

植物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (2): 209-216.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21122 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21122
王浩1, 王明1, 梁婷2, 姚玉新1, 杜远鹏1,*( ), 高振1,*(
), 高振1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-25
接受日期:2021-12-28
出版日期:2022-03-01
发布日期:2022-03-24
通讯作者:
杜远鹏,高振
作者简介:gaoz89@sdau.edu.cn基金资助:
Hao Wang1, Ming Wang1, Ting Liang2, Yuxin Yao1, Yuanpeng Du1,*( ), Zhen Gao1,*(
), Zhen Gao1,*( )
)
Received:2021-07-25
Accepted:2021-12-28
Online:2022-03-01
Published:2022-03-24
Contact:
Yuanpeng Du,Zhen Gao
摘要: 为探究气温和根区温度对葡萄(Vitis vinifera)叶片光合荧光特性的影响, 以一年生巨峰葡萄为试材, 设置对照、高气温、高根区温度和两者交叉作用共4组处理。结果表明, 相较于对照和高气温, 高根区温度以及交叉处理叶片最大光化学效率(Fv/Fm)降低更明显; 与对照相比, 高根区温度以及高气温与高根区温度交叉处理下光系统II (PSII)实际光化学效率Y(II)显著降低, 非调节能量耗散的量子产量Y(NPQ)及QA氧化还原状态(1-qP)值显著上升。同时, 高根区温度以及高气温与高根区温度交叉处理显著增加了J点的可变荧光(Vj), 而用于电子传递的量子产额(φEo)及性能指数(PIABS)显著降低。此外, 高根区温度以及高气温与高根区温度交叉处理下单位面积有活性的反应中心数目(RC/CSm)也显著下降, K点相对可变荧光(Wk)明显上升。综上所述, 高根区温度是高气温与根区高温交叉胁迫的主导因子, PSII受体侧是主要的伤害位点, 高气温加剧了高根区温度对PSII造成的伤害。
王浩, 王明, 梁婷, 姚玉新, 杜远鹏, 高振. 气温和根区温度对葡萄叶片光合荧光特性的影响. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 209-216.
Hao Wang, Ming Wang, Ting Liang, Yuxin Yao, Yuanpeng Du, Zhen Gao. Effects of High Air and Root Zone Temperature on Photosynthetic Fluorescence Characteristics of Grape Leaves. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(2): 209-216.
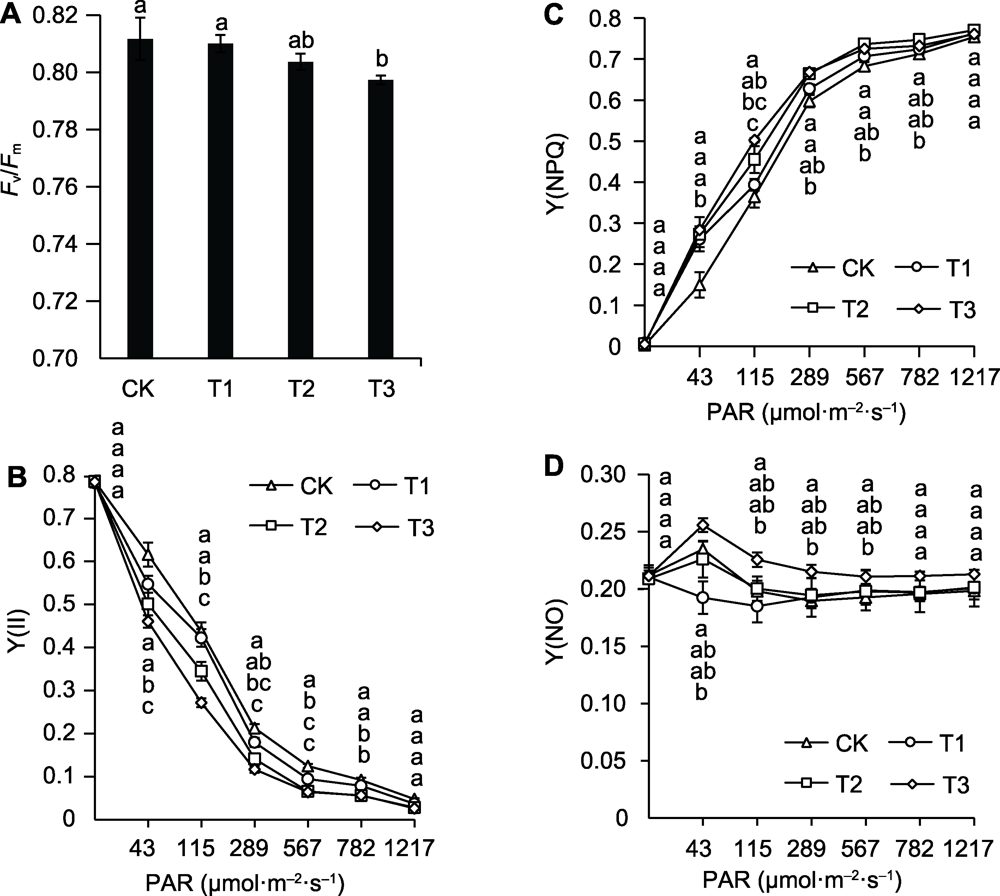
图1 不同空气温度/根区温度处理对巨峰葡萄叶片Fv/Fm (A)、Y(II) (B)、Y(NPQ) (C)和Y(NO) (D)的影响 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Fv/Fm: PSII最大光化学效率; Y(II): PSII实际光化学量子产量; Y(NPQ): 调节性能量耗散的量子产量; Y(NO): 非调节性能量耗散的量子产量; PAR: 光合有效辐射; CK: 对照; T1: 高气温; T2: 高根区温度; T3: 高气温和高根区温度交叉作用
Figure 1 The influence of different air temperature/root zone temperature treatments on the Fv/Fm (A), Y(II) (B), Y(NPQ) (C) and Y(NO) (D) of Kyoho grape leaves Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05). Fv/Fm: PSII maximum photochemical efficiency; Y(II): PSII actual photochemical quantum yield; Y(NPQ): Regulated energy dissipation quantum yield; Y(NO): Non-regulated energy dissipation quantum yield; PAR: Photosynthetically active radiation; CK: Control; T1: High air temperature; T2: High root zone temperature; T3: Cross processing of high air temperature and high root zone temperature
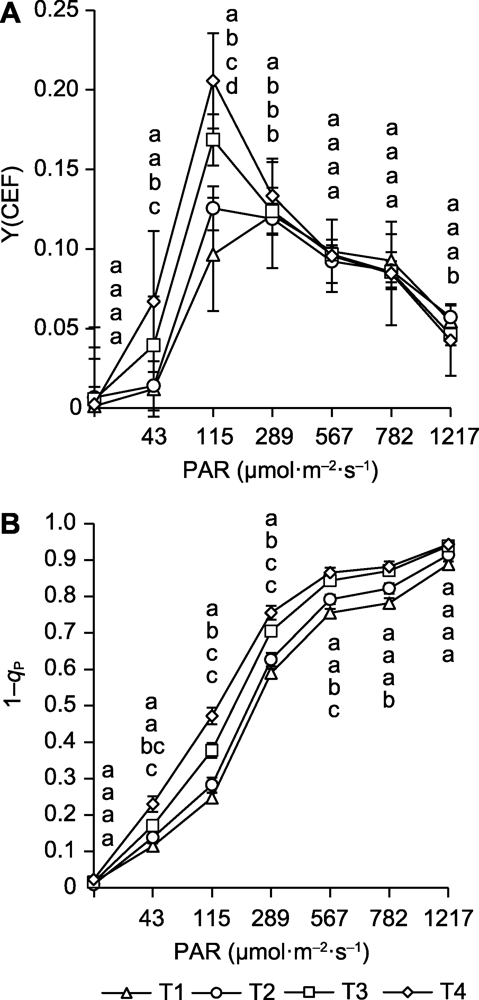
图2 不同空气温度/根区温度处理对巨峰葡萄叶片Y(CEF) (A)和1-qP (B)的影响 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。Y(CEF): 环式电子传递的有效量子产量; 1-qP: QA氧化还原状态; PAR、CK及T1-T3同图1。
Figure 2 The influence of different air temperature/root zone temperature treatments on the Y(CEF) (A) and 1-qP (B) of Kyoho grape leaves Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05). Y(CEF): Circular electron transfer effective quantum yield; 1-qP: QA redox state; PAR, CK and T1-T3 are shown in Figure 1.
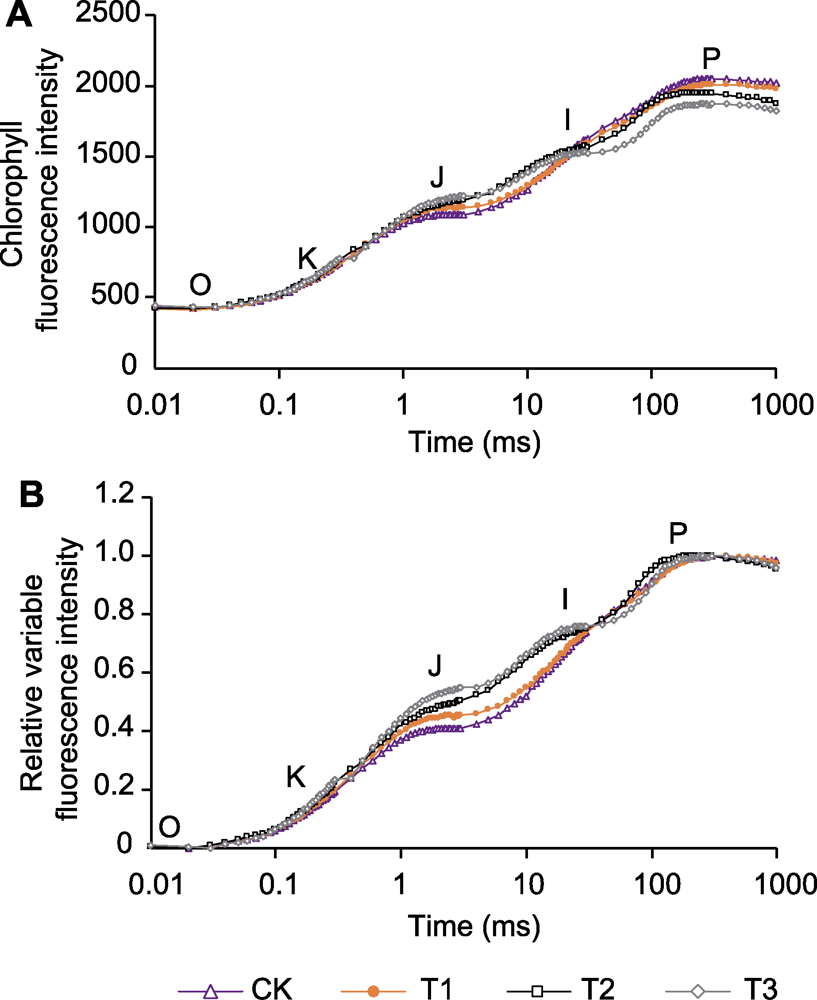
图3 不同空气温度/根区温度处理对实际叶绿素荧光诱导曲线(A)和相对叶绿素荧光诱导曲线(B)的影响 CK及T1-T3同图1。
Figure 3 Effect of different air temperature/root zone temperature treatments on the actual chlorophyll fluorescence induction curve (A) and the relative variable chlorophyll fluorescence induction curve (B) CK and T1-T3 are the same as shown in Figure 1.
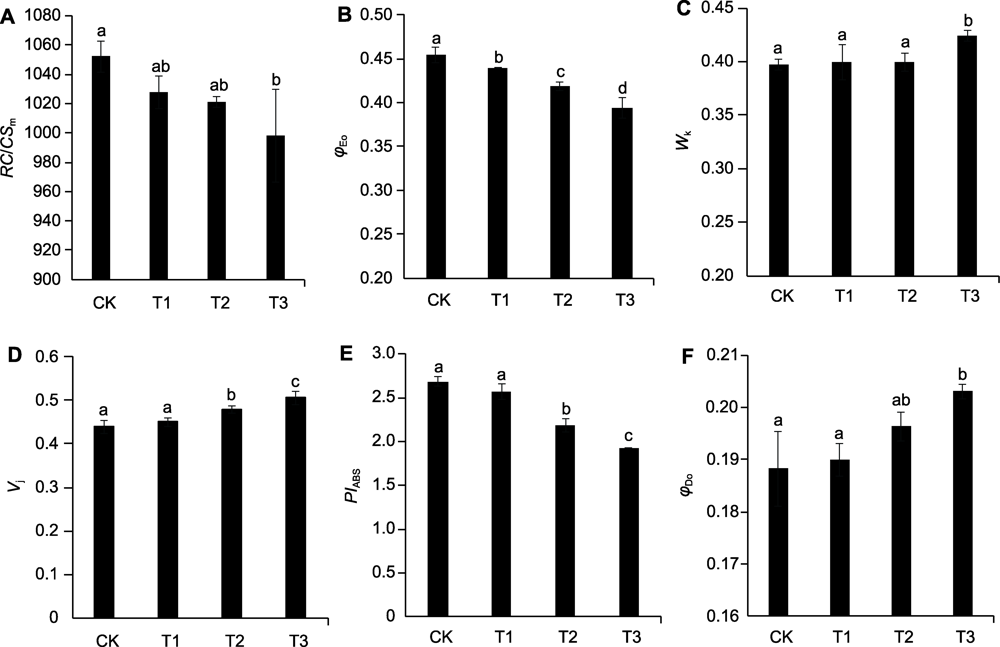
图4 不同空气和根区温度处理对巨峰葡萄叶片RC/CSm (A)、φEo (B)、Wk (C)、Vj (D)、PIABS (E)和φDo (F)的影响 The effect of different air and root zone temperature treatments on the RC/CSm (A), φEo (B), Wk (C), Vj (D), PIABS (E) and φDo (F) of Kyoho grape leaves不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。RC/CSm: 单位面积内有活性的反应中心数量; φEo: 用于电子传递的量子产额; Wk: K点相对可变荧光的变化; Vj: J点的相对可变荧光; PIABS: 性能指数; φDo: 用于热耗散的量子比率; CK及T1-T3同图1。
Figure 4 Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05). RC/CSm: The number of active reaction centers per unit area; φEo: Quantum yield used for electron transfer; Wk: Relatively variable fluorescence of K point; Vj: Relatively variable fluorescence of J point; PIABS: The performance index; φDo: Quantum ratio used for heat dissipation; CK and T1-T3 are shown in Figure 1.
| [1] | 陈景玲, 王静, 王谦, 吴明作, 袁远, 赵勇 (2014). 基于叶绿素荧光的荆条灌丛对栓皮栎幼苗庇荫效应研究. 西北林学院学报 29(4), 46-53. |
| [2] | 高玉录, 仝亚军, 杨兴旺, 翟衡, 杜远鹏, 孙永江 (2020). 乙酸及ABA对田间高温胁迫下 ‘摩尔多瓦’ 葡萄叶片光抑制的影响. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒 (5), 1-5. |
| [3] |
郭倩倩, 周文彬 (2019). 植物响应联合胁迫机制的研究进展. 植物学报 54, 662-672.
DOI |
| [4] | 侯丽媛, 董艳辉, 李亚莉, 王育川, 赵佳, 刘江, 秦永军, 吴慎杰 (2021). 藜麦抗旱性研究进展与展望. 江苏农业科学 49(11), 22-28. |
| [5] | 李鹏民, 高辉远, Strasser RJ (2005). 快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学分析在光合作用研究中的应用. 植物生理与分子生物学学报 31, 559-566. |
| [6] | 罗海波, 马苓, 段伟, 李绍华, 王利军 (2010). 高温胁迫对 ‘赤霞珠’ 葡萄光合作用的影响. 中国农业科学 43, 2744-2750. |
| [7] | 孙永江, 付艳东, 杜远鹏, 翟衡 (2013). 不同温度/光照组合对 ‘赤霞珠’ 葡萄叶片光系统II功能的影响. 中国农业科学 46, 1191-1200. |
| [8] | 夏镇卿, 司雷勇, 金岩, 扶亚芳, 王奇, 路海东 (2020). 根区增温对玉米幼苗主要代谢物傅里叶红外光谱特性及叶绿素含量的影响. 光谱学与光谱分析 40, 1283-1288. |
| [9] | 向芬, 周强, 田向荣, 陈功锡, 肖艳 (2014). 不同生境吉首蒲儿根叶片形态和叶绿素荧光特征的比较. 生态学报 34, 337-344. |
| [10] | 许大全, 张玉忠, 张荣铣 (1992). 植物光合作用的光抑制. 植物生理学通讯 28, 237-243. |
| [11] | 赵秀婷, 王延双, 段劼, 马履一, 何宝华, 贾忠奎, 桑子阳, 朱仲龙 (2021). 盐胁迫对红花玉兰嫁接苗生长和光合特性的影响. 林业科学 57, 43-53. |
| [12] |
Al-Khatib K, Paulsen GM (1984). Mode of high temperature injury to wheat during grain development. Physiol Plant 61, 363-368.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Baker NR (2008). Chlorophyll fluorescence: a probe of photosynthesis in vivo. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59, 89-113.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Ding XT, Jiang YP, He LZ, Zhou Q, Yu JZ, Hui DF, Huang DF (2016). Exogenous glutathione improves high root- zone temperature tolerance by modulating photosynthesis, antioxidant and osmolytes systems in cucumber seedlings. Sci Rep 6, 35424.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Foster WJ, Ingram DL, Nell TA (1991). Photosynthesis and root respiration in Ilex crenata ‘rotundifolia’ at supraoptimal root-zone temperatures. HortScience 26, 535-537.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Gur A, Hepner J, Shulman Y (1979). The influence of root temperature on apple trees. IV. The effect on the mineral nutrition of the tree. J Hortic Sci 54, 313-321.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Hao HP, Jiang CD, Zhang SR, Tang YD, Shi L (2012). Enhanced thermal-tolerance of photosystem II by elevating root zone temperature in Prunus mira Koehne seedlings. Plant Soil 353, 367-378.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Jiang CD, Jiang GM, Wang XZ, Li LH, Biswas DK, Li YG (2006). Increased photosynthetic activities and thermostability of photosystem II with leaf development of elm seedlings (Ulmus pumila) probed by the fast fluorescence rise OJIP. Environ Exp Bot 58, 261-268.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Kramer DM, Johnson G, Kiirats O, Edwards GE (2004). New fluorescence parameters for the determination of QAredox state and excitation energy fluxes. Photosynth Res 79, 209-218.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Kyle DJ (1987). The biochemical basis for photoinhibition of photosystem II. In: Kyle DJ, Osmond CB, Arntzen CJ, eds. Photoinhibition. Amsterdam: Elsevier. pp. 197-226. |
| [21] |
Liu XZ, Huang BR (2000). Heat stress injury in relation to membrane lipid peroxidation in creeping bentgrass. Crop Sci 40, 503-510.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Mehta P, Allakhverdiev SI, Jajoo A (2010). Characterization of photosystem II heterogeneity in response to high salt stress in wheat leaves (Triticum aestivum). Photosynth Res 105, 249-255.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Strasser BJ (1997). Donor side capacity of photosystem II probed by chlorophyll a fluorescence transients. Photosynth Res 52, 147-155.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Takahashi S, Badger MR (2011). Photoprotection in plants: a new light on photosystem II damage. Trends Plant Sci 16, 53-60.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
van der Westhuizen MM, Oosterhuis DM, Berner JM, Boogaers N (2020). Chlorophyll a fluorescence as an indicator of heat stress in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). S Afr J Plant Soil 37, 116-119.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Wu HY, Liu LA, Shi L, Zhang WF, Jiang CD (2021). Photosynthetic acclimation during low-light-induced leaf senescence in post-anthesis maize plants. Photosynth Res 150, 313-326.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Xia ZQ, Si LY, Jin Y, Fu YF, Wang Q, Lu HD (2021). Effects of root zone temperature increase on physiological indexes and photosynthesis of different genotype maize seedlings. Russ J Plant Physiol 68, 169-178.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Xu QZ, Huang BR (2000). Growth and physiological responses of creeping bentgrass to changes in air and soil temperatures. Crop Sci 40, 1363-1368.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Xu QZ, Huang BR, Wang ZL (2002). Photosynthetic responses of creeping bentgrass to reduced root-zone temperatures at supraoptimal air temperature. J Am Soc Hort Sci 127, 754-758.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Yamori W, Hikosaka K, Way DA (2014). Temperature response of photosynthesis in C3, C4, and CAM plants: temperature acclimation and temperature adaptation. Photosynth Res 119, 101-117.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 闫小莉, 刘贵梅, 李小玉, 江宇翔, 全小强, 王燕茹, 曲鲁平, 汤行昊. 不同氮添加水平和铵硝态氮配比环境下木荷幼苗光合及叶绿素荧光特性[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 624-637. |
| [2] | 王贝贝, 吴苏, 王苗苗, 胡锦涛. 日光诱导叶绿素荧光不同组分在作物总初级生产力估算中的贡献比例: 多时间尺度分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 562-572. |
| [3] | 刘柯言, 韩璐, 宋午椰, 张初蕊, 胡旭, 许行, 陈立欣. 基于日光诱导叶绿素荧光探测干旱对黄土高原植被光合稳定性的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(3): 415-431. |
| [4] | 全小强, 王燕茹, 李小玉, 梁海燕, 王立冬, 闫小莉. 氮添加和铵硝态氮配比对杉木幼苗光合特性及叶绿素荧光参数的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(8): 1050-1064. |
| [5] | 师生波, 周党卫, 李天才, 德科加, 杲秀珍, 马家麟, 孙涛, 王方琳. 青藏高原高山嵩草光合功能对模拟夜间低温的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(3): 361-373. |
| [6] | 任培鑫, 李鹏, 彭长辉, 周晓路, 杨铭霞. 洞庭湖流域植被光合物候的时空变化及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(3): 319-330. |
| [7] | 师生波, 师瑞, 周党卫, 张雯. 低温对高山嵩草叶片光化学和非光化学能量耗散特征的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(10): 1441-1452. |
| [8] | 薛金儒, 吕肖良. 黄土高原生态工程实施下基于日光诱导叶绿素荧光的植被恢复生产力效益评价[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(10): 1289-1304. |
| [9] | 吴霖升, 张永光, 章钊颖, 张小康, 吴云飞. 日光诱导叶绿素荧光遥感及其在陆地生态系统监测中的应用[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(10): 1167-1199. |
| [10] | 周稳, 迟永刚, 周蕾. 基于日光诱导叶绿素荧光的北半球森林物候研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(4): 345-354. |
| [11] | 丁键浠, 周蕾, 王永琳, 庄杰, 陈集景, 周稳, 赵宁, 宋珺, 迟永刚. 叶绿素荧光主动与被动联合观测应用前景[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(2): 105-118. |
| [12] | 温兴, 晋莲, 郭红卫. 甜蜜的相遇—营养与激素信号协同调节植物生长的新机制[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 138-141. |
| [13] | 刘建福, 陈育才, 王文建, 王河川, 蔡金福, 王明元, 李丹丹, 张斌, 黄昆. 航天搭载对武夷名丛相关生理及生长特性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 564-572. |
| [14] | 郭庆华, 胡天宇, 马勤, 徐可心, 杨秋丽, 孙千惠, 李玉美, 苏艳军. 新一代遥感技术助力生态系统生态学研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(4): 418-435. |
| [15] | 张亮, 王志磊, 薛婷婷, 郝笑云, 杨晨露, 高飞飞, 王莹, 韩星, 李华, 王华. 葡萄园生态系统碳源/汇及碳减排策略研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2020, 44(3): 179-191. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||