearranged chloroplast genome of land plants. Mol Biol Evol 23, 2175-2190. |
| [10] | Darling ACE, Mau B, Blattner FR, Perna ANT ( 2004). Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res 14, 1394-1403. |
| [11] | Dong WP, Xu C, Cheng T, Lin K, Zhou SL ( 2013). Sequencing angiosperm plastid genomes made easy: a complete set of universal primers and a case study on the phylogeny of Saxifragales. Genome Biol Evol 5, 989-997. |
| [12] | Flora of China Editorial Committee ( 1995). Flora of China, Vol. 16. Beijing & St. Louis: Science Press & Missouri Botanical Garden Press. pp. 143-188. |
| [13] | Flora of China Editorial Committee ( 1996). Flora of China, Vol. 15. Beijing & St. Louis: Science Press & Missouri Botanical Garden Press. pp. 272-319. |
| [14] | Frazer KA, Pachter L, Poliakov A, Rubin EM, Dubchak I ( 2004). Vista: computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 32, W273-W279. |
| [15] | Gao L, Su YJ, Wang T ( 2010). Plastid genome sequencing, comparative genomics, and phylogenomics: current status and prospects. J Syst Evol 48, 77-93. |
| [16] | Gray BN, Ahner BA, Hanson MR ( 2009). Extensive homologous recombination between introduced and native regulatory plastid DNA elements in transplastomic plants. Transgenic Res 18, 559-572. |
| [17] | Greiner S, Wang X, Rauwolf U, Silber MV, Mayer K, Meurer J, Haberer G, Herrmann RG ( 2008). The complete nucleotide sequences of the five genetically distinct plastid genomes of Oenothera, subsection Oenothera. I. Sequence evaluation and plastome evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 36, 2366-2378. |
| [18] | Guisinger MM, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Jansen RK ( 2011). Extreme reconfiguration of plastid genomes in the angiosperm family Geraniaceae: rearrangements, repeats, and codon usage. Mol Biol Evol 28, 583-600. |
| [19] | Hansen DR, Dastidar SG, Cai ZQ, Penaflor C, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Jansen RK ( 2007). Phylogenetic and evolutionary implications of complete chloroplast genome sequences of four early-diverging angiosperms: Buxus( Buxaceae), Chloranthus 45, 547-563. |
| [20] | He YX, Liu LX, Yang SH, Dong MF, Yuan WJ, Shang FD ( 2017). Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of chinese fringetree (Chionanthus retusus). Conserv Genet Resour 9, 431-434. |
| [21] | Hirao T, Watanabe A, Kurita M, Kondo T, Takata K ( 2008). Complete nucleotide sequence of the Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. chloroplast genome and comparative chloroplast genomics: diversified genomic structure of coniferous species. BMC Plant Biol 8, 70. |
| [22] | Hiratsuka J, Shimada H, Whittier R, Ishibashi T, Sakamoto M, Mori M, Kondo C, Honji Y, Sun CR, Meng BY, Li YQ, Kanno A, Nishizawa Y, Hirai A, Shinozaki K, Sugiura M ( 1989). The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet 217, 185-194. |
| [23] | Hu YC, Zhang Q, Rao GY , Sodmergen ( 2008). Occurrence of plastids in the sperm cells of Caprifoliaceae: biparental plastid inheritance in angiosperms is unilaterally derived from maternal inheritance. Plant Cell Physiol 49, 958-968. |
| [24] | Huang H, Shi C, Liu Y, Mao SY, Gao LZ ( 2014). Thirteen Camellia chloroplast genome sequences determined by high-throughput sequencing: genome structure and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Evol Biol 14, 151. |
| [25] | Jeandroz S, Roy A, Bousquet J ( 1997). Phylogeny and phylogeography of the circumpolar genus Fraxinus( Oleaceae) based on internal transcribed spacer sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Mol Phylogenet Evol 7, 241-251. |
| [26] | Katayama H, Ogihara Y ( 1996). Phylogenetic affinities of the grasses to other monocots as revealed by molecular analysis of chloroplast DNA. Curr Genet 29, 572-581. |
| [27] | Khakhlova O, Bock R ( 2006). Elimination of deleterious mutations in plastid genomes by gene conversion. Plant J 46, 85-94. |
| [28] | Kim C, Kim HJ, Do HDK, Jung J, Kim JH ( 2018). Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Fraxinus chiisanensis( Oleaceae), an endemic to Korea. Conserv Genet Resour 11, 63-66. |
| [29] | Kim HW, Lee HL, Lee DK, Kim KJ ( 2016). Complete plastid genome sequences of Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai (Oleaceae), a Korea endemic genus. Mitochondr DNA Part B 1, 596-598. |
| [30] | Knox EB, Downie SR, Palmer JD ( 1993). Chloroplast genome rearrangements and the evolution of giant lobelias from herbaceous ancestors. Mol Biol Evol 10, 414-430. |
| [31] | Kurtz S, Choudhuri JV, Ohlebusch E, Schleiermacher C, Stoye J, Giegerich R ( 2001). Reputer: the manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res 29, 4633-4642. |
| [32] | Lee HL, Jansen RK, Chumley TW, Kim KJ ( 2007). Gene relocations within chloroplast genomes of Jasminum and Menodora( Oleaceae) are due to multiple, overlapping inversions. Mol Biol Evol 24, 1161-1180. |
| [33] | Li JH, Alexander JH, Zhang DL ( 2002). Paraphyletic Syringa( Oleaceae): evidence from sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS and ETS regions. Syst Bot 27, 592-597. |
| [34] | Maier RM, Neckermann K, Igloi GL, Kösel H ( 1995). Complete sequence of the maize chloroplast genome: gene content, hotspots of divergence and fine tuning of genetic information by transcript editing. J Mol Biol 251, 614-628. |
| [35] | Ogihara Y, Terachi T, Sasakuma T ( 1988). Intramolecular recombination of chloroplast genome mediated by short direct-repeat sequences in wheat species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85, 8573-8577. |
| [36] | Palmer JD ( 1985). Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu Rev Genet 19, 325-354. |
| [37] | Posada D ( 2008). jModeltest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25, 1253-1256. |
| [38] | Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP ( 2003). Mrbayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19, 1572-1574. |
| [39] | Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J ( 2008). A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the raxml web servers. Syst Biol 57, 758-771. |
| [40] | Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney R, Graner A ( 2003). Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106, 411-422. |
| [41] | Van de Paer C, Bouchez O, Besnard G ( 2018). Prospects on the evolutionary mitogenomics of plants: a case study on the olive family (Oleaceae). Mol Ecol Res 18, 407-423. |
| [42] | Wallander E ( 2008). Systematics of Fraxinus( Oleaceae) and evolution of dioecy. Plant Syst Evol 273, 25-49. |
| [43] | Wallander E, Albert VA ( 2000). Phylogeny and classification of Oleaceae based on rps16 and trnL-F sequence data. Am J Bot 87, 1827-1841. |
| [44] | Wang WB, Yu H, Wang JH, Lei WJ, Gao JH, Qiu XP, Wang JS ( 2017). The complete chloroplast genome sequences of the medicinal plant Forsythia suspensa( Oleaceae). Int J Mol Sci 18, 2288. |
| [45] | Weng ML, Blazier JC, Govindu M, Jansen RK ( 2014). Reconstruction of the ancestral plastid genome in Geraniaceae reveals a correlation between genome rearrangements, repeats, and nucleotide substitution rates. Mol Biol Evol 31, 645-659. |
| [46] | Zhang TW, Fang YJ, Wang XM, Deng X, Zhang XW, Hu SN, Yu J ( 2012). The complete chloroplast and mitochondrial genome sequences of Boea hygrometrica: insights into the evolution of plant organellar genomes. PLoS One 7, e30531. |
| [47] | Zhang X, Zhou T, Yang J, Sun JJ, Ju MM, Zhao YM, Zhao GF ( 2018). Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes of Cucurbitaceae species: lights into selective pressures and phylogenetic relationships. Molecules 23, 2165. |
| [1] | Hong Deyuan. A brief discussion on methodology in taxonomy [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24541-. |
| [2] | Yajun Sun. What do higher or lower organisms mean—Clarify the meaning and validity of the biological ladder implied by On the Origin of Species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24394-. |
| [3] | Hua He, Dunyan Tan, Xiaochen Yang. Cryptic dioecy in angiosperms: Diversity, phylogeny and evolutionary significance [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24149-. |
| [4] | Yanyu Ai, Haixia Hu, Ting Shen, Yuxuan Mo, Jinhua Qi, Liang Song. Vascular epiphyte diversity and the correlation analysis with host tree characteristics: A case in a mid-mountain moist evergreen broad-leaved forest, Ailao Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24072-. |
| [5] | Yanwen Lv, Ziyun Wang, Yu Xiao, Zihan He, Chao Wu, Xinsheng Hu. Advances in lineage sorting theories and their detection methods [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23400-. |
| [6] | Zhi Yang, Yong Yang. Research Advances on Nuclear Genomes of Economically Important Trees of Lauraceae [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 302-318. |
| [7] | Chen-Kun Jiang, Wen-Bin Yu, Guang-Yuan Rao, Huaicheng Li, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. Plant Phylogeny Posters—An educational project on plant diversity from an evolutionary perspective [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [8] | Zhenzhou Chu, Gulbar Yisilam, Zezhong Qu, Xinmin Tian. Comparative Analyses on the Chloroplast Genome of Three Sympatric Atraphaxis Species [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 417-432. |
| [9] | Huiyin Song, Zhengyu Hu, Guoxiang Liu. Assessing advances in taxonomic research on Chlorellaceae (Chlorophyta) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22083-. |
| [10] | Zhizhong Li, Shuai Peng, Qingfeng Wang, Wei Li, Shichu Liang, Jinming Chen. Cryptic diversity of the genus Ottelia in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22394-. |
| [11] | Jinbo Bao, Zhijie Ding, Haoyu Miao, Xueli Li, Shuxian Ren, Ruoyan Jiao, Hao Li, Qianqian Deng, Yingzi Li, Xinmin Tian. Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes of Aleurites moluccana [J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(2): 248-260. |
| [12] | Ting Wang, Jiangping Shu, Yufeng Gu, Yanqing Li, Tuo Yang, Zhoufeng Xu, Jianying Xiang, Xianchun Zhang, Yuehong Yan. Insight into the studies on diversity of lycophytes and ferns in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(7): 22381-. |
| [13] | Jianming Wang, Mengjun Qu, Yin Wang, Yiming Feng, Bo Wu, Qi Lu, Nianpeng He, Jingwen Li. The drivers of plant taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic β-diversity in the gobi desert of northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [14] | XIANG Wei, HUANG Dong-Liu, ZHU Shi-Dan. Absorptive root anatomical traits of 26 tropical and subtropical fern species [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2022, 46(5): 593-601. |
| [15] | WANG Chun-Cheng, ZHANG Yun-Ling, MA Song-Mei, HUANG Gang, ZHANG Dan, YAN Han. Phylogeny and species differentiation of four wild almond species of subgen. Amygdalus in China [J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2021, 45(9): 987-995. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||