

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 175-184.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17144 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17144
收稿日期:2017-08-07
接受日期:2017-10-20
出版日期:2018-03-01
发布日期:2018-03-10
通讯作者:
阳成伟
基金资助:
Han Danlu, Lai Jianbin, Yang Chengwei*( )
)
Received:2017-08-07
Accepted:2017-10-20
Online:2018-03-01
Published:2018-03-10
Contact:
Yang Chengwei
摘要: SUMO化是真核生物中一种重要的蛋白质翻译后修饰。SUMO E3连接酶具有对底物特异的识别功能, 可以促进SUMO化反应, 是SUMO化修饰过程中的重要组成部分。目前, 在植物中已经鉴定出多种SUMO E3连接酶, 它们参与植物重要器官的发育调控。该文对植物SUMO E3连接酶在根系发育、开花途径、配子发育和光形态建成中的作用及其调节机制进行综述。
韩丹璐, 赖建彬, 阳成伟. SUMO E3连接酶在植物生长发育中的功能研究进展. 植物学报, 2018, 53(2): 175-184.
Han Danlu, Lai Jianbin, Yang Chengwei. Research Advances in Functions of SUMO E3 Ligases in Plant Growth and Development. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(2): 175-184.
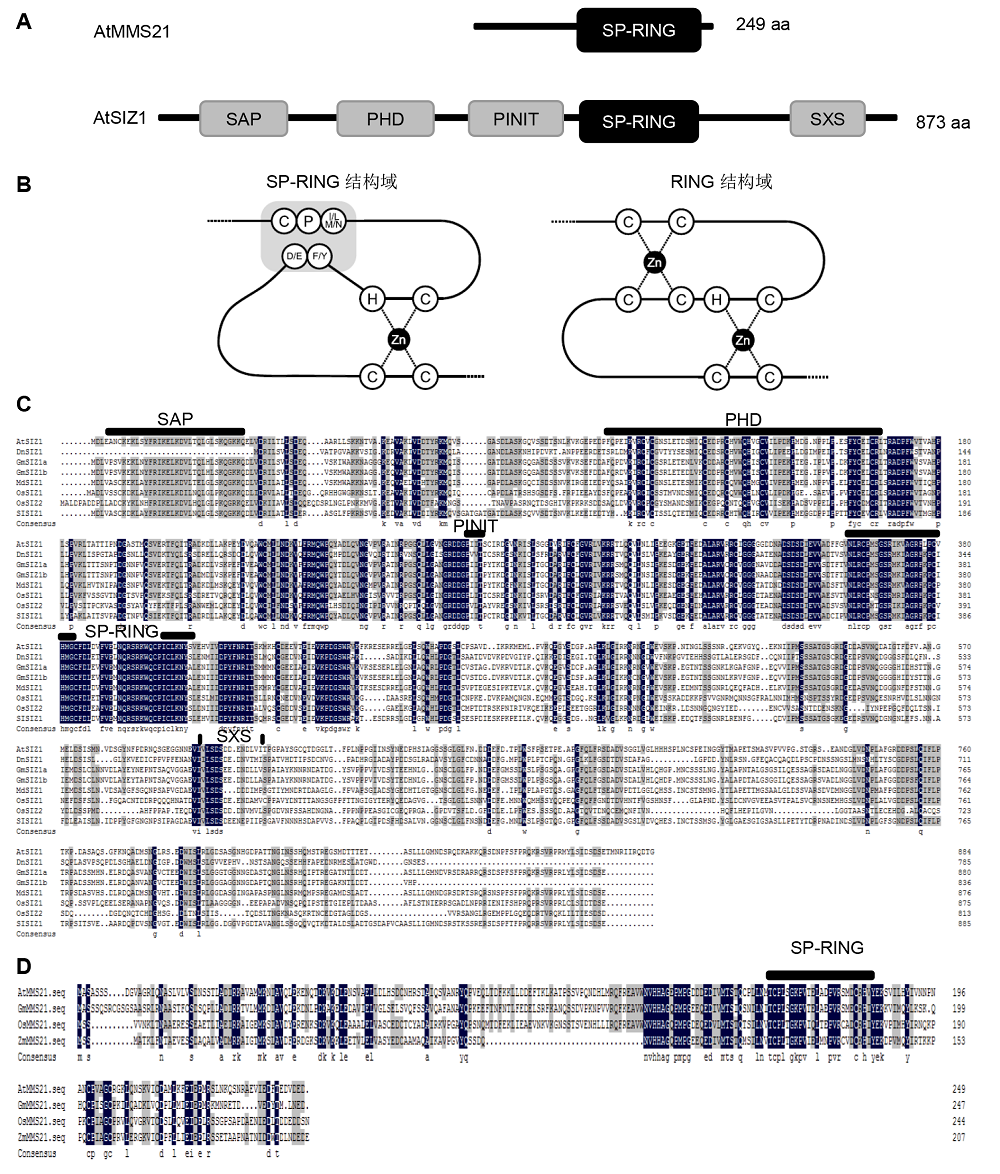
图1 植物SUMO E3连接酶的保守结构域(A) 植物SUMO E3连接酶MMS21和SIZ1的特征结构域。SIZ1具有SAP、PHD、PINIT、SP-RING和SXS结构域, MMS21只具有SP-RING结构域(Ishida et al., 2012); (B) SUMO E3连接酶的SP-RING结构域和泛素E3连接酶的RING结构域构型。RING结构域有2个锌离子结合环, SP-RING只含有1个, 第2个环被范德华力和氢键所替代(Duan et al., 2009; Yunus and Lima, 2009; Ishida et al., 2012; 石田喬志和杉本慶子, 2012); (C), (D) 分别为植物SIZ1和MMS21的同源序列比对。数据来源于NCBI。由DNAMAN定义的氨基酸序列、保守序列(黑色)和相似序列(灰色)。SIZ1的蛋白质氨基酸序列为拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) AtSIZ1 (AAU00414.1)、大豆(Glycine max) GmSIZ1a (KRH24918.1)和GmSIZ1b (KRG89029.1)、水稻(Oryza sativa) OsSIZ1 (BAG97182.1)和OsSIZ2 (BAG89374.1)以及玉米(Zea mays) ZmSIZ1a (AQK95338.1)、ZmSIZ1b (AQK79048.1)和ZmSIZc (ONM41936.1)。MMS21的蛋白质氨基酸序列为拟南芥AtMMS21 (NP_188133.2)、大豆GmMMS21 (XP_003541835.1)、水稻OsMMS21 (XP_015640264.1)和玉米ZmMMS21 (AQK88509.1)。
Figure 1 The domains are conserved in plant SUMO E3 ligases(A) Characteristic domains of plant SUMO E3 ligases. MMS21 and SIZ1 are shown by boxes, SIZ1 possesses SAP, PHD, PINIT, SP-RING and SXS domains, while MMS21 possesses only SP-RING domain (Ishida et al., 2012); (B) A schematic model of the SP-RING domain of SUMO E3 ligases and the RING finger of ubiquitin E3 ligases. The RING domain sports two zinc-coordinating loops, the SP-RING domain contains only one, the second loop is instead held together by hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces (Duan et al., 2009; Yunus and Lima, 2009; Ishida et al., 2012); (C), (D) The sequence data for the plant SIZ1 homologues were obtained from the NCBI protein database. Sequence identities (black boxes) and similarities (gray boxes) of amino acids were identified by DNAMAN. Amino acid sequences of SIZ1 proteins are from Arabidopsis thaliana AtSIZ1 (AAU00414.1), Glycine max GmSIZ1a (KRH24918.1), GmSIZ1b (KRG89029.1), Oryza sativa OsSIZ1 (BAG97182.1), OsSIZ2 (BAG89374.1), and Zea mays ZmSIZ1a (AQK95338.1), ZmSIZ1b (AQK79048.1), ZmSIZc (ONM41936.1). Amino acid sequences of MMS21 proteins are from Arabidopsis thaliana AtMMS21 (NP_188133.2), Glycine max GmMMS21 (XP_003541835.1), Oryza sativa OsMMS21 (XP_015640264.1), and Zea mays ZmMMS21 (AQK88509.1).
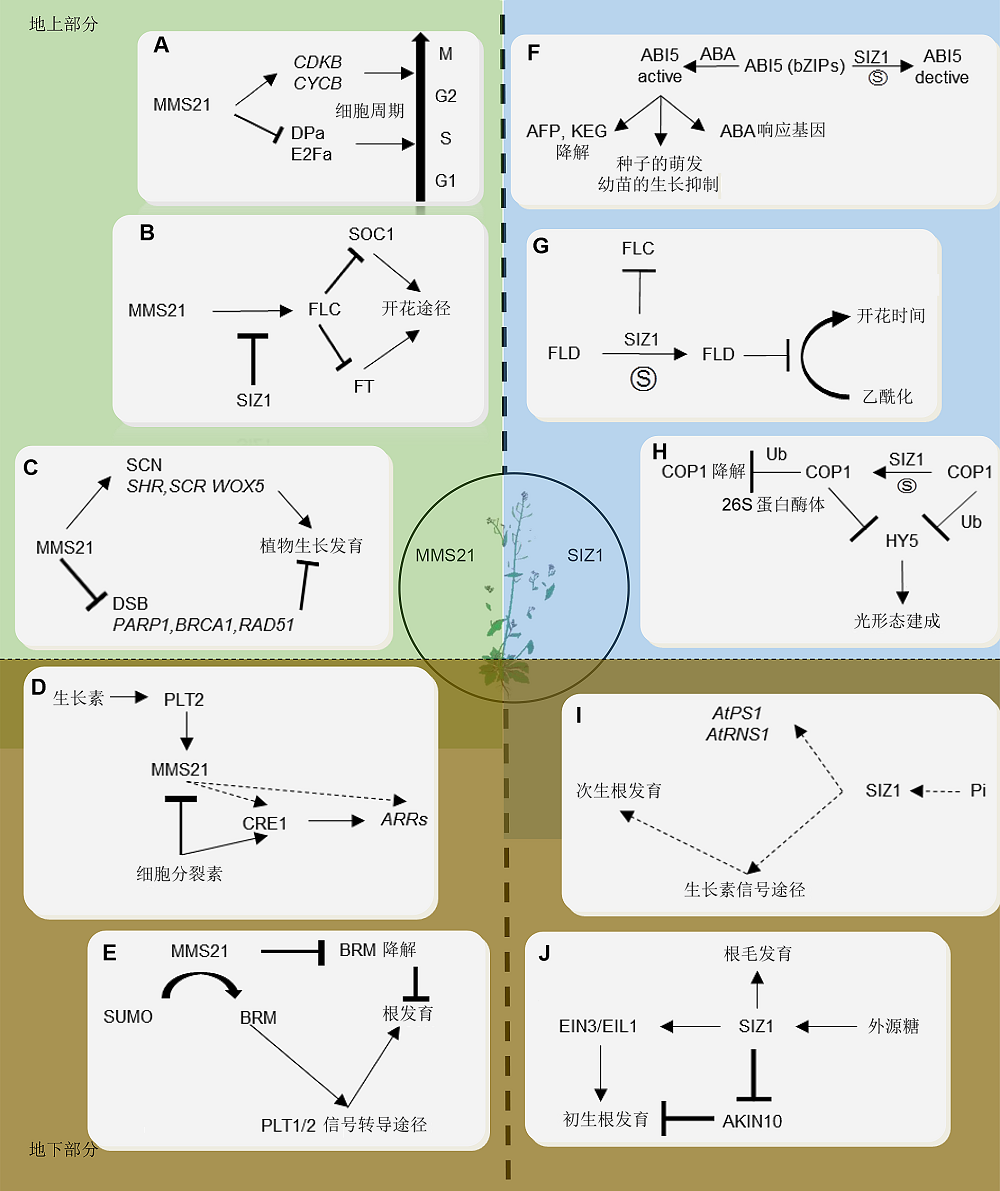
图2 SUMO E3连接酶在拟南芥生长发育中的功能(A) AtMMS21对细胞周期的调节功能(Liu et al., 2016); (B) MMS21和SIZ1对拟南芥开花途径和时间的调控(Kwak et al., 2016); (C) MMS21在拟南芥中响应DNA损伤, 进而影响植物生长发育过程(Xu et al., 2013; Yuan et al., 2014); (D) MMS21通过调节生长素信号途径影响拟南芥根的发育(Ishida et al., 2009; Huang et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2010); (E) MMS21通过染色质重塑复合物调节根分生组织发育(Zhang et al., 2017a); (F) SIZ1通过调节糖代谢途径和ABA途径影响种子的萌发时间(Miura et al., 2009); (G) SIZ1对开花途径的调节(Jin et al., 2008); (H) SIZ1对植物光形态建成的调控(Kim et al., 2016a; Lin et al., 2016); (I) SIZ1对磷酸饥饿响应的调控(Miura et al., 2005; 2011); (J) SIZ1通过糖代谢途径调节根的发育(Castro et al., 2015)
Figure 2 The functions of SUMO E3 ligases in Arabidopsis(A) The function of MMS21 regulates in cell cycle (Liu et al., 2016); (B) MMS21 and SIZ1 are both involved in flowering pathway and time (Kwak et al., 2016); (C) MMS21 responses to the DNA damage to regulate plant growth and development (Xu et al., 2013; Yuan et al., 2014); (D) MMS21 is involved in Arabidopsis root development by auxin (Ishida et al., 2009; Huang et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2010); (E) MMS21 is involved in root development by regulating chromatin remodeling complex (Zhang et al., 2017a); (F) SIZ1 regulate glucose metabolism germinated/seedling development (Miura et al., 2009); (G) SIZ1 is involved in flowering pathway (Jin et al., 2008); (H) SIZ1 regulates the photomorphogenesis (Kim et al., 2016a; Lin et al., 2016); (I) SIZ1 regulation of phosphate starvation-induced root architecture remodeling involves the control of auxin accumulation (Miura et al., 2005, 2011); (J) SIZ1 regulates development of root by sugar pathway (Castro et al., 2015)
| [1] | 徐庞连, 曾棉炜, 黄丽霞, 阳成伟 (2008). 植物SUMO化修饰及其生物学功能. 植物学通报 25, 608-615. |
| [2] | 杨辉霞, 童依平, 王道文 (2007). 拟南芥低磷胁迫反应分子机理研究的最新进展. 植物学通报 24, 726-734. |
| [3] | 石田喬志, 杉本慶子 (2012). 植物におけるSUMOシステムとE3リガーゼの機能. 生化学 84, 440-447. |
| [4] | Almedawar S, Colomina N, Bermúdez-lópez M, Pociño- Merino I, Torres-Rosell J (2012). A SUMO-dependent step during establishment of sister chromatid cohesion.Curr Biol 22, 1576-1581. |
| [5] | Cai B, Kong XX, Zhong C, Sun S, Zhou XF, Jin YH, Wang YN, Li X, Zhu ZD, Jin JB (2017). SUMO E3 ligases GmSIZ1a and GmSIZ1b regulate vegetative growth in soybean.J Integr Plant Biol 59, 2-14. |
| [6] | Cappadocia L, Pichler A, Lima CD (2015). Structural basis for catalytic activation by the human ZNF451 SUMO E3 ligase.Nat Struct Mol Biol 22, 968-975. |
| [7] | Castro PH, Verde N, Lourenço T, Magalhães AP, Tavares RM, Bejarano ER, Azevedo H (2015). SIZ1-dependent post-translational modification by SUMO modulates sugar signaling and metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 56, 2297-2311. |
| [8] | Catala R, Ouyang J, Abreu IA, Hu YX, Seo H, Zhang XR, Chua NH (2007). The Arabidopsis E3 SUMO ligase SIZ1 regulates plant growth and drought responses.Plant Cell 19, 2952-2966. |
| [9] | Cheong MS, Park HC, Hong MJ, Lee J, Choi W, Jin JB, Bohnert HJ, Lee SY, Bressan RA, Yun DJ (2009). Specific domain structures control abscisic acid-, salicylic acid-, and stress-mediated SIZ1 phenotypes.Plant Phy- siol 151, 1930-1942. |
| [10] | De Piccoli G, Cortes-Ledesma F, Ira G, Torres-Rosell J, Uhle S, Farmer S, Hwang JY, Machin F, Ceschia A, McAleenan A, Cordon-Preciado V, Clemente-Blanco A, Vilella-Mitjana F, Ullal P, Jarmuz A, Leitao B, Bressan D, Dotiwala F, Papusha A, Zhao XL, Myung K, Haber JE, Aguilera A, Aragón L (2006). Smc5-Smc6 mediate DNA double-strand-break repair by promoting sister-chromatid recombination.Nat Cell Biol 8, 1032-1034. |
| [11] | Desterro JMP, Rodriguez MS, Kemp GD, Hay RT (1999). Identification of the enzyme required for activation of the small ubiquitin-like protein SUMO-1.J Biol Chem 274, 10618-10624. |
| [12] | Desterro JMP, Thomson J, Hay RT (1997). Ubch9 conjugates SUMO but not ubiquitin.FEBS Lett 417, 297-300. |
| [13] | Dong JS, Piñeros MA, Li XX, Yang HB, Liu Y, Murphy AS, Kochian LV, Liu D (2017). An Arabidopsis ABC transporter mediates phosphate deficiency-induced remodeling of root architecture by modulating iron homeostasis in roots.Mol Plant 10, 244-259. |
| [14] | Duan X, Sarangi P, Liu X, Rangi GK, Zhao X, Ye H (2009). Structural and functional insights into the roles of the Mms21 subunit of the Smc5/6 complex.Mol Cell 35, 657-668. |
| [15] | Eisenhardt N, Chaugule VK, Koidl S, Droescher M, Dogan E, Rettich J, Sutinen P, Imanishi SY, Hofmann K, Palvimo JJ, Pichler A (2015). A new vertebrate SUMO enzyme family reveals insights into SUMO-chain assembly.Nat Struct Mol Biol 22, 959-967. |
| [16] | Gong LM, Li B, Millas S, Yeh ETH (1999). Molecular cloning and characterization of human AOS1 and UBA2, components of the sentrin-activating enzyme complex.FEBS Lett 448, 185-189. |
| [17] | Huang LX, Yang SG, Zhang SC, Liu M, Lai JB, Qi YL, Shi SF, Wang JX, Wang YQ, Xie Q, Yang CW (2009). The Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase AtMMS21, a homologue of NSE2/MMS21, regulates cell proliferation in the root.Plant J 60, 666-678. |
| [18] | Ishida T, Fujiwara S, Miura K, Stacey N, Yoshimura M, Schneider K, Adachi S, Minamisawa K, Umeda M, Sugimoto K (2009). SUMO E3 ligase HIGH PLOIDY2 regul- ates endocycle onset and meristem maintenance in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 21, 2284-2297. |
| [19] | Ishida T, Yoshimura M, Miura K, Sugimoto K (2012). MMS21/HPY2 and SIZ1, two Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligases, have distinct functions in development.PLoS One 7, e46897. |
| [20] | Jin JB, Jin YH, Lee J, Miura K, Yoo CY, Kim WY, Van Oosten M, Hyun Y, Somers DE, Lee I, Yun DJ, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2008). The SUMO E3 ligase, AtSIZ1, regulates flowering by controlling a salicylic acid-mediated floral promotion pathway and through affects onFLC chromatin structure. Plant J 53, 530-540. |
| [21] | Johnson ES, Blobel G (1997). Ubc9p is the conjugating enzyme for the ubiquitin-like protein Smt3p.J Biol Chem 272, 26799-26802. |
| [22] | Johnson ES, Gupta AA (2001). An E3-like factor that promotes SUMO conjugation to the yeast septins.Cell 106, 735-744. |
| [23] | Kim JY, Jang IC, Seo HS (2016a). COP1 controls abiotic stress responses by modulating AtSIZ1 function through its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity.Front Plant Sci 7, 1182. |
| [24] | Kim SI, Kwak JS, Song JT, Seo HS (2016b). The E3 SUMO ligase AtSIZ1 functions in seed germination in Arabidopsis.Physiol Plant 158, 256-271. |
| [25] | Kim SI, Park BS, Kim DY, Yeu SY, Song SI, Song JT, Seo HS (2015). E3 SUMO ligase AtSIZ1 positively regulates SLY1-mediated GA signaling and plant development.Bio- chem J 469, 299-314. |
| [26] | Kwak JS, Son GH, Kim SI, Song JT, Seo HS (2016). Arabidopsis HIGH PLOIDY2 sumoylates and stabilizes Flowering Locus C through its E3 ligase activity.Front Plant Sci 7, 530. |
| [27] | Lin XL, Niu D, Hu ZL, Kim DH, Jin YH, Cai B, Liu P, Miura K, Yun DJ, Kim WY, Lin RC, Jin JB (2016). An Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase, SIZ1, negatively regulates photomorphogenesis by promoting COP1 activity.PLoS Ge- net 12, e1006016. |
| [28] | Ling Y, Zhang CY, Chen T, Hao HQ, Liu P, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Jin JB, Lin JX (2012). Mutation in SUMO E3 ligase, SIZ1, disrupts the mature female gametophyte in Arabidopsis.PLoS One 7, e29470. |
| [29] | Liu F, Wang X, Su MY, Yu MY, Zhang SC, Lai JB, Yang CW, Wang YQ (2015). Functional characterization of DnSIZ1, a SIZ/PIAS-type SUMO E3 ligase fromDendrobium. BMC Plant Biol 15, 225. |
| [30] | Liu M, Shi SF, Zhang SC, Xu PL, Lai JB, Liu YY, Yuan DK, Wang YQ, Du JJ, Yang CW (2014). SUMO E3 ligase AtMMS21 is required for normal meiosis and gametophyte development in Arabidopsis.BMC Plant Biol 14, 153. |
| [31] | Liu YY, Lai JB, Yu MY, Wang FG, Zhang JJ, Jiang JM, Hu H, Wu Q, Lu GH, Xu PL, Yang CW (2016). The Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase AtMMS21 dissociates the E2Fa/ DPa complex in cell cycle regulation.Plant Cell 28, 2225-2237. |
| [32] | Miura K, Jin JB, Hasegawa PM (2007).a Sumoylation, a post-translational regulatory process in plants.Curr Opin Plant Biol 10, 495-502. |
| [33] | Miura K, Jin JB, Lee J, Yoo CY, Stirm V, Miura T, Ash- worth EN, Bressan RA, Yun DJ, Hasegawa PM (2007).b SIZ1-mediated sumoylation of ICE1 controls CBF3/DREB1A expression and freezing tolerance in Ara- bidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 1403-1414. |
| [34] | Miura K, Lee J, Gong QQ, Ma SS, Jin JB, Yoo CY, Miura T, Sato A, Bohnert HJ, Hasegawa PM (2011). SIZ1 regulation of phosphate starvation-induced root architecture remodeling involves the control of auxin accumulation. Plant Physiol 155, 1000-1012. |
| [35] | Miura K, Lee J, Jin JB, Yoo CY, Miura T, Hasegawa PM (2009). Sumoylation of ABI5 by the Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 negatively regulates abscisic acid signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 5418-5423. |
| [36] | Miura K, Rus A, Sharkhuu A, Yokoi S, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG, Baek D, Koo YD, Jin JB, Bressan RA, Yun DJ, Hasegawa PM (2005). The Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 controls phosphate deficiency responses.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 7760-7765. |
| [37] | Okuma T, Honda R, Ichikawa G, Tsumagari N, Yasuda H (1999). In vitro SUMO-1 modification requires two enzymatic steps, E1 and E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 254, 693-698. |
| [38] | Park HC, Kim H, Koo SC, Park HJ, Cheong MS, Hong H, Baek D, Chung WS, Kim DH, Bressan RA, Lee SY, Bohnert HJ, Yun DJ (2010). Functional characterization of the SIZ/PIAS-type SUMO E3 ligases, OsSIZ1 and OsSIZ2 in rice.Plant Cell Environ 33, 1923-1934. |
| [39] | Pichler A, Fatouros C, Lee H, Eisenhardt N (2017). SUMO conjugation—a mechanistic view.Biomol Concepts 8, 13-36. |
| [40] | Reverter D, Lima CD (2005). Insights into E3 ligase activity revealed by a SUMO-RanGAP1-Ubc9-Nup358 complex.Nature 435, 687-692. |
| [41] | Streich Jr FC, Lima CD (2016). Capturing a substrate in an activated RING E3/E2-SUMO complex.Nature 536, 304-308. |
| [42] | Thangasamy S, Guo CL, Chuang MH, Lai MH, Chen J, Jauh GY (2011). Rice SIZ1, a SUMO E3 ligase, controls spikelet fertility through regulation of anther dehiscence.New Phytol 189, 869-882. |
| [43] | Wang HD, Sun R, Cao Y, Pei WX, Sun YF, Zhou HM, Wu XN, Zhang F, Luo L, Shen QR, Xu GH (2015). OsSIZ1, a SUMO E3 ligase gene, is involved in the regulation of the responses to phosphate and nitrogen in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 56, 2381-2395 |
| [44] | Watanabe K, Pacher M, Dukowic S, Schubert V, Puchta H, Schubert I (2009). The STRUCTURAL MAINTENANCE OF CHROMOSOMES 5/6 complex promotes sister chromatid alignment and homologous recombination after DNA damage in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21, 2688-2699. |
| [45] | Wotton D, Pemberton LF, Merrill-Schools J (2017). SUMO and Chromatin Remodeling. In: Wilson VG, ed. SUMO Regulation of Cellular Processes. Cham: Springer. pp. 35-50. |
| [46] | Xu PL, Yuan DK, Liu M, Li CX, Liu YY, Zhang SC, Yao N, Yang CW (2013). AtMMS21, an SMC5/6 complex subunit, is involved in stem cell niche maintenance and DNA damage responses in Arabidopsis roots.Plant Physiol 161, 1755-1768. |
| [47] | Yoo CY, Miura K, Jin JB, Lee J, Park HC, Salt DE, Yun DJ, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2006). SIZ1 small ubiquitin-like modifier E3 ligase facilitates basal thermotolerance in Arabidopsis independent of salicylic acid.Plant Physiol 142, 1548-1558. |
| [48] | Yuan DK, Lai JB, Xu PL, Zhang SC, Zhang JJ, Li CX, Wang YQ, Du JJ, Liu YY, Yang CW (2014). AtMMS21 regulates DNA damage response and homologous recombination repair in Arabidopsis.DNA Repair 21, 140-147. |
| [49] | Yunus AA, Lima CD (2009). Structure of the Siz/PIAS SUMO E3 ligase Siz1 and determinants required for SUMO modification of PCNA.Mol Cell 35, 669-682. |
| [50] | Zhang JJ, Lai JB, Wang FG, Yang SG, He ZP, Jiang JM, Li QL, Wu Q, Liu YY, Yu MY, Du MY, Du JJ, Xie Q, Wu KQ (2017).a A SUMO ligase AtMMS21 regulates the stability of the chromatin remodeler BRAHMA in root deve- lopment.Plant Physiol 173 1574-1582. |
| [51] | Zhang RF, Guo Y, Li YY, Zhou LJ, Hao YJ, You CX (2016). Functional identification of MdSIZ1 as a SUMO E3 ligase in apple.J Plant Physiol 198, 69-80. |
| [52] | Zhang S, Zhuang KY, Wang SJ, Lv JL, Ma NN, Meng QW (2017).b A novel tomato SUMO E3 ligase, SlSIZ1, confers drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco.J Integr Plant Biol 59, 102-117. |
| [53] | Zhang SC, Qi YL, Yang CW (2010). Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase AtMMS21 regulates root meristem development.Plant Signal Behav 5, 53-55. |
| [54] | Zheng Y, Schumaker KS, Guo Y (2012). Sumoylation of transcription factor MYB30 by the small ubiquitin-like modifier E3 ligase SIZ1 mediates abscisic acid response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 12822-12827. |
| [1] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [2] | 曾鑫海, 陈锐, 师宇, 盖超越, 范凯, 李兆伟. 植物SPL转录因子的生物功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 982-997. |
| [3] | 许亚楠, 闫家榕, 孙鑫, 王晓梅, 刘玉凤, 孙周平, 齐明芳, 李天来, 王峰. 红光和远红光在调控植物生长发育及应答非生物胁迫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 622-637. |
| [4] | 黄俊文, 冯琦伊, 郑凯勇, 黄俊杰, 王林博, 赖瑞强, 赖建彬, 阳成伟. 植物蛋白质SUMO化修饰体外高效检测系统[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 490-499. |
| [5] | 王劲东,周豫,余佳雯,范晓磊,张昌泉,李钱峰,刘巧泉. miR172-AP2模块调控植物生长发育及逆境响应的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 205-215. |
| [6] | 曲高平,金京波. 植物蛋白SUMO化修饰检测方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 83-89. |
| [7] | 王梦龙,彭小群,陈竹锋,唐晓艳. 植物凝集素类受体蛋白激酶研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 96-105. |
| [8] | 郭倩倩,周文彬. 植物响应联合胁迫机制的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 662-673. |
| [9] | 任鸿雁, 王莉, 马青秀, 吴光. 油菜素内酯生物合成途径的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(6): 768-778. |
| [10] | 张桂芝, 林继山, 李燕洁, 侯丙凯. 植物激素糖基化修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(5): 515-523. |
| [11] | 徐庞连;曾棉炜;黄丽霞;阳成伟*. 植物SUMO化修饰及其生物学功能[J]. 植物学报, 2008, 25(05): 608-615. |
| [12] | 储昭庆 李李 宋丽 薛红卫. 油菜素内酯生物合成与功能的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2006, 23(5): 543-555. |
| [13] | 宋丽 李李 储昭庆 薛红卫. 拟南芥油菜素内酯信号转导研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2006, 23(5): 556-563. |
| [14] | 梁宇 高玉葆. 内生真菌对植物生长发育及抗逆性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2000, 17(01): 52-59. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||