

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 676-686.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21036 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21036
张文晶1, 杨晓萌1, 高侃1, 魏欣仪1, 石雪彤1, 王瑞瑄1, 武凤霞2, 康菊清1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-10
接受日期:2021-08-09
出版日期:2021-11-01
发布日期:2021-11-12
通讯作者:
康菊清
作者简介:* E-mail: kangjq@snnu.edu.cn基金资助:
Wenjing Zhang1, Xiaomeng Yang1, Kan Gao1, Xinyi Wei1, Xuetong Shi1, Ruixuan Wang1, Fengxia Wu2, Juqing Kang1,*( )
)
Received:2021-02-10
Accepted:2021-08-09
Online:2021-11-01
Published:2021-11-12
Contact:
Juqing Kang
摘要: 转录因子ABI4参与植物激素ABA的绝大多数生物学功能, 它不仅是ABA和GA在植物体内含量平衡的核心调控因子, 同时还连接ABA与植物细胞内多个信号通路。利用拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) ABI4序列在十字花科其它19种植物(除拟南芥外)中检索得到27个同源基因, 通过序列多态性分析、系统发生重建、染色体共线性分析和转录激活活性比较, 探讨了该基因在十字花科植物中的演化历史。结果表明, ABI4蛋白质序列和结构在十字花科植物中具有较高的保守性, 暗示了其功能的重要性; 单独的ABI4蛋白并不具备显著的转录激活活性, 说明其生物学功能的具体分子机制可能相对复杂, 需要进一步探讨。
张文晶, 杨晓萌, 高侃, 魏欣仪, 石雪彤, 王瑞瑄, 武凤霞, 康菊清. 十字花科植物ABI4序列演化与转录激活活性分析. 植物学报, 2021, 56(6): 676-686.
Wenjing Zhang, Xiaomeng Yang, Kan Gao, Xinyi Wei, Xuetong Shi, Ruixuan Wang, Fengxia Wu, Juqing Kang. Analysis on the Evolution and Transcription Activation Activity of ABI4 in Brassicaceae. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 676-686.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| AthABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTAGCTTCCCAACATCAAC |
| AthABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTAATAGAATTCCCCCAAGATGGGATCA |
| AlyABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTAGCTTCCCAACAACACC |
| AlyABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAATAGAATTCCCTTCCTCCTTGTTCCTG |
| CruABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTAGCTTCCAAACAACAACAACA |
| CruABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAATAGAATTCTCCCAAGATAGGATCAATGA |
| BstABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTAGCTTCCAAACAACACC |
| BstABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAGTAGAATTCCCCCAAGATAGGATCA |
| BraABI4#1F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTACCTTCCCAACAACAAC |
| BraABI4#1R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAAAAGTCAAGCAAGAAGGGATCAACA |
| BraABI4#2F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTACCTTCCCAACAAGAAC |
| BraABI4#2R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAAATGTCAAGCAAGGGATCAATAAAA |
| EsaABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTACCTTCCCAAAAACACC |
| EsaABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAAAAGTCAAGCAAGAAGGGATCAACA |
表1 十字花科7个ABI4基因克隆引物序列
Table 1 Primers for 7 ABI4 genes in the Brassicaceae
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| AthABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTAGCTTCCCAACATCAAC |
| AthABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTAATAGAATTCCCCCAAGATGGGATCA |
| AlyABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTAGCTTCCCAACAACACC |
| AlyABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAATAGAATTCCCTTCCTCCTTGTTCCTG |
| CruABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTAGCTTCCAAACAACAACAACA |
| CruABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAATAGAATTCTCCCAAGATAGGATCAATGA |
| BstABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTAGCTTCCAAACAACACC |
| BstABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAGTAGAATTCCCCCAAGATAGGATCA |
| BraABI4#1F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTACCTTCCCAACAACAAC |
| BraABI4#1R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAAAAGTCAAGCAAGAAGGGATCAACA |
| BraABI4#2F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTACCTTCCCAACAAGAAC |
| BraABI4#2R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAAATGTCAAGCAAGGGATCAATAAAA |
| EsaABI4F | ACGCGTCGACATGGACCCTTTACCTTCCCAAAAACACC |
| EsaABI4R | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTCAAAAGTCAAGCAAGAAGGGATCAACA |
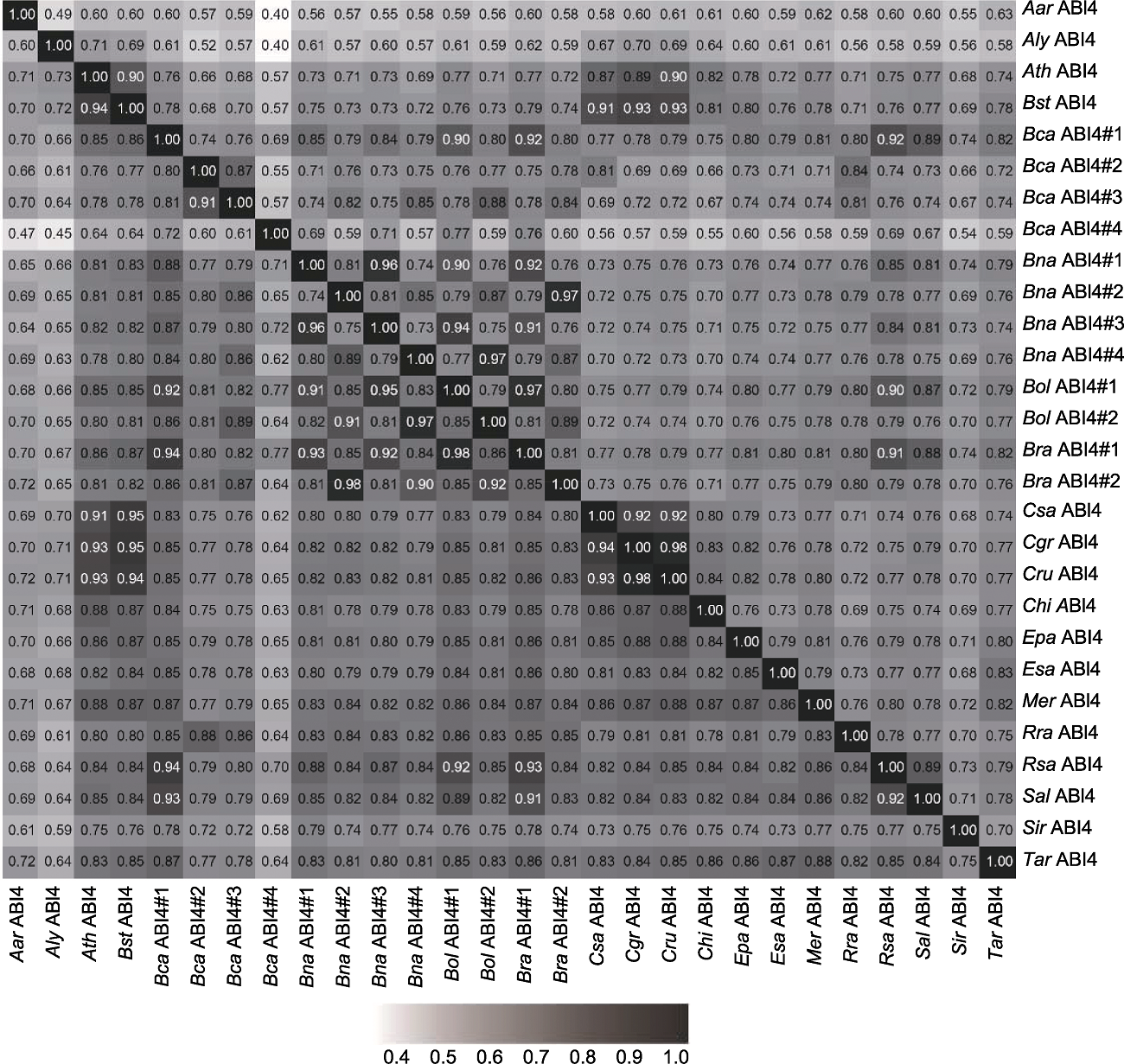
图1 十字花科植物中ABI4同源序列编码的氨基酸序列一致性和相似性比较 上三角示氨基酸序列的一致性, 下三角示氨基酸序列的相似性。Aar: Aethionema arabicum; Aly: 琴叶拟南芥; Ath: 拟南芥; Bst: Boechera stricta; Bca: 埃塞俄比亚芥; Bna: 欧洲油菜; Bol: 野甘蓝; Bra: 芜菁; Csa: 亚麻荠; Cgr: 大花荠菜; Cru: 荠菜; Chi: 碎米荠; Epa: 条叶盐芥; Esa: 小盐芥; Mer: Microthlaspi erraticum; Rra: 野萝卜; Rsa: 萝卜; Sal: 白芥; Sir: 水蒜芥; Tar: 菥蓂
Figure 1 The identity and similarity of the amino acid sequences of ABI4 homologs in the Brassicaceae The upper triangle shows the identity of amino acid sequences and the lower triangle shows the similarity of amino acid sequences. Aar: Aethionema arabicum; Aly: Arabidopsis lyrata; Ath: Ar. thaliana; Bst: Boechera stricta; Bca: Brassica carinata; Bna: Br. napus; Bol: Br. oleracea var. oleracea; Bra: Br. rapa; Csa: Camelina sativa; Cgr: Capsella grandiflora; Cru: Cap. rubella; Chi: Cardamine hirsuta; Epa: Eutrema parvulum; Esa: E. salsugineum; Mer: Microthlaspi erraticum; Rra: Raphanus raphanistrum; Rsa: R. sativus; Sal: Sinapis alba; Sir: Sisymbrium irio; Tar: Thlaspi arvense
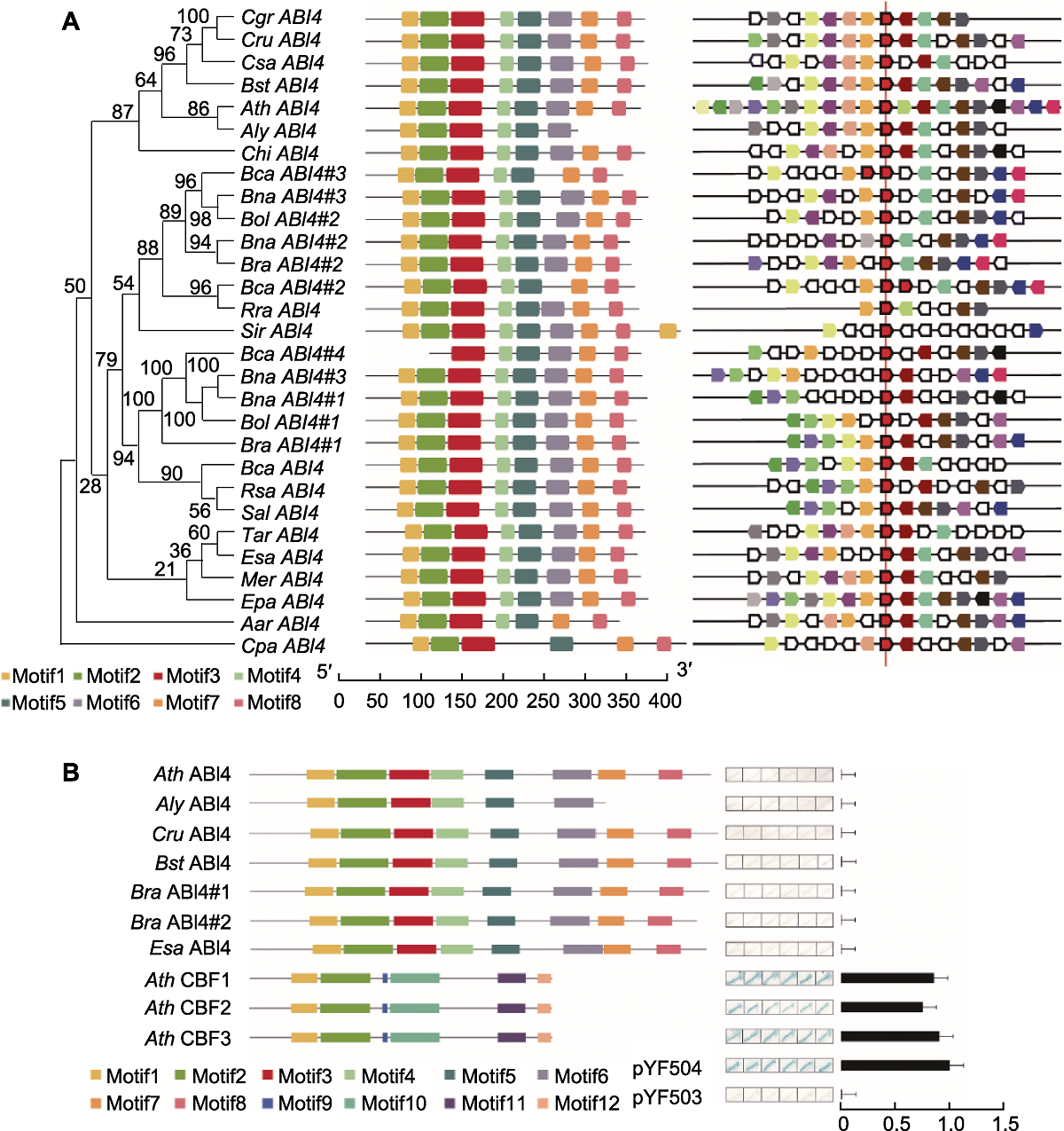
图2 十字花科20种植物中ABI4基因的系统发生关系和6个物种中ABI4的转录激活活性 (A) 20种植物中ABI4基因的系统发生关系(分支上的数字表示最大似然法分析过程中的bootstrap值(100次))、蛋白质保守基序预测和染色体定位的共线性分析; (B) 6种植物中ABI4的蛋白结构和转录激活活性的定性和定量检测。物种缩写见图1; Cpa: 番木瓜
Figure 2 Phylogenetic relationships of ABI4's homologs in 20 Brassicaceae species and transcriptional activation activity of ABI4 in 6 species (A) Phylogenetic relationships (the number above the nodes indicate value in 100 represents of maximum likdihood analysis.), protein motif structure prediction and collinearity analysis of genomic mapping of ABI4's homologs in 20 Brassicaceae species; (B) The protein structure, the qualitative and quantitative detection of transcriptional activation activity of ABI4 in 6 species. Species abbreviations shown in Figure 1; Cpa: Carica papaya
| [1] | 李媛媛, 傅廷栋, 马朝芝 (2007). 芸薹属植物比较基因组学研究进展. 植物学通报 24, 200-207. |
| [2] |
Acevedo-Hernández GJ, León P, Herrera-Estrella LR (2005). Sugar and ABA responsiveness of a minimal RBCS light-responsive unit is mediated by direct binding of ABI4. Plant J 43, 506-519.
PMID |
| [3] |
Arenas-Huertero F, Arroyo A, Zhou L, Sheen J, Leóon P (2000). Analysis of Arabidopsis glucose insensitive mutants, gin5 and gin6, reveals a central role of the plant hormone ABA in the regulation of plant vegetative development by sugar. Genes Dev 14, 2085-2096.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Bajguz A (2009). Brassinosteroid enhanced the level of abscisic acid in Chlorella vulgaris subjected to short-term heat stress. J Plant Physiol 166, 882-886.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bossi F, Cordoba E, Dupré P, Mendoza MS, Román CS, León P (2009). The Arabidopsis ABA-INSENSITIVE (ABI) 4 factor acts as a central transcription activator of the expression of its own gene, and for the induction of ABI5 and SBE2.2 genes during sugar signaling. Plant J 59, 359-374.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Finet C, Berne-Dedieu A, Scutt CP, Marlétaz F (2013). Evolution of the ARF gene family in land plants: old domains, new tricks. Mol Biol Evol 30, 45-56.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Finkelstein RR, Gampala SSL, Rock CD (2002). Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell 14, S15-S45.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Finkelstein RR, Wang ML, Lynch TJ, Rao S, Goodman HM (1998). The Arabidopsis abscisic acid response locus ABI4 encodes an APETALA2 domain protein. Plant Cell 10, 1043-1054.
PMID |
| [9] |
Foyer CH, Kerchev PI, Hancock RD (2012). The ABA-INSENSITIVE-4 (ABI4) transcription factor links redox, hormone and sugar signaling pathways. Plant Signal Behav 7, 276-281.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Giraud E, Van Aken O, Ho LHM, Whelan J (2009). The transcription factor ABI4 is a regulator of mitochondrial retrograde expression of ALTERNATIVE OXIDASE1a. Plant Physiol 150, 1286-1296.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Hanada K, Hase T, Toyoda T, Shinozaki K, Okamoto M (2011). Origin and evolution of genes related to ABA metabolism and its signaling pathways. J Plant Res 124, 455-465.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Huang CH, Sun RR, Hu Y, Zeng LP, Zhang N, Cai LM, Zhang Q, Koch MA, Al-Shehbaz I, Edger PP, Pires JC, Tan DY, Zhong Y, Ma H (2016). Resolution of Brassicaceae phylogeny using nuclear genes uncovers nested radiations and supports convergent morphological evolution. Mol Biol Evol 33, 394-412.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Ikeda M, Ohme-Takagi M (2009). A novel group of transcriptional repressors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 970-975.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Kang JQ, Zhang HT, Sun TS, Shi YH, Wang JQ, Zhang BC, Wang ZH, Zhou YH, Gu HY (2013). Natural variation of C-repeat-binding factor (CBFs) genes is a major cause of divergence in freezing tolerance among a group of Arabidopsis thaliana populations along the Yangtze River in China. New Phytol 199, 1069-1080.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Kazan K (2006). Negative regulation of defence and stress genes by EAR-motif-containing repressors. Trends Plant Sci 11, 109-112.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Kerchev PI, Pellny TK, Vivancos PD, Kiddle G, Hedden P, Driscoll S, Vanacker H, Verrier P, Hancock RD, Foyer CH (2011). The transcription factor ABI4 is required for the ascorbic acid-dependent regulation of growth and regulation of jasmonate-dependent defense signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23, 3319-3334.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Koussevitzky S, Nott A, Mockler TC, Hong F, Sachetto- Martins G, Surpin M, Lim IJ, Mittler R, Chory J (2007). Signals from chloroplasts converge to regulate nuclear gene expression. Science 316, 715-719.
PMID |
| [18] |
Kucera B, Cohn MA, Leubner-Metzger G (2005). Plant hormone interactions during seed dormancy release and germination. Seed Sci Res 15, 281-307.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Laby RJ, Kincaid MS, Kim D, Gibson SI (2000). The Arabidopsis sugar-insensitive mutants sis4 and sis5 are defective in abscisic acid synthesis and response. Plant J 23, 587-596.
PMID |
| [20] |
Liu JY, Osbourn A, Ma PD (2015). MYB transcription factors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Mol Plant 8, 689-708.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Liu SY, Liu YM, Yang XH, Tong CB, Edwards D, Parkin IAP, Zhao MX, Ma JX, Yu JY, Huang SM, Wang XY, Wang JY, Lu K, Fang ZY, Bancroft I, Yang TJ, Hu Q, Wang XF, Yue Z, Li HJ, Yang LF, Wu J, Zhou Q, Wang WX, King GJ, Pires JC, Lu CX, Wu ZY, Sampath P, Wang Z, Guo H, Pan SK, Yang LM, Min JM, Zhang D, Jin DC, Li WS, Belcram H, Tu JX, Guan M, Qi CK, Du DZ, Li JN, Jiang LC, Batley J, Sharpe AG, Park BS, Ruperao P, Cheng F, Waminal NE, Huang Y, Dong CH, Wang L, Li JP, Hu ZY, Zhuang M, Huang Y, Huang JY, Shi JQ, Mei DS, Liu J, Lee TH, Wang JP, Jin HZ, Li ZY, Li X, Zhang JF, Xiao L, Zhou YM, Liu ZS, Liu XQ, Qin R, Tang X, Liu WB, Wang YP, Zhang YY, Lee J, Kim HH, Denoeud F, Xu X, Liang XM, Hua W, Wang XW, Wang J, Chalhoub B, Paterson AH (2014). The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat Commun 5, 3930.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Lysak MA, Koch MA, Pecinka A, Schubert I (2005). Chromosome triplication found across the tribe Brassiceae. Geno Res 15, 516-525. |
| [23] |
Ma DW, Constabel CP (2019). MYB repressors as regulators of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plants. Trends Plant Sci 24, 275-289.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Matsui K, Umemura Y, Ohme-Takagi M (2008). AtMYBL2, a protein with a single MYB domain, acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 55, 954-967.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012). AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul Mech 1819, 86-96. |
| [26] |
Nakamura S, Lynch TJ, Finkelstein RR (2001). Physical interactions between ABA response loci of Arabidopsis. Plant J 26, 627-635.
PMID |
| [27] |
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006). Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140, 411-432.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Niu XP, Helentjaris T, Bate NJ (2002). Maize ABI4 binds coupling element1 in abscisic acid and sugar response genes. Plant Cell 14, 2565-2575.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Ohta M, Matsui K, Hiratsu K, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2001). Repression domains of class II ERF transcriptional repressors share an essential motif for active repression. Plant Cell 13, 1959-1968.
PMID |
| [30] |
Paponov IA, Teale W, Lang D, Paponov M, Reski R, Rensing SA, Palme K (2009). The evolution of nuclear auxin signaling. BMC Evol Biol 9, 126.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Reeves WM, Lynch TJ, Mobin R, Finkelstein RR (2011). Direct targets of the transcription factors ABA-insensitive (ABI) 4 and ABI5 reveal synergistic action by ABI4 and several bZIP ABA response factors. Plant Mol Biol 75, 347-363.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Shkolnik-Inbar D, Bar-Zvi D (2010). ABI4 mediates abscisic acid and cytokinin inhibition of lateral root formation by reducing polar auxin transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22, 3560-3573.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Shu K, Chen Q, Wu YR, Liu RJ, Zhang HW, Wang PF, Li YL, Wang SF, Tang SY, Liu CY, Yang WY, Cao XF, Serino G, Xie Q (2016a). ABI4 mediates antagonistic effects of abscisic acid and gibberellins at transcript and protein levels. Plant J 85, 348-361.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Shu K, Liu XD, Xie Q, He ZH (2016b). Two faces of one seed: hormonal regulation of dormancy and germination. Mol Plant 9, 34-45.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Shu K, Zhang HW, Wang SF, Chen ML, Wu YR, Tang SY, Liu CY, Feng YQ, Cao XF, Xie Q (2013). ABI4 regulates primary seed dormancy by regulating the biogenesis of abscisic acid and gibberellins in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 9, e1003577. |
| [36] |
Shu K, Zhou WG, Chen F, Luo XF, Yang WY (2018a). Abscisic acid and gibberellins antagonistically mediate plant development and abiotic stress responses. Front Plant Sci 9, 416.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Shu K, Zhou WG, Yang WY (2018b). APETALA 2-domain- containing transcription factors: focusing on abscisic acid and gibberellins antagonism. New Phytol 217, 977-983.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Söderman EM, Brocard IM, Lynch TJ, Finkelstein RR (2000). Regulation and function of the Arabidopsis ABA- insensitive 4 gene in seed and abscisic acid response signaling networks. Plant Physiol 124, 1752-1765.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Sun XW, Feng PQ, Xu XM, Guo HL, Ma JF, Chi W, Lin RC, Lu CM, Zhang LX (2011). A chloroplast envelope-bound PHD transcription factor mediates chloroplast signals to the nucleus. Nat Commun 2, 477.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Talboys PJ, Zhang HM, Knox JP (2011). ABA signaling modulates the detection of the LM6 arabinan cell wall epitope at the surface of Arabidopsis thaliana seedling root apices. New Phytol 190, 618-626.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Ton J, Mauch-Mani B (2004). β-amino-butyric acid-induced resistance against necrotrophic pathogens is based on ABA-dependent priming for callose. Plant J 38, 119-130.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Umezawa T, Nakashima K, Miyakawa T, Kuromori T, Tanokura M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010). Molecular basis of the core regulatory network in ABA responses: sensing, signaling and transport. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 1821-1839.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Wang XW, Wang HZ, Wang J, Sun RF, Wu J, Liu SY, Bai YQ, Mun JH, Bancroft I, Cheng F, Huang SW, Li XX, Hua W, Wang JY, Wang XY, Freeling M, Pires JC, Paterson AH, Chalhoub B, Wang B, Hayward A, Sharpe AG, Park BS, Weisshaar B, Liu BH, Li B, Liu B, Tong CB, Song C, Duran C, Peng CF, Geng CY, Koh C, Lin CY, Edwards D, Mu DS, Shen D, Soumpourou E, Li F, Fraser F, Conant G, Lassalle G, King GJ, Bonnema G, Tang HB, Wang HP, Belcram H, Zhou HL, Hirakawa H, Abe H, Guo H, Wang H, Jin HZ, Parkin IAP, Batley J, Kim JS, Just J, Li JW, Xu JH, Deng J, Kim JA, Li JP, Yu JY, Meng JL, Wang JP, Min JM, Poulain J, Wang J, Hatakeyama K, Wu K, Wang L, Fang L, Trick M, Links MG, Zhao MX, Jin MN, Ramchiary N, Drou N, Berkman PJ, Cai QL, Huang QF, Li RQ, Tabata S, Cheng SF, Zhang S, Zhang SJ, Huang SM, Sato S, Sun SL, Kwon SJ, Choi SR, Lee TH, Fan W, Zhao X, Tan X, Xu X, Wang Y, Qiu Y, Yin Y, Li YR, Du YC, Liao YC, Lim Y, Narusaka Y, Wang YP, Wang ZY, Li ZY, Wang ZW, Xiong ZY, Zhang ZH (2011). The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat Genet 43, 1035-1039.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Wind JJ, Peviani A, Snel B, Hanson J, Smeekens SC (2013). ABI4: versatile activator and repressor. Trends Plant Sci 18, 125-132.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Yaish MW, El-kereamy A, Zhu T, Beatty PH, Good AG, Bi YM, Rothstein SJ (2010). The APETALA-2-like transcription factor OsAP2-39 controls key interactions between abscisic acid and gibberellin in rice. PLoS Genet 6, e1001098.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Yang Y, Yu XC, Song LF, An CC (2011). ABI4 activates DGAT1 expression in Arabidopsis seedlings during nitrogen deficiency. Plant Physiol 156, 873-883.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Ye R, Yao QH, Xu ZH, Xue HW (2004). Development of an efficient method for the isolation of factors involved in gene transcription during rice embryo development. Plant J 38, 348-357.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 廉小平, Getachew Melaku, 张石来, 胡凤益. 长寿与短命: 十字花科植物中MADS-box基因的长袖善舞[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 351-354. |
| [2] | 孙稚颖;郑纪庆;李法曾*. 拟南芥属的系统位置: 种皮及分子证据[J]. 植物学报, 2008, 25(05): 565-573. |
| [3] | 刘晓风, 谭敦炎. 24种十字花科短命植物的扩散体特征与扩散对策[J]. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(6): 1019-1027. |
| [4] | 魏琴 周黎军 陈东林 李旭峰 陈放. 十字花科10属种与油菜萝卜胞质不育系杂交的花粉萌发情况观察[J]. 植物学报, 2000, 17(03): 260-265. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||