

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (1): 10-24.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20014 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20014
宋雪彬1,2, 高康1, 黄河1, 刘芷兰1, 戴思兰1,*( ), 嵇彧1
), 嵇彧1
收稿日期:2020-02-02
接受日期:2020-11-11
出版日期:2021-01-01
发布日期:2021-01-15
通讯作者:
戴思兰
作者简介:E-mail: silandai@sina.com基金资助:
Xuebin Song1,2, Kang Gao1, He Huang1, Zhilan Liu1, Silan Dai1,*( ), Yu Ji1
), Yu Ji1
Received:2020-02-02
Accepted:2020-11-11
Online:2021-01-01
Published:2021-01-15
Contact:
Silan Dai
摘要: 中国传统大菊品种叶片形态变异丰富, 然而至今仍未对其进行科学的定义和分类, 无法有效利用这些形态性状进行品种鉴定和叶形遗传解析。利用数量化分析方法对植物形态进行定义和分类, 是植物性状遗传解析的前提。对436个中国传统大菊品种的24个叶形性状进行重新定义及观测, 通过相关性分析确定了8个相对独立的性状, 用变异系数及主成分分析等数量化分析方法筛选出叶长/叶宽、叶片最宽处所在位置/叶长、右下裂片长/右下叶脉长、右下裂片长/右下裂片宽及叶柄长/全叶长5个相对独立且关键的叶部性状。利用这5个性状, 通过Q聚类分析, 最终将菊花(Chrysanthemum × morifolium)叶片分为16种叶型。研究结果为菊花品种鉴定提供了有效的叶部评价标准, 并建立了中国传统菊花品种叶片数量化定义和分类体系, 也为观赏植物复杂性状的解析提供了新方法。
宋雪彬, 高康, 黄河, 刘芷兰, 戴思兰, 嵇彧. 中国传统大菊叶片形态的数量化定义与分类. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 10-24.
Xuebin Song, Kang Gao, He Huang, Zhilan Liu, Silan Dai, Yu Ji. Quantitative Definition and Classification of Leaves in Large- flowered Chinese Chrysanthemum Based on the Morphological Traits. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(1): 10-24.
| Trait No. | Traits and measuring methods |
|---|---|
| C1 | Leaf blade length (T1B1) |
| C2 | Leaf blade width |
| C3 | Widest part length (the length from the leaf apex to the widest part of the leaf blade) |
| C4 | Leaf vein length of left upper lobe (T2B2) |
| C5 | Leaf vein length of right upper lobe (T3B3) |
| C6 | Leaf vein length of left lower lobe (T4B4) |
| C7 | Leaf vein length of right lower lobe (T5B5) |
| C8 | Top leaf lobe length (T1M1) |
| C9 | Left upper leaf lobe length (T2M2) |
| C10 | Right upper leaf lobe length (T3M3) |
| C11 | Left lower leaf lobe length (T4M4) |
| C12 | Right lower leaf lobe length (T5M5) |
| C13 | Top leaf lobe width |
| C14 | Left upper leaf lobe width |
| C15 | Right upper leaf lobe width |
| C16 | Left lower leaf lobe width |
| C17 | Right lower leaf lobe width |
| C18 | Angle of leaf vein in the left upper lobe (α1) |
| C19 | Angle of leaf vein in the right upper lobe (α2) |
| C20 | Angle of leaf vein in the left lower lobe (β1) |
| C21 | Angle of leaf vein in the right lower lobe (β2) |
| C22 | Leaf petiole length |
| C23 | Leaf base shape |
| C24 | Leaf margin shape |
表1 菊花叶部性状及其测量方法
Table 1 Morphological traits of chrysanthemum leaf and their measuring methods
| Trait No. | Traits and measuring methods |
|---|---|
| C1 | Leaf blade length (T1B1) |
| C2 | Leaf blade width |
| C3 | Widest part length (the length from the leaf apex to the widest part of the leaf blade) |
| C4 | Leaf vein length of left upper lobe (T2B2) |
| C5 | Leaf vein length of right upper lobe (T3B3) |
| C6 | Leaf vein length of left lower lobe (T4B4) |
| C7 | Leaf vein length of right lower lobe (T5B5) |
| C8 | Top leaf lobe length (T1M1) |
| C9 | Left upper leaf lobe length (T2M2) |
| C10 | Right upper leaf lobe length (T3M3) |
| C11 | Left lower leaf lobe length (T4M4) |
| C12 | Right lower leaf lobe length (T5M5) |
| C13 | Top leaf lobe width |
| C14 | Left upper leaf lobe width |
| C15 | Right upper leaf lobe width |
| C16 | Left lower leaf lobe width |
| C17 | Right lower leaf lobe width |
| C18 | Angle of leaf vein in the left upper lobe (α1) |
| C19 | Angle of leaf vein in the right upper lobe (α2) |
| C20 | Angle of leaf vein in the left lower lobe (β1) |
| C21 | Angle of leaf vein in the right lower lobe (β2) |
| C22 | Leaf petiole length |
| C23 | Leaf base shape |
| C24 | Leaf margin shape |
| Trait No. | Mean square | Standard deviation | Intravarietal coefficient variation (%) | Intervarietal coefficient variation (%) | P-value (intervarietal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C18 | 33.43 | 7.12 | 14.26 | 21.29 | 0.000 |
| C19 | 33.60 | 7.07 | 13.76 | 21.03 | 0.000 |
| C20 | 45.49 | 11.35 | 15.55 | 24.94 | 0.000 |
| C21 | 46.46 | 11.12 | 14.89 | 23.94 | 0.000 |
| C22 | 3.85 | 1.16 | 11.34 | 29.99 | 0.000 |
| C25 | 1.32 | 0.18 | 4.23 | 13.32 | 0.000 |
| C26 | 0.68 | 0.09 | 7.56 | 13.70 | 0.000 |
| C27 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 12.61 | 27.56 | 0.000 |
| C28 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 14.64 | 33.27 | 0.000 |
| C29 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 13.95 | 32.97 | 0.000 |
| C30 | 0.46 | 0.13 | 11.44 | 27.96 | 0.000 |
| C31 | 0.45 | 0.13 | 11.83 | 28.47 | 0.000 |
| C32 | 1.36 | 0.40 | 13.03 | 29.39 | 0.000 |
| C33 | 0.76 | 0.26 | 11.33 | 33.94 | 0.000 |
| C34 | 0.78 | 0.27 | 11.34 | 34.29 | 0.000 |
| C35 | 1.01 | 0.33 | 9.73 | 32.84 | 0.000 |
| C36 | 0.98 | 0.32 | 9.43 | 32.67 | 0.000 |
| C37 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 8.89 | 21.34 | 0.000 |
表2 菊花叶部性状的描述性统计
Table 2 Descriptive statistics of traits of chrysanthemum leaf
| Trait No. | Mean square | Standard deviation | Intravarietal coefficient variation (%) | Intervarietal coefficient variation (%) | P-value (intervarietal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C18 | 33.43 | 7.12 | 14.26 | 21.29 | 0.000 |
| C19 | 33.60 | 7.07 | 13.76 | 21.03 | 0.000 |
| C20 | 45.49 | 11.35 | 15.55 | 24.94 | 0.000 |
| C21 | 46.46 | 11.12 | 14.89 | 23.94 | 0.000 |
| C22 | 3.85 | 1.16 | 11.34 | 29.99 | 0.000 |
| C25 | 1.32 | 0.18 | 4.23 | 13.32 | 0.000 |
| C26 | 0.68 | 0.09 | 7.56 | 13.70 | 0.000 |
| C27 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 12.61 | 27.56 | 0.000 |
| C28 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 14.64 | 33.27 | 0.000 |
| C29 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 13.95 | 32.97 | 0.000 |
| C30 | 0.46 | 0.13 | 11.44 | 27.96 | 0.000 |
| C31 | 0.45 | 0.13 | 11.83 | 28.47 | 0.000 |
| C32 | 1.36 | 0.40 | 13.03 | 29.39 | 0.000 |
| C33 | 0.76 | 0.26 | 11.33 | 33.94 | 0.000 |
| C34 | 0.78 | 0.27 | 11.34 | 34.29 | 0.000 |
| C35 | 1.01 | 0.33 | 9.73 | 32.84 | 0.000 |
| C36 | 0.98 | 0.32 | 9.43 | 32.67 | 0.000 |
| C37 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 8.89 | 21.34 | 0.000 |
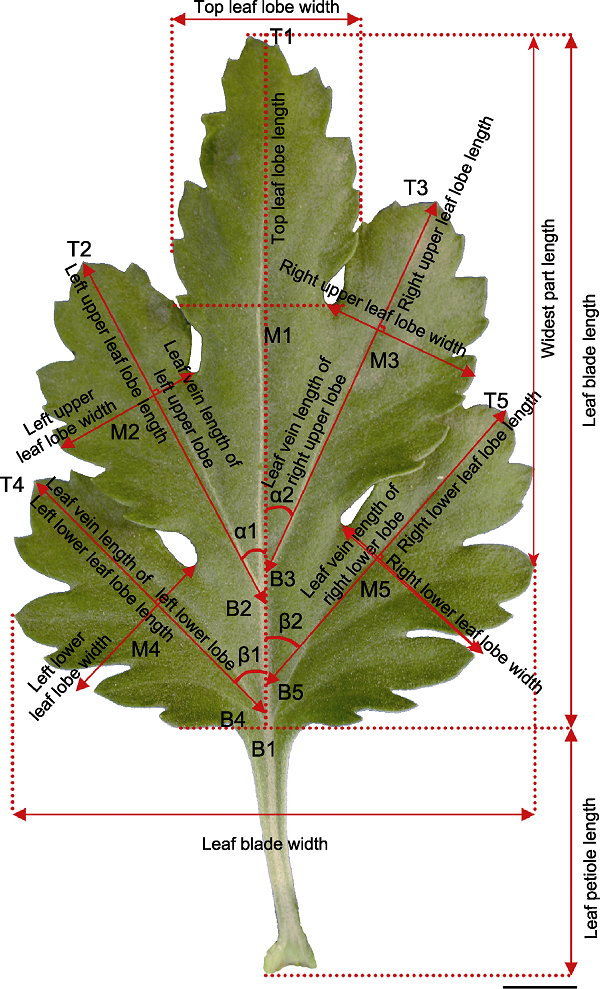
图1 中国传统大菊品种叶部数量性状测量方法示意图 T1B1表示叶长(从T1到B1之间的距离, 其它长度性状以同样的方法描述); T1M1表示顶裂片长; T2B2表示左上叶脉长; T4B4表示左下叶脉长; T3B3表示右上叶脉长; T5B5表示右下叶脉长; T2M2表示左上裂片长; T4M4表示左下裂片长; T3M3表示右上裂片长; T5M5表示右下裂片长。叶宽和叶片最宽处所在位置的测量方法如图所示, 其它的宽度性状以同样的方法描述, 包括顶裂片宽、左上裂片宽、左下裂片宽、右上裂片宽、右下裂片宽。α1和α2分别代表左上叶脉角度和右上叶脉角度, β1和β2分别代表左下叶脉角度和右下叶脉角度。叶柄长的测量方法如图所示。Bar=1 cm
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of quantitative trait measurement for the leaves of large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars T1B1 indicates leaf blade length (the distance from T1 to B1, other length traits are described in the same way); T1M1 indicates top leaf lobe length; T2B2 indicates leaf vein length of left upper lobe; T4B4 indicates leaf vein length of left lower lobe; T3B3 indicates leaf vein length of right upper lobe; T5B5 indicates leaf vein length of right lower lobe; T2M2 indicates left upper leaf lobe length; T4M4 indicates left lower leaf lobe length; T3M3 indicates right upper leaf lobe length; T5M5 indicates right lower leaf lobe length. The measurement method of the leaf blade width and the widest part length is shown in the figure; other width traits are described in the same way, including top leaf lobe width, left upper leaf lobe width, left lower leaf lobe width, right upper leaf lobe width, right lower leaf lobe width. α1 and α2 indicate angle of leaf vein in the left upper lobe and the right upper lobe, respectively, β1 and β2 indicate angle of leaf vein in the left lower lobe, and the right lower lobe, respectively. The measurement method of leaf petiole length is shown in figure. Bar=1 cm
| Traits | Left upper and right upper | Left lower and right lower | Left upper and left lower | Right upper and right lower | Left upper and top lobe | Right upper and top lobe | Left lower and top lobe | Right lower and top lobe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf vein length (cm) | 0.851** | 0.889** | 0.656** | 0.689** | 0.729** | 0.746** | 0.784** | 0.792** |
| Leaf lobe length (cm) | 0.794* | 0.846** | 0.537** | 0.502** | 0.722** | 0.712** | 0.543** | 0.534** |
| Leaf lobe width (cm) | 0.821** | 0.833** | 0.579** | 0.560** | 0.763** | 0.718** | 0.369** | 0.363** |
| Leaf lobe length/leaf vein length | 0.696** | 0.789** | 0.338** | 0.358** | 0.375** | 0.400** | 0.420** | 0.408** |
| Leaf lobe length/leaf lobe width | 0.676** | 0.744** | 0.372** | 0.424** | 0.521** | 0.428** | 0.323** | 0.468** |
| Angle of leaf vein | 0.540** | 0.621** | 0.436** | 0.337** | - | - | - | - |
表3 菊花叶部顶裂片和4个侧裂片各性状之间的相关性分析
Table 3 Pearson analysis of traits between top lobe and four lateral lobes of chrysanthemum leaf
| Traits | Left upper and right upper | Left lower and right lower | Left upper and left lower | Right upper and right lower | Left upper and top lobe | Right upper and top lobe | Left lower and top lobe | Right lower and top lobe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf vein length (cm) | 0.851** | 0.889** | 0.656** | 0.689** | 0.729** | 0.746** | 0.784** | 0.792** |
| Leaf lobe length (cm) | 0.794* | 0.846** | 0.537** | 0.502** | 0.722** | 0.712** | 0.543** | 0.534** |
| Leaf lobe width (cm) | 0.821** | 0.833** | 0.579** | 0.560** | 0.763** | 0.718** | 0.369** | 0.363** |
| Leaf lobe length/leaf vein length | 0.696** | 0.789** | 0.338** | 0.358** | 0.375** | 0.400** | 0.420** | 0.408** |
| Leaf lobe length/leaf lobe width | 0.676** | 0.744** | 0.372** | 0.424** | 0.521** | 0.428** | 0.323** | 0.468** |
| Angle of leaf vein | 0.540** | 0.621** | 0.436** | 0.337** | - | - | - | - |
| C21 | C23 | C24 | C25 | C26 | C31 | C36 | C37 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C21 | 1 | |||||||
| C23 | 0.122* | 1 | ||||||
| C24 | 0.087 | 0.132** | 1 | |||||
| C25 | -0.185** | -0.156** | -0.230** | 1 | ||||
| C26 | -0.005 | 0.194** | 0.051 | -0.203** | 1 | |||
| C31 | -0.007 | 0.083 | -0.264** | -0.008 | 0.226** | 1 | ||
| C36 | -0.053 | -0.069 | -0.334** | 0.120* | 0.051 | 0.782** | 1 | |
| C37 | -0.190** | -0.144** | -0.148** | -0.170** | -0.178** | -0.084 | 0.020 | 1 |
表4 中国传统大菊品种叶部8个重要性状的相关性分析
Table 4 Pearson analysis of 8 important leaf traits of large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars
| C21 | C23 | C24 | C25 | C26 | C31 | C36 | C37 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C21 | 1 | |||||||
| C23 | 0.122* | 1 | ||||||
| C24 | 0.087 | 0.132** | 1 | |||||
| C25 | -0.185** | -0.156** | -0.230** | 1 | ||||
| C26 | -0.005 | 0.194** | 0.051 | -0.203** | 1 | |||
| C31 | -0.007 | 0.083 | -0.264** | -0.008 | 0.226** | 1 | ||
| C36 | -0.053 | -0.069 | -0.334** | 0.120* | 0.051 | 0.782** | 1 | |
| C37 | -0.190** | -0.144** | -0.148** | -0.170** | -0.178** | -0.084 | 0.020 | 1 |
| Traits No. | Principal component | Principal component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| C21 | -0.193 | 0.426 | 0.025 | - | - | - |
| C23 | -0.071 | 0.489 | -0.206 | - | - | - |
| C24 | -0.573 | 0.404 | -0.013 | - | - | - |
| C25 | 0.256 | -0.495 | -0.717 | 0.054 | 0.734 | -0.514 |
| C26 | 0.197 | 0.656 | 0.087 | 0.407 | -0.736 | -0.156 |
| C31 | 0.863 | 0.336 | 0.085 | 0.938 | 0.032 | 0.100 |
| C36 | 0.892 | 0.066 | 0.079 | 0.879 | 0.308 | 0.172 |
| C37 | 0.008 | -0.476 | 0.736 | -0.175 | 0.234 | 0.878 |
| Total | 2.015 | 1.604 | 1.119 | 1.852 | 1.232 | 1.099 |
| Contribution rate (%) | 25.19 | 20.05 | 13.99 | 37.04 | 24.64 | 21.97 |
| Cumulative (%) | 25.19 | 45.24 | 59.23 | 37.04 | 61.68 | 83.65 |
表5 中国传统大菊品种叶部性状的主成分分析
Table 5 Principle component analysis of leaf traits of large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars
| Traits No. | Principal component | Principal component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| C21 | -0.193 | 0.426 | 0.025 | - | - | - |
| C23 | -0.071 | 0.489 | -0.206 | - | - | - |
| C24 | -0.573 | 0.404 | -0.013 | - | - | - |
| C25 | 0.256 | -0.495 | -0.717 | 0.054 | 0.734 | -0.514 |
| C26 | 0.197 | 0.656 | 0.087 | 0.407 | -0.736 | -0.156 |
| C31 | 0.863 | 0.336 | 0.085 | 0.938 | 0.032 | 0.100 |
| C36 | 0.892 | 0.066 | 0.079 | 0.879 | 0.308 | 0.172 |
| C37 | 0.008 | -0.476 | 0.736 | -0.175 | 0.234 | 0.878 |
| Total | 2.015 | 1.604 | 1.119 | 1.852 | 1.232 | 1.099 |
| Contribution rate (%) | 25.19 | 20.05 | 13.99 | 37.04 | 24.64 | 21.97 |
| Cumulative (%) | 25.19 | 45.24 | 59.23 | 37.04 | 61.68 | 83.65 |
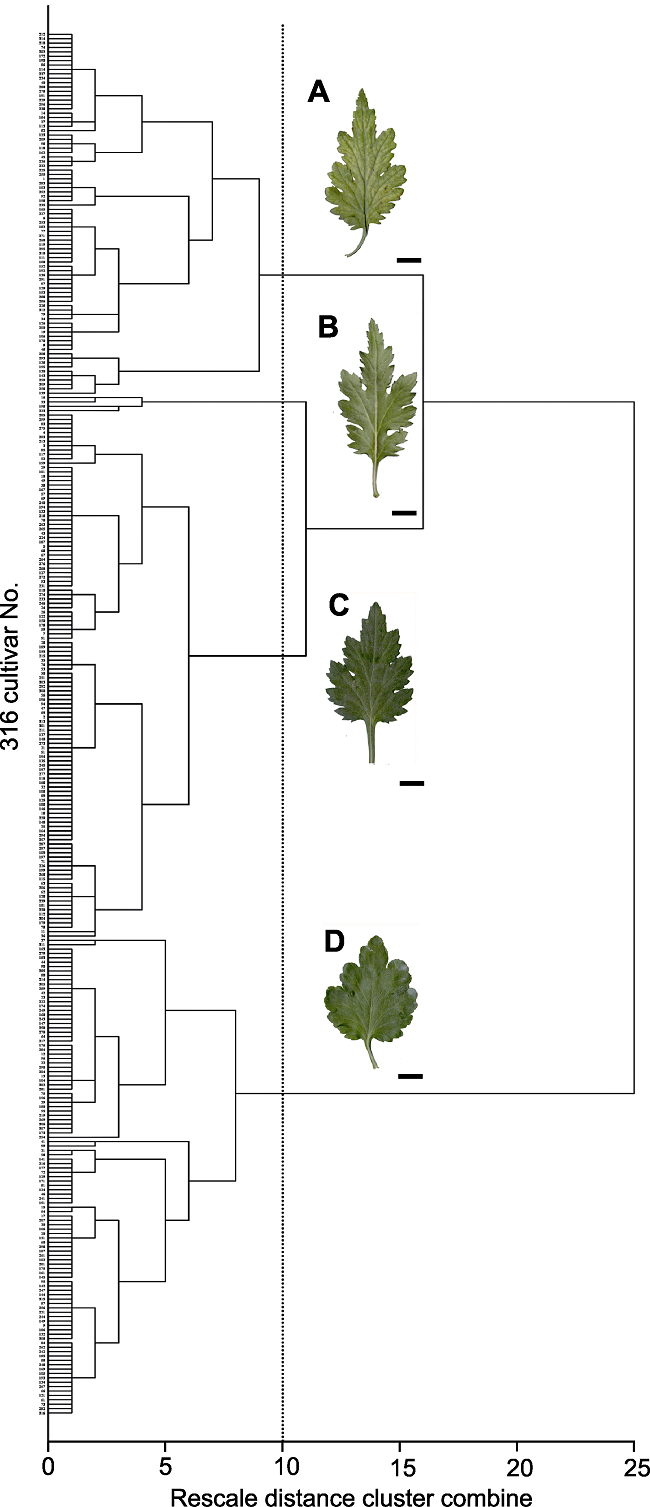
图2 中国传统大菊品种叶片基本形态的Q聚类 (A) 长卵形; (B) 倒长卵形; (C) 卵形; (D) 广卵形。Bars=1 cm
Figure 2 Q cluster of the leaf basic shape of large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars (A) Long ovate; (B) Oblong ovate; (C) Ovate; (D) Broad ovate. Bars=1 cm
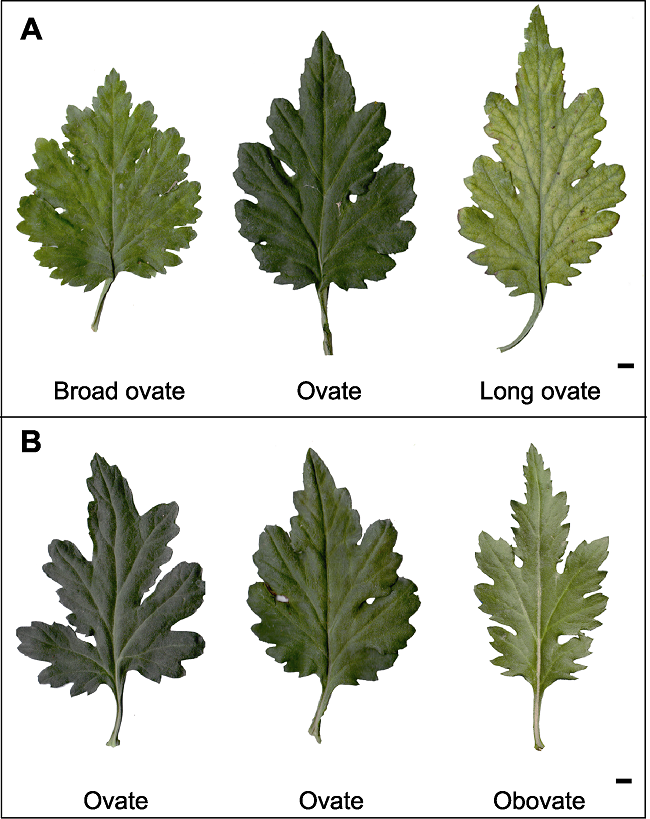
图3 中国传统大菊品种叶片基本形态类型 (A) 叶长/叶宽的不同类型; (B) 最宽处所在位置/叶长的不同类型。Bars=0.5 mm
Figure 3 The different types of leaf basic shape of large- flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars (A) Different types of leaf blade length/leaf blade width; (B) Different types of widest part length/leaf blade length. Bars= 0.5 mm
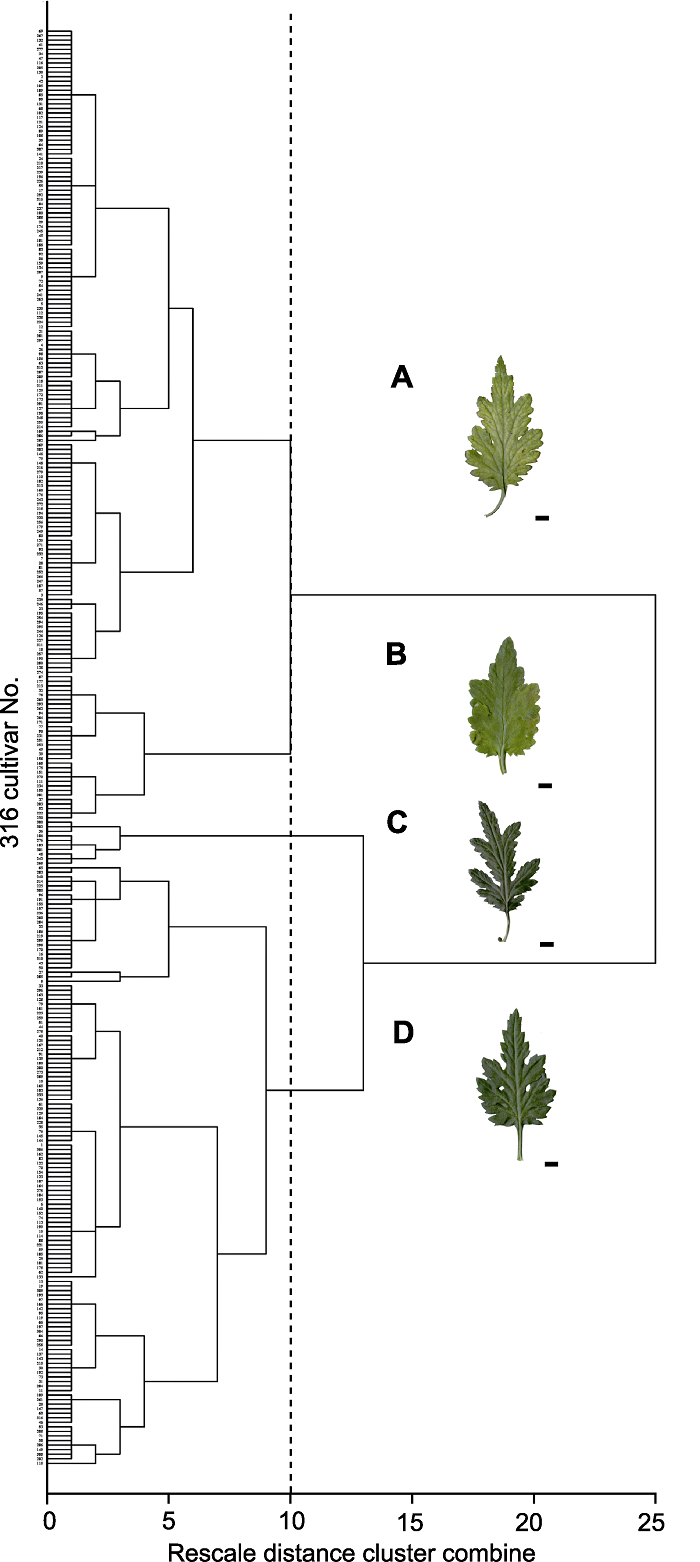
图4 中国传统大菊品种叶裂片形态的Q聚类 (A) 叶片裂刻深度为中裂, 叶裂片大小为宽裂片; (B) 叶片裂刻深度为浅裂, 叶裂片大小为宽裂片; (C) 叶片裂刻深度为深裂, 叶裂片大小为窄裂片; (D) 叶片裂刻深度为深裂, 叶裂片大小为中裂片。Bars=0.5 mm
Figure 4 Q cluster of leaf lobe shape of large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars (A) Medium lobed with wide lobe; (B) Shallow lobed with wide lobe; (C) Deep lobed with narrow lobe; (D) Deep lobed with medium lobe. Bars=0.5 mm
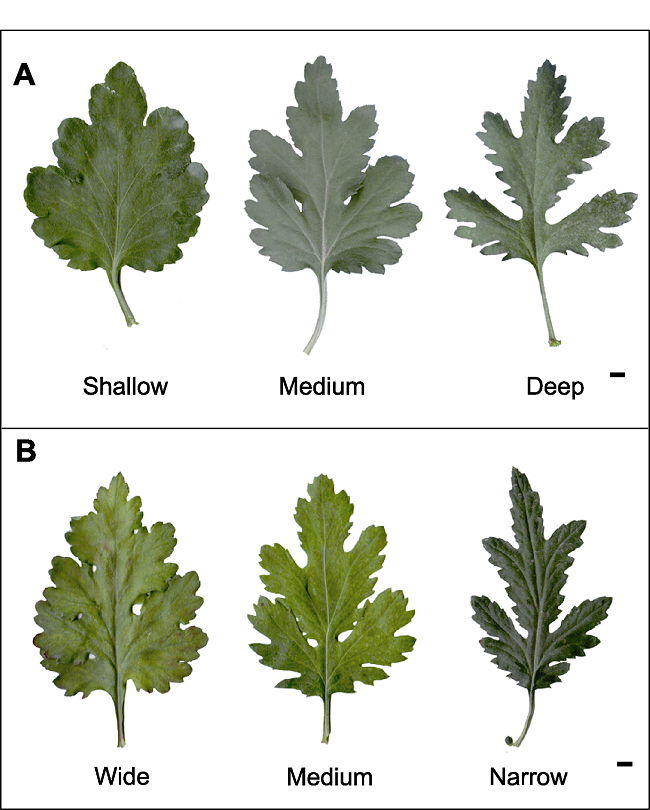
图5 中国传统大菊品种叶裂片形态类型 (A) 叶裂片长/叶脉长(叶裂刻深)的不同类型; (B) 叶裂片长/裂片宽(叶裂片大小)的不同类型。Bars=0.5 mm
Figure 5 The different types of leaf lobe shape of large- flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars (A) Different types of leaf lobe length/leaf vein length; (B) Different types of leaf lobe length/leaf lobe width. Bars=0.5 mm
| No. | Leaf blade shape | Leaf lobe shape/crack depth | Leaf length/leaf width | Widest part length/leaf length | Leaf lobe length/leaf vein length | Leaf lobe length/leaf lobe width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-1 | Broad ovate | Shallow/wide | (0.80, 1.25] | - | (0.15, 0.30] | (0.40, 1.00] |
| I-2 | Medium/wide | (0.80, 1.25] | - | (0.30, 0.50] | (0.40, 1.00] | |
| I-3 | Deep/medium | (0.80, 1.25] | - | >0.50 | (1.00, 1.50] | |
| I-4 | Deep/narrow | (0.80, 1.25] | - | >0.50 | >1.50 | |
| II-1 | Ovate | Shallow/wide | (1.25, 1.40] | - | (0.15, 0.30] | (0.40, 1.00] |
| II-2 | Medium/wide | (1.25, 1.40] | - | (0.30, 0.50] | (0.40, 1.00] | |
| II-3 | Deep/medium | (1.25, 1.40] | - | >0.50 | (1.00, 1.50] | |
| II-4 | Deep/narrow | (1.25, 1.40] | - | >0.50 | >1.50 | |
| III-1 | Obovate | Shallow/wide | >1.40 | ≤0.55 | (0.15, 0.30] | (0.40, 1.00] |
| III-2 | Medium/wide | >1.40 | ≤0.55 | (0.30, 0.50] | (0.40, 1.00] | |
| III-3 | Deep/medium | >1.40 | ≤0.55 | >0.50 | (1.00, 1.50] | |
| III-4 | Deep/narrow | >1.40 | ≤0.55 | >0.50 | >1.50 not found | |
| IV-1 | Long ovate | Shallow/wide | >1.40 | >0.55 | (0.15, 0.30] | (0.40, 1.00] |
| IV-2 | Medium/wide | >1.40 | >0.55 | (0.30, 0.50] | (0.40, 1.00] | |
| IV-3 | Deep/medium | >1.40 | >0.55 | >0.50 | (1.00, 1.50] | |
| IV-4 | Deep/narrow | >1.40 | >0.55 | >0.50 | >1.50 |
表6 316个中国传统大菊品种叶片分类结果
Table 6 The result of 316 large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars based on leaf classification
| No. | Leaf blade shape | Leaf lobe shape/crack depth | Leaf length/leaf width | Widest part length/leaf length | Leaf lobe length/leaf vein length | Leaf lobe length/leaf lobe width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-1 | Broad ovate | Shallow/wide | (0.80, 1.25] | - | (0.15, 0.30] | (0.40, 1.00] |
| I-2 | Medium/wide | (0.80, 1.25] | - | (0.30, 0.50] | (0.40, 1.00] | |
| I-3 | Deep/medium | (0.80, 1.25] | - | >0.50 | (1.00, 1.50] | |
| I-4 | Deep/narrow | (0.80, 1.25] | - | >0.50 | >1.50 | |
| II-1 | Ovate | Shallow/wide | (1.25, 1.40] | - | (0.15, 0.30] | (0.40, 1.00] |
| II-2 | Medium/wide | (1.25, 1.40] | - | (0.30, 0.50] | (0.40, 1.00] | |
| II-3 | Deep/medium | (1.25, 1.40] | - | >0.50 | (1.00, 1.50] | |
| II-4 | Deep/narrow | (1.25, 1.40] | - | >0.50 | >1.50 | |
| III-1 | Obovate | Shallow/wide | >1.40 | ≤0.55 | (0.15, 0.30] | (0.40, 1.00] |
| III-2 | Medium/wide | >1.40 | ≤0.55 | (0.30, 0.50] | (0.40, 1.00] | |
| III-3 | Deep/medium | >1.40 | ≤0.55 | >0.50 | (1.00, 1.50] | |
| III-4 | Deep/narrow | >1.40 | ≤0.55 | >0.50 | >1.50 not found | |
| IV-1 | Long ovate | Shallow/wide | >1.40 | >0.55 | (0.15, 0.30] | (0.40, 1.00] |
| IV-2 | Medium/wide | >1.40 | >0.55 | (0.30, 0.50] | (0.40, 1.00] | |
| IV-3 | Deep/medium | >1.40 | >0.55 | >0.50 | (1.00, 1.50] | |
| IV-4 | Deep/narrow | >1.40 | >0.55 | >0.50 | >1.50 |
| Types | Identifiable fitness (%) | Number of varieties of different leaf types | The total number of varieties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||
| Leaf blade shape | 1 | 96.2 | 51 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 53 |
| 2 | 96.9 | 0 | 31 | 1 | 0 | 32 | |
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | |
| 4 | 65.5 | 0 | 7 | 3 | 19 | 29 | |
| Leaf lobe shape | 1 | 100 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 2 | 92.8 | 1 | 64 | 3 | 1 | 69 | |
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 27 | |
| 4 | 88.9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 9 | |
| Leaf petiole | 1 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0 | - | 20 |
| 2 | 87.7 | 5 | 71 | 5 | - | 81 | |
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 19 | - | 19 | |
表7 120个中国传统大菊品种叶片基本形态、叶裂片形态和叶柄性状的判别分析
Table 7 Discriminant analysis of leaf blade shape, lobe shape and petiole in 120 large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars
| Types | Identifiable fitness (%) | Number of varieties of different leaf types | The total number of varieties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||
| Leaf blade shape | 1 | 96.2 | 51 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 53 |
| 2 | 96.9 | 0 | 31 | 1 | 0 | 32 | |
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 6 | |
| 4 | 65.5 | 0 | 7 | 3 | 19 | 29 | |
| Leaf lobe shape | 1 | 100 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 2 | 92.8 | 1 | 64 | 3 | 1 | 69 | |
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 27 | |
| 4 | 88.9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 9 | |
| Leaf petiole | 1 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 0 | - | 20 |
| 2 | 87.7 | 5 | 71 | 5 | - | 81 | |
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 19 | - | 19 | |
| Types | Identifiable fitness (%) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90.0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 2 | 97.1 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34 |
| 3 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 50.0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 6 | 87.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 16 |
| 7 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 8 | 75.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 9 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 10 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 11 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 13 | 50.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 14 | 93.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 15 | 87.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 8 |
| 16 | 75.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
表8 120个中国传统大菊品种16种叶型的判别分析
Table 8 Discriminant analysis of 16 leaf types in 120 large-flowered Chinese chrysanthemum cultivars
| Types | Identifiable fitness (%) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90.0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 2 | 97.1 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34 |
| 3 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 50.0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 6 | 87.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 16 |
| 7 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 8 | 75.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 9 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 10 | 100.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 11 | 0.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 13 | 50.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 14 | 93.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 15 | 87.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 8 |
| 16 | 75.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| [1] | 陈模舜, 金则新, 柯世省 (2018). 不同光环境下天台鹅耳枥叶形变化的测定与分析. 林业科学 54, 54-63. |
| [2] |
陈旭波, 孟世勇, 刘全儒 (2012). 石竹科繁缕属与鹅肠菜属的数量分类. 植物学报 47, 271-277.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 楚爱香, 杨英军, 汤庚国, 童丽丽 (2009). 河南垂丝海棠品种数量分类研究. 园艺学报 36, 377-384. |
| [4] | 樊光迅, 亓帅, 王文奎, 戴思兰 (2016). 毛华菊形态性状变异的数学分析. 见: 中国观赏园艺研究进展2016. 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 134-141. |
| [5] | 方玉霖, 刘剑秋, 姜业芳 (2002). 福建薯蓣属植物叶脉序特征及其分类学意义. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版) 18(2), 65-69. |
| [6] | 傅弘, 池哲儒, 常杰, 傅承新 (2004). 基于人工神经网络的叶脉信息提取——植物活体机器识别研究. 植物学通报 21, 429-436. |
| [7] | 高鹤, 刘启新, 宋春凤, 吴宝成, 周伟, 韦苏晏 (2015). 基于分形方法探讨槭属(Acer Linn.)植物叶片的形态多样性及其系统学意义. 植物资源与环境学报 24(2), 1-10. |
| [8] | 高永华 (2014). 野生小红菊驯化栽培和花芽分化条件研究. 硕士论文. 晋中: 山西农业大学. pp. 8-9. |
| [9] | 高志朋, 邵秀玲, 范晓虹, 张伟 (2017). 山东常见蒿属植物叶形变异分类研究及在杂草检疫中的应用价值. 植物检疫 31(6), 30-37. |
| [10] | 何江 (2017). 40份番石榴种质资源亲缘关系的形态学性状和SCoT研究. 硕士论文. 南宁: 广西大学. pp. 22-25. |
| [11] | 何文奇 (2012). 翅果菊属Pterocypsela Shih (菊科-菊苣族)分类学研究. 硕士论文. 郑州: 郑州大学. pp. 10-12. |
| [12] | 洪艳, 白新祥, 孙卫, 贾锋炜, 戴思兰 (2012). 菊花品种花色表型数量分类研究. 园艺学报 39, 1330-1340. |
| [13] | 黄文娟, 李志军, 杨赵平, 白冠章 (2010). 胡杨异形叶结构型性状及其相互关系. 生态学报 30, 4636-4642. |
| [14] | 李娜娜 (2012). 单头切花菊新品种培育. 硕士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 31-37. |
| [15] |
李仁伟, 王晨, 戴思兰, 雒新艳, 李宝琴, 朱珺, 卢洁, 刘倩倩 (2012). 菊花品种表型性状与SRAP分子标记的关联分析. 中国农业科学 45, 1355-1364.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 李晓兰, 李雪华, 蒋德明, 刘志民, 王红梅, 姬兰柱 (2005). 科尔沁沙地22种菊科草本植物叶片形态特征研究. 生态学杂志 24, 1397-1401. |
| [17] | 刘孟军 (1996). 枣树数量性状的概率分级研究. 园艺学报 23, 105-109. |
| [18] | 刘倩倩 (2007). 中国大菊品种形态分类及细胞学研究. 硕士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 14-27. |
| [19] | 刘文啟, 陆以云, 康帅, 严华, 魏锋, 马双成 (2015). 不同叶形曼陀罗叶结构比较及鉴别方法研究. 药物分析杂志 35, 1092-1098. |
| [20] | 陆时万, 徐祥生, 沈敏健 (1991). 植物学. 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 144-149. |
| [21] | 雒新艳, 戴思兰 (2010). 大菊品种表型性状的分类学价值. 北京林业大学学报 32(3), 135-140. |
| [22] | 马炜梁 (2009). 植物学. 北京: 高等教育出版社. pp. 68-75. |
| [23] | 祁栋灵, 周庆阳, 刘三军, 李靖 (2005). 利用叶形结构数值分析葡萄种质亲缘关系的研究. 中国南方果树 ( 3), 64-66. |
| [24] | 沈凤, 蒋逍逍, 房伟民, 管志勇, 邓波, 陈发棣 (2018). 切花菊叶片的遗传多样性分析. 南京农业大学学报 41, 275-285. |
| [25] |
唐俊, 邓立苗, 陈辉, 栾涛, 马文杰 (2014). 基于机器视觉的玉米叶片透射图像特征识别研究. 中国农业科学 47, 431-440.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
王江民, 陈发棣, 房伟民, 陈素梅, 管志勇, 唐海艳 (2013). 基于叶形特征的切花菊品种鉴别. 植物学报 48, 608-615.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 王丽君, 淮永建, 彭月橙 (2015). 基于叶片图像多特征融合的观叶植物种类识别. 北京林业大学学报 37, 55-61. |
| [28] | 许炳强, 夏念和, 王少平, 郝刚 (2007). 中国木犀属植物叶脉形态及其分类学意义. 广西植物 27, 697-705, 696. |
| [29] | 徐静静, 赵冰, 申惠翡, 刘旭梅, 高晓宁 (2017). 15个杜鹃花品种叶片解剖和表型数量分类研究. 西北林学院学报 32, 142-149. |
| [30] | 许莹修 (2005). 菊花形态性状多样性和品种分类的研究. 硕士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 1-7. |
| [31] | 薛守纪 (2004). 中国菊花图谱. 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 9-10. |
| [32] | 尹克林, 梁武, 诸葛宏庆 (1998). 酿酒葡萄品种‘蛇龙珠’的叶形结构数值鉴别. 园艺学报 25(2), 189-190. |
| [33] | 翟传敏, 汪青萍, 杜吉祥 (2014). 基于叶缘与叶脉分数维特征的植物叶识别方法研究. 计算机科学 41(2), 170-173. |
| [34] | 张诚 (2006). 葡萄叶形结构和品种鉴别相关性研究. 硕士论文. 重庆: 西南大学. pp. 27-51. |
| [35] |
张莉俊, 戴思兰 (2009). 菊花种质资源研究进展. 植物学报 44, 526-535.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 张蒙蒙, 王青, 戴思兰, 季玉山, 王朔 (2014). 盆栽小菊表型性状筛选与品种分类研究. 见: 中国观赏园艺研究进展(2014). 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 103-109. |
| [37] | 张宁, 刘文萍 (2011). 基于图像分析的植物叶片识别技术综述. 计算机应用研究 28, 4001-4007. |
| [38] | 张树林, 戴思兰 (2013). 中国菊花全书. 北京: 中国林业出版社. pp. 134-278. |
| [39] | 张辕 (2014). 基于三种标记的中国传统菊花品种鉴定及分类研究. 博士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 27-50. |
| [40] | 赵冰, 雒新艳, 张启翔 (2007). 蜡梅品种的数量分类研究. 园艺学报 34, 947-954. |
| [41] | 镇兰萍 (2013). 安徽野生菊属药用植物的形态与显微特征比较研究. 硕士论文. 合肥: 安徽中医药大学. pp. 21-22. |
| [42] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部 (2018). 植物品种特异性、一致性和稳定性测试指南——菊花: GB/T 19557.19—2018. 北京: 中国标准出版社. pp. 12-44. |
| [43] | 周桂玲, 魏岩 (2002). 十字花科四属植物叶片脉序的比较研究. 武汉植物学研究 20, 258-262. |
| [44] | 朱静, 田兴军, 陈彬, 吕劲紫 (2005). 植物叶形的计算机识别系统. 植物学通报 22, 599-604. |
| [45] | 左力辉, 张文林, 邱彤, 张军, 杨敏生 (2015). 新疆野苹果叶形性状变异及其与SSR标记关联分析. 园艺学报 42, 759-768. |
| [46] | Abbasi S, Mokhtarian F, Kittler J (1997). Reliable classification of chrysanthemum leaves through curvature scale space. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Scale-Space Theories in Computer Vision. Utrecht: Springer. pp. 284-295. |
| [47] | Chaki J, Parekh R (2011). Plant leaf recognition using shape based features and neural network classifiers. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 2, 41-47. |
| [48] | Chatrou L (1997). Studies in Annonaceae. XXVIII. Macromorphological variation of recent invaders in northern Central America: the case of Malmea (Annonaceae). Am J Bot 84, 861-869. |
| [49] | Chitwood DH, Headland LR, Kumar R, Peng J, Maloof JN, Sinha NR (2012). The developmental trajectory of leaflet morphology in wild tomato species. Plant Physiol 158, 1230-1240. |
| [50] | Chitwood DH, Kumar R, Headland LR, Ranjan A, Covington MF, Ichihashi Y, Fulop D, Jiménez-Gómez JM, Peng J, Maloof JN, Sinha NR (2013). A quantitative genetic basis for leaf morphology in a set of precisely defined tomato introgression lines. Plant Cell 25, 2465-2481. |
| [51] |
Chitwood DH, Otoni WC (2017). Morphometric analysis of Passiflora leaves: the relationship between landmarks of the vasculature and elliptical Fourier descriptors of the blade. GigaScience 6, giw008.
DOI URL PMID |
| [52] | Chitwood DH, Ranjan A, Kumar R, Ichihashi Y, Zumstein K, Headland LR, Ostria-Gallardo E, Aguilar-Martínez JA, Bush S, Carriedo L, Fulop D, Martinez CC, Peng J, Maloof JN, Sinha NR (2014). Resolving distinct genetic regulators of tomato leaf shape within a heteroblastic and ontogenetic context. Plant Cell 26, 3616-3629. |
| [53] |
da Silva NR, Florindo JB, Gómez MC, Rossatto DR, Kolb RM, Bruno OM (2015). Plant identification based on leaf midrib cross-section images using fractal descriptors. PLoS One 10, e0130014.
URL PMID |
| [54] | Dejong J, Drennan DL (1984). Genetic analysis in Chrysanthemum morifolium. II. flower doubleness and ray floret corolla splitting. Euphytica 33, 465-470. |
| [55] | Gao K, Song XB, Kong DY, Dai SL (2020). Genetic analysis of leaf traits in small-flower chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × morifolium Ramat.). Agronomy 10, 697. |
| [56] | Jones CS (1992). Comparative ontogeny of a wild cucurbit and its derived cultivar. Evolution 46, 1827-1847. |
| [57] | Khadivi-Khub A, Zamani Z, Fatahi MR (2012). Multivariate analysis of Prunus subgen. Cerasus germplasm in Iran using morphological variables. Genet Resour Crop Evol 59, 909-926. |
| [58] | Klingenberg CP (2010). Evolution and development of shape: integrating quantitative approaches. Nat Rev Genet 11, 623-635. |
| [59] | Mallah C, Cope J, Orwell J (2013). Plant leaf classification using probabilistic integration of shape, texture and margin features. In: Computer Graphics and Imaging/798: Signal Processing, Pattern Recognition and Applications. Innsbruck: ACTA Press. pp. 1-8. |
| [60] | McLellan T (2000). Geographic variation and plasticity of leaf shape and size in Begonia dregei and B. homonyma (Begoniaceae). Bot J Linn Soc 132, 79-95. |
| [61] | Min Z, Li RL, Zhao XF, Li RY, Zhang Y, Liu M, Wei XF, Fang YL, Chen SX (2018). Morphological variability in leaves of Chinese wild Vitis species. Sci Hortic 238, 138-146. |
| [62] | Mokhtarian F, Abbasi S (2004). Matching shapes with self-intersections: application to leaf classification. IEEE T Image Process 13, 653-661. |
| [63] | Moreno-Sánchez M (2004). Graphic approach for morphometric analysis of Archaeopteris leaves. Ann Paléontol 90, 161-173. |
| [64] |
Nicotra AB, Leigh A, Boyce CK, Jones CS, Niklas KJ, Royer DL, Tsukaya H (2011). The evolution and functional significance of leaf shape in the angiosperms. Funct Plant Biol 38, 535-552.
URL PMID |
| [65] | Niinemets Ü, Portsmuth A, Tobias M (2007). Leaf shape and venation pattern alter the support investments within leaf lamina in temperate species: a neglected source of leaf physiological differentiation? Funct Ecol 21, 28-40. |
| [66] | Song XB, Gao K, Fan GX, Zhao XG, Liu ZL, Dai SL (2018a). Quantitative classification of the morphological traits of ray florets in large-flowered chrysanthemum. HortScience 53, 1258-1265. |
| [67] | Song XB, Zhao XG, Fan GX, Gao K, Dai SL, Zhang MM, Ma CF, Wu XY (2018b). Genetic analysis of the corolla tube merged degree and the relative number of ray florets in chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × morifolium Ramat.). Sci Hortic 242, 214-224. |
| [68] | Zhang Y, Luo XY, Zhu J, Wang C, Hong Y, Lu J, Liu QQ, Li BQ, Zhu ML, Wang ZF, Zhang YQ, Song XB, Lv PY, Dai SL (2014). A classification study for chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum × grandiflorum Tzvelv.) cultivars based on multivariate statistical analyses. J Syst Evol 52, 612-628. |
| [1] | 刘碧颖, 陈子豪, 源思浩, 周婷. 植被志书研编中图表绘制的常见问题与技术参考[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 1-. |
| [2] | 熊高明, 申国珍, 徐文婷, 谢宗强, 李跃林, 徐耀粘, 陈芳清, 李家湘. 中国低山丘陵热性常绿阔叶灌丛主要类型及群落特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 1-. |
| [3] | 熊高明, 申国珍, 赵常明, 徐文婷, 王杨, 谢宗强, 李家湘, 徐耀粘, 李跃林, 陈芳清. 中国檵木灌丛植被类型及群落特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 1-. |
| [4] | 张坤, 伊丽晴, 刘占军, 张志杰, 王顼, 李明乐, 苗百岭, 张景慧, 李智勇, 董雷, 梁存柱. 毛刺锦鸡儿群落特征及分类[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 0-. |
| [5] | 杜燕 刘鑫 张瀚曰 马少伟 包维楷. 中国高山松群系的群落特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 1-0. |
| [6] | 韦丹丹, 杜燕, 包维楷, 胡斌, 张瀚曰, 王瀚婕, 唐圆圆, 黄龙, 郭昌安, 刘鑫. 冬麻豆群落的地理分布、特征和分类[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 1-. |
| [7] | 陈颖, 王迎雪, 邓清雅, 李培杨, 肖自新, 许艳蓉, 邓传远. 海坛岛典型灌丛群落数量分类与排序[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 653-666. |
| [8] | 周璇, 张生芳, 刘宁, 鲁玉杰, 郑斯竹, 杨晓军, 路园园, 刘梅柯, 白明. 储藏物甲虫系统地位厘清及拉英汉名录更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24238-. |
| [9] | 洪德元. 分类学中的方法论小叙[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24541-. |
| [10] | 陈静, 张丙昌, 刘燕晋, 武杰, 赵康, 明姣. 荒漠生物结皮细鞘丝藻类(Leptolyngbya-like)蓝藻多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24186-. |
| [11] | 李邦泽, 张树仁. 中国莎草科最新物种名录和分类纲要[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24106-. |
| [12] | 王腾, 李纯厚, 王广华, 赵金发, 石娟, 谢宏宇, 刘永, 刘玉. 西沙群岛七连屿珊瑚礁鱼类的物种组成与演替[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 23481-. |
| [13] | 董劭琼, 侯东杰, 曲孝云, 郭柯. 柴达木盆地植物群落样方数据集[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(4): 534-540. |
| [14] | 吴琪, 张晓青, 杨雨婷, 周艺博, 马毅, 许大明, 斯幸峰, 王健. 浙江钱江源-百山祖国家公园庆元片区叶附生苔多样性及其时空变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24010-. |
| [15] | 陈香蕾, 崔树娟, 赵晨军, 顾洪亮, 陈晓萍, 李锦隆, 孙俊. 基于叶形分类的木本植物单叶片面积预测模型[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(12): 1683-1691. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||