

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 208-216.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18089 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18089
所属专题: 逆境生物学专辑 (2019年54卷2期)
收稿日期:2018-04-08
接受日期:2018-08-23
出版日期:2019-03-01
发布日期:2019-09-01
通讯作者:
王开勇
Hongxiu Ma,Kaiyong Wang( ),Kaixiang Zhang,Chunmei Meng,Mengjie An
),Kaixiang Zhang,Chunmei Meng,Mengjie An
Received:2018-04-08
Accepted:2018-08-23
Online:2019-03-01
Published:2019-09-01
Contact:
Kaiyong Wang
摘要: 为探究棉粕对盐碱胁迫下棉花(Gossypium hirsutum)的抗盐碱机理, 通过田间试验, 研究添加不同棉粕用量对8 g·kg -1盐碱胁迫下棉花生理及生长的补偿效应。结果表明, 添加棉粕能够增加盐碱胁迫下棉花不同器官对K +的吸收, 降低对Na +的吸收, 维持盐碱胁迫下细胞内K +和Na +的平衡, 显著促进棉花生长, 提高叶片叶绿素含量和光合作用效率, 有效缓解盐碱胁迫对棉花的伤害。其中, 以添加6 000 kg·hm -2棉粕处理的效果最显著, 且盐胁迫下棉粕的改良效果较好。主成分分析结果表明, 盐碱胁迫下棉花生长生理的主要影响因子为叶片K +/Na +比值、根长、鲜重、干重和胞间CO2浓度(Ci)。
马宏秀,王开勇,张开祥,孟春梅,安梦洁. 棉粕对盐碱胁迫下棉花生理及生长补偿效应. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 208-216.
Hongxiu Ma,Kaiyong Wang,Kaixiang Zhang,Chunmei Meng,Mengjie An. Effect of Cottonseed Meal on Cotton Physiology and Growth Compensation Under Salinity-alkalinity Stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(2): 208-216.
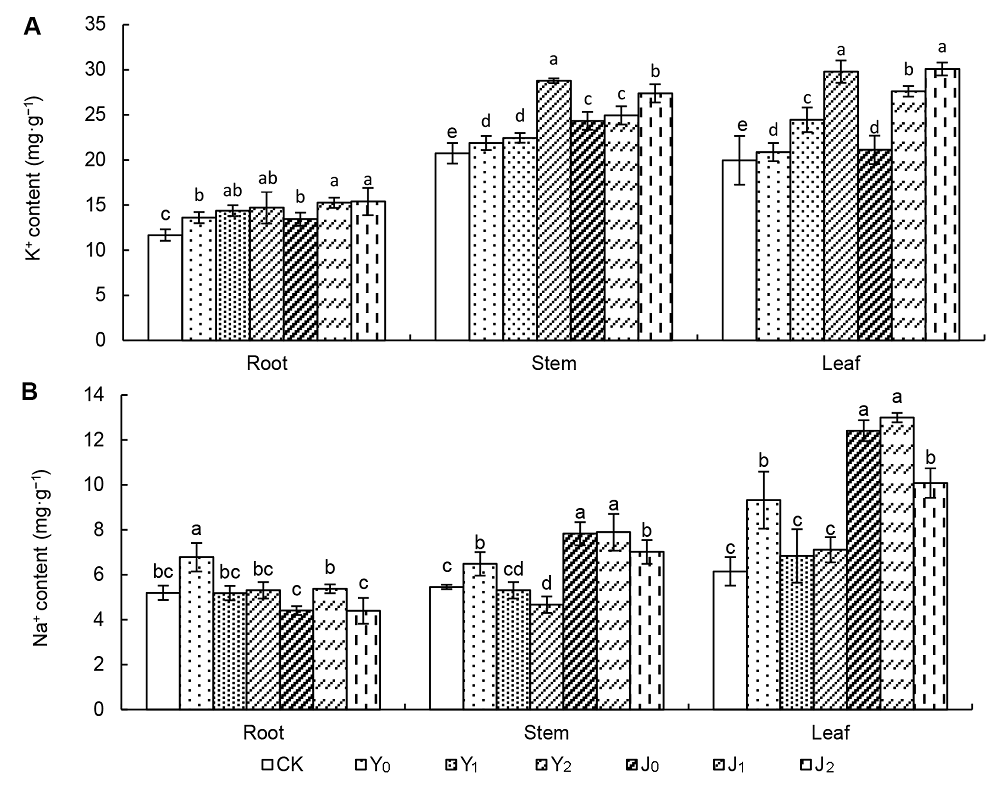
图1 棉粕对盐碱胁迫下棉花不同器官K+ (A)、Na+ (B)含量的影响CK: 对照; Y0: NaCl+0 kg·hm-2棉粕; Y1: NaCl+3 000 kg·hm-2棉粕; Y2: NaCl+6 000 kg·hm-2棉粕; J0: Na2CO3+0 kg·hm-2棉粕; J1: Na2CO3+3 000 kg·hm-2棉粕; J2: Na2CO3+6 000 kg·hm-2棉粕。不同小写字母表示各处理差异显著(P?0.05)。
Figure 1 Effect of cottonseed meal on K+ (A) and Na+ (B) content of cotton under salinity-alkalinity stressCK: Control; Y0: NaCl+0 kg·hm-2 cottonseed meal; Y1: NaCl+3 000 kg·hm-2 cottonseed meal; Y2: NaCl+6 000 kg·hm-2 cottonseed meal; J0: Na2CO3+0 kg·hm-2 cottonseed meal; J1: Na2CO3+3 000 kg·hm-2 cottonseed meal; J2: Na2CO3+6 000 kg·hm-2 cottonseed meal. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among each treatment (P?0.05).
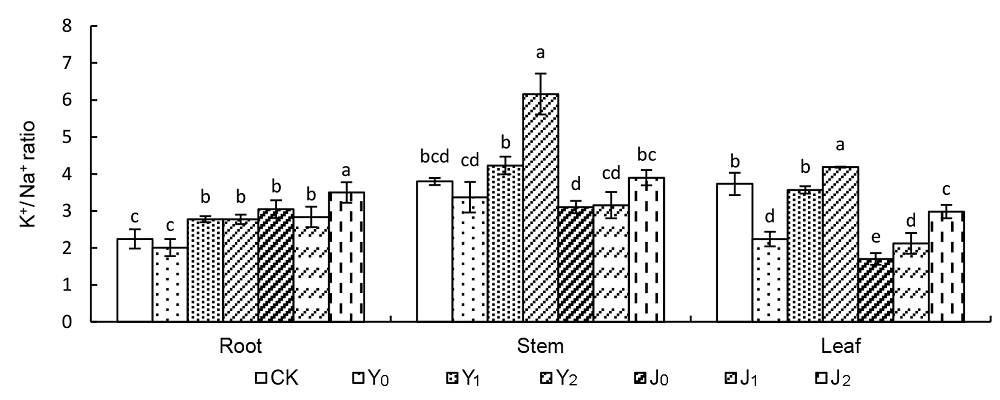
图2 棉粕对盐碱胁迫下棉花不同器官K+/Na+比值的影响CK、Y0、Y1、Y2、J0、J1和J2同图1。不同小写字母表示各处理差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 2 Effect of cottonseed meal on K+/Na+ ratio of cotton under salinity-alkalinity stressCK、Y0、Y1、Y2、J0、J1 and J2see Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among each treatment (P<0.05).
| Treatment | Total chlorophyll content (mg·g-1) | Chlorophyll a content (mg·g-1) | Chlorophyll b content (mg·g-1) | Carotenoid content (mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.51±0.10 a | 1.45±0.08 a | 0.66±0.06 a | 0.64±0.09 a |
| Y0 | 1.51±0.08 c | 1.17±0.10 bc | 0.33±0.13 b | 0.34±0.09 b |
| Y1 | 1.80±0.08 bc | 1.37±0.08 bc | 0.43±0.09 ab | 0.46±0.10 ab |
| Y2 | 2.07±0.13 ab | 1.44±0.09 ab | 0.45±0.10 ab | 0.57±0.13 ab |
| J0 | 2.18±0.19 ab | 1.17±0.13 c | 0.42±0.13 ab | 0.28±0.08 b |
| J1 | 1.78±0.28 bc | 1.37±0.13 ab | 0.33±0.10 b | 0.32±0.09 b |
| J2 | 1.89±0.12 bc | 1.43±0.08 ab | 0.40±0.11 ab | 0.51±0.16 ab |
表1 棉粕对盐碱胁迫下棉花叶片叶绿素含量的影响
Table 1 Effect of cottonseed meal on chlorophyll content of cotton leaves under salinity-alkalinity stress
| Treatment | Total chlorophyll content (mg·g-1) | Chlorophyll a content (mg·g-1) | Chlorophyll b content (mg·g-1) | Carotenoid content (mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.51±0.10 a | 1.45±0.08 a | 0.66±0.06 a | 0.64±0.09 a |
| Y0 | 1.51±0.08 c | 1.17±0.10 bc | 0.33±0.13 b | 0.34±0.09 b |
| Y1 | 1.80±0.08 bc | 1.37±0.08 bc | 0.43±0.09 ab | 0.46±0.10 ab |
| Y2 | 2.07±0.13 ab | 1.44±0.09 ab | 0.45±0.10 ab | 0.57±0.13 ab |
| J0 | 2.18±0.19 ab | 1.17±0.13 c | 0.42±0.13 ab | 0.28±0.08 b |
| J1 | 1.78±0.28 bc | 1.37±0.13 ab | 0.33±0.10 b | 0.32±0.09 b |
| J2 | 1.89±0.12 bc | 1.43±0.08 ab | 0.40±0.11 ab | 0.51±0.16 ab |
| Treatment | Pn (μmol·m-2·s-1) | Gs (mol·m-2·s-1) | E (mmol·m-2·s-1) | Ci (μmol·mol-1) | Ls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.73±0.15 a | 111.13±1.28 a | 1.81±0.25 a | 281.20±0.10 b | 0.25±0.10 a |
| Y0 | 6.32±0.38 b | 79.17±0.70 d | 1.60±1.95 ab | 262.79±0.07 e | 0.28±0.04 a |
| Y1 | 6.57±0.15 a | 85.7±0.49 c | 1.67±1.10 ab | 270.00±0.06 d | 0.25±0.06 a |
| Y2 | 6.63±0.27 a | 94.38±1.81 b | 1.76±1.86 ab | 282.81±0.04 b | 0.21±0.10 a |
| J0 | 5.16±0.07 c | 75.16±1.63 e | 1.58±1.60 b | 274.77±0.08 c | 0.26±0.05 a |
| J1 | 5.76±0.18 bc | 85.78±1.06 c | 1.63±1.54 ab | 282.47±0.06 b | 0.21±0.10 a |
| J2 | 5.82±0.25 b | 86.02±1.51 c | 1.66±1.88 ab | 294.13±0.10 a | 0.21±0.09 a |
表2 棉粕对盐碱胁迫下棉花光合参数的影响
Table 2 Effect of cottonseed meal on photosynthetic parameters of cotton under salinity-alkalinity stress
| Treatment | Pn (μmol·m-2·s-1) | Gs (mol·m-2·s-1) | E (mmol·m-2·s-1) | Ci (μmol·mol-1) | Ls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.73±0.15 a | 111.13±1.28 a | 1.81±0.25 a | 281.20±0.10 b | 0.25±0.10 a |
| Y0 | 6.32±0.38 b | 79.17±0.70 d | 1.60±1.95 ab | 262.79±0.07 e | 0.28±0.04 a |
| Y1 | 6.57±0.15 a | 85.7±0.49 c | 1.67±1.10 ab | 270.00±0.06 d | 0.25±0.06 a |
| Y2 | 6.63±0.27 a | 94.38±1.81 b | 1.76±1.86 ab | 282.81±0.04 b | 0.21±0.10 a |
| J0 | 5.16±0.07 c | 75.16±1.63 e | 1.58±1.60 b | 274.77±0.08 c | 0.26±0.05 a |
| J1 | 5.76±0.18 bc | 85.78±1.06 c | 1.63±1.54 ab | 282.47±0.06 b | 0.21±0.10 a |
| J2 | 5.82±0.25 b | 86.02±1.51 c | 1.66±1.88 ab | 294.13±0.10 a | 0.21±0.09 a |
| Treatment | Plant height (cm) | Root length (cm) | Fresh weight (g·plant -1) | Dry weight (g·plant -1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 89.4±0.36 b | 31.83±0.78 a | 184.59±0.23 a | 54.49±0.26 a |
| Y0 | 84.1±0.17 c | 26.1±0.61 c | 135.81±0.52 g | 37.89±0.46 e |
| Y1 | 91±0.58 b | 29.83±0.35 b | 173.12±0.88 c | 44.21±0.18 c |
| Y2 | 98.67±0.58 a | 30.97±0.40 ab | 181.43±0.88 b | 55.15±0.34 a |
| J0 | 74.33±0.58 d | 22.78±0.40 d | 148.47±0.43 f | 34.42±0.34 f |
| J1 | 76.33±1.15 d | 25.4±0.26 c | 162.33±0.96 e | 39.75±0.27 d |
| J2 | 82.33±0.58 c | 26.4±0.17 c | 165.12±0.42 d | 46.63±0.71 b |
表3 棉粕对盐碱胁迫下棉花生长的影响
Table 3 Effect of cottonseed meal on cotton growth under salinity-alkalinity stress
| Treatment | Plant height (cm) | Root length (cm) | Fresh weight (g·plant -1) | Dry weight (g·plant -1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 89.4±0.36 b | 31.83±0.78 a | 184.59±0.23 a | 54.49±0.26 a |
| Y0 | 84.1±0.17 c | 26.1±0.61 c | 135.81±0.52 g | 37.89±0.46 e |
| Y1 | 91±0.58 b | 29.83±0.35 b | 173.12±0.88 c | 44.21±0.18 c |
| Y2 | 98.67±0.58 a | 30.97±0.40 ab | 181.43±0.88 b | 55.15±0.34 a |
| J0 | 74.33±0.58 d | 22.78±0.40 d | 148.47±0.43 f | 34.42±0.34 f |
| J1 | 76.33±1.15 d | 25.4±0.26 c | 162.33±0.96 e | 39.75±0.27 d |
| J2 | 82.33±0.58 c | 26.4±0.17 c | 165.12±0.42 d | 46.63±0.71 b |
| Index | Salt treatment | Alkali treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | ||
| K+ | Root | -0.05 | 0.94** | -0.67 | 0.69 |
| Stem | 0.47 | 0.78* | -0.68 | 0.70 | |
| Leaf | 0.73 | 0.60 | -0.09 | 0.96** | |
| Na+ | Root | -0.83* | 0.01 | 0.41 | -0.15 |
| Stem | -0.87* | -0.36 | -0.98** | 0.02 | |
| Leaf | -0.81* | 0.23 | -0.95** | 0.00 | |
| K+/Na+ ratio | Root | 0.61 | 0.61 | -0.67 | 0.59 |
| Stem | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.58 | |
| Leaf | 0.96** | 0.15 | 0.93** | 0.28 | |
| Physiology index | Total chlorophyll content | 0.79* | -0.52 | 0.63 | -0.55 |
| Chlorophyll a content | 0.82* | -0.07 | 0.60 | 0.55 | |
| Chlorophyll b content | 0.56 | -0.68 | 0.78* | -0.35 | |
| Carotenoid content | 0.78* | -0.29 | 0.83* | 0.19 | |
| Pn | 0.61 | -0.16 | 0.94** | 0.10 | |
| Gs | 0.75* | -0.61 | 0.98** | -0.03 | |
| Ci | 0.94** | -0.11 | 0.16 | 0.97** | |
| E | 0.74 | -0.36 | 0.78* | 0.06 | |
| Ls | -0.36 | -0.12 | 0.02 | -0.27 | |
| Growth index | Plant height | 0.82* | 0.52 | 0.97** | 0.17 |
| Root length | 0.96** | -0.10 | 0.97** | 0.11 | |
| Fresh weight | 0.97** | -0.11 | 0.97** | 0.16 | |
| Dry weight | 0.96** | -0.13 | 0.95** | 0.28 | |
表4 棉花盐碱胁迫下不同处理因子载荷
Table 4 Load of different treatment factors of cotton under salinity-alkalinity stress
| Index | Salt treatment | Alkali treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | ||
| K+ | Root | -0.05 | 0.94** | -0.67 | 0.69 |
| Stem | 0.47 | 0.78* | -0.68 | 0.70 | |
| Leaf | 0.73 | 0.60 | -0.09 | 0.96** | |
| Na+ | Root | -0.83* | 0.01 | 0.41 | -0.15 |
| Stem | -0.87* | -0.36 | -0.98** | 0.02 | |
| Leaf | -0.81* | 0.23 | -0.95** | 0.00 | |
| K+/Na+ ratio | Root | 0.61 | 0.61 | -0.67 | 0.59 |
| Stem | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.58 | |
| Leaf | 0.96** | 0.15 | 0.93** | 0.28 | |
| Physiology index | Total chlorophyll content | 0.79* | -0.52 | 0.63 | -0.55 |
| Chlorophyll a content | 0.82* | -0.07 | 0.60 | 0.55 | |
| Chlorophyll b content | 0.56 | -0.68 | 0.78* | -0.35 | |
| Carotenoid content | 0.78* | -0.29 | 0.83* | 0.19 | |
| Pn | 0.61 | -0.16 | 0.94** | 0.10 | |
| Gs | 0.75* | -0.61 | 0.98** | -0.03 | |
| Ci | 0.94** | -0.11 | 0.16 | 0.97** | |
| E | 0.74 | -0.36 | 0.78* | 0.06 | |
| Ls | -0.36 | -0.12 | 0.02 | -0.27 | |
| Growth index | Plant height | 0.82* | 0.52 | 0.97** | 0.17 |
| Root length | 0.96** | -0.10 | 0.97** | 0.11 | |
| Fresh weight | 0.97** | -0.11 | 0.97** | 0.16 | |
| Dry weight | 0.96** | -0.13 | 0.95** | 0.28 | |
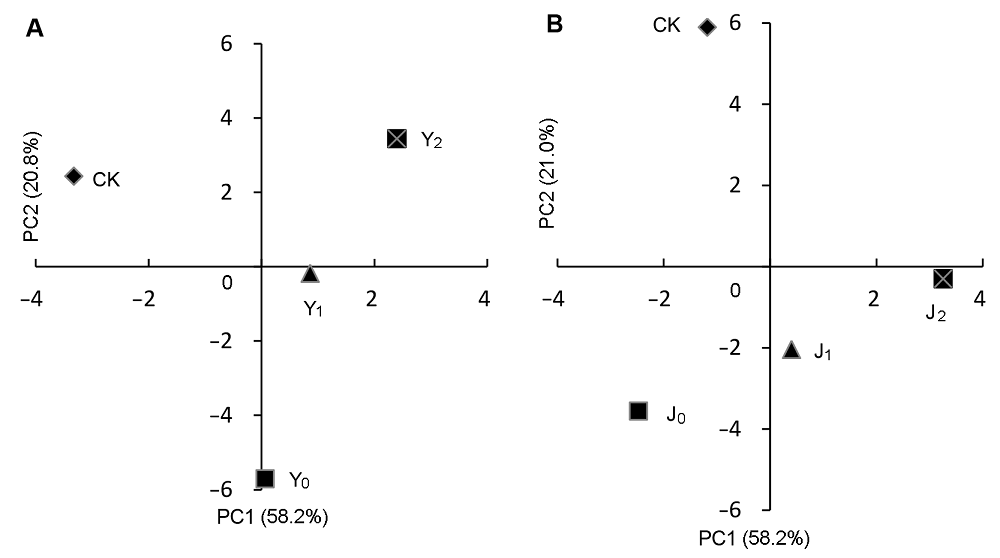
图3 棉花盐(A)和碱(B)胁迫下各指标主成分(PC)分析CK、Y0、Y1、Y2、J0、J1 和 J2同图1。
Figure 3 Analysis of principal components (PC) of each index of cotton under salinity (A) and alkalinity (B) stressCK、Y0、Y1、Y2、J0、J1 and J2see Figure 1.
| [1] | 阿曼古丽·买买提阿力, 拉扎提·努尔布拉提, 高丽丽, 张巨松, 田立文 ( 2017). 盐胁迫对海岛棉和陆地棉幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 植物学报 52, 465-473. |
| [2] | 鲍士旦 ( 2000). 土壤农化分析(第3版). 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp.270-271. |
| [3] | 陈俊 ( 2006). 碱地肤幼苗抗氧化酶系统对盐碱混合胁迫的生理响应特点. 硕士论文. 长春: 东北师范大学. pp.4-10. |
| [4] | 陈琪, 石剑华 ( 2013). 棉籽饼使用脱毒剂和生物发酵脱毒的营养分析. 当代畜禽养殖业( 10), 6-7,8. |
| [5] | 郭凯, 巨兆强, 封晓辉, 李晓光, 刘小京 ( 2016). 咸水结冰灌溉改良盐碱地的研究进展及展望. 中国生态农业学报 24, 1016-1024. |
| [6] | 黄清荣, 祁琳, 柏新富 ( 2018). 根环境供氧状况对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗光合及离子吸收的影响. 生态学报 38, 528-536. |
| [7] | 贾玉珍, 朱禧月, 唐予迪, 蔡养廉, 林同保, 罗先宝, 杨兆庚, 韩海江 ( 1987). 棉花出苗及苗期耐盐性指标的研究. 河南农业大学学报 21, 30-41. |
| [8] | 焦伟红 ( 2011). 燕麦耐盐碱渗透调节机制研究. 硕士论文. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. pp.15-20. |
| [9] | 李合生, 陈华癸 ( 2000). 21世纪农林本科生物系列课程改革的研究与实践(上). 中国农业教育 ( 4), 19-22. |
| [10] | 蔺吉祥, 李晓宇, 唐佳红, 张兆军, 李卓琳, 高战武, 穆春生 ( 2011). 盐碱胁迫对小麦种子萌发、早期幼苗生长及Na +、K +代谢的影响 . 麦类作物学报 31, 1148-1152. |
| [11] | 刘玉国, 谭兰兰, 卞龙, 王开勇 ( 2013). 盐渍化土壤改良剂的筛选. 农业科技与信息(20), 48-49, 50 . |
| [12] | 牛花朋, 李胜荣, 申俊峰, 李祯, 佟景贵 ( 2006). 粉煤灰与若干有机固体废弃物配施改良土壤的研究进展. 地球与环境 34(2), 27-34. |
| [13] | 石德成, 殷丽娟 ( 1993). 盐(NaCl)与碱(Na2CO3)对星星草胁迫作用的差异. 植物学报 35, 144-149. |
| [14] | 田长彦, 周宏飞, 刘国庆 ( 2000). 21世纪新疆土壤盐渍化调控与农业持续发展研究建议. 干旱区地理 23, 177-181. |
| [15] |
王安平, 吕云峰, 张军民, 赵青余, 王加启, 田科雄 ( 2010). 我国棉粕和棉籽蛋白营养成分和棉酚含量调研. 华北农学报 25(S1), 301-304.
DOI |
| [16] | 王文杰, 贺海升, 祖元刚, 赵修华, 杨磊, 关宇, 许慧男, 于兴洋 ( 2009). 施加改良剂对重度盐碱地盐碱动态及杨树生长的影响. 生态学报 29, 2272-2278. |
| [17] | 韦本辉, 申章佑, 周佳, 甘秀芹, 劳承英, 周灵芝, 刘斌, 胡泊, 李艳英 ( 2017). 粉垄改造利用盐碱地效果初探. 中国农业科技导报 19(10), 107-112. |
| [18] | 翁永玲, 宫鹏 ( 2006). 土壤盐渍化遥感应用研究进展. 地理科学 26, 369-375. |
| [19] | 杨国会, 石德成 ( 2011). 盐碱胁迫对小冰麦相对生长率及茎叶离子积累的影响. 河南农业科学 40, 45-47, 57. |
| [20] | 杨淑萍, 危常州, 梁永超 ( 2010). 盐胁迫对不同基因型海岛棉光合作用及荧光特性的影响. 中国农业科学 43, 1585-1593. |
| [21] | 员学锋, 汪有科, 吴普特, 冯浩 ( 2005). PAM对土壤物理性状影响的试验研究及机理分析. 水土保持学报 19(2), 37-40. |
| [22] | 张华宁, 李孟军, 郭秀林, 张艳敏, 刘子会 ( 2017). 盐胁迫下不同K+吸收抑制剂对小麦根系K+/Na+比和质膜相关蛋白活性的影响 . 华北农学报 32(5), 154-162. |
| [23] | 张景云, 缪南生, 白雅梅, 万新建, 吕文河 ( 2014). 盐胁迫下二倍体马铃薯叶绿素含量和抗氧化酶活性的变化. 作物杂志 ( 5), 59-63. |
| [24] | 张娜, 潘思轶, 侯旭杰 ( 2009). 棉籽蛋白提取工艺及其主要理化性质研究. 食品研究与开发 30(7), 36-38. |
| [25] | 张树文, 杨久春, 李颖, 张养贞, 常丽萍 ( 2010). 1950s中期以来东北地区盐碱地时空变化及成因分析. 自然资源学报 25, 435-442. |
| [26] | 赵可夫, 王韶唐 ( 1990). 作物抗性生理. 北京: 农业出版社. pp. 300-304. |
| [27] | 周志林, 唐君, 曹清河, 赵冬兰, 张安 ( 2017). NaCl胁迫对甘薯植株体内K+、Na+和Cl-含量及生长的影响 . 中国农业科技导报 19(4), 17-23. |
| [28] | 罗宾BA ( 陈恺元等译) ( 1983). 棉花生理学. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社. pp. 116-118. |
| [29] | Boscaiu M, Estrelles E, Soriano P, Vicente O ( 2005). Effects of salt stress on the reproductive biology of the halophyte Plantago crassifolia . Biol Plant 49, 141-143. |
| [30] | Jalees MM, Khan MZ, Saleemi MK, Khan A ( 2011). Effects of cottonseed meal on hematological, biochemical and behavioral alterations in male Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica). Pak Vet J 31, 211-214. |
| [31] | Li RL, Shi FC, Fukuda K, Yang YL ( 2010). Effects of salt and alkali stresses on germination, growth, photosynthesis and ion accumulation in alfalfa ( Medicago sativa L.). Soil Sci Plant Nutr 56, 725-733. |
| [32] |
Munns R ( 2002). Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ 25, 239-250.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Nedjimi B, Daoud Y ( 2009). Ameliorative effect of CaCl2 on growth, membrane permeability and nutrient uptake in Atriplex halimus subsp. schweinfurthii grown at high (NaCl) salinity. Desalination 249, 163-166. |
| [34] |
Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Gassmann W ( 1994). Perspectives on the physiology and structure of inward-rectifying K+ channels in higher plants: biophysical implications for K+ uptake . Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 23, 441-471.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Štefanić PP, Koffler T, Adler G, Bar-Zvi D ( 2013). Chloroplasts of salt-grown Arabidopsis seedlings are impaired in structure, genome copy number and transcript levels. PLoS One 8, e82548.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Wang LW, Showalter AM, Ungar IA ( 2005). Effects of intraspecific competition on growth and photosynthesis of Atriplex prostrata . Aquat Bot 83, 187-192. |
| [37] | Zhang JT, Mu CS ( 2009). Effects of saline and alkaline stresses on the germination, growth, photosynthesis, ionic balance and anti-oxidant system in an alkali-tolerant leguminous forage Lathyrus quinquenervius . Soil Sci Plant Nutr 55, 685-697. |
| [38] | Zhang TB, Zhan XY, Kang YH, Wan SQ, Feng H ( 2017). Improvements of soil salt characteristics and nutrient status in an impermeable saline-sodic soil reclaimed with an improved drip irrigation while ridge planting Lycium barbarum L. J Soils Sediments 17, 1126-1139. |
| [1] | 平晓燕, 杜毅倩, 赖仕蓉, 孔梦桥, 余国杰. 植物应对食草动物采食的化学防御策略研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 667-680. |
| [2] | 李欣怡, 张丽芳, 吴友贵, 郭静, 兰荣光, 吕洪飞, 于明坚. 不同海拔高度下百山祖冷杉幼苗的生长特征及其影响因素[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 610-623. |
| [3] | 欧阳子龙, 贾湘璐, 石景忠, 滕维超, 刘秀. 生长调节剂对低温胁迫及复温下红海榄幼苗光合特性的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 638-652. |
| [4] | 王贝贝, 吴苏, 王苗苗, 胡锦涛. 日光诱导叶绿素荧光不同组分在作物总初级生产力估算中的贡献比例: 多时间尺度分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 562-572. |
| [5] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [6] | 陆珍, 谢光杰, Qaisar KHAN, 覃英, 黄毓燕, 郭道君, 杨婷婷, 杨丽涛, 邢永秀, 李杨瑞, 王震. 伯克霍尔德菌通过改善生理适应性及调节铝响应基因的表达增强甘蔗对铝胁迫的耐受性[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(3): 475-487. |
| [7] | 田奥, 李苇洁, 曹洋, 贾真真, 曾松. 马缨杜鹃幼苗生长对土壤水分胁迫的响应及其生理机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(3): 488-501. |
| [8] | 陈文义, 王智勇, 周梦岩, 麻文俊, 王军辉, 罗志斌, 周婧. 幼龄楸树生物量分配规律与异速生长模型[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(2): 356-366. |
| [9] | 李思雨, 杨风亭, 王辉民, 戴晓琴, 孟盛旺. 杉木和木荷木质部形成季节动态及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(2): 295-307. |
| [10] | 范惠玲, 路妍, 金文海, 王慧, 彭小星, 武学霞, 刘玉皎. 基于根系表型性状的蚕豆耐盐碱性鉴定与综合评价(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 204-217. |
| [11] | 韩大勇, 李海燕, 张维, 杨允菲. 东北碱化草甸芦苇匍匐型分株超速生长过程及生理机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(2): 320-330. |
| [12] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [13] | 李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [14] | 夏敏菖, 李倩倩, 钱清清, 任淑君, 梁应冲, 陈亭颖, 李映佳, 牟宗敏, 陈穗云. 青霉菌灭活菌丝体对白车轴草和黑麦草生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(1): 189-198. |
| [15] | 王麟, 李雪, 王愉, 王新, 胡小文, 杨梅, 朱剑霄. 不同配方种衣剂对高寒草地乡土草种种子生长与建植的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(1): 118-128. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||