

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 664-675.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21115 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21115
收稿日期:2021-07-12
接受日期:2021-10-12
出版日期:2021-11-01
发布日期:2021-11-12
通讯作者:
秦源
作者简介:* E-mail: yuanqin@fafu.edu.cn基金资助:Received:2021-07-12
Accepted:2021-10-12
Online:2021-11-01
Published:2021-11-12
Contact:
Yuan Qin
摘要: 真核生物基因组上的核小体呈现不均匀分布, 转录活跃区域的染色质结构相对松散且易被调节蛋白结合, 这些区域的可接近程度称为染色质可及性。随着测序技术的发展, DNase-seq、ATAC-seq、MNase-seq和NOMe-seq等组学技术的应用, 全基因组范围内染色质可及性检测变得简便且高效。该文主要介绍了真核生物染色质可及性的4种基本检测方法的技术原理, 总结了核小体定位、组蛋白修饰以及转录因子结合与染色质可及性的关系, 并综述了染色质可及性参与植物生长发育和环境响应研究进展, 以期为植物领域全基因组水平染色质可及性研究、顺式调控元件挖掘及发育和环境响应过程中基因表达调控网络的解析提供借鉴。
李占杰, 秦源. 染色质可及性与植物基因表达调控. 植物学报, 2021, 56(6): 664-675.
Zhanjie Li, Yuan Qin. Chromatin Accessibility and the Gene Expression Regulation in Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(6): 664-675.
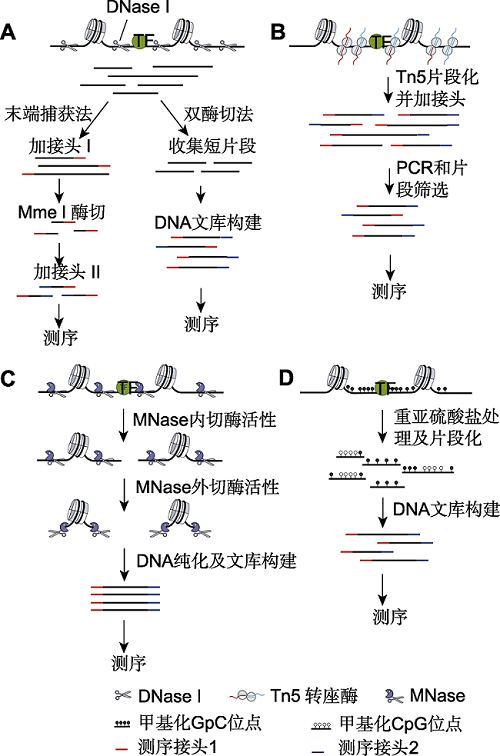
图1 常见染色质可及性检测方法 (A) DNase-seq方法是利用核酸内切酶DNase I消化开放染色质区DNA并进行建库的方法。其中, 末端捕获法通过提取单酶切后的染色质DNA大片段, 经加测序接头1、Mme I酶切和加测序接头2等步骤, 完成含有插入片段20 bp的测序文库构建; 双酶切法则通过提取双酶切后的染色质小片段, 经加测序接头1和2完成测序文库的构建。(B) ATAC-seq方法利用Tn5超敏感转座酶的高效转座活性在完成开放染色质区DNA打断的同时加入测序接头, 实现高效文库构建。(C) MNase-seq方法利用MNase的内切酶和外切酶活性将开放染色质区DNA切开, 同时消化linker DNA, 构建核小体DNA文库, 可实现核小体占位及染色质可及性的同时检测。(D) NOMe-seq方法利用GpC甲基转移酶对开放染色质区GpC二核苷酸进行甲基化修饰。人类细胞中仅存在CPGm位点而无内源的GpCm位点, 经亚硫酸氢盐处理后进行全基因组测序, 即可同时检测开放染色质区及全基因组的DNA甲基化位点。
Figure 1 Principal methods for measuring chromatin accessibility (A) DNase-seq uses the endonuclease DNase I to cleave DNA within accessible chromatin and constructs the DNase- seq library. In the end-capture method, the large DNA frag-ments from open chromatin regions released by single cut are collected, and then processed by several steps including adding adapter 1, cutting 20 bp of the DNA using a type II restriction enzyme Mme I, and adding adapter 2 to complete the sequencing library. In the double-hit method, the small DNA fragments from open chromatin regions released by double cut are collected, then processed by steps including adding adapter 1 and adapter 2 to complete the sequencing library; (B) ATAC-seq uses a hyperactive transposase (Tn5) to simultaneously cleave and ligate adaptors to accessible DNA. The efficiency of library construction is thus increased; (C) MNase-seq uses the endonuclease/exonuclease activity of MNase to both cleave and eliminate accessible DNA and linker DNA. Therefore, the DNA library from nucleosomal DNA can both detect the nucleosome occupancy and open chromatin; (D) NOMe-seq uses a GpC methyltransferase to me-thylate GpC dinucleotide in accessible DNA. There is only CPGm sites but not GpCm sites in human cells. The DNA se- quencing following bisulfite conversion of nonmethylated cyto- sine to uracil nucleotides can simultaneously provide the ge-nome-wide measure of accessibility and DNA methylation sites.
| [1] |
Almer A, Hörz W (1986). Nuclease hypersensitive regions with adjacent positioned nucleosomes mark the gene boundaries of the PHO5/PHO3 locus in yeast. EMBO J 5, 2681-2687.
PMID |
| [2] |
Almer A, Rudolph H, Hinnen A, Hörz W (1986). Removal of positioned nucleosomes from the yeast PHO5 promoter upon PHO5 induction releases additional upstream activating DNA elements. EMBO J 5, 2689-2696.
PMID |
| [3] |
Bao XM, Rubin AJ, Qu K, Zhang JJ, Giresi PG, Chang HY, Khavari PA (2015). A novel ATAC-seq approach reveals lineage-specific reinforcement of the open chromatin landscape via cooperation between BAF and p63. Genome Biol 16, 284.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Bernstein BE, Humphrey EL, Erlich RL, Schneider R, Bouman P, Liu JS, Kouzarides T, Schreiber SL (2002). Methylation of histone H3 Lys 4 in coding regions of active genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 8695-8700.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Boyle AP, Davis S, Shulha HP, Meltzer P, Margulies EH, Weng ZP, Furey TS, Crawford GE (2008). High-resolution mapping and characterization of open chromatin across the genome. Cell 132, 311-322.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Buenrostro JD, Giresi PG, Zaba LC, Chang HY, Greenleaf WJ (2013). Transposition of native chromatin for fast and sensitive epigenomic profiling of open chromatin, DNA- binding proteins and nucleosome position. Nat Methods 10, 1213-1218.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Cai HY, Chai MN, Chen FQ, Huang YM, Zhang M, He Q, Liu LP, Yan MK, Qin Y (2021a). HBI1 acts downstream of ERECTA and SWR1 in regulating inflorescence architecture through the activation of the brassinosteroid and auxin signaling pathways. New Phytol 229, 414-428.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Cai HY, Huang YM, Chen FQ, Liu LP, Chai MN, Zhang M, Yan MK, Aslam M, He Q, Qin Y (2021b). ERECTA signaling regulates plant immune responses via chromatin-mediated promotion of WRKY33 binding to target genes. New Phytol 230, 737-756.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Cai HY, Liu LP, Zhang M, Chai MN, Huang YM, Chen FQ, Yan MK, Su ZX, Henderson I, Palanivelu R, Chen XM, Qin Y (2021c). Spatiotemporal control of miR398 biogenesis, via chromatin remodeling and kinase signaling, ensures proper ovule development. Plant Cell 33, 1530-1553.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Cai HY, Zhang M, Chai MN, He Q, Huang XY, Zhao LH, Qin Y (2019). Epigenetic regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by an antagonistic interaction between H2A.Z and H3K4me3. New Phytol 221, 295-308.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Cai HY, Zhao LH, Wang LL, Zhang M, Su ZX, Cheng Y, Zhao HM, Qin Y (2017). ERECTA signaling controls Arabidopsis inflorescence architecture through chromatin-mediated activation of PRE1 expression. New Phytol 214, 1579-1596.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Chung HR, Dunkel I, Heise F, Linke C, Krobitsch S, Ehrenhofer-Murray AE, Sperling SR, Vingron M (2010). The effect of micrococcal nuclease digestion on nucleosome positioning data. PLoS One 5, e15754.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Clapier CR, Iwasa J, Cairns BR, Peterson CL (2017). Mechanisms of action and regulation of ATP-dependent chromatin-remodelling complexes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18, 407-422.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Conconi A, Ryan CA (1993). DNase I and micrococcal nuclease analysis of the tomato proteinase inhibitor I gene in chromatin. J Biol Chem 268, 430-435.
PMID |
| [15] |
Corces MR, Trevino AE, Hamilton EG, Greenside PG, Sinnott-Armstrong NA, Vesuna S, Satpathy AT, Rubin AJ, Montine KS, Wu BJ, Kathiria A, Cho SW, Mumbach MR, Carter AC, Kasowski M, Orloff LA, Risca VI, Kundaje A, Khavari PA, Montine TJ, Greenleaf WJ, Chang HY (2017). An improved ATAC-seq protocol reduces background and enables interrogation of frozen tissues. Nat Methods 14, 959-962.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Crawford GE, Davis S, Scacheri PC, Renaud G, Halawi MJ, Erdos MR, Green R, Meltzer PS, Wolfsberg TG, Collins FS (2006). DNase-chip: a high-resolution method to identify DNase I hypersensitive sites using tiled microarrays. Nat Methods 3, 503-509.
PMID |
| [17] |
Crawford GE, Holt IE, Mullikin JC, Tai D, National Institutes of Health Intramural Sequencing Center, Green ED, Wolfsberg TG, Collins FS (2004). Identifying gene regulatory elements by genome-wide recovery of DNase hypersensitive sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 992-997.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Dai XZ, Bai YH, Zhao LH, Dou XY, Liu YH, Wang LL, Li Y, Li WM, Hui YN, Huang XY, Wang ZH, Qin Y (2017). H2A.Z represses gene expression by modulating promoter nucleosome structure and enhancer histone modifications in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 10,1274-1292.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Du YH, Liu ZP, Cao XK, Chen XL, Chen ZY, Zhang XB, Zhang XQ, Jiang CZ (2017). Nucleosome eviction along with H3K9ac deposition enhances Sox2 binding during human neuroectodermal commitment. Cell Death Differ 24, 1121-1131.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Dutta A, Gogol M, Kim JH, Smolle M, Venkatesh S, Gil-more J, Florens L, Washburn MP, Workman JL (2014). Swi/Snf dynamics on stress-responsive genes is gover-ned by competitive bromodomain interactions. Genes Dev 28, 2314-2330.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Felsenfeld G, Groudine M (2003). Controlling the double helix. Nature 421, 448-453.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Fullwood MJ, Liu MH, Pan YF, Liu J, Xu H, Bin Mohamed Y, Orlov YL, Velkov S, Ho A, Mei PH, Chew EGY, Huang PYH, Welboren WJ, Han YY, Ooi HS, Ariyaratne PN, Vega VB, Luo YQ, Tan PY, Choy PY, Wansa KDSA, Zhao B, Lim KS, Leow SC, Yow JS, Joseph R, Li HX, Desai KV, Thomsen JS, Lee YK, Karuturi RKM, Herve T, Bourque G, Stunnenberg HG, Ruan XA, Cacheux-Rataboul V, Sung WK, Liu ET, Wei CL, Cheung E, Ruan YJ (2009). An oestrogen-receptor-α-bound human chromatin interactome. Nature 462, 58-64.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Han JL, Wang PX, Wang QL, Lin QF, Chen ZY, Yu GR, Miao CY, Dao Y, Wu RX, Schnable JC, Tang HB, Wang K (2020). Genome-wide characterization of DNase I-hypersensitive sites and cold response regulatory landscapes in grasses. Plant Cell 32, 2457-2473.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
He HH, Meyer CA, Hu SES, Chen MW, Zang CZ, Liu Y, Rao PK, Fei T, Xu H, Long H, Liu XS, Brown M (2014). Refined DNase-seq protocol and data analysis reveals intrinsic bias in transcription factor footprint identification. Nat Methods 11, 73-78.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Hesselberth JR, Chen XY, Zhang ZH, Sabo PJ, Sandstrom R, Reynolds AP, Thurman RE, Neph S, Kuehn MS, Noble WS, Fields S, Stamatoyannopoulos JA (2009). Global mapping of protein-DNA interactions in vivo by digital genomic footprinting. Nat Methods 6, 283-289.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Jégu T, Veluchamy A, Ramirez-Prado JS, Rizzi-Paillet C, Perez M, Lhomme A, Latrasse D, Coleno E, Vicaire S, Legras S, Jost B, Rougée M, Barneche F, Bergounioux C, Crespi M, Mahfouz MM, Hirt H, Raynaud C, Benhamed M (2017). The Arabidopsis SWI/SNF protein BAF60 mediates seedling growth control by modulating DNA accessibility. Genome Biol 18, 114.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Keene MA, Corces V, Lowenhaupt K, Elgin SC (1981). DNase I hypersensitive sites in Drosophila chromatin occur at the 5' ends of regions of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78, 143-146.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Kelly TK, Liu YP, Lay FD, Liang GN, Berman BP, Jones PA (2012). Genome-wide mapping of nucleosome positioning and DNA methylation within individual DNA molecules. Genome Res 22, 2497-2506.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Klemm SL, Shipony Z, Greenleaf WJ (2019). Chromatin accessibility and the regulatory epigenome. Nat Rev Genet 20, 207-220. |
| [30] |
Kodama Y, Nagaya S, Shinmyo A, Kato K (2007). Map-ping and characterization of DNase I hypersensitive sites in Arabidopsis chromatin. Plant Cell Physiol 48, 459-470.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Kumar SV (2018). H2A.Z at the core of transcriptional regulation in plants. Mol Plant 11, 1112-1114.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Lai WKM, Pugh BF (2017). Understanding nucleosome dynamics and their links to gene expression and DNA replication. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18, 548-562.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Lee CK, Shibata Y, Rao B, Strahl BD, Lieb JD (2004). Evidence for nucleosome depletion at active regulatory regions genome-wide. Nat Genet 36, 900-905.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Lieberman-Aiden E, van Berkum NL, Williams L, Imakaev M, Ragoczy T, Telling A, Amit I, Lajoie BR, Sabo PJ, Dorschner MO, Sandstrom R, Bernstein B, Bender MA, Groudine M, Gnirke A, Stamatoyan-nopoulos J, Mirny LA, Lander ES, Dekker J (2009). Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science 326, 289-293.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Lohr D, Kovacic RT, Van Holde KE (1977). Quantitative analysis of the digestion of yeast chromatin by staphylo-coccal nuclease. Biochemistry 16, 463-471.
PMID |
| [36] |
Lorzadeh A, Bilenky M, Hammond C, Knapp DJHF, Li LL, Miller PH, Carles A, Heravi-Moussavi A, Gakkhar S, Moksa M, Eaves CJ, Hirst M (2016). Nucleosome density ChIP-Seq identifies distinct chromatin modification signatures associated with MNase accessibility. Cell Rep 17, 2112-2124.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | Lu Z, Hofmeister BT, Vollmers C, DuBois RM, Schmitz RJ (2017). Combining ATAC-seq with nuclei sorting for discovery of cis-regulatory regions in plant genomes. Nuc- leic Acids Res 45, e41. |
| [38] | Lu ZF, Marand AP, Ricci WA, Ethridge CL, Zhang XY, Schmitz RJ (2019). The prevalence, evolution and chromatin signatures of plant regulatory elements. Nat P-lants 5, 1250-1259. |
| [39] |
Luger K, Mäder AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Rich-mond TJ (1997). Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature 389, 251-260.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Luo YX, Hou XM, Zhang CJ, Tan LM, Shao CR, Lin RN, Su YN, Cai XW, Li L, Chen S, He XJ (2020). A plant- specific SWR1 chromatin-remodeling complex couples histone H2A.Z deposition with nucleosome sliding. EMBO J 39, e102008. |
| [41] |
Mavrich TN, Ioshikhes IP, Venters BJ, Jiang CZ, Tomsho LP, Qi J, Schuster SC, Albert I, Pugh BF (2008a). A barrier nucleosome model for statistical positioning of nu-cleosomes throughout the yeast genome. Genome Res 18, 1073-1083.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Mavrich TN, Jiang CZ, Ioshikhes IP, Li XY, Venters BJ, Zanton SJ, Tomsho LP, Qi J, Glaser RL, Schuster SC, Gilmour DS, Albert I, Pugh BF (2008b). Nucleosome organization in the Drosophila genome. Nature 453, 358-362.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
McGhee JD, Wood WI, Dolan M, Engel JD, Felsenfeld G (1981). A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult β-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell 27, 45-55.
PMID |
| [44] | Meyer CA, Liu XS (2014). Identifying and mitigating bias in next-generation sequencing methods for chromatin biology. Nat Rev Genet 15, 709-721. |
| [45] |
Mieczkowski J, Cook A, Bowman SK, Mueller B, Alver BH, Kundu S, Deaton AM, Urban JA, Larschan E, Park PJ, Kingston RE, Tolstorukov MY (2016). MNase titra-tion reveals differences between nucleosome occupancy and chromatin accessibility. Nat Commun 7, 11485.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Mirny LA (2010). Nucleosome-mediated cooperativity between transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 22534-22539.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Mueller B, Mieczkowski J, Kundu S, Wang P, Sadreyev R, Tolstorukov MY, Kingston RE (2017). Widespread changes in nucleosome accessibility without changes in nucleosome occupancy during a rapid transcriptional in-duction. Genes Dev 31, 451-462.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Mueller PR, Wold B (1989). In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science 246, 780-786.
PMID |
| [49] |
Murphy KE, Meng FW, Makowski CE, Murphy PJ (2020). Genome-wide chromatin accessibility is restricted by ANP32E. Nat Commun 11, 5063.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Nair VS, El Salhat H, Taha RZ, John A, Ali BR, Elkord E (2018). DNA methylation and repressive H3K9 and H3K27 trimethylation in the promoter regions of PD-1, CTLA- 4, TIM-3, LAG-3, TIGIT, and PD-L1 genes in human pri-mary breast cancer. Clin Epigenet 10, 78. |
| [51] |
Nedospasov SA, Georgiev GP (1980). Non-random cleavage of SV40 DNA in the compact minichromosome and free in solution by micrococcal nuclease. Biochem Bio-phys Res Commun 92, 532-539.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Noll M (1974). Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res 1, 1573-1578.
PMID |
| [53] |
Pajoro A, Madrigal P, Muiño JM, Tomás Matus J, Jin J, Mecchia MA, Debernardi JM, Palatnik JF, Balazadeh S, Arif M, Ó'Maoileidigh DS, Wellmer F, Krajewski P, Riechmann JL, Angenent GC, Kaufmann K (2014). Dynamics of chromatin accessibility and gene regulation by MADS-domain transcription factors in flower development. Genome Biol 15, R41.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Qin Y, Zhao LH, Skaggs MI, Andreuzza S, Tsukamoto T, Panoli A, Wallace KN, Smith S, Siddiqi I, Yang ZB, Yadegari R, Palanivelu R (2014). ACTIN-RELATED PROTEIN6 regulates female meiosis by modulating meiotic gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 1612-1628.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Qiu ZK, Li R, Zhang SB, Wang KT, Xu M, Li JY, Du YC, Yu H, Cui X (2016). Identification of regulatory DNA elements using genome-wide mapping of DNase I hypersensitive sites during tomato fruit development. Mol Plant 9, 1168-1182.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Rando OJ, Ahmad K (2007). Rules and regulation in the primary structure of chromatin. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19, 250-256.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Rao S, Procko E, Shannon MF (2001). Chromatin remodeling, measured by a novel real-time polymerase chain reaction assay, across the proximal promoter region of the IL-2 gene. J Immunol 167, 4494-4503.
PMID |
| [58] |
Raxwal VK, Ghosh S, Singh S, Katiyar-Agarwal S, Goel S, Jagannath A, Kumar A, Scaria V, Agarwal M (2020). Abiotic stress-mediated modulation of the chromatin landscape in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 71, 5280-5293.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Ribeiro-Silva C, Vermeulen W, Lans H (2019). SWI/SNF: complex complexes in genome stability and cancer. DNA Repair 77, 87-95.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
Rothbart SB, Strahl BD (2014). Interpreting the language of histone and DNA modifications. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1839, 627-643.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Sabo PJ, Humbert R, Hawrylycz M, Wallace JC, Dor-schner MO, McArthur M, Stamatoyannopoulos JA (2004). Genome-wide identification of DNase I hypersen-sitive sites using active chromatin sequence libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 4537-4542.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Sabo PJ, Kuehn MS, Thurman R, Johnson BE, Johnson EM, Cao H, Yu M, Rosenzweig E, Goldy J, Haydock A, Weaver M, Shafer A, Lee K, Neri F, Humbert R, Singer MA, Richmond TA, Dorschner MO, McArthur M, Hawrylycz M, Green RD, Navas PA, Noble WS, Stama-toyannopoulos JA (2006). Genome-scale mapping of DNase I sensitivity in vivo using tiling DNA microarrays. Nat Methods 3, 511-518.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Schep AN, Buenrostro JD, Denny SK, Schwartz K, Sherlock G, Greenleaf WJ (2015). Structured nucleosome fingerprints enable high-resolution mapping of chromatin architecture within regulatory regions. Genome Res 25, 1757-1770.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Schones DE, Cui KR, Cuddapah S, Roh TY, Barski A, Wang ZB, Wei G, Zhao KJ (2008). Dynamic regulation of nucleosome positioning in the human genome. Cell 132, 887-898.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
Sijacic P, Bajic M, McKinney EC, Meagher RB, Deal RB (2018). Changes in chromatin accessibility between Arabidopsis stem cells and mesophyll cells illuminate cell type- specific transcription factor networks. Plant J 94, 215-231.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Sullivan AM, Arsovski AA, Lempe J, Bubb KL, Weirauch MT, Sabo PJ, Sandstrom R, Thurman RE, Neph S, Reynolds AP, Stergachis AB, Vernot B, Johnson AK, Haugen E, Sullivan ST, Thompson A, Neri III FV, Weaver M, Diegel M, Mnaimneh S, Yang A, Hughes TR, Nemhauser JL, Queitsch C, Stamatoyannopoulos JA (2014). Mapping and dynamics of regulatory DNA and transcription factor networks in A. thaliana. Cell Rep 8, 2015-2030.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
Svaren J, Klebanow E, Sealy L, Chalkley R (1994). Analysis of the competition between nucleosome forma-tion and transcription factor binding. J Biol Chem 269, 9335-9344.
PMID |
| [68] |
Swinstead EE, Paakinaho V, Presman DM, Hager GL (2016). Pioneer factors and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling factors interact dynamically: a new perspec-tive: multiple transcription factors can effect chromatin pioneer functions through dynamic interactions with ATP- dependent chromatin remodeling factors. BioEssays 38, 1150-1157.
DOI PMID |
| [69] |
Taberlay PC, Kelly TK, Liu CC, You JS, De Carvalho DD, Miranda TB, Zhou XJ, Liang GN, Jones PA (2011). Polycomb-repressed genes have permissive enhancers that initiate reprogramming. Cell 147, 1283-1294.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Thurman RE, Rynes E, Humbert R, Vierstra J, Maurano MT, Haugen E, Sheffield NC, Stergachis AB, Wang H, Vernot B, Garg K, John S, Sandstrom R, Bates D, Boatman L, Canfield TK, Diegel M, Dunn D, Ebersol AK, Frum T, Giste E, Johnson AK, Johnson EM, Kut-yavin T, Lajoie B, Lee BK, Lee K, London D, Lotakis D, Neph S, Neri F, Nguyen ED, Qu HZ, Reynolds AP, Roach V, Safi A, Sanchez ME, Sanyal A, Shafer A, Simon JM, Song LY, Vong S, Weaver M, Yan YQ, Zhang ZC, Zhang ZZ, Lenhard B, Tewari M, Dorschner MO, Hansen RS, Navas PA, Stamatoyannopoulos G, Iyer VR, Lieb JD, Sunyaev SR, Akey JM, Sabo PJ, Kaul R, Furey TS, Dekker J, Crawford GE, Stamatoyanno-poulos JA (2012). The accessible chromatin landscape of the human genome. Nature 489, 75-82.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Tian H, Li YR, Wang C, Xu XW, Zhang YJ, Zeb Q, Zicola J, Fu YF, Turck F, Li LG, Lu ZF, Liu LY (2021). Photo-period-responsive changes in chromatin accessibility in phloem-companion and epidermis cells of Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell 33, 475-491.
DOI URL |
| [72] | Vallianatos CN, Raines B, Porter RS, Bonefas KM, Wu MC, Garay PM, Collette KM, Seo YA, Dou YL, Keegan CE, Tronson NC, Iwase S (2020). Mutually suppressive roles of KMT2A and KDM5C in behaviour, neuronal structure, and histone H3K4 methylation. Commun Biol 3, 278. |
| [73] |
Vogelauer M, Wu JS, Suka N, Grunstein M (2000). Global histone acetylation and deacetylation in yeast. Nature 408, 495-498.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
Workman JL, Kingston RE (1992). Nucleosome core dis-placement in vitro via a metastable transcription factor- nucleosome complex. Science 258, 1780-1784.
PMID |
| [75] |
Wu C (1980). The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature 286, 854-860.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Yuan GC, Liu YJ, Dion MF, Slack MD, Wu LF, Altschuler SJ, Rando OJ (2005). Genome-scale identification of nucleosome positions in S. cerevisiae. Science 309, 626-630.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Zeng ZX, Zhang WL, Marand AP, Zhu B, Buell CR, Jiang JM (2019). Cold stress induces enhanced chromatin ac-cessibility and bivalent histone modifications H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 of active genes in potato. Genome Biol 20, 123.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
Zhang WL, Wu YF, Schnable JC, Zeng ZX, Freeling M, Crawford GE, Jiang JM (2012a). High-resolution map-ping of open chromatin in the rice genome. Genome Res 22, 151-162.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
Zhang WL, Zhang T, Wu YF, Jiang JM (2012b). Genome-wide identification of regulatory DNA elements and pro-tein-binding footprints using signatures of open chromatin in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 2719-2731.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
Zhang XY, Clarenz O, Cokus S, Bernatavichute YV, Pellegrini M, Goodrich J, Jacobsen SE (2007). Whole- genome analysis of histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol 5, e129.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
Zhao HN, Zhang WL, Chen LF, Wang L, Marand AP, Wu YF, Jiang JM (2018a). Proliferation of regulatory DNA elements derived from transposable elements in the maize genome. Plant Physiol 176, 2789-2803.
DOI URL |
| [82] | Zhao HN, Zhang WL, Zhang T, Lin Y, Hu YD, Fang C, Jiang JM (2020). Genome-wide MNase hypersensitivity assay unveils distinct classes of open chromatin associated with H3K27me3 and DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Biol 21, 24. |
| [83] | Zhao LH, Cai HY, Su ZX, Wang LL, Huang XY, Zhang M, Chen PJ, Dai XZ, Zhao HM, Palanivelu R, Chen XM, Qin Y (2018b). KLU suppresses megasporocyte cell fate through SWR1-mediated activation of WRKY28 expression in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E526-E535. |
| [84] |
Zhu B, Zhang WL, Zhang T, Liu B, Jiang JM (2015). Genome-wide prediction and validation of intergenic enhancers in Arabidopsis using open chromatin signatures. Plant Cell 27, 2415-2426.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 夏春皎, 李运广, 夏姝, 庞伟, 陈春丽. 植物基因组学中的流式细胞分析及分选技术[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 774-782. |
| [2] | 韩美玲,谭茹姣,晁代印. “绿色革命”新进展: 赤霉素与氮营养双重调控的表观修饰助力水稻高产高效育种[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 5-8. |
| [3] | 陈威,杨颖增,陈锋,周文冠,舒凯. 表观遗传修饰介导的植物胁迫记忆[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 779-785. |
| [4] | 国春策, 张睿, 山红艳, 孔宏智. 调控进化与形态多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(1): 72-79. |
| [5] | 郑小国, 陈亮, 罗利军. 植物中表观遗传修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2013, 48(5): 561-572. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
