

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (4): 671-680.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24002 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24002
• 专题论坛 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-01-03
接受日期:2024-05-15
出版日期:2024-07-10
发布日期:2024-07-10
通讯作者:
*陈析丰, 浙江师范大学生命科学学院教授, 浙江省遗传学会理事。团队聚焦作物与病原菌互作的分子机制, 近年来在国际上率先克隆水稻抗白叶病基因Xa7, 相关成果作为封面文章发表在Plant Communications期刊(2021年入选ESI热点和高被引论文)。E-mail: xfchen@zjnu.cn
基金资助:
Lumei He, Bojun Ma, Xifeng Chen*( )
)
Received:2024-01-03
Accepted:2024-05-15
Online:2024-07-10
Published:2024-07-10
Contact:
*E-mail: xfchen@zjnu.cn
摘要: 在与病原菌的长期斗争过程中, 植物进化出复杂而精细的免疫防御系统。抗病(resistant, R)基因的克隆和功能研究极大地促进了人们对植物免疫防御系统的理解。执行者(executor, E)基因作为一类新的植物抗病基因, 具有独特的抗病特点, 同时也是重要的抗病基因资源, 因此成为植物免疫领域的研究热点。近年来, E基因的克隆和功能机制研究取得了一系列重要进展, 但尚未见相关中文综述。该文全面总结了E基因的蛋白序列特征、与病原菌的互作机制、生物学功能及育种应用, 以期为深入理解植物-病原菌互作机制和作物抗病育种提供重要参考。
何璐梅, 马伯军, 陈析丰. 植物执行者抗病基因研究进展. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 671-680.
Lumei He, Bojun Ma, Xifeng Chen. Advances on the Executor Resistance Genes in Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 671-680.
| 基因 | 蛋白登录号 | 基因编码区长度(bp) | 蛋白氨基酸数目(aa) | 跨膜次数 | 物种 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bs3 | ABW82012 | 1366 | 342 | 0 | Capsicum annuum | Römer et al., |
| Bs4C-R | AFW98885 | 495 | 164 | 4 | C. pubescens | Strauß et al., |
| Xa7 | UMZ39519 | 342 | 113 | 2 | Oryza sativa | Chen et al., |
| Xa10 | AGE45112 | 381 | 126 | 4 | O. sativa | Tian et al., |
| Xa23 | AIX09985 | 342 | 113 | 3 | O. rufipogon | Wang et al., |
| Xa27 | AFO69279 | 342 | 113 | 2 | O. minuta | Wu et al., |
表1 执行者(E)基因及其编码蛋白的基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of the executor (E) genes and their encoding proteins
| 基因 | 蛋白登录号 | 基因编码区长度(bp) | 蛋白氨基酸数目(aa) | 跨膜次数 | 物种 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bs3 | ABW82012 | 1366 | 342 | 0 | Capsicum annuum | Römer et al., |
| Bs4C-R | AFW98885 | 495 | 164 | 4 | C. pubescens | Strauß et al., |
| Xa7 | UMZ39519 | 342 | 113 | 2 | Oryza sativa | Chen et al., |
| Xa10 | AGE45112 | 381 | 126 | 4 | O. sativa | Tian et al., |
| Xa23 | AIX09985 | 342 | 113 | 3 | O. rufipogon | Wang et al., |
| Xa27 | AFO69279 | 342 | 113 | 2 | O. minuta | Wu et al., |
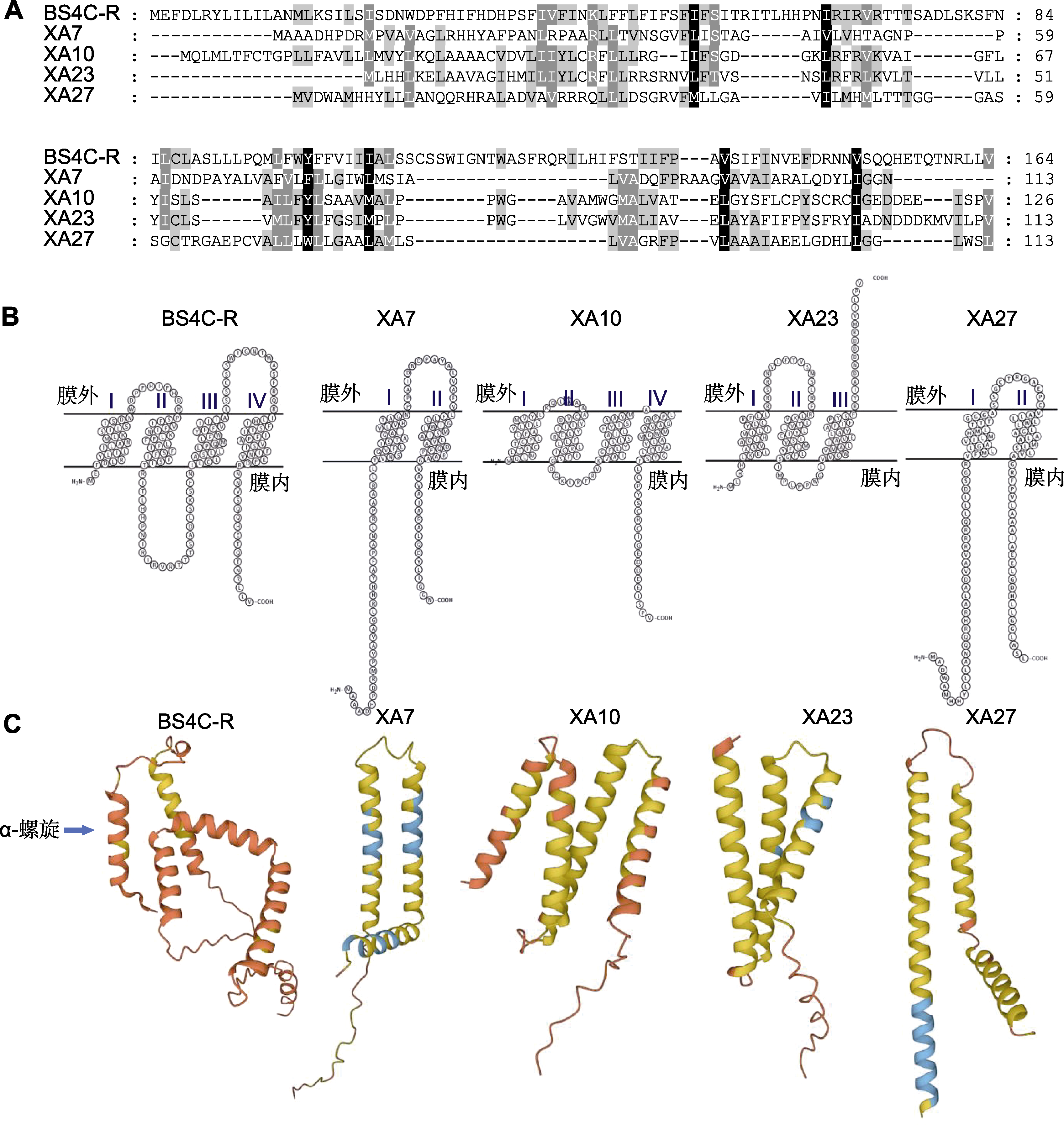
图1 执行者(E)基因编码蛋白的结构特征 (A) 用ClustalX软件进行5个E蛋白的氨基酸序列比对; (B) 用SOSUI软件预测的5个E蛋白的跨膜结构域(BS4C-R与XA10具有4个跨膜结构域, XA23具有3个, XA7与XA27均具有2个); (C) 用AlphaFold 2预测的5个E蛋白的三级结构(均含多个α-螺旋)。
Figure 1 Structural characteristics of proteins encoded by the executor (E) genes (A) Sequence alignment of the five E proteins using ClustalX; (B) Transmembrane domains of five E proteins predicted by SOSUI (BS4C-R and XA10 have four transmembrane domains, XA23 has three transmembrane domains, while XA7 and XA27 have two transmembrane domains); (C) 3D structure of the five E proteins predicted by AlphaFold 2 (each E protein contains multiple α-helix).

图2 转录激活类效应因子(TALE)的重复区高度变异的残基(RVD)与执行者(E)基因启动子效应蛋白结合元件(EBE)的配对关系 绿色字母表示与RVD完美匹配的核苷酸, 红色字母表示与RVD不完美匹配的核苷酸, 携带*的RVD因缺失第13位氨基酸残基, 无碱基偏好性。
Figure 2 Recognition relationship between the repeat variable diresidue (RVD) of repeat domains in transcription activation- like effector (TALE) and the effector binding element (EBE) in promoter of executor (E) gene The green letters represent nucleotides that perfectly match RVD, while the red letters represent nucleotides do not perfectly match, RVD carrying * means no base preference due to the absence of the 13th amino acid residue.
| 效应子 | 基因 | EBE | 匹配度得分值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AvrBs3 | Bs3 | Bs3-EBEAvrBs3 | 11.05 |
| Upa20 | Upa20-EBEAvrBs3 | 11.42 | |
| AvrXa7 | Xa7 | Xa7-EBEAvrXa7 | 19.65 |
| Sweet14 | Sweet14-EBEAvrXa7 | 26.72 | |
| PthXo3 | Xa7 | Xa7-EBEPthXo3 | 29.95 |
| Sweet14 | Sweet14-EBEPthXo3 | 31.87 |
表2 转录激活类效应因子(TALE)与靶基因启动子效应蛋白结合元件(EBE)的结合能力预测得分
Table 2 Prediction score of the binding ability of the transcription activation-like effector (TALE) to the effector binding element (EBE) in the target gene promoter
| 效应子 | 基因 | EBE | 匹配度得分值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AvrBs3 | Bs3 | Bs3-EBEAvrBs3 | 11.05 |
| Upa20 | Upa20-EBEAvrBs3 | 11.42 | |
| AvrXa7 | Xa7 | Xa7-EBEAvrXa7 | 19.65 |
| Sweet14 | Sweet14-EBEAvrXa7 | 26.72 | |
| PthXo3 | Xa7 | Xa7-EBEPthXo3 | 29.95 |
| Sweet14 | Sweet14-EBEPthXo3 | 31.87 |
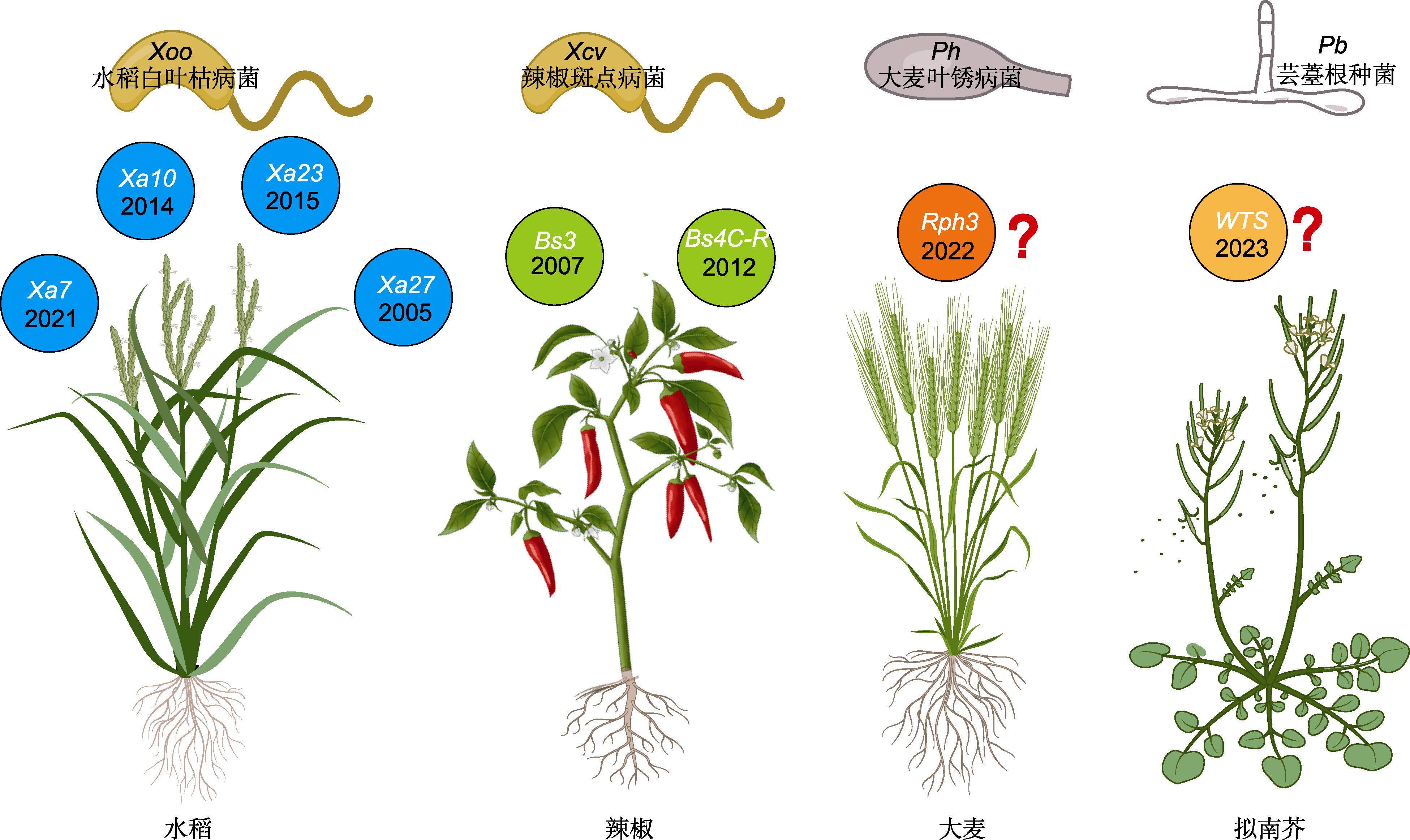
图3 执行者(E)基因与其互作病原菌的模式图 来源于水稻的E基因Xa7、Xa10、Xa23和Xa27能够增强水稻对白叶枯病菌Xoo的抗性, 来源于辣椒的E基因Bs3和Bs4C-R具有对辣椒斑点病菌Xcv的抗性。来源于大麦的Rph3基因赋予大麦对叶锈病菌(Puccinia hordei, Ph)的抗性, 而从拟南芥中克隆的WTS基因能增强对芸薹根肿菌(Plasmodiophora brassicae, Pb)的抗性。
Figure 3 Pattern diagram of executor (E) genes and their interacting pathogens The E genes Xa7, Xa10, Xa23 and Xa27 derived from rice enhance the resistance of rice to Xoo, while the E genes Bs3 and Bs4C-R derived from pepper enhance the resistance to pepper Xcv. The Rph3 gene originated from barley confers resistance to Puccinia hordei (Ph), while the WTS gene cloned from Arabidopsis enhances resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae (Pb).
| [1] | Antony G, Zhou JH, Huang S, Li T, Liu B, White F, Yang B (2010). Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3. Plant Cell 22, 3864-3876. |
| [2] |
Bi GZ, Su M, Li N, Liang Y, Dang S, Xu JC, Hu MJ, Wang JZ, Zou MX, Deng YN, Li QY, Huang SJ, Li JJ, Chai JJ, He KM, Chen YH, Zhou JM (2021). The ZAR1 resistosome is a calcium-permeable channel triggering plant immune signaling. Cell 184, 3528-3541.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Boch J, Scholze H, Schornack S, Landgraf A, Hahn S, Kay S, Lahaye T, Nickstadt A, Bonas U (2009). Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science 326, 1509-1512.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Bogdanove AJ, Schornack S, Lahaye T (2010). TAL effectors: finding plant genes for disease and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13, 394-401.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Chen LQ, Hou BH, Lalonde S, Takanaga H, Hartung ML, Qu XQ, Guo WJ, Kim JG, Underwood W, Chaudhuri B, Chermak D, Antony G, White FF, Somerville SC, Mudgett MB, Frommer WB (2010). Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 468, 527-532. |
| [6] | Chen XF, Liu PC, Mei L, He XL, Chen L, Liu H, Shen SR, Ji ZD, Zheng XX, Zhang YC, Gao ZY, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Ma BJ (2021). Xa7, a new executor R gene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Commun 2, 100143. |
| [7] |
Cruz CMV, Bai JF, Oña I, Leung H, Nelson RJ, Mew TW, Leach JE (2000). Predicting durability of a disease resistance gene based on an assessment of the fitness loss and epidemiological consequences of avirulence gene mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 13500-13505.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | de Lange O, Schreiber T, Schandry N, Radeck J, Braun KH, Koszinowski J, Heuer H, Strauß A, Lahaye T (2013). Breaking the DNA-binding code of Ralstonia solanacearum TAL effectors provides new possibilities to generate plant resistance genes against bacterial wilt disease. New Phytol 199, 773-786. |
| [9] | Dinh HX, Singh D, de la Cruz DG, Hensel G, Kumlehn J, Mascher M, Stein N, Perovic D, Ayliffe M, Moscou MJ, Park RF, Pourkheirandish M (2022). The barley leaf rust resistance gene Rph3 encodes a predicted membrane protein and is induced upon infection by avirulent pathotypes of Puccinia hordei. Nat Commun 13, 2386. |
| [10] | Doyle EL, Booher NJ, Standage DS, Voytas DF, Brendel VP, Vandyk JK, Bogdanove AJ (2012). TAL effector- nucleotide targeter (TALE-NT) 2.0: tools for TAL effector design and target prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 40, W117- W122. |
| [11] | Förderer A, Li ET, Lawson AW, Deng YN, Sun Y, Logemann E, Zhang XX, Wen J, Han ZF, Chang JB, Chen YH, Schulze-Lefert P, Chai JJ (2022). A wheat resistosome defines common principles of immune receptor channels. Nature 610, 532-539. |
| [12] | Gu KY, Yang B, Tian DS, Wu LF, Wang DJ, Sreekala C, Yang F, Chu ZQ, Wang GL, White FF, Yin ZC (2005). R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 435, 1122-1125. |
| [13] |
Gupta A, Liu B, Chen QJ, Yang B (2023). High-efficiency prime editing enables new strategies for broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight of rice. Plant Biotechnol J 21, 1454-1464.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Gupta A, Liu B, Raza S, Chen QJ, Yang B (2024). Modularly assembled multiplex prime editors for simultaneous editing of agronomically important genes in rice. Plant Com- mun 5, 100741. |
| [15] | He LM, Liu PC, Mei L, Luo HC, Ban TX, Chen XF, Ma BJ (2024). Disease resistance features of the executor R gene Xa7reveal novel insights into the interaction between rice and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Front Plant Sci 15, 1365989. |
| [16] | Huang S, Antony G, Li T, Liu B, Obasa K, Yang B, White FF (2016). The broadly effective recessive resistance gene xa5 of rice is a virulence effector-dependent quantitative trait for bacterial blight. Plant J 86, 186-194. |
| [17] |
Hui SG, Shi YR, Tian JJ, Wang L, Li YY, Wang SP, Yuan M (2019). TALE-carrying bacterial pathogens trap host nuclear import receptors for facilitation of infection of rice. Mol Plant Pathol 20, 519-532.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Hummel AW, Doyle EL, Bogdanove AJ (2012). Addition of transcription activator-like effector binding sites to a pathogen strain-specific rice bacterial blight resistance gene makes it effective against additional strains and against bacterial leaf streak. New Phytol 195, 883-893.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Ji CH, Ji ZY, Liu B, Cheng H, Liu H, Liu SZ, Yang B, Chen GY (2020). Xa1 allelic R genes activate rice blight resistance suppressed by interfering TAL effectors. Plant Commun 1, 100087. |
| [20] | Ji ZY, Guo W, Chen XF, Wang CL, Zhao KJ (2022). Plant executor genes. Int J Mol Sci 23, 1524. |
| [21] |
Kay S, Hahn S, Marois E, Hause G, Bonas U (2007). A bacterial effector acts as a plant transcription factor and induces a cell size regulator. Science 318, 648-651.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Kourelis J, van der Hoorn RAL (2018). Defended to the nines: 25 years of resistance gene cloning identifies nine me- chanisms for R protein function. Plant Cell 30, 285-299. |
| [23] |
Krönauer C, Kilian J, Strauß T, Stahl M, Lahaye T (2019). Cell death triggered by the YUCCA-like Bs3 protein coincides with accumulation of salicylic acid and pipecolic acid but not of indole-3-acetic acid. Plant Physiol 180, 1647-1659.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Krönauer C, Lahaye T (2021). The flavin monooxygenase Bs3 triggers cell death in plants, impairs growth in yeast and produces H2O2 in vitro. PLoS One 16, e0256217. |
| [25] | Liu PC, Mei L, He LM, Xu YL, Zhang YT, Zeng DL, Zhang XM, Qian Q, Chen XF, Ma BJ (2021). Development of markers for identification and maker-assisted breeding of Xa7gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 217, 134. |
| [26] |
Liu YD, Ren DT, Pike S, Pallardy S, Gassmann W, Zhang SQ (2007). Chloroplast-generated reactive oxygen species are involved in hypersensitive response-like cell death mediated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Plant J 51, 941-954.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Luo DP, Huguet-Tapia JC, Raborn RT, White FF, Brendel VP, Yang B (2021). The Xa7resistance gene guards the rice susceptibility gene SWEET14 against exploitation by the bacterial blight pathogen. Plant Commun 2, 100164. |
| [28] | Nowack MK, Holmes DR, Lahaye T (2022). TALE-induced cell death executors: an origin outside immunity? Trends Plant Sci 27, 536-548. |
| [29] |
Oliva R, Ji CH, Atienza-Grande G, Huguet-Tapia JC, Perez-Quintero A, Li T, Eom JS, Li CH, Nguyen H, Liu B, Auguy F, Sciallano C, Luu VT, Dossa GS, Cunnac S, Schmidt SM, Slamet-Loedin IH, Cruz CV, Szurek B, Frommer WB, White FF, Yang B (2019). Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 37, 1344-1350.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Römer P, Hahn S, Jordan T, Strauss T, Bonas U, Lahaye T (2007). Plant pathogen recognition mediated by promoter activation of the pepper Bs3 resistance gene. Science 318, 645-648. |
| [31] | Römer P, Jordan T, Lahaye T (2010). Identification and application of a DNA-based marker that is diagnostic for the pepper (Capsicum annuum) bacterial spot resistance gene Bs3. Plant Breed 129, 737-740. |
| [32] | Schornack S, Minsavage GV, Stall RE, Jones JB, Lahaye T (2008). Characterization of AvrHah1, a novel AvrBs3-like effector from Xanthomonas gardneri with virulence and avirulence activity. New Phytol 179, 546- 556. |
| [33] | Schwartz AR, Morbitzer R, Lahaye T, Staskawicz BJ (2017). TALE-induced bHLH transcription factors that activate a pectate lyase contribute to water soaking in bacterial spot of tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E897-E903. |
| [34] |
Siddens LK, Krueger SK, Henderson MC, Williams DE (2014). Mammalian flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO) as a source of hydrogen peroxide. Biochem Pharmacol 89, 141-147.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Strauß T, Strauß A, Römer P, Minsavage GV, Singh S, Wolf C, Strauß A, Kim S, Lee HA, Yeom SI, Parniske M, Stall RE, Jones JB, Choi D, Prins M, Lahaye T (2012). RNA-seq pinpoints a Xanthomonas TAL-effector activated resistance gene in a large-crop genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 19480- 19485. |
| [36] |
Szurek B, Marois E, Bonas U, Van den Ackerveken G (2001). Eukaryotic features of the Xanthomonas type III effector AvrBs3: protein domains involved in transcriptional activation and the interaction with nuclear import receptors from pepper. Plant J 26, 523-534.
PMID |
| [37] | Tariq R, Wang CL, Qin TF, Xu FF, Tang YC, Gao Y, Ji ZY, Zhao KJ (2018). Comparative transcriptome profiling of rice near-isogenic line carrying Xa23 under infection of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Int J Mol Sci 19, 717. |
| [38] |
Thomas V (2010). Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Mol Plant 3, 2-20.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Tian CY, Fang YL, Shen Q, Wang HJ, Chen XF, Guo W, Zhao KJ, Wang CL, Ji ZY (2023). Genotypic diversity and pathogenisity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae isolated from southern China in 2019-2021. Chin Bull Bot 58, 743-749. (in Chinese) |
|
田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远 (2023). 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究. 植物学报 58, 743-749.
DOI |
|
| [40] | Tian DS, Wang JX, Zeng X, Gu KY, Qiu CX, Yang XB, Zhou ZY, Goh M, Luo YC, Murata-Hori M, White FF, Yin ZC (2014). The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 26, 497- 515. |
| [41] |
Timilsina S, Potnis N, Newberry EA, Liyanapathiranage P, Iruegas-Bocardo F, White FF, Goss EM, Jones JB (2020). Xanthomonas diversity, virulence and plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 18, 415-427.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
van Berkel WJH, Kamerbeek NM, Fraaije MW (2006). Flavoprotein monooxygenases, a diverse class of oxidative biocatalysts. J Biotechnol 124, 670-689.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Wang CL, Zhang XP, Fan YL, Gao Y, Zhu QL, Zheng CK, Qin TF, Li YQ, Che JY, Zhang MW, Yang B, Liu YG, Zhao KJ (2015). XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol Plant 8, 290-302.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Wang CY, Chen S, Feng AQ, Su J, Wang WJ, Feng JQ, Chen B, Zhang MY, Yang JY, Zeng LX, Zhu XY (2021). Xa7, a small orphan gene harboring promoter trap for AvrXa7, leads to the durable resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Rice 14, 48. |
| [45] | Wang J, Tian DS, Gu KY, Yang XB, Wang LL, Zeng X, Yin ZC (2017). Induction of Xa10-like genes in rice cultivar Nipponbare confers disease resistance to rice bacterial blight. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 30, 466-477. |
| [46] | Wang J, Zeng X, Tian DS, Yang XB, Wang LL, Yin ZC (2018). The pepper Bs4C proteins are localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane and confer disease resistance to bacterial blight in transgenic rice. Mol Plant Pathol 19, 2025-2035. |
| [47] | Wang MX, Li SF, Li HY, Song CF, Xie WY, Zuo SM, Zhou XP, Zhou CY, Ji ZY, Zhou HB (2024). Genome editing of a dominant resistance gene for broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial diseases in rice without growth penalty. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 529-531. |
| [48] |
Wang W, Qin L, Zhang WJ, Tang LH, Zhang C, Dong XJ, Miao P, Shen M, Du HL, Cheng HY, Wang K, Zhang XY, Su M, Lu HW, Li C, Gao Q, Zhang XJ, Huang Y, Liang CZ, Zhou JM, Chen YH (2023). WeiTsing, a pericycle- expressed ion channel, safeguards the stele to confer clubroot resistance. Cell 186, 2656-2671.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Wei Z, Abdelrahman M, Gao Y, Ji ZY, Mishra R, Sun HD, Sui Y, Wu CY, Wang CL, Zhao KJ (2021). Engineering broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight by CRISPR- Cas9-mediated precise homology directed repair in rice. Mol Plant 14, 1215-1218. |
| [50] |
Wu DS, von Roepenack-Lahaye E, Buntru M, de Lange O, Schandry N, Pérez-Quintero AL, Weinberg Z, Lowe-Power TM, Szurek B, Michael AJ, Allen C, Schillberg S, Lahaye T (2019). A plant pathogen type III effector protein subverts translational regulation to boost host polyamine levels. Cell Host Microbe 26, 638-649.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Wu LF, Goh ML, Sreekala C, Yin ZC (2008). XA27 depends on an amino-terminal signal-anchor-like sequence to localize to the apoplast for resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae. Plant Physiol 148, 1497-1509. |
| [52] | Xia ZH, Han F, Gao LF, Yuan QH, Zhai WX, Liu D, Luo YH (2009). Application of functional marker to identify genes for bacterial blight resistance in Oryza rufipogon. Chin J Rice Sci 23, 653-656. (in Chinese) |
|
夏志辉, 韩飞, 高利芬, 袁潜华, 翟文学, 刘迪, 罗越华 (2009). 利用功能标记鉴定普通野生稻中的白叶枯病抗性基因. 中国水稻科学 23, 653-656.
DOI |
|
| [53] | Xiang X, Chen LL, Zhang DD, Zhai WX, Xia ZH (2019). Physical mapping and functional markers of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice. Mol Plant Breed 17, 509- 516. (in Chinese) |
| 向贤, 陈露露, 张丹丹, 翟文学, 夏志辉 (2019). 水稻白叶枯病抗性基因物理图谱定位与功能标记. 分子植物育种 17, 509-516. | |
| [54] | Yang B, White FF (2004). Diverse members of the AvrBs3/ PthA family of type III effectors are major virulence determinants in bacterial blight disease of rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17, 1192-1200. |
| [55] | Zeng X, Tian DS, Gu KY, Zhou ZY, Yang XB, Luo YC, White FF, Yin ZC (2015). Genetic engineering of the Xa10 promoter for broad-spectrum and durable resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Biotechnol J 13, 993-1001. |
| [56] | Zhang JL, Yin ZC, White F (2015). TAL effectors and the executor R genes. Front Plant Sci 6, 641. |
| [57] | Zhao KJ, Zhang Q (2021). A climate-resilient R gene in rice traps two pathogen effectors for broad and durable resistance to bacterial blight. Mol Plant 14, 366-368. |
| [58] |
Zhao Q, Dixon RA (2011). Transcriptional networks for lignin biosynthesis: more complex than we thought? Trends Plant Sci 16, 227-233.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [2] | 吴锁伟, 安学丽, 万向元. 玉米雄性不育机理及其在工程核不育制种中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [3] | 车佳航, 李纬楠, 秦英之, 陈金焕. 木本植物叶色变异机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 319-328. |
| [4] | 黄慧梅, 高永康, 台玉莹, 刘超, 曲德杰, 汤锐恒, 王幼宁. 硝酸盐转运蛋白NRT2在植物中的功能及分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 783-798. |
| [5] | 罗韶凡, 蒋凯, 黄卫昌. 植物花距表型趋同进化和发育机制多样化的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23249-. |
| [6] | 王璐瑶, 陈謇, 赵守清, 闫慧莉, 许文秀, 刘若溪, 麻密, 虞轶俊, 何振艳. 水稻镉积累特性的生理和分子机制研究概述[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 236-249. |
| [7] | 王霞, 严维, 周志勤, 常振仪, 郑敏婷, 唐晓艳, 吴建新. 水稻雄性不育突变体ms102的鉴定和基因定位[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 42-55. |
| [8] | 张慧, 刘倩, 黄晓磊. 社会性昆虫级型和行为分化机制研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(4): 507-516. |
| [9] | 宋松泉, 刘军, 杨华, 张文虎, 张琪, 高家东. 细胞分裂素调控种子发育、休眠与萌发的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 218-231. |
| [10] | 陈孙禄, 詹成芳, 蒋红, 李琳涵, 张红生. 水稻籽粒灌浆速率的分子机制与遗传调控研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 80-89. |
| [11] | 陆静, 陈赢男, 尹佟明. 木本植物性别决定基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 90-103. |
| [12] | 周亭亭, 饶玉春, 任德勇. 水稻卷叶细胞学与分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(6): 848-855. |
| [13] | 张继伟, 赵杰才, 周琴, 陈国雄. 植物表皮毛研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(5): 726-737. |
| [14] | 王韵茜, 苏延红, 杨睿, 李鑫, 李晶, 曾千春, 罗琼. 云南疣粒野生稻稻瘟病抗性[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(4): 477-486. |
| [15] | 王红飞, 尚庆茂. 被子植物下胚轴细胞伸长的分子机理[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(2): 276-287. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||